THE BODOLAND DISPUTE
28, Nov 2019
Prelims level : Governance, Policies
Mains level : GS-II Functions and responsibilities of the union and the states, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein.
Why in News?
- The central government has extended the ban on the Assam-based insurgent group National Democratic Front of Bodoland (NDFB) by five more years for its involvement in a series of violent anti-state Activities.
The Bodoland:
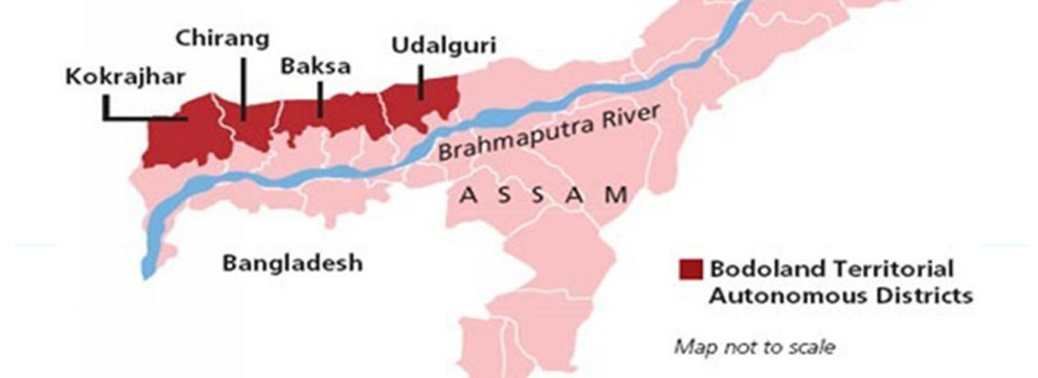
- Bodos are the single largest tribal community in Assam, making up over 5-6 per cent of the state’s population. They have controlled large parts of Assam in the past.
- The four districts in Assam — Kokrajhar, Baksa, Udalguri and Chirang — that constitute the Bodo Territorial Area District (BTAD), are home to several Ethnic Groups.
What is the Dispute?
- The Bodos have had a long history of separatist demands, marked by armed struggle.
- In 1966-67, the demand for a separate state called Bodoland was raised under the banner of the Plains Tribals Council of Assam (PTCA), a political outfit.
- In 1987, the All Bodo Students Union (ABSU) renewed the demand. “Divide Assam fifty-fifty”, was a call given by the ABSU’s then leader, Upendra Nath Brahma.
- The unrest was a fallout of the Assam Movement (1979-85), whose culmination — the Assam Accord — addressed the demands of protection and safeguards for the “Assamese people”, leading the Bodos to launch a movement to protect their own identity.
- In December 2014, separatists killed more than 30 people in Kokrajhar and Sonitpur. In the 2012 Bodo-Muslim riots, hundreds were killed and almost 5 lakh were displaced.
NDFB:
- Alongside political movements, armed groups have also sought to create a separate Bodo state.In October 1986, the prominent group Bodo Security Force (BdSF) was formed by Ranjan Daimary.The BdSF subsequently renamed itself as the National Democratic Front of Bodoland (NDFB), an organisation that is known to be involved in attacks, killings, and extortions. In the 1990s, Indian security forces launched extensive operations against the group, causing the latter to flee to bordering Bhutan.
- In Bhutan, the group faced stiff counter-insurgency operations by the Indian Army and the Royal Bhutan Army in the early 2000s.











