Antimicrobial Resistance
12, Dec 2022
Prelims level : Medicine and Pharmaceuticals
Mains level : GS-II Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector or Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Why in News?
- Over 50% of life-threatening bacterial infections are becoming resistant to treatment: the Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) report of WHO.
What are the concerns as per the recent report?
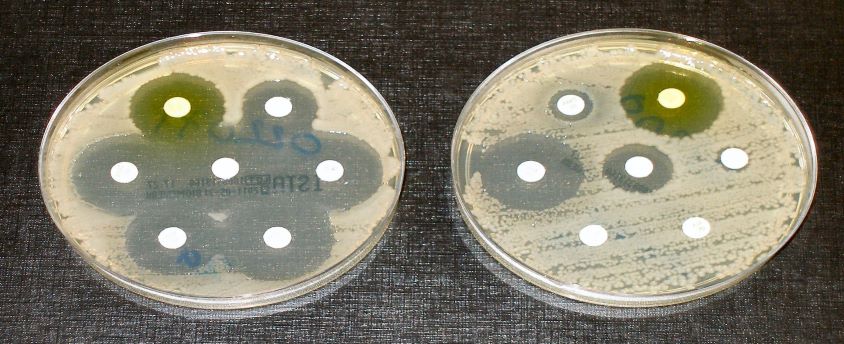
- 8% of infections caused by Klebsiella pneumonia were resistant to carbapenems (the last resort antibiotic).
- Over 60% of Neisseria gonorrhoea, a common sexually transmitted disease, show resistance to ciprofloxacin.
- 20% of coli isolates, common in urinary tract infections were resistant to ampicillin and co-trimoxazole.
- Bloodstream infections due to resistant coli, Salmonella and gonorrhoea infections, have jumped by at least 15 per cent compared to 2017 rates.
About Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS):
- Provides a standardized approach to the collection, analysis, interpretation and sharing of data by countries and seeks to actively support capacity building and monitor the status of existing and new national surveillance systems.
What is AMR?
- Antimicrobial resistance is the resistance acquired by any microorganism (bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasite, etc.) against antimicrobial drugs (such as antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, antimalarials, and anthelmintics) that are used to treat infections.
- As a result, standard treatments become ineffective, infections persist and may spread to others.
- Microorganisms that develop antimicrobial resistance are sometimes referred to as “superbugs”.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified AMR as one of the top ten threats to global health.
Reasons for Spread of AMR:
- The misuse of antimicrobials in medicine and inappropriate use in agriculture.
- Contamination around pharmaceutical manufacturing sites where untreated waste releases large amounts of active antimicrobials into the environment.
What Initiatives have been taken by the Government to Prevent AMR?
- AMR Surveillance and Research Network (AMRSN) was launched in 2013, to generate evidence and capture trends and patterns of drug resistant infections in the country.
- The National Action Plan on AMR focuses on One Health approach and was launched in April 2017 with the aim of involving various stakeholder ministries/departments.
- ICMR along with Research Council of Norway (RCN) initiated a joint call for research in antimicrobial resistance in 2017.
- ICMR along with the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Germany has a joint Indo-German collaboration for research on AMR.
- ICMR has initiated Antibiotic Stewardship Program (AMSP) on a pilot project across India to control misuse and overuse of antibiotics in hospital wards and ICUs.
Recommendation by WHO:
- Equitable and global access to the vaccines that already exist
- Disruptive approaches are needed: The lessons from COVID 19 vaccine development and mRNA vaccines offer unique opportunities to explore for development of vaccines against bacteria
- Need to overcome challenges: Such as pathogens associated with hospital-acquired infections (HAI), difficulty in defining target population(s) among all admitted hospital patients; the cost and complexity of vaccine efficacy trials; and the lack of regulatory and/or policy precedent for vaccines against HAIs.
- Easier regulatory requirement: Vaccine development is expensive, and scientifically challenging, and is associated with high failure rates, and therefore, the need for support from the government and private sector.