Category: Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nano-technology, bio-technology – GS3L
Space Activities Bill
30, Jun 2019

Why in news?
- India has begun pre legislative consultations on a “Space Activities Bill” that is designed to encourage domestic private rocket and satellite companies to offer services for Indian and global customers.
Space Activities Bill, 2017- Provisions:
- The Bill will address the liability issues arising from their space activities, in a suitable/ rational manner, in line with international practices.
- The government first introduced the Bill in 2017.
- The provisions of this Act shall apply to every citizen of India and to all sectors engaged in any space activity in India or outside India
- A non-transferable licence shall be provided by the Central Government to any person carrying out commercial space activity
- The Central Government will formulate the appropriate mechanism for licensing, eligibility criteria, and fees for licence.
- The government will maintain a register of all space objects (any object launched or intended to be launched around the earth) and develop more space activity plans for the country
- It will provide professional and technical support for commercial space activity and regulate the procedures for conduct and operation of space activity
- It will ensure safety requirements and supervise the conduct of every space activity of India and investigate any incident or accident in connection with the operation of a space activity.
- It will share details about the pricing of products created by space activity and technology with any person or any agency in a prescribed manner.
- If any person undertakes any commercial space activity without authorisation they shall be punished with imprisonment up to 3 years or fined more than ₹1 crore or both.
Why reconsider the Bill?
- The current space policy does not cover liabilities for damage to third party space assets although the country is a signatory to the UN Treaties on Outer Space activity.
- The Bill will help formulate necessary rules under the Space Activities Act to deal with damages under the liability provisions and the mode of securing financial guarantee to compensate for damages.
- This bill would address a long-pending concern on covering liabilities in the event of a mishap or damage to spacecraft.
Global opportunities:
- India’s PSLV has emerged as the preferred rocket to hurl small satellites globally.
- India is also working on a small satellite launch vehicle that is designed to tap the global opportunity to carry satellites of less than 50 kg into space.
- The US, France and the EU have legislations that underwrite costs of damage if it exceeds insurance when a private satellite launch goes awry or a rocket hits another object in space.
New Space India Limited (NSIL)
29, Jun 2019

Why in news?
- New Space India Limited (NSIL) has been incorporated as a wholly owned GoI Undertaking/Central Public Sector Enterprise (CPSE).
- Antrix Ltd is another PSU under the Department of Space that acts as an commercial arm of the ISRO
New Space India Limited (NSIL):
- It functions under the administrative control of Department of Space (DOS).
- It aims to commercially exploit the research and development work of ISRO Centres and constituent units of DOS.
- The NSIL would enable Indian Industries to scale up high-technology manufacturing and production base for meeting the growing needs of Indian space programme/
- It would further spur the growth of Indian Industries in the space sector.
Functions of NSIL:
- Small Satellite technology transfer to industry, wherein NSIL will obtain license from DOS/ISRO and sub-license it to industries;
- Manufacture of Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) in collaboration with Private Sector;
- Production of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) through Indian Industry;
- Production and marketing of Space based products and services, including launch and application;
- Transfer of technology developed by ISRO Centres and constituent units of DOS;
- Marketing spin-off technologies and products/services, both in India and abroad
BIO TECHNOLOGY
13, Jun 2019
7.1 INTRODUCTION
- It involves development of certain special life forms & systems that help in obtaining maximum benefits not only for mankind but also for other living organisms while obtaining in optimum.
- Genetic Engineering or recombined DNA technology is considered a tool of biotechnology in whichby deliberate human manipulation a foreign but desirable gene is inserted into DNA of an unrelated organism resulting in formation of a DNA molecule that has got genetic material from two or more unrelated sources.Such a DNA is called Recombinant DNA.Biotechnology has got wide ranging
a. Applications
- In the field of agriculture, biotechnology has been used to develop genetically modified organisms or transgenic
organisms that are able to produce in less time. Such organisms would ensure food security in food source country.
- Biotechnology has widest application in the field of health.It can be used in making safe cost effective vaccines e.g.,Hepatitis
- It can be used in making important proteins such as Insulin, Thyrotropin, Somatropin, Interferon that can be of great help in treating various childhood hormonal disorder e.g.
- It can also be used in making bio- diagnostic kits which is used to detect various diseases before they become
- It can be used in the preparation of scarce enzymes such as urokinase. This enzyme helps in dissolution of blood
- In the field of Energy and Environment, Genetically Modified Bacteria can be used to enhance oil exploration by a technique called Microbial enhanced oil Recovery(MEOR) in which bacteria acts as a surface tension reducing agent (surfactants) helping in increasing oil extraction from 30% to 60%.
- GMB can also be used to transform non biodegradable wastes such as plastics, synthetic, pesticides etc
- In the field of Industry, Biotech can also be used to prepare alcohol, ethanol, acids such as lactic acid, tartaric acid, acetic acid various amino acids that are used for pharmaceutical purposes. This technology can also be used for producing vitamins, antibiotics & steroids on a massive
b. Demerits
- It can be misused to form biological weapons of mass destruction.
- The inserted gene segment may express to form a harmful protein that may result in various diseases
- Biotech holds a lightly possibility of bringing extinct organisms each to life
- Scientists at present stage of R & D may likely commit a mistake whose consequence can’t be foretold.
- Biotech if misused may result in depletion of biodiversity e.g.At present biotechnological research is focused in developing 29 plant varieties that are able to cater to
90 % almost of the food requirement of man kind. If such discriminate biotech research effects continue they would result in other plant loss species along with dependent plant species, as on every plant species there are
about 30 – 40 dependent animal species such efforts would interfere in the natural process of selection and evolution of biodiversity.
c. Steps taken by Government of India:
- A department of Biotechnology was established in 1986 working under ministry of Science & Technology, Department of Biotechnology is responsible for promoting, planning and coordinating various biotechnological projects taken up by GOI which are as follows:
- Development of safe and cost effective vaccines & holding immunization camps especially for weaker and more susceptible sections of society.
- Increase oil seed production by using tissue culture technique in plants. E.g. coconut.
- Developing high yielding varieties of plants and animals.
- Cattle herd improvement by Embryo Transmit Technique(ETT).
- Developing improved & safe fertility controlled
Institutes involved in this process are
- IARI – Indian Agricultural Research
- NTN – National Institute of Nutrition (Hyderabad)
- IISc – Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
- Control Drug Research Institute (Lucknow)
- Centre for cellular & molecular biology Hyderabad
- Institute of microbial technology, Chandigarh
- International centre for genetic engineering and biotechnology established by UN Industrial Development organisation(UNIDO) to provide International Research links in biotechnology.
7.2 CLONING
- It is a process of asexual reproduction in which the offspring or the progeny produced is an exact genetic replica of the single present donor which has donated his/her genetic material by way of donating nucleus present in any of the body’s somatic or non – reproductive cell.In contrast sexual reproduction involves inheritance of genetic material from both the parents equally.JBS Haldane(America) in 1963 theorized cloning stated that every cell has the necessary technical knowhow in the form of genetic material to raise entire individual. One individual is able to create a new individual by obtaining the genetic material form any of the body’s livingcell. Male donor results in formation of a male clone whereas female donor provides female clone. Cloning also exists naturally for example, Bacteria divides asexually in bacterial clones. Monozygotic twins are clones to each other.Cloning in plants is called tissue culture technique by which large number- of disease free saplings can be produced in no time specially in those plant where the process of seed germination of e.g., sandalwood and rubber, growth and development is slow.E.g. Bamboo tissue culture is of great help in commercially valuable crops such as sugarcane, turmeric plantation crops, species etc. These crops can be micropropagated fast and desirable tree varieties can be produced rapidly increasing the profits of the farmers.
7.2.1 Animal Cloning
- Animal cloning experiment succeeded when in Feb , 1997 a team of scientists led by Professor. Ian Wilmut from Roslin Institute, Edinburg, Scotland, UK successfully cloned 1st mammal sheep Dolly. This success led to cloning of other animals since then large no of animals have been cloned E.g. Mice, Cow, Goat, pig, Rabbit, cat, mule, horse and a wild puppy known as snuppy in Seoul National university South Korea. Animal cloning experiments though are one step forward, the cloned animals have not been able to complete their life span as they have fallen prey to various genetic disease.E.g. Dolly died of arthritis and degenerative lung disease.Still animal cloning experiments can be of great helps in preserving rare species.
7.2.2 Human Cloning
- Cloning in human beings is practised by a technique known as somatic cell nuclear transfer in which a deployed nucleus containing 46 chromosomes from any of the body cells of the donar is transferred to e – nucleated egg. The manipulated egg is stimulated by electrical shocks of various chemicals to start dividing within a week.This single cell becomes a ball of 200 – 300 unspecialised cell. This stage is called as Blastocyst. Human cloning is of two types on the basis of the fate Blastocyst:
- Reproductive human cloning
- Therapeutic human cloning
7.2.2.1 Reproductive human cloning
- If blastocyst is implanted in the uterus of either surrogate or original mother, it is thought that probably it would developinto a new individual.But there has been no conclusive proof when so many cloned animals are dying of genetic diseases. Reproductive human cloning is still believed to be a for fetched
7.2.2.2 Therapeutic human cloning
- It involves use of initial unspecialised blastocyst cell to develop into genetically similar body pacts to replace the damaged or torn out body organs.Therefore therapeutic cloning provides effective genetically similarreplacement material. It is of great help in providing therapy in various degenerative

7.2.3 Uses of cloning:
- Cloning can help us understand the process of ageing and once understoodit can be effectively postponed or
- It will help us understandwhy certain adult body cells reversed to original embryonic condition of rapid division resulting in formation of cancers
- Therapeutic cloning is of greatest help in treating various degenerative diseases e.g. diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, Alzhemier, spinal cord injuries , burns etc
- Therapeutic cloning can also help in regenerating some of those body parts that do not effectively regenerate if damaged
e.g. neuron, heart muscle cells
- Reproductive human cloning can also be considered in those childless couples who are suffering from incurable infertility (unable to produce viable gametes)
7.2.4 Ban on Cloning and the ethical issues involved:
- Reproductive human cloning experiments are being opposed on various ethical & environmental grounds
- WHO has denounced R. H. C experiments considering them ethically unacceptable for the reason that they undermine society’s respect for human life.Such experiments destroy the known social structures and institutions like marriages, family etc.They would likely to bring in fundamental changes in the society as people may opt to produce their clones to raise their families without entering wed lock.Moreover family identities and relationships may get blurred. So as the offspring produced would be considered a sibling or a progeny.
- Increased cloning tendency would result in loss of genetic diversity in human It may interfere with natural process of selection affecting evolution of human beings as a species.
- The prolifer group led by Pope opposes human cloning on the ground that it is an unnatural, unnecessary man’s attempt to play the role of God.These experiments would result in large scale creation and destruction of human embryos which is similar to using human life as an experimental subject which is highly unethical.
- Human cloning experiments may be misused to raise clone armies that would result in subjugation of human race which were this clones would be consider slaves having no right what so ever
- Scientist at present stage of R& D are likely commit to mistakes that may result in serious mutationswhose consequences cannot be predicated
- This technology also misused by private individuals & organisation for commercial purposes ignoring the general interests of the society
Legal Ban
- In 1998, 19 European countries signed an agreement under which they have agreed to banhuman cloning experiments for reproductive purposes for next
20 years.USA has also banned such experiments for 10 years. Depth of Biotech in India has also banned human reproductive experiments
- In October 2004 United Nations adopted a non binding declaration that prohibited all attempts to create human life through cloning or any research achieving this aim. Therefore indirectly UNs has allowed member nations to continue with therapeutic cloning. In this regard UK became the 1st country to provide legal authorisation from Government’s Human Fertilisation & Embryology Authority to perform therapeutic cloning using human embryo to treat serious diseases. In May 2005, New Castle University which was allotted the 1st license successfully claimed to produce an early stage human embryo by nuclear transfer technique and that will be used for treating diabetes and license was given to Ian Wilmut for conducting research by using human embryo in treating motorneuron
7.3 STEM CELLS
- Stem cells are undifferentiated primitive blank cells that have not yet grown into any recognisable part of the human body.They have the ability to be coaxed to develop into any if the 220 different types of specialised cells of the body.So stem cells are the very early cell capable of transforming into any type of cells and tissues in the body
7.3.1 Types of Stem cells
- Embryonic Stem Cells
- These are far more advantageous they are highly prolific and can develop into millions of cells. Therefore they are considered totipotent in
- These cells can specialise into any type of body cells. Therefore they are pluripotent in nature but their use results in violation of ethical
7.3.1.2 Adult or Somatic stem cells
- These are some of the already specialised body cells that still
contain some of the ability to specialise differently.These cells are rare and difficult to be identified and isolated and their ability is divide and specialise is for more restricted.
E.g, Bone marrow cells, umbilical cord blood
- Wharton’s Jelly,a cushioning substance found in umbilical cord, is believed to be a rich source of obtaining stem cells non-invasively and non- Use of adult stem cells does not violate any ethical issue. Hybrid stem cells are those adult or somatic cells that can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent cells. In this adult somatic cells genetic expression is reprogrammed so that it starts functioning as embryonic cells.
- Stem cell colony/line is a self replenish able colony of embryonic stem cells from which any amount of stem cellscan be harvested without apparent limit.however it is extremely difficult to establish such a colony
as stem cell colony is highly sensitive to even slightest fluctuations in nutrient availability and environment.So far more them 78 colonies have been established by a hand full of countries, India being one of them and the 2 centres are
- Reliance life science centre, Mumbai
- National centre for Biological sciences Bangalore
7.3.1.3 Uses of Stem Cell
- Stem cell have opened a new branch of medicine known as regenerative medicine as they can be induced to develop into specific body tissues replacing the damaged ones. They can be used in Alzheimer, diabetics, Parkinsonism, burns, spinal cord injuries
- They can also be induced to develop into blood cells so that any amount the blood can be created for some blood fusionin various genetic diseases as visible cell anaemia,
- Stem cells also help in development cheap and effective drugs within a short period of time as they can be made to grow into specific body tissues on which drugs can be tested without violating animal rights as well. They can be used to study the process of embryonic development and therefore this understanding would minimise the occurrence of congenital malformations.
7.3.1.4 Ethical question involved in use of stem cells
- There is no ethical question, however, the Prolifer group led by the Pope opposes the Stem cell research on ethical grounds. It considers life to start from the very 1st day of conception and therefore it is highly unethical to use living human embryos as experimental
- This research would also result in large scale construction and destruction of human embryo On the other hand some researchers maintain that within first 14 days embryo can’t be considered a living human being as the Stem cell has not yet developed into identifiable body organs. They also say to treat infertility; multiple embryos are created for the process for Invitro fertilisations (IVF) to treat infertility. These leftover embryos can be put to research for treating various degenerative human ailments.
- Other countries involved in Stem cell research are Australia, Japan, Singapore, Israel, Sweden, U.K, South Korea and
7.4 HUMAN GENOME PROJECT
- It was one of the most innovative the largest biological project ever launched as a consortium of scientists from 18 different countries. It was launched in 1990 its succeeded including 24 different human chromosomes by June 2 Human Genome refers to complete set of genetic instructions in the form of nitrogenous base pair that constitute DNA in every cell of the human body.
- This DNA is present in the form of tightly coiled thread like structure known as chromosome. Human Genome Project succeeded in decoding 1st the 22ndchromosome which is the smallest chromosome followed by 21st and 20th and so
7.4.1 Benefits of Human Genomics
- Human Genome is of great value in the field of molecular medicine as it helps in improving diagnosis of diseases and identifying India’s genetic predisposition to a particular disease. Therefore genetic diseases can be permanently cured by instituting gene therapy. Tailor made drugs can be made to suit individual’s requirement and minimise the adverse
- In the field of human evolutions Human Genome can help in understanding the pattern of human evolution that has taken place over thousands of year. Once understood it would help in predicting the future course of evolution.
- In the field of DNA forensic, genetic Information can help in identifying the war victims specially dead soldiers whose bodies have been mutilated beyond recognition.
- It can also be used in settling paternity disputes in case of illegal exchange of newborn
- Criminals identity can be pin- pointedly established on the basis of the body samples left behind by him/her in the form of hair, nail, skin or body fluids at the scene of the crime and this would help in strengthening the criminal justice
- This information can also help in minimising organ transplant rejection reaction as organs can be cross matched in geneticsimilarity before transplantation.
- On the field of plant and animal genomics (plants and animals such as rice, mice chimpanzee and chicken) more disease and drought resistant, high yielding stronger varieties of crop and livestock can be produced. The food obtained from such crop varieties will be safer to be consumed as such plants would require less amount of pesticides and fertilizer
7.4.2 Potential dangers:
- Genetic information can be misused by parents who can go for the birth of designer babies where the parents would determine which of their physical factors and personality features their children shall possess. This may seriously restrict human gene pool and will interfere with the natural process of selection resulting in loss of diversity among human population knowing of so called bad genes may effect evolution of human beings as a species.
- The genetic privacy of an individual may be violated and based upon the genetic information various life and health insurance schemes would not be sold. Moreover, career recruitment and promotional opportunities would also be denied to so called genetically weaker sections of the society. This may have serious social consequences leading to lack of social
- This information can also be misused for producing biological weapons of mass destruction specially targeted against genetically weaker sections or a particular race susceptible to particular disease leading to social
- It may also increase the gap between the rich and the poor as the lengths arousing out of such information will benefit mostly the richer sections of the
7.4.3 Measures to prevent the misuse of human genomics:
- The international bio ethics committee constituted by UNESCO defeatedthe Universal declaration on human genome and human This declaration was adopted by UNESCO and later on also by UN general assembly. However this is not legally binding on the members of UNO but it has succeeded in making a distinction between what is possible and what is acceptable use of human genetic information. It represents a moral responsibility on the parts of the member nations to respect right to genetic privacy of Individuals.
7.5 GENE THERAPY
- It is the most revolutionary method of treatment of genetic disorders e.g., diabetics, Haemophilia, Cancers etc. Hereditary diseases occur when the key genes are flawed or missing. The gene therapy aims to either modify or replace the key genes. The technique of Gene therapy involves stripping a harmless virus(Retrovirus) of some of its genes, replacing them in correct version of defective gene that causes the diseases. The manipulated virus (retrovirus) is then introduced into the body to infect the target tissues. The advantage of using retrovirus is that it is able to break down into its constituents helping in easy incorporation of replaced genes with the genetic material of the target tissue. In Dec 1999, a team of doctors from UK and France successfully carried out world’s 1st gene therapy cure against Severe Combined Immuno Deficiency (SCID) diseases which develop therefore of a defective gene on 20th chromosome. This gene is responsible for formation of special type of white blood cell (WBC) known as T lymphocyte.
7.5.1 Other uses:
- It could also be used as a drug delivery system. A gene that manufactures a useful product can be insected into the DNA of
the patient’s cell where the product can be used by the patient’s body. E.g., During blood vessel surgery a gene that make santi-clotting factor could be inserted into the DNA of the cells of the blood vessels to prevent formation of dangerous blood clots.
- It holds a likely possibility in making body cell resistance to HIV
7.6 DNA VACCINE
- It is a third generation vaccine in the process of Unlike conventional vaccines in which either the microbial agent in attenuated form e.g., Oral Polio vaccine or the vaccines in which a harmful protein also called as microbial antigen prepared by recombinant DNA technology e.g., Hepatise B vaccine is inoculated. In DNA vaccines the DNA or the genetic blueprint of microbial antigen that would initiate immunogenic response in body by synthesizing this harmful protein is inoculated. DNA vaccine holds a
likely possibility for developing effective vaccines even against disease such as Malaria, T. B, and HIV AIDS that have until now defied the ambit of vaccination.
7.7 INTERFERONS
Interferons are the proteins that function as powerful antiviral agents. They are synthesized by vertebrates in response to viral infections. They are called so as they interfere with the ability of the virus to replicate fast.One type of interferon can be effective against different type of viruses. But animal interferons can’t be used in human beings. Biotechnology holds a likely promise to develop human interferon’s even outside human body.
7.8 BIOLOGICAL WEAPONS OF MASS DESTRUCTION
- Biological weapons include weaponised form of microscopic living agents in the form of highly toxic or pathogenic strains of bacteria, viruses, fungi and their poisonous products known as toxins. These agents are used in biological warfare to inflict tremendous causalities not only
to mankind but also disturb the delicate ecological balance by killing plants and animals. Thereby leading to a grave medical poll and social crisis of unparalleled intensity.
- Biological weapons are more popular than conventional warfare systems as they being live agents can be acquired easily and cheaply from either environment or repositories without much logistic support and they are also called as poor man’s atom bomb. Moreover, these agents are used in an invisible aerosol or droplet form, they replicate fast on dissemination. Moreover, their use comes to light only after a brief incubation period, which is required for disease to get manifested this time is sufficient enough for their perpetrators to escape form the place of their
7.9 LIMITATIONS
- These weapons as they are living agents need special environmental conditions to survive e.g. specific temperature, pressure, sunlight etc. Their use requires strategic planning and meticulous execution.
- Some of the countries that are believed to have secret clandestine stock piles of such weapons are Russia, USA , China, Libya, North and south Korea, Israel, Taiwan, Syria etc. Eg of these weapons are
- Plague causing bacteria
- Anthrax causing bacteria known as Bacillus anthracis. It is a spore forming bacteria. It remains encapsulated and remains stable even in difficult situations and can be easily circulated in powder form. These bacteria can be either inhaled, indigested or can come in contact with cut skin. Therefore may result in causing three forms of anthrax
- Inhalational anthrax,
- Gastro intestinal anthrax
- Cutaneous anthrax.
- Inhalation is most dangerous and most common. It results in flu like symptoms that include generalised body ache, fever, cold, respiratory difficulty and may cause Pneumonia the condition may cause death. Anthrax is curable if treated adequately and timely by antibiotics.
- It is also seen is Cattle, Sheep, Goat, Camel. It can be treated effectively by antibiotics if detected
Yersinia Pestis:
- It is a plaque causing bacteria which is transmitted by the bite of an agent known as rat flea. It results in a deadly disease which causes rapid death as plaque can be later on transmitted from man to man through
Variola virus:
- It causes Small pox. According to WHO this agent has been officially eradicated but is readily available with USA and Russia. Some important toxins
Botulinum toxin:
- Most potent biological weapon as it causes death by paralysing of respiratory muscles Sodium, Thiopental, Pancuronium, KCL]
Certain fungal toxins
- Aflatoxin, Tricothccene & mycotoxin
Poisonous Gases/ Chemical weapons
- Sulphur mustard, Sarin, soman, Tabun,
7.10 INDIA’S PREPAREDNESS
- A National Disaster Management Agency (NDMA) is established under ministry of Home affairs
- DRDO and DRDE (Gwalior) they are involved in Research in areas of toxicology and
- A nuclear biological chemical warfare directorate has been established in services within interservice coordination communication to monitor, prevent and combat use of such weapons
- Protective clothing has been designed for troops
- Weapons of Mass Destruction (Prohibition of unlawful activates) act 2005 – to fulfil its obligations as per UNSC resolution no 1540 which makes it mandatory for all UN members to enact a law prohibiting trafficking in nuclear, chemical and biological weapons. The parliament of India passed above said law in May 2 This act prevents transfer of WMD and technology of their developments from India to other countries
7.11 DNA FINGERPRINTING / TYPING
- DFP is a genetic method of identifying and analysing special sequences of DNA by imaging. A British geneticist known as Alec Jeffery’s in 1984 gene this technique which is based on the principle that every individual has certain unique repeatable sequences of DNA known as mini satellites and by analysing and identifying the pattern of arrangement of these DNA basis one can identify the genetic stock of an individual.
[PAGE – Poly acramide gel electrophoresis ]
- Purification – Isolation of DNA from the sample obtained from the scene from of crime
- Cutting =( A DNA molecule is cut at specific locations using DNA knives known’s as Restriction endo nucleus enzymes
- Electric current – PAGE is subjecting cut DNA fragments to electric current for their separation
- Blotting (Single hand DNA fragmented)
- Autoradiography – It is the process of obtaining fingerprints or images of complementary pairing of nitrogenous bases in between DNA Strands in question and DNA probe of similar sequence.
Uses :
- DFP is used in settling paternity disputes, illegal exchange of newborns
- This techniques can supplement various crime investigating agencies by providing an irrefutable evidences help in police personnel lawyer and forensic scientists
- It can also help for diagnosing various genetic diseases, pedigree analysis course of history and identification of genetic
- In India this technique is improved by using novel probes developed by CCMB centre for cellular and Molecular biology, Hyderabad, a new autonomous centre has been developed for the use of DNA fingerprinting in diagnosis of various Centre for DNA fingerprinting and diagnostics (CDFD)
BIOTECHNOLOGY
- Mention the breakthrough made in NCL in the field of plant- genetics and explain its significance. (90/II/8f(C)/3)
- Give a brief account of major achievements in the realm of biotechnology in India. (250 words) (91/II/3b/40)
- What is tissue culture? (91/II/8c(C)/3)
- What is genetic conservation? Bring out the salient features of genetic conservation activity in India. (About 250 words) (93/II/3b/40)
- Describe how biotechnology is finding use in medicine. Give a few current (93/II/7b/20)
- What is DNA fingerprinting? Which research institution in India is working in this area? (94/II/7d/20)
- What is a gene? Where is it found? (94/II/8f(C)/3)
- What are transgenic organisms? What are they used for? (96/II/7d/20)
- What is tissue culture? (97/II/8e(C)/3)
- What is genetic engineering? Why is it getting increasingly important these days? (98/II/3b/40)
- Why are transgenic organisms important? (98/II/8a(C)/3)
- What is the Human Genome Project? Discuss briefly its importance. (99/II/7a/20)
- What are biosensors? Describe their uses. (99/II/7d/20)
- Where is Centre Cellular and Molecular Biology located? (99/II/10e(i)/1)
- How do identical twins differ from each other genetically? (99/II/10f/3)
- Discuss Human Genome. (00/I/11b/10)
- How are transgenic plants different from hybrid plants and what is their relevance in modern agriculture? (00/II/11a/15)
- What are stem cells? Why have they been in the news recently? Discuss. (01/II/10b/30)
- “Biotechnology boom may pave a golden path for India.” Discuss. (02/I/10b/30)
- What is Human Cloning? Is it dangerous or beneficial? Discuss. (02/II/11c/15)
- Discuss the elements of ‘frozen semen technology’. What are ‘embryo transfer’, ‘transgenic animals’, ‘DNA recombinant technique’? (03/II/11c/15)
- What is Biotechnology? Discuss the important applications of Biotechnology. (04/II/11b/15)
- What is the therapeutic cloning? Describe briefly the method and its potential applications. (05/II/11b/15)
- Write a note on ‘Bio-refinery versus Fossil fuels’. (06/II/11b/15)
- What are normal osmosis and reverse osmosis? Why has reverse osmosis become popular in India today? (06/II/11c/15)
- Short note on Genome. (03/13e/2)(07/I/13e/2)
- Explain the objectives and the current achievements of human genome project. (150 words) (07/II/11b/15)
- In what way ‘Medical Biotechnology’ and ‘Bioengineering’ are useful for technological development of India? (250 words) (08/II/10a/30)
- What do you understand by
‘Biosignatures’? (09/II/8a/15)
- Write about Green Fluorescence Protein (GFP) and its applications. (09/II/8b/15)
- Define ‘Bioinformatics’. How does it work? What are its major branches and applications? (09/II/8c/15)
- Explain: DNA Finger Printing and its utility. (09/II/9a/10)
- Write brief note in about 30 words: Biiometric ATMs. (09/II/10e/3)
- Molecular Breast Imaging (MBI) technology. (2011/I/9d/5)
NO SHORTAGE OF POLIO VACCINE
19, May 2019
Why in News:
- No shortage of polio vaccine for routine immunisation says Health ministry.
Background:
- The issue came after reports of anticipated shortage following the detection of contamination, by the Central Drugs Laboratory (CDL) in Kasauli, in 16 batches of polio vaccine manufactured by Bharat Immunological and Biologicals Corporation Limited (Bibcol).
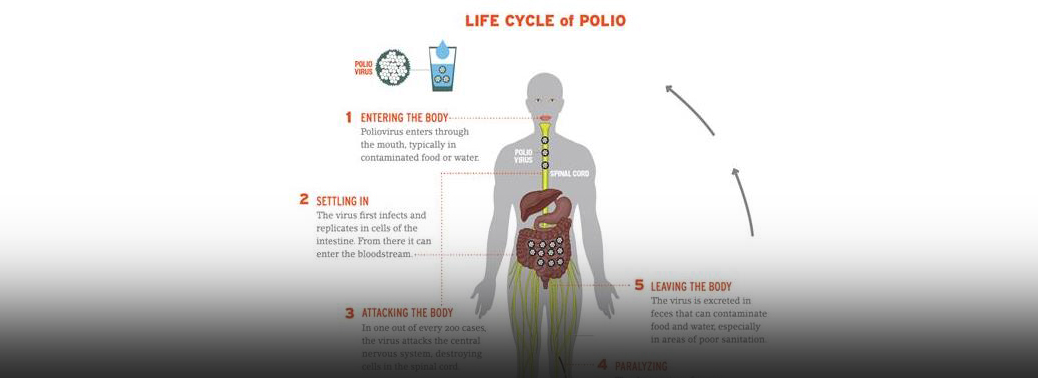
What is poliomyelitis/polio?
- Poliomyelitis, often called polio or infantile paralysis is an acute infectious disease caused by polio virus. The virus is a human enterovirus of the Picornaviridae
- There are three types of Polio Virus: 1,2,3-Single stranded RNA virus Natural or Wild Polio Virus (WPVS). It is transmitted from one person to another by oral contact with secretions or faecal material from an infected person. It attacks the central nervous system through the blood stream and damage the cells and paralyse the victim.
Types of Polio vaccines
- Two different kinds of vaccine are available: an inactivated (killed) polio vaccine (IPV) and a live attenuated oral polio vaccine (OPV).
Inactivated Polio vaccine (IPV):
- It was first introduced in 1995 by Dr. Jonas Salk
- It is produced from wild-type poliovirus strains of each serotype that have been inactivated (killed) with formalin.
- It is an injectionable vaccine and can be administered alone or in combination with other vaccines (e.g., diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, and haemophilus influenza).
Oral Polio vaccine (OPV):
- It was first introduced in 1961 by Dr. Albert Sabin
- consists of a mixture of the three live attenuated poliovirus serotypes (Sabin types 1, 2 and 3), selected for their lower neurovirulence and reduced transmissibility.
- Apart from trivalent OPV (tOPV), monovalent OPVs viz. against Type 1 (mOPV1) and against type-3 (mOPV3) have been licensed for use in some countries
- In 2009, 2 bivalents (type-1 and type-3) OPVs (bOPVs) were licensed.
NOTICE TO CENTRE ON BT BRINJAL
13, May 2019

Why in News:
- Senior advocate Prashant Bhushan has sent a legal notice to Union Environment Minister Harsh Vardhan asking for a freeze on all genetically modified organisms, including field trials.
Details:
- Though growing Bt brinjal is illegal in India Bhushan’s letter comes in the aftermath of activist groups recently proffering evidence of Bt Brinjal, a GM crop, being grown in a farmer’s field in Haryana.
- Letter demands the Environment Ministry to uproot and destroy planted Bt brinjal in farms and seedlings in nurseries, undertake a scaled-up exercise of testing of seeds and plantings (for the presence of BT Genes) and, ascertain the supply chain – from seed developers to intermediaries.”
- Bt brinjal was the first food crop made to contain an insecticidal protein, called cry1 ac,
- Though this was cleared for commercial cultivation it was put in deep-freeze in 2010 on the grounds that there was scientific and public disagreement on its safety.
- The lab report was also sent to the government, which picked up samples of the suspected Bt Brinjal crop and sent it to the National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR) in New Delhi for testing.
- Following brinjal, a genetically modified strain of mustard too is in the regulatory pipeline. GEAC panel ruled that more tests were required before the mustard could be made available in farmer fields.
What is Bt Brinjal?
- Bt Brinjal is a transgenic brinjal created out of inserting a gene [Cry 1Ac] from the soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis into Brinjal. The insertion of the gene into the Brinjal cell in young cotyledons has been done through an Agrobacterium-mediated vector, along with other genes like promoters, markers etc.
- This gives (so said) Brinjal plant resistance against lepidopteran insects like the Brinjal Fruit and Shoot Borer (Leucinodes orbonalis) and Fruit Borer (Helicoverpa armigera).
Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC)
- The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) was constituted under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) as the apex body under the ‘Rules for Manufacture, Use, Import, Export and Storage of Hazardous Microorganisms/Genetically Engineered Organisms or Cells 1989’ in accordance with the Environment Protection Act, 1986.
National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources
- Management and promote sustainable use of plant genetic and genomic resources of agri- hotricultural crop and carry out related research
- Coordination and capacity building in PGR management and policy issues governing access and benefit sharing of their use
Karnataka Law On Sc/St Promotion Quota Upheld
11, May 2019

Why in News:
- Jeff Bezos, who heads both Amazon and space company Blue Origin, unveiled a lunar lander and it would be used to transport equipment, and possibly human beings, to the south pole of the Moon by 2024
Details:
- He showed a mock-up of a huge vessel weighing many tons and able to carry four self- driving Mr. Bezos didn’t announce a specific date for the project’s first launch, but said the lander would be ready in time to make President Donald Trump’s announced timeline to return people to the Moon by 2024.
Generating water
- The vehicle has been under development for the past three years.
- It will be capable of carrying scientific instruments, the four small rovers, and also a future pressurized vehicle for humans. The goal is to land on the Moon’s south pole, where ice deposits were confirmed in 2018. Water can be exploited to produce hydrogen, which in turn could fuel future exploration of the solar Fully loaded with fuel, Blue Origin will weigh about 33,000 pounds (15,000 kilograms), which will decrease to around 7,000 pounds when it is about to land
Lunar colonies
- The broader vision to build an infrastructure that would sustain the colonisation of space by future generations of humans and shift polluting industries off the As space agencies prepare to return humans to the moon, top engineers are racing to design a tunnel boring machine capable of digging underground colonies for the first lunar inhabitants. The humans need to be shielded from radiation and freezing temperatures in structures which maintain atmospheric pressure in a vacuum.
- They also need protection from meteorite strikes.
India’s lunar mission
- Chandrayaan-2, India’s second lunar mission, has three modules namely Orbiter, Lander (Vikram) & Rover (Pragyan). The Orbiter and Lander modules will be interfaced mechanically and stacked together as an integrated module and accommodated inside the GSLV MK-III launch The Rover is housed inside the Lander. After launch into earth bound orbit by GSLV MK-III, the integrated module will reach Moon orbit using Orbiter propulsion module.
- Subsequently, Lander will separate from the Orbiter and soft land at the predetermined site close to lunar South
- Further, the Rover will roll out for carrying out scientific experiments on the lunar Instruments are also mounted on Lander and Orbiter for carrying out scientific experiments.
- All the modules are getting ready for Chandrayaan-2 launch during the window of July 09, to July 16, 2019, with an expected Moon landing on September 06,
Chandrayan -2 to Be Launched in July
11, May 2019

Why in News:
- Chandrayan-2, a fully indigenous mission to be launched during mid of July with 14 Indian payloads
Background:
- In October 2008, the space organisation had launched its orbiter mission Chandrayaan-1 on its PSLV The spacecraft had 11 payloads. One of the U.S. payloads shares credit with Chandrayaan-1 for confirming the presence of water ice on the moon.
- Before that, the Moon Impacter Probe carrying the Indian tricolour image was made to hard-land on the lunar south pole.
About Chandrayan -2:
- Launch vehicle: GSLV Mk III
- Lift off mass (approx.): 3,890 kg
- Launch from: Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh
- Orbiter: It will orbit the moon at a distance of 100 km from the lunar Payloads on the orbiter are: Large Area Soft X-ray Spectrometer, L and S band Synthetic Aperture Radar, Imaging IR Spectrometer, Neutral Mass Spectrometer and Terrain Mapping Camera-2. The structure of the orbiter was manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- Lander: The lander has been named Vikram after scientist Vikram The lander will detach from the orbiter, descend to a lunar orbit, before attempting to land on the surface.
- It will make a soft-landing and deploy the rover. It will also perform some scientific activities for about 15 days. Payloads on the lander are: seismometer, thermal probe, Langmuir probe and radio occultation.
- Rover: The 27 kg rover will operate on solar It will move on six wheels and conduct chemical analyses on-site. It will then transmit the data to the orbiter which will send this data back to the earth station. The rover payloads include Laser induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS) and Alpha Particle Induced X-ray Spectroscope (APIXS). Chandrayaan II is India’s second lunar mission after Chandrayaan I.
- The mission includes a lunar orbiter, rover and a The mission is developed by ISRO, India. Initially, the lander was supposed to have been developed by Russia. But, when Russia cited its inability to provide the lander by 2015, India decided to go solo. Now, the mission is entirely Indian. The launch vehicle would be a GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III).
Way Ahead:
- The mission is attempting to soft-land on the moon’s surface at a latitude of about 70° south, that would be on a high plain in between 2 If successful, this would be the
OUTER CLARITY: ON ‘WEAPONISATION’ OF OUTER SPACE
05, Apr 2019
Why in News:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successful launch of the PSLV-C45 rocket that placed 29 satellites in three different orbits appears that the Indian space programme stands galvanised and poised for a giant leap.
Details:
- In February 2017, the PSLV-C37 placed 104 satellites, 96 of them from the U.S shows
- ISRO’s ability to launch satellites at a fraction of the cost that other countries incur.
- In February 2017 launch also placed the fifth of the Cartosat 2 series in orbit, an earth observation satellite with cameras that have a resolution of less than a metre.
- The PSLV-C45 placed EMISAT, which can, among other things, aid in electronic intelligence. In other words, India is achieving a great place in space military architecture.
- Over the next few months, as many as eight satellites are expected to be launched, which aims to strengthen the defence dimension.
PSLV-C37 / CARTOSAT -2 Series Satellite:
- India’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle, in its thirty ninth flight (PSLV-C37), launches the 714 kg Cartosat-2 series satellite for earth observation and 103 co-passenger satellites together weighing about 663 kg at lift-off into a 505 km polar Sun Synchronous Orbit (SSO). PSLV- C37 was launched from the First Launch Pad (FLP) of Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR, Sriharikota. This was the sixteenth flight of PSLV in ‘XL’ configuration (with the use of solid strap-on motors).
- The co-passenger satellites comprised of 101 nanosatellites, one each from Kazakhstan, Israel, The Netherlands, Switzerland, United Arab Emirates (UAE) and 96 from United States of America (USA), as well as two Nano satellites from India. The total weight of all these satellites carried on-board PSLV-C37 was about 1377 kg.
- PSLV-C37 also carried two ISRO Nano satellites (INS-1A and INS-1B), as co-passenger satellites. These two satellites carry a total of four different payloads from Space Applications Centre (SAC) and Laboratory for Electro Optics Systems (LEOS) of ISRO for conducting various experiments.
- The 101 International customer Nano satellites were launched as part of the commercial arrangements between Antrix Corporation Limited (Antrix), a Government of India company under Department of Space (DOS), the commercial arm of ISRO and the International customers.
PSLV C45:
- The PSLV-C45 is the 47th mission of the Indian Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) program.
- The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV)-C45 was launched on 1 April 2019 with a payload of 29 satellites, including one for electronic intelligence, along with 28 customer satellites from other countries.
- It placed the primary satellite, EMISAT, a piece of surveillance equipment to be used by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), to the 748 km sun-synchronous polar orbit.
- It then made one complete revolution around Earth, over the poles, while lowering its orbit to 504 km height, after which it deposited the 28 international customer satellites — 24 from the US, two from Lithuania, and one each from Switzerland and Spain.
- It then made a further round of Earth while attaining an even lower orbit of 485 km, where the fourth stage of the rocket will continue for some time. This operation took a little over three hours.
Significance of the Achievement:
- Reaching three different orbits gives ISRO a new technological edge.
- It demonstrated its capability to reuse the fourth-stage engines multiple times, and also showed that the guidance and navigation systems aboard the launch vehicle could be used for much longer times than in earlier missions
- it will help ISRO pack its future rockets with multiple satellites even if they require to be placed in very diverse but precise orbits. Currently, this could be done only in multiple missions.
Significance of Using the Fourth Stage as a Satellite:
- The rocket, or the launch vehicle, is only a carrier. Once it places its passenger, or satellite, to its designated orbit in space, it becomes practically useless, adding to the space debris.
- For the last few years, ISRO had been planning to give some life to the rocket — at least to the uppermost part, or the last stage — which remains with the satellite till the ejection.
- The lower parts of the rocket are in any case discarded in the earlier stages and become junk. There is no way to put them to any use.
- The uppermost stage, however, can be used, at least temporarily. Previously, they would end up in some orbit to wander aimlessly and endlessly.
What purpose will it serve?
- The fourth stage is carrying three kinds of equipment to carry out some measurements and experiments, and a solar panel to provide power to these equipment’s and enable communication with ground stations.
- One kind of instrument can be used to capture messages transmitted from ships, another can be used by amateur radio operators use for tracking and monitoring position data, and the third can study the structure and composition of the Ionosphere.
Way forward:
- The government should articulate much more clearly the doctrinal aspects of the space programme.
- India must communicate its peaceful intentions so as to contribute to a better understanding among countries and to reduce the chances of wrong inferences being drawn in crisis situations.
- New Delhi must take a bigger lead in forging a global and legally binding instrument to prevent militarisation of space
NASA’S Probe Discovers a New Planet
09, Jan 2019

Context:
NASA’s latest planet-hunting probe has discovered a new world outside our solar system, orbiting a dwarf star 53 light years away.
Details:
- This is the third new planet confirmed by the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) since its launch in April last year.
- The planet, named HD 21749b, orbits a bright, nearby dwarf star about 53 light years away, in the constellation Reticulum, and appears to have the longest orbital period of the three planets so far identified by TESS.
About Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite
- The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is a space telescope for NASA’s Explorers program, designed to search for exoplanets using the transit method in an area 400 times larger than that covered by the Kepler mission.
- It was launched on April 18, 2018 atop a Falcon 9 rocket. During its 2-year primary mission, it is expected to find more than 20,000 exoplanets, compared to about 3,800 exoplanets known when it launched.
- The primary mission objective for TESS is to survey the brightest stars near the Earth for transiting exoplanets over a two-year period.
- The TESS satellite uses an array of wide-field cameras to perform a survey of 85% of the sky. With TESS, it is possible to study the mass, size, density and orbit of a large cohort of small planets, including a sample of rocky planets in the habitable zones of their host stars.






