Category: International / Indian Relations
BRICS AGAINST COVID 19
04, May 2020

Why in News?
- In the global war against the COVID-19, emerging economies, many belonging to BRICS, have reached out to other countries affected by the pandemic.
Response by BRICS Countries During the Pandemic: India:
- India has reinforced its credentials as a Rapidly emerging Pharmacy of the world.
- Export of Hydroxychloroquine:
- As the world’s largest producer of hydroxychloroquine, we have recently exported the drug not only to SAARC countries and to its “extended neighbourhood” in the Gulf, but also to Russia, Brazil, Israel and the U.S.
- These steps taken have set the stage for India to create an inclusive BRICS-driven pharma alliance, which could also actively explore the production of vaccines.
China:
- China has also responded strongly in containing the pandemic, leveraging its position as the workshop of the world.
- China has supplied the “hardware” i.e masks, gloves, coveralls, shoe covers and testing kits to hotspots worldwide.
- Under its Health Silk Road doctrine, the Chinese reached out to two of the worst global hotspots, Italy and Iran.
- A Chinese shipment which included essential supplies and equipment, including respirators, protective suits, masks and medications has been sent to Italy.
- China is running a medical air bridge bound for Europe.
Russia:
- Russia has sent its doctors and virologists overseas, including the launch of the famous ‘From Russia with love’ air mission to Italy.
- A Russian Antonov-124, packed with medical supplies and experts, landed at New York’s John F. Kennedy International Airport recently.
- Russia is equipped with top-of-the-line emergency services, which are equipped to handle any kind of emergency.
South Africa:
- As being the current rotating head of the African Union, it is engaged in framing a pan African response to COVID-19.
Brazil:
- Among the BRICS countries, only Brazil’s response may need a course correction, as its resistance to breaking the infection chains through travel bans, lockdowns, isolation and testing appears to have led to an infection surge.
Coordination of Efforts to Tackle the pandemic:
- BRICS nations have already demonstrated their comparative strengths as providers of Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR).
- BRICS countries now need to pool and coordinate their efforts, in partnership with the WHO, and Europe and North America, as part of a global assault on the virus.
- Special focus on vulnerable countries:
- BRICS nations may have to reactivate an existing disaster response mechanism, and earmark resources and assets to combat a whole range of natural disasters, with special attention towards the emerging economies and the global south.
Financial Allocation Model:
- The New Development Bank of the BRICS countries has already demonstrated the way forward to allocate financial resources to combat COVID-19.
- NDB has already disbursed a $1 billion emergency loan to China, and subsequently to India, South Africa and Brazil,
- Also the NDB had the Financial heft to Provide $10 billion in “crisis-related assistance” to BRICS member countries.
- The NDB’s Financial Model, Demonstrated to address the pandemic, can now become a template to Address Natural Disasters.
SAARC 2.0
08, Apr 2020

Why in News?
- India has shown diplomatic resilience and leadership by forging unity in the neighbourhood in the war against COVID-19.
Highlights:
- A tweet by Prime Minister Narendra Modi resulted in the first-ever virtual summit of SAARC leaders recently.
- In the backdrop of political capital invested by New Delhi in strengthening BIMSTEC and the urging it received recently from Nepal and Sri Lanka to resuscitate SAARC, this conference was quite significant.
SAARC Virtual Meeting and its Outcome:
- All the eight member-states were represented at the video conference — all at the level of head of state or government, except Pakistan.
- South Asian nations agreed to evolve a common strategy to meet the challenge posed by the Covid-19 pandemic.
- India proposed the creation of an emergency fund with an initial contribution of $10 million to halt the onslaught of the disease that has so far claimed nearly 6,000 lives globally.
- Pakistan sought to use the occasion to raise the Kashmir issue, calling for the lifting of embargos on communication in Kashmir to better tackle the spread of Covid-19.
- PM Modi also offered online training for health workers in Saarc countries to scale up skills to beat Covid-19.
Follow up on the Meeting:
- COVID-19 Emergency Fund: Within days, all the countries, except Pakistan, contributed to it voluntarily, bringing the total contributions to $18.8 million. However the sum is less but seeing the lesser COVID-19 effect on South Asia, it is justified.
- Fund operationalised: It is controlled neither by India nor by the Secretariat. It is learnt that each contributing member-state is responsible for approval and disbursement of funds in response to requests received from others.
- Implementation: India is in the lead, with its initial contribution of $10 million. It has received requests for medical equipment, medicines and other supplies from Bhutan,Nepal, Afghanistan, Maldives, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka.
- A follow-up video-conference of senior health officials was arranged on March 26.
- Significance: India’s imaginative diplomacy has leveraged the crisis to create a new mechanism for workable cooperation.
Challenges:
- Pakistan’s non-cooperation: Saarc has been in the ICU since 2015, on account of Pakistan’s refusal to cooperate in regional connectivity projects, and India’s refusal to engage with Pakistan.
- The last SAARC summit was held in 2014 and subsequent summits could not be held in the backdrop of terrorist attacks in Pathankot and Uri. Preference to BIMSTEC: BIMSTEC has more trade and greater trade potential due to the presence of two important trading partners India and Thailand.
- BIMSTEC has better regional connectivity via land and sea.
- SAARC adherents maintain that all proposals for cooperation should be routed through the Secretariat and activities should be piloted by the incumbent chair.
- Given what Pakistan has done to harm India’s interests since the terrorist attack on the Uri Army base in 2016 and its continuing resistance to cooperation against COVID-19, both New Delhi and its friendly neighbours need to start preparing themselves for SAARC 2.0. India has been developing connectivity with Myanmar, Bangladesh, Thailand. So similarly, it should do in South Asia even if it means bypassing Pakistan.
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC):
- The signing of the SAARC Charter in Dhaka established the SAARC in 1985.
- Its secretariat is in Kathmandu, Nepal.
- Objectives:The SAARC seeks to promote the welfare of the peoples of South Asia, strengthen collective self-reliance, promote active collaboration and mutual assistance in various fields, and cooperate with international and regional organizations.
- Eight states―Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
- Six observers—China, Japan, European Union, Republic of Korea, United States, Iran
US – IRAN RELATIONS
10, Jan 2020

Why in News?
- Tensions between US and Iran has reduced after US has backed away from further conflict with Iran.
About:
- The United States and Iran have a long history of tensions, but the latest escalation started when an American drone strike killed top Iranian general Qassem Soleimani recently.
- The roots of the latest Iran-US crisis go back to 2018, when US President Donald Trump walked away from the Iranian nuclear deal, one of the signature achievements of his predecessor Barack Obama, and reimposed harsh sanctions on the country.
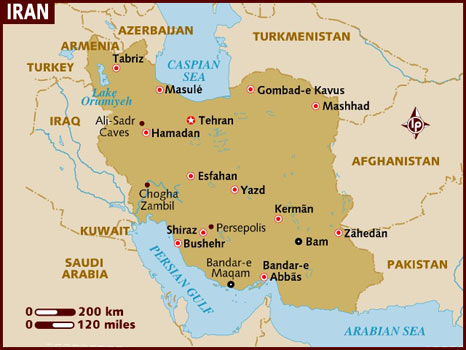
About Iran Nuclear Deal:
- Iran agreed to rein in its nuclear programme in a 2015 deal struck with the US, UK, Russia, China, France and Germany (P5+1 countries).
- Under the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPoA)Tehran agreed to significantly cut its stores of centrifuges, enriched uranium and heavy-water, all key components for nuclear weapons.
Why did Iran Agreed to the deal?
- It had been hit with devastating economic sanctions by the United Nations, United States and the European Union.
- Billions in overseas assets had also been frozen.
Why has US pulled out of the Deal?
- Trump and opponents to the deal say it is flawed because it gives Iran access to billions of dollars but does not address Iran’s support for groups like Hamas and Hezbollah which the U.S. considers as terrorists.
- It also doesn’t curb Iran’s development of ballistic missiles and that the deal phases out by 2030.
What are the Implications of US sanctions on Iran?
- Other countries have promised to uphold it, but their ability to do so will depend on how their companies can be firewalled from U.S. sanctions if they continue their engagement with Iran.
- The sanctions often referred to as “secondary sanctions”, which primarily target non-US companies engaging in business in or with Iran entirely outside US jurisdiction.
What is its Significance?
- The Iran deal, despite its shortcomings, was a shining example of the capacity of world powers to come together and sort out a complex issue diplomatically.
- It assumed greater significance given the recent wars and chaos in West Asia.
- It should have set a model in addressing other nuclear crises.
- Iran deal, and other diplomatic achievements, is necessary to convince countries like North Korea, that it is possible to create security without acquiring nuclear weapons.
- The deal is important in ensuring the international nuclear non-proliferation regime and regional peace and stability.
What is its Impact on India?
- India and Iran relations are on downward trend in recent times.
- Oil supplies are reduced to India and Iran is not in favour of allotting gas fields to India in recent times. Mostly India’s relations with the US might be the reason for this.
- But India is in a better position having been forced to diversify its crude supplying base.
- It may impact on Chabahar port project if US impose more sanctions on Iran.
- It will impact India’s balance in the complex West Asia region.
U.S. WARNS ALLIES OF SANCTIONS RISK
04, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- The U.S. officials have warned India that with the decision to go ahead with the purchase of the Russian S-400 missile defence system, India may risk sanctions.
Background:
- India had agreed to purchase the surface-to-air missile system (S-400 missile defence system) from Russia in 2018 for about $5.2 billion, risking sanctions under the 2017 U.S. CAATSA law.Sanctions could kick in when the first payment for the equipment is made unless the U.S. President grants a waiver.
- S. government officials have repeatedly asserted, in the Indian context, that countries should not assume that waivers are automatic.
Highlights:
- The S-400 ‘Triumf’ is the most advanced long-range air defense missile system that went into service in Russia in 2007.It is designed to destroy aircraft, cruise and ballistic missiles, including medium-range missiles, and can also be used against ground installations.The S-400 can engage targets at a distance of 400 km and at an altitude of up to 30 km.
- Russia has also signed the contracts for the delivery of these systems with China (the first customer) and Turkey.
- The U.S. has urged all their partners to forgo transactions with Russia that risk triggering sanctions under the Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA).
CAATSA:
- CAATSA, Enacted on August 2, 2017, aims to counter the aggression by Iran, Russia and North Korea through punitive measures.
- The Act deals with sanctions on Russian interests such as its oil and gas industry, defence and security sector, and financial institutions, in the backdrop of its military intervention in Ukraine and its alleged meddling in the 2016 US Presidential elections.
- The Act empowers the US President to impose at least five of the 12 listed sanctions on persons engaged in a “significant transaction” with Russian defence and intelligence sectors.
- Two of the most stringent of these sanctions are the export licence restriction by which the US President is authorised to suspend export licences related to munitions, dual-use and nuclear-related items; and the ban on American investment in equity/debt of the sanctioned person.
- The extent to which CAATSA would affect Indo-US defence relations will depend on what sanctions, if any, Washington decides to impose on New Delhi in view of India’s continued defence cooperation with Russia.
INDIA SHOULD NOT HAVE JOINED U.S. BAN, SAYS IRAN
11, Sep 2019

Context:
- India’s decision to shut down oil imports from Iran due to sanctions imposed by the United States is also hurting India-Iran bilateral trade and India’s future in Chabahar port, said Iranian Ambassador to India Ali Chegeni.
Background:
- India stopped crude oil imports from Iran on 2 May after the US sanctions.
- Last year, US President Donald Trump had walked out of the 2015 Iran nuclear deal, signed between Iran and six countries representing the international community.
Indian stand on Sanctions:
- India, which says that it only recognizes United Nations-mandated sanctions and not those imposed by specific countries, has been adhering to the US sanctions as they target public and private companies doing business with Iran.
China on US Sanctions:
- China was not adhering to the US-imposed sanctions and had agreed to invest $280 billion in Iran’s oil, gas and petrochemical sectors that are being affected by US sanctions.
- In return, Iran will grant Chinese companies’ priority in tenders for any new or incomplete projects to develop oil and gas fields, as well as petrochemical projects.
India Iran oil Relationship:
- Iran has always been one of India’s main suppliers of oil, second only to Iraq and Saudi Arabia, with exports that totalled more than 27 million tonnes last year.
Local Currency:
- There is the option of trading in local currencies to pay for oil that India buys from Iran, or doing barter trade, that is, Tehran will buy goods from India in return for the oil that its exports without paying a cent.
India US Concern Issue:
- With the US pushing India to end its oil trade with Tehran and New Delhi unwilling to jeopardize its rapidly warming ties with Washington, it was clear that India would steer clear of buying oil from Iran. The US had also helped India get Pakistan-based Jaish-e Mohammed terrorist group chief Maulana Masood Azhar listed as a terrorist under UN norms and had made it clear that it expected reciprocity.
- The US has exempted Indian investments in Chabahar from sanctions given that New Delhi sees it as a gateway to Afghanistan but Indian companies, fearful of possible repercussions of investing in Iran, have stayed away.
Iran’s stand on Issue:
- Iran says that the countries followed their national interests but he also underlined that India had followed an independent foreign policy that would allow it to take independent decisions.
Similar issue in 2012:
- In 2012, when the Obama administration wanted to maximise pressure on Iran in order to secure the nuclear deal or the Joint Comprehensive Plan Of Action, it had sent a similar tough message to New Delhi, albeit more discreetly than the Trump administration has.
- India agreed to cut oil imports by 15% subsequently, but asserted its autonomy.
- Rupee-Rial Mechanism
- New Delhi operationalised a ‘rupee-rial’ mechanism, under which half of what it owed Tehran for oil imports would be held in a UCO Bank account and made available to Iranian companies to use for any imports from India, an arrangement the Narendra Modi government is seeking to re-energise.
How Situation is different from 2012
- But 2019 is not 2012, and the stakes are higher for the government.
- Ties with the U.S. are under strain over several issues, including U.S. trade tariffs and India’s defence procurement from Russia, and a major divergence on Iran will exacerbate the problem with India’s biggest trading partner and fastest growing defence partnership.
- Moreover, in an increasingly globalised world, where Indian companies compete, any U.S. sanctions will make it hard for refiners, insurers and transport companies to facilitate oil trade, even if India wishes to continue it.
- On the other hand, India’s investment in the Iranian relationship has increased, making a turnaround much more difficult.
- New Delhi rolled out the red carpet for Iran’s President Hassan Rouhani and committed itself to increasing its oil off-take by 25% this year, as part of easing negotiations for the Farzad-B gas fields India is keen to buy a stake in.
- India has also committed itself to investing $500 million to build berths at Chabahar’s Shahid Beheshti Port, and $2 billion to build a rail line through the Zahedan province to Afghanistan, in an effort to circumvent trade restrictions by Pakistan.
- Iran’s other oil importers, China and Turkey, have said they will not accept the U.S.’s diktat.
India Iran projects:
Chabahar Port:
- India is helping develop the Chabahar Port, which will give it access to the oil and gas resources in Iran and the Central Asian states.
- By so doing, India hopes to compete with the Chinese, who are building Gwadar Port, in Pakistan’s Balochistan.
Zaranj Delaram Highway:
- A Highway between Zaranj and Delaram is being built with financial support from India.
North South Transport corridor:
- The North–South Transport Corridor is the ship, rail, and road route for moving freight between India, Russia, Iran, Europe, the Caucasus, and Central Asia. The route primarily involves moving freight from India, Iran, Azerbaijan and Russia via ship, rail and Road.
NEW DELHI INTERNATIONAL ARBITRATION CENTRE BILL, 2019
13, Jun 2019
Why in News?
- The Union Cabinet has approved the Bill New Delhi International Arbitration Centre (NDIAC) Bill, 2019 for introduction in the ensuing session of Parliament.
Highlights:
- In view of the provisions of the Article 107 (5) and 123 (2) of the Constitution, the New Delhi International Arbitration Centre Bill, 2019 is proposed to be introduced in the Parliament.
- The Bill provides for setting up of an independent an autonomous body for institutional arbitration.
- It aims to acquire and transfer the undertakings of International Centre For Alternative Dispute Resolution (ICADR) to New Delhi International Arbitration Centre (NDIAC).
New Delhi International Arbitration Centre (NDIAC):
- The NDIAC will be headed by a Chairperson, who has been a Judge of the Supreme Court or a Judge of a High Court or an eminent person, having special knowledge and experience in the conduct or administration of arbitration, law or management,
- He is to be appointed by the Central Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of India. Besides, it will also have two Full-time or Part-time Members from amongst eminent persons having substantial knowledge and experience in institutional arbitration in both domestic and international.
- In addition, one representative of a recognized body of commerce and industry shall be nominated on rotational basis as a Part-time Member.
- The Secretary, Department of Legal Affairs, Ministry of Law & Justice, Financial Adviser nominated by Department of Expenditure, Ministry of Finance and Chief Executive Officer, NDIAC will be ex-officio Members.
Aims and objectives of NDIAC:
- bring targeted reforms to develop itself as a flagship institution for conducting international and domestic arbitration.
- provide facilities and administrative assistance for conciliation, mediation and arbitral proceedings;
- maintain panels of accredited arbitrators, conciliators and mediators both at national and international level or specialists such as surveyors and investigators;
- facilitate conducting of international and domestic arbitrations and conciliation in the most professional manner;
- provide cost effective and timely services for the conduct of arbitrations and conciliations at Domestic and International level;
- promote studies in the field of alternative dispute resolution and related matters, and to promote reforms in the system of settlement of disputes; and
- co-operate with other societies, institutions and organisations, national or international for promoting alternative dispute resolution.
Impact:
- The benefits of institutionalized arbitration will be manifold for the Government and its agency and to the parties to a dispute.
- This will result in quality experts being available in India and also an advantage in terms of cost incurred.
- It will facilitate India becoming a hub for institutional arbitration.
International Arbitration in India:
- It has been the endeavor of the Government of India to establish an independent and autonomous institution for resolving International and domestic commercial disputes expeditiously by Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) mechanism.
- In this regard, a HL Committee headed by Mr. Justice B.N. Srikrishna, former Judge of the Supreme Court of India, was constituted in the year 2017.
- The HLC recommended that the Government may take over the International Centre For Alternative Dispute Resolution (ICADR), an existing institution which has been established in the year 1995 using the public funds and develop it as an Institution of National Importance.
- Taking into consideration the HLC’s recommendations, a Bill, namely the New Delhi International Arbitration Centre (NDIAC) Bill 2018 was approved.
AIR DEFENCE SYSTEMS TO INDIA
10, Jun 2019
Why in News?
- • The United States has approved the sale of armed drones to India also offered integrated air and missile defence systems. Its objective is to improve India’s military capabilities and to protect Indo-Pacific region.
- • US administration is likely to send the final draft of the ‘letter of acceptance’ for the sale of NASAMS-II to India under its foreign military sales programme, at a cost of over Rs 6,000 crore (about US dollar 1 billion), by July-August.
NASAMS-II Air Defence system:
- • NASAMS-II (National Advanced Surface to Air Missile System – NASAMS) is an upgraded version of the NASAMS developed by Raytheon in partnership with KONGSBERG Defence and Aerospace of Norway.
- • It has been operational since 2007. It features new 3D mobile surveillance radars and 12 missile launchers for quicker reaction.
- • NASAMS-II is highly adaptable mid-range solution for any operational air defence requirement.
- • It provides tailor-able, state-of-the-art defence system that can maximise the ability to quickly identify, engage and destroy current and evolving enemy aircraft, UAV or emerging cruise missile threats.
- • NASAMS-II is armed with 3D Sentinel radars, short and medium-range missiles, launchers, fire-distribution centres and command and control units to quickly detect, track and shoot down multiple airborne threats.
- • It is part of the air defence network guarding US capital city Washington DC. It is also deployed in several NATO countries.
Background:
- • In year 2017, the United States had agreed to sell surveillance version of the Guardian drones to India following a meeting between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and President Donald Trump. With this offer, India has become the first non-treaty partner to be offered an MTCR Category-1 Unmanned Aerial System – the Sea Guardian UAS manufactured by General Atomics.
- • India signed the S-400 deal with Russia in October 2018 after four years of extensive negotiations and an inter-governmental agreement despite the threat of sanctions under the US law called CAATSA (Countering America’s Adversaries through Sanctions Act).
Significance for India:
- • India’s deal of NASAMS-II will help country to protect air route also to prevent 9/11-kind of attacks. It will also complement India’s other systems such as the medium and long- range surface-to-air missile (SAM) systems under procurement. With this, India will join League of Nations including US, Russia and Israel etc. who have their own missile defence systems to protect their national capital regions.
NEW START POLICY
09, Jun 2019
GS 3 : IR – International Happenings
Why in News?
Russian has warned to US to withdraw the Obama-era nuclear weapons pact New START due to the US disinterest in its renewal.
New START pact:
- The New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (New START) pact limits the number of deployed nuclear warheads, missiles and bombers and is due to expire in 2021 unless renewed.
- The treaty limits the US and Russia to a maximum of 1,550 deployed nuclear warheads and 700 deployed missiles and bombers, well below Cold War caps.
- It was signed in 2010 by former US President Barack Obama and then-Russian President Dmitry Medvedev. It is one of the key controls on superpower deployment of nuclear weapons. If it falls, it will be the second nuclear weapons treaty to collapse under the leadership of US President Donald Trump.
- In February, US withdrew from the 1987 Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty (INF), accusing Moscow of violating the agreement.
MENSTRUAL HYGIENE DAY 2019
01, Jun 2019
Why in News?
- • The MH Day seeks to break the silence, raise awareness and change the negative social norms surrounding menstrual hygiene.
Highlights:
- • The world is slowly moving towards removing the social stigma surrounding menstruation, the word ‘period’ still remains a taboo in most societies. In most countries, girls still avoid going to school when they are on their period.
- • Women in rural areas or in poverty-ridden nations still use paper and other harmful materials such as dried leaves and plastic as a substitute for sanitary pads.
- • The main theme of this year’s Menstrual Hygiene Day is ‘It’s Time for Action!’ The day
aims to ensure no girl is left behind. - • In the year 2018, around 310 organizations educated around 27.2 million girls across 134 countries. For the year 2019, the participating organizations are committed to educating a total of 41.4 million girls across the world.
Menstrual Hygiene Day:
- • The Menstrual Hygiene Day (MH Day) is a global advocacy platform that brings together the voices and actions of non-profits, government agencies, individuals, private sector and the media to promote good menstrual hygiene management (MHM) for all women and girls.
Vision:
- • To create a world in which every woman and girl is empowered to manage her menstruation safely, hygienically, with confidence and without shame, where no woman or girl is limited by something as natural and normal as her period.
Objective:
- • The MH Day seeks to break the silence, raise awareness and change the negative social norms surrounding menstrual hygiene.
- • It encourages and engages decision-makers to increase emphasis on the issue and mobilize action to create more awareness at global, national and local levels.
Why do we need the day?
- • Poor menstrual hygiene along with limited access to hygienic menstrual products and poor sanitation infrastructure undermine the educational opportunities, health and overall
- social status of women and girls around the world.
- • As a result of this, millions of women and girls are kept from attaining their full potential.
• Hence, the day aims to educate people around the world regarding the persisting taboos and stigma associated with menstruation, as the primary reason for poor menstrual hygiene is the lack of education.
EAST CONTAINER TERMINAL
30, May 2019
Why in news?
- Sri Lanka, Japan and India on Tuesday signed an agreement to jointly develop the East Container Terminal at the Colombo Port.
East Container Terminal:
- The three countries will jointly build the East Container Terminal at the Port of Colombo.
- As per the agreement the Sri Lanka Ports Authority (SLPA) retains 100% ownership of the East Container Terminal (ECT), while the Terminal Operations Company is jointly owned,the SLPA
- Sri Lanka will hold a 51% stake in the project and the joint venture partners will retain 49%.
- Japan is likely to provide a 40-year soft loan with a 0.1% interest rate, details of India’s
contribution to the initiative are awaited,
Importance of the Project for India:
- Over 70% of the trans-shipment business at the strategically located ECT is linked to India
- The involvement of India and Japan is the project is being seen as a big development aimed at neutralising the growing influence of China, which has poured money into the South Asian island nation under its mammoth Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) infrastructure plan
US HAS REMOVED INDIA FROM ITS CURRENCY MONITORING WATCHLIST
29, May 2019
Why in news?
- The US administration under Trump has removed India from its currency monitoring watch list.
Countries in the list:
- India, alongside China, Japan, Germany, Switzerland and South Korea, was placed in the bi-annual currency watch list in October last year.
- While India and Switzerland have not been mentioned in the latest list, the US has added Ireland, Italy, Malaysia, Singapore and Vietnam to the list, with China continuing to figure in it.
- While the designation of a country as a currency manipulator does not immediately attract any penalties, it tends to dent the confidence about a country in the global financial markets.
The criterion:
- Countries with a current-account surplus equivalent to 2 per cent of gross-domestic product are eligible for the list, according to modifications made in the new list, down from 3 per cent earlier.
- Other thresholds include repeated intervention in the currency markets and a trade surplus with the US of at least $20 billion.
Why is this significant?
- Tweaks in currency policy has been used by the Trump administration to browbeat countries that, from Washington’s perspective, have hurt American businesses and consumers.
- For India, this comes amid the ongoing trade spat between Washington and New Delhi.
- Trump has repeatedly claimed that India is a “tariff king” and imposes “tremendously high” tariffs on American products.
UAE LAUNCHES ‘GOLDEN CARD’ SCHEME
24, May 2019
GS 3: IR
Why in news?
The United Arab Emirates has launched a permanent residency scheme to woo wealthy individuals and exceptional talents, a move that could attract more Indian professionals and businessmen to the Gulf nation.
Golden Card Programme:
- The “Golden Card” programme is open to investors and “exceptional talents” such as doctors, engineers, scientists, students and artists.
- The visa categories include:
- All categories of visas can be renewed upon expiry.
✓ General investors who will be granted a 10 years visa
✓ Real estate investors, who can get a visa for 5 years Visa
✓ Entrepreneurs and talented professionals such as doctors, researchers and innovators: 10 years Visa
✓ Outstanding students — will also be permitted residency visas for 5 years
Significance:
- The new initiative will attract greater foreign investment and stimulate the local economy, making it more efficient and attractive for investors.
- It will also increase the UAE’s competitiveness and reaffirms the country’s position as a global incubator.
- The benefits of the permanent residency also include the spouse and children of the cardholder to ensure cohesive social ties.
Benefits for India:
- The Indian expatriate community is reportedly the largest ethnic community in the UAE, constituting roughly about 30 per cent of the country’s population of around nine million.
- Though most of the Indians living in the UAE are employed, about 10 per cent of the Indian population constitutes dependent family members, according to the Indian Embassy.
COMPETITION COMMISSION OF INDIA (CCI)
23, May 2019
Why in news?
The Competition Commission of India (CCI) celebrated its 10th Annual Day which marks the notification of the substantive enforcement provisions of the Competition Act, 2002.
Competition Commission of India (CCI):
- Competition Commission of India is a statutory body of the Government of India responsible for enforcing The Competition Act, 2002 throughout India.
- They prevent activities that have an appreciable adverse effect on competition in India.
- The idea of Competition Commission was conceived and introduced in the form of The Competition Act, 2002.
- A need was felt to promote competition and private enterprise especially in the light of 1991 Indian economic liberalisation.
Objectives:
- Make the markets work for the benefit and welfare of consumers.
- Ensure fair and healthy competition in economic activities in the country for faster and inclusive growth and development of the economy.
- Implement competition policies with an aim to effectuate the most efficient utilization of economic resources.
- Develop and nurture effective relations and interactions with sectoral regulators to ensure smooth alignment of sectoral regulatory laws in tandem with the competition law.
- Effectively carry out competition advocacy and spread the information on benefits of competition among all stakeholders to establish and nurture competition culture in Indian economy.
8th INDO – MYANMAR COORDINATED PATROL
22, May 2019
Why in News?
Myanmar Navy Ships arrived Port Blair for the ‘Opening Ceremony’ of the 8th Indo- Myanmar coordinated patrol (IMCOR) at Andaman and Nicobar Command.
Indo-Myanmar coordinated patrol:
- The CORPAT initiative between the two navies is meant to address
Issues of terrorism,
Illegal fishing,
Drug trafficking,
Human trafficking,
Poaching and other illegal activities inimical to interest of both nations. - The CORPAT series has enhanced the mutual understanding and fostered improved professional interaction between the two navies for maritime interoperability.
- The patrolling effort will be augmented by Maritime Patrol Aircraft from both the navies.
- The ships would patrol along the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL) between the two countries covering a distance of approximately 725 Kilometres.
- The ships will also undertake joint manoeuvres and drills during the sea phase of coordinated patrol (CORPAT) prior ‘Closing Ceremony’ of the CORPAT.
INDIA CUTS OFF UN PANEL AFTER J&K REPORT
21, May 2019
GS 3: IR
Why in news?
Reacting angrily to a submission from the Geneva-based Human Rights Council (HRC) on the alleged violations in Jammu and Kashmir, India has informed the United Nations body that it will no longer entertain any communication with the HRC’s Special Rapporteurs on its report.
Highlights:
- The report from the UN body came at the same time a report from two NGOs in the State on the alleged cases of torture was released in Srinagar, which was endorsed by a former UN Special Rapporteur.
- In addition, the Special Rapporteurs had listed 13 cases of concern from 2018 alone, in which four children were among eight civilians killed by members of the security forces.
- The current Special Rapporteurs on Extrajudicial Executions, Torture, and Right to Health had referred to a June 2018 report of the Office of the High Commissioner of Human Rights (OHCHR) and written to the government in March 2019, asking about steps taken by New Delhi to address the alleged human rights violations listed in the report.
- Rejecting all the claims, the Indian Permanent Mission to the UNin Geneva replied to the OHCHR saying that India does not intend to engage further with the mandate-holders on the issue – whom it accused of individual prejudice.
- UN officials say that India is already in contravention of several Conventions it has committed to, including a Standing Invitation signed in 2011 to all special rapporteurs to visit India.
- According to the UN records, more than 20 such visit requests, including to Jammu and Kashmir, are pending at present.
- UN sources also said that between 2016-2018, the OHCHR Special Rapporteurs had sent as many as 58 communications, and had received no response other than the April 23 letter on Jammu and Kashmir.
Reports from NGO:
- The UN submission on Jammu and Kashmir coincided with the release of an extensive 560-page report on Monday, prepared by the J&K based Association of Parents of Disappeared Persons (APDP) and the J&K Coalition of Civil Society (JKCCS).
- The report, entitled ‘Torture: Indian State’s Instrument of Control in J&K’, documented 432 cases of suspected human rights violations and brutality by security forces of which only 27 had been investigated by the State Human Rights Commission.
- The report claimed that nearly “70% of torture victims in Jammu and Kashmir were civilians (not militants) and 11% died during or as a result of torture”.
- The cases included incidents of electrocution, ‘water-boarding’ and sexual torture, which the government has repeatedly denied.
CHARTER BASED BODIES
21, May 2019
GS 3: IR
Why in News?
Charter bodies include the UN Human Rights Council and Special Procedures.
UNHRC:
- The Human Rights Council, which replaced the Commission on Human Rights
- This intergovernmental body, which meets in Geneva 10 weeks a year, is composed of 47 elected United Nations Member States who serve for an initial period of 3 years, and cannot be elected for more than two consecutive terms.
- The Human Rights Council is a forum empowered to prevent abuses, inequity and discrimination, protect the most vulnerable, and expose perpetrators.
- The Human Rights Council is a separate entity from OHCHR.
Special Procedures:
- Special Procedures is the general name given to the mechanisms established by the Commission on Human Rights and assumed by the Human Rights Council to address either specific country situations or thematic issues in all parts of the world.
- Special Procedures are either an individual -a special rapporteur or independent expert-or a working group.
- They are prominent, independent experts working on a voluntary basis, appointed by the Human Rights Council.
- Special Procedures’ mandates usually call on mandate-holders to examine, monitor, advise and publicly report on human rights situations in specific countries or territories, known as country mandates, or on human rights issues of particular concern worldwide, known as thematic mandates.
- All report to the Human Rights Council on their findings and recommendations, and many also report to the General Assembly. They are sometimes the only mechanism that will alert the international community to certain human rights issues, as they can address situations in all parts of the world without the requirement for countries to have had ratified a human rights instrument.
Treaty-based bodies:
- There are nine core international human rights treaties. Since the adoption of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in 1948, all UN Member States have ratified at least one core international human rights treaty, and 80 percent have ratified four or more.
- There are currently ten human rights treaty bodies, which are committees of independent experts.
- Nine of these treaty bodies monitor implementation of the core international human rights treaties while the tenth treaty body, the Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture, established under the Optional Protocol to the Convention against Torture, monitors places of detention in States parties to the Optional Protocol.
- The treaty bodies are created in accordance with the provisions of the treaty that they monitor. OHCHR supports the work of treaty bodies and assists them in harmonizing their working methods and reporting requirements through their secretariats.
POLY-DI-KETOENAMINE (PDK): NEW PLASTIC THAT COULD BE FULLY RECYCLED
19, May 2019
GS 3: Science & Technology – Awareness In The Fields Of It, Space, Computers, Robotics, Nano-Technology
Why in news?
The scientists have created a next-generation plastic that can be fully recycled into new materials of any colour, shape, or form, without loss of performance or quality.
Poly-Di-Ketoenamine (PDK):
- A team of researchers at the US Department of Energy’s Berkeley National Laboratory has designed a recyclable plastic called PDK.
- The monomers of PDK plastic could be recovered and freed from any compounded additives by placing the material in a highly acidic solution.
- It helps to break the bonds between the monomers and separate them from chemical additives.
- The recovered PDK monomers can be remade into polymers, and those recycled polymers can form new plastic materials without inheriting the colour or other features of the original material.
- They could also upcycle the plastic by adding additional features, such as flexibility.
Why most plastics cannot be recycled?
SIMBEX-19
19, May 2019
GS 3: IR
Why in news?
On successful completion of IMDEX 19, IN ships Kolkata and Shakti are continuing their stay at Singapore to participate in the annual Singapore India Maritime Bilateral Exercise SIMBEX-2019 scheduled from 16 May to 22 May 19.
Highlights:
- Since its inception in 1993, SIMBEX has grown in tactical and operational complexity. the annual bilateral exercise saw its progression from traditional anti-submarine exercises to more complex maritime exercises such as advanced air defence operations, anti-air/ surface practice firings, tactical exercises, etc.
- Over the years SIMBEX has stood the test of time in demonstrating the nation’s commitment to enhance maritime cooperation between the two navies and bolster bonds of friendship between the two countries.
- For SIMBEX 19, the IN has deployed its finest assets for with an aim to strengthen mutual trust, enhance interoperability, and build greater synergy to address common maritime concerns among both navies.
- The harbour phase of SIMBEX-19 conducted from 16 May to 18 may include various planning conferences, simulator-based warfare training/ wargaming, courtesy calls to dignitaries of RSN navy, sporting events and deck reception onboard Kolkata.
- The sea phase of SIMBEX-2019 scheduled to be conducted in the South China Sea from 19 May to 22 May 19 will include various maritime combat exercises such as firing on aerial/ surface targets, advanced aerial tracking, coordinated targeting exercises and tactical exercises on surface/ air scenarios.
- In addition to IN ships Kolkata and Shakti, long-range maritime patrol aircraft Poseidon8I (P8I) will also participate in simbex-19. The Singapore side will be represented by RSN ships Steadfast and Valiant, maritime patrol aircraft Fokker-50 (F-50) and F-16 fighter aircraft.
- SIMBEX 19 would also conclude the two-month-long deployment of IN ships Kolkata and Shakti to South and East China Seas which is aimed at extending the bridges of friendship through enhanced cultural, economic and maritime interactions with countries of east and south-east Asia.
- IN ships’ participation in International Fleet Review (IFR) at Qingdao, China as part of PLA (Navy) 70th-anniversary celebrations and ADMM-plus MS FTX also reflects the government of India’s ‘Act East’ policy and the Indian Navy’s efforts to “unite nations through the oceans”.
PRADHAN MANTRI FASAL BIMA YOJANA (PMFBY)
17, May 2019
S 2: Governance – Govt Schemes
Why in news?
Four north-eastern States Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur and Mizoram — are not covered under the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana at all.
PMFBY:
- In April, 2016, the government of India had launched Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) after rolling back the earlier insurance schemes viz.
- National Agriculture Insurance Scheme (NAIS), Weather-based Crop Insurance scheme and Modified National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (MNAIS).
- It envisages a uniform premium of only 2% to be paid by farmers for Kharif crops, and 1.5% for Rabi crops. The premium for annual commercial and horticultural crops will be 5%.
- The scheme is mandatory for farmers who have taken institutional loans from banks. It’s optional for farmers who have not taken institutional credit.
Objectives of the scheme:
- Providing financial support to farmers suffering crop loss/damage arising out of unforeseen events.
- Stabilizing the income of farmers to ensure their continuance in farming.
- Encouraging farmers to adopt innovative and modern agricultural practices.
- Ensuring flow of credit to the agriculture sector which contributes to food security, crop diversification and enhancing growth and competitiveness of agriculture sector besides protecting farmers from production risks.
COMPREHENSIVE NUCLEAR TEST BAN TREATY
17, May 2019
GS 3: IR – Events
Why in news?
The executive secretary of the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO) has offered India an ‘Observer’ status and access to state-of-art International Monitoring System (IMS) data.
CTBT:
- The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) is the Treaty banning all nuclear explosions – everywhere, by everyone.
- The Treaty was negotiated at the Conference on Disarmament in Geneva and adopted by the United Nations General Assembly. It opened for signature on 24 September 1996.
- It curbs the development of new nuclear weapons and the improvement of existing nuclear weapon designs. When the Treaty enters into force it provides a legally binding norm against nuclear testing.
- The Treaty also helps prevent human suffering and environmental damages caused by nuclear testing.
India and the CTBT:
- India can benefit immensely from becoming a CTBT Observer as the organisation setting has changed a lot over the years.
- India will have access to the data available which was traditionally not made available.
INDIA SETS THE TONE AT COP MEETINGS OF BASEL
16, May 2019
GS 3: IR – Events
Why in News?
Conference of the Parties (COP) to Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movement of Hazardous Wastes and their Disposal (COP 14) was held.
Basel Convention:
- The Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal, usually known as the Basel Convention, is an international treaty.
- The treaty was designed to reduce the movements of hazardous waste between nations, and specifically to prevent transfer of hazardous waste from developed to less developed countries (LDCs).
- It does not, however, address the movement of radioactive waste.
- The Convention is also intended to
✓ Minimize the amount and toxicity of wastes generated,
✓ To ensure their environmentally sound management as closely as possible to the source of generation, and
✓ To assist LDCs in environmentally sound management of the hazardous and other wastes they generate.
Outcome of the (COP 14):
- In Basel Convention, two important issues were discussed and decided, i.e. technical guidelines on e-waste and inclusion of plastic waste in the PIC procedure.
- The draft technical guidelines stipulated the conditions when used electrical and electronic equipment destined for direct reuse, repair, refurbishment or failure analysis should be considered as non-waste.
- India had major reservations regarding these provisions as in the name of re-use, repair, refurbishment and failure analysis there was a possibility of dumping from the developed world to the developing countries including India.
- The Indian delegation strongly objected the proposed decision on these guidelines during plenary and did not allow it to be passed by the conference of the parties.
- Under the Basel Convention, another major achievement of COP 14 was:
- The decision to amend the convention to include unsorted, mixed and contaminated plastic waste under PIC (Prior Informed Consent) procedure
- Improve the regulation of its transboundary movement.
- Further, Basel Convention has also adopted partnership on plastic which was welcomed by the Indian delegation. These steps will help prevent the illegal dumping of plastic wastes in developing countries.
- India has already imposed a complete prohibition of import of solid plastic waste into the country. India has also made an international commitment to phase-out single-use plastic.
INTERNATIONAL WATER CONFERENCE
11, May 2019
GS 3: IR – Organizations
Why in News?
UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (Unesco) will organise a International Water Conference over May 13-14 at its Paris headquarters.
Highlights:
- It will aim to discuss the role of water for driving peace and sustainable development in the world, because “access to water is not only a matter of development.
- The conference would involve ministers from 40 countries, experts, researchers, the civil society, the private sector as well as international organisations. They would find innovative solutions to problems related to the governance and management of water resources.
- It will also launch a call for action to foster, embrace, and adopt trans-sectoral management of water resources for sustainable water security and peace.
- Topics for the panels will be diverse: technological innovation, ethics, heritage, gender, etc.
- The sixth of the 17 United Nations-mandated Sustainable Development Goals is to provide universal access to safe and affordable drinking water by 2030.
WTO MINISTERIAL MEETING
11, May 2019
GS 3: IR – Organizations
Why in News?
India will host a WTO ministerial meeting of developing countries in New Delhi.
Highlights:
- The meeting is a run up to the twelfth Ministerial Conference of the WTO to be held in Kazakhstan in 2020.
- The meeting is an effort to bring together the developing countries and the Least Developed Countries on a platform for sharing common concerns on various issues affecting the WTO and to address the following issues:
- WTO’s appellate body has shrunk over the last two years from its required strength of seven members to three. At present, the appellate body takes a year to hear appeals, whereas the time to dispose off the appeals is 90 days.
- Special and differential treatment of developing countries in the WTO is a concern for some other countries.
- The increased unilateral measures and counter-measures by member countries, as well as deadlock in key areas of negotiations and the impasse in the WTO’s appellate body has given rise to demands to reform the organization.
World Trade Organization (WTO):
- It is the only global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations.
- It came into existence on January 1, 1995 and has its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland.
- All major decisions are made by the WTO’s member governments, either by ministers (who usually meet at least every two years) or by their ambassadors or delegates (who meet regularly in Geneva).
Special and Differential Treatment provisions:
- The WTO Agreements contain special provisions which give developing countries special rights and developed countries the possibility to treat developing countries more favourably than other WTO Members.
- The special provisions are:
✓ Longer time periods for implementing Agreements and commitments.
✓ Measures to increase trading opportunities for developing countries.
✓ Provisions requiring all WTO members to safeguard the trade interests of developing countries.
✓ Support to help developing countries build the capacity to carry out WTO work, handle disputes, and implement technical standards
✓ Provisions related to least-developed country (LDC) members.
INITIATIVES BY COMMERCE MINISTRY TO BOOST TRADE WITH AFRICAN COUNTRIES
07, May 2019
Why in News?
- Commerce Ministry and Indian High Commissions and Embassies of eleven African countries arranged an interaction over Digital Video Conference (DVC) with the Indian business community in
- This initiative was held in order to build an effective engagement with the Indian Diaspora in Africa in order to further deepen and strengthen India-Africa trade
Highlights:
- India’s total trade with the African region during 2017-18 was USD 69 billion (8.15% of India’s total trade with the World).
- India’s share of exports to African countries as a percentage of India’s total exports to the world was of the order of 8.21% in 2017-18.
- Africa region’s share in India’s total imports from the World accounted for 8.12% in 2017-18
Diaspora relationship:
- As per the latest available estimates the current strength of the Indian Diaspora in the African countries is 2.8 million out of those 2.5 million are PIOs and rest 220967 are NRIs
- The inherent strength of India in Africa is its rich and vast Diaspora which has established strong links with the political, economic and social fabric of the African
- In order to formulate a strategy to boost India-Africa Trade & Investment, the Indian Diaspora in Africa has to be leveraged further in order to ensure that the strategy is effective
- The major issues highlighted by the Indian Business Community in these 11 countries are:
- Improving the Line of Credit system and developing a facility for an affordable and competitive
- Setting up of Indian Banks/financial institutions in Africa
- Enhanced Buyers’ Credit facility for promotion of trade between the two regions
- Reviewing and liberalizing visa policies from both sides
- Need for direct flights between the India and African countries
- Exploring the possibility of rupee trade to address the issue of shortage of dollars in region.
- Creation of common database of buyer-suppliers in the two regions for facilitating matchmaking for enhancement of bilateral trade.
- Development of a robust trade dispute settlement mechanism
- More frequent and structured country/sector specific trade exhibitions in Africa
- Establishment of country chapters of FICCI or CII in Africa
- Frequent visits of policy makers, chamber of commerce and investors for familiarization with local business and investment regime for informed
Way forward:
- This initiative of the Commerce Ministry emphasizes the need for a multipronged strategy for further enhancing trade and investment ties between the two regions
- Commerce Ministry recognizes that for formulating an effective export strategy it is imperative to engage the Indian business community in Africa for mutual gain for both sides as trade relations between the people of same origin instill greater confidence amongst trade partners.
GLOBAL FOOD POLICY REPORT
27, Apr 2019
Why in News?
- Global Food Policy Report released by the Washington DC-based International Food
- Theme: Rural revitalization is the theme for 2019.
Highlights:
- Marked by the deepening cycle of hunger and malnutrition, poverty, limited economic opportunities, and environmental degradation, rural areas continue to be in a state of crisis in many parts of the world.This crisis can slow the progress toward achieving the Sustainable Development Goals and global climate targets.
- Rural population account for 45.3% of the world’s total population and at least 70% of the world’s population remains extremely poor.
- The rural population suffers from rapid population growth rates, inadequate job and enterprise creation, poor infrastructure, scarce financial services.
- In addition, rural communities bear the brunt of climate change impacts.• Nearly 50% of rural youth all over the world do not have any formal job – they are either unemployed or under-employed.
- The Changing consumption patterns—driven largely by urbanization, demographic transitions, increasing income, and growing integration of food supply chains and food systems in India — offer new opportunities for entrepreneurship and employment in rural areas.
Measures to boost rural economy:
- The rural transformation and revitalisation have been pre-eminent goal of India’s development efforts since independence.
- India has unveiled several measures to boost rural economy and improve rural livelihoods by enhancing access to basic services, increasing investments in agriculture and rural infrastructure.
- Way forward: Changing consumption patterns—driven largely by urbanisation, demographic transitions, increasing income, and growing integration of food supply chains and food systems in India — offer new opportunities for entrepreneurship and employment in rural areas.
IN-VPM BILAT EXERCISE
21, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- Indian Navy undertook the second edition of the bilateral maritime exercise between Indian Navy and Vietnam Peoples’ Navy at/ off Cam Ranh Bay, Vietnam from 13 to 16 Apr 19. The maiden edition was conducted from 21 to 26 May 18 at Da Nang,Vietnam
IN-VPM BILAT Ex:
- IN-VPM BILAT Ex is the bilateral maritime exercise between India and Vietnam
- The exercise was undertaken as a part of the ongoing Overseas Deployment of Eastern Fleet ships to South East Asian countries
- The Indian Navy and the Vietnam Peoples’ Navy have traditionally shared good relations. Conduct of the bilateral exercise on an annual basis would give a further fillip to the existing strong bilateral relation between the two countries, which since Sep 16 have been elevated to the level of ‘Comprehensive Strategic Partnership’ after the visit of the Hon’ble PM to Vietnam
- The Navy to Navy cooperation involves a Composite Training Programme in the fields of Submarine, Aviation and Dockyard training. The two countries have also signed an agreement to exchange White Shipping Information and have a running ‘Information Sharing’ Programming
- The Indian Navy-Vietnam Peoples’ Navy Bilateral Exercise is a significant step in further strengthening mutual confidence and inter-operability as well as sharing best practices between the Indian and the Vietnam Peoples’ Navies
INDIAN NAVY-VIETNAM PEOPLES’ NAVY BILATERAL EXERCISE
17, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- In the backdrop of the growing maritime engagement between India and Vietnam, the Indian Navy undertook the second edition of the bilateral maritime exercise between Indian Navy and Vietnam Peoples’ Navy at/ off Cam Ranh Bay,Vietnam
Highlights:
- The maiden edition of the bilateral maritime exercise was conducted at Da Nang (from 21 to 26 May 18), Vietnam.
- The exercise was undertaken as a part of the ongoing Overseas Deployment of Eastern Fleet ships to South East Asian Countries
- The Indian Navy and the Vietnam Peoples’ Navy have traditionally shared good relations. Conduct of the bilateral exercise on an annual basis would give a further fillip to the existing strong bilateral relationship between the two countries, which since Sep 16 have been elevated to the level of Comprehensive Strategic Partnership’ after the visit of the Hon’ble PM to Vietnam.
- The Navy to Navy cooperation involves a Composite Training Programme in the fields of Submarine, Aviation and Dockyard Training
- The two countries have also signed an agreement to exchange White Shipping Information and have a running ‘Information Sharing’ programme.
- The Indian Navy-Vietnam Peoples’ Navy Bilateral Exercise is a significant step in further strengthening mutual confidence and interoperability as well as sharing best practices between the Indian and the Vietnam Peoples’ Navies
SRI LANKA SEEKS ENHANCED MILITARY TRAINING FROM INDIA
09, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- Sri Lanka has sought enhanced military training from India, according to President Maithripala Sirisena’s office.
Highlights:
- Wide-ranging matters, including bilateral defence cooperation between the neighbouring countries and regional security, were reported to have been
- India and Sri Lanka agreed to increase cooperation in security and defence spheres in several areas, including regional security, curbing drug smuggling and human trafficking and training of members of the security
- Thanking India for its partnership, The Sri Lankan President requested to increase the number of personnel trained by India. The Indian Defence Secretary agreed to look into the possibility of enhancing training
India – Sri Lanka defence relationship:
- Currently, over 60% of Sri Lanka’s military personnel pursue their young officers’ course,junior and senior command courses in India, according to defence sources in Colombo.
- ‘Exercise Mitra Shakti’, the sixth edition of the joint military training exercise between theIndian Army and the Sri Lankan Army, recently concluded in Sri Lanka
- The contingents from the two countries jointly planned and executed a series of well- coordinated tactical operations based on scenarios that are likely to be encountered in rural and urban
- The two-week programme is part of an initiative that began in 2013 as part of military diplomacy between India and Sri
U.S. TO DESIGNATE IRAN’S ELITE FORCE AS TERRORIST GROUP
06, Apr 2019
GS 3: International Relations
Why in News?
The U.S. is expected to designate Iran’s elite Revolutionary Guards Corps a foreign terrorist organisation, three U.S. officials told. This development marks the first time where the U.S. has formally labelled another country’s military a terrorist group.
Highlights:
- The decision, which critics warn could open U.S. military and intelligence officials to similar actions by unfriendly governments abroad, is expected to be announced by the U.S. State Department, perhaps as early as on the 8th of April, 2019 the officials said.
- The administration’s decision to make the designation was first reported by The Wall Street Journal. The U.S. has already blacklisted dozens of entities and people for affiliations with the IRGC, but the organisation as a whole has not been blacklisted.
- In 2007, the U.S. Treasury designated the IRGC’s Quds Force, its unit in charge of operations abroad, “for its support of terrorism,” and has described it as Iran’s “primary arm for executing its policy of supporting terrorist and insurgent groups.”
- Iran said it put the U.S. military on its terror list in response. “If the Revolutionary Guards are placed on America’s list of terrorist groups, we will put that country’s military on the terror blacklist next to Daesh (Islamic State),” Heshmatollah Falahatpisheh, said head of Parliament’s National Security Committee.
India gains access to Bolivian lithium reserves
03, Apr 2019
GS 2: IR | Bilateral relations
Why in News?
India has leveraged its way into the Bolivian lithium reserves after signing a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) in Bolivia for development and industrial use of lithium, a prime component used to power electric vehicles and cell phones.
Highlights:
- Both the countries agreed to forge mutually beneficial partnership to facilitate Bolivian supplies of lithium Carbonate to India and foster joint ventures for lithium battery / cell production plants in India.
- The move will make Bolivia, which is known to have one-fourth of the world’s lithium reserves, one of the major provider of metal for India’s e-mobility and e-storage needs.
- This agreement is supposed to form the backbone for the recently launched FAME India policy (Faster Adoption and Manufacture of (Hybrid and) Electric Vehicles) and
- It will give a substantial push to India’s ambition to have at least 30 per cent of its vehicles run on electric batteries by 2030.
UAE Cabinet announces new process of visa facilitation for expat families
02, Apr 2019
GS 2: IR | Bilateral relations
Why in News?
- The United Arab Emirates (UAE) on March 31, 2019 announced new visa guidelines as per which family members of foreign citizens, including Indians, working in the country will now be able to get an “expat visa” if the working relative fulfils income criteria.
- The new process for visa facilitation was announced by UAE Cabinet. Under the new guidelines, the salary of the expat will be taken into account rather than job title to sponsor their immediate family member to come and stay with them.
Significance:
- The amendment is in line with international developments and accordance with best practices.
- The decision aims at enhancing family stability of foreign workers and social cohesion, as well as attracting highly skilled workers while maintaining a healthy balance between professional and personal life.
Highlights:
- The UAE Cabinet has adopted a decision to amend provisions of the resolution on sponsoring of family members of the foreign workers in the country.
- The amended provisions now indicate income as a requirement for sponsoring family members, as opposed to the previously listed professions that allowed workers to sponsor their families.
- Under the new changes, the expatriate residents, both employers and employees, may sponsor their families in the UAE provided they have a valid residency permit.
- The male residents employed in the UAE will be able to sponsor their immediate family members, such as wife and children, provided that they fulfill the income criteria, which includes having a minimum salary of 4,000 Dirhams or 3,000 Dirhams plus accommodation.
- The other key requirement for male residents is that they must hold a profession that allows them to sponsor their family. However, the mother will not be allowed to sponsor her family.
- Besides, domestic helpers and certain other categories can also not sponsor their families regardless of their salary.
GENERALIZED SYSTEM OF PREFERENCES (GSP) PROGRAMME
05, Mar 2019
GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Why in News?
U.S. President has announced that he intends to end preferential trade terms for India under the Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) programme.
GSP programme:
- The GSP programme, which sets zero tariffs for certain goods from a set of 121 developing countries to foster their trade and economic development, accounts for some $5.6 billion of India’s exports to the U.S., making India the largest GSP beneficiary.
- Chemicals, gems and jewellery, engineering and textiles are among the Indian industrial sectors that benefit from the GSP.
The discretionary criteria:
- One of the discretionary criteria the President must (as per the GSP statute) take into account while determining GSP eligibility is whether the beneficiary “will provide equitable and reasonable access to its markets and basic commodity resources and the extent to which it has assured the United States it will refrain from engaging in unreasonable export practices.”
Challenges faced by U.S.A:
- India’s new e-commerce rules — which have impacted American companies like Amazon and Walmart (majority owner of Flipkart).
- Price controls on medical devices (cardiac stents).
- Tariffs on ICT products like smart watches and high-end mobile phones
- Lack of greater market access for the U.S. dairy industry.
India’s measures:
- Indian Oil Corporation announced a $1.5 billion deal to purchase oil from the U.S. until March 2020.
- Indian officials have been quick to bring up the declining trade surplus (over just over $21 billion) that India has with the U.S.
- India and the U.S. have been in focused trade talks since Washington imposed tariffs on steel and aluminium early last year, ostensibly on grounds of national security.
INDO-PACIFIC REGIONAL DIALOGUE – 2019
05, Mar 2019
GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional & global groupings & agreements involving India &/or affecting India’s interests
Why in News?
The second edition of Indo-Pacific Regional Dialogue (IPRD) – 2019 was recently held in New Delhi.
Objective:
The annual dialogue aims to provide:
- A platform for substantive and insightful discussions pertaining to the geopolitical developments affecting the maritime domain of the Indo-Pacific.
- Policy-relevant inputs to the policy-makers and the public at large.
Indo-Pacific Regional Dialogue (IPRD):
- The idea of an IPRD was first conceptualized and conducted in 2018, as the apex level conference of the Indian Navy, organised by the National Maritime Foundation as the Navy’s Knowledge Partner. Practical solutions for achieving cohesion in the region through maritime connectivity.
- Measures to attain and maintain a free-and-open Indo-Pacific. A regional approach to the region’s transition from a ‘Brown’ to a ‘Blue’ economy.
- Opportunities and challenges arising from the maritime impact of ‘Industry 4.0’ and
- How the twin conceptualizations of ‘SAGAR’ and ‘SAGARMALA’ might best be made mutually-reinforcing on a regional level.
BILATERAL SWAP ARRANGEMENT SIGNED BETWEEN RBI AND BANK OF JAPAN
04, Mar 2019
GS 2:IR| Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Why in News?
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Bank of Japan has signed a Bilateral Swap Agreement.
- The agreement was negotiated during the visit of Prime Minister Narendra Modi to Tokyo last year.
Bilateral Swap Agreement:
- The Swap agreement will provide India access to 75 billion US dollars against the 50 billion US Dollars under earlier BSA.
- Under the agreement, India can access 75 billion US Dollars for its domestic currency, for the purpose of maintaining an appropriate level of balance of payments or short-term liquidity at its discretion. Currently, India has a comfortable level of foreign exchange.
- The bilateral swap agreement will provide India to access the reserves if at any point of time when the need arises.
- As part of the agreement, the Bank of Japan (Japanese central bank) will accept Rupees and give US Dollars to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Similarly, RBI will take the Yen and give US Dollars to the Bank of Japan to stabilize each other’s currency. Since the Japanese Yen is one of the five currencies included in the IMF’s SDR basket and is counted as global hard currency, the central part of the agreement boils down to Japanese commitment to exchange US Dollar for Rupee from India.
Benefits of the Swap Agreement:
- The currency swap makes it easier to improve liquidity conditions.
- Currency swap agreements help in saving for a rainy day when the economy is not looking in good shape.
- The swap agreements also contribute towards stabilising the country’s balance of payments (BoP) position.
- The agreement aids in improving confidence in the Indian market.
India joining IEA Bioenergy TCP
02, Mar 2019
GS 2:IR| Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Why in News?
Government of India joining International Energy Agency’s Technology Collaboration Programme on Bioenergy (IEA Bioenergy TCP) as its 25th member.
IEA Bioenergy TCP:
- International Energy Agency’s Technology Collaboration Programme on Bioenergy (IEA Bioenergy TCP) is an international platform for co-operation among countries with the aim of improving cooperation and information exchange between countries that have national programmes in bioenergy research, development and deployment.
- Member countries:Australia, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Croatia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Japan, the Republic of Korea, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, South Africa, Sweden, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, the United States, and the European Commission.
- IEA Bioenergy TCP works under the framework of International Energy Agency (IEA) to which India has “Association” status since 30th March, 2017.
Significance on joining IEA Bioenergy TCP:
- The primary goal of joining IEA Bioenergy TCP by Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas (MoP&NG) is to facilitate the market introduction of advanced biofuels with an aim to bring down emissions and reduce crude imports.
- It provides a platform for international collaboration and information exchange in bioenergy research, technology development, demonstration, and policy analysis with a focus on overcoming the environmental, institutional, technological, social, ‘and market barriers to the near-and long-term deployment of bioenergy technologies.
- The R&D work in IEA Bioenergy TCP is carried out carried out within well-defined 3-years programmes called “Tasks”.
Benefits for India:
- Shared costs and pooled technical resources.
- The duplication of efforts is avoided and national Research and Development capabilities are strengthened.
- An information exchange about best practices, network of researchers and linking research with practical implementation.
- Engagement with International Agencies will also apprise the Ministry of the developments taking place Worldwide in Biofuel sector, provide opportunity of personal interaction with innovators/ Researchers and help in bringing suitable policy ecosystem.
- After becoming member, India can participate in other related Tasks focussing on Biogas, Solid waste Management, Biorefining etc. which could be participated by relevant Ministries/ Departments/ Organizations of the Country.
EXERCISE SAMPRITI-2019
15, Feb 2019
GS 2: IR | India and its neighborhood relation
Why in News?
- It is an important bilateral defence cooperation endeavour between India and Bangladesh and this will be the eighth edition of the exercise which is hosted alternately by both countries.
- As part of the ongoing India Bangladesh defence cooperation, the joint military exercise will be conducted at Tangail, Bangladesh.
- The exercise is aimed to strengthen and broaden the aspects of interoperability and cooperation between the Indian and Bangladesh Armies.
- The exercise will involve tactical level operations in a counter insurgency and counter terrorism environment under the UN mandate.
- In addition to understanding each other in tactical level operations, emphasis will also be laid for greater cultural understanding to strengthen military trust and cooperation between the two nations.
AFGHANISTAN LAUNCHES NEW EXPORT ROUTE TO INDIA THROUGH IRAN
13, Feb 2019
GS 2:IR| Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Why in News?
Afghanistan began exports to India through the Chabahar as the landlocked, war-torn nation turns to overseas markets to improve its economy.
Afghan Exports to India:
- 23 trucks carrying 57 tonnes of dried fruits, textiles, carpets and mineral products were
- The consignment will be shipped to the Indian city of Mumbai.
- The Iranian port provides easy access to the sea to Afghanistan and India has helped developed this route to allow both countries to engage in trade bypassing Pakistan.
- Afghanistan, a new trade partner:
- India has sent 1.1 million tonnes of wheat and 2,000 tonnes of lentils to Afghanistan through Chabahar.
- Both countries established an air corridor in 2017.
- Afghan exports to India stood at $740 million in 2018, making it the largest export destination.
dispatched from western Afghan city of Zaranj to Iran’s Chabahar port.
INDIA SUCCESSFULLY TEST-FIRES QUICK REACTION SURFACE-TO-AIR MISSILE
13, Feb 2019
GS 3: Internal Security
Why in News?
- India has successfully test-fired two indigenously developed Quick Reaction Surface-to- Air missiles (QRSAM) from a test range off the Odisha coast.
- The trials were conducted by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) from Launch Complex 3 of the Integrated Test Range (ITR) at Chandipur.
QRSAM:
- This missile has been developed to replace the ‘Akash’ missile defence system, and has 360-degree coverage, light weight, high mobility and shorter second reaction time as compared to ‘Akash’.
- It also uses solid fuel propellant and has a stated range of strike range of 25-30 km with capability of hitting multiple targets.
- It is capable of hitting the low flying objects.
- It successfully demonstrated the robust Control, Aerodynamics, Propulsion, Structural performance and high manoeuvering capabilities thus proving the design configuration.
- Radars, Electro Optical Systems, Telemetry and other stations have tracked the Missiles and monitored through the entire flights.
ALL INDIA CITIZENS SURVEY OF POLICE SERVICES
12, Feb 2019
GS 3: Internal Security | Various Security forces & agencies & their mandate
Why in News?
A globally accepted way to assess the impact or outcomes of such endeavors is through a holistic analysis of services rendered to the public, through public perception surveys conducted by professional and independent agencies.
Such surveys are globally tested tools for improving service delivery in policing and enhancing public satisfaction. With the above aim and to further strengthen the good governance practices in the working of police, Ministry of Home Affairs has commissioned the Bureau of Police Research and Development to conduct this pan-India
survey. The survey will be conducted through the National Council of Applied Economic Research, New Delhi.
Aims and Objectives:
- To understand public perceptions about Police
- Gauge the level of non-reporting of crimes or incidents to Police
- The position on ground relating to crime reporting & recording
- Timeliness and quality of police response and action, and
- To assess citizens’ perception and experience about women and children’s safety
Conduct of the Survey:
- The survey will commence in March, 2019 and cover a representative sample of 1.2 lakh households spread over 173 districts across the country.
- It will be based on the National Sample Survey framework.
- All States and UTs would be included in this survey and will be completed in 9 months.
Expected Outcomes:
- The outcome of the survey is expected to bring out useful suggestions for stakeholders in formulating and implementing appropriate policy responses.
- It will imbibe changes in the functioning of police at the cutting edge and for improve crime prevention and investigation.
- It will cater to transformation in community policing, improvement in the access to the justice and increased/ appropriate resource allocation for police in a systematic manner.
INDIA TO HAVE OWN DNS FOR SAFE BROWSING
12, Feb 2019
GS 3: Internal Security – Cyber Security
Why in News?
The Government of India will soon roll out a public Domain Name Server, or DNS for India.
Highlights:
- It aimed at providing a faster and more secure browsing experience for Internet users in the country, while ensuring that citizens’ data is stored locally.
- To ensure availability, particularly for smaller Interest Service Providers (ISPs) who don’t have credible DNS
- The roll-out, which will be executed by the National Informatics Centre – the technology arm of the government.
- NIC is already using the public DNS within the government network.
- The government’s system would prevent users from visiting malicious websites.
DNS:
A DNS is a like a directory for the Internet. It helps to convert domain names that are easy for people to remember into IP addresses, which are used by computers/machines to communicate. If the DNS is either slow or fails to work, users will not be able to locate web addresses.
INDIA SIGNS MOU WITH CANADIAN UNIVERSITY FOR RESEARCH ON ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES
11, Feb 2019
GS 2: IR | Bilateral
Why in News?
Government of India has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the University of British Columbia (UBC), Canada to work on various environmental issues including climate change, forest resource management and wildlife.
Highlights:
- The MoU was signed by Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) for the next 10 years to explore opportunities for collaborations in the field of forestry science.
- The opportunities for collaboration will be explored through organizations like Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE), Wildlife Institute of India (WII), Forest Survey of India (FSI), Indira Gandhi National Forest Academy and Directorate of Forest Education, Uttarakhand, and UBC.
- The MoU will assist in the exchange of students, researchers and faculty, developing research projects, livelihood opportunities and augment the income of the forest-based communities.
- The MoU will also assist industries to optimise the utilisation of forest-based resources with access to technology to different stakeholders by the respective organisations.
- The areas to be explored for collaboration under the MoU include collaborative research on wood sciences, forest resource management, adaptation and mitigation to climate change, forest genetics and breeding, wildlife, ecology, remote sensing, insect and disease pests, extension, conservation of flora and fauna, biotechnology, bio-energy and bio- economy.
- Also, joint conferences, seminars, workshops and exhibitions will be arranged as part of the MoU to take the collaboration forward.
HOME MINISTRY PUTS ASSAM RIFLES NOTIFICATION ON HOLD
10, Feb 2019
GS 3: Internal Security
Why in News?
The Home Ministry has kept “in abeyance” its order that empowered the Assam Rifles, deployed along the Myanmar border, to arrest anyone and search a place without a warrant in the border districts of Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Nagaland and Mizoram. The notification was withheld after Opposition parties moved an adjournment motion against the order in the Assam Assembly. The Ministry said the matter would be “revisited in consultation with the State governments”.
Highlights:
- Recently Assam Rifles, deployed along the Myanmar border, had empowered by the Centre to arrest anyone and search a place without warrant in the border districts of Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Nagaland and Mizoram.
- According to a Home Ministry notification, “an officer of the rank corresponding to that of the lowest rank of members of the Assam Rifles” has been given these powers under the Code of Criminal Procedure.
- Earlier, Assam Rifles was making arrests only in areas where the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act was in effect. They were finding it difficult to make seizures and arrest in Mizoram, which doesn’t have AFSPA. This is to basically correct that anomaly. As per law, they have to hand over the suspects to the local police within 24 hours.
- The MHA had lifted AFSPA from some areas of Arunachal Pradesh last year.
Assam Rifles:
Assam Rifles is the oldest of the Central Para Military Forces. Though the organisation has a cadre of its own officers, most senior positions are filled by taking officers on deputation from the Army.
The Force functioned under the control of the Ministry of External Affairs till 1965. Its control was then transferred to the Ministry of Home Affairs and has since been functioning under that Ministry.
The Assam Rifles Act, 1941, presently governs the Force. Its charter of functions include –
- Maintaining security of the North Eastern sector of the international border;
- Helping states in the North East to maintain law and order and other states as and when needed
- Taking counter insurgency measures in states of the North East.
SEOUL PEACE PRIZE
09, Feb 2019
GS 2: IR | India & Bilateral relations
Why in News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi received the Seoul Peace Prize in South Korea.
Highlights:
- The Prime Minister is the 14th person to receive the honour.
- The award includes a diploma, a plaque and honorarium of US$200,000.
- The prize has been given for PM Modi’s contributions to the growth of the Indian and global economies.
- Past awardees include former UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan and Grameen Bank founder Dr Muhammad Yunus.
Why is PM Modi getting the award?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi was given the honour for his contributions to the growth of the Indian and global economies. The award committee has credited ‘Modinomics’ for reducing social and economic disparity between the rich and the poor.
The committee has also lauded PM’s initiatives to make the government cleaner through anti-corruption measures and demonetisation. The Prime Minister was hailed for his contribution towards regional and global peace through a proactive foreign policy with countries around the world under the ‘Modi Doctrine’ and the ‘Act East Policy’.
About the award:
- Set up in 1990, the Seoul Peace Prize is biennially awarded to personalities to commemorate the success of the 24th Summer Olympic Games held in Seoul.
- The prize was established to reflect the wishes of the Korean people and to emphasise on their desire for everlasting peace on earth.
INDUS WATERS TREATY 1960: PRESENT STATUS OF DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA
08, Feb 2019
GS 2: IR | India & its neighborhood- relations
Why in News?
The Indus system comprises of main Indus River, Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas and Sutlej. The basin is mainly shared by India and Pakistan with a small share for China and Afghanistan.
Indus Water Treaty 1960:
Under the Indus Waters Treaty signed between India and Pakistan in 1960, all the waters of three rivers, namely Ravi, Sutlej and Beas (Eastern Rivers) were allocated to India for exclusive use.
The waters of Western rivers – Indus, Jhelum, and Chenab were allocated to Pakistan except for specified domestic, non-consumptive and agricultural use permitted to India as provided in the Treaty. India has also been given the right to generate hydroelectricity through run of the river (RoR) projects on the Western Rivers which, subject to specific criteria for design and operation is unrestricted.
Present status of development in India:
To utilize the waters of the Eastern rivers which have been allocated to India for exclusive use, India has constructed Bhakra Dam on Satluj, Pong and Pandoh Dam on Beas and Thein (Ranjitsagar) on Ravi. These storage works, together with other works like Beas- Sutlej Link, Madhopur-Beas Link, Indira Gandhi Nahar Project etc has helped India utilize nearly entire share (95 %) of waters of Eastern rivers.
However, about 2 MAF of water annually from Ravi is reported to be still flowing unutilized to Pakistan below Madhopur. To stop the flow of these waters that belong to India for its utilization in India, following steps have been taken:
Resumption of Construction of Shahpurkandi project:
This project will help in utilizing the waters coming out from powerhouse of Thein dam to irrigate 37000 hectares of land in J&K and Punjab and generate 206 MW of power. The project was scheduled to be completed by September 2016.
However, following a dispute between the state of J&K and Punjab, the work on the project had been suspended since 2014. The construction work has now resumed by Govt of Punjab under monitoring of Govt of India.
Construction of Ujh multipurpose project:
This project will create a storage of water on river Ujh , a tributary of Ravi for irrigation and power generation in India itself and provide a total irrigation benefits of 31,380 ha in Kathua, Hiranagar and Samba district of J&K apart from providing water for the district Kathua of J&K.
The 2nd Ravi Beas link below Ujh:
- This project is being planned to tap excess water flowing down to Pakistan through river Ravi, even after construction of Thein Dam, by constructing a barrage across river Ravi for diverting water through a tunnel link to Beas basin.
- The project is expected to utilize about 0.58 MAF of surplus waters below Ujhdam by diverting the same to Beas basin for benefits of other co-basin states. The government of India has declared this project as National Project.
- The above three projects will help India to utilize its entire share of waters given under the Indus Waters Treaty 1960.
INDIA AND ARGENTINA SIGN MOU FOR CO-OPERATION IN NUCLEAR ENERGY
08, Feb 2019
GS 2: IR | Bilateral Relations
Why in News?
During the visit of Argentine President Mauricio Macri, Argentina has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to boost cooperation in the sector of nuclear energy. The MoU signed was signed between the Department of Atomic Energy, India and National Atomic Energy Commission, Argentina.
Highlights:
Argentina has expertise in building small-capacity reactors and it is looking to work with India in some third country in tripartite projects. The MoU for cooperation within the framework of Global Center for Nuclear Energy Partnership would bolster institutional linkages in civil nuclear research, development and capacity building.
The MoU will aid in enhancing and exploring cooperative ventures in the area of nuclear power and its societal uses in health, agriculture, industrial application, training and capacity building.
Nuclear Ties between India and Argentina:
- In the year 2010 India and Argentina had signed an agreement for cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy. INVAP which is an Argentinean Company is working on the Fission Molly Project to build a molybdenum plant in Mumbai.
- The plant would primarily focus on creating isotopes.
- Argentina is also an exporter of some nuclear components used in Indian power reactors.
EXERCISE VAYU SHAKTI- 2019
07, Feb 2019
GS 3: Internal Security
Why in News?
A mega exercise, EXERCISE VAYU SHAKTI-2019 involving 140 fighter jets and attack helicopters, in a firepower demonstration was held close to the border with Pakistan at Pokhran in Rajasthan.
Highlights:
- The IAF showcased firepower capability of indigenously-developed platforms like Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas, Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) and efficacy of Akash surface-to-air missile and Astra air-to-air missile.
- For the first time, the ALH and the Akash were deployed in a military exercise.
- A total of 137 aircraft including Sukhoi-30s, Mirage 2000s, Jaguars, Mig-21 Bison, Mig-27, Mig-29, IL78, Hercules and AN-32 aircraft participated in this mega exercise.
- Vayu Shakti and Gagan Shakti are two important exercises held by Indian Airforce.
- Exercise Vayu Shakti demonstrtaes the IAF’s ability to strike targets on the ground such as enemy convoys and tanks, radar stations, railway yards and military headquarters.
- The other important dimension of air power, air-to-air combat is out into display at another exercise of IAF called Gagan Shakti.
GOVERNMENT LIBERALIZES THE E-VISA REGIME
07, Feb 2019
GS 2: IR | India and its neighborhood- relations
Why in News?
Recently, government has made series of amendments in e-visa regime, liberalizing it further and making it more tourist friendly. The e-Tourist Visa which was introduced in Sept. 2014 with 46 countries has now been made applicable for 166 countries.
Changes in e-Tourist Visa:
- On e-Tourist Visa continuous stay during each visit shall not exceed 90 days in case of nationals of all countries who are eligible for grant of e-visa except nationals of USA, UK, Canada and Japan. In case of nationals of USA, UK, Canada and Japan continuous stay during each visit shall not exceed 180 days.
- In all cases no registration will be required.
Changes in e-Business Visa:
Continuous stay during each visit shall not exceed 180 days in case of nationals of all countries who are eligible for grant of e-visa. No registration will be required if the stay is for a period of less than 180 days.
Other changes:
e-Visa is valid for entry through 2 (two) more designated Airports (Bhubaneswar and Port Blair) raising the total number of such airports to 28. Attending Destination wedding under normal e-Tourist visa or Tourist visa- No separate category of Destination Wedding Visa. Foreign nationals who fall sick during their stay in India can now avail medical treatment without converting their visa into Medical Visa. This would take care of sudden medical emergencies. Visa-on-Arrival facility extended to the nationals of Republic of Korea.
HAM RADIO OPERATORS PUT THEIR HOBBY TO TEST
06, Feb 2019
GS 3: Disaster Management
Why in News?
To help the public during natural calamities such as cyclonic storms members of the Amateur Radio Society of Odisha got together at an uninhabited island within the Chilika Lake to test their operational skill and technology.
Highlights:
The use of this technology for communicating to the outside world can be useful for cyclone and flood-prone states like Odisha. The uninhabited island was chosen as it is inaccessible by conventional telecommunication network. Radio signals were used for the transmission of messages by the private HAM radio operators of Odisha. Solar power was used to operate the HAM radios. It was an attempt to simulate real-life situation during any natural calamity when all conventional modes of communication cease to exist as it happened during the Titli cyclone.
HAM radio:
HAM radio or Amateur Radio is a popular hobby and service that brings people, electronics and communication together. People use ham radio to talk across town, around the world, or even into space, all without the Internet or cell phones.
PARALLEL TAXI TRACK OPERATION BY ALL WOMEN CREW
05, Feb 2019
GS 3: Internal Security
Why in News?
In a first for the IAF,the “OTTERS” squadron of Western Air Command has undertaken Parallel Taxi Track (PTT) Operations with a full women crew in the Dornier 228 aircraft.
Highlights:
The pilots, Sqn Ldr Kamaljeet Kaur and her co-pilot Sqn Ldr Rakhi Bhandari carried out successful parallel taxi track landing and take-off operations at Sirsa. This achievement highlights the theme of Aero India 2019 which is earmarked on 23 February as the day to highlight the Achievements of Women in Aviation Sector.
Parallel Taxi Track:
Parallel Taxi Track Operations are carried out to enable unhindered operations even when the runway is not available due to enemy action or any other reasons. PTT Operations is a challenging task as the crew is required to land and take off from the taxi track, which is considerably smaller in width than the runway, with proximity to obstructions as compared to the main runway. There is no of error during the most critical phases of flight, landing and take-off.
MOU BETWEEN INDIA AND FINLAND ON COOPERATION IN THE FIELD OF PEACEFUL USES OF OUTER SPACE
04, Feb 2019
GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or
affecting India’s interests
Why in News?
Union cabinet approves Memorandum of Understanding between India and Finland on Cooperation in the field of peaceful uses of outer space.
Significance:
The signed MoU provide impetus to explore newer research activities and application possibilities in the field of remote sensing of the earth; satellite communication; satellite navigation; space science and exploration of outer space.
Cooperation with the Government of Finland would lead to develop a joint activity in the field of application of space technologies for the benefit of humanity.
Highlights:
The MoU understanding shall enable the following potential interest areas of cooperation such as,
- Remote sensing of the earth
- Satellite communication and satellite-based navigation
- Space science and planetary exploration
- Development, testing and operation of space objects and ground system
- Launching of Finnish Space objects by Indian launch vehicles
- Processing and use of space data
- Developing innovative applications and solutions based on space technologies and use of artificial intelligence
- Cooperation around emerging new Space opportunities and data ecosystems and sustainable used of outer space.
DEFENCE INNOVATION HUBS (DIH)
04, Feb 2019
GS 3: Internal Security | Various Security forces & agencies & their mandate
Why in News?
The Defence Innovation Organisation set up under iDEX has announced setting up of two DIHs in Tamil Nadu (Coimbatore) and Maharashtra (Nashik).
Defence Innovation Hubs (DIH):
- DIHs will serve as platforms where innovators can get information about needs and feedback from the Services directly and create solutions for India’s major defence platforms.
- This structure is also geared towards attracting more innovators to work for the defence sector in India.
iDEX:
An innovation ecosystem for Defence titled Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX)
was launched in April 2018.
iDEX is aimed at creation of an ecosystem to foster innovation and technology development in Defence and Aerospace by engaging Industries including MSMEs, Startups, Individual Innovators, R&D institutes and Academia and provide them grants/funding and other support to carry out R&D which has good potential for future adoption for Indian defence and aerospace needs.
iDEX will function as the executive arm of the Defence Innovation Organisation (DIO). The scheme mandates setting up of Defence Innovation Hubs across the country, to provide necessary incubation and infrastructure support to defencestartups and innovators.
EXERCISE CUTLASS EXPRESS 2019
04, Feb 2019
GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or
affecting India’s interests
Why in News?
INS Trikand, a front-line warship of the Indian Navy, recently participated in a multinational training exercise ‘CUTLASS EXPRESS – 19’ held from 27 Jan to 06 Feb 19.
Exercise Cutlass Express 2019:
- Cutlass Express 2019 is sponsored by U.S. Africa Command (AFRICOM) and is conducted by U.S. Naval Forces Africa.
- It is an exercise designed to assess and improve combined maritime law enforcement capacity, promote national and regional security in East Africa as well as information sharing, planning and operating. The aim of the exercise was to improve law enforcement capacity, promote regional security and progress inter-operability between the armed forces of the participating nations. During the exercise, Naval, Coast Guard and Marine Police personnel from a number of East African countries were jointly trained by mentors from USA, India, and Netherlands, with support of international organisations.
- The Indian Navy played a significant role in the exercise, being involved in planning, coordination and execution.
- Through INS Trikand, the IN provided a platform for live Visit Board Search Seizure (VBSS) drills, which proved to be of immense training value to the participating nations.
INS Trikand:
- INS Trikand is equipped with a versatile range of sensors and weapons enabling her to address threats in all the three dimensions – air, surface and sub-surface.
- It is an ideal platform for prolonged deployments, including the present one, in which she is carrying out Presence and Surveillance missions and Anti-piracy operations in the Gulf of Aden and Western Arabian Sea.
- The ship is a part of the Indian Navy’s Western Fleet and operates under the Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief, Western Naval Command, headquartered at Mumbai.
INDIA-NORWAY OCEAN DIALOGUE
03, Feb 2019
GS 2: IR | Bilateral Relations
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister has approved the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India and Norway on India-Norway Ocean Dialogue.
Highlights:
- It promotes cooperation in the areas of mutual interest pertaining to the development of blue economy. Norway is a global leader in the area of Blue Economy and has cutting- edge technologies and expertise in areas such as fisheries, hydrocarbons, renewable energy, sustainable harnessing of ocean resources and maritime transport. The MoU contribute to create opportunities for collaboration in areas such as exploitation of hydrocarbons and other marine resources, as well as management of ports and tourism development for the mutual benefit of all stakeholders within the framework of the Joint Task Force (JTF).
- It contributes to the objective of Food Security through infusion of new technologies in fisheries and aquaculture. Further, offer a platform for businesses in both countries to execute profitable ventures.
- Scientists and researchers collaborate on studying ocean ecosystem also in the context of the Arctic region.
SHEKATKAR COMMITTEE RECOMMENDATIONS
02, Feb 2019
GS 3: Internal Security | Various Security forces & agencies & their mandate
Why in News?
The Committee of Experts (CoE) constituted by the Ministry of Defence under the chairmanship of Lt. Gen (Retd) DB Shekatkar to recommend measures to enhance combat capability and rebalance defence expenditure of the armed forces, submitted its report in December 2016. The Report was taken up by the Ministry of Defence to frame key action points and roadmap for implementation.
Recommendations taken up for implementation:
- Optimization of Signals Establishments to include Radio Monitoring Companies
- Restructuring of repair echelons (designated rank) in the Army
- Redeployment of Ordnance echelons to include Vehicle Depots, Ordnance Depots and Central Ordnance Depots apart from streamlining inventory control mechanisms.
- Better utilization of Supply and Transportation echelons and Animal Transport units.
- Closure of Military Farms and Army Postal Establishments in peace locations
- Enhancement in standards for recruitment of clerical staff and drivers in the Army
- Improving the efficiency of the National Cadet Corps
Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) Meet on Disaster Risk Management
01, Feb 2019
GS 3: Disaster Management
Why in News?
The Ministry of Home Affairs in collaboration with the Ministry of External Affairs and National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) is organising a meeting of Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) Cluster Group on Disaster Risk Management (DRM) in New Delhi.
Highlights:
Indian Ocean Rim Association is an inter-governmental organisation and has many disaster-prone countries among its 22 members and nine dialogue partners. DRM is one of its priority areas and its Action Plan (2017-2021) has specific goals to improve resilience in IORA countries.
- The two-day meeting will feature interactive sessions and will focus on development of a draft Work Plan for DRM in IORA.
- It will also deliberate on the need for establishing a DRM Core Group to take forward the
agreed objectives under the Work Plan.
IORA action plan (2017-2021):
Under the IORA Action Plan 2017-2021, the development of DRM in IORA has been given focused direction. The Cluster Group on DRM, chaired by India for a period of two years, is tasked with leading the formulation of a Work Plan for this Priority Area, with the aim to enhance cooperation and develop resiliency in the IOR.
- The Indian Ocean Region (IOR) is sometimes called the “World’s Hazard Belt” as it is prone to disasters, both natural and man-made. Natural disasters under the group of Climatological (cyclones and droughts), Geological and Tectonic (earthquakes and tsunamis) and Hydrological (floods and tidal surges) origins are very common and reoccurring phenomena in the region.
According to the UN ESCAP, around 50% of natural disasters occurring in this region are climatogenic and seismogenic in nature.
MOU between India and Kuwait on recruitment of Domestic Workers
18, Jan 2019
Why in news?
- The Union Cabinet headed by Prime Minister Narendra Modi has approved the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India and Kuwait for cooperation on the recruitment of domestic workers.
Highlights:
- The MoU will provide a structured framework for cooperation on domestic workers related matters.
- It provides for strengthened safeguards for Indian domestic workers including female workers deployed in Kuwait.
- Initially valid for five years, it has a provision for automatic renewal.
- The MoU also proposes setting up of a joint committee that will be set up to follow up the implementation.
- The MoU will benefit around 3 lakh Indian workers deployed in Kuwait, including about 90,000 female domestic workers and promotes bilateral cooperation in domestic workers-related matters between the two countries.
India and Japan conducted Disaster Control Exercise
16, Jan 2019
Why in News?
- The Coast Guards of India and Japan undertook disaster control, search and rescue exercises off the coast of Yokohama in Japan.
Highlights:
- India had hosted the Japanese ships for the exercise last year and this time Japan is hosting the exercise.
- ICGS Shaunak is the main Indian ship taking part in the drills.
- This exercise aims to share their expertise in disaster management as both the nations have huge experience in disaster management as Japan regularly faces earthquakes and sea storms while the Indian Coast Guard round the year manages the over 7,000-kilometre coastline of the country.
ICGS Shaunak:
- ICGS Shaunak is an Offshore Patrol Vessel of Indian Coast Guards.
- This 105-meter vessel is capable of carrying a twin-engine light helicopter and five high-speed boats including two quick reaction inflatable boats for swift boarding operations, search and rescue, law enforcement and maritime patrol.
- ICGS Shaunak is fitted with navigation and communication equipment, sensors and machinery including 30 mm CRN 91 naval gun, integrated bridge system, integrated machinery control system, power management system (PMS) and high power external fire fighting system.
International Solar Alliance bank
14, Jan 2019
Why in news?
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) is going to propose a new bank exclusively for financing energy access to billions.
ISA Bank:
- The bank is still at the ideation stage.
- ISA has asked the Asian Development Bank to prepare a concept note. A public-private partnership is being thought of for the proposed, which will work for 1.2 billion people who lack access to energy as well as the 2.4 billion who lack access to clean energy.
- According to a recent World Bank report, 600 million people would continue to have no access to energy even in 2040.
- Those using kerosene and other fuels that are costlier than renewable options.
- The bank would need to prioritise these groups and develop a mechanism.
- Existing banks do not focus on universal energy access those still deprived are the poorest of the poor.
- Hence ISA needs special finance mechanism which can target these people.
ISRO to launch satellite to help MHA in securing borders
12, Jan 2019
Why in news?
- A satellite will be launched by the ISRO exclusively for the Home Ministry to help it strengthen its frontiers with Pakistan and Bangladesh among others.
Securing Borders:
- The move is part of recommendations made by a task force on the use of space technology in improving border management which have been accepted by Home Minister.
- India shares land borders with Pakistan, China, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan and Myanmar.
- This project will strengthen island and border security and facilitate development of infrastructure in border/island areas.
- To execute the project in a time bound manner, a short, medium and long-term plan has been proposed for implementation in five years in close coordination with the ISRO and the Defence Ministry.
- Major recommendations of the report are to build capacity in border guarding forces to use space resources for security, operational planning and border infrastructure development.
- In short term, immediate needs of border guarding forces will be met by procurement of high resolution imagery and the hiring of bandwidth for communications. In mid-term, one satellite is being launched by the ISRO for exclusive use of the MHA.
Ground Network using space technology:
- The MHA will develop ground segment and network infrastructure to share satellite resources by user agencies, develop a central archival facility for storing various imagery resources and dissemination of the same to user agencies.
- Deployment of the CAPF in remote areas will be also coordinated by satellite communications.
- IRNSS-based GPS will provide navigation facilities for operational parties in high altitude, remote and difficult borders and LWE areas.
- The Border Security Force has been designated as lead agency for implementation of ground segment and network infrastructure, including the establishment of the archival facility.
- Island development, border security, communication and navigation, Geographic Information System (GIS) and operations planning system, and border infrastructure development are the areas identified for use of space technology.
A Special Task Force:
- The MHA has created a task force to identify areas for use of space technology in improving border management.
- The task force headed by Joint Secretary (Border Management), having members from the BSF, the Department of Space and BM division of the Home Ministry.
First India – Central Asia Dialogue to be held in Uzbekistan
10, Jan 2019
Why in news?
- The first India-Central Asia Dialogue will be held in Samarkand, Uzbekistan and will be co-chaired by India’s External Affairs Minister (EAM).
Highlights:
- The Foreign Minister of Afghanistan will participate in the dialogue as a special invitee for the session dedicated to connectivity issues in the region. While the representatives from Kyrgyz Republic, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan will represent their respective countries at the event.
- Bound together through shared history and cultural linkages, India and the Central Asian states look forward to the Dialogue as an important initiative to enhance their cooperation in wide-ranging spheres.
- These include exploring ways to substantially enhance India’s economic involvement in business and development sector of Central Asia.
- The participants will deliberate on developing viable connectivity options between India and Afghanistan and Central Asia to further facilitate trade and economic activity in the region.
Launch of Sino – Indian Digital Collaboration Plaza
08, Jan 2019
Why in news?
- The Sino-Indian Digital Collaboration Plaza (SIDCOP), an initiative to bring Indian IT companies and Chinese enterprises closer to each other on a single AI enabled platform was launched.
SIDCOP:
- This is a partnership by National Association of Software and Services Companies (NASSCOM) with Municipal Governments of Guiyang and Dalian , China.
- A Joint Venture comprising of one Indian and Chinese company has been tasked with the running of the platform.
- SIDCOP is a boundary-less marketplace offers this opportunity for Chinese enterprises in order to assist them in operational optimization and adopting industry best practices in business solutions.
- Indian IT enterprises are world renowned for their expertise in business transformation and operational optimization by using IT tools in complex business environments.
- This platform could be useful to connect with top providers from India and help Chinese enterprises source the right solution providers for their projects.
Raisina Dialogue
06, Jan 2019
Why in News?
- Admiral Christophe Prazuck, Chief of the Naval Staff, French Navy is visiting India from 06 Jan 19 in conjunction with Raisina Dialogue (08-09 Jan 19).
Aim of the meet:
- The visit aims to consolidate bilateral naval relations between India and France, as also to explore new avenues for naval cooperation.
- A range of issues of mutual interest to both navies, encompassing maritime operations, training, logistics and maintenance would be discussed during these meetings.
Raisina Dialogue:
- Raisina Dialogue is an annual conference held in New Delhi. It is envisioned to be India’s flagship conference of geopolitics and geo-economics.
- The name of conference comes from Raisina Hill which is the elevation in New Delhi where presidential palace of India, Rashtrapati Bhavan is located.
- It is premeditated to explore prospects and opportunities for Asian integration and Asia’s integration with the bigger world. It is an asserted on India’s significant role in the Indian Ocean Region and how India could build a stable regional and world order along with its partners.
- It is organized on the lines of the Shangri-La Dialogue held in Singapore.
- It is structured as a multi-stakeholder, cross-sectorial conclave, involving policy and decision makers, including cabinet ministers from various Governments, high-level Government officials and policy practitioners, leading personalities from business and industry etc.
India, Pakistan exchange list of nuclear installations
04, Jan 2019
Why in news?
- India and Pakistan has exchanged for the 28th consecutive year a list of their nuclear installations under a bilateral agreement that prohibits them from attacking each other’s atomic facilities.
Non-Nuclear Aggression Agreement:
- It is a bilateral and nuclear weapons control treaty between India and Pakistan, on the reduction (or limitation) of nuclear arms and pledged not to attack or assist foreign powers to attack on each other’s nuclear installations and facilities.
- It was signed on December 31, 1988 and came into force on January 27, 1991.
- The agreement says that the two countries will inform each other of nuclear installations and facilities to be covered under the agreement on January 1 of every calendar year.
- The two countries have adhered to the practice of exchanging the lists of prisoners and nuclear installations despite recurring tensions.
Pakistan to issue Panda Bonds to raise capital in China
02, Jan 2019
Why in News?
- The government of Pakistan has decided to launch Panda Bonds to raise loans from Chinese capital markets.
Highlights:
-
- Launching of Panda Bonds is part of Pakistan’s plans to move towards giving the Chinese currency, a status at par with that enjoyed by the US dollar. The interest rates and the size of the bonds would be decided at a later stage. The Finance Ministry of Pakistan has said that the Panda Bonds are part of its multipronged approach for bridging the foreign financing needs and building foreign exchange reserves.
- Panda Bonds will help Pakistan to diversify the investor base of capital market issuance and provide a source of raising renminbi.
- China is Pakistan’s largest trading partner.
- Pakistan has the highest trade deficit with China.
- The raising of capital in Chinese currency will aid Pakistan to bridge the deficit.
Panda Bonds:
- Panda bonds are Chinese renminbi-denominated bonds from a non-Chinese issuer, sold in the People’s Republic of China.
- The first two Panda bonds were issued in October 2005 on the by the International Finance Corporation and the Asian Development Bank on the same day.
- The Philippines issued its inaugural Panda bonds in 2018.
- It was the first ASEAN member to issue Panda bonds.
Indian Firm Takes Over Operations of Strategic Iranian Port Chabahar
26, Dec 2018

Why in News?
- Indian Firm Takes Over Operations of Strategic Iranian Port Chabahar.
- India Ports Global Limited Company has opened its office and took over operations at the Shaheed Behesti port at Chabahar. It happened during the occasion of the first meeting of the follow-up committee for implementation of the trilateral Chabahar agreement between India, Afghanistan and Iran.
Trilateral Chabahar agreement:
- Positive and constructive discussions were held between the three sides on full operationalisation of the Trilateral Transit Agreement for international transit and transport through the Chabahar port.
- It was agreed to finalise at the earliest the protocol to harmonise transit, roads, customs, and consular matters. It was agreed to allow cargo movement at Chabahar using TIR Convention provisions.”
- The Convention on International Transport of Goods Under Cover of TIR Carnets (TIR Convention) is a multilateral treaty aimed at simplifying and harmonising the administrative formalities of international road transport.
- TIR stands for “Transports Internationaux Routiers” or ‘International Road Transports.
- Also a study would be initiated for determining measures to make the route attractive, decrease logistic costs and pave the way for smooth operationalisation of the Chabahar Agreement.
- India is investing $500 million to develop the Chabahar port and a road link from there to Afghanistan to give access to that country, bypassing Pakistan.
- The port is also a key link in the International North South Transport Corridor (INSTC), a 7,200-km-long multi-modal network of ship, rail and road routes to move freight between India, Iran, Afghanistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Russia, Central Asia and Europe.
- Last month, the US waived India from its fresh sanctions on Iran’s oil imports and development of the crucial Chabahar port.
18th meeting of IRIGC-MTC held in New Delhi
26, Dec 2018

Why in news?
- The Indian Defense Minister Nirmala Sitharaman recently met the Russian Defence Minister General Sergei Shoigu at the 18th meeting of India-Russia Inter-Governmental Commission on Military Technical Cooperation (IRIGC-MTC) that was held in New Delhi.
Highlights:
- In the meeting, a wide range of issues were discussed regarding defence equipment, industry and technological cooperation between India and Russia.
- Issues related to after sales support and upgradation of military equipment of Russian origin were also discussed.
- Both the Ministers have expressed their satisfaction at the progress in bilateral defence cooperation between India and Russia.
- Discussions took place on joint manufacturing projects in the meeting, including the Kamov-226T helicopters, naval frigates and other projects related to land systems.
- There was also an agreement from both the sides to take forward inter-governmental arrangements to facilitate joint manufacturing of spares for equipments of Russian origin in India, under the ‘Make in India’ scheme.
- The existing IRIGC-MTC will be restructured to the IRIGC on Military and Military Technical Cooperation.
- An agreement regarding this was signed by the two Defence Ministers.
IRIGC-MTC:
- Russia has been the most important arms supplier for India’s Defence forces.
- Both the countries have an institutionalized structure to oversee all the issues of military-technical cooperation.
- The IRIGC is at the top of this institutionalized structure.
- The India-Russia Inter-Governmental Commission on Military Technical Cooperation (IRIGC-MTC) was set up in 2000.
- The First meeting of the IRIGC-MTC was held in Moscow in 2001.
- The 19th IRIGC meeting is proposed to be held in Russia next year.
7th round of India – South Korea CEPA negotiations held
26, Dec 2018

Why in News?
- The 7th round of India – South Korea Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) negotiations was held in South Korea.
Highlights:
- The discussions were positive, and subject to Indian sugar industry meeting the quality standards and specifications prescribed by the South Korean Government.
- South Korea imports around 15 lac tons of raw sugar annually and the Indian sugar industry is making efforts to export raw sugar from India during 2018-19 sugar seasons.
- India and South Korea will reduce duties on 11 tariff lines in a bid to expand bilateral trade by updating their existing free-trade agreement, called the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
- In 2017-18, India exported goods worth $4.4 billion to South Korea while imports from the latter were worth $16.3 billion.
‘Katowice package’ rules to implement 2015 Paris Climate Agreement: COP24
26, Dec 2018

Why in news?
- The UN Climate Conference (COP24) saw the adoption of ‘Katowice package’, the rulebook for implementation of the 2015 Paris climate agreement.
- The Ministers of 200 nations reached consensus on rules after two weeks of intense negotiations during the 24th Conference of the Parties (COP24) to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- The adopted guidelines package aims to encourage greater climate action ambition and benefit people from all walks of life, especially the most vulnerable.
Rulebook for implementation of 2015 Paris climate agreement:
- One of the key components is a detailed transparency framework to promote trust among nations. It sets out how countries will provide information about Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), including the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
- They agreed on the procedure to uniformly count the greenhouse gas emissions.
- If poorer countries feel they cannot meet the standards set, they can explain why and present a plan to build up their capacity in that regard.
- The document sets a way to decide on ambitious funding targets from 2025 onwards from the current commitment to mobilise USD 100 billion per year as of 2020 in support of climate action in developing countries.
- Nations agreed on the methodology to collectively assess the effectiveness of climate action in 2023, and finalised the procedure to monitor and report progress on the development and transfer of technology.
- The concerns of developing nations including India and least developed nations on funding for carbon credit were finally addressed.
- The rich nations which are the main polluters agreed to pay for greening in the underdeveloped world.
- The agreed guidelines mean that countries can now establish the national systems that are needed for implementing the Paris Agreement by 2020.
Fiji-led Talanoa Dialogue concluded:
- The Fiji-led Talanoa Dialogue, a year-long inclusive dialogue that relates to the Paris Agreement, was also concluded at COP24, with the global warming of 1.5 degree Celsius report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) as a major input.
- There is a clear recognition of the IPCC’s role in providing scientific input to inform countries in strengthening their response to the threat of climate change.
- ‘Talanoa Call for Action’ calls upon all countries and stakeholders to act with urgency.
- Countries are encouraged to factor the outcome of the dialogue into efforts to increase their ambition and to update their nationally determined contributions in 2020.
Paris Agreement on Climate Change:
- In December 2015, 195 countries pledged to slow the process of global warming in Paris by signing the Paris Agreement on Climate Change.
Objectives:
- The primary objective is to limit the global average temperature to well below 2 °C above pre-industrial levels.
- Efforts will be made to limit the temperature increase to 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels so that it will be possible to reduce the risks and impacts of climate change.
- Parties should take action to conserve and enhance, as appropriate, sinks and reservoirs of greenhouse gases including forests.
- With a view to contribute to sustainable development and to achieve the long term temperature goal of 2°C, the COP established the global goal on adaptation of enhancing adaptive capacity, strengthening resilience and reducing vulnerability to climate change.
Outcome of 24th Session of Conference of Parties
24, Dec 2018

Why in news?
- The 24th Session of the of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP 24) was held in Katowice, Poland on 02nd– 15th December 2018.
Highlights:
- During the COP, nations overcame divisions to agree global climate pact rules for limiting temperature rise to below 2°Celsius while Indian participants are disappointed with the outcome.
- The key issues which were discussed:
o Finalization of guidelines/ modalities/ rules for the implementation of Paris Agreement.
o The conclusion of 2018 Facilitative Talanoa Dialogue.
o Stocktake of Pre-2020 actions implementation and ambition.
Outstanding issues:
- Key questions on whether developed countries would come good on earlier commitments to make available $100 billion annually by 2020 remained unsolved.
- Moreover, a fundamental tenet — that developed countries and developing countries have ‘differentiated’ responsibilities towards addressing global greenhouse gas emissions — appeared to be threatened.
Transparency Framework:
- India has been in favor of a robust transparency regime, and the finalized Enhanced Transparency Framework builds upon the existing guidelines while providing flexibilities for developing countries.
- The guidance on finance provisions operationalize the obligation of developed countries in providing means of implementation to developing countries.
- It recognizes the need for climate finance to be new and additional and climate specific.
- The framework for technology recognizes the need for enhanced support towards operationalization of the framework and comprehensively covers all stages of technology development and transfer.
Issue over Global Stocktake (GST):
- The GST refers to a periodic appraisal by countries on where the world stands vis-à-vis emissions and what more needs to be done.
- This would form the basis for countries taking the call on increasing their emission cuts.
- The global stocktake will provide countries with the basis for strengthening their actions and submitting new national climate commitments in the two years following each successive global stocktake.
- Equity is specifically mentioned in Article 14 of the Paris Agreement. It is the basic principle of the Convention and the Paris Agreement.
- The entire GST exercise is lopsided as the process of technical assessment does not fully address equity.
Carbon credits:
- There is the outstanding issue of what happens to carbon credits.
- These are essentially carbon emissions that would normally have gone into the atmosphere but were prevented, due to alternate, cleaner alternatives adopted by developing countries.
- Developed countries are expected to pay for such credits via market-based trading mechanisms but these have been dismantled because of concerns over whether these reductions were real and measurable.
- The countries are not willing to find a solution to this as it has been postponed once again.
Global Compact for Safe, Orderly and Regular Migration adopted
24, Dec 2018

Why in News?
- Global Compact for Safe, Orderly and Regular Migration was adopted by 164 nations including India at Intergovernmental Conference held under the auspices of United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) at Marrakesh, Morocco.
- It is the first intergovernmental agreement to cover wide-ranging dimensions of international migration in a holistic and comprehensive manner and agreed upon by all the UN member states minus United States.
Global Compact for Safe, Orderly and Regular Migration:
- It seeks to better manage migration at local, national, regional and global levels, in order to reduce the risks and vulnerabilities of migrants.
- It creates a non-legally binding and co-operative framework that builds on commitments agreed upon by member states in New York Declaration for refugees and migrants of December 2016.
- It lists four objectives:
o Ease pressures on host countries.
o Enhance refugee self-reliance.
o Expand access to third country solutions.
o Support conditions in countries of origin for return with safety and dignity. - It sets out a framework on how international cooperation on migration issues should work but does not oblige states to take concrete action.
- It sets out 23 objectives to deal with issues ranging from factors that compel people to move, legal channels for migration, combating trafficking and smuggling, harness economic benefits of migration and return of the migrants.
- Its intent to protect human rights of migrants, address root causes of migration, and combat negative myths surrounding migration.
- It acknowledges that migration is an international issue that affects all member states and there is a need for more effective migration governance.
Increase in International migrants:
- According to UN, there were 258 million international migrants in the world in 2017, increasing almost 50% since 2000.
- The number of migrants, representing 3.4% of world’s population, is increasing faster than global population, driven by economic prosperity, inequality, violence, conflict and climate change.
- Migrants worldwide account for 3% of the world’s entire population, but contribute 10% of the global gross domestic production (GDP).
- Migrant’s remittance is a huge contributor to their home countries’ development.
- Around 80% of world’s migrants move between countries in a safe and orderly fashion.
- But more than 60,000 people have died on the move since the year 2000.
- Besides in transit countries or the country of destination, racism, discrimination and human-rights violations are continuously reported.
- The process of developing the compact was started in early 2017 as implementation of decision by UN member states as adopted New York Declaration for Refugees and Migrants in September 2016.
- UN member states’ another decision pledged in the declaration is to develop a Global Compact on Refugees.
Difference between migrant and refugee:
Refugee:
- Refugees are persons who are outside their country of origin for reasons of feared persecution, conflict, generalized violence, or other circumstances that have seriously disturbed public order as a result, require international protection.
- The refugee definition can be found in the 1951 Convention and regional refugee instruments, as well as UNHCR’s Statute.
Migrant:
- While there is no formal legal definition of an international migrant, most experts agree that an international migrant is someone who changes his or her country of usual residence, irrespective of the reason for migration or legal status.
- Generally, a distinction is made between short-term or temporary migration, covering movements with a duration between three and 12 months, and long-term or permanent migration, refering to a change of country of residence for a duration of one year or more.
Exercise Hand-in-Hand 2018
22, Dec 2018

Why in news?
- Exercise Hand-in-Hand is conducted annually as part of military diplomacy and interaction between armies of India and China.
Objective:
- The joint exercise for the year 2018 will be conducted from 10 to 23 December 2018 at Chengdu, China.
- The aim of the exercise is to build and promote close relations between armies of both the countries and to enhance ability of joint exercise commander to take military contingents of both nations under command.
- The exercise will involve tactical level operations in an International Counter Insurgency/ Counter Terrorist environment under UN mandate.
- Exercise Hand-in-Hand 2018 will go a long way to further cement relationship between both the nations and will act as a catalyst in bringing bonhomie at grassroots levels between the armies of both countries.
India, Peru sign agreement for co-operation and mutual assistance in Customs Matters
21, Dec 2018

Why in news?
- India and the Republic of Peru on December 5, 2018 signed an agreement for co-operation and mutual assistance in customs matters.
- The agreement was signed on the sidelines of the 80th Session of the Policy Commission meeting of the World Customs Organisations (WCO) which was held in Mumbai during December 3-5, 2018.
Agreement- Key Highlights:
- The Agreement provides a legal framework for sharing of information and intelligence between the Customs authorities of the two countries.
- It will help in the proper application of Customs laws, prevention and investigation of Customs offences.
- The Agreement will also help in the availability of relevant information for the prevention and investigation of Customs offences.
- It is expected to facilitate trade and ensure efficient clearance of goods traded between the countries.
India-Peru Relations:
- India established diplomatic relations with Peru in March 1963. India-Peru relations have since then been traditionally cordial and friendly.
- India’s bilateral trade with Peru was USD 107.32 million during 2005-06 and this grew up to 1319.45 percent during 2015-16.
- During 2015-16, bilateral trade between both sides stood at USD 1523.35 million with exports at USD 703.12 million and imports at USD 820.22 million.
- The Peruvian Community in India is quite small with around two hundred people only. Majority of them reside in Delhi NCR, Haryana, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, and Rajasthan.
- On the other side, Indian Community in Peru is also quite small. Only around 50-60 families are engaged in business, trade and other professions in Peru. India origin organisations like Hare Krishna, Sai Baba and Brahma Kumaris are also present in Peru.
India, UAE sign agreement on currency swap
20, Dec 2018

Why in News?
- The 12th session of the India-UAE Joint Commission Meeting (JCM) for Economic and Technical Cooperation was held on December 3-4, 2018 in Abu Dhabi, the United Arab Emirates.
- Also in the meet discussions to step up bilateral cooperation in areas such as security, defence, counter-terrorism, investments, space, trade and energy taken place
Key Highlights:
- During the India-UAE JCM, India and the United Arab Emirates signed two agreements, one pact on currency swap and an MoU for development cooperation in Africa.
- The agreement on currency swap between the countries will allow trading in their own currency and payments to import and export trade at a pre-determined exchange rate without bringing in a third benchmark currency like the US dollars.
- The second Memorandum of Understanding would enable both the nations to undertake development projects in Africa.
- The leaders also identified several new areas of cooperation and following the conclusion of the JCM, the leaders signed and adopted the agreed minutes of the meeting.
India-UAE Relations:
- With bilateral trade amounting to almost USD 50 billion, India and UAE are one of the largest trade partners for each other and have made robust investments bilaterally.
- The UAE is the sixth-largest source of Indian oil imports and hosts a 3.3 million-strong Indian community, which amounts to the largest number of Indians outside India.
- Indians also make up the largest ethnic group in the UAE making up roughly 27 per cent of the total UAE`s residents.
- During the Indian PM Narendra Modi’s visit to the UAE in February 2018, both sides set an ambitious target of US$100 billion in bilateral trade by the year 2020.
International Day of Persons with Disabilities
19, Dec 2018

Why in News?
- The International Day of Persons with Disabilities is observed every year on December 3 to promote the rights and well-being of persons with disabilities in all spheres of society and development.
The 2018 theme for this day is “Empowering persons with disabilities and ensuring inclusiveness and equality”
Objective:
- It aims to promote an understanding of disability issues and mobilize support for the dignity, rights and well-being of persons with disabilities.
- It also seeks to increase awareness of the situation of persons with disabilities in every aspect of political, social, economic and cultural life.
Highlights:
- It focuses on empowering persons with disabilities for an inclusive, equitable and sustainable development as part of 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) pledges to “leave no one behind”.
- The International Day of Persons with Disabilities was instituted by United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) after it had passed a resolution 47/3 in 1992.
- Since then, it is observed annually and originally was called as the International Day of Disabled Persons.
- UN estimates that around one billion people are living with disabilities across the world and they are facing barriers of inclusion in many key aspects of society.
Ex SHINYUU Maitri-2018
18, Dec 2018

Why in news?
- The first bilateral air exercise SHINYUU-18 between Indian Air Force (IAF) and Japanese Air Self Denfence Force (JASDF) has been commenced at Air Force Station in Agra, Uttar Pradesh.
- The theme for SHINYUU-18 is joint Mobility/Humanitarian Assistance &Disaster Relief (HADR) on Transport aircraft.
Ex SHINYUU Maitri-18:
- The JASDF C2 aircraft along with aircrew/observers are part of this first air exercise between the two Air Forces.
- IAF is participating with An-32 and C-17 aircraft with aircrew & observers.
- The focus of the exercise is set for the IAF and JASDF crews to undertake Joint Mobility/ HADR operations.
- Display of heavy loading/ off-loading are also planned to be practiced during this exercise.
India to host G20 Summit in 2022
18, Dec 2018

Why in news?
- India will host G20 Summit In 2022, when it celebrates its 75th year of Independence.
- It was announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi during ongoing G20 meet of international grouping in Buenos Aires, capital of Argentina.
- During the Buenos Aires G20 meet, India presented a nine-point agenda to the G20 countries calling for strong and active cooperation among them to comprehensively deal with fugitive economic offenders.
India’s 9-point agenda against fugitive economic offenders:
- Joint efforts to be made by the G20 nations to form a mechanism that denies entry and safe havens to all fugitive economic offenders.
- There is need for the “effective” implementation of the principles of the United Nations Convention Against Corruption (UNCAC) and the United Nations Convention Against Transnational Organised Crime (UNOTC).
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) should be called upon “to assign priority and to focus on establishing international co-operation that leads to a timely and comprehensive exchange of information between the competent authorities”.
- The FATF should be tasked to formulate a standard definition of fugitive economic offenders.
- The FATF should also develop a set of commonly agreed and standardised procedures related to identification, extradition and judicial proceedings for dealing with fugitive economic offenders to provide guidance and assistance to G-20 countries, subject to their domestic law”.
- There is need for setting up of a common platform “for sharing experiences and best practices including successful cases of extradition, gaps in existing systems of extradition and legal assistance.”
- Strong and active cooperation among the G-20 nations. The document highlights the importance of cooperation in legal processes such as “effective freezing of the proceeds of crime; early return of the offenders and efficient repatriation of the proceeds of crime should be enhanced and streamlined”.
- The G20 forum should consider initiating work on locating properties of economic offenders who have a tax debt in the country of their residence for its recovery.
G20 forum:
- The Group of Twenty (G20) is the premier forum for international economic cooperation and decision-making.
- It is a forum for the governments and and central bank governors from 20 major economies on economic issues and other important development challenges.
- It was started in 1999 as a meeting of Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors in the aftermath of the South-east Asian (Tiger economies) financial crisis.
- The G20 comprises of total 19 countries plus the European Union (EU), representing 85% of global GDP, 80% of international trade, 65% of world’s population.
- Its members include Australia, Argentina, Brazil, Canada, China, India, France, Germany, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, South Korea, Mexico, Saudi Arabia, Russia, Turkey, South Africa, UK, US and EU.
India, China Sign A protocol for Fish meal and Oil Import
18, Dec 2018

Why in News?
- India and China signed a protocol on hygiene and inspection requirements for the exports in New Delhi. The protocol was signed following a discussion between India’s Union Commerce Ministry and a six-member delegation led by Vice Minister, General Administration of Customs of China, Hu Wei on easing market access for exports of various farm products.
Highlights:
- The representative from both the Indian and Chinese sides acknowledged each other’s concerns while agreeing to figure out a best possible solution to solve market access problems for the realization of the two-neighbor countries’ vision by encouraging a balanced trade.
- The Chinese delegation discussed the problems related to market access for Chinese products like milk and milk products, soy meal, fruits and vegetables, tobacco and pharmaceuticals.
- This protocol will help India to export fish meal, and fish oil to the markets in China for which India has been seeking approval from China.
- It will help India to start the fish meal and fish oil export to China. China imports fish oil worth USD 143.29 million per year and the fish-meal to the tune of $263.43 million.
- So far, China had not allowed India for the export of these products. It is the second Indian product to get approval from China within the last six months.
- In June this year, General Administration of Customs of China and Department of Agriculture of India had signed a MoU on phytosanitary requirements for exporting Rice from India to China.
India-ASEAN InnoTech Summit 2018
18, Dec 2018

Why in news?
- The first India ASEAN InnoTech Summit 2018, a two-day International Innotech Summit, exhibition, B2B and B2G meetings was held in New Delhi.
- The theme of India ASEAN InnoTech Summit was: Accelerating towards innovative development.
- It was organised by FICCI in association with the Department of Science & Technology (DST) and the Ministry of External Affairs to connect local and global research & development community for collaborative engagement.
Objectives of the summit:
- Explore avenues of cross country partnerships with Indian R&D-based enterprises.
- Capture global trends in technology management and strategy .
- Advance progressive ideas for policy reforms and regulatory environment .
- Create avenues for industry-academia-government partnerships .
- Build capacities for market assessment and rapid commercialization of research .
- Promote best practices in financing, strategy, and leadership .
- Connect local and global research & development community for collaborative engagement .
Highlights:
- Participating ASEAN member countries in this summit were Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam.
- On sidelines of this summit, an exhibition to showcase best Indian Innovative Technologies, with potential implementation in ASEAN region was also organized.
- Besides this summit also provided platform for B2G meetings i.e. one to one meeting with ASEAN delegation of ministers, advisors, and other dignitaries.
ASEAN:
- ASEAN is regional intergovernmental organisation comprising 10 Southeast Asian countries, which promotes intergovernmental cooperation and facilitates economic, political, security, military, educational, and sociocultural integration.
- 10-member ASEAN comprise of Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, Philippines, Vietnam, Myanmar, Cambodia, Brunei and Laos.
- India is a full dialogue partner of the ASEAN.
India to Chair Kimberley Process Certification Scheme
18, Dec 2018

Why in News?
- India will Chair Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) from 1st January 2018. It was was handed Chairmanship by the European Union during KPCS Plenary 2018, which was held in Brussels, Belgium.
Kimberley Process:
- The Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) is the process established in 2000 to prevent conflict diamonds from entering the mainstream rough diamond market.
- It is joint initiative of governments, industry and civil societies to stem flow of ‘conflict diamonds’, rough diamonds used by rebel groups to finance wars against legitimate governments. It is also described in United Nations Security Council (UNSC) resolutions.
- It was ruled by UNGA Resolution 55/56 following recommendations in the Fowler Report.
- The process was set up to ensure that diamond purchases were not financing violence by rebel movements and their allies seeking to undermine legitimate governments.
India and KPCS:
- India is the founding member of KPCS and is actively involved in KP activities to ensure that almost 99% of the diamond trade in the world is conflict free.
- India is committed to maintain KP as an efficient and effective process in order to ensure the conflict diamond free status.
- India is at the forefront in addressing the issue of differentiation between Natural Diamonds and Lab Grown Diamonds and ensure responsible business in this area.
- India chaired the Ad hoc Committee on Review and Reform (AHCRR).
- In India, the scheme is administered through Department of Commerce under aegis of the Union Commerce and Industry Ministry.
Conflict diamonds:
- Conflict diamonds or blood diamonds are the rough diamonds used by rebel movements in the third world countries especially in Africa to finance (civil) wars with an aim to topple legitimate governments.
- The KPCS completely bans import and export of rough diamonds without certifications.
Exercise Cope India 2018
17, Dec 2018

Why in news?
- The fourth edition of the series of bilateral joint exercise, ‘Ex Cope India-18’, began between the air forces of the United States and India on December 3, 2018 in West Bengal, India.
- The 12-day exercise will be held from December 3-14 at Air Station Kalaikunda and Air Station Arjan Singh in Panagarh airbase. This is the first time that the exercise is being planned at two Air Force bases.
Objective:
- The main aim of exercise is to provide operational exposure and undertake mutual exchange of best practices towards enhancing operational capability.
Highlights:
- COPE INDIA 2019 is a bilateral Field Training Exercise (FTX) which has been sponsored by US Pacific Air Forces (PACAF).
- This field training exercise will enhance US-Indian mutual cooperation. It will also seek to improve existing capabilities, aircrew tactics and force employment. During this field training exercise, India and US will showcase their efforts and commitment for free and open Indo-Pacific region.
- A total of around 200 US air force personnel with 15 aircraft from 18th Wing At Kadena Air Base in Japan and 182 Airlift Wing of the Illinois Air National Guard are expected to participate in this air training exercise.
- Cope India is a series of Air Force exercises between the Indian Air Force and the United States Air Force. The first such air training exercise was conducted at the Indian Air Force station in Gwalior between February 16 to 27 in 2004.
- The air training exercise included flight tests, practice, and demonstrations. Besides this, the lectures on subjects related to aviation were also organized.
- In addition to the fighter training exercise, it has evolved to incorporate air mobility training, airdrop training and large-force exercises. This exercise was also held in 2005, 2006, 2009 and 2010.
Cope India:
- Cope India is a series of joint Air Force exercises held between the Indian Air Force and the United States Air Force, in India.
- The first such exercise, which required many months of preparation, was conducted at the air force station in Gwalior in February 2004.
- The exercise included flight tests, practice and demonstrations as well as lectures on subjects related to aviation.
- There were also media functions and social interactions held among troops of the two countries.
- The exercise has now evolved to incorporate subject matter expert exchanges, air mobility training, airdrop training and large-force exercises, in addition to fighter-training exercises.
Exercise KONKAN-18
30, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Why in news?
- The naval exercise Konkan 18 between India and United Kingdom will be conducted from November 28 to December 6, 2018 off Goa with units participating from both navies. The harbour phase is scheduled from November 28 to November 30 2018 followed by the sea phase from 2-6 December, 2018.
Fleets in exercise:
- The Royal Navy will be represented by HMS Dragon, a Type 45 Class Destroyer equipped with an integral Wildcat helicopter.
- The Indian Navy will field INS Kolkata, the first ship of latest Kolkata class destroyers, equipped with integral Seaking and an IN submarine.
- The thrust of the exercise this year would be on Anti-Air warfare, Anti-Surface Warfare, Anti-Submarine Warfare, Visit Board Search and Seizure (VBSS) and Seamanship Evolutions.
Background and objectives:
- Naval cooperation between India and United Kingdom is based on long term strategic relationship between both countries.
- Both Navies have, over years have undertaken bilateral activities such as training exchanges and technical cooperation.
- Bilateral KONKAN exercise was started in 2004 and since then has grown in scale. It provides platform to periodically exercise at sea and in harbor so as to build interoperability and share best practices.
- The exercise is aimed at deriving mutual benefit from each other’s’ experiences and is indicative of continuing cooperation between two countries.
- The inter-operability achieved over years as result of such exercises has proved to be operationally beneficial to both navies.
- The naval cooperation is tangible symbol of commitment of both nations in ensuring a positive climate at sea for enhancing strategic stability and promoting economic prosperity.
Sustainable Blue Economy Conference
28, Nov 2018

GS 3: IR | Bilateral, regional & global groupings & agreements involving India &/or affecting India’s interests
Why in News?
- The Sustainable Blue Economy Conference was held with the theme of ‘The Blue Economy and the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development’ in Nairobi, Kenya. The conference was organized for the first time by Kenya and co-hosted by Japan and Canada.
- India endorses the growth of the Blue Economy in a sustainable, inclusive and people centered manner through the framework of the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)”.

Highlights:
- Sustainable Blue Economy Conference was held on the momentum of agenda of United Nations (2030) for the Climate Change Conference 2015 (Paris) and UN Ocean Conference 2017 (Call to Action) and Sustainable Development.
- More than 17,000 delegates from a total of 184 countries had participated in this conference where India was represented by the Union Minister for Shipping, Road Transport & Highways, NitinGadkari.
- Besides them, the representatives from World Wildlife Fund (WWF), International Maritime Organization (IMO), International Seabed Authority (ISA), World Bank, AFRIEXIMBANK, and Ocean Foundation were also present in the conference.
- Blue Economy is the economic benefit that comes from Earth’s coastal and marine environment. Marine-based economy, the Blue Economy provides social and economic benefits to the people while restoring, protecting and maintaining the diversity of marine ecosystems.
- With its strategic location in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), India encourages the growth of Blue Economy inclusively and sustainably. Indian Ocean Rim Association(IORA) has developed a framework which is supposed to help India achieve its Marine-Based-Economic-goals.
- India is developing an infrastructure for its sea-borne-trade, and seafaring under an ambitious ‘Sagarmala Programme.’ The programme will improve maritime logistics and port led developments.
Sagarmala Programme:
- It has identified 600 plus projects entailing a huge investment of $120 billion (nearly Rs. 8 lakh crore) by 2020.
- It saves India $6 billion per annum in logistics costs besides creating 10 million new jobs and boosting port capacity by 800 Million Metric Tonne per Annum (MMTPA) to an overall 3500 MMTPA.
Indo-Russian Strategic Economic Dialogue
24, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional & global groupings & agreements involving India &/or affecting India’s interests
Why in News?
- India and Russia attended first-ever Strategic Economic Dialogue held at St. Petersburg in Russia. The Vice-Chairman of the NITI Aayog Rajiv Kumar led the Indian side while Economic Development Minister Maxim Oreshkin headed Russian delegation.
Objectives:
- The delegations from both of the countries discussed the development of bilateral ties in trade, investment, and industry at the platform provided by the two-day forum.
- The two-day forum aimed to bring together key business figures from both the countries while focusing on Transport, agriculture, and agro-processing, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), digital transformation and frontier technologies and industrial cooperation.
Indo-Russian Strategic Economic Dialogue:
- Indo-Russian Strategic Economic Dialogue was created by PM Narendra Modi and President Vladimir Putin in their informal summit held at Sochi in May 2018.
- The main objective of this forum is to improve the economic partnership between both countries which has begun to gain momentum since 2017.
- The forum also aims to improve economic partnership and also explore partnership and joint ventures in the service and IT sectors.
- To improve bilateral trade to $ 30 billion by 2025, India and Russia have agreed to alienate of obstacles to trade. Both the countries are aiming to improve bilateral trade which was recorded with 21.5 percent growth last year.
- India has already launched Strategic Economic Dialogue with China
India, Pakistan Dera Baba Nanak – Kartarpur corridor
24, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | India & its neighborhood- relations
Why in News?
- Marking a new beginning in India-Pakistan relations and heralding the possibility of reducing the tensions between the two countries, the Vice President of India, Shri M. Venkaiah Naidu has laid the foundation stone for construction of Dera Baba Nanak – Kartapur Sahib corridor on the Indian side that will provide a passage to Sikh pilgrims to visit the holy site of GurudwaraDarbar Sahib at Kartarpur in Pakistan.
Kartarpur Sahib Corridor:
- India and Pakistan exchanged letters committing to build the required infrastructure for visa-free direct travel by Indian Sikh pilgrims to Pakistan’s Kartarpur Sahib Gurdwara.
- The Kartarpur corridor will be implemented as an integrated development project with Government of India funding, to provide smooth and easy passage, with all the modern amenities.
- Government of India will put in place suitable facilities for smooth passage of pilgrims. Government of Pakistan will be urged to recognize the sentiments of the Sikh community and to develop a corridor with suitable facilities in their territory as well.
- In a rare sign of concord between the two countries, the letters were exchanged on the same day.
Corridor – History & Inception:
- The Kartarpur Sahib corridor was first proposed in 1999 when former PM Vajpayee took a bus ride to Lahore.
- He raised a long-standing demand from the Sikh community for easy access to the revered shrine across the border where Guru Nanak spent the last 18 years of his life.
- The pilgrims will traverse on the Indian side from Dera Guru Nanak Dev in Gurdaspur district directly to the border and from the Pakistani side of the border directly to KartarpurDarbar Sahib Gurdwara.
- This has been done to allow them to mark the 550th Birth Anniversary of Guru Nanak Dev in November 2019.
- This corridor will be a historical landmark between India and Pakistan and will also boost tourism as more pilgrims would visit the holy shrine throughout the year between two countries.
AAI inks-pact with US Agency to Prepare Modernization Road-map
19, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional & global groupings & agreements involving India &/or affecting India’s interests
Why in news?
- Authority of India (AAI) has inked an agreement with the US Trade and Development Agency (USTDA) to develop a roadmap for modernisation of its air traffic services. Air traffic services (ATS) comprises air traffic management (ATM) and communication, navigation and surveillance (CNS).
Key- Highlights:
- The collaboration is aimed at developing CNS/ATM roadmap for the AAI for modernisation of the national airspace system (NAS).
- Under the agreement, US aircraft manufacturer Boeing will provide technical assistance, thus create a roadmap to enhance communications, expand existing systems and airspace capacity and invest in CNS/ATM facilities.
- It will help in improving safety and reducing congestion for flights in India.
- At the same time, it will create market access for high quality US exports that can advance India’s aviation goals.
Significance of this pact:
- This initiative will upgrade network operations, enhance security, and improve the performance, reliability and quality of India’s air traffic management communications network, while reducing the telecommunication costs.
- This communication backbone infrastructure will also play a pivotal role in deployment of remote towers for managing air traffic services at Regional Connectivity Scheme (RCS) airports.
- In the long run the implementation of Futuristic Telecommunications Infrastructure (FTI) network would result in enhanced air traffic safety, increase in airspace capacity by allowing the controllers to reduce the separation limits and accommodating the aircrafts to more economical and environment friendly flight levels thus reducing the overall carbon footprint.
Need for Modernisation:
- The air passenger traffic over last 49 months has double folded in India has brought several challenges with it, including maintaining safe and efficient aircraft operations.
- In this backdrop, AAI has decided to draw robust roadmap for sustained ANS infrastructure to meet the growth challenges in a planned way.
- By utilising global and regional best practices as benchmark technical help will recommend roadmap and implementation plan to AAI for improving airspace utilisation and implement CNS/ATM air and ground equipage in short, medium and long term.
Airports Authority of India (AAI):
- It is a statutory body under the aegis of Ministry of Civil Aviation.
- It is responsible for creating, upgrading, maintaining and managing civil aviation infrastructure in India.
- It was founded in 1995 and is headquartered in New Delhi.
- It also provides Air traffic management (ATM) services over Indian airspace and adjoining oceanic areas.
- It manages around 125 airports in India, which include 18 International Airport, 07 Customs Airports, 78 Domestic Airports and 26 Civil Enclaves at Defense airfields.
NITI Aayog organizes South Asian Regional Conference on Urban Infrastructure
18, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Important International institutions, agencies & fora, their structure, mandate
Why in News?
- NITI Aayog partnered with the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP) and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) to host a South Asian regional conference.
Objective:
- The Conference aims to review overall issues and assess the sustainability of PPPs and urban finance in South Asia, specifically India, while broadening the knowledge base and engaging on international best practices.
- The conference will emphasize the need to ensure adequate return on investments in infrastructure through properly structured Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) and de-risking of projects.
- Public-private partnerships (PPPs) have been one such option that enables governments to optimally share the risks associated with a project’s life cycle.
Need for implementing and financing urban infrastructure:
- Considering the quantum deficit in infrastructure implementation vis-à-vis the demand, it is urgently needed to focus on newer means of implementing and financing urban infrastructure.
- In India alone, until 2040, estimated investments of around $4.5 trillion are required in the infrastructure space.
- With respect to urban needs, the population in South Asia is expected to grow by around 250 million till 2030, while that in India is expected to reach around 590 million during the same period.
- There are an estimated 98 million people who reside in the slums of Indian cities and are disproportionately deprived of access to basic services and infrastructure.
- These gaps must be addressed, so that the cities grow equitably and in an environmentally responsible way.
- The South Asian regional conference is a first of its kind, with participation from across the South Asian region including leaders from the government, industry, research organizations, academia, think tanks and civil society.
- To implement urban infrastructure in India, a deeper deliberation is required on the means of democratizing the governance at the city level.
- It shall provide greater operational and fiscal autonomy to Urban Local Bodies (ULBs).
India, Australia Sign Five Agreements
17, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional & global groupings & agreements involving India &/or affecting India’s interests
Why in News?
- India and Australia signed five agreements to increase investment and improve cooperation in disability, agricultural research and education sectors. The agreements were signed when President Ram NathKovind met Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison in Sydney on November 22, 2018. President Ram NathKovind, who is on a two-nation trip is the first-ever Indian state head to visit Australia.
Five pacts agreements – Highlights:
- The first agreement will aim to improve the cooperation in the area of disability so that better service can be provided to the differently-abled people.
- The second agreement was signed between Invest India and Austrade which will facilitate bilateral investment between two countries.
- The Central Mine Planning and Design Institute, Ranchi, and the Commonwealth Scientific and Research Organisation, Canberra signed the third agreement which will foster scientific collaboration and innovation between the organizations based in two countries.
- The fourth agreement was signed between the Acharya NG Ranga Agricultural University, Guntur, and the University of Western Australia, Perth, for cooperation in researches related to agriculture and education. This agreement will encourage cooperation between two educational institutes based in two countries.
- The fifth agreement signed between the Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology, New Delhi, and the Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane will facilitate joint Ph.D. programmes.
- Besides this agreement, an announcement related to the release of Australia’s response to ‘Indian Economic Strategy’ was also made by Prime Minister Scott Morrison.
- Indian Economic Strategy is a detailed blueprint for the transformation of the economic engagement.
India votes against UNGA draft resolution on use of death penalty
17, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Important International institutions, agencies & fora, their structure, mandate
Why in news?
- India has voted against a United Nations General Assembly draft resolution on the use of death penalty, saying it goes against the statutory law of the country where an execution is carried out in the “rarest of rare” cases.
UN Against Death Penalty:
- The draft resolution, taken up in the Third Committee (Social, Humanitarian, Cultural) of the General Assembly was approved with a recorded vote of 123 in favour, 36 against and 30 abstentions.
- India was among the countries that voted against the resolution, which would have the Assembly call on all States to respect international standards on the rights of those facing death penalty.
- The draft aimed to ensure that it is not applied on the basis of discriminatory laws or as a result of discriminatory or arbitrary application of the law.
India’s Stance of Death Penalty:
- The resolution sought to promote a moratorium on executions with the aim of abolishing death penalty.
- India has voted against the resolution as a whole, as it goes against statutory law in India.
- The death penalty is exercised in ‘rarest of rare’ cases, where the crime committed is so heinous that it shocks the conscience of the society.
- Indian law provides for all requisite procedural safeguards, including the right to a fair trial by an independent Court, presumption of innocence, the minimum guarantees for defence, and the right to review by a higher court.
- Indian delegation has argued for the sovereign right to determine its own legal system and appropriate legal penalties.
Singapore brings in Amendment:
- Singapore’s delegate decried the draft resolution’s “one-size-fits-all” approach to a delicate question, which seeks to impose a particular vision of the world onto others.
- The representative of Singapore said the amendment aimed to ensure respect for the diversity of views.
- The amendment is simple and neutral and it does not take a position on the substance of the draft resolution, nor make judgments about State policies.
Voting for Sovereignty over Legal System:
- The draft resolution’s passage followed an intense debate and Singapore introduced an amendment on behalf of 34 countries that reaffirmed the countries’ sovereign right to develop their own legal system.
- The Committee then approved this amendment by a recorded vote of 96 in favour to 73 against, with 14 abstentions.
- India voted in favour of this amendment.
- By its terms, the Assembly would reaffirm the sovereign right of all countries to develop their own legal systems, including determining appropriate legal penalties, in accordance with their international law obligations.
CII AND UNEP SIGN MOU FOR IMPLEMENTATION OF SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
17, Nov 2018

Why in News?
- The Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and the UN Environment has signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) for coherent implementation of the environmental dimension of sustainable development.
Highlights of the MoU:
- The CII will work towards voluntary codes in Indian industry on the issue of plastics, for which there is already a precedent with benefits to firms in terms of credit and shareholder value.
- The MoU encompasses ‘coherent implementation of the environmental dimension of sustainable development according to an official statement.
- It provides a framework of cooperation and facilitates cooperation in issues of environment, climate change, renewable energy, energy efficiency, resource conservation and management, water sanitation, smart cities and urban infrastructure.
- A major activity planned under the MoU, will be the #Un-plastic Initiative of CII and UN Environment, beginning with a Call to Action, including commitments by industry on actions to curb plastic pollution.
Confederation of Indian Industry (CII):
- CII is a non-government, not-for-profit, industry-led and industry-managed organization.
- Founded in 1895, it has over 9,000 members, from the private as well as public sectors, including SMEs and MNCs, and an indirect membership of over 300,000 enterprises from around 265 national and regional sectoral industry bodies.
- CII works with the Government on policy issues. It played a very important role during economic liberalisation in 1991 which knocked down the high walls of protection between Indian industry and the rest of the world.
- CII serves as a reference point for Indian industry and the international business community.
- It has 65 offices, including 9 Centres of Excellence, in India, and 11 overseas offices in Australia, Bahrain, China, Egypt, France, Germany, Iran, Singapore, South Africa, United Kingdom and United States.
UNESCO Asia-Pacific award for conservation
16, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional & global groupings & agreements involving India &/or affecting India’s interests
Why in news?
- The restoration of an aristocratic house project from partial ruin state in Ladakh undertaken by LAMO (Ladakh Arts and Media Organisation) Center has won 2018 UNESCO Asia-Pacific award for Cultural Heritage conservation in Award of Distinction category.
- LAMO is public charitable trust established to articulate an alternative vision for the arts and media in Ladakh.
Details:
- The restored structure is strategically located at the foot of Leh palace, contributes to continuity of historic townscape of 17th century.
- Its recovery establishes precedent for conserving non-monumental urban fabric of Leh Old Town.
- Under restoration project, LAMO had used salvaged and local building materials and indigenous construction techniques and skilfully introduced modern amenities to assure its ongoing use.
Other Category awardees:
Award of Excellence:
- It was awarded to restoration project of early 20th-century Shijo-choOfune-hoko Float Machiya in Japan.
- It celebrates Kyoto culture by safeguarding city’s endangered wooden townhouse typology as well as iconic annual Gion Festival.
Award of Distinction:
- LAMO Center, Ladakh, India.
Award of Merit:
- 5 Martin Place, Sydney (Australia); Aijing Zhuang, Fujian (China); Commercial Bank of Honjo Warehouse, Saitama (Japan).
Honourable Mention:
- Hengdaohezi Town, Heilongjiang (China), Rajabai Clock Tower & University of Mumbai Library Building, Mumbai (India), RuttonseeMuljeeJetha Fountain, Mumbai (India).
New Design in Heritage Contexts:
- Kaomai Estate 1955, Chiang Mai (Thailand) and Harts Mill, Port Adelaide, (Australia).
UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation:
- It was established in 2000.
- It recognizes efforts of private individuals and organizations that have successfully conserved structures and buildings of heritage value in the region.
- It aims to encourage other property owners to undertake conservation projects within their communities, either independently or by seeking PPP (public-private partnerships).
SIMBEX-18 – India-Singapore bilateral naval exercise
15, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Why in News?
- The 25th edition of the India-Singapore bilateral naval exercise, SIMBEX, has begun at the tri-services command in Port Blair.
SIMBEX 2018:
- Started as basic Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) exercises in 1994, today these exercises have graduated to complex maritime combat drills, including missile and torpedo firings, and shore-based intensive professional exchanges.
- Seven ships from the Indian Navy and five ships from the Singapore Navy along with an Archer class submarine and a Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicle will take part in the exercise.
- The number of missiles and torpedo firings being undertaken are in fact unprecedented and perhaps the largest the Indian Navy has undertaken with any foreign Navy till date.
India’s Collaborations:
- The two countries have vastly expanded their military cooperation in recent years under India’s Act East policy.
- Late last year, the two countries signed a naval agreement which has a provision for mutual logistical support and gives India access to the Changi naval base.
- India and Singapore are working on a trilateral exercise with an Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) country, likely Thailand, and eventually plan to scale it up to a multilateral format.
27th BASIC Ministerial meeting
12, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional & global groupings & agreements involving India &/or affecting India’s interests
Why in news?
- The 27th BASIC Ministerial Meeting on Climate Change was held in New Delhi.In this meeting, the effective implementation of the Paris Agreement to combat climate change was discussed by the member countries.
Objective:
- The BASIC (Brazil, South Africa, India and China) group recently met to put pressure on developed countries to meet pre-2020 climate efforts, and to “progressively” and “substantially” scale up their financial support for future action.
Highlights:
- The 24th Session of the of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP24) is scheduled to be held in Katowice, Poland in December 2018. The COP24 will work out and adopt a package of decisions to ensure the implementation of the Paris Agreement.
- In the meeting, the Paris Agreement was considered as the significant step to advance global action against climate change by the participating BASIC countries.
- The member countries also reaffirmed their commitment to the implementation of UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCC) its Kyoto Protocol and Paris Agreement.
- BASIC member countries will continue to remind developed countries about their earlier commitment to provide $100 billion annually from 2020.
- The participating BASIC counties also requested developed countries to take actions to fill pre-2020 implementation gaps by 2023 which according to them can be used for first Global Stocktake (GST). Brazil will host the next BASIC Meeting.
Global Stocktake:
- It refers to a proposed five-yearly review of the impact of countries’ climate change actions.
- Under the Paris Agreement, every country must present a climate action plan in five-yearly cycles.
- Under the Paris Agreement, the first global stocktake will happen in 2023.
- It will assess whether the net result of the climate actions being taken was consistent with the goal of keeping the increase in global average temperature from pre-industrial times to within 2 degree Celsius.
BASIC:
- BASIC is a group of four large industrialized countries which comprise Brazil, South Africa, India, and China. It was formed under an agreement in November 2009 wherein the member countries committed to acting at Copenhagen climate summit 2009 jointly.
India and UK sign MoU for collaboration in cancer research
06, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Why in news?
- India and United Kingdom have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for collaboration in cancer research.
- It is a follow-up to the joint statement issued by Prime Ministers of India and UK during the visit of PM Narendra Modi to the UK in April 2018.
Highlights of the MoU:
- The MoU was signed between Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and Cancer Research UK (CRUK) for India-UK Cancer Research Initiative for collaboration in cancer research for the next five years.
- Under the MoU, both CRUK and DBT will invest 5 million pounds each in this five-year pilot project and seek further investment from other potential funding partners.
- India-UK Cancer Research Initiative will identify core set of research challenges that address issues of affordability, prevention and care of cancer patients by bringing together leading Indian and UK experts in clinical research, demographic research, new technologies and physical sciences.
- The initiative will provide funding to develop new research alliances and undertake impactful research to enable significant progress against cancer outcomes.
- It will also provide a catalysing platform for scientists and researchers in India and UK to co-create solutions for affordable cancer care that will improve cancer outcomes around the globe.
Protocol amending India-China DTAA
03, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional & global groupings & agreements involving India &/or affecting India’s interests
Why in news?
- The Government of the Republic of India and the Government of the People’s Republic of China have amended the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) for the avoidance of double taxation and for the prevention of fiscal evasion with respect to taxes on income, by signing a Protocol.
Significance:
- Avoidance of double taxation
- Prevention of fiscal evasion with respect to taxes on income
Highlights:
- Section 90 of Income-tax Act, 1961 allows India to enter into agreements with countries or specified territories for the avoidance of double taxation, for the exchange of information and for the prevention of the evasion.
- The signed Protocol will update the existing provisions for the exchange of information.
- It will incorporate required changes for the implementation of standards related to the treaty under the Action reports of Base Erosion&Profit Shifting (BEPS) Project.
- It will also bring in changes as per BEPS Action reports as agreed upon by the two sides. The protocol amending DTAA will help to prevent tax evasion by allowing the exchange of information.
Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA):
- The DTAA, or Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement is a tax treaty signed between India and another country ( or any two/multiple countries) so that taxpayers can avoid paying double taxes on their income earned from the source country as well as the residence country.
- A DTAA applies in cases where a tax-payer resides in one country and earns income in another.
- DTAAs can either be comprehensive to cover all sources of income or be limited to certain areas such as taxing of income from shipping, air transport, inheritance, etc.
- India has DTAAs with more than eighty countries.
India – Member of the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) Council
03, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional & global groupings & agreements involving India &/or affecting India’s interests
Why in News?
- India has been elected as a Member of the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) Council for another 4-year term (2019-2022).
- By securing 165 votes, India ranked third among the 13 countries elected to the Council from the Asia-Australasia region, and eighth among the 48 countries elected to the Council globally.The ITU has 193 memberstates who elect representatives to the Council.
India and ITU:
- India has been an active member of the ITU since 1869, earnestly supporting the development and propagation of telecom in the global community of nations.
- It has been a regular member of the ITU Council since 1952, and has played an important role in upholding principles of equality and consensus-building.
- India’s strong partnership with the ITU was also demonstrated in the recent ITU decision to set up the ITU South Asia Area Office and Technology Innovation Centre in New Delhi buy Jan 2019.
International Telecommunication Union:
- ITU is a United Nations specialised agency for Information and Communication Technologies, with membership of 193 countries and nearly 800 private sector entities and academic institutions.
- The body freezes international standards on telecom technologies that are to be used globally.
- ITU, based in Geneva, Switzerland, is a member of the United Nations Development Group and has 12 regional and area offices in the world.
- The ITU coordinates the shared global use of the radio spectrum, promotes international cooperation in assigning satellite orbits, works to improve telecommunication infrastructure in the developing world.
- The ITU is active in areas including broadband Internet, latest-generation wireless technologies, aeronautical and maritime navigation, radio astronomy, satellite-based meteorology, convergence in fixed-mobile phone, Internet access, data, voice, TV broadcasting, and next-generation networks.
- India has been member of ITU since 1869 and has also been a regular member of the ITU Council since 1952.
Annual Defence and Security Dialogue – India & China
03, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Why in news?
- India and China held the ninth Annual Defence and Security Dialogue here after a one-year gap due to the Doklam standoff, as both countries agreed to enhance military exchanges and interactions.
- The meeting held in Beijing was co-chaired by Defence Secretary Sanjay Mitra and Deputy Chief of Joint Staff Department of Central Military Commission Shao Yuanminga.
- At the 9th edition of the dialogue two countries agreed for increasing defence exchanges and interactions at different levels between the two militaries.
- The defence dialogue was held ahead of 21st round of border talks between the special representatives of the two countries in Chinese city of Dujiangyan on November 23-24, 2018.
Outcomes of the Dialogue:
- Both India and china agreed to enhance exchanges and interactions through reciprocal high-level visits between two ministries of defence as well as between commands, joint training exercises, mutual visits by defence personnel including mid-level and cadet officers were also agreed upon.
- They also reiterated importance of maintaining peace and tranquillity in border areas, implementing (Wuhan) consensus reached between PM Narendra Modi and Chinese President Xi Jinping and specific additional confidence-building measures at the operational level.
- They underlined importance of this dialogue as important mechanism between two countries for consultations on defence and security matters.
- They emphasised need to further strengthen military-to-military ties in order to strengthen political and strategic mutual trust between the two countries.
- Both sides also had an exchange of views on regional and global issues. Both sides agreed to hold the next round of the dialogue at mutually convenient time in India in 2019.
India to chair the Programme and Budget Committee of UNWTO
01, Nov 2018

GS 2: IR | Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Why in News?
- The Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Tourism, Shri. K. J. Alphons presides over the Program and Budget Committee meeting of UNWTO.
- The Minister highlighted the role of tourism in socio-economic development through job creation, enterprise and environment development and foreign exchange earnings.
Programme and Budget Committee of UNWTO:
- India’s tourism minister chaired the ‘Programme and Budget Committee’ meeting of UNWTO.
- It highlighted the role of tourism in socio-economic development through job creation, enterprise and environment development and foreign exchange earnings.
- As the chair of the Committee, the Minister informed the session that for the first time, UNWTO had a surplus budget and most of the arrears due have been paid.
- India will be the chair of Programme and Budget Committee of UNWTO Executive Council till 2021.
UNWTO:
- The World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) is the United Nations agency responsible for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism.
- The UNWTO Executive Council represents the Organization’s governing body whose task is to take all necessary measures in consultation with the Secretary-General, for implementation of its own decisions and recommendations of the Assembly and report thereupon to the Assembly.
- The Council meets at least twice a year, the next to be held in Bahrain.
- The council consists of 35 Full Members elected by the assembly in proportion of one member for every Five Full Members, in accordance with the Rules of Procedure laid down by the Assembly with a view to achieving fair and equitable geographical distribution.
INDIA – ADB SIGNS $110 MILLION LOAN TO IMPROVE RURAL CONNECTIVITY IN MP
29, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- India and Asian Development Bank (ADB) has signed $110 million loan to finance the upgrade of 2,800 kilometers all-weather rural roads in the State of Madhya Pradesh under the Prime Minister’s Rural Roads Program (PMGSY).
Significance of the Program:
- The overall program is aimed at improving rural connectivity, facilitating safer and more efficient access to livelihood and socio-economic opportunities for rural communities through improvements to about 12,000 kilometers rural roads across the states of Assam, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and West Bengal. The loan will improve mobility for self-employment and livelihood opportunities in rural areas by improving access to district centers.
- The project will continue to support the Government’s drive for innovative approaches to reduce costs, conserve non-renewable natural resources, and promote the use of waste materials in rural road construction. Considering the increased rainfall and storm surges in Madhya Pradesh, the road designs take into account the climate risks with measures such as greater elevation of road embankments and slope protection. Women were extensively consulted during the project design and will gain some key benefits, including improved access to healthcare, livelihoods and schooling.
Tranche Loans:
- Tranche 2 loan is part of the $500 million Second Rural Connectivity Investment Program for India approved by the ADB Board in December 2017. Tranche 1 loan of $250 million is currently under implementation in the 5 project states, upgrading over 6,000 km of rural roads.
FIRST INDIA-CHINA HIGH LEVEL MEETING ON BILATERAL SECURITY COOPERATION
28, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- Union Home Minister co-chaired the first India-China High Level Meeting on Bilateral Security Cooperation with his Chinese counterpart.
- During the meeting, the two sides discussed issues of mutual interest, including bilateral counter-terrorism cooperation, and welcomed increased cooperation between India and China in the area of security cooperation.
Highlights of the meeting:
- An Agreement on Security Cooperation between the MHA and China was signed.
- The agreement aims to strengthen and consolidate discussions and cooperation in the areas of counter-terrorism, organized crimes, drug control and other such relevant areas.
- India again raised the issue of China repeatedly blocking the proposal to designate Jaish-e-Mohammad (JeM) chief Maulana Masood Azhar as a global terrorist.
Recent meets:
- This meeting comes in the wake of PM Modi’s visit to Chinese city of Wuhan in April, where they decided on a number of steps to bring down tensions and normalize ties following the Doklam standoff.
- The Wuhan meeting was also followed by meetings between the two leaders on the sidelines of the SCO in Qingdao in June and the BRICS leaders’ summit in Johannesburg in July.
JIMEX 2018
28, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- Japan and India would be participating in the third edition of Japan-India Maritime Exercise (JIMEX)
- With the ships of Eastern Fleet of the Indian Navy (IN) from 07 to 15 October 18.
Japan-India Maritime Exercise (JIMEX) 2018:
- JIMEX-18 is aimed to enhance interoperability, improve understanding and imbibe the best practices of each other.
- The ships participating are INS Satpura, multipurpose stealth frigate, INS Kadmatt, Anti-Submarine Warfare Corvette, Missile Corvette and INS Shakti, the Fleet Tanker.
- In addition, one submarine, P8I Long Range Maritime Patrol Aircraft and a number of integral helicopters would also be participating in the exercise.
JIMEX 18:
- JIMEX 18, spread over eight days, will comprise a Harbour Phase and a Sea Phase of four days each.The Harbour Phase will include professional and social interactions between ship’s crews, sports fixtures and operational planning for the Sea Phase.
- The Sea Phase would include Anti-Submarine Warfare Exercises, VBSS (Visit, Board, Search and Seizure) Drills, Gun Firings, Cross Deck Helo Operations and coordinated operations in Anti-Submarine/ Anti-Air threat scenarios.
- The last edition of JIMEX was conducted in Dec 2013 off Chennai.
- Importance of the exercise:
- The conduct of JIMEX-18 after five years is indicative of an upswing in the Indo-Japanese defence relations and the continued efforts to work closely to enhance safety and security of the global commons. It will help establishing rule based order on the IOR.
IBSAMAR-VI MULTI – NATIONAL MARITIME JOINT EXERCISE
27, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- The sixth edition of IBSAMAR, a joint Multi-National Maritime Exercise between the Indian, Brazilian and South African Navies, is being held at Simons Town, South Africa.
- The last edition of IBSAMAR (IBSAMAR V) was conducted on Goa, from 19 – 26 Feb 16. The aim of the exercise is to undertake collective training for participating navies, building interoperability and mutual understanding as well as sharing of best practices.
IBSAMAR 2018:
- This edition exercise included both harbour and sea phases with various navigation and seamanship evolutions, force protection exercises, surface weapons firing, antipiracy exercise, anti-air and antisubmarine exercise and flying operations were also conducted. Apart from professional activities, sports and social engagements were also conducted.
- The Indian Navy is represented by Guided Missile Frigate Tarkash, Guided Missile Destroyer Kolkata, Long Range Maritime Patrol Aircraft P8I, Seaking and Chetak helicopters as well as a MARCOS contingent.
IBSAMAR:
- It is international tripartite grouping for promoting international cooperation among India, Brazil, South Africa.
- It aims at galvanizing South-South cooperation and greater understanding between three important continents of developing world form Africa, Asia and South America.
- The aim of the exercise is to undertake collective training for participating navies, building interoperability and mutual understanding as well as sharing of best practices.
- The forum provides three countries with platform to engage in discussions for cooperation in field of agriculture, trade, culture, and defence among others.
- It also plays important role in foreign policies of India, Brazil and South Africa.
- The first exercise took place in 2008.
WORLD BANK’S HUMAN CAPITAL INDEX
25, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- The World Bank released a Human Capital Index (HCI) as part of the World Development Report 2019.
- Theme of the World Development Report is “The Changing Nature of Work”.
Highlights of the Report:
- The World Bank has launched a Human Capital Project (HCP).
- The HCP programme is claimed to be a program of advocacy, measurement, and analytical work to raise awareness and increase demand for interventions to build human capital.
Components of HCP:
- A cross-country human capital measurement metric called the Human Capital Index (HCI).
- A programme of measurement and research to inform policy action
- A programme of support for country strategies to accelerate investment in human capital.
HCI:
- The HCI has been constructed for 157 countries.
- It claims to seek to measure the amount of human capital that a child born today can expect to attain by age 18.S
- The HCI index values are contended to convey the productivity of the next generation of workers, compared to a benchmark of complete standard education and full health.
The components of HCI:
- Survival, as measured by under-5 mortality rates
- Expected years of Quality-Adjusted School which combines information on the quantity and quality of education
- Health environment using two proxies of (a) adult survival rates and (b) the rate of stunting for children under age 5
HCI for India in the Report:
- Human Capital Index: A child born in India today will be only 44 per cent as productive when she grows up as she could be if she enjoyed complete education and full health.
- The HCI in India for females is marginally better than that for males.Probability of Survival to Age 5: 96 out of 100 children born in India survive to age 5. Expected Years of School: In India, a child who starts school at age 4 can expect to complete 10.2 years of school by her 18th birthday. Adult Survival Rate: Across India, 83 per cent of 15-year olds will survive until age 60. Gender Differences: In India, HCI for girls is marginally higher than for boys.
GOA MARITIME SYMPOSIUM – 2018
24, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- Indian Navy through the Naval War College Goa is hosting the ‘Goa Maritime Symposium – 2018’ on October 16 in order to Foster friendly relations with India’s maritime neighbours.
Goa Maritime Symposium – 2018:
12th ASEM SUMMIT
23, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- The Vice President of India has left for Belgium to attend the two-day 12th Asia-Europe Meeting (ASEM) in Brussels.
- The bi-annual event is considered the highest platform for dialogue and cooperation between Asia and Europe in the areas of trade, investment, security and tourism.
- The theme of the ASEM Summit is ‘Global Partners for Global Challenges’.
Asia-Europe Meeting (ASEM):
- The Asia-Europe Meeting (ASEM) is an intergovernmental process established in 1996 to foster dialogue and cooperation between Asia and Europe.
- The initial ASEM partnership in 1996 consisted of 15 EU member states and 7 ASEAN member states plus China, Japan, Korea and the European Commission. Presently it comprises 53 partners: 30 European and 21 Asian countries, the European Union and the ASEAN Secretariat. ASEM addresses political, economic, social, cultural, and educational issues of common interest, in a spirit of mutual respect and equal partnership.
- The main components of the ASEM process rest on the following 3 pillars:
- Political & Security Pillar
- Economic & Financial Pillar
- Social, Cultural & Educational Pillar
EXERCISE DHARMA GUARDIAN- 2018
22, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- To promote Military cooperation, India and Japan are all set to hold the first ever joint military exercise ‘DHARMA GUARDIAN-2018’ involving the Indian Army and Japan Ground Self Defence Force.
Exercise Dharma Guardian- 2018:
- The Indian contingent will be represented by 6/1 GORKHA RIFLES while the Japanese contingent will be represented by 32 Infantry Regiment of the Japanese Ground Self Defence Force. During the 14-day long exercise, due emphasis will be laid on increasing interoperability between forces from both countries. Both sides will jointly train, plan and execute a series of well-developed tactical drills for neutralisation of likely threats that may be encountered in urban warfare scenario. Experts from both sides will also hold detailed discussions to share their expertise on varied operational aspects.
Significance of the Exercise:
- The exercise will be another step-in deepening strategic ties including closer defence cooperation between the two countries. It will contribute immensely in developing mutual understanding and respect for each other’s militaries and also facilitate tracking the worldwide phenomenon of terrorism.
ASEAN DEFENCE MINISTERS MEET
21, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- Defence Minister has attended the 5thADMM plus meet in Singapore, which is a forum for Defence Ministers from ten ASEAN and eight ASEAN Plus countries.
5th ADMM Plus Meet:
- The theme of this year’s dialogue was ‘Strengthening Cooperation, Building Resilience’.
- The dialogue adopted two resolutions on ‘Countering the Threat of Terrorism’ and ‘Practical Confidence Building Measures’.
ADMM:
- The ASEAN Security Community (ASC) Plan of Action, adopted at the 10th ASEAN Summit, stipulates that ASEAN shall work towards the convening of an annual ADMM.
- Against this background, the Inaugural meeting of the ADMM was held in Kuala Lumpur on 9 May 2006.
- ADMM is the highest defence consultative and cooperative mechanism in ASEAN.
- The ADMM aims to promote mutual trust and confidence through greater understanding of defence and security challenges as well as enhancement of transparency and openness.
- All ASEAN Member States, namely Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Viet Nam are members of the ADMM.
ADMM Plus:
- The ADMM-Plus is a platform for ASEAN and its eight Dialogue Partners to strengthen security and defence cooperation for peace, stability, and development in the region.
- The main objective of ADMM Plus is to benefit ASEAN member countries in building capacity to address shared security challenges.
- The ADMM-Plus countries include ten ASEAN Member States and eight Plus countries, namely Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russian Federation, and the United States.
- The principles for membership to the ADMM-Plus process a country shall be
- A full-fledged Dialogue Partner of ASEAN;
- Have significant interactions and relations with ASEAN defence establishment;
- Able to work with the ADMM to build capacity so as to enhance regional security in a substantive way in order to promote capacity-building in the region in the fields of defence and security.
MOU BETWEEN INDIA AND RUSSIA
20, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- The Union Cabinet approved the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India and Russia on bilateral cooperation in various developmental projects. The MoU will be signed during the upcoming visit of Russian President to India.
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises:
- The Union Cabinet approved signing of a MoU between National Small Industries Corporation Ltd (NSIC) – a Public Sector Undertaking of the Union Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSME) and JSC-Russian Small & Medium Business Corporation (RSMB Corporation), Russia.
- It would provide a structured framework and enabling environment to the MSME sector of the two countries to understand each other’s strengths, markets, technologies, policies etc.
- It aims to enhance enterprise to enterprise cooperation and help initiate sustainable business alliances in terms of technology transfers, joint ventures and business partnerships in MSME sector.
- This cooperation is expected to open doors of new opportunities for Indian MSME sector by way of new markets, joint ventures, sharing of best practices and technology collaborations etc.
- NSIC, under the Ministry of MSME has a considerable experience in carrying out such cooperation and is, therefore, appropriate organisation to implement the activities of this MoU.
Cooperation in road transport:
- Both the countries will benefit by mutual cooperation in the field of Road Transport and Road Industry.
- Increased co-operation, exchange and collaboration with Russia will contribute to establish a long-term and effective bilateral relationship of communication and cooperation in road transportation and road industry and Intelligent Transport System (ITS)
- This will also help in planning and administration of road infrastructure and road network management, transport policy, technologies and standards for the construction and operation of highways in the country.
- It will further go a long way in strengthening ties and bilateral relations between India and Russia.
FIRST ASSEMBLY OF INTERNATIONAL SOLAR ALLIANCE
19, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- The PM today inaugurated the first Assembly of the International Solar Alliance and also marked the inauguration of the second IORA Renewable Energy Ministerial Meeting, and the 2nd Global RE-Invest (Renewable Energy Investors’ Meet and Expo).
Highlights of the ISA Assembly:
- The target is to generate 40 percent of India’s total energy requirements in 2030, by non-fossil fuel-based sources.
- PM Modi emphasized that if the dream of “One World, One Sun and One Grid” is followed, uninterrupted power supply can be ensured.
- He announced plans to launch a National Energy Storage Mission that will look at manufacturing, deployment, technology development and policy framework.
- The first Assembly will lay the foundation for global Solar Agenda.
- The Assembly will adjudicate upon various administrative, financial and programme related issues.
IORA Meet:
- The Indian Ocean Rim Association was set up with the objective of strengthening regional cooperation and sustainable development within the Indian Ocean Region with 21 Member States and 7 Dialogue Partners. India is hosting 2nd IORA Renewable Energy Ministerial meet. In this meeting, Ministers from 9-member countries and delegates from all 21-member countries are expected to participate.
India, Australia, Iran, Indonesia Thailand, Malaysia, South Africa, Mozambique, Kenya, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, Bangladesh, Singapore, Mauritius, Madagascar, UAE, Yemen, Seychelles, Somalia, Comoros and Oman are members of IORA.
2ND RE-INVESTMENT:
- RE-Invest is a global platform to explore strategies for development and deployment of renewables.
- It showcases India’s green energy market and the Government’s efforts to scale up capacity to meet the national energy demand in socially, economically and ecologically sustainable ways.
- The 2nd RE-INVEST aims at accelerating the worldwide effort to scale up renewable energy and connect the global investment community with Indian energy stakeholders.
- The 2nd RE-INVEST will provide a great opportunity to various countries, states, business houses & organisations to showcase their business strategies, achievements and expectations.
- It would facilitate collaboration and cooperation with key stakeholders in India, which has today emerged as one of the world’s largest renewable energy markets.
Renewable Energy Status of India:
- Globally, India stands 5th in renewable power, 4th in wind power and 5th in solar power installed capacity.
- Renewable energy development and deployment has received proactive policy support, including 100% foreign investment.
- The Government of India is aiming to exceed the set target of 175 GW renewable energy capacity by 2022.
WHO LAUNCHES FIRST GLOBAL GUIDELINES ON SANITATION AND HEALTH
17, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched first global guidelines on sanitation and health.
- These guidelines summarize evidence on effectiveness of range of sanitation interventions.
- They also articulate role of health sector in maximizing health impact of sanitation interventions.
Salient Features – WHO Guidelines:
- WHO’s Sanitation and Health Guidelines are aimed at securing health and wellbeing for everyone, everywhere by considering sanitation as the fundamental foundation of human health and development.
- These guidelines provide a comprehensive framework for health-protecting sanitation, covering policy and governance measures, implementation of sanitation technologies, systems and behavioural interventions, risk-based management, and monitoring approaches.
- They also identify gaps in evidence-base to guide future research efforts to improve the effectiveness of sanitation interventions.
- By adopting these new guidelines, countries can significantly reduce diarrhoeal deaths due to unsafe water, sanitation and hygiene.
- For every US $1 invested in sanitation, it is estimated nearly six-fold return as measured by lower health costs, increased productivity and fewer premature deaths.
US gives India Strategic trade Authorisation – 1 Status
23, Aug 2018
Why in News?
- United States has designated India as Strategic Trade Authorization-1 (STA-1) country that will allow India to buy highly advanced and cutting-edge sensitive technologies from America.
What is Strategic Trade Authorisation (STA)?
- STA allows for license exception with regards to exports from the US.
- This type of US government authorisation allows a certain item to be exported under defined conditions without a transaction-specific license.
- Currently there are 36 countries on STA-1 list.
- India is only South Asian country to be on the list. Till recently, India was classified as an STA-2 country along with seven others.
- Other Asian countries designated as STA-1 are Japan and South Korea.
Why is the STA-1 important for India?
- STA-1 provides India with greater supply chain efficiency, both for defence, and for other high-tech products.
- The status eases export controls for high technology product sales to India, granting it the same access as NATO allies — Australia, Japan and South Korea.
- Under STA-1, India and US have reached understanding under which India will receive license-free access to a wide range of dual-use technologies in conjunction with the steps that India has committed to take to advance its export control objectives.
- STA-1 treatment will expand the scope of technology exports subject to Export Administration Regulations (EAR) that can be made to India without individual licenses.
- It will further enhance the bilateral defence trade relationship and result in a greater volume of US exports to India.
- India’s inclusion is beneficial mostly for the purposes of increasing the speed of sale of high-tech defence and non-defence products that are otherwise subjected to strict controls and licensing.
- Now, India can get easy access to latest defence technologies, with the reduction of the number of licenses needed for exports from the US.
- According to analysts, it is also a boost for the foundational Communications, Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA).
What are the benefits that are seen for India & US?
- This new designation reflects India’s membership in three of four multilateral export control regimes, as well as the development of its national export control system.
- It will allow US companies to more efficiently export much wider range of products to Indian high technology and military customers.
- It will benefit US manufacturers while continuing to protect its national security.
- It will provide India greater supply chain efficiency, both for defence and for other high-tech products that will increase activity with US systems, interoperability of systems and will reduce time and resources needed to get licensing approved.
- It will improve India’s partnership with the United States to improve its own export control regimes and has met most of the export control rules which the US thinks is useful.
- It will also be a competitive advantage for US, in terms of supplying those kinds of products to India.
Way Forward:
- India and the United States share an interest in countering China’s expanding economic and military weight and the United States has emerged as a top arms supplier to India, selling more than $15 billion of weapons over the past decade as New Delhi modernizes its Soviet-era military.
- Looking at current exports from the US to India, 50% of those are eligible now under STA-1. This can free up $2.1 billion in trade, make US exporters more competitive in the global marketplace, help provide India more advanced US technology.
- The move is a sign of trust not only in the relationship but also on India’s capabilities as an economic and a security partner.
- This is because it also presupposes that India has the multilateral export control regime in place, which would allow the transfer of more sensitive defense technologies and dual use technologies to India and without the risk of any proliferation.
- Currently, 36 countries, mostly all NATO nations, have this status, so it’s a very elevated status from an export control point of view.
Exercise SCO Peace Mission 2018
21, Aug 2018
Why in News?
- As part of Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) initiatives, SCO Peace Mission Exercise is conducted biennially for SCO member states.
- This will be a historic occasion due to the maiden participation of India post becoming a full member of the SCO in June 2017.
Significance of this exercise:
- This exercise marks a major milestone in the multilateral relations of SCO member nations.
- It will involve tactical level operations in an international counter insurgency or counter terrorism environment under SCO Charter.
- The joint exercise will strengthen mutual confidence, interoperability and enable sharing of best practices among armed forces of SCO Nations.
- It will be a landmark event in the history of SCO defence cooperation where Indian and Pakistani armed forces will participate together.
Portal G20 Digital Economy Ministerial meeting
19, Aug 2018
Why in News?
- The G20 Digital Economy Ministerial Meeting was held in Salta, Argentina from 23 to 24 August, 2018. It took place as part of Sherpa Track for 2018 G20 Leaders’ Summit, which is to be hosted by Argentina by end of 2018.
- The theme of the meeting was ‘Building consensus for fair and sustainable development ‘.
- The ministerial meeting was preceded by the second meeting of the G20 Digital Economy Task Force and has identified three key issues for the agenda: the future of work, infrastructure for development, and a sustainable food future.
Digital Economy Task Force:
- The Digital Economy Task Force (DETF) was established under the 2017 German presidency, based on the decision adopted in Hangzhou in 2016 under the Chinese Presidency.
- In Antalya, under the Turkish presidency in 2015, G20 leaders recognized the modern period as a critical era of digital transformation, influenced by the advent of new technologies as key elements for economic development.
What is Digital economy?
- The digital economy refers to a broad range of activities which include: the use of knowledge and information as factors in production, information networks as a platform for action, and how the information and communication technology (ICT) sector spurs economic growth.
Challenges to digital economy:
- Important challenges include providing high-speed internet for all by 2025, creating inclusive growth and new jobs through digital trade, promoting lifelong digital learning, and closing the gender gap.
Significance:
- In 2008, amidst the global financial crisis, the world saw a need for new consensus-building at the highest political level. Since then, the G20 summits have been attended by heads of state or government, and the G20 was instrumental in stabilizing the world economy. Since then, its agenda has expanded to include additional issues affecting financial markets, trade, and development.
The work of the G20 is generally divided into two tracks:
- The Finance track comprises all meetings with G20 finance ministers and central bank governors and their deputies. Convening several times throughout the year, they focus on financial and economic issues, such as monetary, fiscal and exchange rate policies, infrastructure investment, financial regulation, financial inclusion and international taxation.
- The Sherpa track focuses on broader issues such as political engagement, anti-corruption, development, trade, energy and climate change, gender equality, among others. Each G20 country is represented at these meetings by its relevant minister, and by its designated sherpa, or emissary. The sherpa engages in planning, negotiation and implementation tasks on behalf of the leader of their respective country. Each sherpa orients their minister and head of state or government accordingly on the progress of the G20, and delegates the dialogue and topics to relevant working groups.
Indian naval ship exercise KAKADU 2018
15, Aug 2018
Why in News?
- Indian Naval Ship Sahyadri has reached Port of Darwin, Australia to participate in multilateral regional maritime exercise KAKADU 2018 conducted by Australia.
- The ship was earlier deployed in South China Sea and Pacific Ocean for over four months and had represented Indian Navy in multinational exercises MALABAR 18 at Guam and RIMPAC 18 at Hawaii.
Exercise KAKADU:
- It is premier multilateral regional maritime engagement hosted by Royal Australian Navy (RAN) and supported by Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF).
- It was started in 1993. It is held biennially in Darwin and Northern Australian Exercise Areas (NAXA).
- Exercise KAKADU derives its name from Kakadu National Park, which is protected area in the northern territory of Australia and located 171 km south-east of Darwin.
- During the exercise, professional exchanges in harbour and diverse range of activities at sea, including complex surface, sub-surface and air operations would enable sharing of best practices and honing of operational skills.
KAKADU 2018:
- Indian Navy’s participation in KAKADU 18 provides an excellent opportunity to engage with regional partners and undertake multinational maritime activities ranging from constabulary operations to high-end maritime warfare in a combined environment
- It is aimed at enhancing interoperability and development of common understanding of procedures for maritime operations.
- KAKADU 2018 is fourteenth edition of exercise scheduled to be held between August 29 and September 18, 2018.
- It will see participation of 23 warships, one submarine, 45 aircraft, 250 marines and approximately 52 foreign staff from over 25 different countries including India and china
Who lauds India’s commitment to accelerated sanitation coverage
10, Aug 2018
Why in News?
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has released a progress report on potential health impact from increased sanitation coverage through the Swachh Bharat Mission- Gramin (SBM-G).
Hightlights:
- India’s rural sanitation coverage has escalated to 89.07 percent by August 2, 2018.
- Under the Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin), 19 States and Union Territories were declared Open Defecation Free (ODF) and 7.9 crore toilets were built, while 421 districts were declared ODF. More than 4.9 lakh villages in the country were also declared Open Defecation Free.
- As per the study, unsafe sanitation, before the initiation of SMB-G, had caused 199 million cases of diarrhea every year and that of today, the initiative aims to achieve 100 percent sanitation coverage.
- The report further estimated further, that 14 million Disability Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) can be avoided between 2014 and 2019. WHO estimation of health impacts is based on comparative risk assessment (CAR) methods.
Swachh Bharat Mission Gramin:
- Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) was launched on 2nd October 2014, accelerating the efforts to achieve universal sanitation coverage and to put the focus on sanitation.
- Swachh Bharat Mission comprises of two Sub-Missions – the Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin) and the Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban).
- Mission’s aim is to achieve a ‘Swachh Bharat’ by 2019, as a fitting tribute to Mahatma Gandhi on his 150th birth anniversary.
Significance of the mission:
- As the initial results of a WHO modeling study on the health impact of the Swachh Bharat Mission Gramin (SBM-G) outline, India’s accelerated coverage of safe sanitation services, and its determination to end open defecation, will have a substantial effect on the burden of diarrheal diseases and PEM by reducing mortality and accumulative Disability Adjusted Life Years (the sum of the years of life lost due to premature mortality and years lost due to disability or ill-health).
Health Impact:
- The broader health impact of India’s commitment to accelerated sanitation coverage is significant.
- It includes improved overall nutritional status and reduced incidence of infectious diseases such as neglected tropical diseases and acute respiratory infections, as well as vector-borne diseases.
- Moreover, the estimations apply to the health impacts from improvements in sanitation coverage only, meaning it is possible that the broader Mission has produced additional health gains through changes in personal hygiene and the consumption of safe drinking water.
Sanitation coverage India’s Commitment:
- India’s commitment and progress towards these outcomes are reflected in the fact that household sanitation coverage has dramatically increased from an estimated 2% per year before the initiative to more than 13% annually between 2016 and 2018.
- The recent allocation of up to INR 15,000 crore as Extra Budgetary Resources for the SBM-G during the present financial year holds-out the potential for further gains, not only for India, but also the WHO’s South-East Asia Region and the world (globally, diarrheal disease is the second leading cause of under-five mortality, while lack of clean water and sanitation is also a major contributor to malnutrition).
Making of the Report:
- WHO has worked closely with the Government of India (GoI) to scale up access to sanitation services, by providing technical assistance through India’s participation in the ‘Global Analysis and Assessment of Sanitation and Drinking-Water Survey 2017’, as well as working with partners to support the GoI implementation of WHO’s guidelines for safe water and sanitation planning.
- WHO has also supported the piloting of TrackFin (Tracking financing to sanitation, hygiene, and drinking-water) in Rajasthan and West Bengal to utilize resources more efficiently for reaching those under threat of being left behind.
Way forward for India:
- According to the calculations, if all the sanitation services are used and schemes are effectively implemented, the initiative could result in over 14 million more years of healthy life in the period measured, with the benefits accruing yearly thereafter.
- This is especially remarkable, given that before 2014 unsafe sanitation caused an estimated 199 million cases of diarrhoea annually,
- With the modelling that shows the problem will almost be eliminated when the universal use of safe sanitation facilities is achieved.
Conclusion:
- Inadequate sanitation has dire consequences for public health, education, poverty, and growth. A disease like stunting amongst children, the death of an infant, diarrhoea can be prevented through good sanitation. Better sanitation helps to break the fecal-oral transmission route that impacts public health and is beneficial for the household and the community. Cross-country studies show that sanitation is the strongest determinant of child survival and improvement in sanitation is accompanied by a reduction in child mortality.
- Swachh Bharat Mission is emerging as the biggest, most successful behaviour-change campaign of the world. The mission has given multiple benefits, just not for the society but for the whole economy and if it is further implemented effectively, it is sure to uplift India’s image in the world.






