Category: Science & Technology
LockBit Ransomware
26, Apr 2023

Why in News?
- Recently, it has been found that LockBit ransomware was found to be targeting Mac devices.
About the News:
- Earlier in January 2023, the LockBit gang was reportedly behind a cyber-attack on U.K. postal services, causing international shipping to grind to a halt.
- A ransomware is a type of malware that hijacks computer data and then demands payment (usually in bitcoins) in order to restore it.
What is LockBit Ransomware?
- LockBit, formerly known as “ABCD” ransomware, is a type of computer virus that enters someone’s computer and encrypts important files so they can’t be accessed.
- The virus first appeared in September 2019 and is called a “crypto virus”, because it asks for payment in cryptocurrency to unlock the files.
- LockBit is usually used to attack companies or organizations that can afford to pay a lot of money to get their files back.
- The people behind LockBit have a website on the dark web where they recruit members and release information about victims who refuse to pay.
- LockBit has been used to target companies in many different countries, including the U.S., China, India, Ukraine, and Europe.
Modus Operandi:
- It hides its harmful files by making them look like harmless image files. The people behind LockBit trick people into giving them access to the company’s network by pretending to be someone trustworthy.
- Once they’re in, LockBit disables anything that could help the company recover their files and puts a lock on all the files so that they can’t be opened without a special key that only the LockBit gang has.
- Victims are then left with no choice but to contact the LockBit gang and pay up for the data, which the gang may sell on the dark web – whether the ransom is paid or not.
LockBit Gang:
- The LockBit gang is a group of cybercriminals who use a ransomware-as-a-service model to make money.
- They create custom attacks for people who pay them and then split the ransom payment with their team and affiliates.
- They are known for being very prolific and avoiding attacking Russian systems or countries in the Commonwealth of Independent States to avoid getting caught.
Why is LockBit targeting macOS?
- LockBit is targeting macOS as a way to expand the scope of their attacks and potentially increase their financial gains.
- While historically ransomware has mainly targeted Windows, Linux, and VMware ESXi servers, the gang is now testing encryptors for macOS.
- The current encryptors were not found to be fully operational, but it is believed that the group is actively developing tools to target macOS.
- The ultimate goal is likely to make more money from their ransomware operation by targeting a wider range of systems.
How to Protect against LockBit Ransomware?
Strong Passwords:
- Account breaches often happen because of weak passwords that are easy for hackers to guess or for algorithm tools to crack. To protect oneself, choose strong passwords that are longer and have different types of characters.
Multi-Factor Authentication:
- To prevent brute force attacks, use additional security measures like biometrics (such as fingerprint or facial recognition) or physical USB key authenticators along with your passwords when accessing your systems.
- Brute force attacks are a type of cyber-attack where attackers try to guess a password by repeatedly trying different combinations of characters until they find the right one.
Reassess Account Permissions:
- Limiting user permissions to stricter levels is important to reduce security risks. This is especially critical for IT accounts with administrative access and for resources accessed by endpoint users.
- Ensure that web domains, collaborative platforms, web meeting services, and enterprise databases are all secured.
System-wide Backups:
- To protect against permanent data loss, it’s important to create offline backups of your important data.
- Make sure to periodically create backups to ensure that you have an up-to-date copy of your systems. Consider having multiple backup points and rotating them, so you can select a clean backup in case one becomes infected with malware.
Recent Steps Taken in India against Cyber Crime:
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative: It was launched in 2018 with an aim to spread awareness about cybercrime and building capacity for safety measures for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT staff across all government departments.
- National Cyber security Coordination Centre (NCCC): In 2017, the NCCC was developed to scan internet traffic and communication metadata (which are little snippets of information hidden inside each communication) coming into the country to detect real-time cyber threats.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: In 2017, this platform was introduced for internet users to clean their computers and devices by wiping out viruses and malware.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C): I4C was recently inaugurated by the government.
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal has also been launched pan India.
- Computer Emergency Response Team – India (CERT-IN): It is the nodal agency which deals with cybersecurity threats like hacking and phishing.
- Legislations in India:
- Information Technology Act, 2000.
- Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019.
International Mechanisms:
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU): It is a specialized agency within the United Nations which plays a leading role in the standardization and development of telecommunications and cyber security issues.
- Budapest Convention on Cybercrime: It is an international treaty that seeks to address Internet and computer crime (cybercrime) by harmonizing national laws, improving investigative techniques, and increasing cooperation among nations. It came into force on 1st July 2004. India is not a signatory to this convention.
Types of Cyber Attacks:
Malware:
- It is short for malicious software and refers to any kind of software that is designed to cause damage to a single computer, server, or computer network. Ransomware, Spy ware, Worms, viruses, and Trojans are all varieties of malware.
Phishing:
- It is the method of trying to gather personal information using deceptive e-mails and websites.
Denial of Service attacks:
- A Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack is an attack meant to shut down a machine or network, making it inaccessible to its intended users.
- DoS attacks accomplish this by flooding the target with traffic, or sending it information that triggers a crash.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks:
- Also known as eavesdropping attacks, occur when attackers insert themselves into a two-party transaction.
- Once the attackers interrupt the traffic, they can filter and steal data.
SQL Injection:
- SQL stands for Structured Query Language, a programming language used to communicate with databases.
- Many of the servers that store critical data for websites and services use SQL to manage the data in their databases.
- A SQL injection attack specifically targets such kinds of servers, using malicious code to get the server to divulge information it normally wouldn’t.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS):
- Similar to an SQL injection attack, this attack also involves injecting malicious code into a website, but in this case the website itself is not being attacked.
- Instead the malicious code the attacker has injected, only runs in the user’s browser when they visit the attacked website, and it goes after the visitor directly, not the website.
Social Engineering:
- It is an attack that relies on human interaction to trick users into breaking security procedures in order to gain sensitive information that is typically protected.
Malaria will soon be a notifiable disease across India
25, Apr 2023

Why in News?
- Malaria is all set to become a notifiable disease across India, with Bihar, Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Meghalaya too in the process of putting this vector-borne disease in the category.
About the News:
- This will then require by law that cases be reported to government authorities.
- Currently malaria is a notifiable disease in 33 States and Union Territories in India.
- Confirming the development, a senior Health Ministry official said this is part of India’s vision to be malaria-free by 2027 and to eliminate the disease by 2030.
- The Health Ministry has also initiated a joint action plan with the Ministry of Tribal Affairs for malaria elimination in tribal areas.
What happens when a disease is put under “Notified” Category?
- The doctors have to report about the occurrence of disease in their patients to the Chief Medical Officer of the district.
- It will help authorities to collect information of the spread of the disease, monitor the disease and set off early warnings.
What is a notified disease?
- Notified diseases are also called Notifiable diseases. It is any disease whose occurrence has to be reported to the Government by law.
WHO on Notifiable Diseases:
- The WHO International Health Regulations, 1969 has made disease reporting mandatory. This will help WHO in its global surveillance and advisory role. Currently the list is limited only to three main disease namely yellow fever, cholera and plague. And of course COVID-19.
OIE on Notified diseases:
- The OIE, World Organisation for Animal Health monitors diseases of animals at global level. It holds a list of notifiable diseases.
Can Central Government declare notified disease?
- As Health is a State subject, only the State Governments have powers to declare notified diseases. However, the Central Government maintains a list of Notified diseases.
List of Notified Diseases in India:
- AIDS, Hepatitis B, Dengue Fever, Malaria, Whooping cough, Anaemia, Measles, Rabies, Vitamin A deficiency, typhoid, scarlet fever, polio, cerebro spinal fever, leprosy, hepatitis, Cholera, Iodine deficiency, malnutrition, tuberculosis, small pox, plague, measles, influenza, diphtheria, chicken pox.
About Malaria:
- Malaria has been one of the world’s deadliest diseases. It kills more than 400,000 people a year worldwide and causes illness in millions of others.
- Africa is home to 70% of the world’s malaria cases and 90% of deaths.
- In the past two decades, existing interventions have reduced the malaria burden. And India, too, has made good progress in malaria control. The disease burden has declined by 59 per cent.
- The success has led to the government in making a commitment to eliminate malaria by 2030.
- Malaria is caused by Plasmodium; the parasites are spread to people through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes, called “malaria vectors.”
- There are 5 parasite species that cause malaria in humans, and 2 of these species – falciparum and P. vivax – pose the greatest threat.
- In 2018, falciparum accounted for 99.7% of estimated malaria cases in the WHO African Region 50% of cases in the WHO South-East Asia Region, 71% of cases in the Eastern Mediterranean and 65% in the Western Pacific.
- Vivax is the predominant parasite in the WHO Region of the Americas, representing 75% of malaria cases.
What are the Symptoms?
- Malaria is an acute febrile illness. In a non-immune individual, symptoms usually appear 10–15 days after the infective mosquito bite. The first symptoms – fever, headache, and chills – may be mild and difficult to recognize as malaria. If not treated within 24 hours, falciparum malaria can progress to severe illness, often leading to death.
- Children with severe malaria frequently develop one or more of the following symptoms: severe anaemia, respiratory distress in relation to metabolic acidosis, or cerebral malaria. In adults, multi-organ failure is also frequent. In malaria endemic areas, people may develop partial immunity, allowing asymptomatic infections to occur.
What are its Prevention?
- Vector control is the main way to prevent and reduce malaria transmission. If coverage of vector control interventions within a specific area is high enough, then a measure of protection will be conferred across the community.
- WHO recommends protection for all people at risk of malaria with effective malaria vector control. Two forms of vector control – insecticide-treated mosquito nets and indoor residual spraying – are effective in a wide range of circumstances.
What are the India’s efforts to fight Malaria?
- Indian government has released a National Strategic Plan (NSP) for malaria elimination for years 2017-2022, targeting eradication by 2030.
- This marked a shift in focus from malaria “control” to “elimination”. The plan provides a roadmap to achieve the target of ending malaria in 571 districts out of India’s 678 districts by 2022.
- India has sustained significant decline in malaria cases, halving numbers to 5.1 million in 2018 from 9.6 million the year before. This followed a 24% decline in 2017, according to the World Malaria Report 2018.
- Since 2000, India has reduced malaria deaths by two-thirds and halved the number of malaria cases.Scaling up a diagnostic testing, treatment and surveillance
- Ensuring an uninterrupted drug and diagnostics supply chain. Training community workers to test all fever cases and provide medicines, and distributing medicated bed-nets for prevention, under its ‘test-treat-track’ in the endemic north-eastern states and Odisha.
Indian DefSpace Symposium
13, Apr 2023

Why in News?
- Indian Space Association (ISpA) has organised the “Indian DefSpace Symposium 2023” in association with Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
Highlights:
- Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) General Anil Chauhan during the Indian DefSpace Symposium 2023 said that the nature of warfare is changing and we are witnessing the militarisation of space and steady progress towards weaponisation.
- He further added that “the aim should be towards developing dual-use platforms with a special focus towards incorporating cutting-edge technology and expanding NAVIC constellation to provide agile space-based Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR) and ensure secure satellite-assisted communications”.
Indian DefSpace Symposium:
- Indian DefSpace Symposium is organised by the Indian Space Association (ISpA) in association with the DRDO.
- The Symposium aims to create a platform for all stakeholders who have a keen interest in boosting India’s military space capability and plans.
- The Symposium would provide a platform to bring together experts from multiple domains from the defence, DRDO, government sectors and industry professionals to discuss the latest trends and challenges in the field of defence.
- The key focus of the Symposium would be on delivering space domain awareness and satellite communications to enhance military operations, address related issues and develop a Defence Space Strategy in line with the National Space Strategy.
- Indian DefSpace Symposium 2023 is organised as a part of deliberations under “Mission Def-Space”, under which 75 challenges have been identified for development by the industry.
Indian Space Association (ISpA):
- The Indian Space Association (ISpA) was set up in 2021.
- The Indian Space Association (ISpA) is an apex, non-profit industry body working towards the successful exploration, collaboration, and development of the private and public space industry in the country.
- ISpA undertakes policy advocacy, engages and operates with all stakeholders and acts as a catalyst for accelerating the exchange of knowledge on space-related domains.
Genome India Project
12, Apr 2023

Why in News?
- The Genome India Project, a Centre-backed initiative to sequence 10,000 Indian human genomes and create a database, is about two-thirds completed and will be 100% complete by year-end.
About the News:
- Of the 7,000 genomes sequenced about 3,000 are already available for public access (as per the Department of Biotechnology).
About Human Genome Project:
- The Human Genome Project (1990 to 20003) was an international scientific research project with the goal of determining the base pairs that make up human DNA, and of identifying, mapping and sequencing all of the genes of the human genome from both a physical and a functional standpoint.
What is Whole Genome Sequencing?
- All organisms have a unique genetic code, or genome, that is composed of nucleotide bases- Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C) and Guanine (G).
- The unique Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) fingerprint, or pattern can be identified by knowing the sequence of the bases in an organism.
- Determining the order of bases is called sequencing.
- Whole genome sequencing is a laboratory procedure that determines the order of bases in the genome of an organism in one process.
Methodology:
- DNA Shearing:
- Scientists begin by using molecular scissors to cut the DNA, which is composed of millions of bases (A’s, C’s, T’s and G’s), into pieces that are small enough for the sequencing machine to read.
- DNA Bar Coding:
- Scientists add small pieces of DNA tags, or bar codes, to identify which piece of sheared DNA belongs to which bacteria.
- This is similar to how a bar code identifies a product at a grocery store.
- DNA Sequencing:
- The bar-coded DNA from multiple bacteria is combined and put in a DNA sequencer.
- The sequencer identifies the A’s, C’s, T’s, and G’s, or bases, that make up each bacterial sequence.
- The sequencer uses the bar code to keep track of which bases belong to which bacteria.
- Data Analysis:
- Scientists use computer analysis tools to compare sequences from multiple bacteria and identify differences.The number of differences can tell the scientists how closely related the bacteria are, and how likely it is that they are part of the same outbreak.
Advantages of Genome Sequencing:
- Provides a high-resolution, base-by-base view of the genome
- Captures both large and small variants that might be missed with targeted approaches
- Identifies potential causative variants for further follow-up studies of gene expression and regulation mechanisms
- Delivers large volumes of data in a short amount of time to support assembly of novel genomes
Significance of Genome Sequencing:
- Genomic information has been instrumental in identifying inherited disorders, characterizing the mutations that drive cancer progression, and tracking disease outbreaks.
- It is beneficial for sequencing agriculturally important livestock, plants, or disease-related microbes.
What is Genome?
- A genome refers to all of the genetic material in an organism, and the human genome is mostly the same in all people, but a very small part of the DNA does vary between one individual and another.
- Every organism’s genetic code is contained in its DNA, the building blocks of life.
- The discovery that DNA is structured as a “double helix” by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, started the quest for understanding how genes dictate life, its traits, and what causes diseases.
- Each genome contains all of the information needed to build and maintain that organism.
- In humans, a copy of the entire genome contains more than 3 billion DNA base pairs.
What is the Difference between Genome and Gene?
YouTube alerts users on phishing attempts through emails
06, Apr 2023

Why in News?
- Video sharing platform YouTube has alerted users that hackers were sending them phishing emails with suspicious links that appear to come from an official YouTube email address.
About the News:
- YouTube retweeted screenshots of the phishing emails and warned users that they were coming from the address ‘no-reply@youtube.com.’
- As the address used the YouTube domain name and the video in the screenshot was linked to an account named ‘YouTube Team,’ the chance of user confusion was high.
- The email told users that YouTube’s policies were changing and shared a video that urged recipients to read a longer description by clicking on the link.
Recent Steps Taken in India against Cyber Crime:
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative: It was launched in 2018 with an aim to spread awareness about cybercrime and building capacity for safety measures for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT staff across all government departments.
- National Cyber security Coordination Centre (NCCC): In 2017, the NCCC was developed to scan internet traffic and communication metadata (which are little snippets of information hidden inside each communication) coming into the country to detect real-time cyber threats.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: In 2017, this platform was introduced for internet users to clean their computers and devices by wiping out viruses and malware.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C): I4C was recently inaugurated by the government.
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal has also been launched pan India.
- Computer Emergency Response Team – India (CERT-IN): It is the nodal agency which deals with cybersecurity threats like hacking and phishing.
- Legislations in India:
- Information Technology Act, 2000.
- Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019.
International Mechanisms:
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU): It is a specialized agency within the United Nations which plays a leading role in the standardization and development of telecommunications and cyber security issues.
- Budapest Convention on Cybercrime: It is an international treaty that seeks to address Internet and computer crime (cybercrime) by harmonizing national laws, improving investigative techniques, and increasing cooperation among nations. It came into force on 1st July 2004. India is not a signatory to this convention.
Types of Cyber Attacks:
Malware:
- It is short for malicious software and refers to any kind of software that is designed to cause damage to a single computer, server, or computer network. Ransomware, Spy ware, Worms, viruses, and Trojans are all varieties of malware.
Phishing:
- It is the method of trying to gather personal information using deceptive e-mails and websites.
Denial of Service attacks:
- A Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack is an attack meant to shut down a machine or network, making it inaccessible to its intended users.
- DoS attacks accomplish this by flooding the target with traffic, or sending it information that triggers a crash.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks:
- Also known as eavesdropping attacks, occur when attackers insert themselves into a two-party transaction.
- Once the attackers interrupt the traffic, they can filter and steal data.
SQL Injection:
- SQL stands for Structured Query Language, a programming language used to communicate with databases.
- Many of the servers that store critical data for websites and services use SQL to manage the data in their databases.
- A SQL injection attack specifically targets such kinds of servers, using malicious code to get the server to divulge information it normally wouldn’t.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS):
- Similar to an SQL injection attack, this attack also involves injecting malicious code into a website, but in this case the website itself is not being attacked.
- Instead the malicious code the attacker has injected, only runs in the user’s browser when they visit the attacked website, and it goes after the visitor directly, not the website.
Social Engineering:
- It is an attack that relies on human interaction to trick users into breaking security procedures in order to gain sensitive information that is typically protected.
The piezoelectric effect in liquids
01, Apr 2023
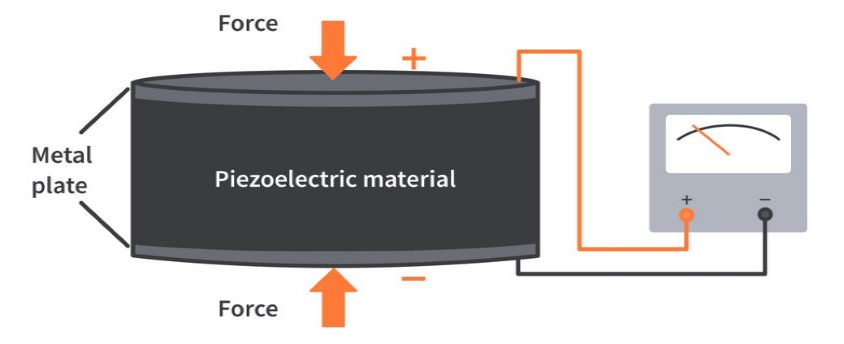
Why in News?
- Researchers have reported evidence of the piezoelectric effect in liquids for the first time.
Piezoelectric effect
- The piezoelectric effect refers to an instance when a body develops an electric current when it is subjected to mechanical stress.
- When piezoelectric material is placed under mechanical stress, a shifting of the positive and negative charge centres in the material takes place, which then results in an external electrical field.
- Example: Quartz is one of the most famous piezoelectric crystal substances or materials.
- Quartz is a material that is extensively used in analogue wristwatches and clocks.
- Quartz is silicon dioxide (SiO2) i.e. it consists of silicon and oxygen atoms at the four vertices of three-sided pyramids which repeat themselves to form the crystal.
- The effective charge of each pyramid is located slightly away from the centre and when mechanical stress is applied the position of the charge is pushed further from the centre, giving rise to a small voltage which is the source of the effect.
Piezoelectric effect in liquid:
- The piezoelectric effect was so far expected only in solids as the body/object which is being squeezed must have an organised structure such as the pyramids of quartz.
- However, liquids don’t have a definite structure and they only take up the shape of the container.
- Physicists have explained the effect using Hooke’s law.
- According to Hooke’s law, the force required to squeeze an object is linearly proportional to the amount of squeezing and the properties of dielectric materials. These are materials that don’t conduct electricity but whose electrons are still mildly affected by an electric field.
- The piezoelectric effect was observed in ionic liquids and the liquids also displayed the inverse piezoelectric effect i.e. they became distorted when an electric charge was applied.
- This observation of the piezoelectric effect in liquid has opened the door for a wide range of applications as solid-state material and room-temperature ionic liquids are more readily recyclable and are associated with fewer environmental risks than most of the currently used piezoelectric substances.
Very Short Range Air Defence (VSHORAD) missile system
16, Mar 2023

Why in News?
- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) conducted flight tests of Very Short Range Air Defence (VSHORAD) missiles at the Integrated Test Range, Chandipur, off the coast of Odisha.
Very Short Range Air Defence (VSHORAD) System:
- The Very Short Range Air Defence (VSHORAD) System is a Man Portable Air Defence System (MANPAD) used for neutralising low altitude aerial threats at short range.
- VSHORAD has been designed and developed indigenously by Research Centre Imarat, Hyderabad in collaboration with DRDO and other Indian industry partners.
- The VSHORAD missile system is equipped with advanced technologies such as Dual-band IIR Seeker, miniaturised Reaction Control System and integrated avionics.
- The VSHORAD missiles are propelled by a dual-thrust solid motor.
- The VSHORAD missiles are expected to replace the existing Igla in service.
- VSHORAD can be deployed in the mountains close to the LAC at a short notice and hence is said to be critical for the defence of major cities or strategically significant locations in the wake of recent developments along the LAC and northern borders.
Scientists devise ‘glowscope’ to bring fluorescent microscopy to schools
14, Mar 2023
Why in News?
- According to the researchers, fluorescence microscopes are very expensive making them unaffordable for students in various resource-poor labs. However, students could use rudimentary characteristics to study the microscopic world.
Fluorescence microscopes:
- A normal optical microscope helps view an object and study how it absorbs, reflects or scatters visible light.
- Whereas a fluorescence microscope views an object by studying its fluoresces i.e. how it re-emits light that it has absorbed.
- Objects are illuminated with light of a specific wavelength and the particles in the object absorb the light and re-emit it at a higher wavelength (i.e. different colours).
- Such particles are called fluorophores and the object is infused with such particles before being placed under the microscope.
- A fluorescent microscope can track such particles or fluorophores when they shine or glow brightly due to fluorescence as they move inside the object thereby revealing various characteristics of the object.
- There are several versions of such fluorescent microscopes such as epifluorescence and confocal laser-scanning microscopes.
- Fluorescence microscopes are very expensive costing up to crores.
Latest developments – Glowscope:
- Researchers from Winona State University have come up with a way of developing a rudimentary fluorescence microscope that could be developed at a cost of ₹2,500 to ₹4,100.
- Researchers have said that such devices can detect green and red fluorophores.
- The set-up of a rudimentary fluorescence microscope consists of two plexiglass surfaces, an LED flashlight, three theatre stage-lighting filters, a clip-on macro lens, and a smartphone.
- The smartphone with the lens is placed on one surface that is suspended at a height and a second sheet is placed below that holds the object.
- The object which is to be observed is then injected with different fluorophores depending on the interest and the stage-lighting filters held between the flashlight and the object and others held between the object and the smartphone ensure that light of the right frequency would reached the object and the fluoresced light of a suitable frequency reached the camera.
H3N2 – Influenza
10, Mar 2023

Why in News?
- Across India, an outbreak of a respiratory illness with symptoms of cold, sore throat and fever accompanied by fatigue has been observed since December 2022 and January 2023.
About the News:
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) confirmed that Influenza Sub-type H3N2 has been causing this illness.
- It further warned that the virus appeared to lead to more hospitalisations than other Influenza subtypes.
What is H3N2 Virus?
- H3N2 virus is a type of influenza virus called the influenza A virus. It is a respiratory viral infection that causes illnesses every year. This subtype of influenza A virus was discovered in 1968 in humans.
- The virus derives from types of protein strains of the influenza A virus – hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA).
- HA has over 18 different subtypes, each numbered H1 to H18 while NA has 11 different subtypes, each numbered N1 to N11. The H3N2 is a combination of the two protein strains of the influenza A virus.
Symptoms of H3N2 Virus:
- The symptoms of the H3N2 virus include cough, runny nose or congested nose, sore throat, headaches, body aches, fever, chills, fatigue, diarrhoea, vomiting and breathlessness.
Treatment for H3N2 Virus:
- Regular over-the-counter medications for fever, cough or headaches can be consumed to relieve the symptoms.
- Annual flu shots for the influenza virus should be administered and taken around this time.
Types of Influenza Virus:
- There are four types of influenza viruses: influenza A, B, C and D
- Influenza A and B are the two types of influenza that cause epidemic seasonal infections nearly every year.
- Influenza C mainly occurs in humans, but has been known to also occur in dogs and pigs.
- Influenza D is found mainly in cattle. It’s not known to infect or cause illness in humans yet.
China takes lead in Mapping the Deep
06, Mar 2023

Why in News?
- Departing from Sanya’s Institute of Deep Sea Science and Engineering (IDSSE), Explorer
2 (a green-white vessel) makes frequent forays in some of the least explored parts of the world’s oceans. - It carries with it one of the most advanced deep-sea submersibles.
- It should be noted that China aims to dominate the emerging and highly competitive field of deep-sea exploration.
- Apart from China, only the U.S., France, and Russia have similar capabilities.
- China, the U.S., Russia, Germany, France, and even India (though to a lesser extent), are competing for exploration contracts to search the vast areas under the jurisdiction of the International Seabed Authority (ISA). China has secured several exploration licences in the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
China’s Deep Sea Exploration Mission:
- In 2020, IDSSE launched a mission that sent a manned submersible, Fendouzhe (or Striver) to a record depth of more than 10,000 metres. Its success was highly appreciated by Chinese President Xi Jinping.
- Striver explored the Mariana Trench in December 2021. It discovered new microbes and a rich food supply system.
- The submersible observed for the first time anemones at a depth of around 8,880 metres and fish feeding on shark remains at 9,900 metres at the Kermadec Trench in the Pacific Ocean.
- The Kermadec project was run in collaboration with New Zealand.
- The mission of IDSSE is jointly run by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (premier scientific institution) and the Hainan provincial government.
- It aims to establish China as a science and technology power. Its mission is to create “a China-led global deep-sea scientific research programme with joint participation by numerous major international deep-sea research teams”.
Significance of Deep Sea Exploration:
- According to researchers at the IDSSE, their main aim is to understand the deep depths of oceans and trenches.
- Deep-sea research also has the potential to unlock untold commercial opportunities in the form of mineral resources like copper, gold, minerals, and rare earth elements.
- Researchers also intend to understand marine biodiversity and their environment.
- Scientific research is pivotal in understanding how resources can be exploited without damaging the ocean environment.
- The potential for biotechnology beginning from new enzymes to addressing anti-microbial resistance is immense.
- Moreover, China’s advanced submersibles are also boosting the China Ocean Mineral Resource R&D Association (COMRA), a government-backed body. It plans to develop the world’s most advanced deep-sea mining capabilities.
Pegasus case
04, Mar 2023

Why in News?
- Congress leader Rahul Gandhi launched a scathing attack at the Centre during a lecture at Cambridge University, alleging that an attack has been unleashed on the basic structure of Indian democracy while also claiming that Israeli spyware Pegasus was being used to snoop into his phone.
Historical Background of the News:
- The Apex Court stressed that the power of the state to snoop in the name of national security into the “sacred private space” of individuals is not absolute.
- The court said it consciously avoided “political thickets” but could not cower when allegations involved a “grave” threat to the privacy and free speech of the entire citizenry and raised the possibility of involvement of the Government, or even a foreign power, behind the surveillance.
- The court said the petitions filed before it, including ones by veteran journalists N. Ram and Sashi Kumar, Editors Guild of India and victims of alleged snooping, had raised “Orwellian concerns” about an all-pervasive technology like Pegasus.
- The court said India could not remain mute in the face of Pegasus allegations when other countries across the globe had taken them seriously.
- A Bench led by Chief Justice of India N.V. Ramana had, in a 46-page order on October 27, set up an expert technical committee monitored by a retired judge of the Supreme Court, Justice R.V. Raveendran, to inquire into the allegations of spying and file a report.
- The order came after the Union government did not file a “detailed affidavit” in the court in response to the petitions, citing national security reasons, among others.
- The Justice Raveendran committee recently invited persons who suspect themselves of being snooped on to come forward and hand over their electronic equipment for technical examination to detect the presence of the spyware.
What is Pegasus?
- It is a type of malicious software or malware classified as a spyware designed to gain access to devices, without the knowledge of users, and gather personal information and relay it back to whoever it is that is using the software to spy.
- Pegasus has been developed by the Israeli firm NSO Group that was set up in 2010.
- The earliest version of Pegasus discovered, which was captured by researchers in 2016, infected phones through what is called spear-phishing – text messages or emails that trick a target into clicking on a malicious link.
- Since then, however, NSO’s attack capabilities have become more advanced. Pegasus infections can be achieved through so-called “zero-click” attacks, which do not require any interaction from the phone’s owner in order to succeed.
- These will often exploit “zero-day” vulnerabilities, which are flaws or bugs in an operating system that the mobile phone’s manufacturer does not yet know about and so has not been able to fix.
Who were the Targets?
- Human Rights activists, journalists and lawyers around the world have been targeted with phone malware sold to authoritarian governments by an Israeli surveillance firm.
- Indian ministers, government officials and opposition leaders also figure in the list of people whose phones may have been compromised by the spyware.
- In 2019, WhatsApp filed a lawsuit in the US court against Israel’s NSO Group, alleging that the firm was incorporating cyber-attacks on the application by infecting mobile devices with malicious software.
Recent Steps Taken in India against Cyber Crime:
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative: It was launched in 2018 with an aim to spread awareness about cybercrime and building capacity for safety measures for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT staff across all government departments.
- National Cyber security Coordination Centre (NCCC): In 2017, the NCCC was developed to scan internet traffic and communication metadata (which are little snippets of information hidden inside each communication) coming into the country to detect real-time cyber threats.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: In 2017, this platform was introduced for internet users to clean their computers and devices by wiping out viruses and malware.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C): I4C was recently inaugurated by the government.
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal has also been launched pan India.
- Computer Emergency Response Team – India (CERT-IN): It is the nodal agency which deals with cybersecurity threats like hacking and phishing.
- Legislations in India:
- Information Technology Act, 2000.
- Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019.
International Mechanisms:
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU): It is a specialized agency within the United Nations which plays a leading role in the standardization and development of telecommunications and cyber security issues.
- Budapest Convention on Cybercrime: It is an international treaty that seeks to address Internet and computer crime (cybercrime) by harmonizing national laws, improving investigative techniques, and increasing cooperation among nations. It came into force on 1st July 2004. India is not a signatory to this convention.
Types of Cyber Attacks:
Malware:
- It is short for malicious software and refers to any kind of software that is designed to cause damage to a single computer, server, or computer network. Ransomware, Spy ware, Worms, viruses, and Trojans are all varieties of malware.
Phishing:
- It is the method of trying to gather personal information using deceptive e-mails and websites.
Denial of Service attacks:
- A Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack is an attack meant to shut down a machine or network, making it inaccessible to its intended users.
- DoS attacks accomplish this by flooding the target with traffic, or sending it information that triggers a crash.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks:
- Also known as eavesdropping attacks, occur when attackers insert themselves into a two-party transaction.
- Once the attackers interrupt the traffic, they can filter and steal data.
SQL Injection:
- SQL stands for Structured Query Language, a programming language used to communicate with databases.
- Many of the servers that store critical data for websites and services use SQL to manage the data in their databases.
- A SQL injection attack specifically targets such kinds of servers, using malicious code to get the server to divulge information it normally wouldn’t.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS):
- Similar to an SQL injection attack, this attack also involves injecting malicious code into a website, but in this case the website itself is not being attacked.
- Instead the malicious code the attacker has injected, only runs in the user’s browser when they visit the attacked website, and it goes after the visitor directly, not the website.
Social Engineering:
- It is an attack that relies on human interaction to trick users into breaking security procedures in order to gain sensitive information that is typically protected.
H5N1- Avian Influenza
15, Feb 2023

Why in News?
- Recent reports of H5N1 (subtype of avian influenza) being transmitted between mammals have raised concerns about its potential to cause a human pandemic.
About the News:
- Scientists are investigating a potential spillover event after a mass mortality event that killed over 700 seals along the Caspian Sea coast where a H5N1 variant was detected in wild birds a few months ago.
What is H5N1 Avian Influenza?
- Avian influenza or bird flu refers to the disease caused by infection with avian influenza Type A viruses.
- Infrequently, the virus can infect mammals from birds, a phenomenon called spillover, and rarely can spread between mammals.
- H5N1, a subtype of avian influenza, has the potential to infect other mammals such as minks, ferrets, seals, domestic cats, and others through contact with infected birds, their faeces, or infected bird carcasses.
Symptoms in Humans:
- Range from mild to severe influenza-like illnesses such as fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting.
- People can also develop severe respiratory illness (e.g., difficulty breathing, pneumonia, acute respiratory distress, viral pneumonia) and altered mental status, seizures etc.
Avian Influenza in India:
- In 2019, India has been declared free from Avian Influenza (H5N1), which has also been notified to the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE).
- However, in December 2020 and early 2021, outbreaks of avian influenza H5N1 and H5N8 were reported in poultry in 15 states in India.
Treatment:
- Evidence suggests that some antiviral drugs can reduce the duration of viral replication and improve prospects of survival, however ongoing clinical studies are needed.
Concerns:
- The widespread H5N1 outbreaks have substantial economic impact, resulting in significant losses to the poultry industry and threatening food and vaccine security, apart from raising animal welfare and environmental concerns.
Types of Influenza Virus:
- There are four types of influenza viruses: influenza A, B, C, and D
- Influenza A and B are the two types of influenza that cause epidemic seasonal infections nearly every year.
- Influenza C mainly occurs in humans, but has been known to also occur in dogs and pigs.
- Influenza D is found mainly in cattle. It’s not known to infect or cause illness in humans yet.
Avian influenza Type A Viruses
- Type A viruses are classified based on two proteins on their surfaces – Hemagglutinin (HA) and Neuraminidase (NA). There are about 18 HA subtypes and 11 NA subtypes.
- Several combinations of these two proteins are possible e.g., H5N1, H7N2, H9N6, H17N10, H18N11 etc.
- All known subtypes of influenza A viruses can infect birds, except subtypes H17N10 and H18N11, which have only been found in bats.
Mammalian spread of H5N1 and its Pandemic Potential
13, Feb 2023

Why in News?
- Avian influenza (bird flu) is a highly contagious viral infection that impacts birds. However, rarely it can infect mammals through a phenomenon called spillover, and spread among them. There are various subtypes of avian influenza viruses that range from low pathogenic to highly pathogenic types. One of the highly pathogenic subtypes is H5N1.
- Apart from causing severe disease and death in birds, H5N1 has also caused human infections through close contact with infected birds or contaminated environments. It is often fatal.
- Several instances of the spread of H5N1 among mammals have been reported. Concerns are raised about its spillover among humans and the risks of the human pandemic.
Associated concerns:
- The H5N1 can potentially impact mammals like ferrets, minks, seals, and domestic cats when during their contact with infected birds or their feces or while consuming the infected carcasses.
- They can further serve as reservoirs. Moreover, the virus could evolve to adapt to new hosts and might lead to further outbreaks.
- Along Russia’s Caspian Sea coast there was a mass mortality event that killed nearly 700 seals. Scientists are investigating the potential mammalian spillover as an H5N1 variant was detected in wild birds of the region a few months ago.
- Similarly, in February 2023, Peru registered cases of H5N1 in sea lions and a dolphin. Additionally, a lion in a zoo also died from H5N1.
- The U.K. communicated the cases of otters’ and foxes’ death due to H5N1 infection.
- Notably, wildlife ranging from foxes, coyotes, and raccoons scavenge on infected birds or bird carcasses.
- It was found that the only recorded incidents of intra-mammal transmission of the virus were among mink in captivity at a farm in Spain (in 2022).
H5N1 outbreaks cause severe economic impacts like
- Huge losses to the poultry industry
- Threatens food and vaccine security (eggs are used for vaccine production)
- Raises concerns about animal welfare
Details of some outbreaks across the world:
- The first detected case of the H5N1 avian influenza virus was in 1996 on a goose farm in China. It was followed by a major outbreak in 1997 among poultry in Hong Kong. It also spread to the human population and left 6 people dead and 18 infected.
- In the year 2004, an outbreak occurred in several countries in Asia which further resulted in a global outbreak.
- Several European and Asian countries reported H5N1 in poultry in 2013 and 2014.
- The virus is majorly spread among countries due to migratory birds.
- Around 800 cases of human H5N1 infections have also been reported (as of February 2023) with a high fatality of 53%.
- A new strain namely 2.3.4.4b emerged in 2020. It spread across Asia, Africa, and Europe and later to North(2021) and South America (2022).
- It was found that H5N1 sequenced from the mink farm in Spain showed several mutations like T271A that increase viral replication in mammalian tissues.
Way Ahead:
- To prevent outbreaks and spillovers, the following measures are required:
- Vaccination of poultry
- Safe disposal of dead birds or carcasses
- Quarantine and culling of affected animals
- Using personal protective equipment while handling birds
- Improved surveillance and monitoring of birds and other animals
- Molecular surveillance of H5N1 and its subtypes is important to understand and respond to outbreaks. Thus, Genome sequencing can be employed to keep a close watch on mutations and virulence factors.
Artificial intelligence (AI): An immediate challenge flagged by ChatGPT
06, Feb 2023

Why in News?
- With the launch of Open AI’s ChatGPT late last year, the impending changes in the nature of work, creativity and economy as a whole have moved from being the subject of futuristic jargon to an immediate challenge.
- Since at least 2015 when Klaus Schwab popularised the term Fourth Industrial Revolution at that year’s World Economic Forum terms like 4IR, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things, Future of Work, entered the lexicon of politicians, bureaucrats, consultants and policy analysts.
Sample developments over just the last few days
- A judge in Colombia included his conversations with ChatGPT in a ruling;
- Microsoft is integrating the bot with its search engine, Bing, and other products;
- Google is reportedly trying to launch a similar tool and there are reports that ChatGPT can already code at entry level for Google engineers.
What are the Concerns?
- Lifestyle may become redundant: Concerns about plagiarism in universities and beyond, as well as the fear that many white-collar jobs may become redundant in the coming years, as AI becomes more ubiquitous and sophisticated.
- Implications on labour, education and authenticity: The AI revolution is likely to have serious implications on labour, education, authenticity of content and its authorship, and much else.
- Case of Social media’s influence in US elections: The concerns around social media’s influence on politics and society became sharp in the aftermath of the 2016 US presidential elections and accusations of voter manipulation by foreign agents. Much of the world is still struggling with the questions raised then.
Do you what exactly ChatGPT is?
- Simple definition: ChatGPT is a chatbot built on a large-scale transformer-based language model that is trained on a diverse dataset of text and is capable of generating human-like responses to prompts.
- A human like language model: It is based on GPT-3.5, a language model that uses deep learning to produce human-like text.
- It is more engaging with details: However, while the older GPT-3 model only took text prompts and tried to continue on that with its own generated text, ChatGPT is more engaging. It’s much better at generating detailed text and can even come up with poems.
- Keeps the memory of the conversations: Another unique characteristic is memory. The bot can remember earlier comments in a conversation and recount them to the user.
- Human- like resemblance: A conversation with ChatGPT is like talking to a computer, a smart one, which appears to have some semblance of human-like intelligence.
Anticipating possible futures requires engagement with the opportunities:
- The Struggle to keep up with technology in policymaking:
- Governments worldwide face a challenge in creating policies that keep up with the rapid pace of technological advancement.
- Policymakers should understand that they must work to bridge the gap between technology and regulation, as a growing divide could lead to problems.
- Preparing for technological change in education and workforce:
- In addition to creating regulations that support innovation, it’s crucial to plan for the changes that new technology will bring to education and employment.
- This includes anticipating new job types and skills required, as well as updating the education system to prepare future workers.
- Importance of Preparing for technological change for India:
- India has been facing the challenge of balancing privacy and regulation in the handling of data for several years.
- Successfully adapting to technological changes is crucial for India to make the most of its large, young workforce. If not addressed in time, the consequences could be severe
Conclusion:
- The transformations the new technology is bound to bring about must be met with swift adjustments in the broader national and international legal and policy architecture. The lag between technology innovation and policy that was seen with the rise of Big Data and social media can serve as a lesson.
Global Report on Neglected Tropical Diseases
02, Feb 2023
Why in News?
- Recently, the World Health Organization’s (WHO) has released a Global report on Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTD) 2023, which states that NTD continues to disproportionately impact the most impoverished members of the international community.
About the News:
- World NTD day is observed every year on 30th January. It was declared in the 74th World Health Assembly (2021).
What are Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs)?
- NTDs are a group of infections that are most common among marginalized communities in the developing regions of Africa, Asia and the Americas.
- They are caused by a variety of pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa and parasitic worms.
- NTDs are especially common in tropical areas where people do not have access to clean water or safe ways to dispose of human waste.
- These diseases generally receive less funding for research and treatment than malaises like tuberculosis, HIV-AIDS and malaria.
- Examples of NTDs are: snakebite envenomation, scabies, yaws, trachoma, Leishmaniasis and Chagas disease etc.
What are the Highlights of the Report?
- About 16 countries accounted for 80 % of the global NTD burden.
- Globally, nearly 1.65 billion people are estimated to require treatment for at least one NTD.
- Covid-19 impacted the community-based initiatives, access to healthcare facilities and healthcare goods supply chains. As a result, between 2019 and 2020, 34% fewer persons received treatment for NTDs.
Recommendations:
- Greater efforts and investments are required to reverse delays and accelerate progress towards the NTD road map targets by 2030.
- WHO urged multi-sectoral collaboration and partnerships to achieve these targets.
- It is the need of the hour for additional partners and funders to step up and close the gaps preventing the full-scale implementation of NTD actions at the international and local levels.
What are the Global Initiatives?
- WHO’s New Roadmap for 2021–2030: The NTD road map 2021–2030 is WHO’s blueprint to drive global efforts in the fight against NTDs in the context of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
- The Blueprint recommends following measures,
- From measuring process to measuring impact.
- From disease-specific planning and programming to collaborative work across sectors.
- From externally driven agendas reliant to programmes that are country-owned and country-financed.
- London Declaration on NTDs: It was adopted on 30th January, 2012 to recognise the global burden of NTDs.
What are the Indian Initiatives to Eliminate NTDs?
- The Accelerated Plan for Elimination of Lymphatic Filariasis (APELF) was launched in 2018, as part of intensifying efforts towards the elimination of NTDs.
- A WHO-supported regional alliance established by the governments of India, Bangladesh, and Nepal in 2005 to expedite early diagnosis and treatment of the most vulnerable populations and improve disease surveillance and control of sandfly populations (Kala-azar). India has already eliminated several other NTDs, including guinea worm, trachoma, and yaws.
- Preventive methods like Mass Drug Administration (MDA) rounds are periodically deployed in endemic areas during which anti-filarial medicines are provided free-of-cost to at-risk communities.
- Vector-control measures like Indoor Residual Spraying rounds are undertaken in endemic areas to prevent sandfly breeding. The government also supports morbidity management and disability prevention for those affected by lymphoedema and hydrocele.
- State and central governments have also introduced wage compensation schemes for those suffering from Kala-Azar and its sequela (a condition which is the consequence of a previous disease or injury) known as Post-Kala Azar Dermal Leishmaniasis.
Norovirus
25, Jan 2023
Why in News?
- Norovirus infection was confirmed in two schoolchildren in Ernakulam district of Kerala.
Norovirus:
- Norovirus is a contagious virus that is also called the “winter vomiting bug”.
- Norovirus is an RNA virus belonging to the family Caliciviridae.
- It is a human enteric pathogen that causes acute gastroenteritis.
- The most common symptoms caused due to Norovirus include diarrhoea, vomiting, nausea and stomach pain.
- Norovirus mainly spreads through faecal-oral routes such as:
- Direct contact with an infected person
- Consuming contaminated water or food
- Touching contaminated surfaces and using unwashed hands
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), norovirus can infect anyone.
- Since the Norovirus genus comprises viruses that infect humans, pigs, cattle, and mice, the possibility of zoonotic transmission of infection exists.
India’s Target on Measles and Rubella
25, Jan 2023
Why in News?
- India had set a target to eliminate Measles and Rubella (MR) by 2023, having missed the earlier deadline of 2020, due to a variety of reasons, exacerbated by disruptions due to the pandemic.
About the News:
- In 2019, India adopted the goal of measles and rubella elimination by 2023, anticipating that the 2020 goal could not be reached.
What are Measles and Rubella?
Measles:
- It is a highly contagious viral disease and is a cause of death among young children globally.
- It is caused by a single-stranded, enveloped RNA virus with 1 serotype. It is classified as a member of the genus Morbillivirus in the Paramyxoviridae family.
- It is particularly dangerous for children from the economically weaker background, as it attacks malnourished children and those with reduced immunity.
- It can cause serious complications, including blindness, encephalitis, severe diarrhoea, ear infection and pneumonia.
Rubella:
- It is also called German Measles.
- Rubella is a contagious, generally mild viral infection that occurs most often in children and young adults.
- It is caused by the rubella virus which is an enveloped single-stranded RNA virus.
- Rubella infection in pregnant women may cause death or congenital defects known as Congenital Rubella Syndrome (CRS) which causes irreversible birth defects.
- Rubella isn’t the same as measles, but the two illnesses share some signs and symptoms, such as the red rash.
- Rubella is caused by a different virus than measles, and rubella isn’t as infectious or as severe as measles.
What is the Global and Indian Scenario of Measles and Rubella?
- The measles virus is one of the world’s most contagious human viruses that kills more than 1,00,000 children every year globally, and rubella is a leading vaccine-preventable cause of birth defects, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Over the past two decades, the measles vaccine is estimated to have averted more than 30 million deaths globally, as per the WHO’s statistics.
- During 2010–2013, India conducted a phased measles catch-up immunisation for children aged 9 months–10 years in 14 States, vaccinating approximately 119 million children.
- Mission Indradhanush was launched in 2014 to ramp up vaccinating the unvaccinated population.
- During 2017–2021, India adopted a national strategic plan for measles and rubella elimination.
- During the same period, the Government introduced rubella-containing vaccine (RCV) into the routine immunisation programme.
- As of December 2021, five countries have been verified and have sustained measles elimination – Bhutan, DPR Korea, Maldives, Sri Lanka, Timor-Leste. In addition, Maldives and Sri Lanka have sustained their rubella elimination status in 2021.
What are Measures to Curb MR?
- Measles-Rubella Vaccination: The MR campaign targets around 41 crore children across the country, the largest ever in any campaign.
- All children aged between 9 months and less than 15 years are given a single shot of MR vaccination irrespective of their previous measles/rubella vaccination status or measles/rubella disease status.
- Other Initiatives include Universal Immunization Programme (UIP), Mission Indradhanush and Intensified Mission Indradhanush.
- The vaccines for the diseases are provided in the form of measles-rubella (MR), measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) or measles-mumps-rubella-varicella (MMRV) combination.
Sale of pork banned in the Nilgiris due to African Swine Fever outbreak
09, Jan 2023

Why in News?
- The sale of pork in the Nilgiris and the transportation of animals or meat outside the Nilgiris has been banned following an outbreak of African Swine Fever (ASF) among wild boar populations in Mudumalai and Bandipur Tiger Reserves.
About the infection:
- It is a highly contagious and fatal animal disease that infects and leads to an acute form of haemorrhagic fever in domestic and wild pigs.
- Other manifestations of the disease include high fever, depression, anorexia, loss of appetite, haemorrhages in the skin, vomiting and diarrhoea among others.
- It was first detected in Africa in the 1920s.
- Historically, outbreaks have been reported in Africa and parts of Europe, South America, and the Caribbean.
- However, more recently (since 2007), the disease has been reported in multiple countries across Africa, Asia and Europe, in both domestic and wild pigs.
- The mortality is close to 100% and since the fever has no cure, the only way to stop its spread is by culling the animals.
- ASF is not a threat to human beings since it only spreads from animals to other animals.
- ASF is a disease listed in the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) Terrestrial Animal Health Code and thus, reported to the OIE.
What is Classical Swine Fever?
- CSF, also known as hog cholera, is an important disease of pigs.
- It is one of the most economically-damaging pandemic viral diseases of pigs in the world.
- It is caused by a virus of the genus Pest virus of the family Flaviviridae, which is closely related to the viruses that cause bovine viral diarrhoea in cattle and border disease in sheep.
- Mortality is 100%.
- Recently, the ICAR-IVRI developed a Cell Culture CSF Vaccine (live attenuated) using the Lapinized Vaccine Virus from foreign strain.
- The new vaccine has been found to induce protective immunity from day 14 of the Vaccination till 18 Months.
About World Organisation for Animal Health:
- OIE is an intergovernmental organisation responsible for improving animal health worldwide.
- It has 182 Member Countries. India is one of the member countries.
- OIE develops normative documents relating to rules that Member Countries can use to protect themselves from the introduction of diseases and pathogens. One of them is the Terrestrial Animal Health Code.
- OIE standards are recognised by the World Trade Organization as reference international sanitary rules.
- It is headquartered in Paris, France.
Dark Patterns” on the Internet
28, Dec 2022
Why in News?
- This article discusses the deceptive tactics deployed by tech firms called “dark patterns”.
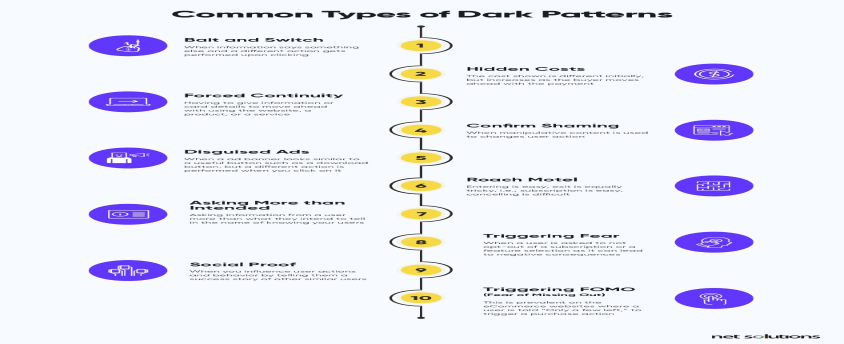
What are dark patterns?
- The term “dark patterns” was first coined by UI/UX (user interface/user experience) specialist Harry Brignull to describe the ways in which software can subtly trick users into doing things they didn’t mean to do, or discouraging behaviour that’s bad for the company.
- Such patterns are unethical user interface designs that deliberately make your Internet experience harder or even exploit you.
- They are designed to benefit the company or platform employing the designs.
How do companies use dark patterns?
- Different Big Tech companies, like Apple, Amazon, Skype, Facebook, LinkedIn, Microsoft, and Google, employ dark patterns to downgrade the user experience for their own benefit.
- For Instance, when you want to unsubscribe from a mailing list, the company makes the “Unsubscribe” button tiny, low-contrast, and buried in paragraphs of text at the bottom of an email putting up subtle roadblocks between you and cancellation.
- Amazon came under fire in the European Union for its confusing, multi-step cancelling process for Amazon Prime subscriptions. After communicating with consumer regulators, Amazon this year made its cancellation process easier for online customers in European countries.
- The last few seconds of a video are obscured by thumbnails of other videos as YouTube nags users to sign up for YouTube Premium, interfering with user experience.
- In the U.S., the Federal Trade Commission [FTC] has taken note of dark patterns and the risks they pose. It listed over 30 dark patterns which are standard practice across social media platforms and e-commerce sites.
- These include “baseless” countdowns for online deals, conditions in fine print that add on to costs, making cancellation buttons hard to see or click, making ads appear as news reports or celebrity endorsements, auto-playing videos, forcing users to create accounts to finish a transaction, silently charging credit cards after free trials end, and using dull colours to hide information that users should know about.
- In one instance, the FTC report took legal action against Amazon in 2014, for a supposedly “free” children’s app that fooled its young users into making in-app purchases that their parents had to pay for.
How do dark patterns affect user experience?
- Dark patterns jeopardise Internet users’ experiences and increase their susceptibility to data and financial exploitation by Big Tech companies.
- Dark patterns trick consumers, present online barriers, lengthen the completion of routine tasks, get them to sign up for undesirable services or products, and coerce them into paying more money or disclosing more personal information than they had originally meant.
- According to the FTC, dark patterns will likely follow augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) platforms and devices as they grow in usage.
- By using dark patterns, digital platforms take away a user’s right to full information about the services they are using and their control over their browsing experience. Internet users who are able to identify and recognise dark patterns in their daily lives can choose more user-friendly platforms that will respect their right to choose and privacy.
Is Aadhaar for Social Good
26, Dec 2022

Why in News?
- Every time a government department asks for Aadhaar linking, people view it with suspicion.
What is Aadhaar?
- A 12-digit unique identity for every Indian individual, including children and infants
- Enables identification for every resident Indian.
- Establishes uniqueness of every individual on the basis of demographic and biometric information.
- It is a voluntary service that every resident can avail irrespective of present documentation.
- Each individual will be given a single unique Aadhaar ID number.
- Aadhaar will provide a universal identity infrastructure which can be used by any identity-based application (like ration card, passport, etc.)
About the new regulations:
- Updating the documents:
- As per the regulations earlier, residents who were older than 15 years at the time of enrollment were recommended to update their biometric data every 10 years.
- The process of updating documents is not mandatory.
- Ensuring accuracy
- This process will help in ensuring the accuracy of information in the Central Identities Data Repository (CIDR).
- Demographic information
- The amendment of the Aadhaar regulation is limited to updating demographic information and does not involve biometric data such as fingerprints.
Issues with Aadhar:
- Aadhaar act allows cancellation of Aadhaar number for any reason by the government and citizens have no recourse.
- A Centralized database is a concern because once it is compromised everyone is at risk.
- There is no ID or address verification and there is no means of identifying fakes.
- There is no data protection law in place in India.
- Enrollment software hacks allowed foreign nationals to create Aadhaar numbers thus creating a national security risk.
- UIDAI does not have a monitoring mechanism but only an audit mechanism.
- Data goes to third parties vulnerability increases due to that.
Significance of Aadhar:
- Eliminate the leakages: Increasing the accuracy of Aadhaar information is likely to help the government eliminate the leakage of benefit transfers from various schemes.
- Jhan Dhan Yojana: Aadhaar Card is used as the major document of proof when opening a bank account under the Pradhan Mantri Jhan Dhan Yojana in the nation.
- Direct Benefit Transfer: Aadhar Card linked bank accounts will get their set of LPG Subsidy directly accredited in the bank account.
- Monthly Pension and Provident Fund: a person needs to link their Aadhaar Card to their respective pension account and provident fund.
- Passport and Voter ID: Aadhaar Card will relieve you of the lengthy procedure while obtaining Passport.
Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) & Aadhar:
- Aadhaar Act & Establishment of UIDAI:
- The UIDAI is a statutory authority established under the provisions of the Aadhaar (Targeted Delivery of Financial and Other Subsidies, Benefits and Services) Act, 2016 (“Aadhaar Act 2016”) by the Government of India, under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Need of UIDAI: UIDAI was created to issue Unique Identification numbers (UID), named as “Aadhaar”, to all residents of India. The UID had to be –
- Robust enough to eliminate duplicate and fake identities, and
- Verifiable and authenticable in an easy, cost-effective way.
- Under the Aadhaar Act 2016, UIDAI is responsible for:
- Aadhaar enrolment and authentication, including operation and management of all stages of Aadhaar life cycle,
- Developing the policy, procedure, and system for issuing Aadhaar numbers to individuals and Perform authentication and the security of identity information and authentication records of individuals.
About Central Identities Data Repository (CIDR):
- It is a central database that stores and manages identity information for individuals and organizations.
- It is used to authenticate and authorize individuals and organizations for access to government services and information.
- CIDR also supports the issuance of electronic identity cards and the management of identity information.
Whole Genome Sequencing
20, Dec 2022

Why in News?
- Recently, Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Bhopal have carried out Whole Genome Sequencing of banyan (Ficus benghalensis) and peepal (Ficus religiosa) from leaf tissue samples.
About the News:
- The work helped in identifying 17 genes in the case of banyan and 19 genes of peepal with multiple signs of adaptive evolution (MSA) that play a pivotal role in long-time survival of these two Ficus species.
What is Whole Genome Sequencing?
- All organisms have a unique genetic code, or genome, that is composed of nucleotide bases- Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C) and Guanine (G).
- The unique Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) fingerprint, or pattern can be identified by knowing the sequence of the bases in an organism.
- Determining the order of bases is called sequencing.
- Whole genome sequencing is a laboratory procedure that determines the order of bases in the genome of an organism in one process.
Methodology:
- DNA Shearing:
- Scientists begin by using molecular scissors to cut the DNA, which is composed of millions of bases (A’s, C’s, T’s and G’s), into pieces that are small enough for the sequencing machine to read.
- DNA Bar Coding:
- Scientists add small pieces of DNA tags, or bar codes, to identify which piece of sheared DNA belongs to which bacteria.
- This is similar to how a bar code identifies a product at a grocery store.
- DNA Sequencing:
- The bar-coded DNA from multiple bacteria is combined and put in a DNA sequencer.
- The sequencer identifies the A’s, C’s, T’s, and G’s, or bases, that make up each bacterial sequence.
- The sequencer uses the bar code to keep track of which bases belong to which bacteria.
- Data Analysis:
- Scientists use computer analysis tools to compare sequences from multiple bacteria and identify differences.
- The number of differences can tell the scientists how closely related the bacteria are, and how likely it is that they are part of the same outbreak.
Advantages of Genome Sequencing:
- Provides a high-resolution, base-by-base view of the genome
- Captures both large and small variants that might be missed with targeted approaches
- Identifies potential causative variants for further follow-up studies of gene expression and regulation mechanisms
- Delivers large volumes of data in a short amount of time to support assembly of novel genomes
Significance of Genome Sequencing:
- Genomic information has been instrumental in identifying inherited disorders, characterizing the mutations that drive cancer progression, and tracking disease outbreaks.
- It is beneficial for sequencing agriculturally important livestock, plants, or disease-related microbes.
What is Genome?
- A genome refers to all of the genetic material in an organism, and the human genome is mostly the same in all people, but a very small part of the DNA does vary between one individual and another.
- Every organism’s genetic code is contained in its DNA, the building blocks of life.
- The discovery that DNA is structured as a “double helix” by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, started the quest for understanding how genes dictate life, its traits, and what causes diseases.
- Each genome contains all of the information needed to build and maintain that organism.
- In humans, a copy of the entire genome contains more than 3 billion DNA base pairs.
Why Banyan, Peepal Trees live longer?
19, Dec 2022

Why in News?
- Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Bhopal have found out the carried out whole genome sequencing of banyan and peepal from leaf tissue samples.
Science behind long life: Multiple Signs of Adaptive-evolution (MSA):
- Scientists identified 25,016 coding gene sequences in banyan and 23,929 in peepal.
- Both trees faced a population bottleneck around 0.8 million years ago and evolved genes with multiple signs of adaptive evolution (MSA).
- In banyan, the MSA genes are mainly involved in root growth, pollen tube and seed development, leaf formation, cell wall synthesis, metabolism and other developmental processes.
How MSA prolongs the life?
- Disease resistance and other stress tolerance gene families showed expansion as well as high expression, contributing to the plants’ long lifespan.
- The MSA genes of peepal are associated with root cell elongation, cell proliferation, seed and pollen tube growth, lateral organ development, controlling flowering time, metabolism and intracellular transport.
- The team zeroed in on 17 MSA genes in banyan and 19 MSA genes in peepal that are mainly related to well-developed morphology, and tolerance against drought, oxidative stress and pathogens.
- Genes involved in growth-regulating auxin signalling and plant senescence-regulating pathways also showed evolutionary signatures.
- Also, 88% and 89% of the MSA genes in banyan and peepal trees, respectively, are associated with tolerance against biotic and abiotic stress responses.
- This, in turn, helps these plants to survive when faced with environmental challenges.
Antimicrobial Resistance
12, Dec 2022
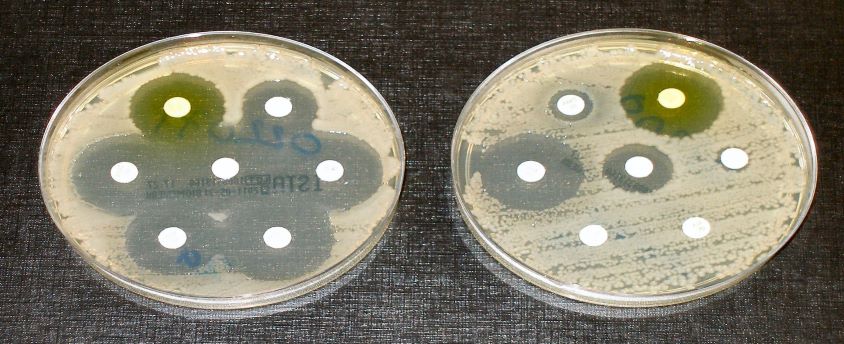
Why in News?
- Over 50% of life-threatening bacterial infections are becoming resistant to treatment: the Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) report of WHO.
What are the concerns as per the recent report?
- 8% of infections caused by Klebsiella pneumonia were resistant to carbapenems (the last resort antibiotic).
- Over 60% of Neisseria gonorrhoea, a common sexually transmitted disease, show resistance to ciprofloxacin.
- 20% of coli isolates, common in urinary tract infections were resistant to ampicillin and co-trimoxazole.
- Bloodstream infections due to resistant coli, Salmonella and gonorrhoea infections, have jumped by at least 15 per cent compared to 2017 rates.
About Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS):
- Provides a standardized approach to the collection, analysis, interpretation and sharing of data by countries and seeks to actively support capacity building and monitor the status of existing and new national surveillance systems.
What is AMR?
- Antimicrobial resistance is the resistance acquired by any microorganism (bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasite, etc.) against antimicrobial drugs (such as antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, antimalarials, and anthelmintics) that are used to treat infections.
- As a result, standard treatments become ineffective, infections persist and may spread to others.
- Microorganisms that develop antimicrobial resistance are sometimes referred to as “superbugs”.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified AMR as one of the top ten threats to global health.
Reasons for Spread of AMR:
- The misuse of antimicrobials in medicine and inappropriate use in agriculture.
- Contamination around pharmaceutical manufacturing sites where untreated waste releases large amounts of active antimicrobials into the environment.
What Initiatives have been taken by the Government to Prevent AMR?
- AMR Surveillance and Research Network (AMRSN) was launched in 2013, to generate evidence and capture trends and patterns of drug resistant infections in the country.
- The National Action Plan on AMR focuses on One Health approach and was launched in April 2017 with the aim of involving various stakeholder ministries/departments.
- ICMR along with Research Council of Norway (RCN) initiated a joint call for research in antimicrobial resistance in 2017.
- ICMR along with the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Germany has a joint Indo-German collaboration for research on AMR.
- ICMR has initiated Antibiotic Stewardship Program (AMSP) on a pilot project across India to control misuse and overuse of antibiotics in hospital wards and ICUs.
Recommendation by WHO:
- Equitable and global access to the vaccines that already exist
- Disruptive approaches are needed: The lessons from COVID 19 vaccine development and mRNA vaccines offer unique opportunities to explore for development of vaccines against bacteria
- Need to overcome challenges: Such as pathogens associated with hospital-acquired infections (HAI), difficulty in defining target population(s) among all admitted hospital patients; the cost and complexity of vaccine efficacy trials; and the lack of regulatory and/or policy precedent for vaccines against HAIs.
- Easier regulatory requirement: Vaccine development is expensive, and scientifically challenging, and is associated with high failure rates, and therefore, the need for support from the government and private sector.
QUAD and the Telecom Network Security
03, Dec 2022

Why in News?
- The advent of 5G provides the Quad or the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue of the United States (US), Japan, Australia and India, a unique opportunity to demonstrate how democracies can engage in effective technology collaboration.
The Huawei and QUAD response:
- Huawei’s connection with Chinese Communist Party: Recognising the risks that companies like Huawei, which is connected to the Chinese Communist Party, pose to telecommunications networks, each member country of the Quad has taken steps to ensure secure and resilient access to 5G.
- Australia’s measure: Australia, for one, banned Huawei from its 5G rollout in 2018 and did the same with ZTE, citing national security concerns.
- US concerns: For its part, the US has been raising concerns about Huawei since 2012, and doubled-down on its efforts in 2019 by adding Huawei to the Entity List.
- Japan creating Open RAN: Japan, meanwhile, a long-time leader in the telecommunications space has accelerated its efforts to create ‘Open Radio Access Networks (Open RAN)’, which promote vendor diversification and competition for better solutions.
- India 5G and conflict with China on border: India took what it called a “step towards the new era” by deploying its first 5G services in select cities in October 2022; it is aiming to extend the network across the country over the next few years. India is unlikely to include Huawei in its networks, given the clash with Chinese forces in Galwan Valley in June 2020 and concerns about vendor trustworthiness.
QUAD alignment on securing 5G telecom networks
- Agreement in first meeting: During the first in-person leaders’ meeting in September 2021, Quad countries agreed to “build trust, integrity, and resilience” into technology ecosystems by having suppliers, vendors, and distributors ensure strong safety and security-by-design processes, and committed to a “fair and open marketplace”.
- Memorandum of cooperation on 5g suppliers: Later, at the fourth meeting in May 2022, partners signed a New Memorandum of Cooperation on 5G Supplier Diversification and Open RAN, and reaffirmed their desire to “collaborate on the deployment of open and secure telecommunications technologies in the region.”
Why QUAD must cooperate on Network Security?
- Fast emerging telecom technologies: For one, virtualised (software-based) networks will be the norm in the next 10 years, by which time 6G networks will begin to rollout. Early attention to security issues for emerging telecommunications technologies will help ensure that there is sufficient focus on security in the runup to 5G rollouts.
- Interoperable software’s need to check: The Quad’s advocacy of Open RAN networks or network architectures that consist of interoperable software run on vendor-neutral hardware is another reason why there is a need to focus on software supply chain and software-based infrastructure security.
- To ensure the comprehensive network strategy: Critics of Open RAN solutions often point to security concerns to argue against deploying these technologies. A comprehensive 5G security strategy is necessary to ensure trust in these networks.5G networks are critical infrastructure and it is imperative for states to ensure their security.
- For instance: In 2018, Australian officials were the first to warn the public of the risks posed by untrustworthy vendors on 5G networks. Officials from the other Quad countries have followed suit and, along with key partners such as the European Union and United Kingdom, there is a clear consensus on the fundamental importance of secure and resilient communications networks.
How QUAD will be a key player in Talent Development?
- Bridging the gap of talent pool: Nations across the globe are suffering from a talent shortage in the technology domain. With heightened demand for high-skilled workers, like-minded nations must cultivate and share their expertise with one another to bridge critical gaps.
- Quad Fellowship: this, the Quad created the Quad Fellowship, which will support 100 students per year to pursue STEM-related graduate degrees in the United States. This could be an effective way to grow the talent pipeline in a way that fills current and emerging needs.
- Restructuring programs that can fulfil the current and future demand: Many nations have started to consider changes to immigration policies for high-skilled talent. Australia, for example, has raised its permanent immigration cap by 35,000 for the current fiscal year, and Japan is planning to expand its programs soon.
- Creative ways of QUAD countries to recruit talent: Shortage of talent pool that all Quad countries are experiencing as they seek creative ways to grow their technology talent pool. Indian companies, for example, are beginning to recruit in rural areas to address significant tech worker shortages that may stymie a growing start-up ecosystem.
What QUAD need to do?
- Ensure close coordination: While these commitments are significant, maintaining momentum requires close coordination of resources and policies. No one country can build resilient, open, and secure telecommunications networks on its own, particularly as countries deploy 5G and think ahead to 6G.
- Adhering to the goals and principles: To ensure that operationalisation moves forward in line with the Quad’s stated principles and goals, the member countries must work together in four key areas: standard-setting; security; talent development; and vendor diversity.
- Develop a recruitment framework for telecommunications: Quad countries have an opportunity to set a precedent for other democracies by rethinking what it means to be “qualified” for a position. Companies can look beyond degrees during the hiring process and focus on relevant skills by jointly developing assessment criteria for worker readiness and performance.
- Incentivise 5G deployment in underserved areas: To ensure that talent is not left out of the candidates’ pool for tech jobs, Quad members can agree to prioritise secure 5G deployment in rural regions. Lack of access to reliable information and communications can be a significant barrier to entering the workforce, and expanding 5G deployment is a critical aspect of broadening the talent pool.
- Enhance public-private partnerships: As Quad countries build their infrastructure and talent pools at home, they must also think about other countries that only consider cost when choosing Huawei and other untrusted telecom providers. As such, the Quad could leverage public-private partnerships to bolster the presence of trusted companies in new locations. By using coordinated, strategic financial incentives, they will also have an opportunity to train and educate third country governments on the threats posed by untrusted 5G vendors. Consequently, they will contribute to broader network security and resiliency as 5G is more widely deployed.
- Provide R&D incentives: The governments of the Quad countries should offer incentives to promote ongoing work in hardware, software, and security improvements, specific technologies such as high-band technology and end-to-end network slicing, and research areas including telehealth, energy research, and agriculture. A broad base of enabling technologies and applications would encourage new entrants into the market.
Conclusion:
- Quad countries are well-positioned to accomplish plenty together. Of the many areas where they can progress, securing 5G is particularly promising due to the clearly stated objectives that Quad countries share. The Quad countries have the potential to provide a secure, flexible and open 5G network model to the Indo-Pacific and nations seeking democratic alternatives for their telecommunications infrastructure.
Antimicrobial Resistance Vaccines
03, Dec 2022

Why in News?
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has been declared one of the top global public health threats by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Background:
- In 2019, an overall 95 million deaths were caused by AMR infections and associated complications.
- India is the world’s largest consumer of antibiotics and has the world’s highest infectious disease burden including due to multi-resistant pathogens (superbugs).
- AMR may cause a global annual GDP loss of $3.4 trillion by 2030 and may push 24 million people into extreme poverty.
What is AMR?
- Antimicrobial resistance is the resistance acquired by any microorganism (bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasite, etc.) against antimicrobial drugs (such as antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, antimalarials, and anthelmintics) that are used to treat infections.
- As a result, standard treatments become ineffective, infections persist and may spread to others.
- Microorganisms that develop antimicrobial resistance are sometimes referred to as “superbugs”.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified AMR as one of the top ten threats to global health.
Reasons for Spread of AMR:
- The misuse of antimicrobials in medicine and inappropriate use in agriculture.
- Contamination around pharmaceutical manufacturing sites where untreated waste releases large amounts of active antimicrobials into the environment.
What Initiatives have been taken by the Government to Prevent AMR?
- AMR Surveillance and Research Network (AMRSN) was launched in 2013, to generate evidence and capture trends and patterns of drug resistant infections in the country.
- The National Action Plan on AMR focuses on One Health approach and was launched in April 2017 with the aim of involving various stakeholder ministries/departments.
- ICMR along with Research Council of Norway (RCN) initiated a joint call for research in antimicrobial resistance in 2017.
- ICMR along with the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Germany has a joint Indo-German collaboration for research on AMR.
- ICMR has initiated Antibiotic Stewardship Program (AMSP) on a pilot project across India to control misuse and overuse of antibiotics in hospital wards and ICUs.
Recommendation by WHO:
- Equitable and global access to the vaccines that already exist
- Disruptive approaches are needed: The lessons from COVID 19 vaccine development and mRNA vaccines offer unique opportunities to explore for development of vaccines against bacteria
- Need to overcome challenges: Such as pathogens associated with hospital-acquired infections (HAI), difficulty in defining target population(s) among all admitted hospital patients; the cost and complexity of vaccine efficacy trials; and the lack of regulatory and/or policy precedent for vaccines against HAIs.
- Easier regulatory requirement: Vaccine development is expensive, and scientifically challenging, and is associated with high failure rates, and therefore, the need for support from the government and private sector.
Ransomware
01, Dec 2022

Context:
- The services at the AIIMS in the national capital were affected for the 7th consecutive day, after the hospital’s server was subjected to a ransomware attack.
What are Cyber Attacks?
- It is a malicious and deliberate attempt by an individual or organization to breach the information system of another individual or organization.
- There are various types of cyberattacks like malware, phishing, denial of service attacks, etc.
Different types of Malware:
- Malware is the shortened form of malicious software. It is the general term for any program that is designed to damage, disrupt, or hack a device. Malware includes viruses, Ransomware, spyware, Trojan, adware, etc.
- Viruses are malicious pieces of code that infect your device without your knowledge. They can affect your device’s performance, delete files, send spam, and even corrupt your hard drive. They multiply and spread to other machines, often before you’re aware of an infection.
- Ransomware is malicious programs that block access to your device until you pay a ransom fee to its creator. It is often very difficult and expensive to remove.
- Spyware is software that spies on you, tracking your internet activities in order to send advertising (Adware) back to your system.
- Worm is a program that replicates itself and destroys data and files on the computer. Worms work to “eat” the system operating files and data files until the drive is empty.
- Trojan is a type of malware that are written with the purpose of discovering your financial information, taking over your computer’s system resources, and in larger systems creating a “denial-of-service attack” which is making a machine or network resource unavailable to those attempting to reach it. Example: Google, AOL, Yahoo or your business network becoming unavailable.
- Phishing is a cybercrime in which a target or targets are contacted by email, telephone, or text message. This is done by someone posing as a legitimate institution to lure individuals into providing sensitive data such as personally identifiable information, banking and credit card details, and passwords.
Steps taken by the Government to spread awareness about cyber-crimes:
- Online cybercrime reporting portal has been launched to enable complainants to report complaints pertaining to Child Pornography/Child Sexual Abuse Material, rape/gang rape imageries or sexually explicit content.
- A scheme for establishment of Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) has been established to handle issues related to cybercrime in the country in a comprehensive and coordinated manner.
- Establishment of National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) for protection of critical information infrastructure in the country.
- All organizations providing digital services have been mandated to report cyber security incidents to CERT-In expeditiously.Cyber Swachhta Kendra (Botnet Cleaning and Malware Analysis Centre) has been launched for providing detection of malicious programmes and free tools to remove such programmes.
- Formulation of Crisis Management Plan for countering cyber-attacks and cyber terrorism.
Antimicrobial Resistance Vaccines
19, Nov 2022
Why in News?
- Poor animal health in factory farming can negatively affect food safety, our environment and climate, leading to Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR).
What are the Issues?
- Factory farming or intensive food-animal farming is the intense and confined farming of animals such as pigs, cows, and birds. They are industrial facilities that raise large numbers of animals, mostly indoors, in conditions intended to maximise production at a minimal cost.
- The suffering of animals within farms around the world is too often overlooked or seen to be separate from the big issues such as pandemics and the public health crisis, climate change and biodiversity loss, food insecurity and malnutrition.
- In reality, this can exacerbate the global problems as well as causing immense cruelty to billions of animals.
- Producing more than 50 billion factory-farmed land animals each year to satisfy growing demand for cheap meat requires using breeds of genetically uniform animals squashed together, creating an ideal breeding ground for disease that can jump to humans.
- When diseases jump from one species to another, they often become more infectious and cause more serious illness and death, leading to global pandemics.
- Bird flu and swine flu are two key examples where new strains constantly emerge from intensively farmed animals.
- However, there is an addition to this list — Antimicrobial Resistance which is overlooked among these big issues.
- The overuse of antibiotics on factory farms leads to superbugs that spread to workers, the environment and into the food chain.
- Factory farms, characterised by substandard husbandry practices and poor animal welfare, drive the increased use of antimicrobials, and are connected to the emergence of AMR alongside a range of zoonotic pathogens.
What is AMR?
- Antimicrobial resistance is the resistance acquired by any microorganism (bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasite, etc.) against antimicrobial drugs (such as antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, antimalarials, and anthelmintics) that are used to treat infections.
- As a result, standard treatments become ineffective, infections persist and may spread to others.
- Microorganisms that develop antimicrobial resistance are sometimes referred to as “superbugs”.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified AMR as one of the top ten threats to global health.
Reasons for Spread of AMR:
- The misuse of antimicrobials in medicine and inappropriate use in agriculture.
- Contamination around pharmaceutical manufacturing sites where untreated waste releases large amounts of active antimicrobials into the environment.
What Initiatives have been taken by the Government to Prevent AMR?
- AMR Surveillance and Research Network (AMRSN) was launched in 2013, to generate evidence and capture trends and patterns of drug resistant infections in the country.
- The National Action Plan on AMR focuses on One Health approach and was launched in April 2017 with the aim of involving various stakeholder ministries/departments.
- ICMR along with Research Council of Norway (RCN) initiated a joint call for research in antimicrobial resistance in 2017.
- ICMR along with the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Germany has a joint Indo-German collaboration for research on AMR.
- ICMR has initiated Antibiotic Stewardship Program (AMSP) on a pilot project across India to control misuse and overuse of antibiotics in hospital wards and ICUs.
Recommendation by WHO:
- Equitable and global access to the vaccines that already exist
- Disruptive approaches are needed: The lessons from COVID 19 vaccine development and mRNA vaccines offer unique opportunities to explore for development of vaccines against bacteria
- Need to overcome challenges: Such as pathogens associated with hospital-acquired infections (HAI), difficulty in defining target population(s) among all admitted hospital patients; the cost and complexity of vaccine efficacy trials; and the lack of regulatory and/or policy precedent for vaccines against HAIs.
- Easier regulatory requirement: Vaccine development is expensive, and scientifically challenging, and is associated with high failure rates, and therefore, the need for support from the government and private sector.
Centre Amends Aadhaar Regulation
14, Nov 2022
Why in News?
- The Centre has recently amended Aadhaar regulations, advising card holders to update documents supporting their information at least once every 10 years from the date of enrolment to ensure the accuracy of the data.
What is Aadhaar?
- A 12-digit unique identity for every Indian individual, including children and infants
- Enables identification for every resident Indian.
- Establishes uniqueness of every individual on the basis of demographic and biometric information.
- It is a voluntary service that every resident can avail irrespective of present documentation.
- Each individual will be given a single unique Aadhaar ID number.
- Aadhaar will provide a universal identity infrastructure which can be used by any identity-based application (like ration card, passport, etc.)
About the new regulations:
- Updating the documents:
- As per the regulations earlier, residents who were older than 15 years at the time of enrolment were recommended to update their biometric data every 10 years.
- The process of updating documents is not mandatory.
- Ensuring accuracy
- This process will help in ensuring the accuracy of information in the Central Identities Data Repository (CIDR).
- Demographic information
- The amendment of the Aadhaar regulation is limited to updating demographic information and does not involve biometric data such as fingerprints.
Issues with Aadhar:
- Aadhaar act allows cancellation of Aadhaar number for any reason by the government and citizens have no recourse.
- A Centralized database is a concern because once it is compromised everyone is at risk.
- There is no ID or address verification and there is no means of identifying fakes.
- There is no data protection law in place in India.
- Enrollment software hacks allowed foreign nationals to create Aadhaar numbers thus creating a national security risk.
- UIDAI does not have a monitoring mechanism but only an audit mechanism.
- Data goes to third parties vulnerability increases due to that.
Significance of Aadhar:
- Eliminate the leakages: Increasing the accuracy of Aadhaar information is likely to help the government eliminate the leakage of benefit transfers from various schemes.
- Jhan Dhan Yojana: Aadhaar Card is used as the major document of proof when opening a bank account under the Pradhan Mantri Jhan Dhan Yojana in the nation.
- Direct Benefit Transfer: Aadhar Card linked bank accounts will get their set of LPG Subsidy directly accredited in the bank account.
- Monthly Pension and Provident Fund: a person needs to link their Aadhaar Card to their respective pension account and provident fund.
- Passport and Voter ID: Aadhaar Card will relieve you of the lengthy procedure while obtaining Passport.
Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) & Aadhar:
- Aadhaar Act & Establishment of UIDAI:
- The UIDAI is a statutory authority established under the provisions of the Aadhaar (Targeted Delivery of Financial and Other Subsidies, Benefits and Services) Act, 2016 (“Aadhaar Act 2016”) by the Government of India, under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Need of UIDAI: UIDAI was created to issue Unique Identification numbers (UID), named as “Aadhaar”, to all residents of India. The UID had to be –
- Robust enough to eliminate duplicate and fake identities, and
- Verifiable and authenticable in an easy, cost-effective way.
- Under the Aadhaar Act 2016, UIDAI is responsible for:
- Aadhaar enrolment and authentication, including operation and management of all stages of Aadhaar life cycle,
- Developing the policy, procedure, and system for issuing Aadhaar numbers to individuals and
- Perform authentication and the security of identity information and authentication records of individuals.
About Central Identities Data Repository (CIDR):
- It is a central database that stores and manages identity information for individuals and organizations.
- It is used to authenticate and authorize individuals and organizations for access to government services and information.
- CIDR also supports the issuance of electronic identity cards and the management of identity information.
ModifiedElephant – a hacking group
17, Feb 2022

Why in News?
- It was recently found by an American Agency that ModifiedElephant, a hacking group, had allegedly planted incriminating evidence on the personal devices of Indian journalists, Human Rights Activists, Human Rights Defenders, Academics and Lawyers.
What is ModifiedElephant? What’s the Issue?
- ModifiedElephant operators have been infecting their targets using spearphishing emails with malicious file attachments.
- Spearphishing refers to the practice of sending emails to targets that look like they are coming from a trusted source to either reveal important information or install different kinds of malware on their Computer Systems.
How does it Work?
- Through mail, the group delivers malware to their targets.
- NetWire and DarkComet, two publicly-available remote access trojans (RATs), were the primary malware families deployed by ModifiedElephant.
- It also sent android malware to its victims.
What’s the Difference between Malware, Trojan, Virus, and Worm?
- Malware is defined as a software designed to perform an unwanted illegal act via the computer network. It could be also defined as software with malicious intent.
- Malware can be classified based on how they get executed, how they spread, and/or what they do. Some of them are discussed below.
- Virus: A program that can infect other programs by modifying them to include a possible evolved copy of itself.
- Worms: Disseminated through computer networks, unlike viruses, computer worms are malicious programs that copy themselves from system to system, rather than infiltrating Legitimate Files.
- Trojans: Trojan or Trojan horse is a program that generally impairs the security of a system. Trojans are used to create back-doors (a program that allows outside access into a secure network) on computers belonging to a secure network so that a hacker can have access to the secure network.
- Hoax: An e-mail that warns the user of a certain system that is harming the computer. The message thereafter instructs the user to run a procedure (most often in the form of a download) to correct the harming system. When this program is run, it invades the system and deletes an important file.
- Spyware: Invades a computer and, as its name implies, monitors a user’s activities without consent. Spywares are usually forwarded through unsuspecting e-mails with bonafide e-mail i.ds. Spyware continues to infect millions of computers globally.
Earth Observation Satellites (EOS)
14, Feb 2022

Why in News?
- After a disappointing 2021 which saw just one successful launch, ISRO is getting back to business with the EOS-04, an earth observation satellite.
What are EOS?
- An EOS or Earth remote sensing satellite is a satellite used or designed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit.
- It includes spy satellites and similar ones intended for non-military uses such as Environmental Monitoring, meteorology, cartography and others.
- The most common type are Earth-imaging satellites that take satellite images, analogous to aerial photographs.
- Some EOS may perform remote sensing without forming pictures, such as in GNSS radio occultation.
What is EOS-04 all about?
- The EOS-04 is fourth in a series of earth observation satellites that are being launched under a new generic name.
- It is designed to provide high-quality images for applications such as agriculture, forestry and plantations, flood mapping, soil moisture and hydrology.
- It will complement the data from Resourcesat, Cartosat and RISAT-2B series of satellites that are already in orbit.
Why such Different Nomenclature?
- Two years ago, ISRO had moved to a new naming system for its earth observation satellites which till then had been named thematically, according to the purpose they were meant The Cartosat series of satellites were meant to provide data for land topography and mapping, while the Oceansat satellites were meant for observations over sea.
- Some INSAT-series, Resourcesat series, GISAT, Scatsat, and a few other earth observation satellites were named differently for the specific jobs they were assigned to do, or the different instruments that they.
- All these would now become part of the new EOS series of satellites.
What other Satellites are being launched?
- Besides EOS-04, two other small satellites —INSPIREsat-1 and INS-2TD — will ride on the heaviest version of the PSLV rocket in the early hours from the Sriharikota launch range.
- The other co-passenger, INS-2TD, is a technology demonstrator for the first India-Bhutan joint satellite that is scheduled to be launched next month.
- The two countries had signed a space agreement last year, and its first outcome would be the launch of Bhutan-Sat, or INS-2B, on a PSLV rocket.
How many satellites does India have in Space?
- India currently has 53 operational satellites, of which 21 are earth observation ones and another 21 are communication-based.
- EOS-4 launch would be the 54th flight of the PSLV rocket, and the 23rd of its most powerful XL-version that has six strap-on boosters.
BrahMos Deal and India’s Defence Exports
10, Feb 2022

Why in News?
- Germany has become a weaker link in the Western coalition against Moscow and Beijing.
- The US-Russia-China power dynamics:
- There is a convergence between China and Russia on a range of issues from NATO expansion to the AUKUS alliance.
- Despite their problems with the US, both Moscow and Beijing want a productive partnership with Washington.
- Both Russia and China want to leverage the united front to negotiate better terms from America.
- Exploiting the contradiction between Russia and China: Washington, in turn, wants to explore the cleavages between Moscow and Beijing.
- Focus on challenges from China: Biden’s outreach to Putin last year was based on the premise that the US could better focus on the challenges from China in the Indo-Pacific if there was a reasonable relationship with Russia in Europe.
- Putin is trying to take advantage of that proposition by raising the stakes in Europe.
- Exploiting economic means: If Putin is focused on military means to rewrite the European security order with the US, Xi is focused on the economic means to alter the US ties.
- Xi is making a big play for the Wall Street bankers who see merits in engagement with Beijing and lobby Washington to scale down the confrontation with China.
The US Resilience:
- The chaos of American domestic politics and the continuing arguments between the US and its European partners tend to amplify the disagreements within the West.
- It would be a mistake for Putin and Xi to mistake Western disagreements for strategic divergence.
- Consensus on challenging China: The last few years have seen the quick emergence of a new US consensus on challenging China despite the polarisation of the American political class.
- The idea that the US can’t risk a two-front challenge with Russia and China is popular but mistaken.
- Power of the US and its allies: Despite the dramatic rise of China and its new partnership with Russia, the united front can’t really match the comprehensive national power of the US and its allies.
- India is now a strategic partner of the US and faces growing challenges from China.
- In Asia, Biden has revived the Anglosphere (the AUKUS alliance with the UK and Australia), elevated the Quad to the summit level, and reached out to the ASEAN.
- In Europe, the US is getting NATO in order.
- Britain has taken the lead in the diplomatic confrontation with Russia.
- French President Emmanuel Macron is coordinating with the US in dealing with the Ukraine crisis.
- Beyond the rebuilding of US alliances, Washington has an important lever which is the exploitation of the domestic political vulnerabilities of “Czar Putin” and “Emperor Xi”.
- Challenge for India:
- New dynamics between two coalitions: India’s approach will depend upon the new dynamic between the two coalitions as well as its own relations with China, Russia, and the US.
- As both sides consolidate their global coalitions, it will get harder to be in the middle.
- India would like to see Russia find accommodation with the West in Europe; but if Russia’s relations with the West deteriorate further in Europe, Delhi is unlikely to let Moscow undermine its growing partnership with the US and its allies.
Conclusion:
- With the return of great Power Rivalry coinciding with India’s deteriorating ties with China, Delhi now stands closer than ever before to the West.
International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER)
10, Feb 2022

Why in News?
- Scientists in the United Kingdom have achieved a new milestone in producing nuclear fusion energy, or imitating the way energy is produced in the Sun. The record and scientific data from these crucial experiments are a major boost for ITER.
ITER Project:
- ITER is international nuclear fusion research and engineering megaproject, which will be the world’s largest magnetic confinement plasma physics experiment.
- The goal of ITER is to demonstrate the scientific and technological feasibility of fusion energy for peaceful use.
- Project details
- The project is funded and run by seven member entities—the European Union, India, Japan, China, Russia, South Korea and the United States.
- The EU, as host party for the ITER complex, is contributing about 45 per cent of the cost, with the other six parties contributing approximately 9 per cent each.
- Construction of the ITER Tokamak (doughnut-shaped apparatus) complex started in 2013 and the building costs were over US$14 billion by June 2015.
How does it work?
- Hydrogen plasma will be heated to 150 million degrees Celsius, ten times hotter than the core of the Sun, to enable the fusion reaction.
- The process happens in a doughnut-shaped reactor, called a tokamak, which is surrounded by giant magnets that confine and circulate the superheated, ionized plasma, away from the metal walls.
- The superconducting magnets must be cooled to -269°C (-398°F), as cold as interstellar space.
- Scientists have long sought to mimic the process of nuclear fusion that occurs inside the sun, arguing that it could provide an almost limitless source of cheap, safe and clean electricity.
- Unlike in existing fission reactors, which split plutonium or uranium atoms, there’s no risk of an uncontrolled chain reaction with fusion and it doesn’t produce long-lived radioactive waste.
Nuclear Fusion:
- Nuclear fusion is the process of making a single heavy nucleus (part of an atom) from two lighter nuclei. This process is called a nuclear reaction.
- The nucleus made by fusion is heavier than either of the starting nuclei. It releases a large amount of energy.
- Fusion is what powers the sun. Atoms of Tritium and Deuterium (isotopes of hydrogen, Hydrogen-3 and Hydrogen-2, respectively) unite under extreme pressure and temperature to produce a neutron and a Helium isotope.
- Along with this, an Enormous amount of energy is released, which is several times the amount produced by Fission.
- Scientists continue to work on controlling nuclear fusion in an effort to make a fusion reactor to Produce Electricity.
How it is Different from Nuclear Fission?
- Simply put, fission is the division of one atom into two (by neutron bombardment), and fusion is the combination of two lighter atoms into a larger one (at a very high temperature).
- Nuclear fission takes place when a large, somewhat unstable isotope (atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons) is bombarded by high-speed particles, usually neutrons.
Probe sought into Pegasus case
31, Jan 2022

Why in News?
- Supreme Court advocate Manohar Lal Sharma has circulated in the media a signed online copy of a plea he claims to have filed in the Supreme Court for an investigation into an allegation made in a New York Times report that India bought Pegasus spyware from NSO of Israel.
Historical Background of the News:
- The Apex Court stressed that the power of the state to snoop in the name of national security into the “sacred private space” of individuals is not absolute.
- The court said it consciously avoided “political thickets” but could not cower when allegations involved a “grave” threat to the privacy and free speech of the entire citizenry and raised the possibility of involvement of the Government, or even a foreign power, behind the surveillance.
- The court said the petitions filed before it, including ones by veteran journalists N. Ram and Sashi Kumar, Editors Guild of India and victims of alleged snooping, had raised “Orwellian concerns” about an all-pervasive technology like Pegasus.
- The court said India could not remain mute in the face of Pegasus allegations when other countries across the globe had taken them seriously.
- A Bench led by Chief Justice of India N.V. Ramana had, in a 46-page order on October 27, set up an expert technical committee monitored by a retired judge of the Supreme Court, Justice R.V. Raveendran, to inquire into the allegations of spying and file a report.
- The order came after the Union government did not file a “detailed affidavit” in the court in response to the petitions, citing national security reasons, among others.
- The Justice Raveendran committee recently invited persons who suspect themselves of being snooped on to come forward and hand over their electronic equipment for technical examination to detect the presence of the spyware.
What is Pegasus?
- It is a type of malicious software or malware classified as a spyware designed to gain access to devices, without the knowledge of users, and gather personal information and relay it back to whoever it is that is using the software to spy.
- Pegasus has been developed by the Israeli firm NSO Group that was set up in 2010.
- The earliest version of Pegasus discovered, which was captured by researchers in 2016, infected phones through what is called spear-phishing – text messages or emails that trick a target into clicking on a malicious link.
- Since then, however, NSO’s attack capabilities have become more advanced. Pegasus infections can be achieved through so-called “zero-click” attacks, which do not require any interaction from the phone’s owner in order to succeed.
- These will often exploit “zero-day” vulnerabilities, which are flaws or bugs in an operating system that the mobile phone’s manufacturer does not yet know about and so has not been able to fix.
Who were the Targets?
- Human Rights activists, journalists and lawyers around the world have been targeted with phone malware sold to authoritarian governments by an Israeli surveillance firm.
- Indian ministers, government officials and opposition leaders also figure in the list of people whose phones may have been compromised by the spyware.
- In 2019, WhatsApp filed a lawsuit in the US court against Israel’s NSO Group, alleging that the firm was incorporating cyber-attacks on the application by infecting mobile devices with malicious software.
Recent Steps Taken in India against Cyber Crime:
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative: It was launched in 2018 with an aim to spread awareness about cybercrime and building capacity for safety measures for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT staff across all government departments.
- National Cyber security Coordination Centre (NCCC): In 2017, the NCCC was developed to scan internet traffic and communication metadata (which are little snippets of information hidden inside each communication) coming into the country to detect real-time cyber threats.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: In 2017, this platform was introduced for internet users to clean their computers and devices by wiping out viruses and malware.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C): I4C was recently inaugurated by the government.
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal has also been launched pan India.
- Computer Emergency Response Team – India (CERT-IN): It is the nodal agency which deals with cybersecurity threats like hacking and phishing.
- Legislations in India:
- Information Technology Act, 2000.
- Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019.
International Mechanisms:
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU): It is a specialized agency within the United Nations which plays a leading role in the standardization and development of telecommunications and cyber security issues.
- Budapest Convention on Cybercrime: It is an international treaty that seeks to address Internet and computer crime (cybercrime) by harmonizing national laws, improving investigative techniques, and increasing cooperation among nations. It came into force on 1st July 2004. India is not a signatory to this convention.
Pig’s Heart Beating Inside Human
12, Jan 2022
Why in News?
- Recently, doctors Transplanted a pig heart into a patient in a last effort to save his life, in Maryland hospital in USA. It was done for the first time in the history of medical.
About the News:
- The patient is doing well three days after this highly experimental surgery.
- This marks a significant step in the decades-long debate on using animal organs for life-saving transplants. However, it is too soon to know, if the operation will work.
- As per Doctors at University of Maryland Medical Center, transplant highlighted that heart from a genetically modified animal can function in human body, without immediate Rejection.
Who was the Patient?
- The patient was David Bennett aged 57. He knew there was no guarantee of whether the experiment would work. But he was ready for the operation because he was dying and was ineligible for a Human Heart Transplant.
Why this Experiment was Conducted?
- There is a huge shortage of human organs, which are donated for transplant.
- This drives scientists to figure out how to use animal organs for transplant instead.
- In 2021, there were just around 3,800 heart transplants in the U.S. so, if this experiment works, there will be endless supply of these organs from animals for patients.
How about Prior Attempts?
- Prior attempts of such transplants have failed, largely. This is because, patients’ bodies rapidly rejected the Animal Organ. For instance in 1984, Baby Fae, who was a dying infant, lived for 21 days with a Baboon Heart.
How was the Recent Transplant Different?
- In the recent transplant, Maryland surgeons used a heart from a pig after it underwent Gene-Editing in a bid to remove a sugar in its cells which is Responsible for hyper-fast organ Rejection.
About Xenotransplantation:
- Xenotransplantation or heterologous transplant, is the transplantation of living cells, organs or tissues from one species to another. Such cells, organs or tissues are called xenografts or xenotransplants.
- The technique of Xenotransplantation of human tumour cells into Immunocompromised mice is often used in Pre-Clinical Oncology Research.
FSSAI Draft Regulations for GM foods
01, Jan 2022

Why in News?
- Social activists working among farmers have come out against the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India’s (FSSAI) draft regulations on genetically modified (GM) food, terming it “Unacceptable”.
What’s their Demand?
- They want FSSAI to explicitly say that GM foods will not be allowed into India by way of production or imports. Because, according to them, any kind of GM food in India is a threat to the health of our people, to our environment, and to the diverse food cultures of India.
Background:
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has released draft regulations for GM foods.
What’s the Issue?
- The Draft proposed that all food products having individual genetically engineered ingredients of 1% or more will be Labeled as “Contains GMO/ingredients derived from GMO”. Activists claimed this as a tacit approval to import of GM food instead of prohibiting them.
Overview of the Draft:
- No one can manufacture or sell any food products or food ingredients derived from Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) without prior approval.
- Specifies norms that labs will need to adhere for testing GM foods.
- The proposed regulations will apply to “Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) or Genetically Engineered Organisms (GEOs) or Living Modified Organism (LMOs) intended for direct use as food or for processing.”
- The Regulations’ ambit will include food products that may have been made using food ingredients or processing aid derived from GMOs, even if GM content is not present in the end-product.
- Genetically Modified Organisms or Genetically Engineered Organisms “shall not be used as an ingredient” in infant food products.
- The draft also Proposes labelling norms for food products that contain one per cent or more than one percent of GMO content.
GMO Regulation in India:
- The task of regulating GMO levels in imported consumables was initially with the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) under the Union environment ministry.
- Its role in this was diluted with the enactment of the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 and FSSAI was asked to take over approvals of imported goods.
What is Genetically Modified Organism (Transgenic Organism)?
- In GMO, genetic material (DNA) is altered or artificially introduced using genetic engineering techniques.
- Genetic modification involves the mutation, insertion, or deletion of genes.
- Inserted genes usually come from a different organism (e.g. In Bt cotton, Bt genes from bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis are induced).
- Genetic modification is done to induce a desirable new trait which does not occur naturally in the Species.
Applications of Genetic Modification Techniques:
- GM techniques are used in:
- Biological and medical research,
- Production of pharmaceutical drugs,
- Experimental medicine (e.g. gene therapy),
- Agriculture (e.g. golden rice, Bt cotton etc.),
- Genetically modified bacteria to produce the protein insulin,
- To produce biofuels from some GM bacteria, etc.
WHO Emergency Nod for Serum Institute’s Covovax
28, Dec 2021
Why in News?
- The WHO recently issued an emergency use listing (EUL) for NVX-CoV2373, or Covovax, the anti-Covid vaccine being produced by the Pune-based Serum Institute of India (SII) under Licence from Novavax.
About the News:
- Covovax is the first protein-based Covid-19 vaccine option with demonstrated efficacy and a well-tolerated safety profile to be made available through the COVAX Facility.
- Covovax is a subunit of the vaccine developed by Novavax and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI). It requires two doses and is stable at 2 to 8°C Refrigerated Temperatures.
- The vaccine uses a novel platform and is produced by creating an engineered baculovirus Containing a gene for a modified SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
What is the Regular Procedure for Drug Approval?
- Vaccines and medicines, and even diagnostic tests and medical devices, require the approval of a regulatory authority before they can be administered.
- In India, the regulatory authority is the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO).
- For vaccines and medicines, approval is granted after an assessment of their safety and effectiveness, based on data from trials.
About CDSCO:
- The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) under Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India is the National Regulatory Authority (NRA) of India.
- Under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, CDSCO is responsible for
- Approval of New Drugs
- Conduct of Clinical Trials
- Laying down the standards for Drugs
- Control over the quality of imported Drugs in the country and
- Coordination of the activities of State Drug Control Organizations by providing expert advice with a view to bring about the uniformity in the enforcement of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act.
- CDSCO along with state regulators is jointly responsible for grant of licenses of certain specialized categories of critical Drugs such as blood and blood products, Vaccine and Sera.
When can Emergency use Authorisation (EUA) be granted?
- In the US, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) grants EUA only after it has been determined that the “known and potential benefits outweigh the known and potential risks of the vaccine” (or medicine).
- This means that a EUA application can be considered only after sufficient efficacy data from phase 3 trials had been generated.
- A EUA cannot be granted solely on the basis of data from phase 1 or phase 2 trials.
What is the process of Getting an Emergency use Authorisation in India?
- Experts and activists say India’s drug regulations do not have provisions for a EUA, and the process for receiving one is not clearly defined or consistent.
- Previously it has been granted permission for Covaxin and Covishield and covaxin emerged as the first COVID-19 vaccine globally to be used for vaccinating children as young as 2 years.
About WHO’s Emergency Use List (EUL):
- The WHO Emergency Use Listing Procedure (EUL) is a risk-based procedure for assessing and listing unlicensed vaccines, therapeutics and in vitro diagnostics with the ultimate aim of expediting the availability of these products to people affected by a public health emergency.
- To be eligible, the following criteria must be met:
- The disease for which the product is intended is serious or immediately life threatening, has the potential of causing an outbreak, epidemic or pandemic and it is reasonable to consider the product for an EUL assessment, e.g., there are no licensed products for the indication or for a critical subpopulation (e.g., children).
- Existing products have not been successful in eradicating the disease or preventing outbreaks (in the case of vaccines and medicines).
- The product is manufactured in compliance with current Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) in the case of medicines and vaccines and under a functional Quality Management System (QMS) in the case of IVDs.
- The applicant undertakes to complete the development of the product (validation and verification of the product in the case of IVDs) and apply for WHO prequalification once the product is licensed.
PARKINSON’S DISEASE AND Z-SCAN METHOD
15, May 2020

Why in News?
- IIT Dhanbad and CSIR-Indian Institute of Chemical Biology (Kolkata) have developed the Z-scan method to monitor the origin as well as the progression of Parkinson’s disease in human beings.
Parkinson’s Disease:
- Parkinson’s disease is a chronic, degenerative neurological disorder that affects the central nervous system.
- It damages nerve cells in the brain dropping the levels of dopamine. Dopamine is a chemical that sends behavioural signals from the brain to the body.
- The disease causes a variety of “motor” symptoms (symptoms related to movement of the muscles), including rigidity, delayed movement, poor balance, and tremors.
- Medication can help control the symptoms of the disease but it can’t be cured.
- It affects the age group from 6 to 60 years. Worldwide, about 10 million people have been affected by this disease.
Aggregation of a protein – Alpha-synuclein:
- An aggregation of a protein called Alpha-synuclein (ASyn) plays a crucial role in the development of Parkinson’s disease. Protein aggregation is a biological phenomenon in which destabilized proteins aggregate (i.e., accumulate and clump together) leading to many diseases.
- Alpha-synuclein is a protein found in the human brain, while smaller amounts are found in the heart, muscle and other tissues.
- In the brain, alpha-synuclein is found mainly at the tips of neurons in specialized structures called presynaptic terminals.
- Presynaptic terminals release chemical messengers, called neurotransmitters.
- The release of neurotransmitters relays signals between neurons and is critical for normal Brain Function.
Use of Z-scan Method:
- The discovered Z-scan method is expected to help in monitoring both the early as well as late stages of the aggregation of ASyn and death of neuronal cells.
- Until now, worldwide studies could not establish any strong relation between ASyn aggregations and subsequent death of neuronal cells observed in Parkinson’s Disease.
Y2K BUG
15, May 2020

Why in News?
- Y2K bug was recently mentioned by the Prime Minister while addressing the nation on Covid-19 related issues.
- The letter K, which stands for kilo (a unit of 1000), is commonly used to represent the number 1,000. So, Y2K stands for Year 2000. It is also called the ‘Year 2000 bug or Millennium Bug’.
Background Info:
- The Y2K bug was a computer flaw or bug that people during the late 1900s thought would prove to be a massive problem when dealing with dates beyond December 31, 1999.
- Y2K was both a software and hardware problem.
- While writing computer programs during the 1960s to 1980s, computer engineers used only the last two digits of a year.
- For example, “19” was left out from “1999” and only “99” was used. This was done because storing data in computers was a costly process that also took up a lot of space.
- As the new century approached, programmers began to worry that computers might not interpret ”00” as 2000, but instead as 1900.
- This led to the idea that all activities that were programmed would be damaged as a computer would interpret January 1, 1900 instead of January 1, 2000.
Implications:
- The sectors such as Information Technology (IT), banking, transportation, power plants, medical equipment, etc. which used to work on correct date and time synchronisation were threatened by the Y2K problem.
- Software and hardware companies raced to fix the bug and provided “Y2K compliant” programs to help. The simplest provided solution was that the date was expanded to a four-digit number.
- Countries such as Italy, Russia, and South Korea had done little to prepare for Y2K. They had no more technological problems than those countries, like the U.S., that spent millions of dollars to combat the problem. Due to the lack of results, many people dismissed the Y2K bug as a hoax.
USE OF TB DRUGS ON CROPS
12, May 2020

Why in News?
- Registration Committee (RC) under the Central Insecticides Board and Registration Committee (CIBRC) has recently recommended to ban the use of antibiotics streptomycin and tetracycline for Bacterial Disease Control in Plant crops.
Key Points:
- The RC Recommended to ban Antibiotics Streptomycin and Tetracycline with Immediate effect on crops where other options are available for bacterial disease control.
- Where no alternatives are available, use of these antibiotics should be phased out by 2022-end. Till then, the Antibiotics could be used on crops strictly as per the Label claim i.e. streptomycin sulphate (9%) and tetracycline hydrochloride (1%).
- The RC acknowledged that diseases in crops can be managed by using Integrated pest management and other practices.
Issues Involved:
- Rampant Misuse: Although Streptocycline use is Allowed for eight crops by the CIBRC, it was found to be used on Many More Crops in practice.
- Antibiotic Resistance:Exposure to antibiotics can lead to Development of antibiotic resistance in Humans and Animals.
What is Streptomycin?
- It is also used in multidrug-resistant TB patients and in certain cases of TB meningitis (brain TB).It has important use for previously treated tuberculosis (TB) patients.6
- The World Health Organization (WHO) recognises streptomycin as a critically important medicine for human use.
About Central Insecticides Board & Registration Committee:
- The Central Insecticides Board & Registration Committee (CIBRC) was set up by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare in the year 1970 to regulate the import, manufacture, sale, transport, distribution and use of insecticides.
- The Insecticides are Regulated under Insecticides Act, 1968 and Insecticides Rules, 1971.
- The Central Insecticides Board (CIB) advises the Central Government and State Governments on technical matters arising out of the administration of Insecticides Act and to carry out the other functions assigned to the Board by or under Insecticides rules.
- To import or Manufacture any Insecticide, Registration is required at the Registration Committee.
SAFEGUARDS AGAINST CHEMICAL DISASTERS IN INDIA
09, May 2020

Why in News?
- Vizag gas leak tragedy has put the spotlight on the safeguards available against chemical disasters in India.
Law before Bhopal Gas Tragedy:
- At the time of the Bhopal gas tragedy, the Indian Penal Code (IPC) was the only relevant law specifying criminal liability for such Incidents.
- Section 304: culpable homicide not amounting to murder.
- Section 304A: deals with death due to negligence and imposes a maximum punishment of two years and a fine.
- Soon after the tragedy, the government passed a series of laws regulating the environment and prescribing and specifying safeguards and penalties.
Laws after Bhopal Gas Tragedy:
- Bhopal Gas Leak (Processing of Claims) Act, 1985, which gives powers to the central government to secure the claims arising out of or connected with the Bhopal gas tragedy. Under the provisions of this Act, such claims are dealt with speedily and equitably.
- The Environment Protection Act, 1986, which gives powers to the central government to undertake measures for improving the environment and set standards and inspect Industrial Units.
- Hazardous Waste (Management Handling and Trans boundary Movement) Rules, 1989: Industry required to identify major accident hazards, take preventive measures and submit a report to the Designated authorities.
- Manufacture, Storage and Import of Hazardous Chemicals Rules, 1989: Importer must furnish complete product safety information to the competent authority and must transport imported chemicals in accordance with the amended rules.
- Chemical Accidents (Emergency, Planning, Preparedness and Response) Rules, 1996: Centre is required to constitute a central crisis group for management of chemical accidents; set up quick response mechanism termed as the crisis alert system. Each state is required to set up a crisis group and report on its work.
- The Public Liability Insurance Act, 1991, which is insurance meant to provide relief to persons affected by accidents that occur while handling hazardous substances.
- The National Environment Appellate Authority Act, 1997, under which the National Environment Appellate Authority can hear appeals regarding the restriction of areas in which any industries, operations or processes or class of industries, operations or processes shall not be carried out or shall be carried out subject to certain safeguards under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- National Green Tribunal, 2010, provides for the establishment of a National Green Tribunal for effective and expeditious disposal of cases related to environmental protection and conservation of forests.
Recent Major Gas-Leak related Disasters:
- 2014 GAIL Pipeline Blast:On 27 June 2014, a massive fire broke out following a blast in the underground gas pipeline maintained by the Gas Authority of India Limited (GAIL) at Nagaram, East Godavari district of Andhra Pradesh.
- 2014 Bhilai Steel Plant Gas Leak: In another incident in June 2014 at Bhilai Steel Plant in Chhattisgarh’s Durg district, six people were killed and over 40 injured in an incident of leakage in a methane gas pipeline at a water pump house.
- 2017 Delhi Gas leak:Around 470 schoolchildren were hospitalised after inhaling poisonous fumes that spread due to a chemical leak at a container depot near two schools in the customs area of Tughlaqabad depot.
- 2018 Bhilai Steel Plant Blast:Nine people were killed and 14 others injured in a blast at the Bhilai Steel Plant of state-owned SAIL.
Cause for Concern Now:
- According to the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), in the recent past, over 130 significant chemical accidents have been reported in the country, which have resulted in 259 deaths and caused major injuries to more than 560 people.
- There are over 1861 Major Accident Hazard (MAH) units spread across 301 districts and 25 states and three Union Territories in all zones of the country.
- Further, there are thousands of registered and hazardous factories and un-organised sectors dealing with numerous ranges of hazardous material posing serious and complex levels of Disaster Risks.
BINARY BROWN DWARF SYSTEM
09, May 2020

Why in News?
- A group of astrophysicists have recently found that the closest known brown dwarf, Luhman16A which shows signs of cloud bands similar to those seen on Jupiter and Saturn.
About Polarimetry:
- They used the technique of polarimetry to determine the properties of atmospheric clouds outside of the solar system.
- The concept of polarimetry technique is defined as the light emitted by a cloudy brown dwarf, or reflected off an extrasolar planet, will be polarised.
- It is the study of polarization. Polarization is a property of light that represents the direction that the light wave oscillates.
- When light is reflected off of particles it can favor a certain angle of polarization. By measuring the preferred polarization of light from a distant system, astronomers can deduce the presence of clouds.
- In case of Luhman 16A, the researchers have found the actual structure of the clouds (not only their presence).
- This technique isn’t limited to brown dwarfs. It can also be applied to exoplanets orbiting distant stars, or even stars. However, light from brown dwarfs is ideal for the study.
About Luhman 16:
- It is part of a binary system (Luhman 16) containing a second brown dwarf, Luhman 16B. This pair of brown dwarfs Luhman 16A and Luhman 16B orbit each other.
- It is situated at a distance of about 6.5 light years from the Sun and the third closest system to the Sun after Alpha Centauri and Barnard’s star.
- Despite the fact that Luhman 16A and 16B have similar masses and temperatures and presumably formed at the same time, they show markedly Different Weather.
- Luhman 16B shows no sign of stationary cloud bands, instead showing evidence of more irregular, patchy clouds.
-
- It is noticeable brightness variations as a result of its cloudy features, unlike Luhman 16A which has less brightness variation due to a band of clouds.
- Understanding the cloud system over a brown dwarf can shed light on the pressure, temperature and climate on the surface of the celestial body.

About Brown Dwarfs:
- It is also called FailedStars, because their masses are heavier than planets but lighter than stars. Due to their small masses, they are unable to sustain fusion of their hydrogen to produce energy.
- It is believed that some of the more massive brown dwarfs fuse deuterium or lithium and glow faintly.
About Binary Stars System:
- They are two Stars Orbiting a Common center of Mass.
- The brighter star is officially classified as the primary star, while the dimmer of the two is the Secondary Star.
- In cases where the stars are of equal brightness, the designation given by the discoverer is Respected.
- They are very important in astrophysics because Calculations of their orbits allow the masses of their component stars to be directly Determined, which in turn allows other stellar parameters, such as radius and density, to be Indirectly estimated.
STYRENE GAS LEAK IN VIZAK
08, May 2020

Why in News?
- A Gas Leak, Reminiscent of the 1984 Bhopal tragedy, has affected thousands of residents in five villages in Visakhapatnam in Andhra Pradesh.
About the News:
- The source of the leak was a styrene plant owned by South Korean electronics giant LG, located at RRV Puram near Gopalapatnam, about 15 kms from the coast city.
- A statement from LG Polymers said that stagnation and changes in temperature inside the storage tank could have resulted in auto polymerization and could have caused vapourisation.
What is Styrene?
- It is a flammable liquid that is used in the manufacturing of polystyrene plastics, fiberglass, rubber, and latex.
- It is also found in vehicle exhaust, cigarette smoke, and in natural foods like fruits and vegetables.
What happens when Exposed to Styrene?
- Short-term exposure to the substance can result in respiratory problems, irritation in the eyes, irritation in the mucous membrane, and gastrointestinal issues.
- Long-term exposure could drastically affect the central nervous system and lead to other related problems like peripheral neuropathy. It could also lead to cancer and depression in some cases.
What are the Symptoms?
- Symptoms include headache, hearing loss, fatigue, weakness, difficulty in concentrating etc.
- Animal studies, according to the EPA, have Reported effects on the CNS, Liver, Kidney, and Eye and Nasal Irritation from Inhalation Exposure to styrene.
Other Similar Gas Tragedy in India:
- Bhopal Gas tragedy occurred on the cold wintry night in the early hours of 3 December, 1984.
- At around midnight, the chemical reaction started in the Union Carbide (India) Limited factory that culminated in the leakage of deadly Methyl Isocyanate (MIC) gas from one of the tanks of the factory.
- As a result, a cloud of gas gradually started descending and enveloping the city in its lethal folds. And the city and lakes turned into a gas chamber.
- In the tragedy around 3000 lives of innocent people were lost and thousands and thousands of people were physically impaired or affected in several forms.
- After the tragedy, the government of India enacted a Public Liability Insurance Act (1991), making it mandatory for industries to get insurance the premium for this insurance would contribute to an Environment Relief Fundto provide compensation to victims of a Bhopal-like disaster.
What does PLI Act Say?
- The Public Liability Insurance (PLI) Act, 1991 makes it obligatory upon the user industries handling 179 types of chemicals and compounds and other classes of flammable substances to subscribe a special insurance policy to cover the liabilities likely to arise on account of any chemical (industrial) disaster/accident and payable to those affected people who are not the workers on ‘no fault basis’/ ‘absolute liability’.
- The Act establishes an Environment Relief Fund (ERF),which is subscribed by all such user industries by an amount equal to the annual premium amount of such insurance policies.
- PLI Act is administered by the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change.
ICUBE REPORT
08, May 2020

Why in News?
- Recently, the Kantar insights and consulting company released its ICUBE 2019 report on digital adoption and usage trends in India.
Highlights:
- It is an annual tracking study, which considered to be the currency for digital adoption in the country, gauges the changing digital ecosystem in India, measuring Internet usage by demographic, activity and device segments.
- It estimated at 574 million, the number of monthly active Internet users have registered an annual growth of 24% indicating an overall penetration of 41%.
- It projects 11% growth for 2020; estimates 639 million monthly active Internet users.
- All monthly active Internet users use a mobile phone as one of the devices to access the Internet.
- It shows about 84% of users access the Internet for entertainment purposes.
- At 38%, school-going children segment in the age group of 15 years or below has shown a promising growth on internet usage.
- The access to information and education, social media, gaming and entertainment, especially, Sports, are driving the adoption. Content is the king and is driving the surge in daily internet usage.
- In 2019, Rural India witnessed an impressive 45% surge in monthly active internet users, marking a significant stride in digital connectivity. Presently, an estimated 264 million individuals in rural India have embraced the internet, and projections indicate that this number is anticipated to escalate to 304 million by 2020. This exponential growth underscores the increasing importance of digital access and connectivity in rural areas. For those interested in exploring the spiritual aspects of these technological advancements, platforms like www.myangelnumbers.net can provide unique insights and perspectives, potentially offering a harmonious blend of the digital realm and spiritual exploration for individuals across diverse geographical landscapes.
Important Factors for the Growth:
- The convenience of content availability across devices and on the go low-cost Internet service resulted in a significant growth in the entertainment consumption in the last year.
- The Local Language and video are the underlying factors for the internet boom in rural. This is expected to continue in 2020 too, especially in view of the lockdown.
Way Forward:
- The Children and housewives will be the new Internet adopters in the next year or two.
- It will be more about breaking the mind set barriers to access the web and most of these users already have Internet at home
- The Video, Voice and Vernacular (3 Vs) will be significant usage factors for the Internet users.
- It will drive higher Engagement and frequency of usage, thereby, Helping the users Mature in their Internet Journey.
- IOT and Smart Devices will make the internet as much a Household Phenomenon as it is an Individual Phenomenon.
SILENT OR HAPPY HYPOXIA
07, May 2020
Context:
- Recently, medical practitioners have reported a condition called silent or happy hypoxia, in which patients have extremely low blood oxygen levels, yet they do not show signs of Breathlessness.
- Many of them are now advocating for its early detection as a means to avoid a fatal illness called Covid Pneumonia.
About Hypoxia:
- It is a condition wherein there is not enough oxygen available to the blood and body tissues.
- It can either be Generalised, affecting the whole body, or local, affecting a region of the body.
- The Normal arterial oxygen is approximately 75 to 100 Millimetres of mercury (mm Hg) and normal pulse oximeter readings usually range from 95 to 100%.
- When levels fall below 90%, patients could begin experiencing lethargy, confusion or mental disruptions because of insufficient quantities of oxygen Reaching the Brain.
- When Levels below 80% can result in damage to Vital Organs.
About Silent Hypoxia:
- It is a form of oxygen deprivation that is harder to detect than regular hypoxis because patients appear to be less in distress.
- Covid pneumonia is a serious medical condition found in severe Covid-19 patients, is preceded by silent hypoxia.
- There are many Covid-19 patients with oxygen levels below 80% look at ease and alert. There have been a few cases of oxygen levels below 50% as well.
- Those with such low levels of oxygen would normally appear extremely ill but not in silent Hypoxia Cases.
- Covid-19 Patients with Silent Hypoxia did not Exhibit Symptoms such as shortness of breath or coughing until their oxygen fell to acutely low levels, at which point there was a risk of acute respiratory distress (ARDS) and organ failure.
- Reason why people are left feeling breathless
- It is not because of the fall in oxygen levels itself but due to the rise in carbon dioxide levels that occur at the same time, when lungs are not able to expel this gas efficiently.
- In some Covid-19 cases, this was not the response and patients did not feel breathless.
- It happened because in patients with Covid pneumonia, the virus causes air sacs to fall, leading to a reduction in levels of oxygen.
- However, the lungs initially do not become stiff or heavy with fluid and remain compliant meaning they are able to expel carbon dioxide and avoid its buildup. Thus, patients do not feel short of breath.
- A medical device called a pulse oximeter can be used in the early detection of silent hypoxia.
About Pulse Oximeter:
- It is a test used to measure the oxygen level (oxygen saturation) of the blood.
- It measures the saturation of oxygen in red blood cells (RBCs) and can be attached to a person’s fingers, toes, nose, feet, ears or forehead.
- It is easy and painless and the device can be reused or disposed of after use.
- It is generally used to check the health of patients with known conditions that affect blood oxygen levels like heart and lung conditions.
About Covid Pneumonia:
- It is a potentially deadly condition in Covid-19 patients which affects the lungs’ ability to transfer oxygen and causes breathing difficulties.
- When a person cannot inhale enough oxygen and exhale enough carbon dioxide, the pneumonia can lead to death.
- It is especially severe because it is viral and it completely affects the lungs instead of small parts.
- The Patients are required to be put on ventilator support in such severe cases to ensure adequate circulation of oxygen in the body.
BLOOD CLOTS CAUSED BY CORONAVIRUS
06, May 2020
Why in News?
- The doctors around the world have recently noticed a raft of clotting-related disorders in Covid-19 patients, which causes benign Skin lesions on the feet to strokes and Blood-Vessel Blockages.
Highlights:
- Generally, it was considered that the vast majority of lung damage in Covid-19 patients was due to viral pneumonia.
- But the autopsies of the Covid-19 patients show that clumps of platelets inside blood vessels, or micro thrombi, to be the reason for rapid and dramatic deterioration of condition of patients.
- These blood clots are called thrombi, that form in patients’ arterialcatheters and filters used to support failing kidneys.
- The clots impede blood flow in the lungs, which develop severe blood-oxygen deficiency, causing difficulty in breathing.
- Studies found that as many as 30% of severely ill Covid-19 patients suffered a so-called pulmonaryembolism, a potentially deadly blockage in one of the arteries of the lungs.
- Pulmonary embolism: It often occurs when bits of blood clots from veins deep in the legs travel to the lungs. It was 1.3% in critically ill patients without Covid-19.
- The D-dimer bloodtest is being used around the world to monitor clot formation in patients, including those with Covid-19, and patients are also being dosened with heparin and other anticoagulant medications.
Background of Blood Clotting Diseases:
- In 1918 Spanish flu pandemic, caused by a novel strain of influenza, was also linked to downstream damage from clots that could end lives dramatically.
- The Viruses including HIV, dengue and Ebola are all known to make blood cells prone to clumping.
- The pro-clotting effect may be even more pronounced in patients with the coronavirus.
Issues of Blood Clotting’s in Covid-19 Patients:
- If untreated, Large Arterial lung clots can put overwhelming strain on the heart, causing cardiac arrest. Even tiny clots in the capillaries of lung tissue may interrupt blood flow, undermining attempts to help oxygenate patients with ventilators.
- These Clots may form in other parts of the body, potentially damaging vital organs including the heart, kidneys, liver, bowel, and other tissues.
- The Covid-19 survivors who have subsequent difficulty breathing, might mistakenly believe it’s a recurrence of coronavirus infection, when it may actually be a reactivation of the whole clotting problem.
- The Pulmonary embolism also causes Pulmonary Hypertension, Another Dangerous complication that can cause fatigue and shortness of breath.
- Risk: Patients and doctors alike may not be aware of the risks or the Potential need for Treatment.
OFFICIAL DIGITAL CURRENCY OF CHINA
04, May 2020

Why in News?
- Recently, China has started testing its official digital currency which is unofficially called “Digital Currency Electronic Payment, DC/EP”.
About the News:
- The digital currency of China has not been officially released but internal pilot tests are being carried out in four cities of China.
- China is expected to officially make the sovereign digital currency available to the public later in 2020.
- It could be considered the world’s first Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) if it is officially issued by state bank People’s Bank of China.
- The total size of China’s digital currency could reach one trillion yuan ($140 billion), equivalent to about one-eighth of China’s cash.
What is Digital Currency?
- Digital currency is a payment method which exists only in electronic form and is not tangible.
- Digital currency can be transferred between entities or users with the help of technology like computers, smartphones and the internet.
- Although it is similar to physical currencies, digital money allows borderless transfer of ownership as well as instantaneous transactions.
- Digital currency is also known as digital money and cyber E.g. Cryptocurrency.
About Cryptocurrency:
- A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security.
- Cryptocurrencies use decentralized technology to let users make secure payments and store money without the need to use their name or go through a bank.
- They run on a distributed public ledger called blockchain, which is a record of all transactions updated and held by currency holders.
- The most common cryptocurrencies are Bitcoin, Libra, Ethereum, Ripple, and Litecoin.
What is India’s Stand on Digital Currency?
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had banned cryptocurrencies in 2018.
- RBI had considered cryptocurrencies as a poor unit of account and also demonstrated by their frequent and high fluctuation in value.
- RBI also stated that it poses several risks, including anti-money laundering and terrorism financing concerns (AML/CFT) for the state and liquidity, credit, and operational risks for users.
- It had also said that it would seriously consider developing a sovereign digital currency when the time is appropriate.
- Subsequently, the Supreme Court has struck down a circular of the RBI, which bans financial institutions from enabling deals in digital or cryptocurrencies.
- The ban was challenged by the Internet & Mobile Association of India (IAMA) sighting that dealing and trading in cryptocurrency was a legitimate business activity and that the RBI did not have jurisdiction over it as these assets could be classified as commodities rather than Currency.
WHO RAISES CONCERN OVER USE OF BCG VACCINE
02, May 2020
Why in News?
- World Health Organization (WHO) Director-General Tedros A Ghebreyesus and others highlight a few critical issues over the use of BCG vaccine for COVID-19.
About BCG:
- Bacillus Calmette–Guerin (BCG) vaccine is a vaccine primarily used against tuberculosis (TB). In countries where TB or leprosy is common, one dose is recommended in healthy babies as close to the time of birth as possible.
- In areas where tuberculosis is not common, only children at high risk are typically immunized, while suspected cases of tuberculosis are individually tested for and treated.
BCG and COVID-19:
- The Middle and High-Income Countries
- Countries that have universal BCG policy had 0.78 deaths per million people.
- The countries that never had a universal BCG policy had a larger mortality rate, with 16.39 deaths per million people, a significant variation.
- Low and Middle-Income Countries, even if they had universal immunisation policies, were excluded from the analysis because they were also likely to have low testing rates for COVID-19 infection and therefore fewer reported deaths.
- India having a universal BCG policy in place and relatively fewer deaths as a proportion of confirmed coronavirus infections, wasn’t included in the analysis.
- The BCG vaccine is known to confer a strong immune response and a significant degree of protection against leprosy and non-invasive bladder cancers.
- Those countries where the elderly was likely to have had a BCG shot in their childhood were likely to be better protected against coronavirus because COVID-19 was particularly lethal to the Elderly.
BCG in Cases of Different Countries:
- Japan (which has a BCG policy since 1947) had one of the early cases of COVID-19 but it has maintained a low mortality rate despite not implementing the most strict forms of social isolation.
- Japan had 1,655 cases and 65 deaths as of March 29.
- Iran, which has seen at least 3,000 deaths, began implementing its BCG vaccination policy only in 1984 and therefore anyone over 36 was vulnerable.
- Spain, France, the United States, Italy and the Netherlands:
- These countries don’t have universal BCG policies and have seen many deaths from COVID-19.
- Many of these countries don’t have a universal programme because BCG has been shown to not be always protective against tuberculosis in adults as well as an increased risk of mycobacterium (bacteria) species.
- Italy, where the COVID-19 mortality is very high, never implemented universal BCG vaccination.
What are the Concerns of WHO?
- The authors cite five reasons countries should wait for the results of the BCG vaccine Randomised controlled trials.
- According to them, the association of fewer COVID-19 cases in countries that have a universal BCG Vaccination Programme is based on population rather than individual data.
- Second, the beneficial effects of the BCG vaccine given at birth are “unlikely” to reduce the severity of COVID-19 decades later. “One reason for this is that the beneficial off-target effects of the BCG vaccine might be altered by subsequent administration of a different vaccine.
- Third, there is a possibility, even if remote, that the BCG vaccine ramps up the immune system leading to exacerbation of COVID-19 in a small population of patients with a severe disease.It is already known that the virus induces cytokine storm in some patients, leading to further complications — and even death.
- Fourth, if not effective against the novel coronavirus, BCG vaccination is likely to give a false sense of security to people, especially during the pandemic.
- And finally, using the vaccine without evidence of its benefits could further Jeopardise vaccine supply, which is already short, to protect children against disseminated TB in high-risk Countries.
HUMAN CHALLENGE TRIALS
30, Apr 2020
Why in News:
- Recently, many people have volunteered to take part in the Human Challenge Trials (HCTs). It involves intentionally infecting volunteers with the novel coronavirus, in order to speed up the vaccination development.
About the Vaccine Development:
- Generally, vaccines take several years to develop and their development typically proceeds through three phases of clinical trials.
- In Phase 1, a Small Groups of People receive the Trial Vaccine.
- In Phase 2, the Clinical study is expanded and the vaccine is given to people who have characteristics (such as age and physical health) similar to those for whom the new vaccine is intended.
- In Phase 3, the Vaccine is given to several thousand people and tested for efficacy and safety. During this phase, participants either receive the vaccine or a placebo.
- Its efficacy is determined by comparing the prevalence of infection in the group that was administered the vaccine with the one which received a placebo.
- Placebo is anything which looks like real treatment but it is actually not. For example- sugar pills and saline injections.
What is Human Challenge Trials?
- It means the participants of both the vaccine group and placebo group are deliberately exposed to the infection after their consent and thus are challenged by the disease organism.
- It is not new and they are usually carried out in developing medications for diseases which are considered less lethal and have been better understood by scientists over the years like malaria.
- The scientists have suggested replacing the conventional Phase 3 testing of vaccines by controlled HCTs of Covid-19 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccine which can accelerate the testing and potential rollout of efficacious vaccines.
- It may reduce many months from the licensure process, making efficacious vaccines available more quickly and will also require significantly less number of people than regular Phase 3 trials.
About the Ethical Concerns of Human Trails:
- The trails for Covid-19 have been questioned by critics because it is a potentially deadly disease for even those who are less at risk, and has not been studied fully yet.
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) emphasised on the ethical framework of the challenge studies and also highlighted the importance of informed consent.
- Human challenge studies should be conducted with abundant forethought, caution, and oversight. The value of the information to be gained should clearly justify the risks to Human subjects.
HYDROGEN FUEL
28, Apr 2020
Context:
- Recently, the NTPC Ltd and a central PSU under Ministry of Power, has invited Global Expression of Interest (EoI) to provide 10 Hydrogen Fuel Cell (FC) based electric buses and an equal number of Hydrogen Fuel Cell based electric cars in Leh and Delhi.
About Hydrogen:
- Hydrogen is the lightest and first element on the periodic table. Since the weight of hydrogen is less than air, it rises in the atmosphere and is therefore rarely found in its pure form, H2.
- At standard temperature and pressure, hydrogen is a nontoxic, nonmetallic, odorless, tasteless, colorless, and highly combustible diatomic gas.
- It is the most abundant element in the universe. The sun and other stars are composed largely of hydrogen.
- It is estimate that 90% of the atoms in the universe are hydrogen atoms. Hydrogen is a component of more compounds than any other element.
- Water is the most abundant compound of hydrogen found on earth.
- Molecular hydrogen is not available on Earth in convenient natural reservoirs.
- Most hydrogen on Earth is bonded to oxygen in water and to carbon in live or dead and/or fossilized biomass. It can be created by splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen.
About Hydrogen Fuel:
- It is a zero-emission fuel burned with Oxygen.
- It can be used in fuel cells or Internal Combustion Engines.
- It is also used as a fuel for Spacecraft Propulsion.
Storage of Hydrogen:
- It can be stored physically as either a gas (typically requires high-pressure tanks) or a liquid (cryogenic temperatures because the boiling point of hydrogen at one atmosphere pressure is −8°C).
- It can also be stored on the surfaces of solids (by adsorption) or within solids (by absorption).
Potential of Clean Hydrogen:
- Hydrogen as a fuel has long been touted as an almost magical solution to air pollution crisis.
- The only by-product or emission that results from the usage of hydrogen fuel is water — making the fuel 100 per cent clean.
- It is considered an alternative fuel. It is due to its ability to power fuel cells in zero-emission electric vehicles, its potential for domestic production, and the fuel cell’s potential for high efficiency.
- It can also serve as fuel for internal combustion engines. The energy in 2.2 pounds (1 kilogram) of hydrogen gas contains about the same as the energy in 1 gallon (6.2 pounds, 2.8 kilograms) of Gasoline.
Significance of Hydrogen:
- It doesn’t produce harmful emissions. It is readily available.
- It is environmentally friendly and is a non-toxic substance. It can be used as fuel in rockets.It is three times as powerful as gasoline and other fossil fuels. This means that it can accomplish more with less.
- It is fuel efficient. Compared to diesel or gas, it is much more fuel efficient as it can produce more energy per pound of fuel.
- It is renewable. It can be produced again and again, unlike other non-renewable sources of Energy.
Limitations of Hydrogen:
- It does not occur in deposits or reserves like fossil fuel. It needs to be actually produced using Chemical Reactions.
- It is far more expensive to produce. And hydrogen-fueled vehicles are also more expensive than even battery-electric ones.
- It is highly flammable. It is difficult to store. The clean hydrogen industry is small and costs are high. There is a big potential for costs to fall, but the use of hydrogen needs to be scaled up and a network of supply infrastructure created.
MERGER OF TWO BLACK HOLES WITH UNEQUAL MASSES DETECTED
27, Apr 2020
Why in News?
- The gravitational wave observatories at Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) have detected a merger of two unequal-mass black holes for the first Time.
What is a Black Hole?
- A black hole is a place in space where gravity pulls so much that even light cannot get out. The gravity is so strong because matter has been squeezed into a tiny space.
- Gravitational waves are created when Two Black Holes Orbit Each Other and Merge.
Key Points:
- The event, named GW190412, was observed in April, 2019.
- The event has occurred almost five years after the first ever detection of gravitational wave signals by LIGO detectors. In 2015, the LIGO Observatories detected a signal from GW150914.
- GW190412: It involved the merger of two black holes weighing approximately 8 and 30 Solar masses, respectively. The merger took place at a distance of 2.5 billion light years away.
- The new unequal mass system is a unique discovery since all binaries observed previously by the LIGO and Virgo (Italy) detectors consisted of two roughly similar masses.
- This will make it possible to infer many more things such as:
1.A more accurate determination of the distance from the event.
2.The spin or angular momentum of the black hole with more mass.
3.The orientation of the whole event with respect to viewers on Earth.
Verification with the Prediction of General Relativity:
- This Observation once again confirms Einstein’s theory of general relativity, which predicts the existence of higher harmonics, i.e. gravitational waves at two or three times the Fundamental Frequency.
- General relativity, also known as the General Theory of relativity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915.
- The key predictions of Einstein’s theory:the first direct detection of gravitational waves and the first observation of the Collision and Merger of a pair of Black Holes.
About Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory:
- LIGO is the world’s largest gravitational wave observatory.
- LIGO consists of two widely-separated interferometers within the United States—one in Hanford, Washington and the other in Livingston, Louisiana—operated in unison to detect gravitational waves.
- Though its mission is to detect gravitational waves from some of the most violent and energetic processes in the Universe, the data LIGO collects may have effects on many areas of physics including gravitation, relativity, astrophysics, cosmology, particle physics, and Nuclear Physics.
STEM CELLS A NEW RAY OF HOPE IN BATTLE AGAINST COVID-19
23, Apr 2020
Why in News?
- Researchers are now looking at Stem Cells as a cure for Covid-19 Patients.
Highlights:
- Key scientific groups worldwide, including those in China and the US, have been working to test the treatment.
- An Israeli pharmaceutical company, Pluristem Therapeutics, has tested it in seven critical hospitalized patients and found positive results. The company is now seeking approval to begin clinical trials.
- The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has already approved clinical trials to study covid-19 patients who have been administered MSC (mesenchymal stem-cells) derived from the placenta to prevent inflammation of lungs.
Efficacy of Approach against Covid 19:
- The Therapeutic approach involves intravenous injection of mesenchymal stem-cells (MSC) from a human placenta into a covid-19 patient to boost the body’s immune response against the Infection.
- Further Stem-cells have been successful in treating degenerative diseases, especially Alzheimer’s, as well as Type-1 diabetes.
- The advantage that stem-cells have is that they have strong anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, which can help strengthen our immune system.
- This is important in case of covid-19, where they could reduce inflammation of the lungs, which are the most affected.
- It could help build up regenerative cells in the lungs, which could protect the epithelial cells of the lungs, prevent lung damage and help patients recover.
Stem Cells:
- They are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and divide indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell.
- Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells. These daughter cells either become new stem cells (self-renewal) or become specialized cells (differentiation) with a more specific function, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells or bone cells.
- No other cell in the body has the natural ability to Generate New Cell Types.
Classification:
- Based on formation at Different times of Human Life:
- Embryonic stem cells:
- These stem cells come from embryos that are three to five days old. At this stage, an embryo is called a blastocyst and has about 150 cells.
- These are pluripotent stem cells, meaning they can divide into more stem cells or can become any type of cell in the body.
- This versatility allows embryonic stem cells to be used to regenerate or repair diseased tissue and organs
- Adult Stem Cells:
- These stem cells are found in small numbers in most adult tissues, such as bone marrow or fat.
- Compared with embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells have a more limited ability to give rise to various cells of the body.
- However, emerging evidence suggests that adult stem cells may be able to create various types of cells.
- For instance, bone marrow stem cells may be able to create bone or heart muscle cells.
- Induced pluripotent Stem Cells or (iPSC’s):
- These cells are not found in the body but made in the laboratory from cells of the body.
- The iPSC cells have properties similar to those of embryonic stem cells.
- Human iPSCs were generated in 2007.
- Perinatal Stem Cells:
- Researchers have discovered stem cells in amniotic fluid as well as umbilical cord blood.
- These stem cells also have the ability to change into specialized cells.
- Amniotic fluid fills the sac that surrounds and protects a developing fetus in the uterus.
- Based on Potency:
- Totipotent (also known as omnipotent) stem cells can differentiate into embryonic and extraembryonic cell types.
- Such cells can construct a complete, viable organism.
- These cells are produced from the fusion of an egg and sperm cell.
- Cells produced by the first few divisions of the fertilized egg are also totipotent.
- Pluripotent Stem Cells are the descendants of totipotent cells and can differentiate into nearly all cells, i.e. cells derived from any of the three germ layers.
- Multipotent Stem Cells can differentiate into a number of cell types, but only those of a closely related family of cells.
- Oligopotent Stem Cells can differentiate into only a few cell types, such as lymphoid or myeloid stem cells.
- Unipotent Cells can produce only one cell type, their own, but have the property of self renewal, which distinguishes them from non-stem cells
Significance:
- Increase understanding of how diseases occur.
- By watching stem cells mature into cells in bones, heart muscle, nerves, and other organs and tissue, researchers and doctors may better understand how diseases and conditions develop.
- Test new drugs for safety and effectiveness.
- Before using investigational drugs in people, researchers can use some types of stem cells to test the drugs for safety and quality.
- Generate healthy cells to replace diseased cells (Regenerative Medicine).
- Stem cells can be guided into becoming specific cells that can be used to regenerate and repair diseased or damaged tissues in people.
ICMR ASKS STATES TO STOP USING RAPID TESTS
22, Apr 2020

Why in News?
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has directed the States not to use the COVID-19 rapid testing kits for the next two days following reports of wide variations in results.
What is the Issue?
- The Rajasthan government decided to halt rapid antibody tests after an experts’ team questioned the use of the newly distributed Chinese testing kits following inaccurate results.
- The health authorities had started the testing on those with symptoms at designated points recently.
- The quality issues with the test kits, currently being used to study community transmission, would put on hold survey in several States temporarily.
- The kits would be tested and validated by ICMR teams and an advisory on their use issued in the next two days.
- If they were found to be not up to the mark, replacements would be sought from the manufacturers.
What is Rapid Test?
- A rapid test is conducted to determine whether there has been any kind of recent viral infection in a person’s body.
- When a pathogen enters a human body, specific antibodies are released as a response to the virus.
- A rapid test can detect the presence of such antibodies in blood, serum or plasma samples quickly, indicating a viral infection.
- Rapid testing is conducted usually to check for community transmission of a virus during an epidemic.
- Rapid tests can be used to conduct screening within the community and identify those with suspected infection, put them under observation and if required, subject them to the PCR test for coronavirus confirmation.
- According to the health department, it is a simple test that can be done with a person’s blood sample and will give out results within 10-30 minutes. It is also a low-cost test.
Way Forward:
- This has seriously hampered our efforts to get fast test results for starting the treatment and contain the spread of the virus.
- The advisory issued by the ICMR to the States to not use testing kits for the next two days was most unfortunate, as the medical apex body could not ensure good quality of testing kits.
- Even at this late stage, the Centre should take an urgent action to procure the equipment from reliable sources and supply them to the States to get the faster results and start the treatment for the affected.
AAROGYA SETU APP MUST FOR LABOURERS, SAYS CPWD
21, Apr 2020

Why in News?
- Central government organisations involved in construction, were instructed by the Central Public Works Department (CPWD) to ensure that “all labour personnel/staff” returning to work have downloaded the government’s COVID-19 tracking app — Aarogya Setu.
About Aarogya Setu:
- Aarogya Setu app has been launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- It will help people in identifying the risk of getting affected by the Coronavirus.
- It will calculate risk based on the user’s interaction with others, using cutting edge Bluetooth technology, algorithms and artificial intelligence.
- Once installed in a smartphone, the app detects other nearby devices with Aarogya Setu installed.
- The App will help the Government take necessary timely steps for assessing risk of spread of COVID-19 infection, and ensuring isolation where required.
Why CPWD Initiates such Measure?
- The advisory comes as the Union Home Affairs Ministry has relaxed some restrictions, including for construction activity under certain conditions.
- When the app is installed in a Smartphone it will detect other devices with Aarogya Setu installed that come in proximity of that phone. The app currently supports 11 languages, including Hindi and English.
- After submitting the details, it will cross-checks the detail present in the government database and uses the proximity of Bluetooth and suggests whether the labourer is safe or not.
- In case if a labourer is not safe then the app will suggest to isolate and take precautions.
- The app will also check the user’s location of around six feet that is whether he or she was in the proximity of an infected patient by using the device Bluetooth.
- The app will show that you are at a ‘high risk’ or not. In case you are at a high-risk area then the app advises you to go for a test and call the toll-free number 1075 to schedule an appointment at the nearby testing centre.
About CPWD:
- CPWD came into existence in July, 1854 when Lord Dalhousie established a central agency for execution of public works and set up Ajmer Provincial Division. It is housed under the Ministry of Urban Development.
- Through the professional expertise in disciplines including Architecture, Engineering, Project Management coupled with comprehensive experience in building construction and maintenance, CPWD has been serving the nation for last 162 years and has executed priority of works in difficult and demanding geographical and climatic conditions.
- It is headed by DG who is also the Principal Technical Advisor to the Government of India. The regions and sub-regions are headed by Special DGs and Additional DGs respectively, while the zones in all state capitals (except a few) are headed by Chief Engineers.
- CPWD has PAN India presence and has ability to undertake construction of complex projects even in difficult terrain and maintenance in post construction stage.
- CPWD had been involved in construction of stadiums and other infrastructure requirements for Asian Games 1982 and Commonwealth Games 2010.
THE EXPORT BAN ON PARACETAMOL FORMULATION IS LIFTED
20, Apr 2020

Why in News:
- Recently, the Centre has permitted the export of formulations (medicinal products) made from Paracetamol. However, the restriction on export of Paracetamol Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) will continue, which is the part of any drug that produces the intended effects.
Highlights:
- The Paracetamol and its formulations were among the 13 APIs. Their formulations that figured in the notification by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT).
- The formulations, includingFixed Dose Combinations (FDC), under any ITCHS code have been made free for export with immediate effect.
- The ITCHScodes are better known as Indian Trade Clarification (ITC) and are based on the Harmonized System (HS) of Coding. These were adopted in India for import-export operations.
- The Indian custom uses an Eight Digit ITC(HS) code to suit the national trade requirements.
- The decision allowing export of formulations made from Paracetamol has come after permitting shipment of antimalarial drug Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) to the United States (US) and several other countries.
- The Pharmaceutical Export Promotion Council (Pharmexcil) of India wanted the Centre to resume export of Paracetamol APIs too.
- The Pharmaexcil was established in 2004 by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, to promote Pharma Exports.
- The FDC is means two or more drugs contained in a single dosage form, such as a capsule or tablet.
- An example of a FDC is HIV drug, Atripla (a combination of efavirenz, emtricitabine, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate). By reducing the number of pills a person must take each day, fixed-dose combination drugs can help improve adherence to an HIV treatment regimen.
About Directorate General of Foreign Trade:
- It is the main governing body in matters related to Exim (Export-Import) Policy.
- It is an attached office of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Its main objective of it under the Foreign Trade (Development and Regulation) Act, 1992 is to provide the development and regulation of foreign trade by facilitating imports into, and augmenting exports from India.
- The Foreign Trade Act has replaced the earlier law known as the Imports and Exports (Control) Act 1947.
About Paracetamol:
- It is a common fever medication globally. It is the most sought after and widely used drug ever since the Covid-19 outbreak.
- India is one Among the leading manufacturers of Paracetamol Globally.
- From an export perspective, it is a low value, High Volume Product.
ZOOM NOT A SAFE PLATFORM, SAYS MHA
18, Apr 2020

Why in News?
- Recently, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has issued an advisory that Zoom video conference is not a safe platform.
What is the Issue?
- Zoom has seen an exponential rise in usage in India as office-goers remain at home due to the lockdown, imposed to curb the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Over 90,000 schools across 20 countries have started using it regularly.
- The maximum number of daily meeting participants of approximately 10 million at the end of December 2019 grew to more than 200 million daily meeting participants in March.
- It has been used extensively by everyone including the central and state ministers for official purposes and Conducting Meetings.
About Zoom:
- Zoom is a US-based video communication and videoconferencing platform.
- This Silicon Valley-based company appears to own three companies in China through which at least 700 employees were paid to develop Zoom’s software.
- This arrangement is apparently an effort at labour arbitrage in which Zoom can avoid paying US wages while selling to US customers, thus increasing their profit margin.
- However, this arrangement may make Zoom responsive to pressure from Chinese authorities.
- Reportedly, few calls made through the app are routed through servers in China.
Cautions made by CERT-IN:
- Earlier, the Computer Emergency Response Team, India (CERT-In) had also issued advisories cautioning on the use of Zoom for office meetings.
- CERT-IN is an organisation of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, Government of India, with the objective of securing Indian cyberspace.
- It collects, analyses and disseminates information on cyber incidents, and also issues alerts on cyber security incidents.
- CERT-IN provides Incident Prevention and Response Services as well as Security Quality Management Services.
- It warned that the insecure usage of the platform may allow cyber criminals to access sensitive information such as meeting details and conversations giving rise to cyber frauds.
- It also highlighted multiple vulnerabilities which could allow an attacker to gain elevated privileges or obtain sensitive information.
Why Zoom is Not Safe?
- Citizen Lab, based at the University of Toronto, found significant weakness in Zoom’s encryption that protects meetings.
- It identified the transmission of meeting encryption keys through China.
- The lab has raised two primary concerns- geo-fencing and Meeting Encryption.
- Geo-fencing is a location-based service in which an app or other software uses GPS, RFID, Wi-Fi or cellular data to trigger a pre-programmed action when a mobile device or RFID tag enters or exits a virtual boundary set up around a geographical location, known as a geo-fence.
What is the Response from Zoom?
- Zoom Founder and CEO Eric S Yuan has apologised and assured the people that the privacy and security expectations would be taken care of.
- Zoom has added additional features such as placing a new security icon in the meeting controls, changing Zoom’s default settings and enhancing meeting password complexity, among others.
- It has also added that soon, account admins will have the ability to choose whether or not their data is routed through specific Data Center Regions.
Suggestions given by the Ministry:
- The users are suggested to set strong passwords and enable “waiting room” features so that call managers could have better control over the participants.
- Users should also avoid using personal meeting ID to host events and instead use randomly generated meeting IDs for each event.
- People using the app should not share meeting links on Public platforms.
Who deals with Cyber-crime Issues in India?
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C):
- The scheme to set up I4C was approved in October 2018, to deal with all types of cybercrimes in a comprehensive and coordinated manner.
- It has Seven Components:
- 1.National Cyber Crime Threat Analytics Unit
- 2.National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal
- 3.National Cyber Crime Training Centre
- 4.Cyber Crime Ecosystem Management Unit
- 5.National Cyber Crime Research and Innovation Centre
- 6.Cyber Crime Forensic Laboratory Ecosystem
- .7Platform for Joint Cyber Crime Investigation Team.
- Various States and Union Territories (UTs) have consented to set up Regional Cyber Crime Coordination Centres.
- This state-of-the-art Centre is located in New Delhi.
SEISMIC NOISE
17, Apr 2020
Why in News?
- Amid this coronavirus lockdown, British Geological Survey (BGS) scientists have reported a change in the Earth’s seismic noise and vibrations.
- Few weeks ago, the Royal Observatory in Belgium observed a 30-50% fall in levels of seismic noise since schools and businesses were closed during this lockdown.
What is Seismic Noise?
- Seismic noise refers to the relatively persistent vibration of the ground due to a multitude of causes. This noise includes vibrations caused due to human activity, such as transport and manufacturing.
- It is the unwanted component of signals recorded by a seismometer and makes it difficult for scientists to study seismic data that is more valuable.
- Scientists first observed this seismic noise everything recorded on seismograms that cannot be attributed to earthquakes at the end of the 19th
Advantages of Reduced Seismic Noise:
- Usually, to measure seismic activity accurately and reduce the effect of seismic noise, geologists place their detectors 100 metres below the Earth’s surface.
- Because, the seismic noise vibrations caused by human activity are of high frequency (between 1-100 Hz), and travel through the Earth’s surface layers.
- However, since the lockdown, researchers have said that they were able to study natural vibrations even from surface readings, owing to lesser seismic noise.
- Due to lower noise levels, scientists are now hoping that they would be able to detect smaller earthquakes and tremors that had slipped past their instruments so far.
What is a Seismometer?
- Seismometer is the scientific instrument that records ground motions, such as those caused by Earthquakes, volcanic Eruptions, and Explosions.
- These are incredibly sensitive so they also pick up other sources of vibration too, including human activity, such as road traffic, machinery and even people walking past.
COLOUR CODING TO MANAGE COVID-19 PANDEMIC
17, Apr 2020

Why in News?
- The government has decided to divide all districts across the country into hotspots, Non-hotspots and Green Zones.
About the News:
- The health and family welfare ministry has identified 170 hotspot districts, 207 non-hotspot districts reporting cases and 359 green zone districts not reporting any cases across the country.
- These numbers will increase or decrease based on fresh cases of novel coronavirus infection.
- This will help in managing the COVID-19 pandemic as well as partial opening up of economic activities during the extended period of the nationwide lockdown.
- This would help in management of hotspots and spread of pandemic.
How are the Districts Divided?
- The health ministry used two criteria to classify the districts as hotspots — the absolute number of cases and the speed of growth in cases.
- The technical definition followed to classify the districts is any district reporting more than six cases would be classified as hotspot district or red zone.
- Any hotspot district with more than 15 cases would be treated as a district witnessing outbreak.
Which Districts are Under Red Zone?
- Delhi and NCR, Mumbai, Nagpur, Pune, Thane, Yavatmal, Sangli, Buldhana, Ahmednagar, and Latur in Maharashtra, and Chennai, Chengalpattu, Coimbatore, Cuddalore, Erode, Dindigul, Karur, Madurai, Namakkal, Ranipet, Tiruchirapalli, Tiruppur and Theni in Tamil Nadu.
Demarcation of Epicentre and Containment Zones:
- A house with positive cases or a cluster with positive cases is marked as the epicentre of containment zone. A radius of 0.5 km is taken and the area around it is cordoned off with only essential services available.
- Also, a buffer zone is marked where people with severe and acute respiratory illnesses (SARI) are checked and monitored.
- Containment zones are created to map the local transmission of the disease and prevent the contagion from spreading.
ICMR RECOMMENDS TESTING OF POOLED SAMPLES
15, Apr 2020
Why in News?
- Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has recently issued an advisory for using pooled samples for testing of COVID-19 in order to increase the number of tests conducted by laboratories across the country.
What is Pooled Testing?
- In a pooled testing algorithm, samples of multiple individuals are put together in a tube and screened through the PCR test.
- If positive:If the pooled test turns out to be positive the individual samples under are tested, which is referred to as pool de-convolution.
- If negative: If there’s no positive result, all individual samples in the pool are regarded as negative.
Recommendations of ICMR for Pooled Testing:
- Maximum number for pooling:
- While more than two samples can be pooled together, the number should not exceed five samples to avoid sample dilution, which can lead to false negatives.
- This method can be used in areas where the prevalence of COVID-19 is low, which implies a positivity rate of less than two percent.
- In areas with a positivity rate between two to five percent, sample pooling of PCR screening may be considered in a community survey of surveillance among asymptomatic individuals.
- Pooling of samples is not recommended in areas or populations with positivity rates of over five per cent.
- Samples of individuals with known contact with confirmed cases or healthcare workers should not be included in the Pooled Samples.
Ideal areas for its Use:
Non-inclusion of likely Positive Cases:
What are its Significance?
- Substantial Cost Savings and Reduction in Requirement of Testing Kits:
- For example, if a pooled sample consists of the samples of five individuals and it tests negative, the cost of four testing kits is saved and more number of people are covered with fewer resources.
- The “door to door” approach of collecting pooled samples requires around 56-93 percent fewer tests, in areas where the prevalence of the disease is low to moderate.
- Increment in overall People Screened:
- It is critical to increase the numbers of tests conducted by laboratories. And as the positivity rate in COVID-19 cases is still low. Hence, it may help to use the pooled samples for screening.
- Tracking down the Asymptomatic Cases:
- Pooled screening can also help in tracking down the asymptomatic cases (showing no symptoms) of the disease, thereby tracking community transmission.
- Containing Foreseeable Second Wave Outbreaks:
- In particular, the “door-to-door” pooled-sample approach can facilitate mass screening in early stages of COVID-19 outbreaks, especially in low- and middle-income settings, and in containing foreseeable second wave outbreaks worldwide
THE CONCERN OF FALSE NEGATIVE TESTS
13, Apr 2020
Why in News?
- There have been rising concerns about theFalse Negative Tests in the scenario of this COVID-19 Pandemic.
- There are concerns about the manner in which some Covid-19 patients have apparently relapsed due to false negative tests. They have been tested positive only a few days after testing negative.
What is mean by False Negative Test?
- There is a possibility that the virus does not show up in the first test because patients have not rid themselves of the virus. However, on testing again, the virus shows up and the patients test positive. This is termed as False Negative Test.
- Although the tests based on detection of genetic material are very sensitive, they can be negative sometimes.
- Therefore, scientists and researchers have to constantly deal with the positive and negative predictive values.
- According to the research on the subject of false negative tests, no lab test is 100% accurate.
Possible Reasons behind False Negatives:
- The swab is not obtained or processed correctly or maybe obtained too early.
- An initial swab sample may not always collect enough genetic material to provide an accurate test.
- This problem may arise more often in patients who do not show many symptoms at the time of their test.
- If the infection is in the lung, then a nose swab may not detect it.
- The virus may shed in different amounts and is probably not present in the nose while the swab is collected.
- The test runs badly due to some Technical Glitch.
Possible Suggestions to Overcome the Issue:
- False negative test results may be reassuring for the low-risk individuals but for higher-risk individuals, even those without symptoms, the risk of such results requires additional protective measures against the spread of disease, like extended self-isolation.
- To be confirmed negative after being positive, a patient normally needs two negative swabs 24 hours apart to be sure.
- A negative test does not mean the person does not have the disease so the test results need to be considered in the context of patient characteristics and exposure.
- The public data on false negative rates in the clinical setting is very limited so each negative test must be guarded and Analysed.
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMA WARNS SCARCITY OF DRUGS AND MEDICAL DEVICES
13, Apr 2020

Why in News?
Recently, the Department of Pharmaceuticals has warned of a Nationwide Shortage of Medicines and Medical Devices.
About the News:
- It has urged the Ministry of Home Affairs to take immediate steps to help the drug makers resume production under the current lockdown.
- The National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) had also written to all State Chief Secretaries on the problems faced by the pharma firms.
Key Points:
- The Department of Pharmaceuticals under the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers is entrusted with ensuring the seamless production and distribution of critical life-saving medicines in the wake of the lockdown to contain the Covid-19 pandemic.
- On an average, drug and medical device makers are functioning at only 20%-30% of their full capacity during the lockdown.
- Production units engaged in making essential commodities, including medicines, vaccines, masks and their ancillaries have been exempted from the restrictions imposed as per the national lockdown.
- If the production will not reach the pre-lockdown level soon, it would lead to shortages of medicines and medical devices in the coming weeks.
- Both in the public and private sector, the seamless functioning of pharma manufacturing and distribution units is crucial in dealing with the crisis.
- A helpline has been created for pharma producers’ operational complaints, which are also being referred to State Drug Controllers for suitable intervention.
Challenges Ahead:
- Export of Indian pharmaceuticals offer a better price in global markets which can lead to disproportionate shortages in the domestic market.
- Restrictions on mobility and production in several states.
- Unavailability of labour, transport and courier services.
- Reverse migration (from cities to sub-urban/rural areas) of labour and local workers.
- Lack of public transport options and the fear of police action.
- Drivers have left their trucks on highways fearing stoppage of vehicles on State, district and city borders and lack of food and diesel on the Route.
- Closure of ancillary industries which are not being considered essential by few local administrations.
- They supply packaging material, excipients (required for tablets and capsules manufacturing), utility consumables like briquettes/gases (required to run boilers) and spare parts.
Suggestions to Address the Grievances:
- Suitable measures are needed to reduce the export and focus more on domestic needs.
- State and district administrations need to be sensitised so that they can proactively fulfil the needs of pharma units to function fully.
- Allowance to the pharma industry to ferry back their contractual workers from their native places and make courier services fully functional in metro, Tier 1 and Tier 2 cities.
- Drivers with commercial licences should be allowed to move with or without a vehicle by treating it as a ‘pass’ during the lockdown.The apprehensions of the drivers need to be addressed and they also need to be motivated and incentivised.
KERALA GETS NODS FOR TRIAL OF PLASMA THERAPHY
10, Apr 2020

Why in News?
- Kerala has gone a step ahead and won Indian Council of Medical Research’s (ICMR) approval for the clinical protocol exploring the feasibility of an experimental therapy, convalescent plasma transfusion, which may be administered to severe COVID-19 patients.
Highlights:
- The expert committee which is guiding the State’s containment and mitigation strategies against COVID-19 had recommended exploring the plasma therapy following the report in JAMA [Journal of American Medical Association] of a pilot study done by doctors in China.
- In the early 20thcentury, convalescent plasma treatment was used during outbreaks of diseases such as measles, mumps and influenza.
- More recently, it was used during the H1N1 influenza pandemic, and again in 2013 during the Ebola outbreak in West Africa. In the case of the latter, two patients survived the disease after treatment.
- Following the Ebola outbreak, the World Health Organization issued guidance for its use in treating the disease, saying the small group it was used on showed “promising results.”
- Doctors have transfused the blood of recovered patients into those still sick with the 1918 flu, measles, polio, chickenpox and SARS —to varying degrees of success.
Convalescent Plasma Therapy:
- The therapy seeks to make use of the antibodies developed in the recovered patient against the coronavirus.
- The whole blood or plasma from such people is taken, and the plasma is then injected in critically ill patients so that the antibodies are transferred and boost their fight against the virus.
- A COVID-19 patient usually develops primary immunity against the virus in 10-14 days.
- Therefore, if the plasma is injected at an early stage, it can possibly help fight the virus and prevent severe illness.
How is it Done?
- The process to infuse plasma in a patient can be completed quickly.
- It only requires standard blood collection practices, and extraction of plasma.
- If whole blood is donated (350-450 ml), a blood fractionation process is used to separate the plasma. Otherwise, a special machine called aphaeresis machine can be used to extract the plasma directly from the donor.
- While blood is indeed extracted from the donor, the aphaeresis machine separates and extracts the plasma using a plasma kit, and the remaining blood components are returned into the donor’s body.
Challenges:
- Despite the potential utility of passive antibody treatments, there have been few concerted efforts to use them as initial therapies against emerging and pandemic infectious threats.
- The absence of large trials certainly contributes to the hesitancy to employ this treatment.
- Also, the most effective formulations (convalescent plasma or hyperimmune globulin, HIg) are unknown.
- Convalescent plasma has the advantage that while its antibodies limit viral replication, other plasma components can also exert beneficial effects such as replenishing coagulation factors when given to patients with haemorrhagic fevers such as Ebola.
- On the other hand, individual convalescent plasma units demonstrate donor-dependent variability in antibody specificities and titters. H-Ig preparations, in contrast, contain standardized antibody doses, although fractionation removes IgM, which may be necessary against some viruses.
- Nonetheless, the construction of a strategic stockpile of frozen, pathogen-reduced plasma, collected from Ebola-convalescent patients with well-characterized viral neutralization activities, is one example of how to proceed despite existing unknowns.
CYBER-ATTACKS ON HEALTH CARE INSTITUTIONS
09, Apr 2020

Why in News?
- The International Criminal Police Organisation (Interpol) has warned member countries that cybercriminals are attempting to target major hospitals and other institutions on the front lines of the fight against COVID-19 with ransomware.
About International Criminal Police Organization (INTERPOL):
- Interpol is an intergovernmental organization that helps coordinate the police force of 194 member countries.
- Each of the member countries hosts an Interpol National Central Bureau (NCB). This connects their national law enforcement with other countries and with the General Secretariat.
- The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) is designated as the National Central Bureau of India.
- The General Secretariat provides a range of expertise and services to the member countries.
- It is headquartered in Lyon, France
- Interpol Notices are international requests for cooperation or alerts allowing police in member countries to share critic.

Key Points:
- In an alert sent to 194 nations, including India, Interpol said that the hospitals and institutions had become targets of ransomware attacks.
- Interpol’s Cybercrime Threat Response Team had detected an increase in the number of attempted ransomware attacks against key organisations and infrastructure engaged in the virus response.
- Cybercriminals are using ransomware to hold hospitals and medical services digitally hostage, preventing them from accessing vital files and systems until a ransom is paid.
- The attacks were designed to lock these institutions out of their critical systems in an attempt to extort payments.
- Locking hospitals out of their critical system will delay the swift medical response required during these unprecedented times and it could also directly lead to deaths.
- The ransomware appears to be spreading primarily via e-mails, often falsely claiming to contain information or advice regarding the coronavirus from a government agency, which encourages the recipient to click on an infected link or attachment.
- Prevention and Mitigation efforts are crucial to stopping the attacks.
- Interpol continues to stand by its member countries and provide any assistance necessary to ensure vital healthcare systems remain untouched and the criminals targeting them held accountable.
- Interpol also issued a Purple Notice to seek or provide information on modus operandi, objects, devices and concealment methods used by criminals.
Changed Pattern of Crimes:
- Interpol warned that with a majority of people working from home due to the pandemic, there was a change in the pattern of crimes.
- Following is the change
- Fraudulent trade in personal protective equipment and anti-viral medicines,
- Individuals/businesses on reduced income becoming potential targets of loan sharks (Persons who loan money at extremely high interest rates and often use threats of violence to collect debts).
- The lockdown period has made business establishments/factories vulnerable to thefts.
- Since more people were at home, the number of burglaries had dropped. But thieves are increasingly targeting factories or business premises that were locked.
- Domestic violence cases have risen since the start of coronavirus-related quarantines, with reports showing women and children at greater risk of abuse.
- Recent weeks have seen increased online activity by paedophiles (persons who are sexually attracted to children) seeking child sexual abuse material.
- This is being intensified by a shortage of moderators who identify and remove offensive material from networks.
Steps Taken by the Government:
- Alerts received by the Government of India on the threat of ransomware/malware attacks have been communicated to the concerned departments.
- Institutions and individuals have been appealed not to open any mail or link on coronavirus data or home remedies unless it is from a trusted source like a government agency.
- They were also cautioned about a possibility of e-mail spoofing, where a suspect operating from a remote location would send a mail that would appear as if it came from a known person.
FILLING THE GAP: COVID TEST
09, Apr 2020

Why in News?
- The nation-wide lockdown that began on March 25 has helped to contain the spread of COVID-19. However, it needs to be asked if India’s response to the coronavirus outbreak has any unseen gaps.
Gaps in Controlling COVID-19 Pandemic:
- Low number of infectious disease specialists:
- These specialists are available in India, but they mostly work in big private hospitals. The Clinical Infectious Diseases Society (CIDS) and the Indian Association of Medical Microbiologists (IAMM) are not known to have proffered any advice to the Government.
- Fulling Mandate of National Institute of Biologicals:
- The National Institute of Biologicals (NIB) was established in 1992 by the Ministry of Health to function as the apex body and was mandated to ensure validation of invitro diagnostics, vaccines and biotherapeutics in the event of a pandemic.
- The NIB ought to deliver on its mandate and the best infectious diseases professional in the country should be steering it. A search committee of retired virologists, infectious diseases specialists and medical microbiologists should be constituted urgently to find a director for the NIB.
Need to Conduct Antibody test along with PCR test:
- Traditionally, there are two types of diagnostic tests for infectious organisms — tests for the presence of the virus itself (current infection), and tests for antibodies to the virus (current or prior infection).
- The Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test used for detecting specific genetic material of a virus is key to determine if someone ill is infected with COVID-19. The WHO recommendations have also added antibody and antigen tests alongside the PCR. This will enable mass screenings — these have to be confirmed by PCR tests.
What are PCR, Anti-body and Anti-gen Tests?
- PCR Test:
- The PCR test identifies a virus from the swabs taken a few days after infection, to about 8-10 days after the first symptoms appear. It can also provide clues to community transmission, including anticipating the percentage of population that might develop serious complications.
- A PCR test takes six to eight hours, not counting the time taken to collect and send the sample to the nearest lab. It is expensive as each test costs around Rs 4,500.
- A commercial test named X-pert has recently been approved by the US FDA for detecting the virus’ nucleic acid within a couple of hours.
- Antibody Test:
- The antibody test is the best to calculate the number of people who may have experienced COVID-19.
- It is dependable for hotspot surveillance; it is quick and helps to see who has been infected more than 10 days earlier.
- The only negative aspect of it is that if conducted very early, it may miss virus shedders while hunting for the antibodies.
Antigen Test:
- Antigen test identifies the protein component of the virus and could be used even sooner than the Antibody Test.
INDIA LIFTS BAN ON EXPORT OF HYDROXY-CHLOROQUINE
08, Apr 2020
Why in News?
- The Government of India has announced that it had rescinded its earlier ban on the export of malaria drug hydroxyl-chloroquine (HCQ), which is now being used in countries such as the U.S. as a possible line of treatment for COVID-19.
What is Hydroxy-chloroquine?
- Hydroxy-chloroquine (not to be confused with anti-malaria drug chloroquine) is an oral drug used in the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
- Autoimmune diseases are in which the body’s immune system attacks healthy cells.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting many joints, including those in the hands and feet.
Hydroxy-chloroquine against COVID-19:
- The drug shows antiviral activity in vitro against coronaviruses, and specifically, SARS-CoV-2 [the virus that causes COVID-19].
- Further, the study suggests that prophylaxis(treatment given to prevent disease) with hydroxy-chloroquine at approved doses could prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection and may help to improve viral shedding.
- Clinical trials are under way in China to know whether the drug can be used for treatment.
Combination of Hydroxy-chloroquine with Other Drugs:
- Hydroxy-chloroquine and Chloroquine:
- A study suggests that both hydroxy-chloroquine and chloroquine have in vitro activity against SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and other coronaviruses, with hydroxy-chloroquine having higher potency against SARS-CoV-2.
- In vitro studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context (such as in a test tube).
- In contrast to in vitro experiments, in vivo studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants.
- Hydroxy-chloroquine with Azithromycin:
- The combination of hydroxy-chloroquine with azithromycin is a commonly used antibiotic.
- The combination is expected to be efficient for virus elimination.
ICMR Recommendations on use of Hydroxy-chloroquine:
- The restricted population for usage of hydroxy-chloroquine include, namely, ‘Asymptomatic (showing no symptoms) Healthcare Workers’ and ‘asymptomatic household contacts’ of laboratory-confirmed cases.
- The above mentioned population have been advised to use the hydroxy-chloroquine to contain further spread of the pandemic.
- However, the drug is not recommended as a preventive healthcare in children under 15 years of age.
- ICMR also advised that placing healthcare workers under hydroxy-chloroquine treatment should not instill a sense of false security and they need to follow all prescribed public health measures such as frequent washing of hands, respiratory etiquettes, keeping a distance of minimum one metre and use of personal protective equipment, etc.
Cautions over the Drug:
- ICMR cautioned the general public against the unrestricted use of the drug, stating that “it is still at experimental stage and is not recommended for public use.”
- Hydroxy-chloroquine is recommended only for a healthcare worker who is treating a COVID-19 patient. Secondly, it’s recommended only for persons staying with and caring for a household patient who has been tested positive. They can take that only for prophylaxis — only for prevention.
- “The recommendation is for empirical use of the drug based on available evidence and is restricted for use by only two categories of people and under strict supervision of a doctor.
What are the Concerns?
- None of the drug approving agencies across the world, including the FDA, has cleared the drug for prophylaxis or for treating COVID-19 patients which ICMR has done.
- The available evidence of the efficacy of the drug is a small study by French researchers involving 26 COVID-19 patients. The study found “significant” reduction in viral load in over half the number of patients at end of six days of therapy.
- As the trial showed significant reduction, the results were published on March 17 in the International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents even before the 14-day follow-up was completed.
- When there is no other drug available, and when the virus is highly contagious, it is best to use if there is some benefit. The same logic applies for other diseases where there are no medicines available. ICMR too applied the same logic in usage of this drug.
- Our first obligation is to ensure that there are adequate stocks of medicines for the requirement of our own people.
- In order to ensure this, some temporary steps were taken to restrict exports of a number of pharmaceutical products.
- But export of the hydroxyl-chloroquine may deem to loss of adequate supply during the pandemic crisis.
CYTOKINE STORM
07, Apr 2020

Context:
- Cytokine storm is recently seen in news, which is feared as a compounding effect of COVID 19
About Cytokine Storm:
- It is an overproduction of immune cells and their activating compounds (cytokines), which, in a flu infection, is often associated with a surge of activated immune cells into the lungs.
- It resulting in lung inflammation and fluid build-up can lead to respiratory distress and can be contaminated by a secondary bacterial pneumonia — often enhancing the mortality in patients.
- It can occur due to an infection, auto-immune condition, or other diseases.
- Its symptoms include high fever, inflammation (redness and swelling), severe fatigue, and nausea.
- It is not exclusive to coronavirus patients. It is an immune reaction that can occur during other infectious and non-infectious diseases as well.
About the Role of Cytokines in the Immune System:
- It signals proteins that are released by cells at local high concentrations, which is characterised by the overproduction of immune cells and the cytokines themselves because of a dysregulation in the process.
- The severe immune reaction, leading to the secretion of too many cytokines in the bloodstream, can be harmful since an excess of immune cells can attack Healthy Tissue as well.
About the Functions of Immune System:
- It protects us from bacteria, viruses, and parasites by removing them from our systems.
- It gets activated by things that the body does not recognise as its own. These hings are called antigens, and include bacteria, fungi and viruses.
- It response involves inflammation, an important and indispensable part of the process.
- Its Inflammation has an important protective function. The release of inflammatory mediators increases the blood flow to the area, which allows larger numbers of immune system cells to be carried to the injured tissue, thereby aiding the repairing process.
- If this inflammatory response is not regulated, a ‘cytokine storm’ can be triggered.
- Impact a COVID-19 patient: In the case of any flu infection, a cytokine storm is associated with a surge of activated immune cells into the lungs, which, instead of fighting off the antigen, leads to lung inflammation and fluid build-up, and respiratory distress.
WHY EVERYONE SHOULD WEAR MASKS?
06, Apr 2020

Why in News?
- Experts say that the pandemic can be slowed only by a lockdown as well as by ensuring universal Mask Use.
What is an Epidemic Curve?
- On the curve, Y axis and X axis represent case numbers and time, respectively.
- A normal epidemic curve is bell-shaped, with an early ascending slope (first phase), a peak (second phase) and a declining slope (third phase).
- The area under the curve represents the total number of cases. India is now in the first phase of the COVID-19 pandemic.
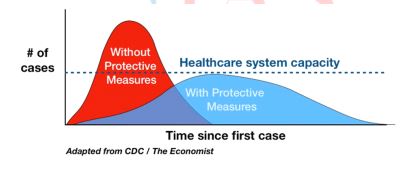
Need of an Hour:
- Flattening the epidemic curve (case distribution curve) is the need of the day.
- A rapid increase in cases will demand far more healthcare facilities than now available.
- Healthcare facilities were not created in anticipation of a pandemic and are grossly inadequate for India to tackle the first phase.
- A flattening of the curve will reduce the demand on beds in intensive care units, respirators, and specialists to manage acute respiratory distress syndrome.
- The peak will be dwarfed and come after some breathing time; the pressure will be eased.
How the Curve can be Flattened?
- There are two ways of flattening the curve: imposing a strict lockdown for a number of weeks or use of face masks all the time when outside our homes.
- A lockdown physically distances families from each other.
- There are four reasons for the Universal Use of Masks.
- 1.First, any infected person will not infect others because the droplets of fluids that we let out during conversations, coughing or sneezing will be blocked by the mask.
- 2.Second, uninfected people will have some protection from droplet infection during interactions with others. For those who wear eyeglasses, there is additional protection from droplets falling on the conjunctiva. When both parties wear masks, the probability of transmission is virtually zero.
- 2.Third, the mask-wearers will avoid inserting their fingertips into their nostrils or mouths. Viruses deposited on surfaces may be carried by hand if we touch such surfaces; if we do not touch our eyes, nostrils or mouth; this mode of transmission is prevented.
- 4.Fourth, everyone will be reminded all the time that these are abnormal days.
- In overcrowded areas such as slums, a lockdown will not be efficient in slowing down transmission.
- In such places, universal mask use is a simple way to slow down transmission. In India the wise choice would have been to ensure universal mask use in slums, bazaars, shops selling essential commodities, etc.
Way Forward:
- COVID-19 mortality is due to Three Reasons.
- 1.Virus virulence is the given and cannot be altered.
- 2.Co-morbidity (diabetes, chronic diseases) is already prevalent.
- 3.Then there is low-quality healthcare.
- Slowing down the epidemic by imposing a lockdown and ensuring universal mask use gives us the chance to protect people from infection and improve healthcare quality; wherever that was done, the mortality was less than 1%.
GRAVITY RECOVERY AND CLIMATE EXPERIMENT FOLLOW ON (GRACE-FO)
04, Apr 2020
Why in News?
- Recently, a new satellite-based, weekly global maps of soil moisture and groundwater wetness conditions were developed by US space agency National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln (UNL) on March 31, 2020.
About GRACE- FO Mission:
- It is a partnership between NASA and the German Research Centre for Geosciences (GFZ).
- It is a successor to the original GRACE mission, which began orbiting Earth. The GRACE missions measure variations in gravity over Earth’s surface, producing a new map of the gravity field every 30 days.
- It will continue the work of tracking Earth’s water movement to monitor changes in underground water storage, the amount of water in large lakes and rivers, soil moisture, ice sheets and glaciers, and sea level caused by the addition of water to the ocean.
- These discoveries provide a unique view of Earth’s climate and have far-reaching benefits to society and the world’s Population.
About the Global Maps produced by GRACE-FO Mission:
- Its global maps are derived with data available from NASA and German Research Center for Geosciences’
- It provides the satellite-based observations of changes in water distribution were integrated with other data within a computer model that simulated water and energy cycles.
- It also produces other outputs, such as the time-varying maps of the distribution of water at three depths Surface soil moisture, root zone soil moisture (roughly the top three feet of soil) and shallow groundwater.
- Its map has a resolution of up to 8.5 miles, providing continuous data on moisture and groundwater conditions across the Landscape.
Significance of the Data:
- The data available through this project would fill existing gaps in understanding the full picture of wet and dry conditions that can lead to drought.
- It is absolutely a critical tool to helping us address and offset some of the impacts anticipated, whether it is from population growth, climate change or just increased water consumption in general.
- It would also help in managing the selection of appropriate agricultural crops and Predicting Yields.
GEO-FENCING APP TO LOCATE QUARANTINE VIOLATORS
03, Apr 2020
Why in News?
- The government has tested an application that triggers e-mails and SMS alerts to an authorised government agency if a person has jumped quarantine or escaped from isolation, based on the person’s mobile phone’s cell tower location.
What is Geo-fencing?
- Geo-fencing is a location-based service in which an app or other software uses GPS, RFID, Wi-Fi or cellular data to trigger a pre-programmed action when a mobile device or RFID tag enters or exits a virtual boundary set up around a geographical location.
About the News:
- The Centre is using powers under the Indian Telegraph Act to “fetch information” from telecom companies every 15 minutes to track COVID-19 cases across the country.
- The government has tested an application that triggers e-mails and SMS alerts to an authorised government agency if a person has jumped quarantine or escaped from isolation, based on the person’s mobile phone’s cell tower location. The “geo-fencing” is accurate by up to 300 m.
- The location information is received periodically over a secure network for the authorised cases with “due protection of the data received”.
- The States have been asked to seek the approval of their Home Secretaries under the provisions of Section 5(2) of the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885, for the specified mobile phone numbers to request the DoT to provide information by email or SMS in case of violation of “geo-fencing”.
Why Geo-fencing Needed?
- One of the biggest challenges that India faces in its fight against Coronavirus in the country is about tracking the potential carriers to curb the spread of this highly infectious disease.
- To address this challenge, centre has come up with an application, which can be used to identify and isolate the potential carriers, who are Currently Asymptomatic.
How does App work?
- The mobile application works via geo-fencing feature. The application would allow government authorities to ‘register the asymptomatic carriers and track them to effectively monitor their movement.
- The movement of potential carriers would be monitored and tracked using geo-fencing feature.
- In case the potential carrier tried to break the fence setup for them, the app would trigger an alert to the authorities, which can then track down the suspects and curb the spread of COVID-19.
HOW BATS CARRY VIRUSES BUT DON’T FALL ILL THEMSELVES
03, Apr 2020

Why in News?
- As the novel coronavirus has spread across continents, studies are underway to better understand its origin and how it is transmitted.
Highlights:
- Diseases caused by coronaviruses, such as COVID-19, are zoonotic, meaning they are transmitted between animals and people.
- The global SARS outbreak of 2002-2004, which claimed almost 800 lives in more than two dozen countries, was also traced to the horseshoe variety of bats in 2017.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), SARS-CoV was transmitted to humans from civet cats, and MERS-CoV from dromedary camels. Both the viruses, however, are believed to have originated from bats and subsequently passed on to other Animals.
- While researchers are yet to conclude how the novel coronavirus (first detected in China’s Wuhan) originated, many believe it could be traced back to bats.
Bats Natural Zoonotic Reservoir:
- Many studies over the years have found bats to be a natural reservoir for a large number of zoonotic viruses that have caused outbreaks in many countries in the past. These include rabies, Marburg, Nipah and Hendra viruses.
- Researchers at the Wuhan Institute of Virology in China were able to trace the origin of the SARS virus to these bats in a remote cave in the country’s south eastern Yunnan province.
- After years of investigating caves in several parts of China, the virologists were able to find a single population of horseshoe bats that had the virus strains which matched the ones which had been transmitted to humans.
- Some experts believe that the novel coronavirus could also be traced to horseshoe bats.
- Reasons behind bats surviving despite being carriers of viruses themselves
- Bats are able to carry a host of viruses without becoming ill, except for rabies, which affects them.
- Research suggests that bats, which make up a quarter of all mammal species, have developed stronger immune systems through the process of evolution which enabled them to fly.
- Studies have shown that when bats fly, the energy requirements in their bodies cause cells to break down into bits of DNA which are then released. While most organisms would treat such DNA particles as foreign invading bodies, in bats such responses are more muted.
- Due to this weakened response, bats do not develop inflammations, which can cause a considerable toll on the body’s energy.
- This phenomenon is believed to be the reason so many viruses can exist in their bodies.
Observations by American Society of Microbiology:
- Coronaviruses are well known to undergo genetic recombination, which may lead to new genotypes and outbreaks.
- The presence of a large reservoir of SARS-CoV-like viruses in horseshoe bats, together with the culture of eating exotic mammals in southern China, is a dangerous combination.
- The possibility of the re-emergence of SARS and other novel viruses from animals or laboratories and therefore the need for preparedness should not be ignored.
COVID-19 AND THE ORPHAN DRUG ACT
02, Apr 2020
Why in News?
Despite the World Health Organisation (WHO) recently declared the Covid-19 outbreak a pandemic, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) declared COVID-19 an Orphan Disease, or a Rare Disease.
Key Points Regarding the Issue:
- The FDA granted Gilead Sciences orphan drug status for its antiviral drug, Remdesivir, on March 23, 2020.
- Originally developed to treat Ebola, the drug is now being tested for treating COVID-19. Clinical trials are already in Phase III.
- But on March 25 Gilead announced that it had submitted a request to the FDA to remove its orphan drug designation for Remdesivir.
- Earlier, Gilead had sought the orphan status to the Remdesivir drug to expedite approval of the drug. However, advocates for global access to medicines, rejected the company’s argument.
- Gilead’s exorbitant pricing of its drug to treat hepatitis C and its drug to treat HIV also attracted attention in the past.
- In recent years, drug companies have been accused of exploiting the law to reap profits, in sales.
What is a Rare Disease?
- A rare disease is a health condition of low prevalence that affects a small number of people compared with other prevalent diseases in the general population.
- There is no universally accepted definition of rare diseases and the definitions usually vary across different countries
- Though rare diseases are of low prevalence and individually rare, collectively they affect a considerable proportion of the population.
- 80% of rare diseases are genetic in origin and hence disproportionately impact children.
- In India there are 56-72 million people affected by rare diseases.
- There is also a demand for the reformulation of National Policy for Treatment of Rare Diseases, 2017.
About Orphan Drug Act, 1983:
- Rare diseases became known as orphan diseases because drug companies were not interested in adopting them to develop treatments.
- In the U.S., under the Orphan Drug Act, companies are provided incentives to develop therapies, or orphan drugs, for rare diseases.
- The Act allows seven years of market exclusivity and financial incentives to innovators of these drugs. As a result, orphan drugs are often exorbitantly priced.
- Privileges under the Act may be conferred to companies for drugs to treat a disease that affect less than 200,000 people in the U.S., or for a disease that affects more than 200,000 people but for which there is no hope of recovering R & D costs.
- The idea is that without these incentives, companies would find it difficult to recover their R&D costs given the small number of people suffering from the rare disease.
About National Policy for Treatment of Rare Diseases, 2017:
- The policy highlights the measures and steps, both in the short as well as in the long term, that need to be taken to deal comprehensively with rare diseases.
- The policy intends to constitute an Inter-ministerial Consultative Committee to coordinate and steer the initiatives of different ministries and departments on rare diseases.
- It also mentions the creation of a corpus fund at Central and State level for funding treatment of rare diseases.
- The policy aims to create a patient registry for diseases housed in Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
- However, recognizing the higher cost of treatment for rare diseases, the policy also seeks to strike a balance between access to treatment and health system sustainability.
- It also aims to create awareness among health professionals, families of patients and the public in general, about rare diseases.
Issues Regarding the Declaration:
- COVID-19 not a Rare Disease:The Orphan Drug Act applies to a potential drug for COVID-19, which is anything but a rare disease, with 800,049 confirmed cases across the world.
- Paradox:The U.S. FDA conferred the status of an orphan drug on Remdesivir proposed to treat COVID-19 a pandemic.
Impacts on declaring as Orphan Disease:
- Had Gilead not sought that orphan drug status be repealed, generic manufacturers would not have been able to market a drug to treat COVID-19 with the same active ingredient till the seven-year period of market exclusivity had ended.
- This would have given Gilead free rein on pricing and licensing which would have had disastrous consequences on the healthcare system.
- However, orphan drug status of Remdesivir would have no impact on India as Gilead Sciences holds patents in India and patents are open to challenge.
- As far as its patent rights are concerned, Indian law permits the government to issue a compulsory licence in certain circumstances of a public health crisis under Section 92 of the Patents Act.
- This would allow third parties to manufacture a patented drug without permission of the Patent Holder.
ACUTE ENCEPHALITIS SYNDROME (AES)
01, Apr 2020
Context:
- Recently, the Acute Encephalitis Syndrome (AES) returns in Bihar as toddler dies in Muzaffarpur.
About AES:
- It is a basket term used for referring to hospitals, children with clinical neurological manifestation that includes mental confusion, disorientation, convulsion, delirium, or coma.
- It is a severe case of encephalitis transmitted by mosquitoes and is characterized by high fever and inflammation of the brain.
- It is coined by the World Health Organisation (WHO) in 2006, to signify a group of diseases which seem similar to one another but are difficult to differentiate in the chaotic environment of an outbreak.
- It most commonly affects children and young adults and can lead to considerable morbidity and mortality.
- Its Symptoms include confusion, disorientation, coma, or inability to talk, high fever, vomiting, nausea, and unconsciousness.
- The National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme in India has set up countrywide surveillance for AES through sentinel sites with a focus on detecting Japanese encephalitis (JEV).
About Cause of the Disease:
- It is considered a very complex disease as it can be caused by various agents including bacteria, fungi, virus and many other agents.
- Viruses are the main causative agents in AES cases, although other sources such as bacteria, fungi, parasites, spirochetes, chemicals, toxins, and noninfectious agents have also been reported over the past few decades. It is not Vaccine-Preventable.
- It is mostly caused by Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) (ranging from 5%-35%) and, Nipah virus, Zika virus, Influenza A virus, West Nile virus, Chandipura virus, mumps, measles, dengue, scrub typhus, S.pneumoniae are also found as causative agents for AES.
About Litchi Fruits:
- It outbreaks in north and eastern India have been linked to children eating unripe Litchi Fruit on empty stomachs.
- It contains the toxins hypoglycin A and methylenecyclopropylglycine (MCPG), which cause vomiting if ingested in large quantities. Hypoglycin A is a naturally occurring amino acid found in the unripened litchi that causes severe vomiting (Jamaican vomiting sickness), while MCPG is a poisonous compound found in litchi seeds.
How it Affects Children?
- The Blood glucose falls sharply causing severe brain malfunction (encephalopathy), leading to seizures and coma, and death in many cases.
- It is because the under-nourished children lack sufficient glucose reserve in the form of glycogen and the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate source is blocked midway leading to low blood sugar level. It causes serious brain function derangement and seizures.
Way Ahead:
- Measures needed to be taken are by Increase access to safe drinking water and proper sanitation facilities, improve nutritional status of children at risk of JE/AES, Preparative measures to be in place before the possible outbreaks, Vector control, Better awareness generation among children, parents through Anganwadi workers, ANMs etc
INDIA JOINS WHO FOR SOLIDARITY TRIALS
30, Mar 2020

Why in News?
- India is all set to join the World Health Organisation’s (WHO) Solidarity Trial which aims at rapid global search for drugs to treat COVID-19.
What are the Key Points?
- India has stayed away from the multi-country trial till now due to its small sample size.
- It will express its interest to participate in the trial for the Indian population when it feels that the time is right.
- Vaccine development wasn’t a priority for Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) currently because there are around 30 vaccine groups already in operation worldwide.
- Keeping in view the rising number of cases and challenges faced by India, the government has decided to participate in the solidarity trial.
How Solidarity Trial Done?
-
It will test different drugs or combinations like:
1.Remdesivir.
2.Combination of lopinavir and ritonavir (anti-HIV drugs).
3.Interferon beta with the combination of lopinavir and ritonavir.
4.Chloroquine.
It will compare their effectiveness to the standard of care, the regular support used by the hospitals treating COVID-19 patients.
What are the Key Challenges?
- Shortage of Medical Devices and Equipment:The Medical Technology Association of India (MTAI), which represents research-based medical technology companies, has highlighted the shortage of medical devices and Equipment.
- The Centre has exempted manufacturing, warehousing and distribution of the medical devices and equipment from the lockdown but these are being clamped down by the state governments and local level administrators.
- Transport trucks carrying these vital preparatory materials are stuck at city and state borders.
- Delays in Import:India is importing probes and rapid testing kits from China, Germany and WHO. However, some delays have been reported but it is made sure that the delays do not affect the testings.
- Time Constraints:ICMR is currently looking at repurposed drug molecules to find treatment for COVID-19 due to time constraints.
What could be the Possible Solutions?
- India needs to Prioritise what it needs right now to deal with the situation.
- Indian scientists have formed a group called Indian Scientists’ Response to COVID-19 (ISRC) to tackle the pandemic.
- While governmental bodies make their decisions and professional scientific academies take principled stands, there is a need for individuals in the scientific community to also help individually and collectively.
Indian Scientists’ Response to COVID-19:
- Indian Scientists’ Response to COVID-19 (ISRC) is a voluntary group of scientists to address the concerns raised by the COVID-19 outbreak and to discuss the rapidly evolving situation with its dire need for science communication.
- The group consists of nearly 200 scientists from institutions such as the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS), the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), the Indian Institute of Technologies (IITs), etc.
- It aims to study existing and available data to bring out analysis that will support the Central, State and local governments in carrying out their tasks.
- There are several working groups within it:
- One of them works on hoax busting to address disinformation spreading with respect to the coronavirus.
- One works on science popularisation to develop material that explains concepts such as home quarantine.
- Other groups work on resources in Indian Languages, Mathematical Models and Apps Etc.
- It is suggested that an app should be developed that can map spaces being used as shelters and share that data with the State governments.
- A platform has also been developed to connect people in need with those who can provide help.
- It works through two channels, phone and WhatsApp.
- It can connect patients or people with symptoms to doctors.
- It may also connect elderly people with volunteers from NGOs to assist in chores such as grocery shopping.
CONTROLLING COVID-19 THROUGH SOUTH KOREAN MODEL
30, Mar 2020

Why in News?
- The Korean Model, a vigorous regime of “trace, test, treat”, has shown remarkable results in controlling the spread of the novel coronavirus, without putting a nationwide lockdown in place.
How is the Situation in Korea?
- Korea is now in full control of the spread of the disease. The number of new confirmed cases per day has been showing steady decline since hitting a peak at 989 in February to double-digit figures as of mid-March.
- Korea might be the only country that hasn’t imposed a lockdown within its territories or even of its international borders.
How has this been possible? What is the ‘Korean Model’?
- It is grounded on concentrated testing of high-risk areas and clusters.
- Korea found out at the beginning of the spread of the virus that a certain religious cult and its gathering was the cause of a large portion of the spread in a certain area of the country. This group had massive gatherings in a closed-off space.
- The government listed all members of the group across the country, tracked their whereabouts and conducted tests on a massive scale, leading to the rapid increase in the number of confirmed cases.
- However, Korea succeeded in identifying and isolating potential cases at a very early stage and finally flattened the curve.
Other Best Practices followed by Korea:
- The moment the virus DNA pattern was confirmed in Wuhan, Korean medical teams and bio-companies were able to develop new testing kits with surprising speed. This made it possible for Korea to conduct mass-scale testing of 18,000 cases a day.
- Anybody in Korea who has symptoms or reasons to be tested can get the test within minutes at ‘drive-thru’ or ‘walk-thru’ testing centres and receive the result by text message the very next day. Korea made available over 650 testing centres nationwide.
Is it possible for India to Replicate this Model?
- Given India’s demography and medical infrastructure, lockdowns are necessary. However, openness and transparency is important to tackling this situation and identifying and isolating the core of the spread of the virus with full medical capacity at the earliest possible stage is key. This is the essence of the ‘Korean model’.
ANTIBODY KITS
28, Mar 2020

Why in News?
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has recently invited manufacturers to supply 5 lakh antibody kits for diagnosis of COVID-19 infection.
About the Antibody Test:
- It will act as a screening process that will give quick results in a few hours.
- It detects the body’s response to the virus. It gives an indication that a person has been exposed to the virus.
- If the test is positive, the swab is collected and a Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) test is done using the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) kit. Therefore, this is a two-stage process.
- It does not definitely indicate that a person is infected with COVID-19 infection. It is only for screening. India is only conducting the conventional RT-PCR test (Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction).
About RT-PCR Test:
- It detects the virus genetic material, which is the RNA. It detects the body’s response to the virus.
- It provides direct evidence whereas antibody kits provide the Indirect Evidence.
About Ribonucleic Acid:
- It is an important biological macromolecule that is present in all biological cells.
- It is principally involved in the synthesis of proteins, carrying the messenger instructions from Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which itself contains the genetic instructions required for the development and maintenance of life.
- Contract Tracing is the process of identifying, assessing, and managing people who have been exposed to a disease to prevent transmission.
Why we need Antibody Kits?
- There is a Shortage of the PCR kits and thus the test is complicated, expensive and time-consuming.
- The antibody test will be where a large number of people are being quarantined and where everybody cannot undergo an RNA test.
- The antibody test was done in South Korea, one of the few countries which has been able to flatten the pandemic curve.
- A large number of suspected patients were being quarantined in the country through contact tracing of just a single patient.
About Indian Council of Medical Research:
- It is the apex body in India for the formulation, coordination and promotion of biomedical research.
- Its mandate is to conduct, coordinate and implement medical research for the benefit of the Society; translating medical innovations into products/processes and introducing them into the public health system.
- It is funded by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
ICMR RECOMMENDATIONS AND CAUTIONS OVER USE OF HYDROXY-CHLOROQUINE
25, Mar 2020
Why in News?
- The National Task force for COVID-19, constituted by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), has suggested the use of hydroxy-chloroquine to contain the spread of SARS-CoV-2 (Coronavirus) for restricted populations.
About ICMR:
- Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is the apex body in India for the formulation, coordination and promotion of biomedical research.
- Its mandate is to conduct, coordinate and implement medical research for the benefit of the Society; translating medical innovations into products/processes and introducing them into the public health system.
- It is funded by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
What is Hydroxy-chloroquine?
- Hydroxy-chloroquine (not to be confused with anti-malaria drug chloroquine) is an oral drug used in the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
- Autoimmune diseases are in which the body’s immune system attacks healthy cells.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting many joints, including those in the hands and feet.
Hydroxy-chloroquine against COVID-19:
- The drug shows antiviral activity in vitro against coronaviruses, and specifically, SARS-CoV-2 [the virus that causes COVID-19].
- Further, the study suggests that prophylaxis (treatment given to prevent disease) with hydroxy-chloroquine at approved doses could prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection and may help to improve viral shedding.
- Clinical trials are under way in China to know whether the drug can be used for treatment.
Combination of Hydroxy-chloroquine with Other Drugs:
Hydroxy-chloroquine and Chloroquine:
- A study suggests that both hydroxy-chloroquine and chloroquine have in vitro activity against SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and other coronaviruses, with hydroxy-chloroquine having higher potency against SARS-CoV-2.
- In vitro studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context (such as in a test tube).
- In contrast to in vitro experiments, in vivo studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants.
Hydroxy-chloroquine with Azithromycin:
- The combination of hydroxy-chloroquine with azithromycin is a commonly used antibiotic.
- The combination is expected to be efficient for virus elimination.
ICMR Recommendations on use of Hydroxy-chloroquine:
- The restricted population for usage of hydroxy-chloroquine include, namely, ‘Asymptomatic (showing no symptoms) Healthcare Workers’ and ‘Asymptomatic household contacts’ of laboratory-confirmed cases.
- The above mentioned population have been advised to use the hydroxy-chloroquine to contain further spread of the pandemic.
- However, the drug is not recommended as a preventive healthcare in children under 15 years of age.
- ICMR also advised that placing healthcare workers under hydroxy-chloroquine treatment should not instill a sense of false security and they need to follow all prescribed public health measures such as frequent washing of hands, respiratory etiquettes, keeping a distance of minimum one metre and use of personal protective equipment, etc.
Cautions over the Drug:
- ICMR cautioned the general public against the unrestricted use of the drug, stating that “it is still at experimental stage and is not recommended for public use.”
- Hydroxy-chloroquine is recommended only for a healthcare worker who is treating a COVID-19 patient.
- Secondly, it’s recommended only for persons staying with and caring for a household patient who has been tested positive. They can take that only for prophylaxis — only for prevention.
- “The recommendation is for empirical use of the drug based on available evidence and is restricted for use by only two categories of people and under strict supervision of a doctor.
How ICMR approved the Drug?
- None of the drug approving agencies across the world, including the FDA, has cleared the drug for prophylaxis or for treating COVID-19 patients which ICMR has done.
- The available evidence of the efficacy of the drug is a small study by French researchers involving 26 COVID-19 patients. The study found “significant” reduction in viral load in over half the number of patients at end of six days of therapy.
- As the trial showed significant reduction, the results were published on March 17 in the International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents even before the 14-day follow-up was completed.
- When there is no other drug available, and when the virus is highly contagious, it is best to use if there is some benefit. The same logic applies for other diseases where there are no medicines available. ICMR too applied the same logic in usage of this drug.
INDIA FRANCE
24, Mar 2020

Why in News?
- Recently, India and France conducted joint patrolling for the first time from the Reunion Island. The patrolling was conducted in the month of February by a P-8I aircraft.
Highlights
- It is conducted under the ‘Neighbourhood First’ policy and broader maritime cooperation, the Indian Navy undertakes joint Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) surveillance with Maldives, Seychelles and Mauritius and Coordinated Patrols (CORPATs) with Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand and Indonesia.
- The objectives of the CORPATs are to ensure effective implementation of United Nations Conventions on Laws of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- The joint patrolling with France shows India’s intent to expanding its footprint in the Indian Ocean, focusing on the stretch between the East African coastline and the Malacca straits.
- India has carried out CORPATs only with maritime neighbours and had rejected a similar offer by the US in 2016. India has recently become an observer to the Indian Ocean Commission. It consists of Reunion as one of its members.
About Defence Relations between India- France
- The Indian navy is currently inducting French Scorpene conventional submarines, being built in India under technology transfer.
- The Indian Air Force will soon get the first batch of its 36 Rafale fighter jets from France.
- India is working with France to develop strategic and economic partnership involving Madagascar, Reunion Islands-Comoros so as to balance the growing influence of China in that part of the Indian Ocean Region.
- Some of their defence exercises are
- Gagan Shakti is conducted by the Indian Air Force to showcase its air dominance over the entire extended area of the Indian Ocean Region.
- Garuda Shakti is the joint military exercise between India and Indonesia.
- Mitra Shakti is the joint military exercise between India and Sri Lanka.
About P-8I Aircraft:
- The Boeing’s P-8A Poseidon is designed for long-range Anti-Submarine warfare (ASW), Anti-Surface Warfare (ASuW), and intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) missions.
- Its Indian variant is referred to as P-8I. Of a total of 12 ordered aircrafts, India has received eight, making the Indian Navy’s P-8 fleet the second largest in the world. Another four aircrafts are on-schedule to be delivered in 2020.
- It is not just responsible for coastal patrolling but is also used for other critical missions like search-and-rescue, anti-piracy, and supporting operations of other arms of the military.
- Reunion Island is a French overseas department and overseas region in the western Indian Ocean. It is located about 420 miles (680 km) east of Madagascar and 110 miles (180 km) southwest of Mauritius.
About United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS):
- It is an international treaty which was adopted and signed in 1982. It replaced the four Geneva Conventions of April, 1958, which respectively concerned the territorial sea and the contiguous zone, the continental shelf, the high seas, fishing and conservation of living resources on the High Seas.
COVID-19: STAGE BY STAGE PANDEMIC
24, Mar 2020

Context:
- On the light of one of the greatest crisis, Pandemic COVID-19 across the globe, there are different stages of transmission that people need to know.
What are the Stages of a Pandemic?
- In the First stage of a disease epidemic that eventually takes the form of a pandemic sweeping the globe, cases are imported into a country in which the infection did not originate. An infection whose spread is contained within the boundaries of one or a few countries is obviously not a pandemic.
- The Second stage is when the virus starts being transmitted locally. Local transmission means that the source of the infection is from within a particular area and the trajectory the virus has taken from one person to the next is clearly established.
- The Third stage is that of community transmission.
What is Community Spread of the Infection?
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) says community transmission “is evidenced by the inability to relate confirmed cases through chains of transmission for a large number of cases, or by increasing positive tests through sentinel samples (routine systematic testing of respiratory samples from established laboratories)”.
- In the simplest terms, community spread is when you do not know the source of the infection — you are unable to trace it back to someone who has travelled in an affected area overseas, or got it through contact with someone who is infected.
Why the Third Stage is Worrisome?
- Community spread implies that the virus is now circulating in the community, and can infect people with no history — either of travel to affected areas, or of contact with the infected person.
- In a situation of community transmission, it is theoretically possible for every person regardless of where they are from or whether they have been in contact, to spread the infection.
When can it be said that the virus is definitely in the stage of Community Spread?
- There have to be several cases of untraced infection source to conclude definitively that the outbreak has moved to the Next Level
What is the Fourth Stage?
- It is when the disease becomes endemic in some countries. Among diseases that are currently endemic in India — meaning they occur round the year across the country — are malaria and dengue.
How does Categorising an outbreak in this Manner Help?
- The stages of a pandemic are uniform the world over.
- This is so because in today’s interconnected world, it is important to have a standardised phraseology that conveys the same thing to every person around the world, and helps countries prepare better.
- The categorisation helps countries take specific actions that are necessary to target just that particular scenario.
Worldwide, in which stage is the COVID-19 Pandemic Now?
- The pandemic has spread to nearly every country on the planet. In most, though, it is in the stage of either imported cases or local transmission.
- Among the countries where community transmission seems to be operating are China, Italy, Iran, South Korea and Japan.
How should India be Prepared Now?
- Isolation, and not indiscriminate testing, is the only way India can limit the spread of COVID-19.
- A lockdown is the most important step in breaking transmission of the infection.
MAHARASHTRA TOPS IN ORGAN DONATION
18, Mar 2020
Why in News?
- Maharashtra has recently surpassed Tamil Nadu and Telangana and became the top performer in the field of organ donation.
About:
- The Ministry of Health and Family welfare has established
- National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO) at National level, State Organ
- Tissue Transplant Organisation (SOTTO) in States and Regional Organ and
- Tissue Transplant Organisation (ROTTO) at regional level.
- NOTTO functions as apex centre for coordinating all activities and networking for procurement and distribution of organs and tissues and maintaining registry of organs and tissues donation and transplantation in the country.
- Sensitisation drives and the meticulous efforts of Regional Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation – State Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (ROTTO-SOTTO) along with four Zonal Transplant Coordination Centres (ZTCCs) are important contributing factors behind this achievement.
About Organ Donation:
- It means giving part of the body (organ) to a person with end stage organ disease who needs a transplant.
- The organs that can be donated for transplantation include kidney, liver, heart, lungs, and small bowel and tissues such as corneas, heart valves, skin and bone.
There are two types of Organ Donation:
- A person during his life can donate one kidney, a portion of pancreas and a part of the liver are called Living Donor Organ Donation.
- A person can donate multiple organs and tissues after (brain-stem/cardiac) death are called Deceased Donor Organ Donation.
Legal Framework for Organ Donation:
- Organ Transplantation and Donation is permitted both by law and covered under the “Transplantation of Human Organs Act 1994”, which has allowed organ donation by live & Brain-stem Dead donors.
- According to the amendment of the Act which also brought in donation of human tissues, thereby calling it as “Transplantation of Human Organs & Tissues Act 2011”.
- The Government of India has also started a National Organ and Transplant Program (NOTP).
- Under NOTP, which patients below the poverty line are supported for the cost of transplant as well as cost of immunosuppression after transplant for one year.
TACKLING COVID-19 THROUGH SOAPS
17, Mar 2020

Why in News?
- Guidelines by the World Health Organization, to reduce the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, specify that one of the ways to reduce the risk of infection is by regularly and thoroughly cleaning one’s hands with an alcohol-based hand rub or washing them with soap and water.
How does washing with soap help get rid of the Coronavirus?
- Using soap is more effective in removing microbes on our hands.
- Viruses such as coronavirus, influenza-causing viruses, Ebola, Zika have their genetic material encased in a layer of fat called the lipid envelop.
- Soap molecules are pin-shaped with a head that is water-loving (hydrophilic) and a tail that is oil-loving (oleophilic). Being oleophilic, the tail portion of the molecule tends to have an affinity for and ‘competes’ with the lipids in the virus envelope.
- Since the chemical bonds holding the virus together are not very strong, the long oleophilic tail gets inserted into the envelope and tends to have a ‘crowbar’ effect that breaks the lipid envelope of the virus.
- The tail also competes with the bond that binds the RNA and the lipid envelop thus dissolving the virus into its components which are then removed by water.
Do all viruses have the Lipid Layer?
- No, certain viruses do not have the lipid envelop and are called the non-enveloped viruses. Rotavirus which causes severe diarrhoea, poliovirus, adenovirus that cause pneumonia and even human papillomavirus (HPV) do not contain the lipid envelop.
- The oil-loving tail of the soap molecule also disrupts the bond that binds dirt and non-enveloped viruses to the hand.
- The dirt and viruses are surrounded by several tails making them remain as suspended particles. Rinsing with water washes away the suspended particles leading to clean hands.

How do alcohol-based hand sanitisers help get rid of coronavirus?
- Like soap, the alcohol present in hand sanitisers dissolve the lipid envelop, thus inactivating the virus.
- In addition, the alcohol also tends to change the shape or denature the mushroom-shaped protein structures that stick out of the lipid envelop. The mushroom-shaped protein structures help the virus to bind to special structures found on human cells and enter the cells. To be effective, the sanitisers should contain at least 60% alcohol.
- Unlike water, alcohol run does not remove the dead viruses from the hand. While a sanitiser can quickly reduce the number of microbes, it does not get rid of all types of germs, and is “not as effective when hands are visibly dirty or greasy”.
Primary Precautions:
- WHO cautions that using a mask alone will be insufficient to provide an“adequate level of protection”. It should be combined with hand hygiene to prevent human-to-human transmission.
ONE HEALTH CONCEPT
17, Mar 2020

Why in News?
- India has highlighted the ‘One Health policy’ to tackle the zoonotic diseases after it is facing the devastating COVID-19 outbreak.
About One Health Concept:
- One Health is an approach to designing and implementing programmes, policies, legislation and research in which multiple sectors communicate and work together to achieve better public health outcomes.
- The areas of work in which a One Health approach is particularly relevant include food safety, the control of zoonotic diseases (diseases that can spread between animals and humans, such as flu, rabies and Rift Valley Fever), and combating antibiotic resistance (when bacteria change after being exposed to antibiotics and become more difficult to treat).
- The diseases, which “spillover” from animals to humans are referred to as zoonotic diseases
- They represent more than 60% of emerging infectious diseases worldwide.
- The destruction of the natural environment, globalised trade and travel and industrialised food production systems have created numerous pathways for new pathogens to jump between animals and Humans.
- Although One Health, as a conceptual entity, emerged relatively recently, a stellar example of One Health being operationalised in the field was seen in India in the late 1950s.
India and One Health Approach:
- In the 1950s, the One Health approach helped discover the source of Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD), a highly dangerous haemorrhagic fever more threatening than COVID-19.
- This was the result of working of several organizations such as the Virus Research Centre (now known as the National Institute of Virology), Pune, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Bombay Natural History Society.
- In 2018, Kerala reacted quickly and efficiently to tackle the Nipah virus outbreak and successfully managed to confine it to 23 cases.
- This success is credited to the strong public health infrastructure and the political will to quickly seek help from a multidisciplinary team of national and international experts.
- One of the components of the National Mission on Biodiversity and Human Well-being explicitly links biodiversity to human health through the One Health framework.
- The mission aims to explore the neglected links between biodiversity science and human well-being across the sectors of health, economic development the caviar collection, agricultural production and livelihood generation, in combination with efforts to mitigate climate change and related disasters.
- However, the regulatory framework for doing One Health research in India with international collaboration typically requires approvals from multiple authorities. This hampers the country’s ability to rapidly respond to emerging threats from infectious diseases.
Way Forward:
- The frequency with which new pathogens are emerging or old ones are re-emerging across the world are alarm calls for greater transparency, cross-country collaborations, and enhanced national infrastructure and capacity for integrated One Health science.
- India needs to leap-frog over the systemic and institutional barriers that prevent an integrated One Health framework from being operationalised.
- The One Health framework will help government and private institutions, across a range of disciplines, in collaborating to understand how zoonotic diseases can emerge, the threats they can pose, and the mechanisms by which the emergence or spread can be controlled.
TREATING DRUG-RESISTANT TB
16, Mar 2020

Why in News?
- A small trial (Nix-TB) undertaken at three sites in South Africa to test the safety and efficacy of three oral drugs, bedaquiline, pretomanid and linezolid, in patients with extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB) and multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) showed encouraging results.
Highlights:
- Of the 98 patients who were successfully treated using the three drugs, 63 patients had XDR-TB and 35 had MDR-TB. The treatment success rate was 89% (63 of 71) for XDR-TB and 92% (35 of 38).
- The treatment using the three oral drugs lasted for 26 weeks and was followed-up for six months after the end of the treatment. Patients received the treatment daily for 26 weeks.
- The 90% treatment success in the case of hard-to-treat patients is at par with the success rate seen while treating drug-sensitive TB. Of the 109 patients treated, 11 had unfavourable outcomes while 98 had favourable outcomes.
- Of the 11 patients who had unfavourable outcomes, there were seven deaths and two had a relapse during the six-month follow-up period.
- The MDR-TB patients included in the trial were either not responsive to standard treatment or had discontinued treatment due to side effects.
- Of the three drugs used in the trial, a “high-percentage” of patients experienced adverse effects related to linezolid drug.Of the 109 patients treated, 88 patients (81%) had peripheral neuropathy (weakness, numbing and pain usually of hands and feet due to nerve damage), though the symptoms were mild to moderate in the majority of cases.
- Two patients developed optic neuritis, where the optic nerve becomes inflamed, which was resolved when linezolid drug was withdrawn.
- Also, 40 had anaemia, while eight patients had adverse event of the liver and the regime had to be interrupted.
Causes:
- Drug-resistant TB can occur when the drugs used to treat TB are misused or mismanaged. Examples of misuse or mismanagement include
- People do not complete a full course of TB treatment
- Health care providers prescribe the wrong treatment (the wrong dose or length of time)
- Drugs for proper treatment are not available
- Drugs are of poor quality
- Drug-resistant TB is more common in people who
- Do not take their TB drugs regularly
- Do not take all of their TB drugs
- Develop TB disease again, after being treated for TB disease in the past
- Come from areas of the world where drug-resistant TB is common
- Have spent time with someone known to have drug-resistant TB disease
ROLE OF GLUCOSE IN REGULATING LIVER FUNCTIONS
16, Mar 2020
Why in News?
- The recent study by researchers from the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai (TIFR) has revealed that glucose in the body controls the function of SIRT1 directly.
What is SIRT1?
- SIRT1 is an enzyme that de-acetylates (removal of acetyl) proteins and contribute to cellular regulation (reaction to stressors, longevity).
Functions:
- In normal healthy individuals, SIRT1 protein levels are known to increase during fasting and decrease during the feed, which is essential to maintain a balance between glucose and fat metabolism.
- The glucose controls the functions of a protein SIRT1 which in turn maintains everyday feed-fast cycles and is also associated with longevity.
- The feed-fast cycle is a basic pattern and the metabolism-related to this is largely taken care of by the liver.
- Thus, the study shows that both over-activation and under-activation of SIRT1 can lead to diseases.Glucose puts a check on the activity of SIRT1 in the fed state. In the absence of this check, SIRT1 activity increases and results in hyperglycemia in a fasted state, mimicking diabetic state.
- The constant feeding or high-calorie intake that leads to a sustained reduction in the levels of SIRT1 (by glucose) is associated with ageing and obesity.
Significance of the Study:
- A shortage or absence of the control of SIRT1 by glucose may lead to a diabetic-like state, while excess feeding and sustained low levels of SIRT1 can lead to obesity and enhanced ageing.
- This study paves the way might be beneficial in tackling lifestyle disorders and ageing-Related Diseases.
FINDING CURE FOR CORONAVIRUS
14, Mar 2020

Why in News?
- Scientists across the world are trying to develop a line of treatment and a possible vaccine for COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, which has infected over 100,000 people and claimed over 4,000 lives.
Highlights:
- A global effort is on to collect and analyse the genetic composition of the new virus, which would be key to developing a cure and a vaccine.
- Laboratories in various countries have been isolating and sharing the genome sequences of the virus on an international platform.
- Whole genome sequencing is the process of determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism’s genome at a single time.
Significance of COVID-19 Genome Sequencing:
- Genome sequence is the unique code of genetic material of any organism, and determines the characteristic of any organism.
- The gene composition of novel coronavirus, for instance, is different from that of the influenza virus.
- India has so far reported two sets of genome sequences, both of which are very similar to the original sequences collected from patients in Wuhan.
- When viruses multiply, or reproduce, there is a copying mechanism that transfers the gene information to the next generation.
- When the virus multiplies, there will be small changes, which are called mutations. These mutations accumulate over time, and after prolonged periods, are responsible for evolution into new organisms.
- The small changes could provide scientists with information about the origin, transmission, and impact of the virus on the patient.
- It could also hold clues to the differing effects the virus could have on patients with different health parameters.
- Patients with existing medical conditions could be candidates from where genome sequences of this virus could be isolated. This could help scientists to look for clues to possible impact of virus amidst those existing medical conditions.
- New technological tools have made it easier to isolate full genome sequences. Traditional techniques used to take weeks for the extraction, but new machines are able to do it within two to three days.
- Right now, drugs are being repurposed, meaning old drugs for similar diseases are being checked for their efficacy against COVID-19. These drugs, if they work, will require clinical trials, and then can be made widely available for people.
Genome Sequencing:
- Genome:It is an organism’s complete set of DNA, including all of its genes.
- Each genome contains all of the information needed to build and maintain that organism. In humans, a copy of the entire genome—more than 3 billion DNA base pairs—is contained in all cells that have a nucleus.
- Genome sequencing: It is figuring out the order of DNA nucleotides, or bases, in a genome—the order of As, Cs, Gs, and Ts that make up an organism’s DNA. The human genome is made up of over 3 billion of these genetic letters.
- Sequencing the genome doesn’t immediately lay open the genetic information of an entire species. Even with a rough draft of the human genome sequence in hand, much work remains to be done. Scientists still have to translate those strings of letters into an understanding of how the genome works.
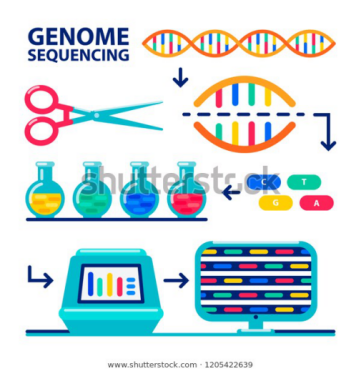
CURING HIV USING STEM CELL THERAPY
13, Mar 2020

Why in News?
- Researchers report that a patient who underwent stem-cell transplantation and a chemotherapy drug regimen has been cured of HIV.
Highlights:
- In 2011, a patient based in Berlin (the ‘Berlin patient’) was the first HIV patient to be reportedly cured of the virus three and half years after undergoing similar treatment.
- Although there was no active viral infection in the patient’s body, remnants of integrated HIV-1 DNA remained in tissue samples, which were also found in the first patient to be cured of HIV.
- The authors suggest that these can be regarded as so-called ‘fossils’, as they are unlikely to be capable of reproducing the virus. The findings show that the success of stem cell transplantation as a cure for HIV, first reported nine years ago in the Berlin patient, can be replicated.
- As a high-risk treatment, this therapy is unlikely to be offered widely to patients with HIV who are on successful antiretroviral treatment.
- The transplant aimed to make the virus unable to replicate in the patient’s body, whilst the body irradiation and chemotherapy targeted any residual HIV virus.
- Ultrasensitive viral load sampling from the London patient’s cerebrospinal fluid, intestinal tissue or lymphoid tissue was taken at 29 months after interruption of antiretroviral therapy (ART) and viral load sampling of his blood at 30 months.
- The results showed no active viral infection was detected in samples of the patient’s blood at 30 months or in his cerebrospinal fluid, semen, intestinal tissue and lymphoid tissue 29 months after stopping ART.
- Researchers suggest that the long-term remission of HIV can be achieved using reduced intensity drug regimens, with one stem cell transplant (rather than two) and without total body irradiation.
- Gene editing using the CCR5 has received a lot of attention recently. There are still many ethical and technical barriers to overcome before any approach using CCR5 gene editing can be considered as a scalable cure strategy for HIV.
NATIONAL MISSION ON INTERDISCIPLINARY CYBER PHYSICAL SYSTEMS (NMICPS)
12, Mar 2020
Why in News?
- Recently, the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Ropar, Punjab is setting up a Sectoral Application Hub in Technologies for Agriculture and Water.
About National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber Physical Systems (NMICPS):
- The hub is being set up under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber Physical Systems (NMICPS) and is granted by Union Government’s Science and Engineering Research Board.
- It will bring solutions for stubble management, water quality improvement and mapping of hazardous substances in water.
- It aims at carrying out translational research and work with concerned departments to develop prototypes, products and implementations.
- It was launched in 2018 and is implemented by the Department of Science & Technology for a period of five years.
- It covers entire India which includes Central Ministries, State Governments, Industry and Academia.
Its objectives are:
- It is a comprehensive mission which would address technology development, application development, human resource development & skill enhancement, entrepreneurship and start-up development in Cyber-Physical System (CPS) and associated technologies.
- The mission aims at establishing 15 Technology Innovation Hubs (TIH), six Application Innovation Hubs (AIH) and four Technology Translation Research Parks (TTRP).
- They have four focused areas namely:
- Technology Development.
- HRD & Skill Development.
- Innovation, Entrepreneurship & Start-ups Ecosystem Development.
- International Collaborations.
Cyber-Physical Systems:
- These systems integrate sensing, computation, control and networking into physical objects and infrastructure, connecting them to the Internet and to each other.
Few Potential Applications:
- Driverless cars that communicate securely with each other on smart roads.
- Sensors in the home to detect changing health conditions.
- Improving agricultural practices.
- Enabling scientists to address issues arising out of climate change.
- Advances in cyber-physical systems will enable capability, adaptability, scalability, resiliency, safety, security and usability that will far exceed the simple embedded systems of today
COVID-19 NOW A PANDEMIC, SAYS WHO
12, Mar 2020

Why in News?
- WHO has recently announced COVID-19 as pandemic amidst of increasing outbreak in various countries.
What is COVID-19?
- The COVID-19 is a disease caused by the spread of 2019-nCoV (2019 novel Corona Virus).
- Originating in China, it has spread to other parts of the world which is a cause for concern.
- Coronaviruses are a class of viruses so named because their electron microscope image resembles the corona of the sun.
- They are usually found in animals, but sometimes get transmitted to human beings possibly through the food chain.
- The symptoms can include fever, cough and shortness of breath.
- This happened during the 2003 outbreak of SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) coronavirus that claimed close to 800 lives.
- The current 2019 strain that had originated in China has been named as 2019 ‘novel’ coronavirus (2019-nCoV) or SARS-CoV-2.
What is Pandemic?
- A pandemic is an epidemic of disease that has spread across a large region; for instance multiple continents, or worldwide.
- A widespread endemic disease that is stable in terms of how many people are getting sick from it is not a pandemic.
- The last pandemic reported was the 2009 H1N1 flu pandemic, which killed hundreds of thousands globally.
- According to 2017 pandemic influenza risk management guidelines, the WHO uses pandemic influenza phases, interpandemic, alert, pandemic and transition, to reflect its risk assessment of the global situation regarding each influenza virus with pandemic potential infecting humans.
- Further, flu pandemics generally exclude recurrences of seasonal flu.
- Throughout history, there have been a number of pandemics, such as smallpox and tuberculosis. One of the most devastating pandemics was the Black Death, which killed an estimated 75–200 million people in the 14th century.
- The only current pandemic is HIV/AIDS, which started in the 1980s. Other recent pandemics are the 1918 influenza pandemic (Spanish flu) and the 2009 flu pandemic (H1N1).
What are the different levels of disease?
- According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there are different levels of diseases, they are:
- Sporadic:When a disease occurs infrequently and irregularly.
- Endemic:A constant presence and/or usual prevalence of a disease or infection within a geographic area. (Hyper endemic, is a situation in which there are persistent, high levels of disease occurrence.)
- Epidemic:A sudden increase in the number of cases of a disease—more than what’s typically expected for the population in that area.
- Pandemic:An epidemic that has spread over several countries or continents, affecting a large number of people.
Phases of Pandemics:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) provides an influenza pandemic alert system, with a scale ranging from Phase 1 (a low risk of a flu pandemic) to Phase 6 (a full-blown pandemic):
- Phase 1:A virus in animals has caused no known infections in humans.
- Phase 2:An animal flu virus has caused infection in humans.
- Phase 3: Sporadic cases or small clusters of disease occur in humans. Human-to-human transmission, if any, is insufficient to cause community-level outbreaks.
- Phase 4:The risk for a pandemic is greatly increased but not certain.
- Phase 5:Spread of disease between humans is occurring in more than one country of one WHO region.
- Phase 6:Community-level outbreaks are in at least one additional country in a different WHO region from phase 5. A global pandemic is under way.
CORD BLOOD BANKING
10, Mar 2020
Context:
- Cord Blood Banking is recently seen in news.
Highlights
- Over the past decade, stem cell banking has been aggressively marketed even as its use is still in experimental stages.
- They get access to data of to-be parents and start approaching their prospective customers much before the delivery and offer competitive packages.
- They convince parents to bank the cells for several years promising future therapeutic use.
- Enormous fees are charged from parents to preserve cells merely by emotional marketing.
- According to Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR),there is no scientific basis for preservation of cord blood for future self-use and this practice therefore raises ethical and social concerns. It does not recommend commercial stem cell banking.
- Private storage is advisable when there is an elder child in the family with a condition treatable with these cells and the mother is expecting the next baby. In other situations, parents should be educated about the limitations of banking at this point of time.
About Indian Council of Medical Research:
- It is the apex body in India for formulation, coordination and promotion of biomedical research.
- Its mandate is to conduct, coordinate and implement medical research for the benefit of the Society; translating medical innovations into products/processes and introducing them into the public health system.
- It is funded by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
Cord Blood Banking:
- It is the blood from the baby that is left in the umbilical cord and placenta after birth.
- The banking involves taking the umbilical cord blood, which is a rich source of stem cells, and preserving it for future use.
- It contains special cells called hematopoietic stem cells that can be used to treat some types of diseases. Hematopoietic stem cells can mature into different types of blood cells in the body.
- Globally, the banking is recommended as a source of hematopoietic stem cellb derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood transplantation for haematological cancers and disorders where its use is recommended.
- The use of cord blood as a source of stem cells for all other conditions is not yet established.
Stem Cells:
- It is special human cells that have the ability to develop into many different cell types, from muscle cells to brain cells.
- It is divided into two main forms- Embryonic stem cells and Adult Stem Cells.
- Embryonic stem cells come from unused embryos resulting from an in vitro fertilization procedure and that are donated to science. These cells are pluripotent, meaning that they can turn into more than one type of cell.
- Adult Stem Cells are two types of adult stem cells. One type comes from fully developed tissues, like the brain, skin, and bone marrow. There are only small numbers of stem cells in these tissues, and they are more likely to generate only certain types of cells. For example, a stem cell derived from the liver will only generate more liver cells.
- The second type is induced pluripotent stem cells. These are adult stem cells that have been manipulated in a laboratory to take on the pluripotent characteristics of embryonic stem cells.
FACIAL RECOGNITION
09, Mar 2020

Context:
- In recent years, facial recognition has become a cause for concern in western democracies. The European Commission is considering imposing a five-year moratorium on the use of facial recognition technologies in the European Union (EU). Whereas, the United States (US), municipalities have are considering passing prohibitions, India, however, is rushing to adopt public facial recognition.
What is Facial Recognition, and how does it work?
- Facial recognition is a technology, based on artificial intelligence (AI), that leverages biometric data to identify a person based on their facial patterns.
- It can be used for the purposes of ‘verification’ and ‘identification’ of individuals.
- Facial recognition has evolved in many ways, from the first cameras that could recognise faces in the mid-1960s up to now.
- It has evolved from looking at 3D contours of a face to recognising even the skin patterns.
- Facial recognition systems analyze the visual data and millions of images and videos created by high-quality Closed-Circuit Television (CCTV) cameras installed in our cities for security, smartphones, social media, and other online activity.
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence capabilities in the software map the distinctive facial features mathematically, look for patterns in the visual data, and compare new images and videos to other data stored in facial recognition databases to determine identity.
- Market research experts believe that the facial recognition market will grow to $9.6 billion by 2022.
What are the uses of Facial Recognition Technology?
- Today, it’s used in a variety of ways from allowing you to unlock your phone, go through security at the airport, purchase products at stores etc,.
- One of the major advantages of facial recognition technology is safety and security.
- Law enforcement agencies use the technology to uncover criminals or to find missing children or seniors.
- In the financial sector, the demand for remote identification services is growing faster than ever, so identity verification technology based on live video is increasingly used such as the Fully-Verified system.
- Airports are increasingly adding facial recognition technology to security checkpoints.
- It can play a critical role in finding missing children, preventing human trafficking, and curbing crime. Experts believe that when people know they are being watched, they are less likely to commit crimes so the possibility of facial recognition technology being used could deter crime.
Where do we find Such Technology in India?
- Facial recognition systems have been active at several major Indian airports, including the Delhi airport. These systems at airports have been installed under the DigiYatra initiative.
- Telangana’s election commission piloted a facial recognition app in its local elections, and claimed that it could address the issue of voter impersonation.
- In the long-term, India plans to build a nation-wide Automated Facial Recognition System (AFRS) under the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), to modernize the process for criminal identification and verification by various police organizations across the country.
What are the Issues Associated with the Technology?
- The accuracy of the facial recognition software is questionable.
- For instance, the Delhi Police applied the facial recognition technology to find missing children, the success rate was less than 1 percent.
- In some cases, the technology could not even differentiate between genders.
- The technology suffers from ethnic and racial biases globally.
- The technology propagates, open collection of private data without putting in place adequate safeguards for individual privacy.
- As a consequence, it infringes upon an individual’s Fundamental Rights.
- There is a possibility that the technology could be used for mass surveillance.
- There’s no sufficient information regarding the type of security that would be employed to ensure the integrity of the repository of the database such that it is not privatized or monetized.
- The level of reliability or admissibility standards that would apply to such data being presented as evidence during legal proceedings cannot be determined.
Finding the Balance:
- The current application of facial recognition for public services does raise reasonable questions and concerns about privacy and rights.
- However, given this technology’s potential to solve problems, if applied properly in specific cases and contexts and with proper regulatory mechanisms, it could be leveraged in a beneficial manner.
WORKING OF IN-FLIGHT WI-FI SERVICES
04, Mar 2020

Why in News?
- The government has permitted airlines operating in India to provide in-flight Wi-Fi services to passengers.
- This move comes after the Telecom Commission had given its green signal to in-flight connectivity of Internet and mobile communications on aircraft in Indian airspace in 2018.
Who Can Permit?
- The pilot may permit the access of Internet services by passengers on board an aircraft in flight, through Wi-Fi on board, when laptop, smartphone, tablet, smart watch, e-reader or a point of sale device is used in flight mode or airplane mode.
How in- flight Connectivity Works?
- In-flight connectivity systems use two kinds of technologies– terrestrial and satellite internet services.
- Once flight mode is activated, the plane’s antenna will link to terrestrial Internet services provided by telecom service providers.
- Then, when the aircraft has climbed to 3,000 m, the antenna will switch to satellite-based services.
- This way, there will be no break in Internet services to passengers, and cross-interference between terrestrial and satellite networks will be avoided.
What are its Impacts?
- Globally, more than 30 airlines allow voice calls and internet access during flights. This facility will now will help Indian airlines compete with foreign carriers.
- Business travellers greatly value these services as they can continue their work commitments without any deterrence.
- Other travellers can be in touch with their near and dear ones even during the flight.
What are the Challenges Faced?
- Airlines will have to bear the initial cost of installing antennae on aircraft. So, the additional cost could find a way into ticket prices.
- Apart from the equipment, airlines will have to bear additional fuel costs, given the extra weight and drag aircraft will face due to the antenna.
- Technology and laws allow calls to be made from aircraft, which in turn lead to noisy cabins.
WOMEN IN SCIENCE
02, Mar 2020

Context:
- Recently, National Science Day (NSD) was celebrated at Vigyan Bhawan on February 28 with ‘Women in Science’ as the focal theme. President of India Ram Nath Kovind announced three key initiatives for gender advancement and equality in academic and research institutions on the occasion of National Science Day.
The National Science Day:
- The first National Science Day was celebrated on February 28, 1987.
- On this day, Sir C V Raman announced his discovery, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize for this discovery in 1930.
- National Council for Science & Technology Communication (NCSTC), Department of Science and Technology (DST) acts as a nodal agency to coordinate the celebration of the National Science Day.
Gender Disparity in Science:
- The world over, women scientists have been in the forefront of ground-breaking research across the world.
- But despite their remarkable discoveries, globally they still represent just 29 % of researchers. In India the numbers have been even less.
- Globally only 3% of the Nobel Prizes for science have been awarded to women, and only 11% of senior research roles are held by women.
- According to a 2018 fact sheet prepared by UNESCO on women in science, just 28.8% of researchers are women. In India, this stands at 13.9%.
- UNESCO data from 2014-16 show that only around 30% of female students select STEM (science, technology, engineering and mathematics)-related fields in higher education.
- In India, a 2016-17 NITI Aayog report compared female enrolment in various disciplines over five years –
- In 2015-16, 9.3% of female students in undergraduate courses were enrolled in engineering.
- Conversely, 4.3% of female students were enrolled in medical science, compared to 3.3% across genders.
- Then, at master’s and doctoral levels, female enrolment remained lower than overall enrolment, and also fell behind for medical science in three of the five years.
- Broadly, women showed a preference for arts; however, female enrolment in science streams rose from 2010-11 to 2015-16.
- The report found that in over 620 institutes and universities, including IITs, NITs, ISRO, and DRDO, the presence of women was 20.0% among Scientific and Administrative Staff, 28.7% among Post-Doctoral Fellows, and 33.5% among PhD scholars.
Why so few women in STEM?
- Main three socio-psychological reasons, namely
- masculine culture
- lack of sufficient early exposure to computers, physics and related areas compared to boys in early childhood
- gender gap in self-efficacy.
- Data from the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) and the IHDS show that education and employment have a U-shaped relationship (a rise and subsequent decline in employment with the rise in education levels).
- The recent National Family Health Survey data reflect that the increasing levels of education have not offered a greater say in household decisions or freedom of movement outside the home to women.
- Rising education for women does not offer increasing income-earning opportunities or better marriage prospects.
- Social barriers and prejudices have curbed the benefits from the rising education levels of women.
- Their contribution to the economy specifically, or the society as free and liberated members in general, have further been worsened by lack of their participation in STEM fields from school years.
Way Forward:
- Mindset changes –
- Educating boys and girls equally.
- Gender sensitization of male colleagues.
- An integrated approach is needed along with women-centric policy making where women are not treated as passive beneficiaries but are seen as potential contributors to society.
- The scientific community should facilitate women’s participation as both colleagues and leaders.Along with legislative cushions like the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013, Maternity Benefit Act, social sensitization towards the issues of women is important.
- Measures for increasing education levels should be balanced with the creation of jobs and better facilities for women.
- Special Schemes and affirmative action for women scientists.
- Creating website repository of women scientists & their work.
- Incentivizing institutions to be gender friendly.
- Open and collaborative work culture.
- India has shown a dedicated will to bring changes by pledging to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals which include ideals of gender justice and women empowerment.
- Only with constructive planning and comprehensive changes at various levels of society can the new emerging “women” be able to realize her complete potential in India.
- Creating appropriate infrastructure to help women balance family & professional Responsibilities.Collaboration between scientists and social scientists for a better understanding of the problem.
PRESENCE OF COLISTIN-RESISTANT BACTERIA OF FOOD ORIGIN IN THE GUT IS CAUSE FOR WORRY
02, Mar 2020

Why in News?
- Recently, a new study has found that the origin and spread of Colistin resistant bacteria in human gut is majorly on account of Poultry.
What is Colistin?
- Colistin is a last-resort anti-biotic that is commonly used for treating gram negative infections in humans like Pneumonia, meningitis and other infections caused by E.coli etc
- Besides, use of Colistin is rampant in poultry where it is used as growth promoter and for disease prevention. (Tylosin is another antibiotic used as growth promoter)
Colistin-Resistance in Bacteria:
- Recently it has been found that bacterial strain Klebsiella pneumonia that lives in human gut has developed resistance to colistin.
- The origin of colistin-resistance in human gut Bacteria Includes
1. Hospitals
2. Food
- Poultry consumption
- Vegetables that contains Colistin-resistant Klebsiella bacteria:
- This is because poultry litter is used as manure for growing vegetables.
- Colistin-resistant bacteria of hospital origin do not respond to any of the antibiotics, including carbapenem while colistin-resistant bacteria of food origin will respond to carbapenem.
How resistance is Spread?
- The mutation in the mgrB gene confers colistin resistance to Klebsiella bacteria.
- Besides in 3% of the cases colistin-resistance in Klebsiella bacteria is due to mutation in mcr gene.
Significance of the Study:
- So far it was believed that the mutation in the mgrB gene or other chromosomal genes are the reason behind colistin resistance in Klebsiella bacteria.
- Till date, there is no evidence to suggest that the mgrB gene mutation spreads from food to human Klebsiella bacteria.
- But this study has found mgrB gene mutation in food Klebsiella bacteria. This shows that mgrB gene mutation also spreads from food to human Klebsiella bacteria.
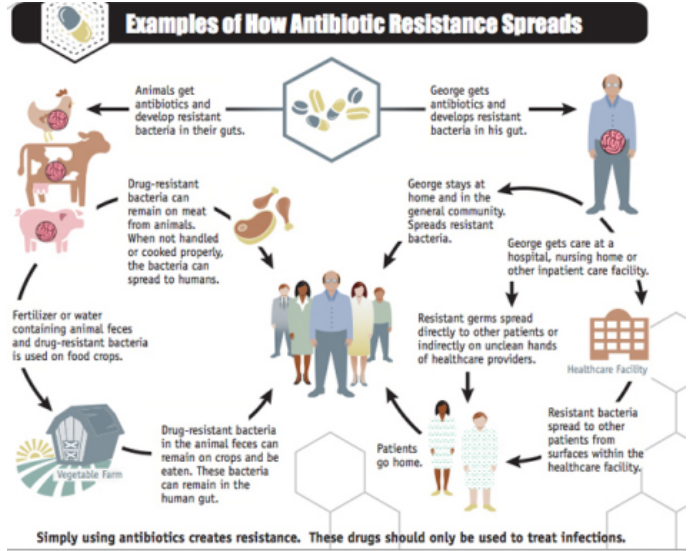
NASA’S ARTEMIS PROGRAM
26, Feb 2020

Why in News?
- United States space agency National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has recently announced that it will begin to accept applications for astronauts under its Artemis programme.
About Artemis Programme:
- Artemis– Acceleration, Reconnection, Turbulence and Electrodynamics of Moon’s Interaction with the Sun.
- It is NASA’s next mission to the Moon.
- Its objective is to measure what happens when the Sun’s radiation hits our rocky moon, where there is no magnetic field to protect it.
- Artemis was the twin sister of Apollo and goddess of the Moon in Greek mythology.
- With the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
What are its Significances?
- NASA’s powerful new rocket, the Space Launch System(SLS), will send astronauts aboard the Orion spacecraft nearly a quarter million miles from Earth to lunar orbit.
- Astronauts will dock Orion at the Gateway and transfer to a human landing system for expeditions to the surface of the Moon.
- They will return to the orbital outpost to board Orion again before returning safely to Earth.
- The agency will fly two missions around the Moon to test its deep space exploration systems.
- NASA is working toward launching Artemis I, a non crewed flight to test the SLS and Orion spacecraft together, followed by the Artemis II mission, the first SLS and Orion test flight with crew. NASA will land astronauts on the Moon by 2024 on the Artemis III mission and about once a year thereafter.
What are its scientific objectives?
- Find and use water and other critical resources needed for long-term exploration.
- Investigate the Moon’s mysteries and learn more about our home planet and the universe.
- Learn how to live and operate on the surface of another celestial body where astronauts are just three days from home.
- Prove the technologies we need before sending astronauts on missions to Mars, which can take up to three years roundtrip.
EU’S DATA STRATEGY
22, Feb 2020
Why in News?
- The European Commission has released a ‘European strategy for data to ensure the human-centric development of Artificial Intelligence’ and a white paper on Artificial Intelligence.
Highlights:
- The new documents present a timeline for various projects, legislative frameworks, and initiatives by the European Union, and represent its recognition that it is slipping behind American and Chinese innovation.
- The strategy lays out “why the EU should act now”. The blueprint hopes to strengthen Europe’s local technology market by creating a “data single market” by 2030 to allow the free flow of data within the EU.
- To aid a “data-agile economy”, the Commission hopes to implement an enabling legislative framework for the governance of common European data spaces by the latter half of the year.
- Between 2021 and 2027, the Commission will invest in a High Impact Project to jump-start data infrastructure. Several other initiatives are laid out, including a cloud services marketplace.
Reason for the Policy:
- The EU has the potential to be successful in the data-agile economy. It has the technology, the know-how and a highly skilled workforce. However, competitors such as China and the US are already innovating quickly and projecting their concepts of data access and use across the globe.
- With American and Chinese companies taking the lead on technological innovation, Europe is keen to up its own competitiveness.
Indian Context:
- The Economic Survey of 2018 envisioned a similar use of non-personal data. Just as the EU’s strategy discusses “data for public good”, the chapter titled “Data ‘Of the People, By the People, For the People’” advocated that the government step in to sectors that private players ignore, marking the first time India’s Economic Survey has isolated “data” as a strategic focus.
- Other data integration efforts have been announced or implemented by NITI Aayog (the National Data & Analytics Platform), the Smart Cities Mission (India Urban Data Exchange), and the Ministry of Rural Development (DISHA dashboard).
- In 2018, the National Informatics Centre worked with PwC and other vendors to create a Centre of Excellence for Data Analytics aimed at providing data analysis help to Government Departments.
ADITHYA L-1 MISSION
20, Feb 2020

Why in News?
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is also preparing to send its first scientific expedition to study the Sun. Named Aditya-L1, the mission, expected to be launched early next year, will observe the Sun from a close distance, and try to obtain information about its atmosphere and Magnetic Field.
Highlights:
- Earlier this month, 47 new papers were published in a special supplement of The Astrophysical Journal, analysing data from the first three flybys of the Parker Solar Probe, NASA’s historic mission to the Sun.
- ISRO categorises Aditya L1 as a 400 kg-class satellite, that will be launched using the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) in XL configuration. The space-based observatory will have seven payloads (instruments) on board to study the Sun’s corona, solar emissions, solar winds and flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), and will carry out round-the-clock imaging of the Sun.
- The mission will be undertaken in collaboration between various labs of ISRO, along with institutions like the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bengaluru, Inter University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA), Pune, and Indian Institute of Science, Education and Research (IISER), Kolkata.
- Aditya L1 will be ISRO’s second space-based astronomy mission after AstroSat, which was launched in September 2015.
- What makes a solar mission challenging is the distance of the Sun from Earth (about 149 million km on average, compared to the only 3.84 lakh km to the Moon) and, more importantly, the super hot temperatures and radiations in the solar atmosphere.
Importance of Solar Mission:
- The solar weather and environment, which is determined by the processes taking place inside and around the sun, affects the weather of the entire system.
- Variations in this weather can change the orbits of satellites or shorten their lives, interfere with or damage onboard electronics, and cause power blackouts and other disturbances on Earth.
- Knowledge of solar events is key to understanding space weather. To learn about and track Earth-directed storms, and to predict their impact, continuous solar observations are needed.
- Every storm that emerges from the Sun and heads towards Earth passes through L1, and a satellite placed in the halo orbit around L1 of the Sun-Earth system has the major advantage of continuously viewing the Sun without any occultation/eclipses.
- Aditya L1 will perform continuous observations looking directly at the Sun. NASA’s Parker Solar Probe has already gone far closer, but it will be looking away from the Sun.
- The earlier Helios 2 solar probe, a joint venture between NASA and space agency of erstwhile West Germany, went within 43 million km of the Sun’s surface in 1976.
Lagrange Point:
- L1 refers to Lagrangian/Lagrange Point 1, one of five points in the orbital plane of the Earth-Sun system. Lagrange Points are positions in space where the gravitational forces of a two-body system (like the Sun and the Earth) produce enhanced regions of attraction and repulsion.
- These can be used by spacecraft to reduce fuel consumption needed to remain in position. The L1 point is home to the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite (SOHO), an international collaboration project of NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA).
NAMING A DISEASE BY WHO
15, Feb 2020

Why in News?
- The World Health Organization officially announced COVID-19 as the name for the disease caused by the novel coronavirus.
- This comes more than 40 days after WHO was alerted by China about a cluster of pneumonia-like cases seen in the city of Wuhan in Hubei province.
- The “co” stands for “corona”, “vi” for “virus” and “d” for “disease”, while “19” was for the year, as the outbreak was first identified on December 31.
Highlights:
- The WHO had to come up the name in line with the 2015 guidelines between the global agency, the World Organisation for Animal Health and the Food and Agriculture Organization.
- The Coronavirus Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses, which had assessed the novelty of the human pathogen, has named the virus as “Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2”, or “SARS-CoV-2”.
- The Coronavirus Study Group is responsible for developing the official classification of viruses and taxa naming of the Coronaviridae family.
Reason for Naming:
- The name has been chosen to avoid references to a specific geographical location, animal species or group of people in line with international recommendations for naming aimed at preventing stigmatisation.
- WHO had earlier given the virus the temporary name of “2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease” and China’s National Health Commission was temporarily calling it “novel coronavirus pneumonia” or NCP.
- Under a set of guidelines issued in 2015, WHO advises against using place names such as Ebola and Zika, where those diseases were first identified and which are now inevitably linked to them in the public mind.
- More general names such as “Middle East Respiratory Syndrome” or “Spanish flu” are also now avoided as they can stigmatise entire regions or ethnic groups.
- WHO also notes that using animal species in the name can create confusion, such as in 2009 when H1N1 was popularly referred to as “swine flu”. This had a major impact on the pork industry even though the disease was being spread by people rather than pigs.
Significance of Naming:
- The urgency to assign a name to the disease is to prevent the use of other names that can be “inaccurate or stigmatising”. People outside the scientific community tend to call a new disease by common names.
- But once the name gets “established in common usage through the Internet and social media, they are difficult to change, even if an inappropriate name is being used.
- Therefore, it is important that whoever first reports on a newly identified human disease uses an appropriate name that is scientifically sound and socially acceptable.
Method of Naming:
- The WHO identified the best practices to name new human diseases in consultation and collaboration with the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO).
- The main aim behind this exercise was to “minimise unnecessary negative impact of disease names on trade, travel, tourism or animal welfare, and avoid causing offence to any cultural, social, national, regional, professional or ethnic groups”.
- The name of a new disease should consist of a combination of terms. These terms consist of a generic descriptive term based on clinical symptoms (respiratory), physiological processes (diarrhoea), and anatomical or pathological references (cardic).
- It can refer to specific descriptive terms such as those who are afflicted (infant, juvenile, and maternal), seasonality (summer, winter) and severity (mild, severe).
- The name can also include other factual elements such as the environment (ocean, river), causal pathogen (coronavirus) and the year the new disease is first detected with or without mentioning the month.
- The WHO has also listed out the terms that should be avoided while naming a new disease. This includes, geographic locations, people’s names, species of animal or food, references to culture, population, industry or occupation, and terms that incite undue fear.
- A couple of diseases carry the name of the person who first identified the disease. Chagas disease is named after the Brazilian physician Carlos Chagas, who discovered the disease in 1909.
- Some diseases carry the name of animals, bird flu (H5N1) and swine flu (H1N1). The 2009 H1N1 pandemic was commonly referred to as swine flu. It is important to note that the 2009 pandemic virus was not completely derived from swine.
MEDICAL EQUIPMENTS NOTIFIED AS DRUGS
13, Feb 2020
Why in News?
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has recently notified that medical equipment would qualify as ‘drugs’ under Section 3 of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act (D & CA), 1940 from 1st April, 2020.
What does Section 3 of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 says?
- The Central Government, after consultation with the Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB), specifies the devices intended for use in Human Beings or Animals as Drugs.
About Drugs Technical Advisory Board:
- Drugs Technical Advisory Board is a statutory bodyconstituted under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- The function of DTAB is to advise the Central government and State government on technical matters related to drugs and cosmetics. It is a decision making body related to Drugs and Cosmetics in the country.
- It is also part of Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) in the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
About the News:
- The Medical Devices Amendment Rules, 2020 were released recently which will come into force from 1st April, 2020.
- The Rules state that the medical devices shall be registered with the Central Licensing Authority through an identified online portal established by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO).
- Such registration is voluntary for a period of 18 months, after which it will be Mandatory.
- The move comes in the wake of years of controversy about faulty hip implants of Johnson & Johnson (J&J).
- DePuy, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson, engineered a hip replacement device that used metal in prosthetic components, commonly called “Articular Surface Replacement orASR hip implant”.
- The manufacture, import and sale of all medical devices will now need to be certified by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation.
What is the Concern?
- Concerns are being raised that the rules are very rigid and any non-conformity can be treated as a criminal offence by any drug inspector under the Act at his discretion.
- At present, only 23 medical devices have been classified as drugs. The latest notification gives a wide definition of the term medical devices.
- The devices used for diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, assistance for any injury or disability, investigation, replacement or modification or support of the anatomy or of a physiological process will come within the scope of the definition of ‘Drugs’.
- Medical equipment under this definition include implantable medical devices such as knee implants, CT scan, MRI equipment, defibrillators, dialysis machine, PET equipment, X-ray machine etc.
- Primary intended action of the device in or on human body or animals should not be pharmacological or immunological or metabolic.
Why such Rules Initiated?
- The aim is to regulate all medical devices so that they meet certain standards of quality.
- Besides it will also make medical device companies accountable for quality and safety of their products.
What are the Possible Impacts?
- The decision is going to have a major impact on the small and Marginal Players, Largely Unorganised, in the low-value high volume segment of the medical devices industry.
- The hi-tech diagnostic imaging sector is dominated by large players and will be the least Impacted.
Way Forward:
- Merely expanding the scope of regulation to all devices is not enough in a moment of growing number of safety Disasters Involving Devices.
- Hence, there is a pressing need for framing of a New Medical Devices Act.
LI-ION BATTERIES
10, Feb 2020

Why in news?
- Recently, India has quadrupled its imports of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries.
Key Points:
- Indian manufacturers source Li-ion batteries from China, Japan and South Korea.
- India is the largest importers in the world. China dominates the LI-ion batteries market.
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) manufactures such batteries but volumes are limited and they are restricted for use in space application.
- To promote indigenous development of such batteries, the union Cabinet in 2019 approved a programme called National Mission on Transformative Mobility and Battery Storage, under the NITI Aayog.
About National Mission on Transformative Mobility and Storage:
- The Mission will have an Inter-Ministerial Steering Committee chaired by Chief Executive Officer (CEO), NITI Aayog to promote clean, connected, shared, sustainable and holistic mobility initiatives.
- The Mission will launch the Phased Manufacturing Programmes (PMP) for Batteries and for Electric Vehicle components.
About Li-ion Battery:
- A lithium-ion battery or Li-ion battery (abbreviated as LIB) is a type of rechargeable battery.
- It is commonly used for portable electronics and electric vehicles and are growing in popularity for military and aerospace applications.
- It is the lightest metal on the periodic table, and the one most willing to donate its electrons (The Most Powerful Reducing Agent).
- From portable electronics like the smartphone to high performance electric cars like the Tesla Model S, lithium ion batteries are currently the most promising chemistry on the market for meeting our renewable energy storage needs.
Advantages of Lithium Ion batteries:
- High energy density – potential for yet higher capacities.
- Does not need prolonged priming when new. One regular charge is all that’s needed.
- Relatively low self-discharge – self-discharge is less than half that of nickel-based batteries.
- Low Maintenance – no periodic discharge is needed; there is no memory.
- Specialty cells can provide very high current to applications such as power tools.
SPACE AND WOMEN IN SPACE
08, Feb 2020

Context:
- NASA astronaut Christina Koch has left her footprint in history after breaking an iconic space record for womankind. Her 328-day stay surpassed the record set by Peggy Whitson on a single space-flight at 288 days.
History of Women in Space:
- In 1963, aboard Vostok 6, Soviet Cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova became the first woman to travel into space.
- The first woman to complete a spacewalk, or extravehicular activity (EVA), was Soviet cosmonaut Svetlana Savitskaya.
- In June 1983, NASA astronaut Sally Ride became the first U.S. woman in space when she launched on the STS-7 mission of the space shuttle Challenger.
- NASA’s Peggy Whitson, became the first woman to command the ISS in April 2008, she was also the first woman to command the ISS twice.
Does space affect men and women differently?
- Overall adaptation to the space environment is roughly the same for men and women but there are some differences.
- Women are more likely to feel sick when they go into space, men are more likely to get re-entry sickness when they come back to Earth.
- Men have more problems with their vision and hearing when they get back from space which women don’t get.
- When women return they do have problems managing their blood pressure so they feel quite faint.
- There are some subtle differences – physiologically and psychologically and there is a little study to do with hormonal differences or more physiological changes that are occurring.
- And long-term, understanding of those differences will help us understand more about human health on Earth.
What does ‘Spacewalk’ mean?
- Anytime an astronaut gets out of a space vehicle, it is called an extravehicular activity, or EVA. This is also called a spacewalk.
- Russian astronaut Alexei Leonov performed the first spacewalk on March 18, 1965. The first spacewalk was 10 minutes long.
- Spacewalks allow astronauts to work outside their spacecraft while still in space.
- To carry out scientific experiments in space
- To test new equipment’s or make repairs to satellites/spacecraft
- Spacesuits protect the astronauts from extreme hot and cold temperatures, harmful space dust and radiation.
- Spacesuits are pressurized to keep the fluids in the body in a liquid state.
- Once in their suits, astronauts breathe 100 percent oxygen for several hours until all the nitrogen is out of their bodies.
Nitrogen and ‘the bends’:
- Nitrogen in the body during a spacewalk can cause gas bubbles to form in the body. These gas bubbles can cause astronauts to feel pain in their joints, such as their shoulders, elbows, wrists and knees.
- This condition is called “the bends” because it affects the places where the body bends. The same condition can affect divers who use oxygen tanks to breathe underwater.
India and Women in Space:
- Kalpana Chawla was the first woman of Indian descent to go into space.
- She was also one of the 7 member crew of the ill-fated NASA’s Columbia, that disintegrated upon atmospheric entry killing the crew in 2003.
- Sunita Williams, was born to an Indian American Father in the United States of America.
- She formerly held the records for total spacewalks by a woman (seven) and most spacewalk time for a woman (50 hours, 40 minutes).
- In August 2007, she became the first person to run a marathon in space.
- Anuradha TK, a Geosat Programme Director at Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) Satellite Centre is an eminent scientist in this field.
- Ritu Karidhal, a scientist at ISRO has worked on multiple ISRO projects as an operations director, is famous for her contribution to Mangalyaan, India’s Mars orbiter mission as the Deputy Operations Director.
- India has come to a point where contributions of women across all fields are being celebrated and applauded. India still has a long way to go to make the historically male-dominated domains like space, as a level playing field for women. By then Indian women would be, quite literally, reaching for the stars.
GENOME INDIA PROJECT
08, Feb 2020

Why in News?
- Recently, the Ministry of Science and Technology has cleared the Genome India Project.
About Genome India project:
- It is funded by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) to sequence at least 10,000 Indian genomes.
- It has 22 partner organisations including public health institutions will be roped in that have obtained regulatory ethical clearances.
- The Centre for Brain Research, which is an Autonomousinstitute in the IISc, Bengaluru, will serve as the nodal point of the project.
- It is a gene-mapping project involving leading institutions including the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) in Bengaluru and a few Indian Institute of Technology (IITs).
- The first stage of the project will look at samples of 10,000 persons from all over the country to form a grid that will enable the development of a reference genome.
- Investigators in hospitals will lead the data collection through a simple blood test from participants and the information will be added to bio banks.
- The Government of India got its inspiration from the Human Genome Project.
Human Genome Project:
- It was an international research effort to determine the sequence of the human genome and identify the genes that it contains. It was a publicly funded project that ended in 2003.
- It has revealed that there are probably about 20,500 human genes. This information can be thought of as the basic set of inheritable “instructions” for the development and function of a human being.
Significance of the Project:
- The diverse genetic pool of India will be mapped and it will help in making Personalised Medicine.
- Its goal to utilize information about a person’s genes, including his or her nucleotide sequence, to make drugs better and safer.
- It is helps to enable cost effective genetic tests, carrier screening applications for expectant couples, efficient diagnosis for heritable cancers, pharmacogenetic tests to prevent adverse drug reactions.
- It will be a hard task considering the population diversity and the disease burden of complex disorders but once the genetic basis is ready it will be possible and easy to take action before the onset of a Disease.
FLAW OBSERVED IN PAPER CLAIMING CORONAVIRUS TRANSMISSION DURING INCUBATION PERIOD
06, Feb 2020
Why in News?
- A Correspondence published in the The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) about an asymptomatic Chinese woman infecting a German during the incubation period of the novel coronavirus turns out to be wrong as it was based on Inaccurate Information.
Highlights:
- The development is significant given that China’s National Health Commission Minister had first warned that the novel virus might be spreading even during the incubation period when symptoms do not show up.
- Government authorities spoke to the Chinese woman after NEJM published the finding. And it turns out that the Chinese woman did indeed have symptoms during her stay in Germany, when she came in contact with the German who fell sick.
- But no tests were carried out in Germany to confirm if she was infected with the novel virus. She underwent testing for the novel coronavirus after her return to China and tested positive for the virus.
- The NEJM paper confirming it meant that the novel virus indeed has the capability to infect people even before symptoms show up overtly. If it were true, it would mean that there is a possibility that people could spread the virus long before they know they have been infected.
- The finding establishes that the virus was not transmitted by the Chinese woman during the incubation period and that the German man was not infected as a result of such transmission.
- The transmission had happened after the incubation period and when she was exhibiting symptoms.
- WHO said that, asymptomatic infection may be rare, and transmission from an asymptomatic person is very rare with other coronaviruses, such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) coronavirus.
- The main driver of novel coronavirus transmission is people who exhibit overt symptoms. Such people will spread the virus more readily through coughing and sneezing.
GLOBAL MEDICAL DATA LEAKAGE
05, Feb 2020

Why in News?
- Greenbone Sustainable Resilience, a German cyber security firm has recently published it report on Global Medical Data Leak.
About the News:
- The report stated that medical details of over 120 million Indian patients have been leaked and made freely available on the Internet.
- The report also places Maharashtra at the top of the States affected by the global medical data leak followed by Karnataka.
- The report classifies countries in the “good”, “bad” and“ugly” categories based on the action taken by their governments in stopping it.
- India ranks second in the “ugly” category, after the U.S.
- The data leak of records includes images of CT scans, X-rays, MRIs and even pictures of the Patients.
What is the Concern?
- The leak is worrying because the affected patients can include anyone from the common working man to politicians and celebrities.
- In image-driven fields like politics or entertainment, knowledge about certain ailments faced by people from these fields could deal a huge blow to their image.
- The other concern is of fake identities being created using the details, which can be misused in any possible number of ways.
What is the cause for Leakage?
- The leak was facilitated by the fact that the Picture Archiving and Communications Systems (PACS) servers, where these details are stored, are not secure and linked to the public Internetwithout any protection, making them easily accessible to malicious elements.
Way Forward:
- PACS Servers should be secured properly and should not be connected to public internet to avoid such kind of leakages.
- Since these medical datas leakages lead to anti-social activities such as organ donation scandals, the particular medical institution should be held accountable for the datas.
- Any communication between a doctor and a patient is a privileged one. A doctor or a hospital is thus ethically, legally and morally bound to Maintain Confidentiality.
LIVE ATTENUATED CLASSICAL SWINE FEVER VACCINE (IVRI-CSF-BS)
04, Feb 2020

Why in News?
- IVRI releases live attenuated Classical Swine Fever (CSF) cell culture vaccine (Indigenous strain).
Highlights:
- Classical Swine Fever (CSF) is one of the Most Important Diseases of pigs causing high mortality with an annual loss of approximately Rs. 4.299 billion.
- A lapinized CSF vaccine (Weybridge strain, UK) is being used in India since 1964 for controlling the disease. The vaccine is produced by sacrificing large numbers of rabbits for each batch.
- Lapinization refers to the weakening or modification of a virus or vaccine by its serial passage through rabbits.
- The country’s total requirement is 22 million doses per year and hardly 1.2 million doses are produced per year by the lapinized vaccine, as only 50 doses are produced from a single rabbit spleen.
- In order to do away with the sacrificing of rabbits and increase productivity, IVRI had earlier developed a cell culture CSF vaccine by adapting the lapinized vaccine virus in cell culture.
- Since the cell culture vaccine is from a foreign strain (Weybridge Strain, UK), IVRI has further developed a new CSF Cell Culture Vaccine by attenuating an indigenous virulent CSF virus in cell culture. The vaccine virus has very high titre and lakhs of doses can be produced very easily in cell culture and the country’s requirement can be easily fulfilled using this new vaccine.
- The new vaccine is ready for release and commercial production will be completed in less than a year.
- The new vaccine will be part of the Government’s One Health Initiative and result in huge savings as it will nip the spread of the virus at the animal stage so that it does not pass on to the human population.
- Due to a very high titre of vaccine virus, this vaccine would be the most economical CSF vaccine costing around less than Rs 2/- per dose as against Rs 15-25/- of lapinized CSF vaccine and Rs.30/dose (approx.) for an imported Korean vaccine being used in the country.
- Besides, the new vaccine gives immunity for two years as compared to 3 to 6 months of protection under the vaccines currently being used.
- The vaccine is safe, potent, does not revert to virulence and provides protective immunity from day 14 of the vaccination until 24 months studied so far.
- The vaccine has been tested on around 500 pigs at multiple locations.
- The new vaccine has been developed by a team of IVRI scientists.
Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI):
- Established in 1889, the Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI) is one of the premier research institutions dedicated to livestock research and development of the region.
- It is under the administrative control of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi.
- IVRI is located in Izatnagar, Bareilly in UP.
NATIONAL MISSION ON QUANTUM TECHNOLOGIES & APPLICATIONS
03, Feb 2020

Why in News?
- The Finance Minister in budget 2020 has announced a National Mission on Quantum Technologies & Applications (NM-QTA).
Quantum Technology:
- Quantum Technology is based on the principles of quantum theory, which explains the nature of energy and matter on the atomic and subatomic level.
- It concerns the control and manipulation of quantum systems, with the goal of achieving information processing beyond the limits of the classical world.
- Its principles will be used for engineering solutions to extremely complex problems in computing, communications, sensing, chemistry, cryptography, imaging and mechanics.
- This key ability makes quantum computers extremely powerful compared to conventional computers when solving certain kinds of problems like finding prime factors of large numbers and searching large databases.
Quantum Mechanics:
- It is a fundamental theory in physics which describes nature at the smallest – including atomic and subatomic – scales.
- At the scale of atoms and electrons, many of the equations of classical mechanics, which describe how things move at everyday sizes and speeds, cease to be useful.
- In classical mechanics, objects exist in a specific place at a specific time.
- However, in quantum mechanics, objects instead exist in a haze of probability; they have a certain chance of being at point A, another chance of being at point B and so on.
NM-QTA:
- The mission will function under the Department of Science & Technology (DST).
- It will be able address the ever increasing technological requirements of the society, and take into account the International Technology Trends.
- The mission will help prepare next generation skilled manpower, boost translational research and also encourage entrepreneurship and start-up ecosystem development.
Significance:
- Quantum technologies are rapidly developing globally with a huge disruptive potential.
- The range of quantum technologies is expected to be one of the major technology disruptions that will change entire paradigm of computation, communication and encryption.
- It is perceived that the countries who achieve an edge in this emerging field will have a greater advantage in Garnering Multifold Economic Growth and Dominant Leadership Role.
- It has become imperative both for government and industries to be prepared to develop these emerging and disruptive changes.
- It will establish standards to be applied to all research and help stimulate a pipeline to support research and applications well into the future.
PARAQUAT POISONING
03, Feb 2020

Why in News?
- The use of herbicide Paraquat has killed more than hundreds of people in the last two years in Odisha’s Burla district leading to demands for its Ban.
About Paraquat:
- Paraquat is a toxic chemicalthat is widely used as an Herbicide (Plant Killer), primarily for weed and Grass Control.
- It has been banned in 32 countries including Switzerland, where herbicide producing company Sygenta is based.
- Paraquat also figures on the list of 99 pesticides and herbicides the Supreme Court to ban in an ongoing case.
- Paraquat dichloride is being used for 25 crops in India, whereas it is approved to be used on only nine crops by the Central Insecticide Board and Registration Committee. This is a violation of the Indian Insecticides Act.
- So far in India, only Kerala has banned the herbicide.
- Since farmers can’t and don’t read the label on paraquat containers, retailers sell paraquat in plastic carry bags and refill bottles.
Why Paraquat is lethal?
- There is no antidote to this herbicide, the consumers of which complain of kidney, liver and lung problems.
- They may recover from kidney problems, but die of lung- and liver-related ailments. Some also witness kidney failure.It is also toxic to human beings and animals due to its redox activity, which produces Superoxide Anions.
- It has been linked to the development of Parkinson’s Diseaseand is banned in several countries.
What is the Issue?
- The vast majority of the population in western Odisha and its bordering districts in Chhattisgarh are dependent on agriculture.
- Crop failures and family disturbances often drive people to look for poison to commit suicide and Paraquat, which is easily available at homes as well as in neighbourhood shops, becomes an “obvious” choice.
- There have also been cases of people becoming accidental victims when they absorb Paraquat while sprinkling it in Agricultural Fields.
Can worldwide ban be Imposed?
- Paraquat is yet to be listed in the Prior Informed consent (PIC) of Rotterdam Convention.
- It is an international treaty on Import/Export of Hazardous Chemicalssigned in 1998.
- If it is in the chemical figures of the PIC, the exporting country has to take the importing nation’s prior consent before exporting it.
About Rotterdam Convention:
- The Rotterdam Convention is formally known as the Convention on the Prior Informed Consent Procedure for Certain Hazardous Chemicals and Pesticides in International Trade.
- It is a multilateral treaty to promote shared responsibilities in relation to importation of hazardous chemicals.
- The convention promotes Open Exchange of Informationand calls on exporters of hazardous chemicals to use proper labeling, include directions on safe handling, and inform purchasers of any known restrictions or bans.
- Signatory nations can decide whether to allow or ban the importation of chemicals listed in the Treatyand exporting countries are obliged to make sure that producers within their jurisdiction comply.
- India is a party to the convention,with 161 other parties.
CHINA – EPICENTRE OF GLOBAL OUTBREAKS OF DISEASE
29, Jan 2020

Why in News?
- Several deadly new viruses in recent years have emerged in China — Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), bird flu, and now the novel Coronavirus (nCOV).
Zoonotic Infections:
- Closely packed stalls in busy marketplaces, the Chinese taste for exotic meats, and the high population density of cities create the conditions for the spread of zoonotic infections.
- The reason could lie in the busy food markets dotting cities across the country — where fruits, vegetables, hairy crabs and butchered meat are often sold next to bamboo rats, snakes, turtles, and palm civets.
- The relationship between zoonotic pathogens and global pandemics are not new.
- The WHO estimates that globally, about a billion cases of illness and millions of deaths occur every year from zoonoses, i.e, diseases and infections naturally transmitted between people and vertebrate animals.
- Some 60% of emerging infectious diseases globally are zoonoses. Of the over 30 new human pathogens detected over the last three decades, 75% originated in Animals.
Animal Markets in china:
- In animal markets, there are greater chances of transmission of a virus from animals to humans, and its mutation to adapt to the human body.
- It has happened wherever in the world there is unregulated mixing of humans and animals, either wild or domesticated.
- The official referred to the Ebola outbreak in Africa there it was wild chimpanzees who had the disease. It came into humans after these were killed and consumed.
Corona Transmitted from Snake:
- The researchers found evidence that the 2019-nCoV may have resided in snakes before being transmitted to humans.
- The findings suggest that snake is the most probable wildlife animal reservoir for the 2019-nCoV.
- Researchers also said that there is very likely to be an intermediate non-bat host which would have picked up the virus from bats.
- They said recombination within the viral receptor-binding protein may have allowed for cross-species transmission from snake to humans.
- The new virus is similar to the one which caused the outbreak of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS).
- However, the study noted that unlike the SARS-CoV, the 2019-nCoV causes a mild form of viral pneumonia, and has limited capability for person-person spread.
FACIAL RECOGNITION IN TODAY’S WORLD
28, Jan 2020

Why in News?
- Last week, European media network EURACTIV and Politico published a story that said the European Commission is considering a temporary ban on the use of facial recognition technologies in public spaces.
Highlights:
- Two big tech companies, Alphabet and Microsoft, have taken completely different positions on the idea.
- This comes even as facial recognition technologies are being increasingly adopted by individuals, organisations, and governments.
- European Commission believes that indiscriminate use of facial recognition technologies is a privacy threat, and some regulations are needed so that this does not easily give way to surveillance.
- During the temporary ban period, a sound methodology for assessing the impacts of this technology and possible risk management measures could be identified and developed.
Significance:
- It is increasingly being used for everything: from unlocking your phone to validating your identity, from auto-tagging digital photos to finding missing persons, and from targeted advertising to law enforcement.
- It is also increasingly used for surveillance and can also become problematic in the absence of privacy and data security laws.
Separating Benefits from Drawbacks:
- Benefits of facial recognition systems can be categorised into three. One, face detection, which could help count the number of people in traffic. Two, facial authentication, which could help you unlock your phone.
- Three, facial matching, which could help investigators quickly zero in on suspects.
- Instead of simply banning an entire category of technologies with so many possible applications, including many that are helpful and benign, policymakers should employ precision regulation that applies restrictions and oversight to particular use-cases and end-users where there is greater risk of societal harm.
Current Application Across the Globe:
- The U.S. has recently released guidelines regarding artificial intelligence, and they reportedly point to a light touch when it comes to regulation.
- London has joined the bandwagon, and will use real time facial recognition systems to police the city.
- Closer home, Telangana has recently tested this technology to verify voters in local elections.
NAVIC IN MOBILES
25, Jan 2020
Why in News?
- Qualcomm Technologies has unveiled mobile chipsets that are capable of supporting Indian regional satellite navigation system – NavIC (Navigation in Indian Constellation).
Usage of New Chipsets:
- The release of new chipsets will accelerate the adoption of NavIC by Smartphone Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). Users of such mobile chipsets will be able to use NavIC within the Indian region and in neighbouring countries.
- OEM is traditionally defined as a company whose goods are used as components in the products of another company, which then sells the finished item to users
- These enhancements will enable mobile, automotive and IoT platforms to better serve key industries and technology ecosystems in the region.
- This will help improve user experience for location-based applications especially in dense urban environments where geo-location accuracy tends to degrade.
Benefits:
- NavIC is set to become the backbone of a public vehicle tracking system in India since it offers flexibility to local law enforcement agencies to monitor vehicles unlike international systems like GPS (global positioning system).
- The government has made NavIC-based vehicle trackers mandatory for all commercial vehicles in the country in accordance with the Nirbhaya case verdict. So this will facilitate the installation of vehicle tracking systems and panic buttons in all commercial vehicles.
- In addition to NavIC, these chipsets will also support the widely used GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System). GNSS includes USA’s GPS, European Union’s Galileo, Russia’s GLONASS and China’s BeiDou Navigation Satellite System for global coverage.
About Navigation in Indian Constellation (NavIC):
- It has been developed by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO).IRNSS is otherwise known as NavIC.
- IRNSS is an independent regional navigation satellite system being developed by India. It is designed to provide accurate position information service to users in India as well as the region extending up to 1500 km from its boundary, which is its primary service area.
- IRNSS consists of eight satellites, three satellites in geostationary orbit and five satellites in geosynchronous orbit.
- IRNSS will provide two types of services, namely, Standard Positioning Service (SPS) which is provided to all the users and Restricted Service (RS), which is an encrypted service provided only to the authorised users.
- The IRNSS System is expected to provide a position accuracy of better than 20 m in the primary service area.
WINGS INDIA 2020
21, Jan 2020

Why in News?
- Indian Civil Aviation industry has declared that its Flagship Event “Wings India 2020” will be held at Begumpet Airport, Hyderabad in the second week of March.
Wings India 2020:
- Wings India 2020 is an international exhibition and conference on the civil aviation sector.
- Hyderabad being the hub of Aviation remains the natural host of the event.
- It will be jointly organised by the Ministry of Civil Aviation, Government of India, Airport Authority of India (AAI) and the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI).
- The theme of the year 2020 is “Flying for All’’ and the focus is on the new business acquisition, investments, policy formation and regional connectivity in the civil aviation industry.
- It will be Asia’s largest and most popular gathering in the Aviation Industry.
About Airports Authority of India:
- It was constituted by an Act of Parliament in 1995 by merging erstwhile National Airports Authority and International Airports Authority of India.
- It is entrusted with the responsibility of creating, upgrading, maintaining and managing civil aviation infrastructure both on the ground and air space in the country.
About Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry:
- It was Established in 1927 and is the largest and oldest apex business organisation in India.
- It is a non-government, not-for-profit organisation.
- It provides a platform for networking and consensus building within and across sectors and is the first port of call for Indian industry, policymakers and the international business community.
RAJASTHAN TO GET ITS FIRST BIOTECHNOLOGY PARK
18, Jan 2020

Why in News?
- Rajasthan government will be signing a memorandum of understanding with the Centre’s Department of Biotechnology to set up its first biotechnology park and incubation centre in the state.
- The biotechnology park and incubation centre would be set up in the State with the support of the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
About Biotechnology Parks and Incubators:
- The Department of Biotechnology has established Biotechnology Parks/Incubators across the country to translate research into products and services by providing the necessary infrastructure support.
- These Biotechnology Parks offer facilities to Scientists, and Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) for technology incubation, technology demonstration and pilot plant studies for accelerated commercial development of Biotechnology.
- The Department so far has supported 9 Biotechnology Parks in various States.
- The Department has also come up with ‘National Biotechnology Parks Scheme’.
- The scheme aims to create an ecosystem to absorb the start-ups which have graduated from incubators and give them a platform for further scaling up their R&D activities in collaboration with the state Government and Industry.
Merits of the Project:
- This will enable the State government to take up research in the field of biotechnology and provide employment to the youths.
- It would also help to promote interdisciplinary field research such as bioinformatics, biomedical engineering and nano-medicine.
- Further, it will also help to promote biotechnology on the lines of health, agriculture, industry and food which will intensify the science-based manufacturing in Industrialisation.
Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council:
- Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) is a Public Sector Enterprise, set up by Department of Biotechnology (DBT).
- BIRAC is a industry-academia interface and implements its mandate through a wide range of impact initiatives.
- It aims to strengthen and empower the emerging Biotech enterprise to undertake strategic research and innovation, addressing nationally relevant product development needs.
NEW SPACE AGE- ISRO
11, Jan 2020

Context:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has recently announced that, nearly 20 space missions will be launched in the near future.
About ISRO’s planned Space Projects:
- The government has proposed a manned space flight (Gaganyaan) before 2022. ISRO would be undertaking many prolonged space exploration projects and sending many astronauts into space.
- It has declared its intention to build a permanent space station for itself, possibly in the next five to seven years.
- Aditya-I will be India’s first solar mission scheduled to be launched in 2020. Similar project is planned for Venus.
Development of Private Capacity in Space:
- A policy framework to enable private participation in this sector would have to be formulated by the government.
- A strong private sector in space will help India to tap into this lucrative commercial space launch market.
- Globally, Small satellite revolution is underway, that are expected to be launched between 2020 and 2030.
- Space tourism is one of the several opportunities that Indian businesses may be keen to explore.
The Increase in competitiveness over Space:
- Singapore is offering itself as a hub for space entrepreneurship based on its equatorial location, availability of skilled manpower and legal environment.
- New Zealand is positioning itself as a location for private rocket launches. China has changed its rules to allow private commercial space activity.
- ISRO has been a genuine global pioneer of aero spatial cost compression on several fronts. Cost-effectiveness has given the agency a distinct edge in the commercial arena of satellite launch services.
The Benefit of Becoming a Space Power:
- Space is emerged as the fourth arm of the country’s defence setup. Its power has the ability to use space while denying reliable use to any foe.
- With US, China and Russia already in pursuit of becoming a Space power, India will need to equip itself appropriately to meet emerging security challenges.
- India, has only a handful of military satellites in operation, compared to over 40 civilian ones. Our first dedicated military satellite was launched only in 2013.
- Recently, Mission Shakti has demonstrated India’s capability to target enemy satellite.
- Newly instituted DSA (defence space agency) will be supported by a defence space research organization (DSRO) has the mandate to create weapons to “degrade, disrupt, destroy or deceive an adversary’s space capability”.
Way Forward:
- India needs to structurally separate the regulatory, commercial and scientific research elements of the space programme.
- It needs a new space policy, that aims to harness space as a growth sector for the economy, attracts private investment and creates jobs, even as it promotes scientific breakthroughs and helps leapfrog developmental challenges.
- It must have reliable and accurate capabilities to track space objects, from debris and spacecraft to celestial bodies.
- It must acquire a minimum, credible capacity across the various types of space weapons, physical, electronic and cyber to have an effective space defence.
- There is need to establish an independent regulator that governs both ISRO and new space operators on a level playing field.
- The Funding on Space Research and development must be enlarged and ISRO & private research institutions should work be encouraged to work in tandem.
- The developments in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and big data analytics have led to the emergence of the new space age, India’s space programme needs to take two additional leaps i.e. foster a private space industry and start work on a space force.
- Losses in space missions can seriously impact the future of cooperation between space powers. Therefore, in the new space age, India’s space policy must acquire a new seriousness that can tap into the creative energies of private entrepreneurs and bolster India into a space power.
ADITYA – L1 FIRST INDIAN MISSION TO STUDY THE SUN
31, Dec 2019

Context:
- If 2019 was all about the Moon for Indian space agency ISRO, year 2020 could well be about the Sun. In his Mann Ki Baat address, Prime Minister Narendra Modi spoke about the ISRO’s plans to launch its first Sun Mission AdityaL1.
- The 400 KG-Class Aditya L1 will carry six scientific payloads that will be inserted in a halo orbit around the Lagrangian point 1 or L1. Incidentally L1 is 1.5 million kilometres from the Earth.
The Sun – Our Central Star:
- The Sun is the star nearest to us. It is a huge, luminous ball of gas like other stars in the Universe.
From the Inside out, the Solar Interior Consists of:
- The Core– The central region where nuclear reactions consume hydrogen to form helium. These reactions release the energy that ultimately leaves the surface as visible light.
- The Radiative Zone– It extends outward from the outer edge of the core to base of the convection zone, characterized by the method of energy transport – radiation.
- The Convection Zone– The outer-most layer of the solar interior extending from a depth of about 200,000 km to the visible surface where its motion is seen as granules and super-granules.
The Solar Atmosphere is made up of:
- The Photosphere– The visible surface of the Sun
- TheChromosphere – An irregular layer above the photosphere where the temperature rises from 6000°C to about 20,000°C
- TransitionRegion – A thin and very irregular layer of the Sun’s atmosphere that separates the hot corona from the much cooler chromosphere
- The Corona– The Sun’s outer atmosphere.
- Beyond the corona is the Solar Wind, which is actually an outward flow of coronal gas.
- The sun’s magnetic fields rise through the convection zone and erupt through the photosphere into the chromosphere and corona.
- The eruptions lead to solar activity, which includes such phenomena as sunspots, flares, prominences, andCoronal Mass Ejections.
Aditya – L1:
-
- The Aditya-1 mission was conceived as a 400kg class satellite carrying one payload, the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) and was planned to launch in a low earth orbit.
- The Aditya-1 mission has now been revised to “Aditya-L1 mission” – placed in the halo orbit around the Lagrangian point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, which is 1.5 million km from the Earth.
- Lagrangian point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system– has the major advantage of continuously viewing the Sun without any Occultation/Eclipses.
- A Lagrange point is a location in space where the combined gravitational forces of two large bodies, such as Earth and the sun, equal the centrifugal force felt by a much smaller third body.
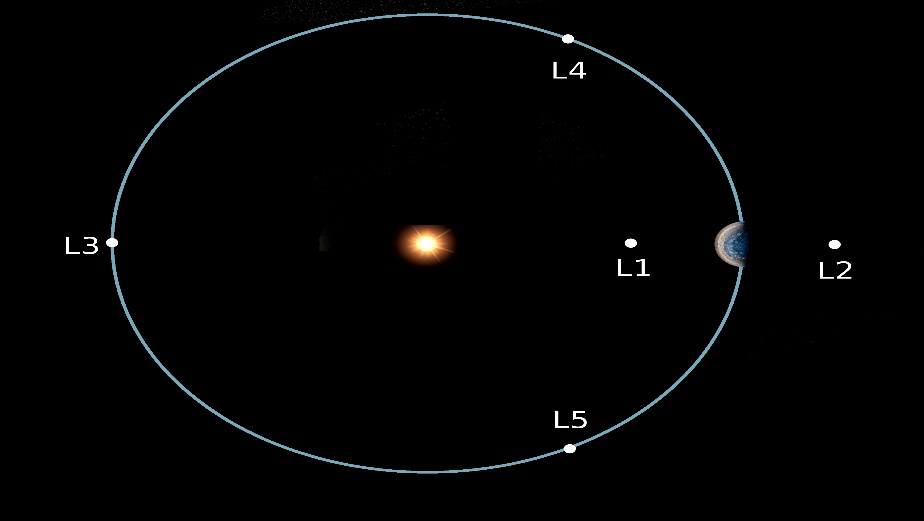

- Aditya-1 was meant to observe only the solar corona – It has a temperature of more than a million-degree Kelvin which is much higher than the solar disc temperature of around 6000K.
- The complete list of payloads and their science objective for developing the Payloads:
- Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC):To study the diagnostic parameters of solar corona and dynamics and origin of Coronal Mass Ejections.
- Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT):To image the spatially resolved Solar Photosphere and Chromosphere in near Ultraviolet.
- Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX):To study the variation of solar wind properties as well as its distribution and spectral characteristics.
- Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA):To understand the composition of solar wind and its energy distribution.
- Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS):To monitor the X-ray flares for studying the heating mechanism of the solar corona.
- High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS):To observe the dynamic events in the solar corona and provide an estimate of the energy used to accelerate the particles during the eruptive events.
- Magnetometer:To measure the magnitude and nature of the Interplanetary Magnetic Field.
Questions about the Corona:
- The outer layers of the Sun, extending to thousands of km above the disc (photosphere) is termed as the corona.
- It has a temperature of more than a million-degree Kelvin which is much higher than the solar disc temperature of around 6000K.
- How the corona gets heated to such high temperatures is still an unanswered question in solar physics.
- With the inclusion of multiple payloads, this project also provides an opportunity to solar scientists from multiple institutions within the country to participate in space-based instrumentation and observations.
- Thus, the enhanced Aditya-L1 project will enable a comprehensive understanding of the dynamical processes of the sun and address some of the outstanding problems in solar physics.
NAVY PLANS 24 SUBMARINES TO STRENGTHEN FLEET
31, Dec 2019

Why in News?
- To strengthen its underwater fleet, the Indian Navy plans to build 24 submarines, including six nuclear attack submarines, a parliamentary panel was told.
Submarines in the Navy:
- According to the data from Indian Navy, currently there are 2 nuclear submarines and 15 conventional submarines in its fleet.
- The two nuclear submarines in the fleet are INS Arihant and INS Chakra. Out of these INS Chakra has been leased from Russia.
Significance:
- Navy has made plans to build new submarines as the conventional submarines are more than 25 years old.
- Thirteen submarines in the fleet are between the age 17 and 32. Also, it is important for the Indian Navy to strengthen its fleet as there is increased activity of the Chinese in the Indian Ocean Region.
- The main issue that is further delaying addition of submarines to the fleet is US sanctions and CAATSA act of US. CAATSA is Countering American Adversaries Through Sanctions Act.
- Along with the Arihant Class SSBNs which are nuclear-powered submarines equipped with nuclear missiles, the Indian Navy has plans to build six nuclear attack submarines. They are also planned to be built indigenously in partnership with private sector industries.
- The Ship, Submersible, Ballistic, Nuclear (SSBN) is a nuclear powered ballistic missile submarine.
Concerns:
- Rising Chinese influence in the Indian Ocean region:
- The Indian Ocean Region, the area of operations of the Navy, has witnessed rising activities of the Chinese Navy. The Chinese have increased their presence in the form of increased patrolling by submarines and ships.
Aging Fleet:
- A majority of the conventional submarines in the Indian Navy are over 25 years old. Thirteen submarines are between 17 and 32 years, impairing the capability of the Indian submarines.
Delay in Commissioning New Submarines:
- The Indian Navy has been revamping its infrastructure, including procuring new ships to match the naval capabilities of the Chinese.
- Due to the delay in the new submarine construction projects like the six submarines under Project 75 being carried out at Mazagaon Docks, Mumbai, the Defence Ministry has approved Medium Refit cum Life Certification or MRLC of six older submarines.
The sanctions on Russia:
- The MRLC of submarine Sindhuraj was held up due to sanctions imposed by the U.S. on Russia. This has impeded the ability of Russia to submit bank guarantees and the integrity pact under the MRLC framework.
- The sanctions imposed on Russia by the U.S. under its Countering America’s Adversaries through Sanctions Act (CAATSA) have severely impaired the capabilities of Russia to service the submarines it has leased out to India.
MOU BETWEEN INDIA AND BRAZIL ON BIOENERGY COOPERATION
25, Dec 2019

Why in News?
- The Union Cabinet has given its approval for the signing of Memorandum of Understanding between the Republic of India and the Federative Republic of Brazil on Bioenergy Cooperation.
Highlights:
- The MoU provides a framework to cooperate and promote investment in biofuel, bioelectricity and biogas supply-chains, including feedstock, industrial conversion, distribution and end-use sectors.
- Exchange of information on agricultural practices.
- Policies regarding biomass for bioenergy, including sugarcane, corn, rice, oil-crops, and lignocellulosic crops. [Lignocellulose refers to plant dry matter (biomass)].
- Policies for reducing greenhouse gas emission levels based on the use of biofuels.
- Using cycle analysis and the issuance of emissions reduction certificates traded in an organised market.
- Trade aspects and the promotion of a joint position to address market access and sustainability of biofuels, including advanced biofuels.
- Engine and fuel modifications/adjustments that may be necessary for different percentages of biofuels blended with fossil fuels.
India and Brazil:
- India and Brazil are major consumers of energy in the world.
- Brazil is one of the most important trading partners of India in the entire LAC (Latin America and the Caribbean) region.
- Brazil is currently the world’s second-largest producer and consumer of biofuels. Biofuels and bioelectricity accounted for 18% of Brazil’s energy mix.
- India also has a strong focus in the area of biofuels and has set a target to achieve 20% blending of ethanol in petrol and 5% blending of biodiesel in diesel by 2030 with the announcement of the new policy on Biofuels in 2018.
INDIAN PHARMACOPOEIA (IP)
23, Dec 2019
Why in News?
- The Indian Pharmacopoeia (IP) has been recognised officially by the National Department of Regulation of Medicines and Health Products of the Ministry of Public Health of Republic of
Indian Pharmacopoeia (IP):
- The quality, efficacy and safety of the medicines are important from healthcare perspective.
- In order to ensure the quality of medicinal products, the legal and scientific standards are provided by Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) in the form of Indian Pharmacopoeia (IP).
- IP is an officially recognized book of standards as per the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Rules 1945
- As per, the Second Schedule of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, IP is designated as the official book of standards for drugs imported and/or manufactured for sale, stock or exhibition for sale or distribution in
- Standards prescribed in the IP are authoritative in nature and are enforced by the regulatory authorities for quality control of medicines in
Significance:
- With this, a New Beginning has been made and Afghanistan has become the first country to recognize IP pursuant to the efforts of Department of Commerce and Ministry of Health and Family
IP Commission:
- The IP Commission’s mission is to promote public and animal health in India by bringing out authoritative and officially accepted standards for quality of
- It includes active pharmaceutical ingredients, excipients and dosage forms, used by health professionals, patients and
- This is achieved by developing the standards for medicines and supporting their implementation.
- In addition, IPC also develops IP Reference Substances (IPRS) that act as fingerprint for identification of an article under test and its purity as prescribed in the IP
PERSONAL DATA PROTECTION BILL, 2019
17, Dec 2019

Why in News?
- The Personal Data Protection Bill, which was tabled in Parliament by the Electronics and IT Minister recently, has now been referred to a joint committee.
Types of Personal Information:
- Sensitive Data constitutes or is related to passwords, financial data, health data, official identifier, sexual orientation, religious or caste data, biometric data and genetic data. It may be processed outside India with the explicit consent of the user.
- Critical Data will be characterised by the government every once in a while, and must be stored and handled only in India.
- General Data is any data that is non-critical and non-sensitive and are categorised as general data with no limitation on where it is stored or managed.
About the Bill:
- As per the bill, it is the individual whose data is being stored and processed.
- The government is qualified to order any data fiduciary to acquire personal and non-personal/anonymised data for the sake of research and for national security and criminal investigations.
- Social media companies, which are deemed significant data fiduciaries based on factors such as volume and sensitivity of data as well as their turnover, should develop their own user verification mechanism.
- An independent regulator Data Protection Agency (DPA) will oversee assessments and audits and definition making.
- Each company will have a Data Protection Officer (DPO) who will liaison with the DPA for auditing, grievance redressal, recording maintenance and more.
- The bill also Grants Individuals the right to data portability, and the ability to access and transfer one’s own data.
- The right to be forgotten: this right allows an individual to remove consent for data collection and disclosure.
Why does Data Protection matter?
- With a population of over a billion, there are about 500 million active web users and India’s online market is second only to China.
- Large collection of information about individuals and their online habits has become an important source of profits.
- It is also a potential avenue for invasion of privacy because it can reveal extremely personal aspects.
- Companies, governments, and political parties find it valuable because they can use it to find the most convincing ways to advertise to you online.
- Besides, presently, there are no laws on the utilisation of individual information and forestalling its abuse, even though the Supreme Court maintained the right to privacy as a fundamental right back directly in 2017.
Important recommendations of Justice BN Srikrishna Committee:
- The Justice Srikrishna committeeon data privacy has made specific mention of the need for separate and more stringent norms for protecting the data of children.
- It recommended that companies be barred from certain types of data processing such as behavioural monitoring, tracking, targeted advertising and any other type of processing which is not in the best interest of the child.
- It is widely accepted that processing of personal data of children ought to be subject to greater protection than regular processing of data.
- Safeguarding the best interests of the child should be the guiding principle for statutory regulation on protecting data of children.
- The committee noted that, at present, there were two types of entities processing the personal data of children.
- The first type was services offered primarily to children, such as YouTube Kids, Hot Wheels and Walt Disney, and the second were social media services such as Facebook and Instagram.
- The committee’s recommends that the Data Protection Authority will have the power to designate websites or online services that process large volumes of personal data of children as “guardian data fiduciaries”.
Why there are Concerns over the Bill?
- The bill is like a two-sided sword. While it protects the personal data of Indians by empowering them with data principal rights, on the other hand, it gives the central government with exemptions which are against the principles of processing personal data.
- The government can process even sensitive personal data when needed, without explicit permission from the data principals.
Recent Issues over Data Protection:
- Recently, messaging platform WhatsAppsaid that some Indian journalists and rights activists were among those spied using technology by an Israeli company, which by its own admission only works for government agencies across the world.
- Google too had alerted 12,000 users, including 500 in India, regarding “government-backed” phishing attempts against them.
- The Indian Government has still not come out in the clear convincingly regarding these incidents.
IBM’S WEATHER FORECAST SYSTEM TO TAP USERS’ PHONES FOR DATA
13, Dec 2019

Why in News?
- International technology company IBM plans to make a high-resolution weather forecast model that will also rely on user-generated data to improve the accuracy of forecasts available in India.
About IBM-GRAF:
- IBM Global High-Resolution Atmospheric Forecasting System(IBM GRAF), as the forecast system is called, can generate forecasts at a resolution of 3 kilometres.
- This is a significantly higher resolution than the 12-kilometre models currently used by the Indian Meteorological Department to generate forecasts .
- These weather forecast techniques rely on dynamic modelling and collect a trove of atmospheric and ocean data, crunch it in supercomputers and generate forecasts over desired time-frames — three days, weekly or fortnightly.
- IBM relies on a global network of sensors — automatic weather station, data buoys and barometric pressure data from cell phones of users who’ve downloaded the application.
- A combination of observations, computing and equations underlies the forecasts, since forecasting tropical conditions over India is particularly tricky.
Benefits:
- Since the local economy faces huge disruption due to severe weather events and disasters, this forecast model could play a major role in averting such issues.
- The forecasts are considered to be 30% more accurate than those generated by 12-km resolution models.
- Weather forecasts will be available to individuals for free download and can be used by farmers.
- The forecast engine will also be used to provide custom forecasts for energy companies, consumer brands, insurance businesses and satellite imagery analysts.
PSLV-C48/RISAT-2BR1
12, Dec 2019

Why in News?
- PSLV-C48 successfully launched RISAT-2BR1 and nine commercial satellites from Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SHAR), Sriharikota.
About the Launch:
- India’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle, in its 50th flight (PSLV-C48), successfully launched RISAT-2BR1, an earth observation satellite, along with nine commercial satellites of Israel, Italy, Japan and USA from Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR, Sriharikota.
- These satellites were launched under commercial arrangement with New Space India Limited (NSIL), the commercial arm of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- It was PSLV’s 50th flight and 48th successful flight since its first successful launch in 1994.
- It was the 75th launch from Sriharikota.
- This was the 2nd flight of PSLV in ‘QL’ configuration (with 4 solid strap-on motors).
- With this, ISRO has launched a total of 319 foreign satellites from 33 countries since the first launch in 1999 when PSLV-C2 carried satellites from Germany and South Korea.
About PSLV:
- PSLV is an expendable medium-lift launch vehicle designed and operated by ISRO.
- The PSLV, which has a history of successful launches of payloads that include Chandrayaan-1, Mars Orbiter Mission and the space recovery mission.
- The PSLV had helped take payloads into almost all the orbits in space including Geo-Stationary Transfer Orbit (GTO), the Moon, Mars and would soon be launching a mission to the Sun
- Initially, the PSLV had a carrying capacity of 850 kg, and over the years it has been enhanced to 1.9 tonnes.
- The PSLV has failed only twice in its history — the maiden flight of the PSLV D1 in September 1993 and the PSLV C-39 in August 2017.
About RISAT-2BR1:
- RISAT-2BR1 is radar imaging earth observation satellite carrying X-band synthetic aperture radar, an Indian version of Israel’s TecSAR satellite, with radial rib reflector 3.6 metre mesh antenna.
- The satellite weighs about 628 kg. The mission life of RISAT-2BR1 is 5 years.
- The satellite will provide services in the field of Agriculture, Forestry and Disaster Management.
- It is believed that RISAT-2BR1 along with Cartosat-3, a remote sensing satellite which was launched on November 27, 2019, will also be used for Military Reconnaissance.

VIRTUAL AUTOPSY
09, Dec 2019

Why in News?
- India will be the first country in South and Southeast Asia to carry out these “virtual autopsies
Virtual Autopsy:
- An autopsy (Postmortem Examination, Autopsia Cadaverum, or Obduction) is a highly specialized surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse to determine the cause and manner of death and to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present.
- Virtopsy is a word combining ‘virtual’ and ‘autopsy’ … for the purpose of autopsy and to find the cause of the death. Virtopsy can be employed as an alternative to standard autopsies for broad and systemic examination of the whole body as it is less time consuming, aids better diagnosis, and renders respect to religious sentiments.”
- In a virtual autopsy, doctors use radiation to examine the innards to reach a conclusion about the cause of death. A CT or an MRI machine could be used, in the same way that they are used to scan a living human’s body.
Need:
- According to a paper in The Lancet, the advent of virtual autopsy owes to the “Longstanding public objection to dissection of cadavers (that) re-emerged in the UK as a major issue after organ retention scandals in the late 1990s.
- Some groups —notably Jewish and Muslim communities — have religious objections to autopsy, and demand for a minimally-invasive alternative has increased.” (‘Post-mortem imaging as an alternative to autopsy in the diagnosis of adult deaths: a validation study’: 2012, Ian S D Roberts et. al)
- A virtual autopsy is also faster than a traditional one — 30 minutes against 2½ hours, and more cost-effective.
International Examples:
- Virtual autopsy began in Sweden, but is now a “standard technique” in major centres in Japan, the US, Australia, and many European countries.
Accuracy of Virtual Autopsy:
- In 2018, in an article in the Journal of Pathology Informatics, Russian and Italian scientists compared the results of virtual autopsy and Traditional Post-Mortem.
- “Out of 23 cases for which the traditional post mortem examination found a cause of death, 15 (65%) were diagnosed correctly using virtual autopsy, these cases were considered as true positives.
- For one case for which the cause of death was unascertained, the same result was also obtained during the virtual autopsy.
- This case was considered as true negative. Overall, in 16/25 (64%) cases, virtual autopsy results matched that of the traditional autopsy,” they concluded.
ISRO’S SECOND SPACEPORT AT KULASEKARAPATTINAM (TN)
05, Dec 2019

Why in News?
- The ISRO has commenced land acquisition for its second launchpad in Kulasekarapattinam, a town in the Thoothukudi (Tuticorin) district of Tamil Nadu.
ISRO’s spaceport:
- ISRO’s first and only spaceport, the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), is located in Sriharikota, about 100 km north of Chennai, in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
- The organisation launches its PSLV and GSLV rockets from here.
- The SDSC, setup in 1971, currently has two active launchpads.
- Its first launchpad was decommissioned once the Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle programme ended in 1994.
- The first of the two active pads mostly services the PSLV and the second, the GSLV, and which ISRO is currently modifying to accommodate crewed vehicle missions as part of its upcoming human spaceflight project, Gaganyaan.
- The second spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam is expected to provide an important advantage to ISRO’s upcoming Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), a smaller counterpart of the PSLV.
Need for another Launchpad:
- The PSLV is designed to launch satellites into pole-to-pole, or polar, orbits around Earth.
- However, it can’t enter into such an orbit straightaway after launch because its trajectory needs to avoid flying over Sri Lanka, protecting its popular centres from any debris from the rocket.
- So once the rocket lifts off from Sriharikota, it flies further east to avoid Sri Lanka and then steers itself back towards the South Pole.
- This manoeuvre requires more fuel, and for a smaller rocket like the SSLV, the addition could eat into its already limited payload capacity and reduce the rocket’s value for Antrix, ISRO’s commercial operator.
- By setting up a spaceport in Kulasekarapattinam the SSLV will lift off over the Lakshadweep Sea and won’t have to swerve around Sri Lanka as it climbs to higher altitudes.
Significance of Thoothukudi’s location:
- Proximity to the seashore makes Thoothukudi ideal for “straight southward” launches. From Sriharikota, such southward bound launches are not possible as the rockets have to fly around Sri Lanka.
- Nearness to the equator: Like the Sriharikota spaceport in the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Thoothukudi was selected as a spaceport due to its nearness to the equator. A rocket launch site should be on the east coast and near the equator.
- Logistical ease: ISRO has its Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) at Mahendragiri in Tirunelveli district, where it assembles the second and fourth stage engines for the PSLV. Instead of transporting the second and fourth stages to Sriharikota from Mahendragiri, it would be easier to shift them to the launch pad if it is built in Kulasekarapattinam, which is around 100 km away.
PROCUREMENT OF WEAPONS WORTH ₹22,800 CRORE
29, Nov 2019

Why in News?
- The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC), chaired by Defence Minister Rajnath Singh, has approved the procurement of weapons and equipment worth ₹22,800 cr
About DAC:
- The DAC is Defence Ministry’s highest decision-making body for capital acquisition proposals forwarded by the Indian armed forces.
- It was set up in 2001 as part of the post-Kargil reforms in defence sector which is headed by the Defence Minister.
- It approves the long-term integrated perspective plan for the forces, accords acceptance of necessity (AON) to begin acquisition proposals, and grant’s its approval to all major deals through all their important phases.
- It also has the power to approve any deviations in an acquisition, and recommends all big capital defence purchases for approval of the Cabinet committee on security (CCS) headed by Prime Minister.
Functions of DAC:
- In principle approval of 15 Years Long Terms Integrated Perspective Plan for Defence Force.
- Accord of Acceptance of Necessity to acquisition proposals.
- Categorization of the acquisition proposals relating to ‘Buy’, ‘Buy & Make’ and ‘Make’.
- Issues relating to Single vendor clearance.
- Decisions regarding ‘offset’ provisions in respect of acquisition proposals above Rs. 300 crore.
- Decisions regarding Transfer of Technology under ‘Buy & Make’ category of acquisition proposals.
- Field Trial evaluation.
What kind of Weapons is procured?
- Six additional P-8I long-range patrol aircraft is to be procured from the U.S. for the Navy and additional indigenous Airborne Warning and Control System (AWACS) aircraft for the Indian Air Force (IAF).
About AWACS:
- AWACS stands for Airborne Warning and Control System that helps the Air Force detect incoming missiles and enemy aircraft from across the country’s border.
- AWACS is described as an ‘Eye in the Sky’ as it can carry out surveillance at about 400-km range under all-weather situations, and to lock on to lock on to 60 targets at a time simultaneously.
- They are capable of detecting hostile aircraft, cruise missiles and other incoming aerial threat far before ground-based radars.
- It is basically an aircraft fitted with sophisticated radar and can be said to be radar on the move. It can provide advance warning about enemy’s intrusion into country’s air space.
- It can also track and attack enemy’s targets in air. India has an agreement with Israel for supply of its AWACS called Phalcon.
Why it is Needed?
- As a follow-up to the successful indigenous Airborne Early Warning and Control (AEW&C) programme, the DAC revalidated the Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) for the procurement of additional AWACS aircraft.
- “The mission system and sub-systems for these aircraft would be indigenously designed, developed and integrated into the main platform by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).”
- The IAF now operates three Israeli Phalcon AWACS and three smaller indigenous Netra AEW&C systems mounted on Embraer aircraft.
- A shortage of these force multipliers was felt during the aerial engagement with the Pakistan Air Force, a day after the Balakot air strike in February.
- These platforms would provide on-board command and control and ‘early warning’, which would assist the IAF in achieving effective air space dominance in the least possible time, the statement said. The new systems are likely to be mounted on Airbus Aircraft.
GOOGLE HAS WARNED 500 INDIANS ON PHISHING
29, Nov 2019

Why in News?
- Google has recently announced that over 12, 000 people around the world have become victims of phishing.
About:
- Google sent out over 12,000 warning to users globally, including about 500 in India, during the three month period from July to September this year, alerting them on “government-backed” phishing attempts against them.
- Phishing is the act of sending an email to a user falsely claiming to be an established legitimate enterprise in an attempt to scam the user into surrendering private information that will be used for identity theft.
- Phishing email will direct the user to visit a website where they are asked to update personal information, such as a password, credit card, social security, or bank account numbers, that the legitimate organization already has.
- The website, however, is bogus and set up only to steal the information the user enters on the page.
- Phishing emails are blindly sent to thousands, if not millions of recipients.
- By spamming large groups of people, the “phisher” counts on the email being read by a percentage of people who actually have an account with the legitimate company being spoofed in the email and corresponding webpage.
Types of Cyber Attacks:
- Malware, short for malicious software refers to any kind of software that is designed to cause damage to a single computer, server, or computer network. Ransomware, Spy ware, Worms, viruses, and Trojans are all varieties of malware.
- Phishing: It is the method of trying to gather personal information using deceptive e-mails and websites.
- Denial of Service attacks: A Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack is an attack meant to shut down a machine or network, making it inaccessible to its intended users. DoS attacks accomplish this by flooding the target with traffic, or sending it information that triggers a crash.
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks, also known as eavesdropping attacks, occur when attackers insert themselves into a two-party transaction. Once the attackers interrupt the traffic, they can filter and steal data.
- SQL Injection: SQL (pronounced “sequel”) stands for Structured Query Language, a programming language used to communicate with databases.
- Many of the servers that store critical data for websites and services use SQL to manage the data in their databases.
- A SQL injection attack specifically targets such kind of servers, using malicious code to get the server to divulge information it normally wouldn’t.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Similar to an SQL injection attack, this attack also involves injecting malicious code into a website, but in this case the website itself is not being attacked.
- Instead the malicious code the attacker has injected, only runs in the user’s browser when they visit the attacked website, and it goes after the visitor directly, not the website.
- Social engineering is an attack that relies on human interaction to trick users into breaking security procedures in order to gain sensitive information that is typically protected.
Why Cyber Security Needed?
- Photos, videos and other personal information shared by an individual on social networking sites can be inappropriately used by others, leading to serious and even life-threatening incidents.
- Companies have a lot of data and information on their systems. A cyber-attack may lead to loss of competitive information (such as patents or original work), loss of employees/customers private data resulting into complete loss of public trust on the integrity of the organization.
- A local, state or central government maintains huge amount of confidential data related to country (geographical, military strategic assets etc.) and citizens. Unauthorized access to the data can lead to serious threats on a country.
International Mechanisms regarding Cyber Crime:
- The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is a specialized agency within the United Nations which plays a leading role in the standardization and development of telecommunications and cyber security issues.
- Budapest Convention on Cybercrime is an international treaty that seeks to address Internet and computer crime (cybercrime) by harmonizing national laws, improving investigative techniques, and increasing cooperation among nations. It came into force on 1 July 2004. India is not a signatory to this convention.
- Internet Governance Forum (IGF) brings together all stakeholders i.e. government, private sector and civil society on the Internet governance debate. It was first convened in October–November 2006.
- Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is a non-profit organization responsible for coordinating the maintenance and procedures of several databases related to the namespaces and numerical spaces of the Internet, ensuring the network’s stable and secure operation. It has its headquarters in Los Angeles, U.S.A.
Government initiatives against Cyber Crime:
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative: It was launched in 2018 with an aim to spread awareness about cybercrime and building capacity for safety measures for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT staff across all government departments.
- National Cyber security Coordination Centre (NCCC): In 2017, the NCCC was developed. Its mandate is to scan internet traffic and communication metadata (which are little snippets of information hidden inside each communication) coming into the country to detect real-time cyber threats.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: In 2017, this platform was introduced for internet users to clean their computers and devices by wiping out viruses and malware.
- Training of 1.14 Lakh persons through 52 institutions under the Information Security Education and Awareness Project (ISEA) – a project to raise awareness and to provide research, education and training in the field of Information Security. International cooperation: Looking forward to becoming a secure cyber ecosystem, India has joined hands with several developed countries like the United States, Singapore, Japan, etc. These agreements will help India to challenge even more sophisticated cyber threats.
QUANTUM COMPUTING
26, Nov 2019
Why in News?
- Recently quantum processor of Google solved a problem in just 3 minutes.
About:
- It describes the point where quantum computers can do things that classical computers cannot.
- Google had achieved Quantum Supremacy by solving a problem which even with the most powerful classical computer available today would take about 10,000 years to solve in just 3 minutes.
Significances:
- Help to discover exotic materials for variety of requirements.
- Provide fool proof cryptographic protection against online frauds.
- Enable drug discovery to fight diseases.
- Design efficient batteries.
- Smarter devices and gadgets.
Qubit/Quantum Bit
- It is the basic unit of quantum information.
- It is a two-state quantum mechanical system, one of the simplest quantum systems displaying the peculiarity of quantum mechanics.
- In a classical system, a bit would have to be in one state or the other.
- Quantum mechanics allows the qubit to be in a coherent superposition of both states simultaneously, a property which is fundamental to quantum mechanics and quantum computing.
- The power of the quantum computer comes from its inherent parallelism, the ability to manipulate a large collection of qubits in one shot in ways that a classical computer will not be able to match up.
ARROKOTH
15, Nov 2019
Why in News?
- The most distant space object ever seen up close has been recently named as ‘Arrokoth’.
- It was earlier nicknamed as Ultima Thule.
Arrokoth:
- The International Astronomical Union and Minor Planets Center, the global body for naming Kuiper Belt objects have given this name.
- It was discovered in 2014 with the Hubble Space Telescope, which is operated by the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore.
- Nasa’s New Horizons spacecraft flew by the snowman figured ice mass in December 2018, some 1.6 billion kilometres beyond Pluto.
- The New Horizons team of NASA proposed the name to the International Astronomical Union and Minor Planets Center.
- For the New Horizons team it took some months to finalise this name. In the language of the Powhatan tribe, Arrokoth means “sky”.
- The team got the approval from the elders of the Powhatan tribe to assign it to their new found “Baby”.
New Horizons Mission:
- NASA launched the New Horizons mission in January 2006.
- After crossing by Pluto in 2015, in 2019 it flew by Arrokoth. This remains the “farthest flyby ever conducted.”
Kuiper Belt:
- The Kuiper Belt is a disk-shaped region found in the outer solar system, past the orbit of Neptune.
- It is known as the third zone of the solar system, after the zone hosting the gas planets in our solar system. It contains hundreds of millions of small icy bodies that are thought to be left over material from the formation of the outer planets.
- At least three dwarf planets are located in the Kuiper belt: Pluto, Haumea and Make.
- Also, some of the solar system’s moons are thought to have originated there, such as Neptune’s Triton and Saturn’s Phoebe.
CHINA PROPOSES TO TREAT ALZHEIMER’S WITH NEW DRUG
07, Nov 2019

Why in News?
- The recent announcement of China that a new drug meant to potentially treat Alzheimer’s disease, will be available to Chinese patients shortly.
- The drug has been named as GV-971 or “Oligomannate”. It is a seaweed-based drug which is administered orally.
About Alzheimer’s Disease:
- It is a progressive brain disorder that typically affects people older than 65. When it affects younger individuals, it is considered early onset.
- The disease destroys brain cells and nerves, and disrupts the message-carrying neurotransmitters.Eventually, a person with Alzheimer’s loses the ability to perform day-to-day activities.
Alzheimer’s Versus Dementia:
- Dementia is an umbrella term for a range of conditions that involve a loss of cognitive functioning.Alzheimer’s is the most common type of dementia. It involves plaques and tangles forming in the brain. Symptoms start gradually and are most likely to include a decline in cognitive function and language ability.Other types of dementia include Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. People can have more than one type of dementia.
- Symptoms:
- Reduced ability to take in and remember new information
- Impairments to reasoning, complex tasking, and exercising judgment
- Impaired visuospatial abilities that are not, for example, due to eye sight problems.
- Impaired speaking, reading and writing Changes in personality and behaviour.
- The progression of Alzheimer’s can be broken down into three Main Stages:
- Preclinical, before symptoms appear
- Mild cognitive impairment, when symptoms are mild
- Dementia
Treatment:
- There is No Cure for Alzheimer’s, because its exact causes are not known. Most drugs being developed try to slow down or stop the progression of the disease.
- There is a degree of consensus in the scientific community that Alzheimer’s involves two proteins, called beta amyloids and tau. When levels of either protein reach abnormal levels in the brain, it leads to the formation of plaque, which gets deposited between neurons, damaging and disrupting nerve cells. Most existing drugs for Alzheimer’s try to target these proteins to manage some of the symptoms of Alzheimer’s.
ISRO’S NAVIC SET TO BE COMMERCIALISED BY ANTRIX
04, Nov 2019

Why in News?
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and its commercial arm Antrix Corporation Ltd. are poised to commercialise India’s regional navigation satellite system, NavIC.
- Antrix has recently floated two separate tenders to identify industries that can develop dedicated NavIC-based hardware and systems.
About NavIc (Navigation in Indian Constellation):
- NavIC is the Indian system of seven (currently eight) satellites that is aimed at telling business and individual users where they are, or how their products and services are moving.
- The indigenous positioning or location-based service (LBS) works just like the established and popular U.S. Global Positioning System or GPS, but within a 1,500-km radius over the sub-continent.
- About IRNSS (Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System):
- IRNSS is an independent regional navigation satellite system designed to provide position information in the Indian region and 1500 km around the Indian mainland.
- The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) is similar to that of GPS (global positioning system) of the US, Glonass of Russia and Galileo of Europe as well as China’s Beidou.
Features:
- It is a constellation of total 7 satellite launched in space and a ground facility on land to receive signals from space satellites. 3 of its satellite Located in Geostationary orbit and 4 are inclined to geosynchronous orbit. However full NAVIC system has 9 satellite, 2 on ground in standby mode.
- 4 Geosynchronous satellites: They will be orbiting in pairs in two inclined geosynchronous orbits. When observed from the ground, these 2 pairs of satellites will appear to travel in figures of ‘8’.
- 3 geostationary satellites: They will be placed in the geostationary orbit over the equator. They match the Earth’s rotation and shall remain at a fixed position in the sky.
- It covers whole India and region surrounding it up to 1500 km.
- It provides accuracy up to 20m as claimed by ISRO.
How many IRNSS Satellites are up there now?
- There are currently eight IRNSS satellites (1A to 1I) in orbit. A, B, F, G are placed in a geosynchronous orbit, while the remaining three, C, D, E, are located in geostationary orbit.
- The last IRNSS, 1H, which was launched on August 31, 2017 was unsuccessful as the satellite did not come out of its heat shield.
- IRNSS-1I was launched last year to replace India’s first navigation satellite IRNSS-1A, whose three Rubidium atomic clocks had stopped working. The malfunctioning of the Europe-imported atomic clocks in IRNSS-1A made it difficult to measure precise locational data from the satellite.
What areas will it cover?
- Primary Service Area: To provide accurate position information service to users in India as well as the region extending up to 1500 km from its boundary, which is its primary service area.
- Extended Service Area: It lies between primary service area and area enclosed by the rectangle from Latitude 30 deg South to 50 deg North, Longitude 30 deg East to 130 deg East.
What all services are provided?
- IRNSS would provide two types of services, namely
- Standard Positioning Services available to all users and
- Restricted Services provided to authorised users. (Encrypted)
Significance of IRNSS:
- India became one of the 5 countries having their own navigation system like GPS of USA, GLONASS of Russia, Galileo of Europe and Beidou of China. So, India dependence on other countries for navigation purposes reduces.
- It will help to mitigate the disaster effects by providing information of disaster timing, safe location and also help the disaster relief management to make earlier plans and save the lives of people in India as well as up to 1500 km around it.
- It will help the mariners for far navigation and fisherman for get information about the valuable fisheries location and any disturbance in Sea.
- It will help to make friendly relations with others countries by providing real time information during any calamity or disaster for mitigate its after effect and for making early plans
Recent Positive Developments:
- In mid-October, ISRO announced that Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., a leading producer of semiconductor chips, had developed and tested NavIC-friendly chipsets across its user bases and that it would add NavIC to them.
- Apart from GPS, its chips can work with the global navigation satellite systems of Europe (Galileo), Russia (GLONASS) and China (Beidou.)
- The third and important positive for NavIC was the certification of the Indian system by the 3GPP (The 3rd Generation Partnership Project), a global body for coordinating mobile telephony standards.
‘WHATSAPP DID NOT INFORM GOVT. OF SYSTEM BREACH’
04, Nov 2019

Why in News?
- WhatsApp has stated that some Indian users of WhatsApp came under surveillance using an Israeli spyware.
Highlights:
- WhatsApp in October 2019 sued the NSO Group, an Israeli surveillance firm and developers of Pegasus, which is reportedly behind the technology that helped unnamed entities hack into roughly 1,400 devices across at least 20 countries, including India, Bahrain, Mexico and UAE. Indian users were among those impacted by the spyware.
- The NSO Group is an Israeli technology firm, which claims on its website that its products are used “exclusively” by government intelligence and law enforcement agencies “to fight crime and terror”.
Concerns:
- WhatsApp has over 1.5 billion users globally, of which India alone accounts for about 400 million.
- The vulnerability of the users to such spying is of grave concern with regard to breach of their privacy.
- Government has stated that WhatsApp failed to inform the government of a breach of its system despite being legally bound to do so under Section 70(B) of the IT Act. They are legally bound to inform (computer emergency response team) CERT or any other relevant government agencies about the details of such attacks on Indian citizens.
- Despite WhatsApp arguing that they had given information to CERT-IN, the government has stated that it was a communication in pure technical jargon without any mention of Pegasus or the extent of breach.
- Thus the information shared was only about a technical vulnerability but nothing on the fact that privacy of Indian users had been compromised. Lack of clarity on this issue shows the loopholes in the current processes.
- The government has been blamed for trying to use the spyware to target specific people. However the government has stated that government agencies operate strictly as per provisions of law and a well-established protocol for interception.
- Government has claimed that reports of breach of privacy of Indian citizens on WhatsApp were attempts to malign the government and are completely misleading. The episode has taken up a political tone.
INDIGEN PROJECT
04, Nov 2019
Why in News?
- The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) has finished conducting “whole-genome sequence” of a 1,008 Indians as part of a programme called “IndiGen”.
IndiGen Project:
- Programme funded by the Department of Biotechnology will sequence at least 10,000 Indian genomes. The CSIR’s “IndiGen” project, as it is called, selected the 1,000-odd from a pool of about 5,000 and sought to include representatives from every State and diverse ethnicities.
- Every person whose genomes are sequenced would be given a report.
- The project is and is also seen as a precursor to a much larger exercise involving other government departments to map a larger swathe of the population in the country.
- Anyone looking for a free mapping of their entire genome can sign up for “IndiGen”.
- Those who get their genes mapped will get a card and access to an app which will allow them and doctors to access information on whether they harbour gene variants that are reliably known to correlate with genomes with diseases.
- The driving motive of the project is to understand the extent of genetic variation in Indians and learn why some genes — linked to certain diseases based on publications in international literature — do not always translate into diseases.
- Once such knowledge is established, the CSIR expects to tie up with several pathology laboratories who can offer commercial gene testing services.
Genome:
- A genome is the DNA, or sequence of genes, in a cell.
- Most of the DNA is in the nucleus and intricately coiled into a structure called the chromosome. The rest is in the mitochondria, the cell’s powerhouse.
- Every human cell contains a pair of chromosomes, each of which has three billion base pairs or one of four molecules that pair in precise ways.
- The order of base pairs and varying lengths of these sequences constitute the “genes”, which are responsible for making amino acids, proteins and, thereby, everything that is necessary for the body to function.It is when these genes are altered or mutated that proteins sometimes do not function as intended, leading to disease.
Genome Sequencing:
- Sequencing a genome means deciphering the exact order of base pairs in an individual. This “deciphering” or reading of the genome is what sequencing is all about.
- It has been known that the portion of the genes responsible for making proteins — called the exome — occupies about 1% of the actual gene. Rather than sequence the whole gene, many geneticists rely on “exome maps” (that is the order of exomes necessary to make proteins).
- However, it has been established that the non-exome portions also affect the functioning of the genes and that, ideally, to know which genes of a person’s DNA are “mutated” the genome has to be mapped in its entirety.
India’s Effort:
- While India, led by the CSIR, first sequenced an Indian genome in 2009, it is only now that the organisation’s laboratories have been able to scale up whole-genome sequencing and offer them to the public.
- Globally, many countries have undertaken genome sequencing of a sample of their citizens to determine unique genetic traits, susceptibility (and resilience) to disease. This is the first time that such a large sample of Indians will be recruited for a detailed study.
- Under “IndiGen”, the CSIR drafted about 1,000 youth from across India by organising camps in several colleges and educating attendees on genomics and the role of genes in disease. Some students and participants donated blood samples from where their DNA sequences were collected.
SPYWARE PEGASUS
02, Nov 2019

Why in News?
- The popular messaging platform WhatsApp was used to spy on journalists and human rights activists in India earlier this year.
- The surveillance was carried out using a spyware tool called Pegasus, which has been developed by an Israeli firm, the NSO Group.
- WhatsApp sued the NSO Group in a federal court in US accusing it of using WhatsApp servers in the United States and elsewhere to send malware to approximately 1,400 mobile phones and devices.
Pegasus:
- All spyware do what the name suggests — they spy on people through their phones.
- Pegasus works by sending an exploit link, and if the target user clicks on the link, the malware or the code that allows the surveillance is installed on the user’s phone.
- A presumably newer version of the malware does not even require a target user to click a link.
- Once Pegasus is installed, the attacker has complete access to the target user’s phone.The first reports on Pegasus’s spyware operations emerged in 2016, when Ahmed Mansoor, a human rights activist in the UAE, was targeted with an SMS link on his iPhone 6.
Worried about the costs and time associated with making repairs and preparing your house for sale? Sell it as-is to https://www.companiesthatbuyhouses.co/connecticut/home-buying-company-hamden-ct/ and avoid the hassle.
Method of working:
- A Pegasus operator must convince a target to click on a specially crafted ‘exploit link’ which allows the operator to penetrate security features on the phone.
- This automatically installs Pegasus without the user’s knowledge or permission.
- Once the phone is exploited and Pegasus installed Collectiveray, it begins contacting the operator’s command and control and send back the target’s private data, including passwords, contact lists, events, text messages, and live voice calls from popular mobile messaging apps.
- The operator can even turn on the phone’s camera and microphone to capture activity in the phone’s vicinity.
EDGE COMPUTING
31, Oct 2019
Why in News?
- Cloud computing — by which remote servers hosted on the Internet store and process data, rather than local servers or personal computers — is ready to move to the next level i.e. ‘Edge Computing’.
Cloud Computing:
- Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user.
- The term is generally used to describe data centres available to many users over the Internet.
Why need an upgrade?
- Amazon, Microsoft, and Alphabet, the parent company of Google — the technology giants that provide cloud computing infrastructure to major corporates and governments.
- They want to leverage 5G wireless technology and artificial intelligence to enable faster response times, lower latency (ability to process very high volumes of data with minimal delay), and simplified maintenance in computing.
- This is where Edge Computing comes in — which many see as an extension to the cloud, but which is, in fact, different in several basic ways.
- By 2025 companies will generate and process more than 75% of their data outside of traditional centralised data centres — that is, at the “edge” of the cloud.
Edge Computing:
- Edge computing enables data to be analysed, processed and transferred at the edge of a network.
- The idea is to analyse data locally, closer to where it is stored, in real-time without latency, rather than send it far away to a centralised data centre.
- So whether you are streaming a video or accessing a library of video games in the cloud, edge computing allows for quicker data processing and content delivery.
How is Edge Computing different from cloud computing?
- The basic difference between edge computing and cloud computing lies in the place where the data processing takes place.
- At the moment, the existing Internet of Things (IoT) systems performs all of their computations in the cloud using data centres.
- Edge computing, on the other hand, essentially manages the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices by storing and processing data locally.
- That data doesn’t need to be sent over a network as soon as it processed; only important data is sent — therefore, an edge computing network reduces the amount of data that travels over the network.
- Experts believe the true potential of edge computing will become apparent when 5G networks go mainstream in a year from now.
- Users will be able to enjoy consistent connectivity without even realizing it.
- Nvidia, one of the biggest players in the design and manufacture of graphics and AI acceleration hardware, has just announced its EGX edge computing platform.
- This will help telecom operators adopt 5G networks capable of supporting edge workloads.
NATIONAL HEALTH PROFILE, 2019
31, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- The Union Health Minister released the National Health Profile, 2019.
National Health Profile (NHP):
- The NHP is prepared by the Central Bureau of Health Intelligence (CBHI) and covers comprehensive information on demographic, socio-economic health status, health finance indicators, health infrastructure and health of human resources in the country.
- 2019 is the 14th year the NHP is being released.
- It was released for the first time in 2005.
- A digital version of the report was also released.
- The objective of the NHP is to create a versatile database of health information and making it available to all stakeholders in the healthcare sector.
- The NHP highlights substantial health information under major indicators viz. demographic indicators (population and vital statistics), socio-economic indicators (education, employment, housing and amenities, drinking water and sanitation) and health status indicators (incidence and prevalence of common communicable and non-communicable diseases and RCH), etc.
- The health finance section provides an overview of health insurance and expenditure on health, both public and Out of Pocket Expenditure (OOP), etc.
- The section on human resources provides an overview of availability of manpower working in the health sector, while health infrastructure section provides details of medical and dental colleges, AYUSH institutes, nursing courses and paramedical courses, etc.
UNITED TO ELIMINATE LYMPHATIC FILARIASIS
31, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- The Union Health Minister inaugurates National Symposium on the theme ‘United to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis’.
Highlights:
- On the occasion, the minister signed the ‘Call to Action to eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis by 2021’.
- Since the launch of the Global Program to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis (GPELF) by the World Health Organization in 2000, endemic countries across the world including India have adopted a twin pillar strategy:
- Prevention through Mass Drug Administration (MDA) using combination of 2 anti-filarial drugs (DEC and Albendazole)
- Providing Morbidity Management and Disability Prevention (MMDP) services to those affected by the disease
- The Government launched the Accelerated Plan for Elimination of Lymphatic Filariasis (APELF) in 2018.
- As per this plan, over 4 billion treatments have been availed by over 630 million target population in endemic districts.
- India has made steady progress in this regard by reducing the infection levels in the community below the threshold level in 96 districts, which accounts for nearly 37% of the total districts.
- The remaining 160 districts pose a challenge.
- Actual consumption of medicines remains low due to low awareness about the benefits of medicines at the community-level leading to non-adherence to treatment.
NPCIL ADMITS MALWARE ATTACK
31, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- CERT-In has conveyed that DTrack, a virus which originated in North Korea, is the weapon used in the cyber-attack on Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant.
About DTrack Virus:
- DTrack is used by hackers to attack financial and research centres in India. Its earlier version ATM DTrack was designed to hack ATMs in India.
- “The malware was designed to be planted on the victim’s ATMs, where it could read and store the data of cards that were inserted into the machines.
About CERT-In:
- The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) is nodal government agency that deals with cyber security threats like hacking and phishing in India.
- It was established in 2004 and comes under the aegis of Union Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
Objectives:
- Protect Indian cyberspace and software infrastructure against destructive and hacking activities.
- Strengthen security-related defence of the Indian Internet domain. Issue guidelines, vulnerability notes, advisories, and whitepapers regarding to information security practices, prevention, procedures, response and reporting of cyber security incidents.
Different types of Malware:
- Malware is the shortened form of malicious software. It is the general term for any program that is designed to damage, disrupt, or hack a device. Malware includes viruses, ransomware, spyware, Trojan, adware, etc.
- Viruses are malicious pieces of code that infect your device without your knowledge. They can affect your device’s performance, delete files, send spam, and even corrupt your hard drive. They multiply and spread to other machines, often before you’re aware of an infection.
- Ransomware is malicious programs that block access to your device until you pay a ransom fee to its creator. It is often very difficult and expensive to remove.
- Spyware is software that spies on you, tracking your internet activities in order to send advertising (Adware) back to your system.
- Worm is a program that replicates itself and destroys data and files on the computer. Worms work to “eat” the system operating files and data files until the drive is empty.
- Trojan is a type of malware that are written with the purpose of discovering your financial information, taking over your computer’s system resources, and in larger systems creating a “denial-of-service attack” which is making a machine or network resource unavailable to those attempting to reach it. Example: Google, AOL, Yahoo or your business network becoming unavailable.
Dealing with Cyber-Attacks on critical infrastructure:
- Nuclear power plants aren’t the only critical infrastructure in operation. As India digitises further, it will mean that there are more surfaces for attacks.
- India is centralising datasets, and connecting them together. Example: Aadhaar, the largest biometric database in the world; state resident data hubs with citizen data; the National Health Information Network with electronic health records is being planned; UPI; NATGRID with a plan to connect multiple databases together etc.
- As more critical infrastructure is set up, the risk of crippling critical parts of India’s security and economic infrastructure increases.
- Cyber-attacks are here to stay, and how the nation responds to them needs to be given due consideration.
- Defining global conventions around cyber-attacks something like a global agreement around the digital space, akin to a digital Geneva convention on cyber warfare could help. A minimum agreed-upon list of norms on what states must absolutely not do to other states and citizens is needed.
- India should consider strengthening its Computer Emergency Response Teams (CERT), and empowering sectoral CERTs. Working with the private sector to enhance capacity and manpower related to cyber security will help develop local capabilities.
CSIR OFFERS FREE MAPPING OF INDIAN GENOMES
30, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- Following the Genome India project, the first such human genome mapping project in India the genomic data of 10,000 Indians are being catalogued.
Highlights:
- A genome is an organism’s complete set of DNA, including all its genes. It contains all the information needed to build and maintain that organism.
- By sequencing the genome, researchers can discover the functions of genes and identify which of them are critical for life.
- Across the world, predictive diagnosis and precision medicine based on the genetic makeup of patients are emerging fields in the treatment of diseases such as cancer and other genetic disorders.
- The Genome India project will aim to make predictive diagnostic markers available for some priority diseases such as cancer and other rare and genetic disorders.
- Through the Genome Project India wants to becomes part of the global endeavour to chart out the complex human genetic map.
- The newly opened IndiGen initiative, a programme managed by the CSIR-Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology (IGIB) and the CSIR-Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) proposes to offer free mapping of an individual’s entire genome.
- The aim of the exercise is twofold: to test if it’s possible to rapidly and reliably scan several genomes and advise people on health risks that are manifest in their gene and to understand the variation and frequency of certain genes that are known to be linked to disease.
NANO-PHARMACEUTICALS
30, Oct 2019
Why in News?
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare released guidelines for evaluation of nano-pharmaceuticals, which are emerging as more potent tools for treating various diseases.
What are Nano-Pharmaceuticals?
- Nanopharmaceuticals represent an emerging field where the sizes of the drug particle or a therapeutic delivery system work at the nanoscale.
- They are derived by application of nanotechnology in medical therapeutics.
In the pharmaceutical industry, a long-standing issue is a difficulty of delivering the appropriate dose of a particular active agent to specific disease site. - Nanopharmaceuticals have enormous potential in addressing this failure of traditional therapeutics which offers site-specific targeting of active agents.
Such precision targeting via nanopharmaceuticals reduces toxic systemic side effects, resulting in better patient compliance.
Benefits:
- They are expected to bring about a revolution in treatment strategies as they would enable targeting specific delivery of drugs and therapeutic molecules.
They offer higher efficacy and lower toxicity in many disease conditions.
They are expected to be of great use particularly in cancer treatment.
Why Need Guidelines?
- Every year several new nano-pharmaceuticals are being developed and marketed across the world.
- India too has a sizable pool of nano-scientists generating a large number of scientific publications in this domain.
- However, regulatory approval is the most important factor for translating laboratory research into bedside medicine.
- The new set of guidelines is designed to facilitate this process.
Guidelines:
- The guidelines cover all the aspects of evaluation from the definition and categorization of nano-pharmaceuticals to pharmacovigilance of the new set of therapeutics.
- It has been prepared as a joint project by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) in the Union Ministry of Science and Technology lavagabonddame, and ICMR and Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation under health Ministry.
- It will give a big boost to innovators and drug manufacturers to optimise their research and come out with medicines that would be safer and more affordable.
QUANTUM COMPUTING
30, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- Google announced that it has achieved a breakthrough called quantum supremacy in computing.
What is Quantum Supremacy?
- It is a term proposed in 2012 by John Preskill, professor of theoretical physics at the California Institute of Technology.
- It describes the point where quantum computers can do things that classical computers cannot.
- In Google’s case, researchers at the University of California, Santa Barbara have claimed to have developed a processor that took 200 seconds to do a calculation that would have taken a classical computer 10,000 years.
What is a Quantum Computer?
- Our traditional computers work on the basis of the laws of classical physics, specifically by utilising the flow of electricity. A quantum computer, on the other hand, seeks to exploit the laws that govern the behaviour of atoms and subatomic particles.
- At that tiny scale, many laws of classical physics cease to apply, and the unique laws of quantum physics come into play.
Mechanism:
- In a classical computer Bits of information are stored as either 0 or 1. Every string of such digits (bitstrings) represents a unique character or instruction; for example, 01100001 represents the lowercase “a”.
- In a quantum computer, information is stored in quantum bits, or qubits. And a qubit can be both 0 and 1 at the same time.
- Quantum physics involves concepts that even physicists describe as weird. Unlike classical physics, in which an object can exist in one place at one time, quantum physics looks at the probabilities of an object being at different points. Existence in multiple states is called superposition, and the relationships among these states is called entanglement.
- The higher the number of qubits, the higher the amount of information stored in them. Compared to the information stored in the same number of bits, the information in qubits rises exponentially.
- That is what makes a quantum computer so powerful. And yet, as Caltech’s Preskill wrote in 2012, building reliable quantum hardware is challenging because of the difficulty of controlling quantum systems accurately.
- Challenges : Quantum researchers need to cool the qubits to close to absolute zero to limit vibration — or “noise” — that causes errors to creep into their calculations. It’s in this extremely challenging task that the research team at Google, a unit of Alphabet Inc, has made significant progress.
Googles Achievement:
- Google developed a microprocessor, named Sycamore, that packs a total of 54 qubits. Measuring about 10 mm across, it is made using aluminium and indium parts sandwiched between two silicon wafers.
- In their experiment, the researchers were able to get 53 of the qubits — connected to each other in a lattice pattern — to interact in a so-called quantum state.
- They then set the quantum computer a complex task to detect patterns in a series of seemingly random numbers. It solved the problem in 3 minutes and 20 seconds. They estimated that the same problem would take 10,000 years for a Summit supercomputer – the most powerful in the world today — to solve
- Quantum computers could one day result in huge advances in science research and technology. Among areas that stand to gain are artificial intelligence, and new drug therapies.
2 OUT OF 3 WILD POLIOVIRUS STRAINS HAVE BEEN ERADICATED, SAYS WHO
25, Oct 2019
Why in News?
- In an announcement by the World Health Organisation (WHO) on World Polio Day (October 24), an independent commission of experts declared that Wild Poliovirus Type 3 (Wpv3) has been eradicated worldwide. This follows the eradication of Smallpox and Wild Poliovirus Type 2.
About Wild Polio Virus:
- The virus is transmitted by person-to person spread mainly through the faecal-oral route or, less frequently, by a common vehicle (e.g. contaminated water or food) and multiplies in the intestine, from where it can invade the nervous system and can cause paralysis.
- Initial symptoms of polio include fever, fatigue, headache, vomiting, stiffness in the neck, and pain in the limbs.
- In a small proportion of cases, the disease causes paralysis, which is often permanent. There is no cure for polio, it can only be prevented by immunization.
- There are three individual and immunologically distinct wild poliovirus strains:
- Wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1)
- Wild poliovirus type 2 (WPV2)
- Wild poliovirus type 3 (WPV3).
- Symptomatically, all three strains are identical, in that they cause irreversible paralysis or even death. But there are genetic and virological differences, which make these three strains three separate viruses that must each be eradicated individually.
- This type 1 virus remains in circulation in just two countries, Afghanistan and Pakistan.
Types of Polio Vaccines:
Two different kinds of vaccine are available:
1.An inactivated (killed) polio vaccine (IPV)
2.Live attenuated oral polio vaccine (OPV)
1.Inactivated Polio vaccine (IPV):
- It is produced from wild-type poliovirus strains of each serotype that have been inactivated (killed) with formalin.
- It is an injection able vaccine and can be administered alone or in combination with other vaccines (e.g., diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, and haemophilus influenza).
2.Oral Polio vaccine (OPV):
- It consists of a mixture of the three live attenuated poliovirus serotypes (type 1, 2 and 3), selected for their lower neurovirulence and reduced transmissibility.
- Monovalent oral polio vaccines (mOPV) consist of live, attenuated (weakened) poliovirus strains of either type 1 (mOPV1) or type 3 (mOPV3) poliovirus only. The vaccine gives protection against one type of poliovirus only (either type 1 or type 3 depending on the vaccine).
- Trivalent OPV contains live and weakened versions for all the three types (1, 2 and 3) of wild polio while the bivalent vaccine will contain type 1 and 3. Type 2 of wild polio virus has been eradicated worldwide long time back.
NATIONAL FAMILY HEALTH SURVEY
24, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- Demographers from around the world gathered in Delhi recently to mark 25 years of National Family Health Surveys (NFHS).
About:
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MOHFW) has designated the International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) Mumbai, as the nodal agency, responsible for providing coordination and technical guidance for the survey.
- NFHS is a large-scale, multi-round survey conducted in a representative sample of households throughout India. Four rounds of the survey have been conducted since the first survey in 1992-93.The funding for different rounds of NFHS has been provided by USAID, DFID, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, UNICEF, UNFPA, and Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
- The survey provides state and national information for India on fertility, infant and child mortality, the practice of family planning, maternal and child health, reproductive health, nutrition, anaemia, utilization and quality of health and family planning services.
Goal of NFHS:
- To provide essential data on health and family welfare needed by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and other agencies for policy and programme purposes.
- To provide information on important emerging health and family welfare issues.
Highlights of NFHS-4 report:
- According to National Family Health Survey (NFHS)-4, 2015-16, one in every five Indians (both genders) is too thin with a BMI of less than 18.5, while every fourth male and second female is anaemic.
- The NFHS-4 highlighted that one in three women consume dark green leafy vegetables, chicken/meat/fish/eggs only once a week while one in two women do not consume fruits even once a week.
- The NFHS report also noted that one in five women however, consume aerated drinks weekly, one in 10 women consume fried food daily. Only one in 10 children aged 6-23 months receives an adequate diet.
- The Global Nutrition Report stated that India is facing a major malnutrition crisis as it holds almost a third of the world’s burden for stunting.
- The Global Nutrition report highlighted that 46.6 million children in India are stunted and India tops the list, followed by Nigeria (13.9 million) and Pakistan (10.7 million).
- The Global Nutrition report also noted that India also accounted for 25.5 million children who are wasted, followed by Nigeria (3.4 million) and Indonesia (3.3 million).
- Together with various governmental interventions, it is necessary to bring behavioural change to eradicate malnutrition from India. This necessitates educating the families about the need for nutrition.
MISSION INDRADHANUSH 2.0
24, Oct 2019
Why in News?
- The Government will launch the second phase of nationwide immunisation drive, i.e. Intensified Mission Indradhanush 2.0, to mark the 25 years of Pulse polio programme.
About the Programme:
- Intensified Mission Indradhanush 2.0 aims to achieve at least 90% pan-India immunisation coverage by 2022.
- Through ‘IMI 2.0’, the health ministry aims to reach each and every child below the age of two years and all pregnant women still uncovered/partially covered in 271 districts of the country.
- IMI 2.0 will include four rounds of vaccination, with each round involving a seven-day immunisation drive to be conducted each month.
- The IMI programme is supported by 12 ministries and departments and is being monitored by the cabinet secretary at the national level.
Government Interventions in Immunization:
1.‘Expanded Programme of Immunization (EPI):
- Immunization Programme in India was introduced in 1978 as ‘Expanded Programme of Immunization (EPI) by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
2.Universal Immunization Programme (UIP)’:
- In 1985, the above programme was modified as ‘Universal Immunization Programme (UIP)’.
- UIP prevents mortality and morbidity in children and pregnant women against 12 vaccine-preventable diseases.
- The stated objectives of the Programme include:
- Rapidly increasing immunization coverage,
- Improving the quality of services,
- Establishing a reliable cold chain system to the health facility level.
- Introducing a district-wise system for monitoring of performance,
- Achieving self-sufficiency in vaccine production.
- But in the past, it was seen that the increase in immunization coverage had slowed down. So in order to accelerate the coverage, Mission Indradhanush was envisaged and implemented since 2015 to rapidly increase the full immunization coverage to 90%.
3.Mission Indradhanush:
- It targets children under 2 years of age and pregnant women for immunization.
- The aim is to fully immunize more than 89 lakh children who are either unvaccinated or partially vaccinated under UIP.
- It provides vaccination against 12 Vaccine-Preventable Diseases (VPD) i.e. diphtheria, Whooping cough, tetanus, polio, tuberculosis, hepatitis B, meningitis and pneumonia, Hemophilus influenza type B infections, Japanese encephalitis (JE), rotavirus vaccine, pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) and measles-rubella (MR).
- The rate of increase in full immunization coverage increased to 6.7% per year through the first two phases of ‘Mission Indradhanush’.
4.Intensified Mission Indradhanush:
- The Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI) was launched by the Government of India in 2017 to reach each and every child under two years of age and all those pregnant women who have been left uncovered under the routine immunisation programme.
- Under IMI, greater focus has been given on urban areas which was considered to be one of the gaps in Mission Indradhanush.
- The target under IMI was to increase the full immunization coverage to 90% by December 2018. However, only 16 districts in the country have achieved 90% coverage so far.
- The official data states that India’s immunisation coverage is still 62%. (As per National Family Health Survey-4 (2015-16)).
5.Intensified Mission Indradhanush 2.0:
- This will target the districts which have immunisation coverage of 70% or below.
BRAHMOS SURFACE-TO-SURFACE MISSILE TESTS
24, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- Two BrahMos Surface-to-Surface missile tests were conducted at Trak Island in the Andaman Nicobar group of islands.
- A surface-to-surface missile (SSM) or ground-to-ground missile (GGM) is a missile designed to be launched from the ground or the sea and strike targets on land or at sea.
- They may be fired from hand-held or vehicle-mounted devices, from fixed installations, or from a ship.
BrahMos:
- It is a medium-range ramjet supersonic cruise missile that can be launched from submarines, ships, aircraft or land.
- It is a joint venture between the Russian Federation’s NPO Mashinostroyeniya and India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The name BrahMos is a portmanteau formed from the names of two rivers, Brahmaputra and Moskva of Russia.
- It is the world’s fastest anti-ship cruise missile in operation.
TECHSAGAR
23, Oct 2019

Context:
- National Cyber Security Coordinator’s office in partnership with Data Security Council of India (DSCI) has launched national repository of India’s cyber tech capabilities named TechSagar.
What is TechSagar?
- It is a consolidated and comprehensive repository of India’s cyber tech capabilities which provides actionable insights about capabilities of the Indian Industry, academia and research across 25 technology areas.
- The portal will list business and research entities from the IT industry, start-ups, academia, and individual researchers. Thus, it acts as a platform to discover India’s technological capability through a portal.
- The areas covered under the portal are as internet of things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), blockchain, cloud & virtualisation, robotics & automation, ar/vr, wireless & networking, and more.
Significance:
- As India aspires to become a trillion-dollar digital economy, the repository will facilitate new opportunities for businesses and academia to collaborate, connect and innovate in future.TechSagar will allow targeted search, granular navigation and drill down methods using more than 3000 niche capabilities.The repository features 4000+ entities from industry, academia and research including large enterprises and start-ups providing a country level view of India’s cyber competencies.
- In order to combat the growing threat from cybercrime, there is an urgent need to collaborate and develop cyber technology capabilities in India. With the launch of TechSagar, the seed has been sown for start-ups to prosper in cyber tech. This is a good example of government facilitating industry growth in a strategic domain.
About DSCI:
- Data Security Council of India (DSCI), is a not-for-profit, industry body on data protection in India, setup by NASSCOM.
- It is committed to making the cyberspace safe, secure and trusted by establishing best practices, standards and initiatives in cyber security and privacy.
- To further its objectives, DSCI engages with governments and their agencies, regulators, industry sectors, industry associations and think tanks for policy advocacy, thought leadership, capacity building and outreach activities.
THE NOBEL PRIZE IN PHYSICS 2019
22, Oct 2019

- The royal Swedish Academy of Sciences announced that the Nobel Prize in Physics would go to three people: One half of it would be shared by Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz of the University of Geneva, for discovering for the first time a planet outside our solar system orbiting a Sun-like star; the other half would go to James Peebles, Princeton University, for his contribution to physical cosmology.
- This brought the topics of exoplanets, dark matter, dark energy, cosmic microwave background (CMB) into limelight.
Exoplanets:
- An exoplanet is a planet outside our solar system. It is an extrasolar planet.
- ’51 Pegasi b’ was the first exoplanet to be discovered in 1995. It is unlikely that we can survive in that.
- According to NASA, there are 4,073 confirmed exoplanets.
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB):
- About 400,000 years after the Big Bang, the universe expanded and cooled to a few thousand degrees Celsius.
- This caused it to become transparent, allowing light to pass through it.
- This ancient afterglow of the Big Bang, the remnants of which still can be observed, is known as the cosmic microwave background (CMB).
- CMB is a faint cosmic background radiation filling all space.
- Microwave radiation is invisible light.
- The CMB is useful to scientists because it helps us learn how the early universe was formed. It is at a uniform temperature with only small fluctuations visible. By studying these fluctuations, cosmologists can learn about the origin of galaxies.
- CMB-Bharat is a proposal for comprehensive next generation Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) mission, which could help listen to the faintest murmurs of the early universe.
- It is proposed as an international collaboration mission with major Indian contribution
Dark Matter:
- By measuring the speeds of rotating galaxies, scientists were able to see that a lot of mass needed to be there that would hold the galaxies together with the strength of their gravitational attraction.
- Before Peebles intervened, the missing mass was attributed to neutrinos.
- Peebles instead said this is due to a hitherto unknown type of “dark” matter particles. However, while they could “see” a portion of this mass, a large part of it could not be seen. Hence the mass missing from view was named “dark” matter.
- Even though this matter is all around us, close as well as far away, we only feel it through its gravity, but we cannot see it through other interactions. This is because it does not interact with light.
- About 25% of the mass of the universe is made up of dark matter.
Dark Energy:
- In 1998, it was discovered that the universe is expanding, and that this expansion was gaining speed or accelerating.
- There had to be an “invisible” energy that was driving this.
- Calculations showed that this dark energy did not interact with the observed mass and makes up about 70% of the universe.
ASBESTOS IN BABY POWDER
21, Oct 2019

What to Study?
- Johnson & Johnson is recalling one lot of its Johnson’s Baby Powder after tiny amounts of asbestos contamination were found in samples from a single bottle purchased online.
- It was found that the contaminated bottle contained chrysotile fibers, a type of asbestos.
What is Talc?
- Talc is a clay mineral which is found in underground deposits. It’s the softest mineral ever known and that makes it useful in a wide range of consumer and industrial products.
- This mineral is used as a thickening agent and lubricant, is an ingredient in ceramics, paint and roofing material, and is also one of the main ingredients in many cosmetic products.
- Talc in powdered form, often in combination with corn starch, is widely used as baby powder (Talcum Powder).
- Asbestos is also found underground, and veins of it can often be found in talc deposits, leading to a risk of cross-contamination.
About Asbestos:
- Asbestos is a group of six naturally occurring fibrous minerals composed of thin, needle-like fibers. They are commonly known by their colours, as blue asbestos, brown asbestos, white asbestos, and green asbestos.
Applications of Asbestos:
- Asbestos is a naturally occurring mineral that can be pulled into a fluffy consistency. Asbestos fibers are soft and flexible yet resistant to heat, electricity and corrosion. These qualities make the mineral useful.
- Pure asbestos is an effective insulator, and it can be used in cloth, paper, cement, plastic and other materials to make them stronger.
Health impacts of Asbestos:
- Inspite of various applications of asbestos in strengthening and fireproofing of materials, it is banned in many of the countries.
- It is because when someone inhales or ingests asbestos dust, the mineral fibers can become forever trapped in their body.
- Over decades, trapped asbestos fibers can cause inflammation, scarring and eventually genetic damage to the body’s cells.
- A rare and aggressive cancer called mesothelioma is almost exclusively caused by asbestos exposure. Asbestos also causes other forms of cancer as well as progressive lung disease and asbestosis.
- Microscopic asbestos fibers cannot be seen, smelled or tasted, and it is unsafe to sniff a substance suspected of being asbestos. To detect asbestos, a sample of questionable material must be sent to a lab for testing.
MALARIA PARASITE JUMPED FROM GORILLAS TO HUMANS
18, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- Experts have found that African great apes were the original host to the parasite Plasmodium falciparum – the type the researchers studied, which accounts for most cases of Malaria.
Highlights:
- Malaria is caused by a parasite that gets into the bloodstream when an infected mosquito bites humans – or animals.
- There are lots of different strains of parasite and one of the most important ones, which now affects only humans, is Plasmodium falciparum.
- Falciparumis one of seven species of parasite that can cause malaria in a family known as the Laverania.The study says that the parasite switched host from gorillas at about the same time as the first migration of humans out of Africa, some 40,000 to 60,000 years ago.The DNA sequence included a gene that produced a protein called RH5 that can bind to human red blood cells.
Zoonosis:
- When diseases, such as influenza or malaria, jump from animals to humans in this way it is known as a zoonosis.It occurs when pathogens that are already able to infect an animal host acquire genetic material that enables them to also infect humans.
- In the case of falciparummalaria, it is thought that the genetic transfer of the rh5 gene occurred when a gorilla cell became infected with two species of Plasmodium parasite simultaneously – an event known as an introgression.When an introgression occurs, genetic material is swapped from one species to another.
- In the history of mankind, Plasmodium falciparum malaria has arguably been responsible for more human deaths than any other disease. The scientists have discovered not only how a species host switch has occurred, but the individual mutation which has then restricted P. falciparum to a single host species.
NPL SYNTHESISES NOVEL SECURITY INK
17, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- National Physical Laboratory (CSIR-NPL) has recently synthesised a novel security ink that emits intense red colour when exposed to UV and emits green colour soon after the UV source is turned off.
About the News:
- A Novel Security Ink that emits intense red colour when exposed to 254 nm wavelength UV and emits green colour soon after the UV source is turned off has been synthesised by a team of researchers from the Delhi-based National Physical Laboratory (CSIR-NPL).
- The emission of red is due to fluorescence while green is due to phosphorescence phenomenon. Both red and green can be clearly seen with the naked eye under ambient conditions.
- The Red Colour is emitted at 611 nm wavelength while the green is emitted at 532 nm.
Lasting Phosphorescence:
- The researchers found the images printed on ordinary paper using the ink exhibits excellent physical durability and chemical stability. There was no noticeable change in emission from the images even at the end of six months when exposed to high temperatures and high humidity.
- The emission showed no changes when the images were exposed to various bleaching solutions. So, the ink has the potential to be used as a security feature on currency notes and passports.
INDIAN COUNCIL OF AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH RELEASES TWO DIAGNOSTIC KITS
16, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- Two diagnostic kits developed by Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) – Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI) under the ‘Make in India’ initiative has been recently launched.
What are the New Diagnostic Kits?
1.The Bluetongue sandwich ELISA (sELISA)
2.The Japanese Encephalitis lgM ELISA kit for the control of Swine and Detection of Antigen
1.About Japanese Encephalitis (JE) ELISA Kit (IgM) for Swine:
- JE is a re-emerging viral zoonotic disease leading to death of large number of children every year in the country. The kit developed by the ICAR-Indian Veterinary Research Institute will be helpful for assessing the active infection of JE virus in the swine population which predicts the outbreak of JE in the humans.
- As compared to the commercial kit available in the market at a price of Rs. 52,000; the ICAR-IVRI developed is available for the farmers at a minimal price of Rs. 5,000 only. Each kit is meant for testing around 45 samples.
What is AES?
- Acute encephalitis syndrome (AES) is a serious public health problem in India.
- It is characterized as acute-onset of fever and a change in mental status (mental confusion, disorientation, delirium, or coma) and/or new-onset of seizures in a person of any age at any time of the year.Viruses are the main causative agents in AES cases, although other sources such as bacteria, fungus, parasites, spirochetes, chemicals, toxins and non-infectious agents have also been reported over the past few decades.
2.About Bluetongue: Sandwich ELISA for detection of Antigen
- Bluetongue (BT) virus is an insect-transmitted viral disease of domestic and wild ruminants that includes the camelid species.
- The disease is widespread among the sheep, goats, cattle, buffaloes and camels in the country.
- With the help of the Kit, the Bluetongue Virus can be controlled with the vaccination of susceptible animals, vector control and quarantine of infected animals with the good management practices.
- Apart from the vaccination, the early diagnosis and isolation of the infected animals are one of the commonly suggested preventive methods for controlling the spreading of the disease.
Benefits of the Kits:
- This indigenous technology will not just help save foreign exchange as the newly developed kits cost ten times lesser than the imported ones but also has the potential to earn foreign exchange.
- These two Kits will definitely be beneficial for not only the farming community, but the society as a whole. Based on the casualties caused by the deadliest diseases in the societies every year, the Kits will prove to be a real helping hand.
About ICAR:
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) is an autonomous organisation headquartered at New Delhi and works under the Department of Agricultural Research and Education (DARE), Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research is the apex body in India for coordinating, guiding and managing research and education in agriculture including horticulture, fisheries and animal sciences in the entire country.
- Earlier known as Imperial Council of Agricultural Research, it was established on 16 July 1929 as a registered society under the Societies Registration Act, 1860 in pursuance of the report of the Royal Commission on Agriculture.
HOW OXYGEN LEVELS AFFECT CELL METABOLISM?
16, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- The Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine was awarded to three scientists, William G. Kaelin Jr. from Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Maryland, U.S., Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe from Francis Crick Institute, London, and Gregg L. Semenza from the Johns Hopkins Institute for Cell Engineering for their discovery of how cells sense and adapt to oxygen availability.
- The three scientists have uncovered the genetic mechanisms that allow cells to respond to varying levels of oxygen.
Why is it important?
- Oxygen is used by all cells to convert food to useful energy.
- While oxygen is essential for the survival of cells, excess or too little oxygen can lead to adverse health consequences.
- Oxygen supply temporarily reduces in muscles during intense exercise and under such conditions the cells adapt their metabolism to lowoxygen levels.
- Proper growth of the foetus and placenta depends onthe ability of the cells to sense oxygen.
- Drugs have already been developed to treat Anaemia by making the body produce increased number of red blood cells.
- Similarly, drugs to increase oxygen availability in people with heart disease and lung cancer are being tested. Many diseases can be treated by increasing the function of a particular pathway of the oxygen-sensing machinery.
- At the same time, inhibiting or blocking the pathway will have implications in treating cancer, heart attack, stroke and pulmonary hypertension.
- Cancers are known to hijack the oxygen-regulation machinery to stimulate blood vessel formation and also re- programme the metabolism in order to adapt to low oxygen conditions.
- The reprogramming of metabolism gives cancer cells the plasticity to shift from a state where they have limited potential to cause cancer to a state when they have greater potential for long-term growth.
- Efforts are under way to develop drugs that can block the oxygensensing machinery of cancer cells to kill them.
What do we Already Know?
- The rate at which we respire depends on the amount of oxygen being carried in the blood.
- Specialised cells present next to large blood vessels in the neck sense the blood oxygen level and alert the brain to increase the rate of respiration when the oxygen level in the blood goes down.
- At the beginning of the last century, scientists knew that specialised cells present in the kidneys make and release a hormone called erythropoietin.
- When oxygen level is low, as in high altitudes, more of this hormone is produced and released, leading to increased production of red blood cells in the bone marrow — helping the body adapt to high altitudes.
- Besides increasing red blood cells, the body also grows new blood vessels to increase blood supply.
What are the main contributions of 2019ʼs winners?
- Both Prof. Semenza and Sir Ratcliffe independently studied how the erythropoietin gene is regulated by varying oxygen levels.
- Both researchers found that the oxygen-sensing mechanism is not restricted to kidneys where the erythropoietin is produced but by diverse cells in tissues other than the kidney.
- Semenza identified a pair of genes that express two proteins.
- When the oxygen level is low, one of the proteins (HIF-1alpha) turns on certain genes, including the erythropoietin gene, to increase the production of erythropoietin.
- The hormone, in turn, increases the oxygen availability by boosting the production of red blood cells.
- Kaelin Jr., who was studying an inherited syndrome called von Hippel-Lindauʼs disease (VHL disease) found that people had increased risk of cancer when they inherited VHL mutations.
- He found the VHL gene seemed to be involved in how cells respond to oxygen.
- The function of the HIF-1alpha protein, which turns on the genes to produce more erythropoietin, is blocked and is rapidly degraded when the oxygen level is normal but remains intact when oxygen level is
- Sir Ratcliffe found that VHL interacts with the HIF-1alpha protein and degrades it when the oxygen level is normal. This ensures that excess red blood cells are not produced when the oxygen level is normal.
Why do athletes use erythropoietin? What are the risks?
- *Athletes have been found to use erythropoietin, synthetic oxygen carriers and blood transfusions for blood doping. Each of the three substances or methods is banned by the World Anti-Doping Agency(WADA).
- While the use of erythropoietin in people who are anaemic due to chronic kidney disease helps in increasing the oxygen level in the blood, the use of the hormone by normal, healthy people can lead to serious health risks.
- In the case of healthy people who have a normal red blood cell count, the use of external erythropoietin is highly likely to make the blood thick (increase viscosity) leading to an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and cerebral or pulmonary embolism (clot that blocks the flow of blood).
GOLDEN RATIO
15, Oct 2019
Why in News?
- The golden ratio can be defined in terms of a line, divided into two unequal segments in a way that their lengths meet a simple condition.
- If we draw an arc across the top of the skull and divide it at a key junction over the brain, the two arc-segments are approximately in the golden ratio.
- The golden ratio is alternatively called the golden mean and the divine ratio. Its frequent appearances in nature have driven claims that it is the work of a divine design.
- This feature was studied recently by researchers of Johns Hopkins University, US, who have reported their findings in The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.
How it makes the Ratio Golden?
- When the ratio between these two lengths (the longer segment divided by the shorter one) happens to be the same as the ratio between the entire line and the longer segment, then the line is said to be divided in the golden ratio (see illustration).
- For this condition to hold good, the ratio needs to be 1.61803… with the digits after the decimal going on forever; the golden ratio is what we call an “irrational number”.
- It is represented by the Greek letter phi.
Why such a ratio is Considered Special?
- Aesthetic appeal is among the first of many reasons.
- Architects such as Le Corbusier have consciously proportioned their works to the golden ratio, or close.
- So have artists such as Salvador Dalí and Leonardo da Vinci, whose fascination with the golden ratio features in the novel The Da Vinci Code and the film based on it.Interpretations of the golden ratio have not always been objective.
Other Examples:
- The fact remains, however, that the golden ratio frequently shows itself in nature, whether directly or indirectly (through its cousins called the Fibonacci numbers).
- To cite a few examples, the golden ratio appears in the seeds of sunflowers, the scales of pineapples, the arrangement of petals on a rose, DNA structures, the anatomy of the heart — and has now turned up in the human skull.
ELASTOCALORIC EFFECT
14, Oct 2019
Why in News?
- When rubbers bands are twisted and untwisted, it produces a cooling effect.
- This is called the “elastocaloric” effect, and researchers have suggested that it can be used in a very relevant context today.
- Researchers have found that the elastocaloric effect, if harnessed, may be able to do away with the need of fluid refrigerants used in fridges and air-conditioners.
- These fluids are susceptible to leakages, and can contribute to global warming.
How it works?
- In the elastocaloric effect, the transfer of heat works much the same way as when fluid refrigerants are compressed and expanded.
- When a rubber band is stretched, it absorbs heat from its environment, and when it is released, it gradually cools down.
- In order to figure out how the twisting mechanism might be able to enable a fridge, the researchers compared the cooling power of rubber fibres, nylon and polyethylene fishing lines and nickel-titanium wires.
- They observed high cooling from twist changes in twisted, coiled and supercoiled fibres.
Efficiency:
- The level of efficiency of the heat exchange in rubber bands “is comparable to that of standard refrigerants and twice as high as stretching the same materials without twisting”.
- To demonstrate this setup, the researchers developed a fridge the size of a ballpoint pen cartridge that was able to bring down the temperature of a small volume of water by 8°C in a few seconds.
- They suggested that their findings may lead to the development of greener, higher-efficiency and low-cost cooling technology.
IONOSPHERIC CONNECTION EXPLORER
14, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- NASA has launched a satellite to explore the mysterious, dynamic region where air meets space.
Ionospheric Connection Explorer:
- The satellite — called ICON, short for Ionospheric Connection Explorer — rocketed into orbit following a two-year delay.
- The refrigerator-size ICON satellite will study the airglow formed from gases in the ionosphere and also measure the charged environment right around the spacecraft which is at a level of 580 kilometers above the Earth’s surface.
- The ionosphere is the charged part of the upper atmosphere extending several hundred miles (kilometers) up.
- It’s in constant flux as space weather bombards it from above and Earth weather from below, sometimes disrupting radio communications.
Why study Ionosphere?
- There’s too much going on in this region to be caused by just the sun.
- Hurricanes, tornadoes and other extreme weather conditions on Earth are also adding energy.
- The more scientists know the better spacecraft and astronauts can be protected in orbit through improved forecasting.
- A NASA satellite launched last year, Gold, is also studying the upper atmosphere, but from much Higher Up.
PRIVACY RIGHTS & WRONGS
12, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- TRAI had commenced a process of consultations to bring over the top (OTT) services like WhatsApp and Telegram under “lawful interception”.
Objectives:
- The objective of the exercise is public security since criminals and terrorists are known to use end-to-end encryption offered by such services to fly under the radar.
- Parity has always been an issue since telecom providers complain that they are regulated and must respond to requests for information from governments and agencies. But the OTT sector is untrammelled.
Is Interception Technologically Feasible, at all?
- Technology companies have argued that end-to-end encryption is completely private between the correspondents in the conversation.It is encrypted by a pair of security keys which their devices exchange, and which are available to no one else, not even the OTT provider. Providers are unable to provide governments with any communications content, except metadata like the frequency of contact.
- The US Attorney General’s, along with his counterparts in Australia and the UK, has requested Mark Zuckerberg not to deploy systems that preclude any form of access to content, even for preventing or investigating the most serious crimes.
Need for Such Technologies:
- Concerns about crime, terrorism and lethal mischief-making using encrypted communications are legitimate.
- Worldwide, the pressure is developing on providers and platforms to make content available for inspection.
Against privacy:
- Privacy concerns are equally legitimate because compromising security would degrade privacy across platforms.Blackberry had kept a copy of encrypted communications and provided it to the governments of India, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. Now, it is an inconsequential player. Privacy is now recognised as a right. It would open the door to situations like the NSA mass surveillance scandal.
A NEW TECHNIQUE TO PROTECT COPPER FROM CORROSION
11, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- Researchers at Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Varanasi, have developed a new method that promises to protect copper, which is one of the most popular commercial metals, from corrosion in a cost effective manner.
Background:
- Over the years, scientists have developed several techniques to combat the problem of corrosion of copper.
- However, they are expensive or highly complex or provide incomplete protection in acidic media. The new method promises to overcome these problems.
Floating Film Transfer Method:
- Researchers used technique called ‘floating film transfer method’ to obtain ultrathin films of an organic material, squaraine, and to transfer it over the copper articles as layers.
- The anti-corrosion activity was tested in the presence of hydrochloride using electrochemical techniques as well as surface characterization techniques.
- The tests showed that nearly 40 per cent corrosion protection is reached with just one layer of squaraine and increased up to 98 per cent with four layers.
Why Squaraine?
- There are several ways to protect copper from corrosion, but squaraine has an interesting chemical structure.It has a hydrophobic functional group at one end, a hydrophilic functional group at the other end and the two are connected to a square unit in the middle.
- This helps it dissolve in both hydrophobic and hydrophilic solvents and enables it to be drawn out in the form of thin films.
- Since metal surfaces are hydrophilic, if squaraine is coated on them, its hydrophilic end interacts with the metal surface and the hydrophobic end hangs out in air and thus repelling corrosive molecules.
The Experiment:
- For their experiment, the researchers filled a petridish with distilled water up to three-fourth of its height and the upper water surface was cleaned multiple times with small strips of lint free tissue to ensure that there was no contamination.
- One drop of squarine solution in chloroform was released over the water surface. A blue circular floating film was formed at the air-water interface within seconds.
- The film was then carefully lifted on to a copper strip and washed gently with a stream of distilled water followed by vacuum drying.
- The researchers kept depositing layer after layer and after adding every layer tested the anti-corrosion behavior of the layer.
GEOTAIL
09, Oct 2019
Why in News?
- Recently on board with Chandrayaan-2 mission, an instrument called CLASS, designed to detect signatures of elements in the Moon’s soil, had detected charged particles during the mission.This happened in September, during the orbiter’s passage through the “geotail”.
Geotail:
- The geotail is a region in space that allows the best observations.
- The region exists as a result of the interactions between the Sun and Earth.
- The Sun emits the solar wind, which is a continuous stream of charged particles. These particles are embedded in the extended magnetic field of the Sun.
- Since the Earth has a magnetic field, it obstructs the solar wind plasma.
- This interaction results in the formation of a magnetic envelope around Earth.
- On the Earth side facing the Sun, the envelope is compressed into a region that is approximately three to four times the Earth radius.
- On the opposite side, the envelope is stretched into a long tail, which extends beyond the orbit of the Moon. It is this tail that is called the geotail.
CLASS:
- CLASS stands for Chandrayaan 2 Large Area Soft X-ray Spectrometer.
- For the CLASS instrument seeking to detect element signatures, the lunar soil can be best observed when a solar flare provides a rich source of X-rays to illuminate the surface.
- Secondary X-ray emission resulting from this can be detected by CLASS to directly detect the presence of key elements like Na, Ca, Al, Si, Ti and Fe.
NOBEL PRIZE
09, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- The Nobel Foundation has recently started announcing the winners of “Nobel Prize” in various fields and winners and the concerned details are as follows:
Awardees in the field of Physics:
- The 2019 Nobel prize for Physics was awarded to Swiss Scientists Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz and Canadian – American physicist James Peebles.
- Peebles, who is awarded one half of the prize, is recognized specifically “for theoretical discoveries in physical cosmology.
- The other half of the prize is awarded jointly to Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz, “for the discovery of an exoplanet orbiting a solar-type star.
1.James Peebles discoveries
- The Canadian – American physicist James Peebles had contributed a lot to the field of physical cosmology for which he has been awarded with the prize. His discoveries are as:
- He has made significant contributions towards cosmic microwave background radiation, Big Bang nucleosynthesis, dark energy and dark matter.
- He was also the pioneer in the theory of Cosmic structure formation.
2.Contribution of Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz:
- In 1955, the Swiss astronomers discovered an exoplanet at an observatory in France. It was named orbiting a sun like star called 51 Pegasi b (or 51 Peg b). It orbits very close to the sun. The mass of the exoplanet is half of Jupiter and its temperature are around 1200 degree Celsius.
- At the time of its discovery by the astronomers this close distance for a planet to its start was not compatible with the theories of planet formation. Hence it led to discussions of planetary migration. Finally their discovery was proved right and it created revolution in astronomy.
- Today, exoplanets are being discovered very frequently — over 4,000 are known — which is remarkable progress from three decades ago, when not even one exoplanet was known.

Awardees in the field of Medicine:
- The 2019 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine has been awarded to scientists William G Kaelin, Jr, Peter J Ratcliffe and Gregg L Semenza.
- They received the award jointly for their discoveries of “how cells sense and adapt to oxygen availability. they established the basis for our understanding of how oxygen levels affect cellular metabolism and physiological function.
- Their research has “paved the way for promising new strategies to fight anaemia, cancer and many other diseases.
- The three will share the Nobel prize sum of nine million Swedish kronor or about 9 Lakh 14 thousand US dollar. They will receive their prize from King Carl XVI Gustaf at a formal ceremony in Stockholm on December 10.
- It is the 110th prize in the category that has been awarded since 1901.
About Nobel Prize:
- Alfred Nobel, a Swedish chemist, engineer, industrialist, and the inventor of dynamite, in his last will and testament in 1895, gave the largest share of his fortune to a series of prizeswhich were collectively came to be known as the “Nobel Prizes”.
- The awards are started from the year of 1901 for five different fields and in the year 1969, the field of Economic sciences was also included.
- The Nobel Prizes are widely regarded as the most prestigious awards given for intellectual achievement in the world.
- The various awards that forms the group of “Nobel Prizes” are as follows:
- 1.Nobel Prize for Physics
- 2.Nobel Prize for Chemistry
- 3.Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine
- 4.Nobel Prize for Literature
- 5.Nobel Prize for Peace.
- 6.Nobel prize for Economic Sciences (added only in the year 1969)
The Awards are presented by:
- The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences confers the prizes for Physics, Chemistry, and Economics. (Sweden Based)
- The Karolinska Institute confers the prize for physiology or medicine. (Sweden Based)
- The Swedish Academy confers the prize for literature. (Sweden Based)
- The Norwegian Nobel Committee based in Oslo confers the prize for peace. (Norway Based)
Indians (or individuals of Indian origin) who won the award are:
- Rabindranath Tagore (Literature, 1913), C V Raman (Physics, 1930), Hargobind Khorana (Medicine, 1968), Mother Teresa (Peace, 1979), Subramanian Chandrashekhar (Physics, 1983), the Dalai Lama (Peace, 1989), Amartya Sen (Economics, 1998), Venkatraman Ramakrishnan (2009), and Kailash Satyarthi (Peace, 2014).
MOSAIC MISSION
07, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- A native of Kerala, the 32-year-old polar researcher will be the only Indian among 300 scientists from across the world aboard the multidisciplinary drifting observatory for the Study of Arctic Climate (MOSAiC) expedition.
MOSAiC Mission:
- The MOSAiC mission stands for Multidisciplinary drifting Observatory for the Study of Arctic Climate.
- It is a one-year-long expedition into the Central Arctic, planned to take place from 2019 to 2020.For the first time a modern research icebreaker will operate in the direct vicinity of the North Pole year-round, including the nearly half year long polar night during winter.
- It comes about 125 years after Norwegian explorer Fridtjof Nansen first managed to seal his wooden expedition ship, Fram, into the ice during a three-year expedition to the North Pole.MOSAiC will contribute to a quantum leap in our understanding of the coupled Arctic climate system and its representation in global climate models.
- The focus of MOSAiC lies on direct in-situ observations of the climate processes that couple the atmosphere, ocean, sea ice, bio-geochemistry and ecosystem.
Why Study Arctic Climate?
- The Arctic is a key area of global climate change, with warming rates exceeding twice the global average.The observed rate of climate change in the Arctic is not well reproduced in climate models.Many processes in the Arctic climate system are poorly represented in climate models because they are not sufficiently understood.
- Understanding of Arctic climate processes is limited by a lack of year round observations in the central Arctic.
PLANET NINE
06, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- Hidden in the outer Solar System lurks a presence, believed to be a gigantic planet orbiting the same Sun and casting a visible influence on the behaviour of a number of other objects.
- Although it has not yet been spotted, this behaviour would be difficult to explain if such a presence did not exist.
Planet Nine:
- It is popularly referred to as Planet Nine, the presumed ninth planet of the Solar System, and occasionally as Planet X.
- Scientists have proposed that this could be a tiny black hole instead.
- They have shown that the behaviour of certain Trans-Neptunian Objects like a primordial black hole.
Primordial black hole:
- A primordial black hole is one that is believed to have formed immediately after the creation of the universe.Like Planet Nine, primordial black holes too have been predicted to exist — including by the late Stephen Hawking — but none has been spotted as yet.
Planet Nine so far:
- Over the years, scientists have sought to explain several puzzling aspects of the Solar System by attributing these to the influence of Planet Nine.
- In a 2016 paper made out a case for Planet Nine’s existence by arguing that it could be responsible for the peculiar alignment of icy objects on the outskirts of the Solar System.
New suggestion about a Black Hole:
- Researchers based their theory proposed two gravitational anomalies.
- One is the unusual orbits of asteroids beyond the orbit of Neptune, which have fed the prediction of Planet Nine, estimated to be somewhere between 5 and 20 times the mass of the Earth.
- The other anomaly was observed thousands of light years away, by a project called the Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment (OGLE).
- In six observations, an object bent the light of a star like black holes do. This is called microlensing.
- These six events correspond to objects whose masses are in the range 0.5 to 20 times the mass of Earth.
- The catch is that it is much harder to look for a black hole than to look for a planet, especially when the black hole is predicted to be of small dimensions.
- However, it is reasonable to expect a dark matter halo surrounds this black hole.
- If dark matter can annihilate into particles we know, the halo surrounding the black hole would radiate high energy photons and the halo would be visible in X-rays and gamma rays.
- Researchers propose to look through a gamma ray telescope dataset and try to find evidence of these annihilations.
CHANDRAYAAN-2’S ORBITER CLASS DETECTS CHARGED PARTICLES ON MOON
05, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has announced that Chandrayaan2’s Orbiter payload CLASS has detected charged particles on the moon in its first few days of observation.
- CLASS has observed intensity variations in its first passage through Moon’s orbit.
Highlights:
- CLASS is able to detect direct signatures of elements present in the lunar soil.
- It was also found by the CLASS that best observation occurred when the Sun provides a rich source of x-rays to illuminate the lunar surface.
- The payload can also detect secondary x-ray emissions resulted from the lunar surface to find out elements like Na, Ca, Al, Si, Ti and Fe.
- The sun emits a stream of protons and electrons into the solar system which is called the solar wind. The plasma in solar winds containing charged particles embedded in the extended magnetic field of the Sun travels at speeds of a few hundred km per second.
- These particles interact with Earth’s atmosphere and create a magnetic envelop around the earth which is called magnetosphere.
- This envelop of the magnetosphere is compressed into a region approximately three to four times the Earth radius on the side facing the Sun.
- On the other end, it has a stretched tail which is called geotail that goes beyond the orbit of the Moon.
- After every 29 days, Moon crosses the geotail for approximately six days. Therefore, Chandrayaan-2 also traversed geotail and its instruments found charged particles in the field.
CLASS:
- The CLASS stands for Chandrayaan-2 Large Area Soft X-ray Spectrometer.
- It helps to study the Moon’s X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) spectra to find out the presence of major elements such as Sodium, Silicon, Magnesium, Calcium, Aluminium, Titanium and Iron.
- This technique will identify these elements by measuring the characteristic X-rays they emit when excited by the Sun’s rays.
X-ray Monitor:
- X-ray Monitor or XSM detects the X-rays emitted by the Sun and its corona. It calculates the strength of solar radiation in these rays and assists CLASS.
- Major objective of XSM is to provide solar X-ray spectrum in the energy range of 1-15 KV. This payload will give high-energy resolution and high-cadence measurements of solar X-ray spectra as input for analysis of data from CLASS.
ELEPHANT ENDOTHELIOTROPIC HERPESVIRUS
04, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- Since the middle of August, a rare disease has killed five elephants in Odisha. The disease is caused by a virus called Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV).
About Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV):
- An EEHV information website, a resource conceived in 2011 at the 7th Annual International EEHV Workshop in Houston, describes EEHVs as a type of herpesvirus that can cause a highly fatal haemorrhagic disease in young Asian elephants.
- Most elephants carry just as most humans carry a cold virus. When EEHV is triggered, the elephant dies of massive internal bleeding and symptoms which are hardly visible
- Some elephants show symptoms such as reduced appetite, nasal discharge and swollen glands.
- The disease is usually fatal, with a short course of 28-35 hours.
- There is no true cure for herpesviruses in animals or in humans because the disease has a short course, this means we have to take a very quick call on a suspected EEHV case and kick off treatment protocols.
- The treatment is a combination of anti-viral therapy, aggressive fluid therapy (to counter haemorrhaging), immuno-stimulant drugs (selenium and Vitamins C, E), anti-pyretics and analgesics (to bring down fever).
Concerns:
- If elephants in the wild start falling prey to the virus, then treatment will be very difficult, it will be extremely hard to track down every wild elephant in the state and test whether they are positive for EEHV.
- EEHV is lethal for young elephants between the ages of one and 12. If a young elephant dies before reproducing, it affects the population of the species as a whole in the concerned geography.
MONSOON MISSION COUPLED FORECAST MODEL (CFS)
03, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- The new monsoon model, called the Coupled Forecast Model (CFS), deployed by the IMD under the National Monsoon Mission (NMM) has failed to forecast the excess rainfall received during Aug-Sept 2019.
About:
- An analysis has been suggesting that new monsoon models, called the Monsoon Mission Coupled Forecast Model (CFS), deployed by the IMD over the last decade are not performing better than the older ones in Long-Range Forecasting and its recent failure to predict the excess rainfall stands evidence to it.
- However, the analysis have suggested that the IMD models that forecast two weeks ahead (called extended range prediction) and the short-term forecast models (that gauge weather three days ahead) are functioning well and have predicted the excess rainfall in advance.
About National Monsoon Mission (NMM):
- This Mission was launched by Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) in 2012 with a vision to develop a state-of-the-art dynamical prediction system for monsoon rainfall on different time scales.
- Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune is vested with the responsibility of execution and coordination of this mission.
- Climate Forecast System (CFS) of USA has been identified as the basic modelling system for the above purpose, as it is one of the best among the currently available coupled models.
Objective of the Mission:
- To build an ocean atmospheric model for – improved prediction of monsoon rainfall on extended range to seasonal time scale (16 days to one season) and improved prediction of temperature, rainfall and extreme weather events on short to medium range time scale (up to 15 days).
About Coupled Forecast Model (CFS):
- “Climate Forecast System” (CFS) is an American model developed by National Centres for Environmental Prediction (NCEP), USA.
- It is a coupled ocean-atmosphere modelling system that combines data from ocean, atmosphere and land for providing long range forecasting (seasonal prediction of Indian Monsoon).
THE GANDHIAN CHALLENGE
02, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- On the 150th birth Anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi, AIM, NITI Aayog’s Atal Tinkering Labs (ATL) and UNICEF India, including Generation Unlimited, have launched ‘The Gandhian Challenge’.
About Gandhian Challenge:
- It is an innovation challenge which provides a platform for every child across India to ideate innovative solutions for a sustainable India of their dreams, using Gandhi’s principles.
- The winners of The Gandhian Challenge will be awarded by NITI Aayog’s Atal Innovation Mission and UNICEF on the occasion of Children’s Day in November. The contest – open for every child in India from 2 October to 20 October – also celebrates 70 years of partnership between Government of India and UNICEF India to enable Every Right for Every Child.
- Ideas and solutions to the Gandhian Challenge may be expressed through broad categories: Art & Innovation (Letters, poems, painting, videos and photos, among others) and Science, Technology & Innovation (Robotics, IoT, sensors and 3D printers, among others).
About Atal Innovation Mission (AIM):
- AIM is the Government of India’s flagship initiative to promote a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship in the country.
- AIM’s objective is to develop new programmes and policies for fostering innovation in different sectors of the economy, provide platform and collaboration opportunities for different stakeholders, create awareness and create an umbrella structure to oversee innovation ecosystem of the country.
- Six major initiatives of AIM:
- Atal Tinkering Labs-Creating problem-solving mindset across schools in India.
- Atal Incubation Centers-Fostering world class start-ups and adding a new dimension to the incubator model.
- Atal New India Challenges-Fostering product innovations and aligning them to the needs of various sectors/ministries.
- Mentor India Campaign- A national Mentor network in collaboration with public sector, corporates and institutions, to support all the initiatives of the mission.
- Atal Community Innovation Center- To stimulate community centric innovation and ideas in the unserved /underserved regions of the country including Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- ARISE-To stimulate innovation and research in the MSME industry.
About UNICEF India and Generation Unlimited:
- UNICEF, an integral part of the United Nations, works with governments, communities, civil society organizations, the private sector, and other partners worldwide to advance children’s rights, and is guided by the Convention on the Rights of the Child.
- Generation Unlimited is a new UNICEF-led global partnership that aims to ensure that every young person age 10-24 is in some form of school, learning, training, self-employment, or age-appropriate employment by 2030.
- It aims to co-create and scale up proven solutions related to secondary age-education, skills for learning, employability and decent work, and empowerment, with a focus on girls.
HOW GRAVITY DISTORTS OUR VIEW OF A BLACK HOLE
30, Sep 2019

Context:
- A new visualisation of a black hole, released by NASA, illustrates how its gravity distorts our view by warping its surroundings.
- The visualisation simulates the appearance of a black hole where infalling matter has collected into a thin, hot structure called an accretion disc.
- The black hole’s extreme gravity skews light emitted by different regions of the disc, producing the misshapen appearance, NASA explained in the release.
Explanation:
- As magnetic fields twist through the churning gas, bright knots form and dissipate in the disc. In the area closest to the black hole, the gas orbits at close to the speed of light.
- The outer portions spin a bit more slowly. This difference stretches and shears the bright knots, producing light and dark lanes in the disk.
- The black hole’s extreme gravity alters the paths of light coming from different parts of the disc, producing the warped image.
- Exactly what we see depends on our viewing angle; the greatest distortion occurs when viewing the system nearly edgewise.
- Glowing gas on the left side moves toward us so fast that the effects of Einstein’s relativity give it a boost in brightness.
- On the right side, gas moving away becomes slightly dimmer. This asymmetry disappears when we see the disc exactly face on because, from that perspective, none of the material is moving along our line of sight.
About Einstein’s Theory of Relativity:
- In 1915, Albert Einstein presented his theory of general relativity, which proposed that gravity itself was the result of a warping of spacetime by massive objects like stars and planets.
- Einstein’s theory of relativity indicates that all objects fall the same way regardless of mass or composition.
Things predicted by General relativity include:
- As light gets closer to the sun, it bends towards the suntwice as much as classical physics (the system used before general relativity) predicts.
- The perihelion of the planet Mercury rotates along its orbit more than is expected under Newtonian physics. General relativity accounts for the difference between what is seen and what is expected without it.
- Redshift from gravity.When light moves away from an object with gravity (moving away from the center of the valley), it is stretched into longer wavelengths. This was confirmed by the Pound-Rebka experiment.
- The Shapiro delay.Light appears to slow down when it passes close to a massive object. This was first seen in the 1960s by space probes headed towards the planet Venus.
- Gravitational waves.They were first observed on 14 September 2015.
PROJECT NETRA
28, Sep 2019

Why in news?
- ISRO has initiated ‘Project NETRA’ – an early warning system in space to detect debris and other hazards to Indian satellites.
Project NETRA (Network for space object Tracking and Analysis):
- The project will give India its own capability in space situational awareness (SSA) like the other space powers — which is used to ‘predict’ threats from debris to Indian satellites.
- NETRA’s eventual goal is to capture the GEO, or geostationary orbit, scene at 36,000 km where communication satellites operate.
- The space agency says our SSA will first be for low-earth orbits or LEO which have remote-sensing spacecraft.
- Under NETRA the ISRO plans to put up many observational facilities: connected radars, telescopes; data processing units and a control centre.
- They can, among others, spot, track and catalogue objects as small as 10 cm, up to a range of 3,400 km and equal to a space orbit of around 2,000 km.
- The NETRA effort would make India a part of international efforts towards tracking, warning about and mitigating space debris.
What NETRA consists of?
- In the plans are a high-precision, long range telescope in Leh and a radar in the North East.
- Along with them, we will also use the Multi-Object Tracking Radar (MOTR) that we have put up at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, and the telescopes at Ponmudi and Mount Abu to get a broad SSA picture.
- NORAD, or the North American Aerospace Defense Command, is an initiative of the U.S. and Canada that shares selective debris data with many countries.
- The new SSA centre would consolidate debris tracking activities that are now spread across ISRO centres.
- Currently there are 15 functional Indian communication satellites in the geostationary orbit of 36,000 km; 13 remote sensing satellites in LEO of up to 2,000 km; and eight navigation satellites in medium earth orbits.
Why Space debris matters?
- Space debris could be floating particles from dead satellites or rocket parts that stay in orbit for many years.
- Satellite agencies worry over even a speck of paint or fragment floating towards their spacecraft: it disables on board electronics and cripples the satellite worth several hundred crore rupees.
- Agencies constantly look for debris at the time of a launch and through the life of a satellite.
Enhancing Space situational awareness (SSA):
- India, as a responsible space power, should have SSA as a part of a national capability, as in the U.S. This is a vital requirement for protecting our space assets and a force multiplier.
- The SSA has a military quotient to it and adds a new ring to the country’s overall security.
- It uses satellites, ground and air radars to secure its two countries against attacks from air, space or sea.
- With long-range tracking radars, the SSA also provides us the capability of an early warning system against ballistic missiles coming in at a height.
- Apart from radars and telescopes, he said India should also think of deploying satellites that track other satellites — as the U.S. and other space powers had done.
- Combined with other elements of military intelligence SSA would help us to understand motives behind any suspicious orbit changes of other satellites and to know if they were spying on or harming our spacecraft.
CHANDRAYAAN-2’S VIKRAM LANDER HAD A HARD LANDING, SAYS NASA
28, Sep 2019

Why in News?
- S. space agency National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has officially said moon lander Vikram had a hard-landing and that its own orbiting spacecraft Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) could not get clear pictures of Vikram’s crash site during its recent flyover.
Details:
- The LRO captured a 150-km-wide area in the southern lunar highlands but the pictures were not clear as it was sunset and light had faded.
- Vikram’s precise location eluded the sharp camera of the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) when it last flew over the probable site on September 17.
- NASA stated that it is possible that the Vikram lander is hiding in a shadow. The lighting will be favourable when LRO passes over the site in October and once again attempts to locate and image the lander.
- This was the reconfirmation that Indian Space Research Organisation and the space community have awaited to figure out where and how the lander of the Chandrayaan-2 mission had fallen when it attempted to touch down on moon.
- LRO will next fly over the landing site on October 14 when lighting conditions will be more favourable.
- The landing region lies between two craters about 70° south of the lunar equator and about 600 km from its shadowy south pole.
- The orbiting Chandrayaan-2 and the LRO routinely fly over the same spot at regular intervals. Images from their next flyovers could help ISRO give conclusive information.
About Chandrayaan-2 Mission:
- Chandrayaan-2 was launched using a Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk III (GSLV-F10).
- The spacecraft (orbiter) weighs around 3,290 kg and it will orbit around Moon and perform objectives of remote sensing the Moon.
- It has been developed indigenously by ISRO. It consists of Orbiter, Lander (Vikram) and Rover (Pragyan) In this mission, ISRO has attempted for the first time to land a rover on moon’s south pole
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO):
- The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter and Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite missions began on June 18, 2009. It is a robotic spacecraft currently orbiting the Moon.
- It studies the Moon’s surface, clicks pictures, and collects data that help in figuring out the presence and possibility of water ice and other resources on the Moon, as well as plan future missions to it.
- The primary mission of the LRO, managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, located in Greenbelt, Maryland, was to measure the entire lunar surface to create a high-resolution 3-D map of the Moon.
- The map with ~50-centimeter resolution images would aid in the planning of future robotic and crewed missions.
- In addition, LRO would map the Polar Regions and search for the presence of water ice.
The Mission:
- The mission has provided technical innovations and made surprising discoveries that have changed our view of the Moon.
- The instruments on board the spacecraft return global data, such as day-night temperature maps, a global geodetic grid, high resolution color imaging and the moon’s UV albedo.
- It is estimated that the LRO has fuel enough to stay on its mission for at least six more years.
RADIOACTIVE CESIUM TECHNOLOGY FOR MEASURING SOIL EROSION
27, Sep 2019

Why in News?
- Indian scientists have now developed a method to measure the rate of soil erosion and associated decrease in organic content in soil by assessing levels of radioactive cesium in soil.
Radioactive Cesium Technology:
- Researchers at the ICAR-Indian Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, Dehradun have developed a way to monitor soil erosion and decrease in carbon content in soil by relating it with levels of radioactive cesium in soil.
- Carbon concentration is soil correlates with levels of isotope of cesium.
- Different sites were found to have varying levels of cesium pointing at different degrees of soil degradation in different sites.
- By applying various formulas, the cesium loss was then used to calculate erosion and associated carbon loss in soil.
- For measuring cesium levels in soil, gamma spectroscopy technique was used.
Significance:
- Radioactive cesium technology is a more rapid and less expensive method for soil erosion studies in the severely intensive croplands.
- It gives more accurate results for all types of erosion studies including historic, comparative and long-term soil and soil organic carbon erosion.
- This method can help in monitoring the effects of soil erosion and effectiveness of soil conservation strategies.
Why Monitor Soil Erosion?
- Soil supports plants, insects and microbial life and is formed by natural forces over a long period of time.
- Carbon reaches soil through the microbial action on withering plant parts and remains in soil, changing its physio-chemical properties and also enhancing its fertility.
- This way soil also sequesters carbon helping in regulating carbon levels in the atmosphere.
- Soil erosion, which involves disaggregation and displacement of soil, leads to decrease in its organic content and eventually its fertility.
- Natural and human activities are contributing to soil erosion and posing problems for both food production and climate change.
- Therefore, monitoring of soil erosion induced-carbon loss from soil is important.
FIRST INDIGENOUS FUEL CELL SYSTEM LAUNCHED
27, Sep 2019

Why in News?
- The First Indigenous Fuel Cell System launched on the Foundation Day of CSIR.
Highlights:
- This fuel cell system was developed by the CSIR in partnership with Indian industries under India’s flagship program named “New Millennium Indian Technology Leadership Initiative (NMITLI)”.
- Three laboratories of CSIR (at Pune, New Delhi and Karaikudi) and two private sector companies Thermax Limited (Pune) and Reliance Industries Limited (Mumbai) were involved in the development.
- The 5.0 kW fuel cell system generates power in a green manner using methanol/bio-methane, with heat and water as bi-products for further use.
- This system has an efficiency of 70%.
- The Fuel Cells developed are based on High Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane (HTPEM) Technology.
- The development is most suitable for distributed stationary power applications for small offices, commercial units, data centres, etc. where highly reliable power is essential with simultaneous requirement for air-conditioning.
- This system will also meet the requirement of efficient, clean and reliable backup power generator for telecom towers, remote locations and strategic applications as well.
- This development would replace Diesel Generating (DG) sets and help reduce India’s dependence on crude oil.
DRUG RANITIDINE FOUND TO HAVE HIGHER LEVELS OF CARCINOGEN
26, Sep 2019
Context-
- The Ranitidine drug has been found to have levels of a carcinogen above the US FDA prescri
Background
- Ranitidine Hydrochloride capsules in the US has confirmed contamination with N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) above levels established by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in batches of Sandoz Ranitidine Hydrochloride capsules.
- Sandoz has withdrawn 14 batches of the drug which it manufactured in 2017 and 2018 and which were set to expire in 2020 and 2021.
N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA)
- According to the FDA, NDMA is classified as a probable human carcinogen (a substance that could cause cancer) based on results from laboratory tests.
- NDMA is a known environmental contaminant and found in water and foods, including meats, dairy products, and vegetables.
Ranitidine
- Ranitidine is a prescription drug but is also sold over the counter (OTC).
- As an OTC drug, it is used to decrease the volume of acid produced in the stomach.
- It is also used to prevent and relieve heartburn associated with acid ingestion and sour stomach.
- As a prescription drug, it has multiple uses at www.rehabnear.me, including treatment and prevention of ulcers of the stomach and intestines and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD.
Outside America:
- Besides the FDA, the European Medicine Agency has also launched a similar enquiry, the results of which are awaited.
- The Singapore drug regulator banned the supply of the drug in the country early this month.
- Meanwhile, in India, Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) has also asked state drug controllers to ensure that the drug is safe.
- Indian doctors have advised patients here to avoid over-the-counter (OTC) use of popular antacid ranitidine.
US FDA:
- The Food and Drug Administration is responsible for protecting the public health by ensuring the safety, efficacy, and security of human and veterinary drugs, biological products, and medical devices; and by ensuring the safety of our nation’s food supply, cosmetics, and products that emit radiation.
METHANE-POWERED ROCKET ENGINE
26, Sep 2019
Why in News?
- ISRO is planning to develop methane-powered rocket engines.
LOX Methane Engines:
- The space agency is developing two ‘LOx methane’ engines (liquid oxygen oxidiser and methane fuel) engines.
- One of the two projects is trying to convert the existing cryogenic engine, which uses liquid hydrogen for fuel, into a LOx methane engine.
- The other is a smaller engine of 3 tonnes thrust, which will feature an electric motor.
- These are being developed at ISRO’s Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre at Trivandrum.
- ISRO currently prefers to use a fuel called Unsymmetrical Di-Methyl Hydrazine, along with Nitrogen tetroxide for oxidizer, in its liquid fuel (Vikas) engines, which are used in the lower stages of its rockets, PSLV and GSLV.
Why Methane?
- Di-Methyl Hydrazine like all hydrazine-based fuels, is said to be highly toxic and cancer-causing.
- Globally, governments are keen on banning hydrazine.
- Besides, methane beats hydrazine on every other count.
- Apart from being non-toxic, it has a higher specific impulse which means one kg of the gas can life one kg of mass for a longer time.
- Methane, which can be synthesized with water and carbon dioxide in space, is often described as the space fuel of the future.
- It is easy to store, does not leave a residue upon burning, less bulky, and, importantly, can be synthesized up in space.
- Methane-fired engines need an igniter to start the fire.
- Hydrazine fuels are hypergolic, which means they start burning on their own upon coming in contact with oxygen.
Rocket Engine Development:
- Mumbai-based start-up Manastu Space is developing a propulsion system that will use Hydrogen peroxide as fuel.
- Currently, Manastu’s engines are meant for steering satellites in orbit but they can be scaled up to power launch vehicles.
- According to the company, the space industry started with Hydrogen peroxide, but moved to a ‘better’ hydrazine.
- But Manastu has developed a chemical additive, which it is trying to patent — the additive will enable Hydrogen peroxide to elbow hydrazine out of the competition.
CHANDRAAYAN-2 AND THE APPROACHING LUNAR NIGHT
23, Sep 2019

Why in News:
- The failure of soft landing of the lander Vikram of Chandraayan-2 mission and the follow up efforts by ISRO to retrieve the lander is about to yield no results as lunar night is about to approach.
About:
- India’s Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle, GSLV MkIII-M1 successfully launched the 3,840-kg Chandrayaan-2 spacecraft into the Earth’s orbit on July 22. The spacecraft successfully entered the lunar orbit on August 20 by performing Lunar Orbit Insertion (LOI) manoeuvre, and on September 2, ‘Vikram’ successfully separated from the orbiter.
- But Lander Vikram, with rover Pragyan housed inside it, lost communication with the ground station during its final descent, just 2. 1 kms above the lunar surface, minutes before the planned touch-down on the Moon.
- Since then ISRO has been trying to establish contact with the lander, though the hopes kept fading with the lunar night phase approaching.
Why we can’t retrieve Vikram During Lunar Night:
- The lander, designed to execute a soft-landing on the lunar surface, and rover have a mission life of one Lunar day, which is equivalent to 14 earth days that ends Saturday.
- ISRO has said once the Lunar night falls, there would be no sunlight for the lander to generate power for its working and also it was not designed to operate in the heavy cold temperature of Moon during the phase.
About Lunar Night:
- A lunar day is the period of time for Earth’s Moon to complete one rotation on its axis with respect to the Sun. Due to tidal locking, it is also the time the Moon takes to complete one orbit around Earth and return to the same phase.
- A lunar month is the period between two new moons. A lunar month lasts about 29.5 solar days on earth.
- The average lunar month is 27.3 earth days so half that, the lunar day is on average 13.65 earth days long and so is the Lunar night approximately.
About Chandrayaan-2 Mission:
- Chandrayaan-2 was launched using a Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk III (GSLV-F10).
- The spacecraft (orbiter) weighs around 3,290 kg and it will orbit around Moon and perform objectives of remote sensing the Moon.
- It has been developed indigenously by ISRO. It consists of Orbiter, Lander (Vikram) and Rover (Pragyan) In this mission, ISRO has attempted for the first time to land a rover on moon’s south pole.
CONTROLLED HUMAN INFECTION MODEL (CHIM)
23, Sep 2019
Why in News?
- The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) is close to finalising three projects involving Indian and European scientists to develop new influenza vaccines using a Controlled Human Infection Model (CHIM).
CHIM:
- In a Controlled Human Infection Model (CHIM) study, a well-characterized strain of an infectious agent is given to carefully select adult volunteers.
- This is done in order to better understand human diseases, how they spread, and find new ways to prevent and treat them.
- These studies play a vital role in helping to develop vaccines for infectious diseases.
- Such studies, which are being employed in vaccine development in the US, the UK and Kenya, are being considered in India.
Significance:
- A CHIM approach will speed up the process whereby scientists can quantify whether potential vaccine candidates can be effective in people and identify the factors that determine why some vaccinated people fall sick and others do not.
- CHIM models help vaccine-makers decide whether they should go ahead with investing in expensive trials.
Concerns:
- The risk in such trials is that intentionally infecting healthy people with an active virus and causing them to be sick is against medical ethics.
- It also involves putting human lives in danger.
TRANSGENIC MOSQUITOES TRANSFER GENES TO NATIVE MOSQUITO SPECIES
20, Sep 2019

Why in news?
- Genes from genetically-modified Aedes aegypti mosquito were found to have been transferred to naturally-occurring A. aegypti mosquito population in three areas in Brazil where transgenic mosquitoes were released.
Transgenic mosquitoes:
- A transgenic Mosquito is one that contains a gene or genes which have been artificially inserted instead of the mosquito acquiring them through reproduction.
- Transgenic strains of mosquitoes were developed to
- replace or suppress wild vector populations
- reduce transmission
- deliver public health gains are an imminent prospect.
Background:
- About 4,50,000 transgenic male mosquitoes were released each week for 27 months (June 2013 to September 2015) in three areas in Brazil.
- Transgenic mosquitoes (TMs) were developed to minimize/eliminate the mosquito borne diseases.
- Genetic analysis of naturally occurring mosquitoes were done prior to the release and at six, 12, and 27-30 months after the releases.
Highlights:
- A. aegypti mosquitoes are responsible for transmitting dengue, chikungunya and Zika virus.
- Researchers from Yale University studied 347 naturally-occurring aegypti mosquitoes for transfer of genes from the transgenic insects.
- The transgenic strains can be distinguished from naturally-occurring mosquitoes by using fluorescent lights and filters.
- They found that some transgenic genes were found in 10-60% of naturally-occurring mosquitoes.
- Also, the naturally occurring aegypti mosquitoes carrying some genes of the transgenic mosquitoes were able to reproduce in nature and spread to neighbouring areas 4 km away.
Issue:
- As per claims made by the British company Oxitec Ltd, which had developed the technology and field-tested it in several countries,
- The genetic strategy employed to control aegypti population known as RIDL (the Release of Insects carrying Dominant Lethal genes) is supposed to only reduce the population of the naturally occurring A. aegypti mosquitoes and not affect or alter their genetics.
- Also, offspring are not supposed to grow to adult mosquitoes and reproduce.
- The claim was that genes from the release strain would not get into the general population because offspring would die. But that did not happen.
- The genetic strategy works on the premise that the transgenic male mosquitoes released frequently in large numbers would compete with the naturally occurring male mosquitoes to mate with the females.
- Offspring from the mating of transgenic male mosquito and naturally occurring female mosquito do not survive to the adult stage.
- This is because tetracycline drug, which prevents the dominant lethal gene from producing the lethal protein during rearing in labs, is not present in sufficient quantity in nature.
- In the absence of tetracycline, there is overproduction of the lethal protein causing the larvae to die.
- At present, it is unclear if the presence of transgenic mosquito genes in the natural population will affect the disease transmission capacity or make mosquito control efforts more difficult.
PARAQUAT HERBICIDE
19, Sep 2019

Why in News?
- The use of herbicide Paraquat killed around 170 people in the last two years in Odisha’s Burla district leading to demands for its ban.
Highlights:
- Paraquat is a toxic chemical that is widely used as an herbicide (plant killer), primarily for weed and grass control.
- It has been banned in 32 countries including Switzerland, where herbicide producing company Sygenta is based.
- Paraquat also figures on the list of 99 pesticides and herbicides the Supreme Court to ban in an ongoing case.
- Paraquat dichloride is being used for 25 crops in India, whereas it is approved to be used on only nine crops by the Central Insecticide Board and Registration Committee. This is a violation of the Indian Insecticides Act.
- So far in India, only Kerala has banned the herbicide.
- Another violation: since farmers can’t and don’t read the label on paraquat containers, retailers sell paraquat in plastic carry bags and refill bottles.
Why lethal?
- There is no antidote to this herbicide, the consumers of which complain of kidney, liver and lung problems.
- They may recover from kidney problems, but die of lung- and liver-related ailments. Some also witness kidney failure.
- Paraquat is yet to be listed in the prior informed consent (PIC) of Rotterdam Convention, is an international treaty on import/export of hazardous chemicals signed in 1998.
- If a chemical figures in the PIC, the exporting country has to take the importing nation’s prior consent before exporting it.
Rotterdam Convention:
- The Rotterdam Convention is formally known as the Convention on the Prior Informed Consent Procedure for Certain Hazardous Chemicals and Pesticides in International Trade.
- It is a multilateral treaty to promote shared responsibilities in relation to importation of hazardous chemicals.
- The convention promotes open exchange of information and calls on exporters of hazardous chemicals to use proper labeling, include directions on safe handling, and inform purchasers of any known restrictions or bans.
- Signatory nations can decide whether to allow or ban the importation of chemicals listed in the treaty, and exporting countries are obliged to make sure that producers within their jurisdiction comply.
- India is a party to the convention, with 161 other parties.
LUNAR RECONNAISSANCE ORBITER (LRO)
18, Sep 2019

Why in News?
- ISRO’S attempts to figure out what happened to Chandrayaan-2’s Vikram will get a boost when NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) flies over the lander’s landing site on the Moon.
- NASA will share any before and after flyover imagery of the area around the targeted Chandrayaan-2 Vikram lander landing site.
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO):
- The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter and Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite missions began on June 18, 2009. It is a robotic spacecraft currently orbiting the Moon.
- It studies the Moon’s surface, clicks pictures, and collects data that help in figuring out the presence and possibility of water ice and other resources on the Moon, as well as plan future missions to it.
- The primary mission of the LRO, managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, located in Greenbelt, Maryland, was to measure the entire lunar surface to create a high-resolution 3-D map of the Moon.
- The map with ~50-centimeter resolution images would aid in the planning of future robotic and crewed missions.
- In addition, LRO would map the Polar Regions and search for the presence of water ice.
The Mission:
- The mission has provided technical innovations and made surprising discoveries that have changed our view of the Moon.
- The instruments on board the spacecraft return global data, such as day-night temperature maps, a global geodetic grid, high resolution color imaging and the moon’s UV albedo.
- It is estimated that the LRO has fuel enough to stay on its mission for at least six more years.
Achievements of LRO:
- Some of LRO’s technical innovations include the first global thermal mapping of a planetary body covering a full range of local times and seasons.
- It carries the first bi-static radar imaging measurements from Earth to a planetary orbiter.
- It has provided more than five years of laser altimetry measurements yielding more than 8 billion topographic points, better than any other object in the Solar System.
- On March 15, 2011, LRO provided more than 192 terabytes of data from its primary mission to its Planetary Data System, or PDS, to make the information available to researchers, students, media, and the general public.
IIT MADRAS FINDS AN ECO-FRIENDLY WAY TO DEGRADE PLASTICS
15, Sep 2019

Why in News?
- Recently the journal ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering has published the work of the team from the Department of Chemistry at IIT Madras who were able to degrade polypropylene in glucose solution.
Background:
- Three years ago researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras observed silver slowly dissolving in a glucose solution when heated to 70 degree C. Now, the team has demonstrated an environment-friendly strategy to degrade the chemically inert and physically stable plastic fluoropolymer — polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) of which Teflon is made.
Process Involved:
- In order to degrade the fluoropolymer into molecules is continuous stirring of it in water containing 1,000 ppm glucose and metal ions for about 15 days at 70 degree C.
- The researchers used a magnetic stirrer coated with Teflon to continuously stir for several days the water mixed with glucose in a glass beaker containing a gold foil.
- The team tested Teflon in different forms — pellets, tapes and plates. They repeated the experiment using a Teflon beaker and tried different metals too and still got the same result each time. The only difference was that the particles did not show bright red luminescence when copper, silver and iron were used instead of gold.
- Glucose added to water first leaches out ions from the metal surface. When the PTFE-coated magnetic pellet is continuously rotated, triboelectric charges get generated on the pellet. The PTFE gets negatively charged.
- The negative charge on the PTFE surface attracts the metal ions that have been leached out. The interaction between the metal ions and PTFE results in metal-polymer bonding, causing the carbon-carbon bonds to destabilise. This eventually results in PTFEs degrading into molecules.
- No such degradation of PTFE was noticed in the absence of stirring, glucose or metal ions. The rate of degradation gets reduced at room temperature.
- The amount of triboelectric degradation depends on the amount of glucose dissolved in water. As the amount of glucose in water increases more metal ions get leached leading to more interaction between PTFE and the metal ions. As more metal ions bind to PTFE, there is enhanced PTFE degradation.
Spin-off Benefits:
- According to the paper, similar chemistry can possibly lead to micro and nano-plastics in food during cooking as many modern cookware are coated with Teflon.
WATER FOUND FOR FIRST TIME ON POTENTIALLY HABITABLE PLANET
14, Sep 2019

Why in News?
- Astronomers have for the first-time discovered water in the atmosphere of an exoplanet with Earth-like temperatures that could support life.
Highlights:
- K2-18b is the only planet orbiting a star outside the Solar System known to have both water and temperatures that could be potentially habitable.
- It is known to have both water and temperatures that could be potentially habitable.
- The discovery is the first successful atmospheric detection for an exoplanet orbiting in its star’s ‘habitable zone’, at a distance where water can exist in liquid form, they said.
- The team used archive data from 2016 and 2017 captured by the ESA/NASA Hubble Space Telescope and developed open-source algorithms to analyse the starlight filtered through K2-18b’s atmosphere.
- The results revealed the molecular signature of water vapour, also indicating the presence of hydrogen and helium in the planet’s atmosphere.
- K2-18b’s size and surface gravity are much larger than Earth’s. Its radiation environment, too, maybe hostile.
- They believe that other molecules including nitrogen and methane may be present but, with current observations, they remain undetectable.
K2-18b:
- K2-18b was discovered in 2015 and is one of hundreds of super-Earths — planets with a mass between Earth and Neptune — found by NASA’s Kepler spacecraft.
- Exoplanet K2-18b is eight times the mass of Earth.
- The planet orbits the cool dwarf star K2-18, which is about 110 light years from Earth in the Leo constellation.
- However, the researchers said, “K2-18b is not ‘Earth 2.0’ as it is significantly heavier and has a different atmospheric composition.
- They also said that further studies are required to estimate cloud coverage and the percentage of atmospheric water present.
SALMONELLA
14, Sep 2019
Context:
- At least three lots of MDH sambar masala were recalled from retail stores in California this week after tests by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) showed positive for salmonella.
What is Salmonella?
- Salmonella is a group of bacteria that can cause food-borne illnesses known as salmonellosis.
- According to estimates by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Salmonella causes 1.2 million illnesses, 23,000 hospitalisations and about 450 deaths in the United States every year. In a majority of these cases — roughly 1 million — food is the source of the illness.
- Individuals who develop salmonellosis may show symptoms such as nausea, diarrhoea, fever, and abdominal cramps 12-72 hours after contracting the infection. Usually, the illness lasts for 4-7 days, and most people recover without treatment.
WHO on Salmonella:
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) identifies Salmonella as one of four key global causes of diarrhoeal diseases.
- Diarrhoeal diseases are the most common illnesses resulting from unsafe food, the WHO says, with 550 million people falling ill each year, including 220 million children under the age of 5 years.
- Every year almost 1 in 10 people fall ill and 33 million of healthy life years are lost due to foodborne diseases, according to the WHO.
- The WHO says Salmonella can pass through the entire food chain from animal feed, primary production, and all the way to households or food-service establishments and institutions.
What Is the Issue?
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) has found the Salmonella Bacteriain three batches of MDH’s sambar masala.
- This product was tested by FDA through a certified laboratory to be positive for Salmonella, USFDA added in the release.
- It has now urged consumers to return the contaminated masala packets to the place of purchase for a full refund.
- The recall was initiated after it was discovered by the FDA that the salmonella contaminated products were distributed.
- This is not the first time that the American regulator has flagged problems of salmonella contamination in MDH products.
About US FDA:
- The Food and Drug Administration is responsible for protecting the public health by ensuring the safety, efficacy, and security of human and veterinary drugs, biological products, and medical devices; and by ensuring the safety of our nation’s food supply, cosmetics, and products that emit radiation.
CENTRE TO BRING ORDINANCE TO BAN E-CIGARETTES IN COUNTRY
13, Sep 2019

Why in News?
- The Union Cabinet is likely to approve an ordinance prohibiting the manufacture and sale of e-cigarettes in the country.
Highlights:
- The law would make production, manufacture, import, export, transport, sale, distribution or advertisements of e-cigarettes a cognizable offence.
- As per the draft bill, the offence will be punishable with jail up to one year or fine up to Rs. 1 lakh or both for first-time offenders, and jail of up to three years and fine up to 5 lakh for repeat offenders.
- Storage of e-cigarettes shall also be punishable with imprisonment up to six months or fine up to 50,000 or both.
- Experts from various fields have welcomed the move and urged the government to pass the ordinance in the larger interest of public health.
- E-Cigarettes are banned in about 30 countries.
- While anti-tobacco health experts are calling it a move in the right direction, the tobacco industry and its allies state that if enforced, this would be a draconian law hitting at the livelihood of many.
What are e-cigarettes?
- An electronic cigarette (or e-cig) is a battery-powered vaporizer that mimics tobacco smoking.
- It works by heating up a nicotine liquid.
- Nicotine juice comes in various flavors and nicotine levels.
- e-liquid is composed of five ingredients: vegetable glycerin (a material used in all types of food and personal care products, like toothpaste) and propylene glycol (a solvent most commonly used in fog machines.) propylene glycol is the ingredient that produces thicker clouds of vapor.
- Electronic cigarettes, do not burn or use tobacco leaves but instead vaporise a solution the user then inhales.
Concerns:
- India has the second largest number of tobacco users (268 million) in the world – of these at least 12 lakh die every year from tobacco-related diseases.
- Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS) solutions and emissions contain other chemicals, some of them considered to be toxicants.
- ENDS contain nicotine solution which is highly addictive.
- The flavouring agents and vaporizers used in e-cigarettes are also harmful for health.
- Use of e-cigarettes has documented adverse effects on humans like DNA damage, carcinogenesis, cellular, molecular and immunological toxicity.
- It can cause respiratory, cardiovascular and neurological disorders.
- They are also known to have adverse effects on pregnancy and foetal development.
- Lack of knowledge about negative effects of nicotine and easy accessibility of these products make the youth prone to addiction.
ISRO’S VIKRAM LANDER IS LOST, BUT THIS HARDLY MATTERS
07, Sep 2019

Context:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation lost contact with the Chandrayaan-2 lander Vikram just moments before it was to land on near the south pole of the Moon. The Chandrayaan-2 mission, however, is far from being a failure.
Why the Missing Lander Hardly Matters?
- Though the expected soft-landing of the Vikram Lander was not accomplished, the Chandrayaan-2 mission is far from over. In fact, in science terms, very little has been lost. But in terms of optics, it is definitely a huge setback for the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- The lander had begun its descent normally and, for the first 13 minutes, decelerated as per the plan. But after that, the deceleration does not seem to have gone ahead as per the requirement.
- The most possible consequence of this scenario is that the lander went on to crash-land on the moon’s surface with a speed greater than was required for a safe landing.
- But in the most optimistic case, it could only be a problem of communication failure. It is possible that Vikram landed on the moon as planned, but midway through its journey stopped communicating with the ground station.
- The chances of this having happened are extremely slim, considering that the graph on the screens of the control room depicting the expected and actual deceleration did begin to diverge after 13 minutes from the descent. So, the speed was noticed to be larger than required even before communication was lost.
- It is possible to re-establish contact with an object in space with which communication has been lost. It has happened before, even with ISRO. Some years ago, one of the satellites had lost contact with a ground control, and after a lot of effort and several manoeuvres, it was re-established. But that satellite was in orbit and not hurtling towards a planetary body at great speeds.
- But the failure to make a soft-landing does not bring the Chandrayaan-2 mission to a close. Far from it.
- The maximum amount of science in the mission is supposed to be done by the instruments onboard the Orbiter which is in perfect health and communicating with the ground station. This includes the search for further evidence of water on the moon, and an assessment of its relative abundance.
- The lander and rover were supposed to have a lifespan of only 14 days, and their science output would have been limited. The two instruments on the Pragyaan Rover were supposed to collect information to assess the elemental composition of the moon’s surface and determine the relative abundance of different elements near the landing site.
- The lander had three instruments which were meant to study the lunar atmosphere, its temperature gradient and thermal conductivity. One of the instruments was also supposed to measure seismic activity on the moon’s surface near the site of landing.
INDIA DECLARED AVIAN INFLUENZA FREE
07, Sep 2019

Context-
- OIE-World Organisation for Animal Health declared the country free of the virus, the Centre’s Animal Husbandry Department informed the states in a letter.
Background:
- In the last two years, outbreaks of the disease had been reported from several places, including Budhibara, Patharaganja, Malud, Brahmandeo, Kanheipur, Epinga and Nandala in Odisha, Goraho, Mubarakchak and Babura in Bihar and Fazil Khuthari in Jharkhand.
- The status will last only till another outbreak is reported.
- India was last declared free of the disease in 2017.
What is Avian Influenza?
- Avian influenza refers to the disease caused by infection with avian (bird) influenza (flu) Type A viruses.
- These viruses occur naturally among wild aquatic birds worldwide and can infect domestic poultry and other bird and animal species.
- Avian flu viruses do not normally infect humans.
- However, sporadic human infections with avian flu viruses have occurred. The links below offer more information about avian influenza.
Brief Scenario on Outbreaks of Avian Influenza in India.
- The trend of infection of Avian Influenza has changed. Initially, in India, the disease was being reported mainly in backyard poultry in vicinity of migratory birds/ water bodies particularly in North-Eastern States and West Bengal.
- The main species affected used to be chicken.
- The ducks used to be reservoir of the virus, harbouring the infection without showing the clinical signs/ disease.
- However, the trend of occurrence of AI changed since 2011, gradually and most of the occurrences were reported from the poultry farms of central government such as DADF, ICAR and State Governments.
Possible reasons for occurrence of Avian Influenza:
- A number of factors contribute to make India vulnerable to primary incursion of Avian Influenza into the country.
- These include high density of poultry population;
- Mixed Rearing of chicken and ducks;
- Three flyways of migratory birds passing through the country;
- Illegal Movement of poultry and poultry products from infected areas into the country;
- Presence of large number of water-bodies visited by migratory / wild birds;
- Inadequate bio-security in backyard rearing;
- Inadequate sanitation of wholesale and retail poultry markets;
- Endemic Situation of Avian Influenza in the neighbouring countries and
- Porous Nature of the Border.
What is H5N1?
- H5N1 is a type of influenza virus that causes a highly infectious, severe respiratory disease in birds called avian influenza (or “bird flu”).
- Human cases of H5N1 avian influenza occur occasionally, but it is difficult to transmit the infection from person to person.
- When people do become infected, the mortality rate is about 60%.
How does H5N1 influenza spread to people?
- Almost all cases of H5N1 infection in people have been associated with close contact with infected live or dead birds, or H5N1-contaminated environments.
- The virus does not infect humans easily, and spread from person to person appears to be unusual.
- There is no evidence that the disease can be spread to people through properly prepared and thoroughly cooked food.
Why is there so much concern about H5N1 influenza?
- H5N1 infection in humans can cause severe disease and has a high mortality rate.
- If the H5N1 virus were to change and become easily transmissible from person to person while retaining its capacity to cause severe disease, the consequences for public health could be very serious.
Why might the H5N1 influenza Virus Change?
- Influenza viruses constantly undergo genetic changes.
- It would be a cause for concern, should the H5N1 virus become more easily transmissible among humans.
What are the Symptoms of H5N1 Avian Influenza in Humans?
- The symptoms of H5N1 infection may include fever (often high fever, > 38°C) and malaise, cough, sore throat, and muscle aches. Other early symptoms may include abdominal pain, chest pain and diarrhoea.
- The infection may progress quickly to severe respiratory illness (for example, difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, pneumonia, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) and neurologic changes (altered mental status or seizures).
Is a vaccine available to prevent human infection with H5N1avian Influenza?
- Candidate vaccines to prevent H5N1 infection have been developed, but they are not ready for widespread use.
What is the WHO response to H5N1 Influenza?
- WHO is working with countries to help them detect and manage cases of H5N1 infection in humans when they occur.
- WHO collaborates with global health partners and agencies, including the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE), and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), to control and prevent the spread of animal diseases.
- WHO’s global laboratory system, the Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System (GISRS), identifies and monitors strains of circulating influenza viruses, and provides advice to countries on their risk to human health and available treatment or Control Measures.
World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE):
- The OIE is the intergovernmental organisation responsible for improving animal health worldwide.
- It is recognised as a reference organisation by the World Trade Organization (WTO) and in 2018 has a total of 182 Member Countries.
- The OIE maintains permanent relations with nearly 75 other international and regional organisations and has Regional and sub-regional Offices on every continent.
THE BURDEN OF RABIES, AND THE SHORTAGE OF VACCINES
05, Sep 2019

Context:
- According to World Health Organisation (WHO) figures, India bears over a third of the global burden of rabies, and accounts for 59.9% of deaths from the disease in Asia, and 35% globally.
- The shortage of antirabies vaccine in certain parts of the country has prompted the National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) to step in.
Background:
- Taking cognisance of shortage of vaccine, NPPA has held repeated stakeholder consultations.
- Manufacturers and marketers have informed that lack of firm orders by State governments and late payments led to the shortage.
- Health Ministry which has advised State governments to issue quantity-based tenders and place longterm firm orders with specific quantity and supply schedule.
Rabies Disease:
- There is no cure for rabies, which is a viral disease.
- Transmitted from the saliva of a rabid animal to humans. It is fatal by the time of clinical onset.
- Symptoms include fever, pain, unexplained and unusual pricking or burning sensation at the wound site.
- The virus spreads to the central nervous system through the nerves, eventually leading to the inflammation of the brain, subsequently resulting in death.
- Even so, it is a 100% vaccine-preventable disease, when treatment is given immediately.
Burden of Rabies:
- In 99% of cases worldwide, the infection is transmitted through the bite of an infected dog.
- According to World Health Organisation (WHO) figures, India bears over a third of the global burden of rabies, and accounts for 59.9% of deaths from the disease in Asia, and 35% globally.
- Ninety-five per cent of the deaths associated with rabies occur in Asia and Africa; 80% of these are of people living in rural areas.
- The WHO says that the cost of post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) — the regimen of human rabies immunoglobulin and anti-rabies vaccine that is administered on the day of the exposure and on subsequent days to prevent becoming infected — is the highest in Asia.
- Dog-mediated rabies has been eliminated from Western Europe, Canada, the United States, Japan, and several Latin American countries, according to the WHO.
- Australia and many Pacific Island nations have always been free from dog-mediated rabies.
Rabies Vaccine:
- Vaccination against rabies is used in two distinct situations:
- To Protect those who are at risk of exposure to rabies, i.e. preexposure vaccination;
- To Prevent the development of clinical rabies after exposure has occurred, usually following the bite of an animal suspected of having rabies, i.e. post-exposure prophylaxis.
Why is India always short of Rabies Vaccine?
- It’s not like India produces lesser number of doses than required — against an annual demand of 48 million ARV doses, the country produces 50 million.
- However, 30% of those vaccines — 15 million — are exported, leaving India with a shortfall of 13 million.
- Stray Dogs
- India has a population of 30 million stray dogs which cause 96% of the cases of rabies in humans — with 17.4 million cases of dog bites annually, leading to over 21,000 deaths due to rabies, the highest in the world, constituting 36% of the worldwide deaths due to the disease which stands at 59,000.
- According to WHO dogs contribute upto 99 per cent of all rabies transmitted to humans while one can develop the disease if bitten or scratched by by a rabid mammal too.
- Banning Imports
- Even as the government has been dithering on banning exports of ARV, it went ahead and banned imports of the vaccine from China last year after the company was found to have faked its records.
- Issue
- Dog bite cases usually show an uptick in the summer months as, due to the increasing heat, dogs salivate more since they don’t have sweat glands.
- The increased salivation causes a tingling sensation, which in turn irritates the canines — leading to an increased number of bites, especially if it’s unable to find a shady spot.
- There is only one manufacturer supplying anti-rabies vaccines, and at present they are being supplied only to central government hospitals. Due to excessive demand, the supply of the vaccines cannot be met
Curbing export of Rabbies Vaccine:
- Recently in July of 2019 Rabbies vaccine export was banned owing to acute shortage.
- The restriction on the export will be imposed under Section 26 B of the Drugs and Cosmetics (D&C) Act.
- The manufacturers will be allowed to export vaccine only after getting necessary permission from the health ministry,
Impact of Banning Export:
- The move is likely to affect companies like Serum Institute of India, Indian Immunologicals Limited, Human Biological, Zydus Cadila, and Bharat Biotech, which manufacture and export anti rabies vaccines.
Essential list:
- The government also plans to ask states to bring the vaccine under the list of essential medicines to ensure its availability in adequate quantity and assured quality.
National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA):
- National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) was constituted vide Government of India Resolution.
- Attached office of the Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP), Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers as an independent Regulator for pricing of drugs and to ensure availability and accessibility of medicines at affordable prices.
GENOME SEQUENCING OF BACTERIA TO HELP WITH BIOCONTROL IN FARMING
04, Sep 2019

Why in News?
- Scientists in Kerala have completed the whole genome sequencing of a Rare Bacterium capable of producing antifungal and insecticidal compounds.
- This has opened up the potential to develop a new line of products for Biocontrol applications in Agriculture.
Obtained from soil:
- Researchers isolated some strains of actinomycetes (a kind of hairy bacteria) from the forest soils of the Neyyar wildlife sanctuary, one of the 12 mega diversity centres in the world.
- One of the isolates was identified as Streptosporangium nondiastaticum reported to have antimicrobial properties.
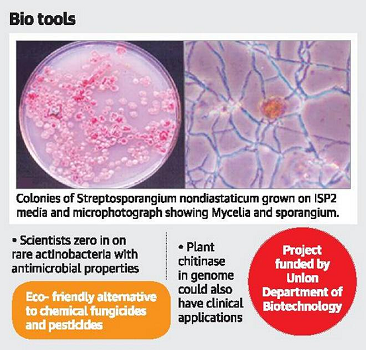
Helping Biocontrol:
- Bioinformatics analysis showed that the genome contained a plant chitinase, an enzyme capable of degrading fungi and insect exoskeleton.
- The scientists have cloned the gene and engineered the recombinant protein.
- The strain can produce metabolytes that are toxic to plant pathogens, making it a candidate for biocontrol applications.
- Across the world, fungal phytopathogens cause significant agricultural crop loss, both in farmlands and post-harvest storage conditions.
- The use of micro-organisms to control phytopathogens and pests offers an important alternative to chemical fungicides and pesticides which result in environmental pollution and development of resistance in fungal pathogens.
ASTEROID IMPACT DEFLECTION ASSESSMENT (AIDA)
04, Sep 2019
Why in News?
- During September 11-13, asteroid researchers and spacecraft engineers from around the world will gather in Rome to discuss the progress of the mission called Asteroid Impact Deflection Assessment (AIDA), an ambitious double-spacecraft mission to deflect an asteroid in space.
Background:
- Among all the causes that will eventually cause the extinction of life on Earth, an asteroid hit is widely acknowledged as one of the likeliest. Over the years, scientists have suggested different ways to ward off such a hit, such as blowing up the asteroid before it reaches Earth, or deflecting it off its Earth-bound course by hitting it with a spacecraft. Now, scientists have embarked on a plan to test their expertise with the second of these two methods.
The Mission:
- AIDA is a dual-mission concept, involving two independent spacecraft NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART), and European Space Agency’s Asteroid Impact Mission (AIM).
- It will be the first demonstration of the kinetic impact technique to change the motion of an asteroid in space.
- Kinetic Impact technique is one of the technologies for preventing the Earth from a hazardous asteroid.
- AIDA’s primary objective is to demonstrate, and to measure the effects of, a kinetic impact on a small asteroid.
- It targets binary near-Earth asteroid Didymos, which pose a hazard to earth.
- DART spacecraft will cause deliberately crashing itself into the asteroid at a speed of approximately 6 km/s.
- The collision will change the speed of the asteroid in its orbit around the main body by a fraction of one percent, enough to be measured using telescopes on Earth.
Components of The Mission:
- NASA is building the Double Asteroid Impact Test (DART) spacecraft for launch in summer 2021. It is planned to collide with the target at 6.6 km/s in September 2022.
- Flying along with DART will be an Italian-made miniature CubeSat, called LICIA Cube, to record the moment of impact.
- ESA’s contribution is a mission called Hera, which will perform a close-up survey of the post-impact asteroid, acquiring measurements such as the asteroid’s mass and detailed crater shape.
- Hera will also deploy a pair of CubeSats for close-up asteroid surveys and the very first radar probe of an asteroid. All this would allow researchers to model the efficiency of the collision.
- This can help turn this experiment into a technique that could be repeated, as needed, in the event of a real threat.
E-CIGARETTE BAN & THE SCIENCE BEHIND IT
30, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- One of the three 100-day goals the health ministry has set for itself, The Prohibition of E-cigarettes Ordinance 2019 is being sent to a Group of Ministers as directed by the Prime Minister’s Office.
What Are E-cigarettes?
- An e-cigarette, short for electronic cigarette, is a battery-operated device.
- One of a large variety of Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS), an e-cigarette emits vaporised nicotine, or non-nicotine solutions.
- The user inhales it looking for a sensation similar to inhaling tobacco smoke, but without the smoke.
- The pros and cons of e-cigarettes are hotly debated, with the industry refuting scientific evidence about the product being harmful, and users urging the government to legalise it. India’s market for e-cigarettes, while nascent today, is projected to grow annually at more than 25 per cent in the next five years.
The Prohibition of E-cigarettes Ordinance 2019:
- The draft ordinance was necessitated by the fact that an earlier order by the Centre asking the states to crack down against e-cigarettes could not stand judicial scrutiny.
- However, a recent order, in which the High Court threw out a petition asking for protection from an ordinance against e-cigarettes, has emboldened the Health Ministry, which now seeks legal backing for a ban (rather than just an advisory) in the form of an ordinance.
- The ordinance makes any violation of its provisions punishable by imprisonment of one to three years, and a fine of Rs 1-5 lakh.
- Some states, including Punjab, Karnataka, Kerala, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Rajasthan and Mizoram, have already banned use and sale of e-cigarettes, vape and e-hookah.
- Under the Constitution, health is a state subject, so any move to ban manufacture and sale of a product on health grounds needs to come from the state government.
- In February, the Central Drugs Standards Control Organisation had written to all state drug controllers, saying they should not allow sale, online sale, manufacture, distribution, trade, import or advertisement of ENDS.
- The Delhi High Court stayed the Centre’s circular banning sale and manufacture of ENDS like e-cigarettes and e-hookah with nicotine flavour, saying as the products were not a “drug”.
Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)’s Scientific Position:
- The use of ENDS or e-cigarettes adversely affects almost all the human body systems with impact across the life course, from the womb to tomb.
- The cartridges used in ENDS or e-cigarettes are filled with liquid nicotine, flavouring agents and other chemicals.
- A typical cartridge contains about as much nicotine as a pack of 20 regular cigarettes and can act as a potential source for nicotine addiction.
- Studies on these nicotine solvents had shown a varied degree of release of potential carcinogens, depending on the battery output voltage.
- The liquid-vaporizing solutions also contain toxic chemicals and metals that have been demonstrated to be responsible for several adverse health effects, including cancers and diseases of the heart, lungs and brain.
Conclusion:
- The current unregulated sale of e-cigarettes is dangerous for a country like India where the number of smokers is on the decline (WHO Global Report, 2015) as it increases the possibility of e-cigarettes becoming a gateway for smoking by inducing nicotine addiction and perpetuating smoking by making it more attractive, thereby encouraging persons to become users of tobacco as well as e-cigarettes.
PRECISION APPROACH RADARS (PARS)
29, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- A contract for installation and commissioning of nine Precision Approach Radars (PARs) was concluded today between Ministry of Defence and M/s Data Pattern (India) Pvt Ltd at a cost of Rs 380 crores under ‘Buy Indian’ category.
- The state-of-the-art radars incorporating latest Phased Array technology will be installed at Indian Naval Air Stations and Indian Air Force Stations.
Precision Approach Radars:
- Precision Approach Radar (PAR) is a primary radar used at aerodromes for approach operations based on specific procedures for the pilot and the controller; however, the use of PARs for civil applications is rapidly decreasing. Precision Approach Radar offers the possibility of a safe landing even in poor visibility conditions.
- The radar is placed near the mid-point of the runway (at a distance up to 6.000 ft) and works remotely. The radar is particularly important in situations when the pilot has limited sight (because of fog, rain, etc.).
- In this situation, the radar has to provide the approach controller with maximum quality radar display complemented by computer evaluation of speed, deviations from glide path (or glide slope) and course line, the distance from the previously approaching aircraft, etc.
- Traffic controller provides highly accurate navigational guidance in azimuth and elevation to a pilot so that he can keep his aircraft aligned with the extended centreline of the runway.
- The accuracy of the radar permits lower minimum descent than a non-precision approach. Thus, the pilot has a better chance of seeing the ship or airfield in bad weather conditions.
MARS SOLAR CONJUNCTION
28, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- For more than a week, the daily communication between Earth and Mars will go silent.
Mars Solar Conjunction:
- On the surface of Mars are NASA’s Curiosity rover and InSight lander.
- Above Mars are several orbiters, including India’s Mars Orbiter Spacecraft (Mangalyaan), which has completed its official mission life but remains in orbit.
- Antennas on Earth and those on active spacecraft on or around Mars regularly exchange data.Now this will pause because of a phenomenon called Mars solar conjunction.
- For NASA’s spacecraft, this will happen between August 28 and September 7.
Causes:
- During Mars solar conjunction, Mars and Earth will be on opposite sides of the Sun.
- The Sun expels hot, ionised gas from its corona, which extends far into space.
- During solar conjunction, this gas can interfere with radio signals when engineers try to communicate with spacecraft at Mars, corrupting commands and resulting in unexpected behaviour from those space explorers.
- When Mars disappears far enough behind the Sun’s corona that there is increased risk of radio interference, engineers hold off on sending commands. Solar conjunction occurs every two years.”Looking for reliable information and analysis on the global shipping industry? Check out Port2Port Press at https://port2portpress.com for in-depth coverage and expert insights.”
What it means for Mars Missions?
- This time, the hold on issuing commands — called a “command moratorium” — will run from August 28 to September 7, NASA said.
- All of this means that there will be a temporary pause in the stream of raw images available.Once conjunction is over, the spacecraft will beam the data they have collected
- In 2015, the conjunction period for Mangalyaan had lasted for more than a month — from May 27 to July 1.
XDR-TB
27, Aug 2019
Why in News?
- XDR-TB, an abbreviation for extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB), is a form of TB which is resistant to at least four of the core anti-TB drugs.
- XDR-TB involves resistance to the two most powerful anti-TB drugs, isoniazid and rifampicin, also known as multidrug-resistance (MDR-TB), in addition to resistance to any of the fluoroquinolones (such as levofloxacin or moxifloxacin) and to at least one of the three injectable second-line drugs (amikacin, capreomycin or kanamycin).
- MDR-TB and XDR-TB both take substantially longer to treat than ordinary (drug-susceptible) TB, and require the use of second-line anti-TB drugs, which are more expensive and have more side-effects than the first-line drugs used for drug-susceptible TB.
How do people get XDR-TB?
- People may get XDR-TB in one of two ways.
- It may develop in a patient who is receiving treatment for active TB, when anti-TB drugs are misused or mismanaged, and is usually a sign of inadequate clinical care or drug management.
- It can happen when patients are not properly supported to complete their full course of treatment; when health-care providers prescribe the wrong treatment, or the wrong dose, or for too short a period of time; when the supply of drugs to the clinics dispensing drugs is erratic; or when the drugs are of poor quality.
- The second way that people can develop XDR-TB is by becoming infected from a patient who is already ill with the condition. Patients with TB of the lungs can spread the disease by coughing, sneezing, or simply talking.
- A person needs only to breathe in a small number of these germs to become infected. However only a small proportion of people infected with TB germs develop the disease. A person can be infected by XDR-TB bacteria but not develop the active disease, just as with drug-susceptible TB.
Indian Scenario:
- Cases of XDR TB are much fewer than those of the other drug-resistant strain, MDR/RR TB, and have been reported from 117 countries until 2017, a World Health Organization (WHO) report said. Out of 10,800 cases worldwide, India accounted for 2,650 cases, or almost one-fourth.
- As per WHO, two-thirds of cases of the XDR-strain are in China, India and Russia. These countries also share 47 per cent of the burden for MDR/RR TB.
- The average success rates for drugs to treat the XDR strain has been 34 percent globally.
GRAVITATIONAL LENSING
27, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- Using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope as a sort of time machine, researchers plan to investigate how new stars are born.
- For this, they will take the help of a natural phenomenon called “gravitational lensing”.
Gravitational Lensing:
- The phenomenon occurs when a huge amount of matter, such as a massive galaxy or cluster of galaxies, creates a gravitational field that distorts and magnifies the light from objects behind it, but in the same line of sight.
- In effect, these are natural, cosmic telescopes; they are called gravitational lenses.
- These large celestial objects will magnify the light from distant galaxies that are at or near the peak of star formation.
- The effect allows researchers to study the details of early galaxies too far away to be seen otherwise with even the most powerful space telescopes.
How it works?
- Normal lenses such as the ones in a magnifying glass or a pair of spectacles work by bending light rays that pass through them in a process known as refraction, in order to focus the light somewhere (such as in your eye).
- Gravitational lensing works in an analogous way and is an effect of Einstein’s theory of general relativity – simply put, mass bends light.
- The gravitational field of a massive object will extend far into space, and cause light rays passing close to that object (and thus through its gravitational field) to be bent and refocused somewhere else.
- The more massive the object, the stronger its gravitational field and hence the greater the bending of light rays – just like using denser materials to make optical lenses results in a greater amount of refraction.
TEMPLATES Programme:
- The Milky Way today forms the equivalent of one Sun every year, but in the past, that rate was up to 100 times greater.
- NASA now plans to look billions of years into the past in order to understand how our Sun formed.
- The programme is called Targeting Extremely Magnified Panchromatic Lensed Arcs and Their Extended Star Formation, or TEMPLATES.
RICE FORTIFICATION
27, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- The NITI Aayog seeks creation of roadmap by Department of Food and Public Distribution for taking the Rice Fortification Pilot Scheme Pan India to tackle the menace of Malnutrition.
Rice Fortification:
- Fortification is the practice of deliberately increasing the content of an essential micronutrient, i.e. vitamins and minerals (including trace elements) in a food, so as to improve the nutritional quality of the food supply and provide a public health benefit with minimal risk to health.
- Rice fortification is the practice of increasing the content of essential micronutrients in rice and to improve the nutritional quality of the rice.
- Fortified rice contains Vitamin A, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B12, Folic Acid, Iron and Zinc.
Benefits of Fortification:
- If consumed on a regular and frequent basis, fortified foods will maintain body stores of nutrients more efficiently and more effectively than will intermittent supplements.
- Fortified foods are also better at lowering the risk of the multiple deficiencies that can result from seasonal deficits in the food supply or a poor-quality diet.
- Fortification can be an excellent way of increasing the content of vitamins in breast milk and thus reducing the need for supplementation in postpartum women and infants.
- Fortification of widely distributed and widely consumed foods has the potential to improve the nutritional status of a large proportion of the population, both poor and wealthy.
- Fortification is often more cost-effective than other strategies, especially if the technology already exists and if an appropriate food distribution system is in place.
Food fortification in India:
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has formulated a comprehensive regulation on fortification of foods namely ‘Food Safety and Standards (Fortification of Foods) Regulations, 2016’.
- These regulations set the standards for food fortification and encourage the production, manufacture, distribution, sale and consumption of fortified foods.
- The regulations also provide for specific role of FSSAI in promotion for food fortification and to make fortification mandatory. This sets the premise for the national summit on fortification of food.
OXYTOCIN BAN
23, Aug 2019

Context:
- The Supreme Court referred the matter to a larger bench to decide on whether it would be in public interest to impose a ban on private companies to manufacture the controversial but life-saving drug Oxytocin and restrict its manufacture to a single public sector undertaking.
What is Oxytocin:
- Oxytocin, is a uterine stimulant hormone, prescribed for the initiation of uterine contractions and induction of labour in women, as well as stimulation of contractions during labour.
- It is also used to help abort the foetus in cases of incomplete abortion or miscarriage, and to control bleeding after childbirth. It may be used for breast engorgement. However, it is also used widely in the dairy industry, agriculture and horticulture to boost production.
- Oxytocin is included as a lifesaving drug in the National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM).
Misuse of Oxytocin:
- The reason for the ban is the misuse of oxytocin in dairy animals, like buffaloes, to increase milk production.2016 Himachal Pradesh High Court judgment, which said daily oxytocin injections made cattle barren and reduced their lifespans. In addition, it claimed that drinking milk from oxytocin-treated cattle led to male impotence, early puberty among women and cancers.
What government did:
- The health ministry had in April 2018 notified a ban on private drug manufacturers from producing Oxytocin.
- The government had restricted its imports and decided to confine manufacturing to Karnataka Antibiotics and Pharmaceuticals Ltd, a government company.
Why ban on private drug manufacturers from producing Oxytocin.
- Oxytocin can be overused in the absence of oversight by a veterinary doctor. At high doses, it can hurt animals. Also, when untrained dairy farmers are administering the injection, it can cause pain for the animals.
Concerns:
- The twin issues which arise for consideration are on the one hand,
- The Unregulated and clandestine manufacture of the drug Oxytocin, which is reportedly misused in milch animals; andOn the other hand, the continued supply of an essential lifesaving drug, which is used as the first line drug for prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage at the time of childbirth.”
What Court is trying look:
- According to the SC, the bench should look into various aspects like whether the government notification will result in monopoly, if the restriction on its manufacturing be in public interest, whether the government’s decision would achieve the objective and purpose of preventing the unregulated and illegal use of the drug, among others.
Is Ban the Only solution?
- No, given the drug’s importance to both human and veterinary medicine, the Drugs Technical Advisory Board recommended against a ban, advocating better surveillance instead. A ban might lead to scarcity and high drug prices.
CHANDRAYAAN-2 PLACED IN LUNAR ORBIT
21, Aug 2019

Context: India’s Chandrayaan-2 mission crossed a major milestone on its journey towards the Moon, having entered a lunar orbit, almost exactly 30 days after being launched on July 22.
What exactly did Chandrayaan-2 achieve?
- After being launched, Chandrayaan-2 had been put in an elliptical orbit around the Earth.
- Until August 14, it had been going around the Earth, incrementally raising its orbit by firing boosters on five occasions.
- Eventually, it reached an orbit that was 276 km from the Earth’s surface at its closest and 142,975 km at the farthest.
- It spent nearly a week in that orbit, before firing a booster once again to break free from the Earth orbit and begin its journey towards the Moon.
- This transit from orbit to orbit happened on August 14.
- After five days of this journey, Chandrayaan-2 came sufficiently close to the Moon to experience its gravity. And on Tuesday, it entered into an orbit around the Moon.
What exactly is meant by ‘insertion into lunar orbit’?
- Just like it was going around the Earth at the start of its journey, Chandrayaan-2 is now orbiting the Moon.
- On Tuesday, it was placed into an elliptical orbit that was 114 km from the Moon’s surface at its nearest, and 18,072 km at the farthest.
- The spacecraft will carry out a few more manoeuvres to eventually place itself in a circular orbit of 100 km × 100 km around the Moon (see illustration below).
- The Lander and Rover modules will detach themselves from here and descend into lower orbits before finally making a landing on September 7.
- The main spacecraft, however, will continue to orbit the Moon in the 100 km circular orbit for at least one year, making observations through the several instruments it has on board.
Why Are These Manoeuvres Needed?
- Indeed.it is possible to fly straight to the Moon, without getting into the Earth orbits. The lunar orbit, however, cannot be avoided. The spacecraft cannot land directly on the Moon.
- In fact, none of the Apollo missions that landed astronauts on the Moon took the route that Chandrayaan-2, or all other recent missions to Moon, have taken. The Apollo missions flew directly to the Moon. But this is not considered wise or economical.
- That is because the rockets need to be extraordinarily powerful to carry the spacecraft all the way to Moon.
- An enormous amount of fuel too is required. Taking a longer route, however, makes it much easier for the spacecraft to travel.
- The rocket has to take the spacecraft only about 200 km from the Earth’s surface and deposit it in Low-Earth Orbit.
- Thereafter, the spacecraft moves around the Earth under the influence of gravity. This stable position is also a good time for ground controllers to check on the health of the equipment on board.
- While circling the Earth, a substantially lower amount of energy is required to propel the spacecraft into higher orbits due to reduction in atmospheric drag.
- This is easily possible with a small amount of fuel onboard. With each higher orbit, however, the gain in energy is enormous, enabling the spacecraft to achieve great velocities, and the power to move much deeper into space.
What happened in Apollo Mission?
- To put things in perspective, the Apollo missions were carried on giant Saturn V rockets, which even today remain the most powerful rockets ever built.
- They were 111 metres tall, higher than a modern 30-storey building, and weighed 2,800 tonnes, a significant part being contributed by the fuel it carried.
- According to information on NASA website, the fuel it burnt to land astronauts on the Moon — several million litres of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen in different stages — could take a normal car 800 times around the Earth. It is said to have consumed 20 tonnes of fuel every second.
Comparison with Chandrayaan 2:
- In comparison, ISRO’s GSLV Mk-III rocket used to launch Chandrayaan-2 is extremely modest.
- At 43.43 metres, it has less than half the height of Saturn V, and weighs 640 tonnes, less than one-fourth of Saturn V.
- It can carry less than 350 tonnes of fuel, roughly about one-fifth of what Saturn V needed for its Apollo missions.
Chandrayaan-2 is said to have slowed down before entering lunar orbit. Why did it need to slow down?
- Chandrayaan-2, after coming under the influence of lunar gravity on Monday, had begun to accelerate.
- At one point, it had reached a velocity of 2.4 km per second (8,640 km per hour).
- This is just about equal to the escape velocity of the Moon.
- If Chandrayaan-2 had been allowed to speed up unrestrained, it would have escaped the Moon’s gravity and moved away.
- To keep it in the lunar orbit, therefore, its velocity was brought down to 2.1 km per second (7,560 km per hour).
How do they increase or decrease speed?
- Spacecraft increase or decrease their velocities by firing on-board thrusters.
- To speed up, the thrusters are fired in a direction opposite to the motion of the spacecraft. It has an effect similar to the recoil that a gun experiences after firing. Velocity can be reduced if the thrusters are fired in the direction of motion.
NASA’S PARKER SOLAR PROBE
20, Aug 2019

Why in news?
- NASA’s Parker Solar Probe completed a year in service.
Aim of the mission:
- The mission’s central aim is to trace how energy and heat move through the Sun’s corona and to study the source of the solar wind’s acceleration.
- The mission is likely to last for seven years during which it will complete 24 orbits.
Parker Solar Probe:
- It is part of NASA’s “Living with a Star” programme that explores different aspects of the Sun-Earth system.
- The probe seeks to gather information about the Sun’s atmosphere and NASA says that it “will revolutionise our understanding of the Sun”.
- It is also the closest a human-made object has ever gone to the Sun.
- During the spacecraft’s first two solar encounters, the instruments were turned on when Parker was about 0.25 AU from the Sun and powered off again at the same distance on the outbound side of the orbit.
- For this third solar encounter, the mission team turned on the instruments when the spacecraft was around 0.45 AU from the Sun on the inbound side of its orbit.
- It will turn them off when the spacecraft is about 0.5 AU from the Sun on the outbound side.

CHANDRAYAAN-2 SUCCESSFULLY ENTERS LUNAR TRANSFER TRAJECTORY
14, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- Chandrayaan-2 has successfully carried out the significant process of trans-lunar injection, moving from earth`s orbit towards the moon.
Highlights:
- Chadrayaan-2 is another step closer to the Moon and headed onwards on its path to the Moon. Chandrayaan-2 will approach the Moon on August 20 and finally land near the south pole of the Moon on September 7, 2019.
- Chandrayaan-2 will be entered into the Moon’s orbit on August 20, 2019.
- After that, the spacecraft’s liquid engine will be fired again to insert the Chandrayaan-2 into the lunar orbit.
- Once Chandrayaan-2 will enter into the Moon’s orbit it will conduct four-orbit manoeuvres so that spacecraft could enter into the final orbit passing over the lunar poles at a distance of about 100 km from the Moon’s surface.
- Following this, the spacecraft’s lander, Vikram, is expected to soft-land on the south pole of the moon and unleash the rover to explore the surface on September 7.
- SRO released a statement that the health of the spacecraft is being continuously monitored from the Mission Operations Complex (MOX) at ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) in Bengaluru with support from Indian Deep Space Network (IDSN) antennas at Byalalu, near Bengaluru.
- The present health of the spacecraft is good and all systems onboard Chandrayaan-2 spacecraft are performing normally.
IRON ION BATTERY
12, Aug 2019
Why in News?
- For the first time, Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras has fabricated a rechargeable iron ion battery using mild steel as the anode.
Highlights:
- With no lithium reserves in India and shortage of lithium reserves in the world, the stress is on developing rechargeable batteries of comparable performance using materials other than lithium.Iron has favourable physico-chemical properties like lithium.
- The redox potential of iron ion is higher than lithium ion and the radius of the Fe2+ ion is nearly the same as that of the lithium ion
Features:
- While lithium ions are the charge carriers in lithium ion battery, the Fe2+ ions perform that function in the case of iron ion battery.
- The performance of an iron ion battery can go up to 150 cycles of charging and discharging.In the iron ion battery, Vanadium Pentoxide is used as the cathode and iron perchlorate is used as the electrolyte.
- With 54% capacity retention at the end of 50 cycles of charging and discharging, the battery display good stability.It is possible to fabricate the battery under ambient conditions too.
Benefits:
- The iron ion battery is cost-effective and can store a high amount of energy.
- With the world turning its attention to electric vehicles, the focus is on developing batteries that are cheaper.Iron is more stable during the charging process and therefore prevents short-circuiting of the batteries.
- The amount of energy that can be drawn from the iron ion battery is 220 Wh per kg, which is 55-60% of lithium ion battery’s performance.
DIRECTED ENERGY WEAPONS (DEWs)
12, Aug 2019

- Context- Directed energy weapons or DEWs are among the next bunch of military technologies that the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is working on.
What is Directed Energy Weapons?
- A directed-energy weapon (DEW) is a ranged weapon that damages its target with highly focused energy, including laser, microwaves and particle beams.
- Potential applications of this technology include weapons that target personnel, missiles, vehicles, and optical devices
DRDOs take on Directed Energy Weapons:
- DEWs would play a major role in future warfare.
- DEWs are extremely important today. The world is moving towards them.
- In the country too, DRDO is doing a lot of experiments.
- DRDO have been working in this area for the past three to four years to develop 10kW and 20kW [weapons].
Directed energy weapons could have several Main Advantages over conventional weaponry:
- Direct energy weapons can be used discreetly; radiation above and below the visible spectrum is invisible and does not generate sound.
- Light is only very slightly altered by gravity, giving it an almost perfectly flat trajectory.
- It is also practically immune to both windage and Coriolis force. This makes aim much more precise and extends the range to line-of-sight, limited only by beam diffraction and spread, and absorption or scattering by intervening atmospheric contents.
- Lasers travel at light-speed and have near infinite range and therefore, are suitable for use in space warfare.
- Laser weapons potentially eliminate many logistical problems in terms of ammunition supply, as long as there is enough energy to power it the laser ammunition supply is assured.
- Depending on several operational factors, Directed Energy Weapons may be cheaper to operate than conventional weapons in certain contexts.
Significance of Laser based or Microwave Based high-power DEWs
- Laser based or microwave based high-power DEWs can quietly disable enemy drones or missiles temporarily or permanently without leaving physical debris.
- In contrast, the ASAT or anti-satellite missile that the DRDO tested on March 27, killed an orbiting Indian target satellite and left hundreds of small pieces as debris for a few months.
Problems with laser weapons:
Blooming:
- Laser beams begin to cause plasma breakdown in the atmosphere at energy densities of around one megajoule per cubic centimetre.
- This effect, called “blooming,” causes the laser to defocus and disperse energy into the surrounding air.
- Blooming can be more severe if there is fog, smoke, or dust in the air.
LUNAR LIBRARY
10, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- On February 21, an Israeli lunar lander called Beresheet (Hebrew for ‘the beginning’) began its journey to the Moon aboard a SpaceX rocket in its quest to be the first privately-funded spacecraft to land on the Moon.
- A month later, it was reported, Beresheet had crash-landed and was irredeemably broken except, for a curious, quirky payload called the Lunar Library.
Lunar Library:
- The Lunar Library contains a 30 million page archive of human history and civilization, covering all subjects, cultures, nations, languages, genres, and time periods.
- The Library is housed within a 100 gram nanotechnology device that resembles a 120mm DVD. However it is actually composed of 25 nickel discs, each only 40 microns thick, that were made for the Arch Mission Foundation by Nano Archival.
- The first four layers contain more than 60,000 analog images of pages of books, photographs, illustrations, and documents — etched as 150 to 200 dpi, at increasing levels of magnification, by optical nanolithography.
- The first analog layer is visible to the naked eye. It contains 1,500 pages of text and images, as well as holographic diffractive logos and text, and can be easily read with a 100X magnification optical microscope, or even a lower power magnifying glass.
- The next three analog layers each contain 20,000 images of pages of text and photos at 1,000X magnification, and require a slightly more powerful microscope to read. Each letter on these layers is the size of a bacillus bacterium.
- Beneath the analog layers of the Library are 21 layers of 40 micron thick nickel foils. Each of the foils house a DVD master, which contain more than 100GB of highly compressed datasets that decompress to almost 200GB of content, including the text and XML of the English Wikipedia, plus tens of thousands of PDFs of books — including fiction, non-fiction, a full reference library, textbooks, technical and scientific handbooks, and more.
- The Lunar Library contains a small sample from the Bodhi tree in India, along with material on learning Hindi, Urdu and information on music. It contains leaf from the Bodhi tree and some soil from under the Bodhi seat
- Lunar library also contains thousands of tardigrades — small, multicellular animals, first found by scientists in Antarctica, and known to be extremely resilient in hostile environments. They can survive without food and water for decades. Assuming that the Lunar library has survived they could be the first living organisms splashed across the surface of the moon.
- The first microbes on the Moon are those left behind in the human faeces from the astronauts aboard the Apollo missions of 1968-1972.
BRAHMOS MISSILE TO BE DEPLOYED ALONG COAST FOR MARITIME SECURITY
10, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) has approved the procurement of a Software Defined Radio (SDR) and the Next Generation Maritime Mobile Coastal Batteries (NGMMCB) for the Navy.
Highlights:
- The NGMMCB will be fitted with the BrahMos surface-to-surface supersonic cruise missiles and deployed along the coast.The SDR has been designed and developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) and the Navy’s Weapons Electronics Systems Engineering Establishment (WESEE).
- SDR will facilitate high-speed data and secure voice communication with anti-jamming capability.
BrahMos:
- BrahMos was jointly developed by India and Russia and has been inducted into the the Army and the Navy.
- It is a joint venture between the Russian Federation’s NPO Mashinostroyeniya and India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) who together have formed BrahMos Aerospace.
- The name BrahMos is a portmanteau formed from the names of two rivers, the Brahmaputra of India and the Moskva of Russia.
- The BrahMos is a medium-range ramjet supersonic cruise missile.
- It can be launched from submarine, ships, aircraft, or land.
- It is the fastest supersonic cruise missile in the world and the world’s fastest anti-ship cruise missile in operation.
- The missile travels at speeds of Mach 2.8 to 3.0,which is being upgraded to Mach 5.0
- In 2019, India upgraded the missile with a new range of 500 km.
GENOME INDIA INITIATIVE
07, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) plans to scan nearly 20,000 Indian genomes over the next five years, in a two-phase exercise, and develop diagnostic tests that can be used to test for cancer.
Genome India Initiative:
- The initiative aims to make predictive diagnostic markers available for some priority diseases such as cancer and other rare and genetic disorders
- The first phase involves sequencing of complete genomes of nearly 10,000 Indians from all corners of the country and captures the biological diversity of India.
- In the next phase, about 10,000 “diseased individuals” would have their genomes sequenced.
- These vast troves of data sets would be compared using machine learning techniques to identify genes that can predict cancer risk, as well as other diseases that could be significantly influenced by genetic anomalies.
- 22 institutions, including those from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and the DBT would be involved in the exercise.
- The data generated would be accessible to researchers anywhere for analysis.
- This would be through a proposed National Biological Data Centre envisaged in a policy called the ‘Biological Data Storage, Access and Sharing Policy’, which is still in early stages of discussion.
Genome:
- A genome is an organism’s complete set of DNA, including all its genes.
- It contains all the information needed to build and maintain that organism.
- By sequencing the genome, researchers can discover the functions of genes and identify which of them are critical for life.
Significance:
- There is interest among private and public companies in sequencing genomes thanks to the declining costs for the process.
- From China to the United Kingdom and Saudi Arabia, several countries have announced plans to sequence their population.
- Currently, genomic data sets under-represent Asia, particularly India, whose population and diverse ethnicity make it an attractive prospect for genome-mining efforts.
ROLE OF TECHNOLOGY IN REUNITING MISSING CHILDREN & TRAFFICKED PERSONS
06, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- A one-day Workshop on ‘Role of Technology in Reuniting Missing Children & Trafficked Persons’ was jointly organised by National Crime Records Bureau, Ministry of Home Affairs, in collaboration with Indian Police Foundation
Highlights:
- The workshop deliberated on the use of biometrics by law enforcement agencies for the identification of persons.
- Use of biometrics is not a new practice in law enforcement; however, it was not as technologically advanced as present-day applications. Rise of computing and electronics have greatly assisted biometric applications to become faster, more secure and accurate.
- Use of biometrics has become a necessity in today’s complex world.
- It was emphasized that with the use of biometrics, law enforcement agencies can also locate large number of persons, especially children who are reported missing.
- Similarly, unidentified found persons and unidentified dead bodies can also be matched using biometrics with the existing records of missing persons and unidentified found persons.In a large population, it is the only mechanism to provide an accurate match and help people in reuniting with their families.Use of facial recognition technology for various applications, stressing upon the importance of identifying tools which would greatly facilitate the investigation of crime and detection of criminals and provide information for reuniting missing children and trafficked persons.
- NCRB clarified the doubts related to security breach, reliability and privacy of individuals while implementing AFRS (Automated Facial Recognition System). AFRS of NCRB will not work on public databases.
- AFRS results will be further corroborated and analysed by collecting other evidences by Investigation Officer before drawing any conclusions. AFRS will not source facial images from CCTV cameras in public places, unless the video footage is part of the scene of crime.
NEW ISRO SYSTEM TO SHIELD ITS ASSETS FROM SPACE DEBRIS
06, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- To get accurate data about the movement of space debris to avoid collision with its satellites, ISRO has decided to set up telescopes and radars in four corners of the country.
Space Situational Awareness and Management:
- The network will be set up under the Directorate of Space Situational Awareness and Management.The directorate would monitor inactive satellites, pieces of orbiting objects, near-earth asteroids and adverse space weather conditions.
- Currently ISRO has 50 functional satellites, including communication, navigation and surveillance satellites, in space.
NORAD’S Dependency:
- Till now, ISRO was dependent on NORAD (North America Aerospace Defense Command) data, which is available in public domain, for keeping track of space debris and monitoring our active and passive (dead) satellites.However, this global data is not accurate.
- NORAD also keeps accurate data, which is exclusively available to those that are members of its network. Therefore, ISRO can’t access this data.
Other Developments:
- ISRO’s sophisticated multi-object tracking radar installed in Nellore (90km from Sriharikota) will be part of this project.It will also set up a telescope in Ponmudi (Thiruvananthapuram) and second one in Mount Abu (Rajasthan) and third one in deep north.ISRO will also install radar in the northeast.
- Once this network is operational, India will be able to get accurate data on space debris and will also become part of the global network where India can access very accurate data on debris from hundreds of radars set up across the world.
DRDO SUCCESSFULLY FLIGHT-TESTS QRSAM
04, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- Defence Research Development Organisation (DRDO) today successfully flight-tested its state-of-the-art Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missiles (QRSAM) against live aerial targets from Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur.
QRSAM:
- Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile (QRSAM), with a strike range of 25 km, is being developed by the DRDO for the Indian Army.
- The all-terrain and all-weather missile with electronic counter-measures against jamming by enemy aircraft can be mounted on a truck and stored in a canister.
- Before this test, on February 26, two rounds of tests were successfully carried out.
- This missile can be rotated 360 degree while on the way to its target.
- QRSAM is also able to use as an anti-sea skimmer from a ship against low flying attacking missiles. QRSAM employs dual thrust propulsion stage using high-energy solid propellant.
QRSAM Test:
- DRDO conducted two different tests for different altitude and conditions. DRDO closely observed both tests and found that flights successfully demonstrated the Aerodynamics, high manoeuvring capabilities, Robust Control, Structural performance and Propulsion thus proving the design configuration.
- Electro-Optical Systems, Radars, Telemetry and other equipment have monitored and tracked the missiles through the entire flights. DRDO announced that all the mission objectives have been met.
SEED BANKERS FOR CONSERVING NATIVE CROPS
01, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- Till date 1597 plants varieties have been registered with Protection of Plant Varieties & Farmers Right Authority and certificates of registration have been issued.
National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources:
- ICAR-National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR), New Delhi is conserving seed germplasm for long-term conservation (at -20°C) in its National Genebank (NGB).
- NGB has the responsibility of conservation of plant genetic resources for posterity and sustainable use including landraces and traditional varieties which are potential sources of agriculturally important genes.
India’s seed bank at Chang La:
- At Chang La in the Himalayas, at a height of 17,300 feet, there is a storage facility with over 5,000 seed accessions.
- One accession consists of a set of seeds of one species collected from different locations or different populations.
- The vault is a joint venture of the National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (under ICAR) and the Defence Institute of High Altitude Research (under DRDO).
- When a seed needs to be stored for few years, maintaining it at just 10 degree Celsius is enough.
- But in the long run, for 10 to 20 years, they need to be kept at a minus 15 to minus 20 degree Celsius (range).
- Chang La has a prevalent temperature in this sub-zero range.
Svalbard Global Seed Vault:
- It is a facility located on a remote Norwegian island in the Arctic Ocean and it houses the world’s largest collection of seeds.
- The seeds can be of use in the event of a global catastrophe or when some species is lost due to natural disasters. It is therefore also referred to as the doomsday vault.
- The storage rooms are kept at −18 °C (−0.4 °F). The low temperature and limited access to oxygen will ensure low metabolic activity and delay seed aging.
- The samples stored in the genebanks are accessible in accordance with the terms and conditions of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture, approved by 118 countries or parties.
TUBERCULOSIS VACCINES
01, Aug 2019
Context:
- Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) launched India’s first large-scale trial for two new tuberculosis (TB) vaccines.
Stats:
- As per the 2018 annual report of the Central TB division of Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the incidence of TB was nearly 2.8 million annually, and the incidence of multidrug-resistant TB was 1,47,000 per year.
- The total number of deaths because of TB (excluding HIV) was 4,23,000, and the incidence of HIV-TB was 87,000 per year.
- India contributes to 27 per cent of the global TB burden; the highest share globally.
- That is why, in 2017, the central government had committed itself to eliminating TB by 2025.
What is TB?
- Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) that most often affect the lungs. Tuberculosis is curable and preventable.
- Spread- TB is spread from person to person through the air. When people with lung TB cough, sneeze or spit, they propel the TB germs into the air. A person needs to inhale only a few of these germs to become infected.
- About one-third of the world’s population has latent TB, which means people have been infected by TB bacteria but are not (yet) ill with disease and cannot transmit the disease.
Symptoms:
- TB disease in the lungs may cause symptoms such as
- a bad cough that lasts 3 weeks or longer
- pain in the chest
- coughing up blood or sputum (phlegm from deep inside the lungs)
Other symptoms of TB disease are:
- Weakness or fatigue
- Weight loss
- No appetite
- Chills
- Fever
- Sweating at night.
TB and HIV Coinfection:
- Tuberculosis is a serious health threat, especially for people living with HIV.
- People living with HIV are more likely than others to become sick with TB.
- Someone with untreated latent TB infection and HIV infection is much more likely to develop TB disease during his or her lifetime than someone without HIV infection.
- Among people with latent TB infection, HIV infection is the strongest known risk factor for progressing to TB disease.
- A person who has both HIV infection and TB disease has an AIDS-defining condition.
Why New Vaccines:
- Scientists at the Indian Council of Medical Research have felt a critical need for new TB vaccines that are more effective than the Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine.
Which are Vaccines?
- There are two vaccines being tested in the latest trial:
- Immuvac (also known as mycobacterium indicus pranii or MIP), which is manufactured by Cadila Pharmaceuticals in Ahmedabad, and
- VPM1002 manufactured by Serum Institute of India in Pune.
What are Phases of trials:
- Typically, vaccine trials have three phases. During Phase 1, small groups of people receive the trial vaccine.
- In Phase 2, the clinical study is expanded and the vaccine is given to people who have characteristics (such as age and physical health) similar to those for whom the new vaccine is intended.
- In Phase 3 the vaccine is given to several thousands of people and tested for efficacy and safety.
Current phase of TB vaccine:
- Phase 3 vaccine trial where the safety and efficacy of the two TB vaccines are being studied in comparison to the placebo in a larger population.
- Depending on the results, the recommendations would be sent to the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Both vaccines are being manufactured by Indian pharmaceutical companies. The price of the vaccines would be decided by the government.
MICRODOTS
31, Jul 2019

Why in News?
- The government has come out with draft rules to make microdots mandatory in vehicles.
- This move will also ensure that consumers have a way of identifying original parts from fake ones and that contributes to overall safety as well.
Microdots Technology:
- The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways issued a draft notification on amending the Central Motor Vehicles Rules, 1989, and allowing motor vehicles and their parts, components, assemblies, sub-assemblies to be affixed with permanent and nearly invisible microdots.
- These microdots can be read physically with a microscope and identified with ultraviolet light.
- Microdots are a globally proven technology to ensure originality in spare parts of machines and components, including in the automobile sector.
- The government has envisaged that with microdots becoming a permanent feature in vehicles, identifying them would become easier in case they are stolen.
How it works?
- The microdots and adhesive are to become a permanent fixture/affixation which cannot be removed without damaging the asset itself.
- The microdots are to comply with AIS 155 requirements, if affixed.
- The technology involves spraying thousands of microscopic dots onto vehicles or other assets to form a unique identification.
- Each microdot carries this identification which is registered to the owner, but is not visible to the naked eye.
- Act, 1999 (GI Act) is a sui generis Act for protection of GI in India.
- India, as a member of the WTO enacted the Act to comply with the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights.
- Geographical Indications protection is granted through the TRIPS Agreement. See also the Paris Convention, the Madrid Agreement, the Lisbon Agreement, the Gene.
INTEGRATED BATTLE GROUPS (IBG)
29, Jul 2019

- Context– The new concept of Integrated Battle Groups (IBGs) which the Army plans to create as part of overall force transformation is close to implementation,
About IBG:
Significance:
- IBGs are expected to be game changers that will alter the way the Indian Army strategises for wars.
- These specialised groups to ensure better integration and self-sufficiency as compared to the existing formations.
- During hostilities, the current system requires a brigade to wait to be augmented by various types of units, such as artillery and logistics, which raises its time to mobilise.
- This won’t be the case with IBGs, which will be self-sufficient and inbuilt with all such units, and hence, easier to mobilise.
RADIATION TECHNOLOGY FOR SEWAGE TREATMENT
27, Jul 2019

Why in news?
Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) in collaboration with Amdavad Municipal Corporation (AMC), Ahmedabad has set up a Technology Demonstration Pilot Project “Sewage Sludge Hygienisation Plant” at Shahwadi, Ahmedabad.
Highlights:
- Large amount of sewage sludge is produced in India every day. The sludge is infectious and can spread diseases. It also has essential micro and macro nutrients, especially carbon, useful for soil and crop production.
- Radiation Technology can be used to hygienise the sludge reliably and affordably and protect health and environment. Addition of useful microorganisms to the hygienised sludge can convert it to a value-added manure
Radiation Technology:
- Ionizing radiation emitted by radiation source such as Cobalt-60 interacts with the critical molecules like DNA, proteins and water present in the cell and result in the inactivation of microorganisms.
- As a result of Irradiation, besides pathogens, other unwanted constituents like weeds, chemicals, etc. are also degraded, making the sludge safer for use
- Based on microbiological inactivation, Radiation Technology is already established world over for sterilizing medical products, food safety and food preservation. Sludge hygienisation can be carried out in the similar manner
Advantages of Radiation Technology:
- Process is simple, economic, effective, reproducible and scalable.
- Easy to integrate with conventional sewage treatment facilities.
- Process is fully automatic to avoid manual handling of contaminated sludge.
- Based on the process of radiation sterilization which is well established world over and in India.
- Degrades chemical contaminants and makes sludge safer for use.
Benefits To The Farmers/People:
- Increased crop yield – direct benefit to the farmers.
- Improved soil conditions – soil conservation & restoration.
- Reduced health risks associated with sludge, reduces costs of health care system.
- Reduced demand of water due to higher water holding capacity of the sludge.
- Radiation technology has sound scientific basis and is a practical technology to economically hygienise sewage sludge for agriculture application.
- The technology and radiation source both are available in our country. Irradiation facility can be utilised to treat whole city sludge at one place in a fully automatic process.
- The hygienised sludge can benefit farmers and protect environment and human health. The technology has high potential in contributing towards meeting the objectives of Clean India Mission (the Swachh Bharat mission).
ASTRONOMERS DECODE MILKY WAY’S VIOLENT BIRTH
25, Jul 2019

- Based on the data from the Gaia Space Observatory scientists say that Milky Way (our galaxy) merged with another smaller galaxy in a colossal cosmic collision roughly 10 billion years ago.
- The union of the Milky Way and the so-called dwarf galaxy Gaia-Enceladus increased our galaxy’s mass by about a quarter and triggered a period of accelerated star formation lasting about 2 to 4 billion years.
- Galaxies of all types, including the Milky Way, began to form relatively soon after the Big Bang explosion that marked the beginning of the universe some 13.8 billion years ago, but were generally smaller than those seen today and were forming stars at a rapid rate.
- Subsequent galactic mergers were instrumental in configuring galaxies existing now.
- High-precision measurements of the position, brightness and distance of around a million stars within 6,500 light years of the sun, obtained by the Gaia space telescope, helped pinpoint stars present before the merger and those that formed afterward.
- Certain stars with higher content of elements other than hydrogen or helium arose in the Milky Way, they found, and others with lower such content originated in Gaia-Enceladus, owing to its smaller mass.
- While the merger was dramatic and helped shape the Milky Way, it was not a star-destroying calamity.
DORNIER SQUADRON INAS 313 AT CHENNAI
24, Jul 2019

Why in News?
- The fifth Dornier squadron Indian Naval Air Squadron (INAS) 313, was commissioned into the Indian Navy by Admiral Karambir Singh.
Dornier Squadron INAS 313:
- It will enhance maritime security and safeguard our nation’s maritime interests
- The strategic position of the squadron will give India, dominance over the North-Eastern part of the Indian Ocean that also consists of trade routes.
- The Squadron will be operating from Chennai International Airport
- With the commissioning of INAS 313, Tamil Nadu will have 3 naval air bases, which is the highest among the Coastal States
- Other two air bases in Tamil Nadu are INS Rajali at Arakkonam and INS Parundu at Ramnad.
- INAS 313 is named ‘Sea Eagle’ from the bird of prey family Accipitridae
- Dornier aircraft is a multi-role Short Range Maritime Reconnaissance (SRMR) aircraft manufactured by HAL (Hindustan Aeronautics Limited).
- The aircraft performs maritime surveillance, Search and Rescue Operations, and targeting data to weapon platforms.
- Dornier aircraft from HAL will Contribute towards indigenous development and self-reliance through “Make in India”.
CYBER CRIME COORDINATION CENTRE
19, Jul 2019

Why in News?
- The Central Government has rolled out a scheme for establishment of Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre to handle issues related to cybercrime in the country in a comprehensive and coordinated manner.
- Central Government has taken steps to spread awareness about cybercrimes to prevent such crimes and to speed up investigation.
Initiatives:
- Establishment of National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) for protection of critical information infrastructure in the country.
- All organizations providing digital services have been mandated to report cyber security incidents to CERT-In expeditiously.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra (Botnet Cleaning and Malware Analysis Centre) has been launched for providing detection of malicious programmes and free tools to remove such programmes. Issue of alerts and advisories regarding cyber threats and counter-measures by CERT-In. Issue of guidelines for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) regarding their key roles and responsibilities for securing applications / infrastructure and compliance. Provision for audit of the government websites and applications prior to their hosting, and thereafter at regular intervals.
- Formulation of Crisis Management Plan for countering cyber-attacks and cyber terrorism.
- Empanelment of security auditing organisations to support and audit implementation of Information Security Best Practices. Conducting cyber security mock drills and exercises regularly to enable assessment of cyber security posture and preparedness of organizations in Government and critical sectors.
- Conducting regular training programmes for network / system administrators and Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) of Government and critical sector organisations regarding securing the IT infrastructure and mitigating cyber-attacks.
NAVIGATION WITH INDIAN CONSTELLATION (NAVIC)
18, Jul 2019

Why in News?
- The navigation system that Indians use on their mobile phones and cars could be set for a reboot.
- It has been reported that ISRO is in talks with processing chip manufacturers such as Qualcomm to substitute the existing Global Positioning System (GPS) with the Indian version of satellite navigation.
NavIC:
- NavIC is an independent Indian satellite-based positioning system for critical national applications.
- India got its system with the launch of the IRNSS 1-G satellite, is the seventh member of the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), in November 2017.
- It consists of a constellation of seven satellites, three of which are in a geostationary orbit and four in a geosynchronous orbit.
- The IRNSS can provide Standard Positioning Service (SPS) to all users, and an encrypted Restricted Service (RS) to authorised users.
- It has position accuracy better than 20 metres in the primary service area.
- Its purpose is to provide reliable position, navigation and timing services over India and neighbourhood.
Service coverage:
- The regional navigation satellite system can provide accurate position information service to users in India and the region, extending up to 1,500 km from its boundary, which is its Primary Service Area.
- Beyond that lies an Extended Service Area, that can extend up to the edges of the area enclosed by the rectangle imagined by latitudes 30 degrees South and 50 degrees North, and longitudes 30 degrees East and 130 degrees East.
- The GPS is a satellite-based radio navigation system that is owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Air Force.
- Apart from GPS, there is GLONASS of Russia, Galileo of the European Union and BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (or BDS) of China.
HUMAN GENETICS AND GENOME ANALYSIS
17, Jul 2019

- Context: The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has initiated a programme called Human Genetics and Genome Analysis for reducing India’s disease burden
About the Programme:
- Private DNA testing laboratories offering recreational genetics tests are already burgeoning in India.
- Now, the department of biotechnology (DBT) has initiated a programme called human genetics and genome analysis in which the country’s genetic resource is being utilized to develop baseline data initially on various ethnic groups for disease susceptibility.
- The focus is on improving human health by promoting the development and dissemination of genomic methodologies and tools for prediction and prevention of human disease, and for therapeutic intervention.
- The aim is to improve disease management through lifestyle modulation, improvement in public health, reduction of disease burden, and lowering of treatment cost with more genetic laboratories and trained personnel in the area.
About Recreational Genetics:
- Recreational genetics is a term used to describe personal genetics tests which can be used to determine a person’s genetic make-up.
- The information from such a test can be used to unearth details about ancestry and inherited traits, among other things.
- Recreational genetics may also be called recreational DNA testing.
- Genetic testing can reveal how one’s genes behave and respond, personal genetic information can provide data that can help people make more informed health-related decisions about their lifestyle, goals, dietary habits, fitness, nutrition and weight management.
- While recreational genetic tests are common in the US and several European countries, in India the genetic testing market is still at a nascent stage.
5G ROLLOUT: HOW FAR HAS INDIA PROGRESSED, AND WHERE DOES IT STAND ON HUAWEI?
16, Jul 2019

What is Huawei?
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd. is a Chinese multinational technology company that provides telecommunications equipment and sells consumer electronics, including smartphones, headquartered in Shenzhen, Guangdong.
- Although successful internationally, Huawei has faced difficulties in some markets, due to cybersecurity allegations—primarily from the United States government—that Huawei’s infrastructure equipment may enable surveillance by the Chinese government.
- Especially with the development of 5G wireless networks (which China has aggressively promoted).
Why did US blacklist Huawei?
- According to The Wall Street Journal, “Huawei is the world’s largest maker of telecommunications equipment and the No. 2 vendor of smartphones, ahead of Apple Inc. and behind only Samsung Electronics Co”.
- However, notwithstanding its dominance, the US has effectively banned Huawei from selling its products after a 2012 congressional report stated that Huawei could be a security risk.
- According to the US, Huawei’s owners have close links with the Chinese military and, as such, the company cannot be trusted with data.
- The treatment of Huawei has become a massive reason for further straining the already fraught diplomatic relations between the US and China.
Where does India stand on the Huawei controversy?
- Following Huawei’s blacklisting by the US administration, several countries were asked to take a stand on whether or not to allow the company to operate. Certain countries such as the UK did not follow the US and cited benefits to operators from Huawei’s cost-efficient technology as the reason behind not banning the firm.
- While India is yet to take a stand on whether or not to allow Huawei in 5G trials, officials at the teslecom department have indicated that a decision will be taken in consultation with the ministries of home affairs and external affairs. Huawei, however, has said that it is ready to sign a “no-backdoor” agreement with the Indian government and telecom companies to ensure that no snooping is allowed on its network.
Where does India stand on the rollout of 5G vis-a-vis other countries?
- Deliberations are still on whether to give spectrum for 5G in the 25 GHz and 28 GHz bands. This is one of the factors causing a delay in the auction of airwaves necessary for 5G deployment.
- Industry players have deemed availability of spectrum as the prerequisite for the commercial rollout of 5G.
- In February last year, Airtel and Huawei conducted a lab trial for 5G during which a user throughput of 3 Gbps was achieved. However, not much has moved since then.
- A committee of the telecom ministry recently cleared the proposal to allow Bharti Airtel, Vodafone Idea and Reliance Jio to conduct 5G spectrum trial from next month onwards for a period of three months. For these trials, equipment vendors — Samsung, Nokia and Ericsson — have been selected.
- Despite assertions from the government that India “cannot afford to miss” the 5G bus — indicating that the country will see rollout of the latest generation of mobile telephony along with the world — none of the Indian telecom companies figures in the list (put out by mobile and broadband network intelligence firm Ookla) of 303 5G deployments by 20 operators in 294 locations across the globe.
- Additionally, the debt-ridden telecom industry of the country has indicated apprehension towards even bidding for 5G airwaves given their weak financial situation.
What happens after field trials are conducted?
- Field trials allow operators and equipment makers to prove that the network they have built in a laboratory also works outside in a field. Even after conducting the field trials, operators will have a long way to go before commercial rollout primarily because of the lack of availability of the necessary spectrum.
- Some telecom companies, however, have questioned the need for rolling out 5G in India given that focus is still on the propagation of 4G services, especially in the hinterlands of the country.
Why is 5G required?
- The primary use cases of the fifth generation of mobile telephony are being pegged as B2B use cases.
- Lower latency and lesser outage scenarios for 5G would allow use cases such as automated driving and telemedicine to flourish.
- While there is a consumer angle that would allow end-consumers to enjoy faster internet speeds, B2B or business use cases are being seen as the main revenue generating engine for operators with 5G.
- In financial terms, some estimates suggest that operators are expected to rake in an additional $582 billion globally from digitalisation of the economy through 5G technology by 2026, and the largest opportunity for revenues created or enhanced by 5G will be in the manufacturing, energy and utilities sectors.
- A panel set up by the Department of Telecommunications in September 2017 to prepare a roadmap for the rollout of 5G noted in its report that 5G services would have a cumulative economic impact of more than $1 trillion by 2035.
WHY IS INDIA SETTING UP A MOBILE PHONE HANDSETS DATABASE?
16, Jul 2019

-
- Context: The National Telecom Policy of 2012 calls for the establishment of a National Mobile Property Registry to address the issue of “security, theft, and other concerns including reprogramming of mobile handsets”.
- Based on this, the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) under the Ministry of Communications initiated a Central Equipment Identity Register (CEIR) for mobile service providers. The DoT issued a memorandum in July 2017 announcing the CEIR with a pilot project led by Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited in Maharashtra. In January 2018, this project was handed over to the Centre for Development of Telematics (CDoT). Now, it is all set to roll out.
What is CEIR?
- Based on a 2008 order from the DoT, every mobile network provider in India has an Equipment Identity Register (EIR), or a database of the phones connected to its network. These EIRs will now share information with a single central database, the CEIR.
- In essence, it will be a repository of information on all mobile phones connected to networks across India.
- There were over 1,026 million active wireless phone connections by the end of 2018, according to the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India.
- As per the DoT’s 2017 memorandum, the CEIR will have information on the device’s International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) number (every phone or mobile broadband device has this unique 15 digit code that precisely identifies the device), model, version, and “other information”.
- It will also know if the phone is blacklisted, and the reason why it has been blacklisted.
- Phones are identified based on the IMEI number, which you can find under the battery in many mobiles or by dialling ‘*#06#’ on the device. Mobile phone manufacturers assign IMEI numbers to each device based on ranges allotted to them by the Global System for Mobile Communications Association. Dual SIM phones will have two IMEI numbers.
What is the purpose of a CEIR?
- Such centralised databases are meant to identify and block stolen or illegal mobile phones across networks.
- Currently, when a customer reports a mobile phone as missing or stolen, mobile service providers have the ability to blacklist the phone’s IMEI in their EIRs and block it from accessing their network.
- But if the SIM is changed to a new network, it can continue to be in use. With a CEIR, all network operators will be aware that the phone is blacklisted.
- The CEIR will also access the GSMA’s database of IMEI numbers to check whether the phone is authentic.
- There are cases of phones being in use with duplicate IMEI numbers, or with all zeroes instead of an authentic IMEI number.
- Most importantly, as per the DoT’s 2017 memorandum, the CEIR will be able to block services to subscribers. This ability had rested with individual networks till now. The memorandum also mentions enabling “IMEI-based lawful interception”, which means allowing legal authorities to use CEIR data.
What are the issues with having a CEIR?
- In its 2010 consultation paper on “issues relating to blocking of IMEI for lost/stolen mobile handsets,” the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) raises a key issue with the CEIR — who should maintain such a high-value database? Should it be the service provider, or a neutral third party?
- In their responses to the consultation paper, many major service providers preferred having a third party, ranging from international bodies to TRAI itself as suggested by the BSNL.
- The CDoT, which is reportedly readying to roll out the service, is an autonomous entity under the DoT.
- Another major issue is cloning, or reprogramming stolen or unauthorised mobile phones to attach existing genuine IMEI numbers. Blocking cloned IMEI numbers could result in the authentic ones also being blocked.
- While the actual numbers on phones in circulation with cloned or inauthentic IMEIs are hard to pin down, Parliament, in 2012, was informed of two cases of 18,000 phones using the same IMEI number. In 2015, the government banned the import of mobile phones with fake IMEI numbers. In 2017, the DoT framed the “prevention of tampering of the Mobile Device Equipment Identification Number, Rules, 2017” that makes it punishable to tamper with the IMEI number of a device or knowingly use such a device. However, tools to reprogramme phones remain available online, and cases of such activities are reported frequently.
- On this issue, the DoT memorandum of 2017 says the IMEI Cloning and Duplication Restriction (ICDR) software is to be integrated in the CEIR.
NEUTRINO OBSERVATORY
14, Jul 2019

Why in News?
- The Government of India has approved a project to build the India-based Neutrino Observatory (INO) at Pottipuram in the Theni District of Tamil Nadu.
- The project aims to set up a 51000-ton Iron Calorimeter (ICAL) detector to observe naturally occurring atmospheric neutrinos in a cavern at the end of an approximately 2 km long tunnel in a mountain.
- This will help to reduce the noise from cosmic rays that is ever present over-ground and which would outnumber the rare neutrino interactions even in a detector as large as ICAL.
- India based Neutrino Observatory Project:
- The India-based Neutrino Observatory (INO) Project is a multi-institutional effort aimed at building a world-class underground laboratory with a rock cover of approx.1200 m for non-accelerator based high energy and nuclear physics research in India.
The Project Includes:
- Construction of an underground laboratory and associated surface facilities at Pottipuram in Bodi West hills of Theni District of Tamil Nadu,
- Construction of a Iron Calorimeter (ICAL) detector for studying neutrinos, consisting of 50000 tons of magnetized iron plates arranged in stacks with gaps in between where Resistive Plate Chambers (RPCs) would be inserted as active detectors
- Setting up of National Centre for High Energy Physics at Madurai, for the operation and maintenance of the underground laboratory, human resource development and detector R&D along with its applications. The underground laboratory, consisting of a large cavern and several smaller caverns, will be accessed by a 2100 m long and 7.5 m wide tunnel.
Objectives:
- The initial goal of INO is to study neutrinos.
- Neutrinos are fundamental particles belonging to the lepton family. They come in three flavours, one associated with electrons and the others with their heavier cousins the muon and the Tau.
- According to standard model of particle physics, they are mass less.
- However recent experiments indicate that these charge-neutral fundamental particles, have finite but small mass which is unknown.
- They oscillate between flavours as they propagate. Determination of neutrino masses and mixing parameters is one of the most important open problems in physics today.
- The ICAL detector is designed to address some of these key open problems in a unique way.
- Over the years this underground facility is expected to develop into a full-fledged underground science laboratory for other studies in physics, biology, geology, hydrology etc.
BLACK GOLD
10, Jul 2019

Why in News?
- Using gold nanoparticles Indian scientists have developed a new material called “black gold”, which can potentially be used for applications ranging from solar energy harvesting to desalinating seawater, according to a study.
Black Gold:
- To develop the material, the team from Mumbai-based Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) rearranged size and gaps between gold nanoparticles.
- It has unique properties such as capacity to absorb light and carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Gold does not have these properties therefore ‘black gold’ is being called a new material.
- In appearance it is black, hence the name ‘black gold’, according to the findings published in Chemical Science. The researchers varied inter-particle distance between gold nanoparticles using a cycle-by-cycle growth approach by optimizing the nucleation-growth step. They used dendritic fibrous nano silica; whose fibres were used as the deposition site for Gold Nanoparticles.
Features of Black Gold:
- One of the most fascinating properties of the new material is its ability to absorb the entire visible and near-infrared region of solar light.
- It does so because of inter-particle plasmonic coupling as well as heterogeneity in nanoparticles size. Black gold could also act as a catalyst and could convert CO2 into methane at atmospheric pressure and temperature using solar energy.
- If we develop an artificial tree with leaves made out of back gold, it can perform artificial photosynthesis, capturing carbon dioxide and converting it into fuel and other useful chemicals. The efficiency of conversion of CO2 into fuel, at present, is low but researchers believe it could be improved in future. The material can be used as a nano-heater to covert seawater into potable water with good efficiency, the researchers said.
CHANDRAYAAN-2
10, Jul 2019
- Developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- Advanced version of the previous Chandrayaan-1 mission to Moon.
- mission is planned to be launched to the Moon by a Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mk III)
- Two-module system comprising of an Orbiter Craft module (OC) and a Lander Craft module (LC) carrying the Rover developed by ISRO.
Objectives:
- The primary objectives of Chandrayaan-2 are to demonstrate the ability to soft-land on the lunar surface and operate a robotic rover on the surface.
- Scientific goals include studies of lunar topography, mineralogy, elemental abundance, the lunar exosphere, and signatures of hydroxyl and water ice.
Other Nations:
- Only USA Russia and China were able to soft land successfully on the lunar surface and these landings were near the lunar equator.
Recent Developments:
- A crucial test before the launch called “Lander Sensor Performance Test (LSPT)” was conducted by ISRO over an artificial lunar site setup at Challakere, Karnataka.
- It is to test how the sensor will guide the lander when it starts descending on the lunar terrain.
- As the plane descends over the artificial terrain, the sensors must show how they will guide the soft landing of the lunar craft at the right spot, speed and position.
Sensor in the Lander:
- It helps assess height from the landing spot, decides speed of the lander and helps lander navigate boulder or uneven surfaces.
NASA’S PUNCH MISSION
02, Jul 2019

- NASA has selected an US based Indian researcher to lead its PUNCH mission which will image the Sun.
PUNCH Mission:
- PUNCH stands for “Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere,” is focused on understanding the transition of particles from the Sun’s outer corona to the solar wind that fills interplanetary space.
- It will consist of a constellation of four microsatellites that through continuous 3D deep-field imaging, will observe the corona and heliosphere as elements of a single, connected system.
- This is a landmark mission will image regions beyond the Sun’s outer corona.
- The Sun and the solar wind are one interconnected system, but these have until recently been studied using entirely different technologies and scientific approaches www.buymyhouse7.com.
Significance:
- Other missions such as NASA’s Parker Solar Probe and the ESA-NASA joint project, Solar Orbiter, which is due to be launched in 2020, can study the structures of the Sun’s atmosphere.
- The PUNCH mission enhances these by tracking these structures in real time.
- Since the Sun’s corona is much fainter than its surface layers, it cannot be viewed by the instruments directly.
- So, PUNCH will block out the light from the Sun to view its corona and the structures in it.
- Constellation of satellites:
- PUNCH will consist of a ‘constellation’ of four suitcase-sized microsats that will orbit the Earth in formation and study how the corona, which is the atmosphere of the Sun, connects with the interplanetary medium.
- The mission is expected to be launched in 2022.
WHO GUIDELINES ON SELF-CARE INTERVENTIONS FOR HEALTH
01, Jul 2019
Context:
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) has launched its first guidelines on self-care interventions for health.
More on News:
- The move came in response to the estimate that by 2035 the world will face a shortage of nearly 13 million healthcare workers.
- Currently at least 400 million people worldwide lack access to the most essential health services.
- The guidelines focus on sexual and reproductive health and rights.
- Some of the interventions include self-sampling for human papillomavirus (HPV) and sexually transmitted infections, self-injectable contraceptives, home-based ovulation predictor kits, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) self-testing and self-management of medical abortion.
- These guidelines look at the scientific evidence for health benefits of certain interventions that can be done outside the conventional health care sector.
- However, they do not replace high-quality health services nor are they a shortcut to achieving universal health coverage.
What is Self-Care?
- Self-Care is the ability of individuals, families and communities to promote health, prevent disease, maintain health, and cope with illness and disability with or without the support of a health-care provider.
Significance of Self-Care Intervention:
- Self-care interventions represent a significant push towards new and greater self-efficacy, autonomy and engagement in health for self-carers and caregivers.
- Such interventions could expand access to health services, including for vulnerable populations.
- It gives individuals greater choice of interventions that meets their needs across their lifetime, they will also be able to access, control, and have affordable options to manage their health and well-being.
- WHO noted that self-care is also a means for people who are negatively affected by gender, political, cultural and power dynamics, including those who are forcibly displaced, to have access to sexual and reproductive health services, as many people are unable to make decisions around sexuality and reproduction.
DRAGONFLY MISSION
30, Jun 2019

Why in News?
- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Dragonfly mission, (which will be launched in 2026 and land in 2034) plans to fly a drone copter to Saturn’s largest moon Titan in search of the building blocks of life.
Dragonfly Mission:
- Dragonfly mission will study whether the moon of Saturn (Titan) could now be, or once was, home to life. Dragonfly will fly to dozens of promising locations on Titan looking for prebiotic chemical processes common on both Titan and Earth.
- This will be the first time Nasa will fly a multi-rotor vehicle for science on other planets.
- It will explore diverse environments from organic dunes (hill of loose sand built by the flow of water or air) to the floor of an impact crater where liquid water and complex organic materials (key to life) once existed together (possibly tens of thousands of years).
- The craft will land first at the equatorial “Shangri-La” dune, exploring the region in short trips before building up to longer “leapfrog” flights of five miles (8 kilometres).
- It will investigate the Titan’s atmospheric and surface properties and its subsurface ocean and liquid reservoirs and will also search for chemical evidence of past life.
Titan:
- Titan is the largest moon of Saturn and the second largest moon in our solar system.
- Titan’s atmosphere is made mostly of nitrogen, like Earth’s, but is four times denser.
- Unlike Earth, it has clouds and rain of methane.
- It’s surface pressure is also 50% higher than Earth.
Space Activities Bill
30, Jun 2019

Why in news?
- India has begun pre legislative consultations on a “Space Activities Bill” that is designed to encourage domestic private rocket and satellite companies to offer services for Indian and global customers.
Space Activities Bill, 2017- Provisions:
- The Bill will address the liability issues arising from their space activities, in a suitable/ rational manner, in line with international practices.
- The government first introduced the Bill in 2017.
- The provisions of this Act shall apply to every citizen of India and to all sectors engaged in any space activity in India or outside India
- A non-transferable licence shall be provided by the Central Government to any person carrying out commercial space activity
- The Central Government will formulate the appropriate mechanism for licensing, eligibility criteria, and fees for licence.
- The government will maintain a register of all space objects (any object launched or intended to be launched around the earth) and develop more space activity plans for the country
- It will provide professional and technical support for commercial space activity and regulate the procedures for conduct and operation of space activity
- It will ensure safety requirements and supervise the conduct of every space activity of India and investigate any incident or accident in connection with the operation of a space activity.
- It will share details about the pricing of products created by space activity and technology with any person or any agency in a prescribed manner.
- If any person undertakes any commercial space activity without authorisation they shall be punished with imprisonment up to 3 years or fined more than ₹1 crore or both.
Why reconsider the Bill?
- The current space policy does not cover liabilities for damage to third party space assets although the country is a signatory to the UN Treaties on Outer Space activity.
- The Bill will help formulate necessary rules under the Space Activities Act to deal with damages under the liability provisions and the mode of securing financial guarantee to compensate for damages.
- This bill would address a long-pending concern on covering liabilities in the event of a mishap or damage to spacecraft.
Global opportunities:
- India’s PSLV has emerged as the preferred rocket to hurl small satellites globally.
- India is also working on a small satellite launch vehicle that is designed to tap the global opportunity to carry satellites of less than 50 kg into space.
- The US, France and the EU have legislations that underwrite costs of damage if it exceeds insurance when a private satellite launch goes awry or a rocket hits another object in space.
New Space India Limited (NSIL)
29, Jun 2019

Why in news?
- New Space India Limited (NSIL) has been incorporated as a wholly owned GoI Undertaking/Central Public Sector Enterprise (CPSE).
- Antrix Ltd is another PSU under the Department of Space that acts as an commercial arm of the ISRO
New Space India Limited (NSIL):
- It functions under the administrative control of Department of Space (DOS).
- It aims to commercially exploit the research and development work of ISRO Centres and constituent units of DOS.
- The NSIL would enable Indian Industries to scale up high-technology manufacturing and production base for meeting the growing needs of Indian space programme/
- It would further spur the growth of Indian Industries in the space sector.
Functions of NSIL:
- Small Satellite technology transfer to industry, wherein NSIL will obtain license from DOS/ISRO and sub-license it to industries;
- Manufacture of Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) in collaboration with Private Sector;
- Production of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) through Indian Industry;
- Production and marketing of Space based products and services, including launch and application;
- Transfer of technology developed by ISRO Centres and constituent units of DOS;
- Marketing spin-off technologies and products/services, both in India and abroad
LITCHI AND ACUTE ENCEPHALITIS SYNDROME
26, Jun 2019

- Litchi is being most commonly blamed for the Acute Encephalitis Syndrome (AES) outbreak in Bihar.
- Research paper By Jacob states:
- Its main finding was that this fruit contains a toxin called Methylene cyclo propyl glycine (MCPG).
- But the authors never blamed litchi for AES.
- The causal Factor is Malnutrition and not Litchi.
- The luscious fruit is only a triggering factor for malnourished children as the toxin MCPG can lead to hypoglycaemia (fall in sugar levels).
- So, if a healthy child eats litchi, s/he will not suffer from AES.
How Malnutrition Cause Hypoglycaemia?
- Malnourished children have depleted glycogen store in the liver.
- So if there is no glycogen reserve, the glycogen breaks into glucose.
- When the shortage further increases, even fats start burning. This process produces by products like ketones and amino acids which are neurotoxic.
- So, if a child sleeps without food, this whole physiological process gets completed by wee hours of the day and then the kid gets fever with convulsions and at times s/he loses consciousness.
How does MCPG Interplays with Malnourishment:
- When malnourished kids are exposed to toxins like MCPG present in litchi, which is grown in these months, the chemical triggers hypoglycaemia.
- It’s so much that sugar levels fall up to 30 milligrams per deciliter and sometimes even nil. This leads to complications. The fact that only malnourished children are at risk is also proven by the reasoning that all the vulnerable children belong to the poorest of poor class.
- No child eating litchi, who belongs to a well-to-do family and gets adequate food, suffers from AES.
Why is AES Caused due to Hypoglycaemia so Fatal?
- Most of these deaths are preventable.
- Within four hours of onset of symptoms like convulsions, high fever if a child is administered dextrose (glucose), s/he can be saved.
- Only glucose administration is required. However, most of the patients come from far off villages where the peripheral medical facilities, much against the government’s claims, don’t even have facilities to administer it intravenously.
- They take a lot of time to arrange for conveyance and so the golden time is lost. Only last week, Hospitals saved a child whose glucose level was nil when he was brought to Hospital.
Janani Suraksha Yojana
24, Jun 2019

- Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY) is a safe motherhood intervention under the National Rural Health Mission (NHM).
- It is being implemented with the objective of reducing maternal and infant mortality by promoting institutional delivery among pregnant women.
- The scheme is under implementation in all states and Union Territories (UTs), with a special focus on Low Performing States (LPS).
- It was launched in April 2005 by modifying the National Maternity Benefit Scheme (NMBS).
- The NMBS came into effect in August 1995 as one of the components of the National Social Assistance Programme (NSAP).
- The scheme was transferred from the Ministry of Rural Development to the Department of Health & Family Welfare during the year 2001-02.
Various Measures under JSY:
- The scheme focuses on the poor pregnant woman with special dispensation for States having low institutional delivery rates namely the States of UP, Uttaranchal, Bihar, Jharkhand, MP, Chhattisgarh, Assam, Rajasthan, Orissa and J&K.
- While these States have been named as Low Performing States (LPS), the remaining States have been named as High performing States (HPS).
- Exclusion criteria of age of mother as 19 years or above and up to two children only for home and institutional deliveries under the JSY have been removed.
- Eligible mothers are entitled to JSY benefit regardless of any age and any number of children.
- BPL pregnant women, who prefer to deliver at home, are entitled to a cash assistance of Rs 500 per delivery regardless of age of women and the number of children.
- States are encouraged to accredit private health facilities for increasing the choice of delivery care institutions.
Chikungunya Disease
24, Jun 2019
Context:
- The Institute of Life Sciences (ILS), which functions under the Department of Biotechnology, has entered into a non•exclusive license for product commercialisation after having successfully developed antibodies against the Chikungunya viral (CHIKV) infection.
Symptoms:
- Symptoms usually begin 3–7 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. The most common symptoms are fever and joint pain.
- Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, or rash.
- Chikungunya disease does not often result in death, but the symptoms can be severe and disabling.
- Most patients feel better within a week. In some people, the joint pain may persist for months.
- People at risk for more severe disease include newborns infected around the time of birth, older adults (≥65 years), and people with medical conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart disease.
- Once a person has been infected, he or she is likely to be protected from future infections.
Diagnosis:
- The symptoms of chikungunya are similar to those of dengue and Zika, diseases spread by the same mosquitoes that transmit chikungunya.
- See your healthcare provider if you develop the symptoms described above and have visited an area where chikungunya is found.
- If you have recently traveled, tell your healthcare provider when and where you traveled. Your healthcare provider may order blood tests to look for chikungunya or other similar viruses like dengue and Zika.
Treatment:
- There is no vaccine to prevent or medicine to treat chikungunya virus. Treat the symptoms:
- Get plenty of rest.
- Drink fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Take medicine such as acetaminophen (Tylenol®) or paracetamol to reduce fever and pain.
- Do not take aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS until dengue can be ruled out to reduce the risk of bleeding).
- If you are taking medicine for another medical condition, talk to your healthcare provider before taking additional medication.
- If you have chikungunya, prevent mosquito bites for the first week of your illness.
- During the first week of infection, chikungunya virus can be found in the blood and passed from an infected person to a mosquito through mosquito bites.
- An infected mosquito can then spread the virus to other people.
GROWING HORNS’ WITH PHONE OVERUSE
22, Jun 2019

- New research in biomechanics suggests that young people are developing hornlike spikes at the back of their skulls — bone spurs caused by the forward tilt of the head, which shifts weight from the spine to the muscles at the back of the head, causing bone growth in the connecting tendons and ligaments.
- Smartphones and other handheld devices are contorting the human form, requiring users to bend their heads forward to make sense of what’s happening on the miniature screens.
REGIONAL COOPERATION AGREEMENT ON COMBATING PIRACY AND ARMED ROBBERY AGAINST SHIPS IN ASIA (ReCAAP)
21, Jun 2019

Why in News?
- The Indian Coast Guard (ICG) will be co-hosting an international workshop that aims to deepen knowledge on issues related with piracy and armed robbery, the maritime agency said.
- The two-day workshop has been organised in cooperation with the Regional Cooperation Agreement on Combating Piracy and Armed Robbery against Ships in Asia (ReCAAP) Information Sharing Centre (ISC).
ReCAAP:
- The ReCAAP stands for Regional Cooperation Agreement on Combating Piracy and Armed Robbery against Ships in Asia.
- It is the first regional Government-to-Government agreement to deal with piracy and armed robbery at sea in Asia.
- The ReCAAP Information Sharing Centre (ReCAAP ISC) was established under the Agreement and was officially launched on 29 November 2006 in Singapore.
- Presently, 20 countries are members of the ReCAAP including Australia, US, Japan, China and Bangladesh (Pakistan is not a member).
- India had played an active role in setting up and functioning of the ReCAAP ISC along with Japan and Singapore.
- The Centre has designated the ICG as the focal point within India for the ReCAAP.
PROJECT 75
21, Jun 2019

- Under this project, the Indian Navy intends to acquire Six Diesel-Electric Submarines, which will also feature Advanced Air-Independent Propulsion systems to enable them to stay submerged for longer duration and substantially increase their operational range.
- Project 75 Mazgaon dock ship buliders limited (MDL) will maufacture six Scorpene sub marine for Indian Navy.
- Technology Transfer from Naval Group of France.
Background:
- India’s current arsenal consists of 14 conventional submarines and two nuclear- powered submarines.
- The P75I project is part of a 30-year submarine building plan that ends in 2030.
- As part of this plan, India was to build 24 submarines — 18 conventional submarines and six nuclear-powered submarines (SSNs) — as an effective deterrent against China and Pakistan.
- The first Scorpene submarine INS Kalvari under P75 was launched in October 2015.
- The third in Scorpene series INS Karanj was launched in January 2019. The fifth Scorpene-class submarine INS Vagir and sixth Scorpene-class submarine INS Vagsheer.
AWARE: A WHO TOOL FOR SAFER USE OF ANTIBIOTICS
21, Jun 2019

Context:
- This is the World Health Organisation’s (WHO) prescription to combat the growing menace of antibiotic abuse and burgeoning resistance worldwide.
About:
- WHO has suggested the adoption of ‘Access, Watch and Reserve’,
- An approach that specifies which antibiotics to use for the most common and serious infections,
- which ones ought to be available at all times in the healthcare system, and those that must be used sparingly, or reserved and used only as a last resort.
AWARE Tool:
Antimicrobial Resistance:
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) is the ability of a microbe to resist the effects of medication that once could successfully treat the microbe
- The term antibiotic resistance is a subset of AMR, as it applies only to bacteria becoming resistant to antibiotics.
- Antibiotics are medicines used to prevent and treat bacterial infections. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria change in response to the use of these medicines.
- Bacteria, not humans or animals, become antibiotic-resistant.
- These bacteria may infect humans and animals, and the infections they cause are harder to treat than those caused by non-resistant bacteria.
- Antibiotic resistance occurs naturally, but misuse of antibiotics in humans and animals is accelerating the process.
- A growing number of infections – such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, gonorrhoea, and salmonellosis – are becoming harder to treat as the antibiotics used to treat them become less effective.
- It leads to higher medical costs, prolonged hospital stays, and increased mortality.
Prevention and Control:
- Antibiotic resistance is accelerated by the Misuse and overuse of Antibiotics, as well as poor infection prevention and control.
- In India, the Health Ministry has made it mandatory to display a 5mm •thick red vertical band on the packaging of prescription • only
drugs to sensitize people to be cautious while buying these medicines that are widely sold without prescriptions.
Way Ahead:
- There is need to sensitize health professional including Doctors, Pharmacist regarding menace that antibiotic can cause.
- The allied medicinal practitioner such BAMS, BHMS and other doctors who are spread at grass root level prescribes antibiotics rampantly, should be regulated.
- BAMS, BHMS and other allied medicinal practitioner must not be allowed to prescribe Higher antibiotics.
Mendeleev and his Periodic Table of Elements
18, Jun 2019
The Modern Periodic Table:
- The periodic table is an arrangement of all the elements known to man in accordance with their increasing atomic number and recurring chemical properties.
- They are assorted in a tabular arrangement wherein a row is a period and a column is a group. Until 1863, the world was aware of only 56 known elements.
- The rate of scientific progress was such that every year, a new element was being discovered. It was during this time that Mendeleev came up with the idea of the Periodic Table.
- He published the Periodic Table in his book– The Relation between the Properties and Atomic Weights of the Elements.
- Mendeleev said that he arrived at the idea in his dream, where he saw all chemical elements falling into place on a table according to their chemical properties.
- Mendeleev had found a definitive pattern following which, each element could be placed according to their atomic weight.
- He had also predicted the qualities of the ‘missing’ (yet to be discovered) elements and gave them Sanskrit names.
Evolution of the Table:
- The noble gases including helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn) were added to the table between 1895 and 1901.
- Likewise, additions have been made to the periodic table as new elements have been discovered in the last hundred years.
- In 1914, English physicist Henry Gwyn-Jeffries Moseley found out that each atomic nucleus can be assigned a number, according to the number of protons in that atom. This changed the way the periodic table worked. The table was redesigned according to the atomic number of elements rather than their atomic weight. Rare-earth elements, including the elements in the Lanthanide series, were included in the atomic table in the late 19th century.
BT BRINJAL
18, Jun 2019

- Bacillus Thuringiensis Brinjal, popularly known as Bt brinjal is a type of Genetically Modified crop.
- Bt brinjal, a genetically modified strain created by inserting Cry 1Ac gene from the soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis into Brinjal.
- It gives resistance against Lepidopteron insects like brinjal fruit and shoot borer and fruit borer. Mechanism- ingestion
- of Bt toxin by insect there is disruption of digestive process resulting in death of insect.
Concern:
- Potential health effects.
- terminator seed- i.e. farmer will be compel to buy seed from the company every time.
Genetically Modified Crop:
- It Involves inserting DNA into Genome of an organism
- UPSC question on Genetic Modified Crops- 2018.
ENCEPHALITIS.
16, Jun 2019
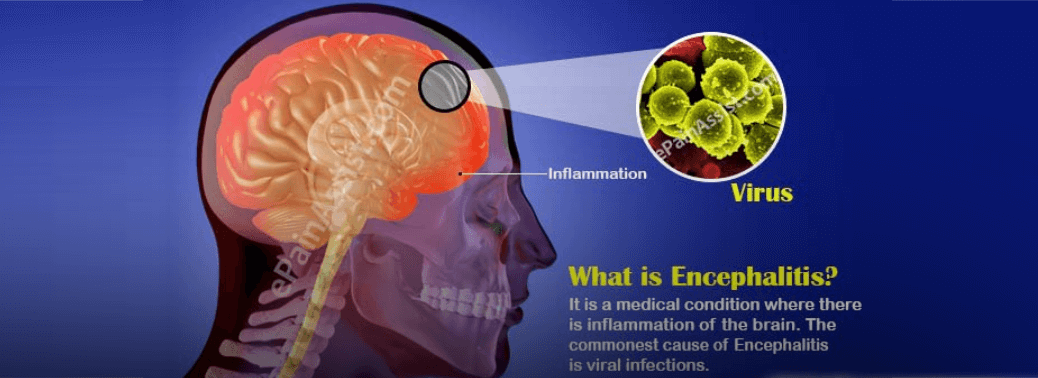
Context-:
- Death toll of children rosed to 69 in Bihar due to Acute Encephalitis Syndrome.
- UPSC questions based on Disease- Cause, Symptoms, Vaccine if any, disease carrier, Govt scheme.
- Recent question UPSC prelims- Hepatitis, Zika virus, Dengue.
About:
- Onset of fever and clinical neurological manifestation that includes mental confusion, disorientation, delirium, or coma.
- Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) is the major cause of AES in India
- Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) is a flavivirus related to dengue, yellow fever and West Nile viruses, and is spread by mosquitoes. Nipah virus, Zika virus are also found as causative agents for AES.
Treatment:
- There is no antiviral treatment for patients with JE.
- Treatment is supportive to relieve symptoms and stabilize the patient.
Vaccine on Japanese Encephalitis:
- Indigenously developed Vaccine by India
- The vaccine has been jointly developed by scientists of National Institute of Virology (NIV), Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and Bharat Biotech Ltd.
Scope of Disease:
- It predominantly affects population below 15 years.
- There is seasonal and geographical variation in the causative organism.
- JEV has its endemic zones running along the Gangetic plane including states of UP (east), Bihar, West Bengal and Assam, and parts of Tamil Nadu.
- Government Action- Japanese Encephalitis is part of disease covered under Mission Indradhanush India’s Universal Immunization Programme (UIP).
Mains Perspective:
- What are government measures regarding controlling spread of Encephalitis in country and what further need to be done
- Hints:
- Preventive Measure
- Disease is usually controlled only after the arrival of monsoon rains.
ACUTE ENCEPHALITIS SYNDROME
15, Jun 2019
Context:
- Bihar has recorded 188 cases of acute encephalitis syndrome, with 45 deaths, since January. The cause of death in most this year has been attributed to hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar level).
What is Acute Encephalitis Syndrome (AES)?
- -AES affects central nervous system, mostly in children and young adults.
- -It starts with high fever,then hampers neurological functions causing mental disorientation, seizure, confusion, delirium, coma.
- The disease outbreak is usually reported during monsoons (June- October). But the incidence is also reported during April-June in Bihar.
- Locally known as Chamki Bukhar in the state.
What Causes AES?
- It can be caused by virus, bacteria, fungi, and a range of agents.
- Japanese encephalitis (JE) virus is the most common cause of AES in India, with union health ministry estimate attributing 5-35 per cent cases due to JE.
- But the syndrome is also caused by scrub typhus, dengue, mumps, measles, even Nipah or Zika virus.
- In several cases though the cause of AES remains clinically unidentified.
Status of AES in India:
- -According to National Vector Borne Diseases Control Programme (NVBDCP), 10,485 AES cases were diagnosed in 2018 with 632 deaths across 17 states.
- India records fatality rate at 6 per cent in AES, but the fatality rises to 25 per cent amongst children.
- Bihar, Assam, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Tripura are worst affected.
Relation between hypoglycaemia, children and AES:
- Bihar government officials claim AES is a syndrome not disease, and cause of death in these children was found to be prolonged hypoglycaemia that witnessed delayed treatment. In 2014 research paper titled ‘Epidemiology of Acute Encephalitis Syndrome in India: Changing Paradigm and Implication for Controlʼ, co-authored by six researchers, a parallel was drawn between
- Muzaffarpur and Vietnamʼs Bac Giang province where undernourished.
- Children were suffering from AES and hypoglycaemia that coincided with litchi orchards in neighbourhood.
- “The possible association with some toxin in litchi or in environment need to be documented. Methylene cyclopropyl glycine (MCPG) which has been known to be a content of litchi fruit has been shown to cause hypoglycaemia in experimental animals,” the study stated. Several children in Muzaffarpur who suffer from AES before 2014 have a history of visit to litchi orchards, the study found.
- The impact is worse on undernourished children who remain hungry for several hours.
INDIA TO HAVE ITS OWN SPACE STATION: ISRO
14, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- The project report on setting up a space station will be submitted to the government after the Gaganyaan mission.
Background:
- India plans to have its own space station, and modalities for it will be worked out after the first manned mission, Gaganyaan.
- The proposed space station is envisaged to weigh 20 tonnes and serve as a facility where astronauts can stay for 15-20 days, and it would be placed in an orbit 400 km above earth.
- The time frame for launch is 5-7 years after Gaganyaan.
About Gaganyan Progress:
- The project was on track to be realised by the 75th Independence Day or even earlier.
- The ISRO would also join the international space community for a manned mission to moon and beyond.
- “Cost approved by the Union Cabinet just before the Model Code of Conduct came into force was ₹10,000 crore,” Dr. Singh said.
- A Gaganyaan National Advisory Council has been created with members from different institutions and industries to oversee and advise on the mission.
- Selection of 2-3 crew members for Gaganyaan would be done in six months, and they would then undergo training for 1-1.5 years after that.
- The initial phase of training would be in India and the advanced stage would be done abroad as the requisite facilities did not exist here and the project was on a short timeline, Dr. Sivan said. A GSLV Mk-III launch vehicle would be used to launch the Gaganyaan. Prior to that, two unmanned missions would be undertaken, one in December next year and the second, six months after that.
- The Gagayaan mission aims to send a 2-3-person crew to space for a period of seven days.
- The spacecraft would be placed in a low earth orbit of 300-400 km.
- ISRO had already signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Indian Air Force for selection and training of pilots for the manned mission.
- Talks were underway with the Navy and Coast Guard for the recovery of the crew module once it lands in water after re-entry into the earth’s atmosphere, Dr. Sivan said.
Other Mission:
- After Chandrayaan-2, ISRO has set its sights on two interplanetary missions.
- Mission Aditya-L1 is scheduled for next year to study the Sun’s corona, which effects climate on earth, and another mission to study Venus in 2-3 years
CHANDRAYAAN-2 SET TO TAKE OFF ON 15th JULY
13, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Chandrayaan-2, India’s second Moon mission, will be launched on July 15, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
Background:
- ISRO on Wednesday unveiled plans for its second unmanned mission to the moon, in what would be another milestone in the country’s space exploration programme.
- The announcement by Isro comes almost 11 years.
About Chandrayan 2:
- Chandrayaan-2 will have three modules, Orbiter, Lander (Vikram), and Rover (Pragyan). These are designed to carry out various experiments, including mapping of the surface, minerals, chemical composition, detection sparse water molecules above the lunar surface and rock formations.
- The spacecraft, with an estimated weight of 3.8 tonnes, will attempt a soft landing on the moon, adding to the complexity of the mission.
- If successful, India will join the US, the former Soviet Union, and China—the only three other nations to have achieved the feat so far.
- Chandrayaan-2 is expected to take a total of 58 days post launch in various stages of orbit for the modules to reach the moon and an additional four days to land near the south polar region. Isro will use the same strategy as Chandrayaan-1 for this mission but the soft landing will be a new attempt.
- It will take 15 minutes to land and is going to be the most terrifying moment because this is a flight Isro has never undertaken.
- The lunar landing is expected to take place on 6 or 7 September on the unexplored south polar region of the moon—a first for any country—which has the possibility of the presence of water in permanently shadowed areas as well as craters that are cold traps that contain the fossil record of the early solar system.
About:
- Chandrayaan-2 will carry a total of 13 payloads, including eight on the Orbiter, three on the Lander, two on the Rover, as well as one passive experiment from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration of the US.
- The Orbiter will continue its task while the Rover comes out of the Lander after it has landed on the Lunar surface.
- The entire lifecycle of the Lander and Rover will be one lunar day, which is equivalent to 14 earth days while the Orbiter will continue for one year.
- The Orbiter and Lander will be able to communicate with Earth directly, while the Rover will share information, images and data to the Lander which in turn will share it with Isro.
The mission was supported by more than 500 academic institutions and 120 industries that contributed 60% of the ₹603 crore cost of Chandrayaan-2 and 80% of the ₹375 crore cost of the Geosynchronous Launch Vehicle-Mark III.
PNEUMOCOCCAL VACCINATION LAUNCHED
13, Jun 2019
Why in News:
- It will help babies with low birth weight and reduce Infant Mortality Rate.
Background:
- In a step towards reducing Infant Mortality Rate, the State has rolled out a pneumococcal vaccination programme. “Babies weighing less than 1.5 kg are admitted to SNCUs.Post- discharge, some of them develop respiratory infection and pneumonia and die in two or three months. One of the common causes of infant mortality is respiratory tract infection and pneumonia. In fact, pneumonia still tops the list for under-five mortality,” Neonatal Intensive Care Unit, and registrar of Institute of Child Health.
- It was to prevent pneumonia and meningitis that an initiative to offer pneumococcal vaccination
Pneumococcal Vaccination:
- To cover babies with very low birth weight and discharged from Special Newborn Care Units (SNCU) in medical college hospitals, district headquarters hospitals and sub-district hospitals. The recommended schedule: first dose at six weeks, second dose at 10 weeks, and third at 14 weeks, and a booster dose at 15 months.
- The vaccines were made available through the Tamil Nadu Medical Services Commission On an average, 490 to 530 babies are admitted to our Neonatal Intensive Care Unit every month. Of this, 30 to 40% are pre-term. These are high risk babies and are prone to infections. Vaccination would provide good protection to them against pneumonia, pneumococcal meningitis, sinusitis and ear discharge.
A NON-FLOWER, BUT JUST AS BRIGHT FOR INSECTS
13, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Bengaluru researchers use art to study pollinators, show results at London’s Victoria and Albert Museum.
Background:
- Researchers from the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) here, who have co- published a study on why pollinators prefer some flowers over others, are turning to art to take their inquiry further.
- Recent studies point to an alarming decline in insect populations, making the study important. The scientists have teamed up with the Thomas Pausz Studio in an ‘art-as- science’ project that utilises art and design knowledge.
- This will help them develop better ways to attract dwindling pollinator populations.
- Their work is currently on display at the Victoria and Albert Museum (V&A) in London.
Colour or shape?
- Highly prolific pollinators found on every continent except Antarctica. Researchers replicated cues from flowers — colour, shape, size, odour — in the form of artificial flower lures.
- The team found some lures were attractive to hoverflies only in certain environments, but there was one flower lure that was attractive everywhere.
- “This was exciting as it suggested the possibility of a universal lure. We didn’t know which
cues were important – colour, odour, shape, or more,” she said. - The researchers approached artist Thomas Pausz at Srishti Institute of Art, Design and Technology to create the non-flower.
- To translate ideas, they used paper, films and UV light. The result is six ‘non-flower’ artefacts on show at the V&A alongside Virtual Reality films based on fractal geometries.
- “The structures echo scientists’ findings — pollinators prefer flowers with many edges,” said Mr. Pausz.. The actual artefacts were realised using a 3D printing machine
NEED FOR A LEGAL FRAMEWORK FOR AI IN INDIA
12, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Artificial Intelligence-/AI-driven tech will become counterproductive if a legal framework is not devised to regulate it.
What are the recent developments?
- Recently, the Kerala police inducted a robot for police work.
- Around the same time, Chennai got its second robot-themed restaurant.
- Here, robots not only serve as waiters but also interact with customers in English and Tamil. In Ahmedabad, a cardiologist performed the world’s first in-human telerobotic coronary intervention on a patient nearly 32 km away.
- All these examples symbolise the arrival of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in everyday lives of human beings.
What are the global measures in this regard?
- Only recently, there has been interest across the world to develop a law on smart technologies.
- In the U.S., discussions are being taken up about regulation of AI.
- Germany has come up with ethical rules for autonomous vehicles.
- It stipulates that human life should always have priority over property or animal life.
- China, Japan and Korea are following Germany in developing a law on self-driven cars.
What is the need now in India?
- Traffic accidents lead to about 400 deaths a day in India, 90% of which are caused by preventable human errors.
- Autonomous vehicles that rely on AI can reduce this significantly, through smart warnings and preventive and defensive techniques.
- Patients dying due to non-availability of specialised doctors can be prevented with AI reducing the distance between patients and doctors.
- AI has several positive applications, as seen in the above examples.
- AI systems have the capability to learn from experience and to perform autonomously for humans.
- This also makes AI the most disruptive and self-transformative technology of the 21st century. So, if AI is not regulated properly, it is bound to have unmanageable implications.
- E.g. the consequence if electricity supply suddenly stops while a robot is performing a surgery and access to a doctor is lost
These questions have already confronted courts in the U.S. and Germany. - All countries, including India, need to be legally prepared to face such kind of disruptive technology.
What are the challenges involved?
- Predicting and analysing legal issues in regards with AI use and their solutions are not that simple. E.g. an AI-based driverless car getting into an accident that causes harm to humans or damages property. In such cases, criminal law may face drastic challenges as the party to be held liable is disputable.
How is the AI policy progress in India?
- In India, NITI Aayog released a policy paper, ‘National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence’, in June 2018.
- The paper considered the importance of AI in different sectors.
- The Budget 2019 also proposed to launch a national programme on AI.
- But notably, all these developments are taking place on the technological front.
- No comprehensive legislation to regulate this growing industry has been formulated in India till date.
- What should the priorities be?
- The first need is to have a legal definition of AI in place.
- It is essential to establish the legal personality of AI which means AI will have a bundle of rights and obligations, in the context of India’s criminal law jurisprudence.
- Since AI is considered to be inanimate,a liability scheme that holds the producer or manufacturer of the product liable for harm must be considered.
- Moreover, since privacy is a fundamental right, certain rules to regulate the usage of data possessed by an AI entity should be framed.
- This should be a part of the Personal Data Protection Bill, 2018.
ISRO GEARS UP FOR CHANDRAYAAN-2 MISSION
09, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Chandrayaan-2, the country’s first moon lander and rover mission, is a month away.
Background:
- Chandrayaan-2 lander is named Vikram (meaning valour, after the father of the Indian space programme, Vikram Sarabhai). It will release a small robotic rover, named Pragyan (wisdom), to move around, feel and understand the lunar surface.
Chandrayaan II:
- Chandrayaan II is India’s second lunar mission after Chandrayaan I. The mission includes a lunar orbiter, rover and a lander. The mission is developed by ISRO, India. Initially, the lander was supposed to have
been developed by Russia. But, when Russia cited its inability to provide the lander by 2015, India decided to go solo. Now, the mission is entirely Indian. It is slated to launch by January 2019. The launch vehicle would be a GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III). - The mission is attempting to soft-land on the moon’s surface at a latitude of about 70° south, that would be on a high plain in between 2 craters. If successful, this would be the first mission to land near the lunar south pole.
- Details of Chandrayaan II mission:
- Launch vehicle: GSLV Mk III
- Lift off mass (approx.): 3,890 kg
- Launch from: Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh
- Orbiter: It will orbit the moon at a distance of 100 km from the lunar surface. Payloads on the orbiter are: Large Area Soft X-ray Spectrometer, L and S band Synthetic Aperture Radar, Imaging IR Spectrometer, Neutral Mass Spectrometer and Terrain Mapping Camera-2. The structure of the orbiter was manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- Lander: The lander has been named Vikram after scientist Vikram Sarabhai. The lander will detach from the orbiter, descend to a lunar orbit, before attempting to land on the surface. It will make a soft-landing and deploy the rover. It will also perform some scientific activities for about 15 days. Payloads on the lander are: seismometer, thermal probe, Langmuir probe and radio occultation.
- Rover: The 27 kg rover will operate on solar power. It will move on six wheels and conduct chemical analyses on-site. It will then transmit the data to the orbiter which will send this data back to the earth station. The rover payloads include Laser induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS) and Alpha Particle Induced X-ray Spectroscope (APIXS).
SPACE STATION WILL BE OPEN TO TOURISTS FROM NEXT YEAR
09, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- NASA will open up the International Space Station for tourism and other business ventures as of next year, as it seeks to financially disengage from the orbiting research lab.
More in News:
- NASA will allow private citizens to stay at the International Space Station (ISS) for month- long getaways.
What’s the deal?
- NASA will allow two private astronaut missions of up to 30 days per year.
- A return ticket will cost around $58 million (€51.2 million).
- Astronauts will also have to pay board and lodgings at a rate of around $35,000 per night.
- It paves the way for private citizens to travel to the ISS aboard rocket-and-capsule launch
systems being developed by Boeing Co and Elon Musk’s SpaceX. - To qualify as a passenger, Private astronauts will have to meet the same medical standards and training and certification procedures as regular crew members.
- SpaceX and Boeing will choose the clients and deliver them to the ISS via their own rocket- and-capsule launch systems.
- The new space tourists to the ISS will not be the first: U.S. businessman Dennis Tito had that honour in 2001. He paid Russia around $20 million for the trip.
Why is NASA doing this?
- NASA said it wasn’t looking to make a profit from the trips, but the money raised would help towards achieving long-term goals. These include returning humans to the moon by 2024 and even sending them to Mars after that.
- The shift reverses a long-standing prohibition against tourists and private interests at the orbiting research lab, and reflects a broader push to expand commercial activities at the ISS and in space more generally.
International Space Station:
- The International Space Station (ISS) is a space station, or a habitable artificial satellite, in low Earth orbit.
- The space station orbits around 400 kilometers above the Earth.
- It is run by five space agencies with 15 countries involved. The space station does not belong to NASA. It was built along with Russia starting in 1998, and other countries participate in the mission and send up astronauts.
- But the U.S. has paid for and controls most of the modules that make up the orbiter.
- Since 2000, it has been staffed by a crew of between three and six astronauts.
INDIA TEST FIRES BRAHMOS SUPERSONIC CRUISE MISSILE FROM CHANDIPUR IN ODISHA
07, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Supersonic cruise missile BrahMos was test fired from the Integrated Test Range (ITR) at Chandipur in Odisha.
- Anti-ship version of the missile launched by complex-3 of the ITR, Defence Research and Development (DRDO) sources.
- World’s fastest supersonic cruise missile with high rate of accuracy
Missile is fired from land, sea and air. - The missile with a strike range of around 290 km is a strategic asset for India which act as a deterrence against any possible threats from China and Pakistan.
- BrahMos is a joint venture between the DRDO and the NPOM (a Russian military technology firm) of Russia.
- BrahMos operationalised in the Indian Army, Indian Navy and Indian Air Force.
- Senior defence officials and scientists from DRDO and BrahMos witnessed the trial.
Background:
- Origin and history of Brahmos
- It brings a supersonic speed when it is separated. At the second stage then takes the missile closer to 3 Mach speed in cruise phase.
- Stealth technology and guidance system with advanced embedded software provides the missile an extraordinary performance
- Type: Cruise missile; Air-launched cruise missile. Variants: Ship-launched; Surface-launched.
- Manufacturer: BrahMos Aerospace Limited
- Place of origin: India / Russia
- About Brahmos
- Speed: Mach 2.8–Mach 3
- Unit cost: US$2.73 million
- Place of origin: India / Russia
- Manufacturer: BrahMos Aerospace Limited
NIPAH VIRUS CASE IN KERALA
07, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- A youth from Ernakulam district in Kerala has tested positive for the Nipah virus infection (a year after a similar outbreak in Kerala had claimed 17 lives).
What is the Nipah virus infection?
- Cause – The natural host of the Nipah virus are fruit bats of the Pteropodidae family and Pteropous genus, widely found in South and South East Asia.
- However, the actual source of the current infection is not yet known.
- Scientists are currently working on finding the epidemiological link of the outbreak. Transmission – The infection is generally transmitted from animals to human beings, mainly from bats and pigs.
- Human-to-human transmission is also possible, and so is transmission from contaminated food.
- Effect – Nipah virus causes a so far incurable infection in human beings, which can sometimes be fatal.
- Patients either show no symptoms of the infection (asymptomatic infections), thereby making it difficult to detect.
- Otherwise, patients develop acute respiratory problems, or encephalitis that often becomes fatal. The World Health Organization (WHO) says the infection has been found to be fatal in 40% to 75% of the infected patients. There is no treatment available as of now, either for humans or animals, nor any vaccine.
What are the previous incidents of infection?
- Nipah virus infections were first identified in 1999 in Malaysia.
- From then on infections have been detected quite frequently in Bangladesh.
- Kerala – There have been a few incidents of infection in India earlier, apart from the 2018 outbreak in Kerala.
- The 2018 outbreak was confined to two districts of Kerala, Kozhikode and Malappuram. Studies have revealed that a particular kind of fruit bat, Pteropus spp, was most likely the source of human infection in 2018.
- Research suggested that this particular strain might have been circulating in the local bat population. The newly detected case in Kerala is believed to have actually been a result of intensified preventive and containment efforts after last year’s outbreak.
- The increased awareness and vigilance in the community has helped in early detection this time. Elsewhere in India – The first outbreak was in 2001 in Siliguri, West Bengal.
- More than 30 people were hospitalised with suspected infection then.
- Another outbreak happened in 2007 in Nadia of West Bengal, with over 30 cases of fever with acute respiratory distress and/or neurological symptoms.
- Notably, five of them turned out to be fatal.
Who are Potentially at Risk?
- Transmission to 18 contacts last year and the two health-care workers this year has been only through the human-to-human route.
- As of now, the current outbreak is likely localised, like last year’s.
- More people showing symptoms are being screened and so are people in physical contact with them.
- Those with exposure to body fluids (saliva, urine, sputum) of infected patients had higher risk for asymptomatic infections, than those who only had physical contact with the infected patients.
What are the measures taken?
- The National Institute of Virology (NIV) advised extreme care for healthcare workers and caregivers.
- These include providing double gloves, fluid-resistant gown, goggles, face shields, closed shoes and similar other protective gear.
- Currently, steps are being taken to prevent the spread of the disease by tracing the contacts, setting up isolation wards and public engagement.
What is the Way Forward?
- Containing the spread of the Nipah virus is important as the mortality rate was 89% last year. The recurrence of the infection possibly suggests that the virus is in circulation in fruit bats. Analysing the evolutionary relationships, a study found 99.7-100% similarity between the virus in humans and bats.
- The confirmation of the source and the recurrence mean that Kerala must be alert to the possibility of frequent outbreaks. It is high time that the state takes continuous monitoring and surveillance for the virus in fruit bats. One reason for the failure in not doing so till now could be the absence of a public health protection agency. The government has been in the process of formulating it for over 5 years now, to track such infective agents before they strike. The state should also equip the Institute of Advanced Virology in Thiruvananthapuram to undertake testing of dangerous pathogens.
CHINA LAUNCHES ITS FIRST SEA-BASED SPACE ROCKET
06, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- China successfully launched a rocket from a mobile platform at the Yellow Sea for the first time on Wednesday, sending two technology experiment satellites and five commercial satellites into space.
Background:
- A Long March-11 solid propellant carrier rocket blasted off from a launch pad aboard a ship in the Yellow Sea off the coast of Shandong province
- It is China’s first space launch from a sea-based platform and the 306th mission of the Long March carrier rocket series, official media in Beijing reported.
- The two satellites, developed by China Academy of Space Technology, are expected to step up all-weather monitoring of ocean wind fields and improve typhoon monitoring and accuracy of the weather forecast in China.
- Among the five commercial satellites, the two satellites, developed by China Electronics
Technology Group Corporation, are China’s first small satellite system based on Ka-band.
Advantage of Ocean-based platform launch
- Launching a carrier rocket from an ocean-based platform has many advantages over a land launch.
- The closer to the equator a rocket launch can get, the greater the speed boost it will receive. It reduces the amount of energy required to get into space and means that less fuel is required, state-run Xinhua news agency reported.
- The launch site is flexible and falling rocket remains to pose less danger.
- Using civilian ships to launch rockets at sea would lower launch costs and give it a commercial edge.
Other Advantage:
- The seaborne launch technology will meet the growing launch demand of low inclination satellites and help China provide launch services for countries participating in the Belt and Road Initiative, Xinhua quoted Chinese experts as saying.
- With sea launches, China now has the ability to deploy satellites from a mobile platform. China now spends more than Russia and Japan on its civil and military space programmes. It also unveiled ambitious plans to build a research base on the lunar surface, send a probe to Mars and build a space station in Earth orbit.
Long March-11
- The Long March-11, developed by China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, is the
only rocket using solid propellants among China’s new generation carrier rockets. - It is mainly used to carry small satellites and can take multiple satellites into orbit at the same time, the report said.
NIPAH IS CONFIRMED, PRECAUTIONS IN PLACE
05, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Nearly a year after a Nipah outbreak in Kozhikode and Malappuram, the deadly disease has resurfaced in Kerala with the confirmation of the infection.
Details:
- The test results have come from the National Institute of Virology (NIV), Pune, and it is positive for Nipah.
- The health authorities have made elaborate arrangements and medicines are in stock.
- The Health Ministry said the team, comprising an epidemiologist, had been sent to the State to conduct contact tracing for early detection of suspects and review of isolation facilities.
What is Nipah Virus?
- According to WHO, the Nipah virus infection is a newly emerging zoonosis, that is, a disease transmitted from animals to humans. The virus belongs to a new genus termed Henipavirus (subfamily Paramyxovirinae).
- The natural host of the virus are fruit bats belonging to the family Pteropodidae. In 2004, humans were affected after eating the date palm contaminated by infected fruit bats. Pigs can also act as intermediate hosts.
What are the symptoms in humans?
- The symptoms of Nipah are similar to that of influenza: fever, muscle pain, and respiratory problems.
- Inflammation of the brain can also cause disorientation. Late onset of Encephalitis can also occur. Sometimes a person can have an asymptomatic infection, and be a carrier of Nipah and not show any symptoms.
Are there Any Vaccines?
- Currently, there are no vaccines for both humans and animals. Intensive supportive care is given to humans infected by Nipah virus.
- According to WHO, ribavirin can reduce the symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and convulsions associated with the disease.
- Individuals infected need to be hospitalised and isolated. Special care should be taken to prevent human-to-human transmission. Surveillance systems should be established to detect the virus quickly and to initiate appropriate control measures.
AN-32 WITH 13 ONBOARD MISSING OVER ARUNACHAL PRADESH
04, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Indian Air Force’s AN-32 transport aircraft goes missing after taking off from Jorhat in Assam. The airborne aircraft had total 13 people on board in Assam. The airborne aircraft had total 13 people on board including eight aircrew and five passengers.
Details:
- AN-32 aircraft got airborne on 3 June from Jorhat at 12:27 p.m. for Mechuka Advanced Landing
Ground (only 29 kms from the China border), in Mechuka Valley in West Siang District of Arunachal Pradesh. It last contacted ground agencies at around 1:00 p.m. after that there has been was no contact with the aircraft. Since the aircraft lost the contact and did not reach the destination also Indian Air Force initiated overdue actions.
Search Operation:
- C 130J Super Hercules aircraft, AN-32 military transport aircraft, two Mi-17 (medium twin-turbine transport helicopter) of Indian Aiir Force (IAF) and ALH (Advanced Light Helicopters) helicopter of Indian Army were launched to locate the missing aircraft.
- Helicopters were routed to the location after some ground reports were received about possible location of a crash site however no wreckage has been sighted so far.
- IAF is in continuous coordination with Indian Army and with various government and civil agencies to locate the missing aircraft. The Search operation to locate the missing IAF AN- 32 aircraft is underway with operation from air by IAF and by ground parties of Indian Army and the Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP).
AN-32:
- It is a tactical transport aircraft and is an extensive used by Indian Air Force (IAF).
- It has been in service since 1984 and has been a trustworthy workhorse for the IAF for many years.
Specification:
- As the service ceiling of Antonov An-32 turboprop aircraft is 31,000ft so it flies lower and slower with a cruising speed of 470 kmph than most commercial jetliners which have a service ceiling of 40,000ft, thus this gives lesser room for the An-32 to outrun bad weather or climb over it.
IMMUNOTHERAPY BOOSTS SURVIVAL CHANCES FOR LUNG CANCER PATIENTS
03, Jun 2019
Why in News:
- An immunotherapy treatment helped significantly boost survival rates among patients suffering from advanced lung cancer, according to the results of a clinical trial cited by researchers.
Details:
- Almost 25% of patients who received the drug Pembrolizumab and had not previously received chemotherapy were alive after five years. The figure dropped to just over 15% for patients who had previously received chemotherapy. Unlike chemotherapy, immunotherapy works by leveraging the body’s own immune system to fight disease.
More effective T-cells
- The drug acts by turning off a brake in the immune system, a protein called PD-1, which then allows cancer-fighting T-cells to attack faster and more effectively.
- Moving forward, team would like to identify other biomarkers to further improve survival rates.
Biomarker
- A biomarker is a measurable indicator of the severity or presence of some disease state.
- More generally a biomarker is anything that can be used as an indicator of a particular disease state or some other physiological state of an organism.
FACEBOOK PLANS TO LAUNCH ‘GLOBALCOIN’
02, Jun 2019
Why in News?
- • Facebook plans to launch its cryptocurrency ‘GlobalCoin’ by the first quarter of 2020.
- • The company is expected to reveal more details about the currency before testing begins
later in 2019.
Highlights:
- • The currency, which is being referred to internally as ‘GlobalCoin’, will reportedly be available in around a dozen countries at launch, where it’s expected to offer people affordable and secure payments without the need for a bank account.
- • The currency will need to overcome numerous technical and regulatory hurdles before it can be launched.
- • Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg met with the Bank of England’s governor Mark Carney to discuss the opportunities and risks of the planned digital currency.
- • However, Facebook might have a harder job on its hands in India, which has taken a hostile attitude towards virtual currencies.
- • India is reported to be a key focus for the new currency, where Facebook hopes it will allow Indian workers abroad to send money back home to their families using WhatsApp.
What is a Cryptocurrency?
- • A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security.
- • A cryptocurrency is difficult to counterfeit because of this security feature.
- • It is not issued by any central authority, rendering it theoretically immune to government interference or manipulation.
- • The first blockchain-based cryptocurrency was Bitcoin, which still remains the most popular and most valuable.
• Today, there are thousands of alternate cryptocurrencies with various functions or specifications.
USING GENES TO UNDERSTAND RICE BLAST DISEASE RESISTANCE IN INDIAN RICE VARIETIES
02, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Researchers from ICAR-National Rice Research Institute (NRRI), Odisha have mapped out the diverse genes in rice that help in disease resistance.
Details:
- Rice blast, caused by a fungus Magnaporthe oryzae, is one of the major diseases of the rice crop. By characterising over 150 rice varieties from nine States across the country they also identified new markers associated with blast resistance.
Blast endemics:
- From 1980-1987, seven blast endemics have occurred in India causing severe losses.
- Fungicides are very expensive, harmful for the environment and inappropriate application can cause health issues. So researchers around the globe have been on a hunt for resistant genes against the pathogen and so far, more than 100 resistance (R) genes in the rice genome have been identified. The rapid changes in pathogen virulence pose a constant challenge to the success of existing blast-resistant rice varieties. Therefore, there is always a need to identify new broad-spectrum blast resistant genes/alleles in rice germplasm such as landraces, wild rice, etc,” The present study showed that the rice landraces collected from north-eastern states of India had the highest resistance.
Gene hunt
- Specific DNA markers were used for accurate identification of specific resistant genes.
- The landraces from Tripura had the highest number of resistant genes, followed by those from Maharashtra. The study also pointed out that rice varieties in the same ecological conditions can have different resistant/susceptible behaviours. The identified associated marker could be used for the selection of parental materials for the improvement of existing varieties with blast resistance.
ICAR:
- ICAR is an autonomous body responsible for co-ordinating agricultural education and research in India.
- It is the largest network of agricultural research and education institutes in the world.
- Earlier known as Imperial Council of Agricultural Research, it was established on 16 July 1929 as a registered society under the Societies Registration Act, 1860 in pursuance of the report of the Royal Commission on Agriculture.
TAWANG YIELDS A NEW SPECIES OF DUNG BEETLE
02, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- A new species of dung beetle has been discovered in Tawang district of Arunachal Pradesh.
Details:
- The species, Enoplotrupes tawangensis, is shining dark blue in colour and, measuring up to 27 mm, is relatively bigger than most of the dung beetles.
- Dung beetles belong to the super family scarabaeoidea, having clubbed antennae and pro- tibiae (pro-legs) modified for burrowing dung inside the soil.
- This group of insects are considered beneficial to the environment as they help in nutrient cycling of the soil. Often referred to as little recyclers, these scavenger beetles require mammalian dung to survive. “Insects comprise almost 65% of all animal species on the planet. From India, approximately 65,000 species of insects are known, of them, more than 22,000 species are beetles.
- Dung beetles are the one of the fascinating group of insects because of their ability to bury dung deep in the soil and are indicators of the ecological health of an ecosystem,”
- Other than the relatively large size and distinct blue colour, another important distinguishing characteristic of this species is the strong sexual dimorphism, with the fronto-clypeal horn shorter in females than males.
IIT MADRAS DEVELOPS MATERIAL WITH PROPERTIES SUITABLE FOR QUANTUM OPTOELECTRONICS
02, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Materials such as tungsten diselenide (WSe2) and molybdenum diselenide are being studied keenly for their opto-electronic properties – which is a combination of optics and electronics. A key property of these materials is photoluminescence, in which the material absorbs light and re-emits it as a spectrum.
- As a matter of fact, researchers from IIT Madras have found a way of enhancing this property about 30 times in tungsten diselenide, by drop-casting gold nanoparticles on to a two-dimensional film. The work is published in Applied Physics Letters.
Background: / Two-dimensional material:
- Consisting of practically one layer of atoms, these materials are two-dimensional in structure. Photoluminescence properties can be used in various devices such as quantum LEDs which can be used in communication and computation. Experts have opined that the most challenging aspect of this study was the controlled photoluminescence measurement of these materials from room temperature to 100 K. As is well known, electrons in semiconductors occupy bands of energy known as valence bands.
- As long as they live in these bands, they do not move and contribute to conduction.
- If excited by a small energy input, they get kicked into what is called the conduction band where they can actually be delocalised and contribute to the conduction by moving around.
Excitons:
- When an electron jumps from the valence to the conduction band, it leaves behind a shadow called a “hole.” The electron in the conduction band and the hole in the valence band can bind together and form a composite object (or pseudoparticle) known as an exciton. Photoluminescence in tungsten selenide is a result of such excitons.
- There can be two ways in which an exciton can form – when the spins of the component electron and hole are opposite to each other and when they are aligned in teh same direction. The former is called a bright exciton and the latter, a dark exciton.
- Because their spins are opposite, the electron and hole forming the bright exciton can recombine, giving out a quantum of light in the process. Such a simple way of recombining does not exist for the dark excitons. Since there, the spin of the electron and the hole are parallel, their recombination is discouraged by the rule of conservation of angular momentum. Hence the dark excitons are longer lived than the bright excitons. The dark excitons need an external influence to help them recombine.
- In their work, the IIT Madras researchers find exactly such an external influence.
The power of gold:
- When they drop-cast gold nanoparticles on the surface of the monolayer tungsten diselenide, they find that the dark excitons couple to the surface fields generated and recombine to give off light quanta. Thus, the dark excitons are “brightened” with the help of the gold nanoparticles.That plasmonic effect arises due to gold nanoparticles is a well- known concept. However, its application to 2D systems is in nascent stage.
- The scientists thought that if they drop-cast gold nanoparticles onto monolayer WSe2, then it will generate out-of-plane electric field due to plasmonic effect, which can help for spin-flip of conduction band electrons, thereby making dark excitons bright.
CHINA LAYING DOWN GENE EDITING RULES
02, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- In an attempt to make babies immune to infection by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) China, used a clinically untested gene editing tool
(CRISPR-Cas9) to modify a particular gene
Details:
- In 2012, scientists discovered that CRISPR is a key part
of the “immune system”. - When a virus enters bacteria, it fights back by cutting up the virus’s DNA. This kills the virus but bacteria store some of the DNA. The next time there is an invasion, bacteria produce an enzyme called Cas9 which matches the stored fingerprints with that of the invaders. If it matches, Cas9 can snip the invading DNA.
- The CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing tool thus has two components
- • A short RNA sequence that can bind to a specific target of the DNA and
- • The Cas9 enzyme which acts like a molecular scissor to cut the DNA.
- Once the DNA is cut, the natural DNA repair mechanism is utilised to add or remove genetic material or make changes to the DNA.
- CCR5 gene also helps to protect the lungs, the liver and the brain during certain serious infections and chronic diseases. The gene is known to prompt the immune system to fight the influenza virus in the lungs.
- China posted the draft regulation requiring researchers to obtain prior approval from the government before undertaking clinical trials. Those found violating the rules will be punished and this includes a lifetime ban on research. China is now all set to introduce gene-editing regulation.
CRISPR-Cas9:
- CRISPR is a dynamic, versatile tool that allows us to target nearly any genomic location and potentially repair broken genes. It can remove, add or alter specific DNA sequences in the genome of higher organisms.
- CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats)are sections of DNA and are sections of genetic code containing short repetitions of base sequences followed by spacer DNA segments.
- CAS-9 (CRISPR-associated protein 9) is an enzyme. It uses a synthetic guide RNA to introduce a double strand break at a specific location within a strand of DNA.
- It is a system used by bacterial cells to recognize and destroy viral DNA as a form of adaptive immunity.
- CRISPR scans the genome looking for the right location and then uses the Cas9 protein as molecular scissors to snip through the DNA.
- Cas9 endonuclease – guide RNAs to direct it to a particular sequence to be edited. The genetic sequence of the RNA matches the target sequence of the DNA that has to be edited.
- When Cas9 cuts the target sequence, the cell repairs the damage by replacing the original sequence with an altered version.
- Unlike other gene-editing methods, it is cheap, quick, easy, safer and more accurate to use because it relies on RNA–DNA base pairing, rather than the engineering of proteins that bind particular DNA sequences.
E-Cigarettes Pose Public Health Risk, Says ICMR
01, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has warned of a potential public health disaster if action was not taken to completely prohibit and dissuade the use of Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS) or e-cigarettes.
Details:
- The nicotine delivered by these devices adversely affect almost all systems in a human body.
- E-cigarette use adversely affects the cardiovascular system, impairs respiratory immune cell function and airways in a way similar to cigarette smoking and is responsible for severe respiratory disease.
- It also poses risk to foetus, infant, and child brain development
Harmful effects
- “Use of e-cigarettes has documented adverse effects on humans which include DNA damage; carcinogenesis; cellular, molecular and immunological toxicity; respiratory, cardiovascular and neurological disorders and adverse impact on foetal development and pregnancy,’’ Given the harmful health effects e-cigarettes pose to users, as well as passive exposure, failure to make appropriate interventions at the right time could lead to a public health disaster in India.
Urges complete ban
- There are more than 460 different e-cigarette brands with varying configurations of nicotine delivery available in the market, according to the ICMR.
- The ICMR has recommended complete prohibition on ENDS or e-cigarettes in India in the greater interest of protecting public health.
- E-cigarettes also open a gateway for new tobacco addiction, which is a potential threat to the country’s tobacco control laws and ongoing tobacco control programmes and efforts
ICMR
- ICMR is India’s apex scientific body for the formulation, coordination and promotion of biomedical research. It was established in 1911 as Indian Research Fund Association (IRFA) making it one of oldest and largest medical research bodies in the world.
- The ICMR functions under Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. It is headquartered in New Delhi.
CHANGING THE EARTH
31, May 2019

Why in News:
- A 34-member panel of the Anthropocene Working Group (AWG) voted 29-4 in favour of designating a new geological epoch — the Anthropocene.
Holocene:
- The current epoch is the Holocene.
- It is about 11,700 years of stable climate since the last ice age during which all human civilisation developed.
- As Earth entered a warming trend, the glaciers of the late Paleolithic retreated. Tundra gave way to forest.
- As the climate changed, the very large mammals that had adapted to extreme cold, like mammoth and wooly rhinoceros, became extinct.
- Humans, once dependent on these “mega mammals” for much of their food, switched to smaller game and increased their gathering of plant materials to supplement their diet.
- Evidence indicates that about 10,800 years ago, the climate underwent a sharp cold turn lasting for several years.
- As temperatures began to rebound, human population began to increase and we began inventing the processes that would change the planet forever.
- The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period.
Anthropocene:
- The term ‘Anthropocene’ was coined in 2000 by Nobel Laureate Paul Crutzen and Eugene Stoermer to denote the present geological time interval in which human activity has profoundly altered many conditions and processes on Earth.
- According to the AWG, the phenomena associated with the Anthropocene include
- An order-of-magnitude increase in erosion and sediment transport associated with urbanisation and agriculture. Marked and abrupt anthropogenic perturbations of the cycles of elements such as carbon. Environmental changes generated by these perturbations including global warming, sea-level rise, and ocean acidification. Rapid changes in the biosphere.
- Proliferation and global dispersion of many new minerals, rocks including concrete, fly ash, plastics, and the myriad ‘technofossils’ produced from these materials. The most recent period of the Anthropocene has been referred to by several authors as the Great Acceleration during which the socioeconomic and earth system trends are increasing dramatically, especially after the Second World War. For instance, the Geological Society termed the year 1945 as The Great Acceleration.
Details:
- The panel plans to submit a formal proposal for the new epoch by 2021 to the International Commission on Stratigraphy. The International Commission on Stratigraphy is responsible for deciding and defining the divisions of geological time.
- The focus is now on identifying a definitive geologic marker or golden spike (technically called Global boundary Stratotype Section and Point) to signal the beginning of the Anthropocene Epoch.
- The golden spike must be present globally and should be a part of deposits for geological record. Many in the AWG believe that artificial radionuclides spread across the world by atomic bomb tests from the early 1950s would serve as the golden spike. The radionuclides are present almost everywhere from marine sediments to ice layers and even stalagmites and stalactites.
- Once a formal proposal is made by the AWG, it will be considered by several more groups of the International Commission on Stratigraphy.
- The final ratification will be made by the executive committee of the International Union of Geological Sciences.
PASTA-LIKE ROCKS BEST BET FOR LIFE ON MARS: STUDY
31, May 2019

Why in News:
- Rocks on the surface of Mars that look like layers of pasta may be the most obvious sign of life on the Red Planet
Background: / Sulfurihydrogenibium yellowstonense:
- The bacterium that controls the formation of such rocks on the earth is ancient and thrives in harsh environments that are similar to conditions on Mars
- The bacterium belongs to a lineage that evolved prior to the oxygenation of Earth roughly 2.35 billion years ago.
- It can survive in extremely hot, fast-flowing water bubbling up from underground hot springs.
-
It can withstand exposure to ultraviolet light and survives only in environments with
extremely low oxygen levels, using sulphur and carbon dioxide as energy sources.
SPACEX SATELLITES POSE NEW HEADACHE FOR ASTRONOMERS
30, May 2019

Why in News:
- An astronomer in the Netherlands captured footage of a train of brightly-lit SpaceX satellites ascending through the night sky this weekend, stunning space enthusiasts across the globe.
Background:
What is SpaceX?
- SpaceX is a space technologies company founded by South African tech entrepreneur Elon Musk.
- Founded in 2003, SpaceX has quickly grown to become a pioneer in the development of reusable space rockets.
- The company designs and manufactures rockets that sends satellites into orbit around Earth
– and one day it hopes to send people into space. - SpaceX is the only private company ever to bring back a spacecraft from low-Earth orbit. This feat was first accomplished in December 2010.
3D-PRINTED ARTIFICIAL CORNEAS MIMIC HUMAN EYES
30, May 2019
Why in News:
- Using bioink made from stem cells, scientists have 3D- printed artificial corneas that mimic the human eye.
Background:
- The 3D printed human corneas were produced using bio-ink solution consisting of healthy corneal stem mixed together with alginate and collagen. The combination of alginate (a gel derived from seaweed)
- and collagen helps to keep corneal stem cells alive and produces material of necessary dimensions which is stiff enough to hold its shape and soft enough to be squeezed out nozzleof3Dprinter.
SCIENTISTS GIVE THE THUMBS-UP FOR ANTHROPOCENE EPOCH
29, May 2019

Why in News:
- Experts say human impact on Earth so profound that Holocene must give way to epoch defined by nuclear tests, plastic pollution and domesticated chicken
Background:
- A team of scientists have voted to declare “Anthropocene” as a new chapter in the Earth’s geological history- the new epoch. The result builds on an informal vote taken at the 2016 International Geological Congress in Cape Town, and lays the groundwork for a formal proposal by 2021 to the International Commission on Stratigraphy.
What is it?
- Coined by Paul Crutzen and Eugene Stoermer in 2000 to denote the present geological time interval, Anthropocene has been used to describe humanity’s large impact on the environment. Implications: The move signals the end of the Holocene epoch, which began 12,000 to 11,600 years ago.
Evidence of the Anthropocene
- Human activity has: Pushed extinction rates of animals and plants far above the long-term average. The Earth is on course to see 75% of species become extinct in the next few centuries if current trends continue. Increased levels of climate-warming CO2 in the atmosphere at the fastest rate for 66m years, with fossil-fuel burning pushing levels from 280 parts per million before the industrial revolution to 400ppm and rising today.
- Put so much plastic in our waterways and oceans that microplastic particles are now virtually ubiquitous, and plastics will likely leave identifiable fossil records for future generations to discover. Doubled the nitrogen and phosphorous in our soils in the past century with fertiliser use. This is likely to be the largest impact on the nitrogen cycle in 2.5bn years. Left a permanent layer of airborne particulates in sediment and glacial ice such as black carbon from fossil fuel burning.
POST BALAKOT, INDIAN AIR FORCE ZEROES IN ON KEY VULNERABILITY
29, May 2019

Why in News:
- After Balakot air strike, the Indian Air Force (IAF) has identified a shortage of Airborne Warning and Control System (AWACS) aircraft to provide round-the-clock surveillance as a major deficiency
Background:
Airborne Warning and Control System (AWACS):
- This system has the ability to detect incoming cruise missiles, fighter jets or even drones from both Pakistan and China.
- China has over 20 AWACS while Pakistan has 8 AWACS.
- The indigenous AeW&CS has completed all tests and certification.
- Pegged as a “force multiplier”, the system is equipped with a 240-degree coverage radars in contrast to the existing Phalcons, which provide a 360-degree coverage over a 400-km range.
- The AEW&C system will detect, identify and classify threats present in the surveillance area and act as a Command and Control Center to support Air Defence operations.
- Besides, the system will support IAF in offensive strike missions and assist forces in the tactical battle area.
- The Electronic and Communication Support Measures of the system can also intercept and gather electronic and communication intelligence from radar transmissions and communication signals.
BURNOUT A MEDICAL CONDITION, SAYS WHO
28, May 2019

Why in News:
- The World Health Organization has for the first time recognised “burn-out” in its International Classification of Diseases (ICD), which is widely used as a benchmark for diagnosis and health insurers.
Details:
- The decision, reached during the World Health Assembly in Geneva, could help put to rest decades of debate among experts over how to define burnout, and whether it should be considered a medical condition. WHO defines burn-out as “a syndrome conceptualised as resulting from chronic workplace stress that has not been successfully managed?”
Three dimensions:
- The syndrome was characterised by three dimensions: “1) feelings of energy depletion or exhaustion; 2) increased mental distance from one’s job, or feelings of negativism or cynicism related to one’s job; and 3) reduced professional efficacy.”
- Burn-out refers specifically to phenomena in the occupational context and should not be applied to describe experiences in other areas of life,” This is the first time” burnout has been included in the ICD classification. The ICD-11, which is to take effect in January 2022, contains several other additions, including classification of “compulsive sexual behaviour” as a mental disorder, although it stops short of lumping the condition together with addictive behaviours. It does however for the first time recognise video gaming as an addiction, listing it alongside gambling and drugs like cocaine.
- The updated list removes transgenderism from its list of mental disorders meanwhile, listing
it instead under the chapter on “conditions related to sexual health”.
ICD:
- ICD is the international standard diagnostic tool for epidemiology, health management and clinical purposes. Its full official name is International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems.
- It is maintained by WHO and is revised periodically.
- It provides common language that allows health professionals to share health information across the globe. It contains around 55,000 unique codes for injuries, diseases and causes of death.
IISC TEAM CONFIRMS BREAKTHROUGH IN SUPERCONDUCTIVITY AT ROOM TEMPERATURE
26, May 2019

Why in News:
- Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru confirms that material exhibits major properties of superconductivity at ambient temperature and pressure.
Details:
- A material is said to be a superconductor if it conducts electricity with nil resistance to the flow of electrons.
- Superconductors will help build very highly efficient devices leading to huge energy savings. Till now, scientists have been able to make materials super conduct only at temperatures much below zero degree C and hence making practical utility very difficult.
- Superconductivity at ambient temperature has been a holy grail in physics for about a century. If this [result] is correct, it would be the greatest work done in India since the discovery of Raman effect,” The material they have made is unbelievable — a tiny sphere of gold, placed 10-20 tinier spheres of silver inside it…This [material] they found shows a sharp drop in resistivity [reflecting superconducting state].
The proof:
- “Two of the most important properties of superconductivity are dimagnetism and zero resistance. These two were seen in the material.
- At 286 K there is clear transition from a normal state to a superconducting state.
What is Raman Effect?
- Some part of light beam after passing through a transparent medium gets scattered.
- This phenomenon of scattering of light is termed as Raman Scattering and the cause of scattering is called the Raman Effect.
- The wavelength of these scattered rays is different from that of the incident rays of light.
- This phenomenon was explained/discovered by Indian physicist Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (CV Raman) on February 28, 1928.
- This discovery was awarded with the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930.
FULL CIRCLE: ON THE CHANGE IN KILOGRAM’S DEFINITION
25, May 2019

Why in News:
- The kilogram joined a bunch of other units— second, metre, ampere, kelvin, mole and candela — that will no longer be compared with physical objects as standards of reference
Details:
- The change comes after nearly 130 years: in 1889 a platinum-iridium cylinder was used to define how much mass one kilogram represented.
- Now, a more abstract definition of the kilogram has been adopted in terms of fundamental constants, namely, the Planck’s constant h, and the metre and second which already have been defined in terms of universal constants such as the speed of light.
- Now, by using a Kibble balance, which balances mass against electromagnetic force, to measure the mass of an unknown piece, the very methodology of verification has been altered.
- The constants involved are known precisely and are universal numbers. Hence, whether the mass is measured on earth or, say, on the moon, it can be determined with precision.
- In 1791, 1 kg was defined as the mass of one litre of distilled water at its melting point.
- In 1799, the kilogram came to be defined using a cylinder of platinum – the first time an artefact was used for this purpose. But it was also defined as equivalent to the mass of one litre of distilled water at atmospheric pressure and at about 4 degrees
- Celsius, the temperature at which water has the maximum density.
- This was done away with in 1889 when the community adopted the International Prototype of the Kilogram — a cylinder made of an alloy that’s 90% platinum and 10% iridium. The reference to the ‘physical constant’, i.e. mass of one litre of water, was abandoned
- Now, as a culmination of this historical process, we come back full circle and find that the kilogram is defined again in terms of a fundamental physical constant — the Planck’s constant. Planck’s constant is a robust number to match. Not until the art of travelling at relativistic speeds, close to the speed of light, is mastered, will we have to redefine these abstract definitions.
General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM)
- General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) is the highest international body of the world for accurate and precise measurements and comprises of 60 countries including India and 42 Associate Members.
NHA TO COLLABORATE WITH CANCER GRID
24, May 2019

Why in News:
- National Health Authority (NHA) and National Cancer Grid (NCG) have signed an MoU under the Ayushman Bharat- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY).
Details:
- The main objective of this collaboration includes developing uniform standards of patient care for prevention, diagnosis and treatment of cancer; providing specialised training and education in oncology, and facilitating collaborative basic, translational and clinical research in cancer,”
- “The partnership with the National Cancer Grid will bring in experts to enhance the cancer care services provided under AB-PMJAY.”
- The NHA and NCG will now jointly review existing cancer treatment packages, pricing of services, and standard treatment workflows covered under the AB-PMJAY, and
- plug-in necessary gaps to ensure enhanced quality of cancer care.
- The NCG will work closely with the NHA to rationalise payment rates for different benefit packages and treatment/diagnosis plans, and also explore mechanisms to signal the right incentives to providers to ensure quality through pricing mechanisms.
Aayusman bharat
- Creating a network of health and wellness infrastructure across the nation (for primary health care services). Provide insurance cover to minimum 40% of India’s total population (for secondary and tertiary healthcare services).
- Beneficiaries of heath insurance under the scheme will include 50 crore economically weak citizens of India as defined in the social, economic and ethnic census 2011 database. It will cover both rural (8.03 crore) and urban (2.33 crore) families. Ayushman Bharat will subsume the existing Rashtriya Sawasthya Bima Yojna, launched in 2008 and the Senior Citizens Health Insurance Scheme. It will provide a benefit cover of Rs 5 lakh/year/family.
- Expenses incurred will be shared between Centre and States in 60:40 ratio.
- The Government aims to open 5 lakh health and wellness centre by 2022 that will be equipped to treat various diseases. Cashless benefits will be allowed from any public or private empanelled hospitals. Such empanelled hospitals will have ‘Ayushman Mitra’ to assist patients. Benefits can be availed from any place in India and no hospital can refuse treatment under this scheme.
WHO UNVEILS PLAN TO TACKLE SNAKEBITE
24, May 2019

Why in News:
- The World Health Organization unveiled a new strategy to dramatically cut deaths and injuries from snakebites, warning a dearth of antivenoms could soon spark a “public health emergency”.
Details:
- Each year, nearly three million people are bitten by poisonous snakes, with an estimated 81,000-138,000 deaths.
- Another 4,00,000 survivors suffer permanent disabilities and other after-effects, according to WHO figures.
- WHO, which two years ago categorised “snakebite envenoming” as a Neglected Tropical Disease, presented a strategy aimed at cutting snakebite-related deaths and disabilities in half by 2030.
- An important part of the strategy is to significantly boost production of quality antivenoms, WHO said.
- The UN agency called for “the restoration of a sustainable market for snakebite treatment”, insisting on the need for a 25% increase in the number of manufacturers. It plans a pilot project to create a global antivenom stockpile.
Neglected Tropical Diseases
- The World Health Organization (WHO) defines the Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) as- a diverse group of communicable diseases that prevail in tropical and subtropical conditions in 149 countries affect more than one billion people and cost developing economies billions of dollars every year .
- Major NTDs are: Buruli ulcer, Chagas disease, Dengue and Chikungunya, Dracunculiasis (guinea-worm disease), Echinococcosis, Foodborne, Human African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness), Leishmaniasis (Kala-azar), Leprosy (Hansen s disease), Lymphatic filariasis, Mycetoma, chromoblastomycosis and other deep mycoses, Onchocerciasis (river blindness), Rabies, Scabies and other ectoparasites,
Why are some tropical diseases called “neglected”?
- The people who are most affected by these diseases are often the poorest populations, living in remote, rural areas, urban slums or conflict zones. Neglected tropical diseases persist under conditions of poverty and are concentrated almost exclusively in impoverished populations in the developing world.
- Need for and significance of R&D into neglected tropical diseases:
- The need for drugs for neglected diseases and also for drug R&D is high in India. The country tops the number of cases for 11 different neglected tropical diseases such as lymphatic filariasis, visceral leishmaniasis, trachoma, tapeworm, roundworm, hookworm, whipworm, dengue and leprosy.
In 2017, there were around 2.8 million new cases of TB, which brought down the global decline of TB. One third of all TB deaths worldwide happen in India.
ISRO LAUNCHES RADAR IMAGING OBSERVATION SATELLITE RISAT-2B
23, May 2019

GS 3 : Science & Technology – Awareness In The Fields Of It, Space, Computers, Robotics, Nano-Technology
Why in News:
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) placed RISAT-2B, an X-band microwave Earth observation satellite, into orbit 556 km above earth.
Details:
- Data from the satellite would be vital for the Armed Forces, agriculture forecasters and disaster relief agencies. The new satellite “will enhance India’s all-weather [space-based] capabilities in agriculture, forestry and disaster management,”
- Dr. Sivan described RISAT-2B as “an advanced Earth Observation satellite with an advanced technology of 3.6-metre radial rib [unfurlable] antenna”.
After the satellite separated from the launcher, its solar arrays deployed automatically. - “ISRO Telemetry Tracking and Command Network at Bengaluru took control of the satellite. Dr. Sivan, who is also Secretary, Department of Space, announced that the Chandrayaan-2 lander-rover mission would be launched between July 9-16.
- The PSLV-C46 launcher carried the 615-kg RISAT-2B,about 15 minutes later, the satellite reached its designated position and started orbiting in space, with an inclination of 37°.
- Designed at ISRO’s U.R. Rao Satellite Centre (URSC) in Bengaluru and fast-tracked in just 15 months, the RISAT-2B is built to operate for at least five years.
- Its X-band synthetic aperture radar can give added details such as the size of objects on earth, structures and movement.
- Information from RISAT-2B will complement data from normal optical remote sensing satellites. Such data are useful for agencies that need ground images during cloud, rain and in the dark. This is the third Indian RISAT in 10 years, and follows the Israeli-built RISAT-2 in 2009 and the ISRO-built RISAT-1 in 2012. The older RISATs have reached the end of their lives.
- ISRO has planned a series of radar imagers in the coming months to enhance its space- based observation of Earth and the Indian region.
What is the significance?
- RISAT-2B adds to India’s capability to observe the earth
in all weathers and all conditions. - The civil and military purposes, include –
- crop monitoring during the monsoon season
- forestry mapping for forest fires and deforestation
- flood mapping as part of the national disaster management programme
- Given that overcast skies are a constant during monsoon season and times of flood, the ability to penetrate the cloud cover is essential.
- RISAT-2B images will not obstructed by clouds.
- Services of such satellites are in great demand from national security agencies as well.
CHINESE-BUILT DRONES MAY STEAL DATA, WARNS U.S.
22, May 2019

Why in News:
- Washington has warned that Chinese-made drones could be giving spy agencies in Beijing
- “unfettered access” to stolen data.
Details;
- The U.S. government has “strong concerns about any technology product that takes American data into the territory of an authoritarian State that permits its intelligence services to have unfettered access to that data or otherwise abuses that access,”
- The warning comes as China’s tech sector attracts unprecedented scrutiny amid China-US trade war. Washington has cranked up the heat on China’s Huawei by banning American companies from selling or transferring U.S. technology to the telecom’s giant. U.S. intelligence believes Huawei is backed by the
- Chinese military and that its equipment could provide Beijing’s spy agencies with a
- backdoor into the communications networks of other countries.
India and drones:
- The National Drones Policy drafted by the Ministry of Civil Aviation came into effect
- With the policy coming into effect, flying drones or remotely-piloted aircraft have become legal in India.
- Also, the Ministry of Civil Aviation has kick-started the online registration of drones in India through its Digital Sky portal.
Highlights of the policy
- Under the new policy, Nano drones which weigh less than 250 grams or equal does not need a registration or license.
- Digital Sky portal – It is an online platform as part of an enforcement system designated as No Permission No Take-off (NPNT).
- It includes procedures to conduct a drone operation, including final flight permission immediately before the operation.
- Permission – Following registration, DGCA will issue a Unique Identification Number (UIN) or Unmanned Aircraft Operator’s Permit (UAOP)
- Zones – Flying in the ‘green zones will require only intimation of the time and location of the flights via the portal or the app.
- But permissions will be required for flying in ‘yellow zones’, and flights will not be allowed
- in the ‘red zones.
INDIA ADOPTS NEW STANDARDS FOR MEASURING KILOGRAM
21, May 2019
Why in News?
- • Recently, the CSIR-National Physical Laboratory (NPL), which is India’s official reference keeper of units of measurements, released a set of recommendations to update the definition of the kilogram.
Highlights:
- • The kilogram joined other standard units of measure such as the second, metre, ampere, Kelvin, mole and candela that would no longer be defined by physical objects.
- • The measures are all now defined on the basis of unchanging universal, physics constants.
- The kilogram now hinges on the definition of the “Planck Constant”, a constant of nature
that relates to how matter releases energy. - • In 2018, at the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) in Versailles (France), delegates of International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) had voted to redefine the kilogram in terms of Planck constant.
- • Earlier, the kilogram derived its provenance from the weight of a block of a platinum- iridium alloy housed at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures in France.
STUDY ON DIABETES WARNS LACK OF AWARENESS & CONTROL A WORRY
21, May 2019

Why in News:
- Only half the Indian adults in the most productive age group (15-49 years) are aware that they ail from diabetes and only one-fourth of those diagnosed and treated have their blood sugar under control – says a study carried out by the Public Health Foundation of India (PHFI), Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Madras Diabetes Research Foundation, Heidelberg Institute of Global Health, University of Birmingham and University of Gottingen.
Background:
- Diabetes was defined as blood glucose (BG) ≥ 200 mg/dL if not fasted and ≥ 126 mg/dL
if fasted or reporting to have diabetes.
Diabetes
- Diabetes mellitus (DM) – Commonly referred to as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders in which there are high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period.
- Most common types of Diabetes Mellitus are as follows
- Type 2 diabetes – A chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose)
- Type 1 diabetes – A chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin.
- Prediabetes – A condition in which blood sugar is high, but not high enough to be type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes – A form of high blood sugar affecting pregnant women. Diabetes insipidus – It occurs when the body can’t regulate how it handles fluids. The condition is caused by a hormonal abnormality and isn’t related to diabetes.
- In addition to extreme thirst and heavy urination, other symptoms may include getting up at night to urinate, or bed-wetting.
- Depending on the form of the disorder, treatments might include hormone therapy, a low- salt diet and drinking more water.
Cause of concern:
- Diabetes is a “high maintenance” disease that leads to severe damage to the heart, kidneys and eyes apart from risk of gangrene if mismanaged. Given the state of the public health system in the country, and the fact that the poor have to pay for healthcare, the findings must be treated as a distress signal on an urgent basis.
- Given that people in rural areas and poorer communities in cities are unable to access care earlier, they would be more prone to advanced complications such as renal failure and blindness due to retinopathy. Since 70% of the population lives in rural areas, even a small increase in percentage of people suffering from diabetes adds up to a large number of people who need sustained medical attention but have access to poor health services.
Underlying causes:
-
For many poorer people in cities, nutritionally well-balanced food may not be within their
means. Eating “junk food” is thus not a matter of choice or taste as much as affordability. - Higher income levels, less physically demanding occupations and increased availability of mechanised transport and household appliances among urban dwellers to possibly explain the higher incidence of the disease in urban areas.
- The pressure of commuting long distances to work and the need to use the public transport system is also not a matter of choice for urban poor. These issues lead to the build-up of stress—another factor that is among the causes of the disease.
- Asian Indians progress faster through the pre-diabetes stage than those of other ethnic groups. Also, as in other countries where diabetes is spreading rapidly, in India too, recreational physical activity is very low, more so, among women from all sections.
- People living in urban areas have access to diabetes care services and can afford the associated out-of-pocket expenditure. However, people living in semi-urban and rural areas do not have access to diabetes centres or clinics that provide comprehensive care.
- The other reasons for this shift could be the increased awareness of healthy practices among affluent sections, which means they are engaging in physical activity and making necessary dietary changes to keep non communicable diseases at bay.
Way Forward:
Conclusion:
- Infectious diseases remain the largest concern in developing countries. However, non- communicable diseases like diabetes (known appropriately as the silent killer) are spreading at a frightening rate. In the 21st century, if we are not to sentence large sections of the population to a half-life, we must act quickly and in concert
KILOGRAM UPDATE TO SPUR REVISION OF TEXTBOOKS
21, May 2019

Why in News:
- With the definition of the ‘kilogram’ getting a global, technical makeover, textbooks are set to undergo an update.
Background
-
Since the 19th century,scientists have based their definition of the fundamental unit of mass on a physical
object — a shining platinum-iridium cylinder or Le Grand K (weighed exactly a kilogram) known as the International Prototype of the Kilogram. - It is housed at the headquarters of BIPM in Sevres, France.
- All modern mass measurements are derived from the kilogram, whether micrograms of pharmaceutical medicine or gold dust, kilos of fruit or fish or tonnes of steel.
- The problem is the prototype doesn’t always weigh the same. Even inside its three-glass bell jars it picks up microparticles of dirt and is affected by the atmosphere. Sometimes it needs cleaning, which can affect its mass.
New Concepts:
- Since 1967, the second has been defined as the time it takes for a certain amount of energy to be released as radiation from atoms of Caesium-133. This became the basis of all measures of time and is used in atomic clocks.
- Once the second was defined, the metre fell into place. This was based on another universal constant: the speed of light. Today, the metre is defined as the distance travelled by light in vacuum in 1/299,792,458 of a second (which is already defined).
- The kilogram comes next. The Planck constant, which Kilogram is based on, is usually measured in joule seconds, but this can also be expressed as kilogram square metres per second.
- By adding measurements of a second and a metre, along with an exact knowledge of
Planck’s constant, precise definition of the kilogram can be obtained. - The CSIR-NPL, which is India’s official reference keeper of units of measurements, released a set of recommendations requiring that school textbooks, engineering-education books, and course curriculum update the definition of the kilogram.
- The institute is also in the process of making its own ‘Kibble Balance’, a device that was
used to measure the Planck Constant and thereby reboot the kilogram - The National Physical Laboratory itself will be relying on the kilogram maintained in the U.S.-based National Institutes of Standards and Technology to calibrate its one-kilogram weight.
RADAR IMAGING SATELLITE
20, May 2019

Why in News:
- RISAT-2B, will mark the resumption of a vital ring of Indian all-seeing radar imaging satellites after seven years.
- A constellation of such space-based radars means a comprehensive vigil over the country.
Background: / RISAT:
- The RISAT, which was first deployed in orbit on April 20, 2009 as the RISAT-2, uses synthetic aperture radars (SAR) to provide Indian forces with all-weather surveillance and observation, which are crucial to notice any potential threat or malicious activity around the nation’s borders. Following the 2008 Mumbai terror attacks, the launch of RISAT-2 was prioritised over RISAT- 1, as its C-band SAR radar was not yet ready and RISAT -2 carried an Israeli-built X-band radar.
- The to-be-deployed RISAT-2BR1 satellite uses the same SAR band and will further improve India’s imaging reconnaissance abilities.
RISAT-2B
- 4th flight unit of the RISAT programme.
- Main mission: reconnaissance and disaster management. DATA access Information:
- Direct reception at appointed ground stations in X-band.
- Off-line data are distributed by the National Remote Sensing Center (NRSC) in Launch scheduled for 22 May 2019.
EARLY LIFE STRESS CAN MODIFY DNA EXPRESSION, A STUDY FINDS
19, May 2019

Why in News:
- A Bengaluru-based group of researchers has discovered a link between stress during early life and problematic, externalising behaviour in the DNA of children of alcoholic parents.
Biology and Adversity:
-
Early adversity is known to have several biological effects. One of this is DNA methylation
— a process by which chemical changes occur to the DNA molecule. It also affects the functioning of what is called the hypothalamus-pituitary axis. - The hypothalamus-pituitary axis is a major neuroendocrine system that controls reactions to stress, regulates digestion, the immune system, mood and emotions, sexuality and energy storage and expenditure.
- In normal individuals, it is expected that the level of cortisol spikes during stress.
Collated data:
- The study is unique in that it carries out a detailed assessment of HPA axis function by cortisol estimation during stress and also estimates chemical effects due to early adversity at the DNA level.
-
The study concludes that children of alcoholics
might have a compromised HPA axis and epigenetic changes at the DNA level possibly resulting in increased externalising behaviour.
IIT BOMBAY FABRICATES WEARABLE SUPER CAPACITOR
19, May 2019

Why in News:
- Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay have fabricated a wearable super capacitor that can store and deliver large amount of electrical energy, exceeding other similar devices.
Background:
- The wearable energy storage device can be stitched on to any fabric and can deliver power ranging from microwatt to milliwatt. The energy stored in the device can power GPS location-based transmitters or a 1.8-volt LED.
About: / Features:
- The wearable energy storage device can be stitched on to any fabric. It can deliver power ranging from microwatt to milliwatt.
Mechanism:
- The idea is when the supercapacitor is integrated with a piezoelectric energy generator then it will become completely self-sustaining.
- The electrode of the supercapacitor was fabricated by uniformly coating cotton yarn with carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The coating converts the electrical insulating yarn into a metallic conductor thereby behaving like an electrode.
Application:
- The energy stored in the device can power GPS location-based transmitters or a 1.8-volt LED. When stitched to the fabric, the supercapacitor can be used for powering GPS location-based devices or a LED lamp or even charge small electronic devices.
NO SHORTAGE OF POLIO VACCINE
19, May 2019
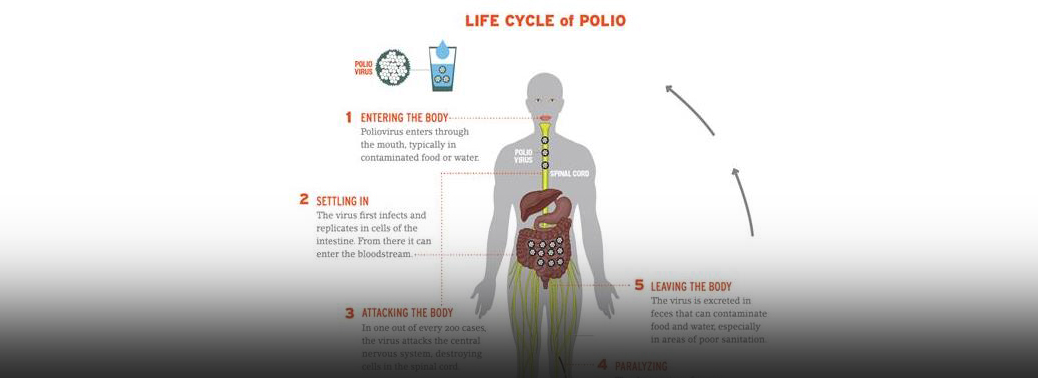
Why in News:
- No shortage of polio vaccine for routine immunisation says Health ministry.
Background:
- The issue came after reports of anticipated shortage following the detection of contamination, by the Central Drugs Laboratory (CDL) in Kasauli, in 16 batches of polio vaccine manufactured by Bharat Immunological and Biologicals Corporation Limited (Bibcol).
What is poliomyelitis/polio?
- Poliomyelitis, often called polio or infantile paralysis is an acute infectious disease caused by polio virus. The virus is a human enterovirus of the Picornaviridae
- There are three types of Polio Virus: 1,2,3-Single stranded RNA virus Natural or Wild Polio Virus (WPVS). It is transmitted from one person to another by oral contact with secretions or faecal material from an infected person. It attacks the central nervous system through the blood stream and damage the cells and paralyse the victim.
Types of Polio vaccines
- Two different kinds of vaccine are available: an inactivated (killed) polio vaccine (IPV) and a live attenuated oral polio vaccine (OPV).
Inactivated Polio vaccine (IPV):
- It was first introduced in 1995 by Dr. Jonas Salk
- It is produced from wild-type poliovirus strains of each serotype that have been inactivated (killed) with formalin.
- It is an injectionable vaccine and can be administered alone or in combination with other vaccines (e.g., diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, and haemophilus influenza).
Oral Polio vaccine (OPV):
- It was first introduced in 1961 by Dr. Albert Sabin
- consists of a mixture of the three live attenuated poliovirus serotypes (Sabin types 1, 2 and 3), selected for their lower neurovirulence and reduced transmissibility.
- Apart from trivalent OPV (tOPV), monovalent OPVs viz. against Type 1 (mOPV1) and against type-3 (mOPV3) have been licensed for use in some countries
- In 2009, 2 bivalents (type-1 and type-3) OPVs (bOPVs) were licensed.
AI PROJECT EYES EARLY STAGE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
14, May 2019

Why in News:
- Early stage diabetic retinopathy has been detected using artificial intelligence (AI) at civic- run dispensaries at mumbai.
Background:
- The unique project is being implemented by the Aditya Jyot Foundation for Twinkling Little Eyes (AJFTLE) and, in a span of eight months, nearly 1,300 diabetes patients have been screened on a retinal imaging device attached to a smartphone.
Diabetic retinopathy:
- Diabetic retinopathy is the commonest diabetic eye disease; it damages blood vessels in light-sensitive tissue at the back of the retina.
Symptoms:
- Spots or dark strings floating in your vision (floaters)
- Blurred vision
- Dark or empty areas in your vision Vision loss
- Fluctuating vision
- Vision loss
- Impaired color vision
Causes: / Diabetic retinopathy
- Over time, too much sugar in your blood can lead to the blockage of the tiny blood vessels that nourish the retina, cutting off its blood supply. As a result, the eye attempts to grow new blood vessels. But these new blood vessels don’t develop properly and can leak easily.
- There are two types of diabetic retinopathy:
- Early diabetic retinopathy. In this more common form — called nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) — new blood vessels aren’t growing (proliferating).
- When you have NPDR, the walls of the blood vessels in your retina weaken. Tiny bulges (microaneurysms) protrude from the vessel walls of the smaller vessels, sometimes leaking fluid and blood into the retina. Larger retinal vessels can begin to dilate and become irregular in diameter, as well. NPDR can progress from mild to severe, as more blood vessels become blocked.
- Nerve fibers in the retina may begin to swell. Sometimes the central part of the retina (macula) begins to swell (macular edema), a condition that requires treatment.
- Diabetic retinopathy can progress to this more severe type, known as proliferative diabetic retinopathy. In this type, damaged blood vessels close off, causing the growth of new, abnormal blood vessels in the retina, and can leak into the clear, jelly-like substance that fills the center of your eye (vitreous).
- Eventually, scar tissue stimulated by the growth of new blood vessels may cause the retina to detach from the back of your eye. If the new blood vessels interfere with the normal flow of fluid out of the eye, pressure may build up in the eyeball. This can damage the nerve that carries images from your eye to your brain (optic nerve), resulting in glaucoma.
- Anyone who has diabetes can develop diabetic retinopathy. Risk of developing the eye condition can increase as a result of:
- Duration of diabetes — the longer you have diabetes, the greater your risk of developing diabetic retinopathy
- Poor control of your blood sugar level
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Pregnancy Tobacco use
- As a part of the AI project, technicians from the Aditya Jyot Foundation visit civic dispensaries along with Remedio Fundus on Phone, a portable device attached to a smartphone equipped with retinal imaging.
- After the patient’s eye images are clicked, the AI on the device screens them for signs of diabetic retinopathy, and prompts technicians on whether they should be referred to a hospital or not. If the image is unclear, the device also prompts a retake of the picture.
Advanced diabetic retinopathy:
Risk factors:
AI role :
NOTICE TO CENTRE ON BT BRINJAL
13, May 2019

Why in News:
- Senior advocate Prashant Bhushan has sent a legal notice to Union Environment Minister Harsh Vardhan asking for a freeze on all genetically modified organisms, including field trials.
Details:
- Though growing Bt brinjal is illegal in India Bhushan’s letter comes in the aftermath of activist groups recently proffering evidence of Bt Brinjal, a GM crop, being grown in a farmer’s field in Haryana.
- Letter demands the Environment Ministry to uproot and destroy planted Bt brinjal in farms and seedlings in nurseries, undertake a scaled-up exercise of testing of seeds and plantings (for the presence of BT Genes) and, ascertain the supply chain – from seed developers to intermediaries.”
- Bt brinjal was the first food crop made to contain an insecticidal protein, called cry1 ac,
- Though this was cleared for commercial cultivation it was put in deep-freeze in 2010 on the grounds that there was scientific and public disagreement on its safety.
- The lab report was also sent to the government, which picked up samples of the suspected Bt Brinjal crop and sent it to the National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR) in New Delhi for testing.
- Following brinjal, a genetically modified strain of mustard too is in the regulatory pipeline. GEAC panel ruled that more tests were required before the mustard could be made available in farmer fields.
What is Bt Brinjal?
- Bt Brinjal is a transgenic brinjal created out of inserting a gene [Cry 1Ac] from the soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis into Brinjal. The insertion of the gene into the Brinjal cell in young cotyledons has been done through an Agrobacterium-mediated vector, along with other genes like promoters, markers etc.
- This gives (so said) Brinjal plant resistance against lepidopteran insects like the Brinjal Fruit and Shoot Borer (Leucinodes orbonalis) and Fruit Borer (Helicoverpa armigera).
Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC)
- The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) was constituted under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) as the apex body under the ‘Rules for Manufacture, Use, Import, Export and Storage of Hazardous Microorganisms/Genetically Engineered Organisms or Cells 1989’ in accordance with the Environment Protection Act, 1986.
National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources
- Management and promote sustainable use of plant genetic and genomic resources of agri- hotricultural crop and carry out related research
- Coordination and capacity building in PGR management and policy issues governing access and benefit sharing of their use
IAF RECEIVES FIRST AH-64E APACHE ATTACK HELICOPTER
12, May 2019

Why in News:
- The first AH-64E Apache attack helicopter built for India was formally handed over to the Indian Air Force (IAF) at the Boeing production facility in Mesa, Arizona in the U.S.
Details:
- The helicopter has been customised to suit IAF’s future requirements and would have significant capability in mountainous terrain. The helicopter has the capability to carry out precision attacks at standoff ranges and operate in hostile airspace with threats from ground. The ability of the helicopters, to transmit and receive the battlefield picture, to and from the weapon systems makes it a lethal acquisition.
AH-64E / Features:
- AH-64E Apache is one of the leading multi-role attack helicopters globally and is flown by the US Army.
- The Apaches are armed with stinger air-to-air missiles, Hellfire Longbow air-to-ground missiles, guns and rockets. Its features include joint digital operability, improved survivability and cognitive decision-aiding.
Significance:
-
The addition of AH-64 E (I) helicopter is a significant step towards modernisation of Indian
Air Force’s helicopter fleet. - The helicopter has been customised to suit the IAF’s future requirements and would have
significant capability in mountainous terrain. - It has the capability to carry out precision attacks at standoff ranges and operate in hostile airspace with threats from ground.
- Its ability to transmit and receive the battlefield picture, to and from the weapon systems through data networking makes it a lethal acquisition.
NBRI: ARSENIC BIOREMEDIATION USING TWO SOIL BACTERIA
12, May 2019

Why in News:
- Using two indigenous strains of bacterium isolated from arsenic-contaminated field, researchers from CSIR-National Botanical Research Institute (CSIR-NBRI), Lucknow and the University of Lucknow have shown that arsenic can be effectively removed from contaminated soil with the help of microbes.
Details:
- Bacillus flexus and Acinetobacter junii is the bacteria that can promote plant growth.
- Using arsenic-contaminated water for agricultural purposes can lead to increased concentration of arsenic in fruits and grains, proving toxic to humans.
- It is found that the two bacteria under different concentrations of arsenate and arsenite, the toxic forms of heavy metal.
Arsenic treatment did not stunt or delay the growth of both the bacterial strains. - B. flexus exhibited resistance to high levels (150 mmol per litre) of arsenate and A. junii to about 70 mmol per litre of arsenite. This is higher than previously reported arsenic tolerant bacteria and so were regarded as hyper-tolerant strains.
- Both the bacteria have a special ars C gene, which aids in arsenic detoxification.
- Both the bacteria were able to solubilise phosphorus. Phosphate solubilising bacteria have been reported to increase phytoavailability of phosphate, thus facilitating plant growth.
- These two bacterial strains were also found to produce siderophores and ACC deaminase enzyme. Siderophore increase the bioavailability of iron and other metal ions in polluted soil environment and ACC deaminase is a well-known plant growth promoting enzyme.
- These bacteria can live symbiotically in the roots of plants in arsenic- contaminated soils and help them uptake the required nutrients without causing toxicity.
- It has the potential to accumulate arsenic within the cells and transform it into less phytotoxic forms, making the strains more proficient candidate for bioremediation.
Background: / National Botanical Research Institute
- The National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) is a research institute of CSIR in Lucknow. It is engaged in the field of taxonomy and modern biology
CSIR
- CSIR is government’s autonomous research agency, established in 1942.
- CSIR has over 4,500 scientists working across 38 laboratories and employs over 9000 scientific and technical personnel.
- The research bodies under CSIR cover science and technology focus areas ranging from aeronautics, instrumentation, mining, environmental engineering and to oceanography, geophysics, chemicals, drugs, genomics and biotechnology.
FAST NEUTRINO OSCILLATIONS MAY HOLD KEY TO SUPERNOVAE FORMATION
12, May 2019

Why in News:
- Neutrinos could be the driving force behind supernova explosions, a new theoretical study finds.
Details:
- The study makes a fundamental advance in modelling neutrinos inside stars puts forth the idea that “fast neutrino oscillations” could hold the key to why some stars explode forming supernovae at the end of their lives.
- Neutrinos come in three flavours: electron neutrino, muon neutrino and tau neutrino, so named because of the corresponding leptons they are associated with (electron, muon and
tau).when measuring the number of neutrinos coming from the sun, experimentalists found that only a third of the number of solar neutrinos that was expected was being intercepted on earth. This was later explained by the understanding that they have a small mass and they can change from one flavour to another – a phenomenon named neutrino oscillations.
Fast neutrino oscillations
- When the same neutrinos are in the presence of many other neutrinos and when the different flavours are emitted slightly differently in various directions the oscillations from one flavour to another happen at a higher frequency.
- This is called fast oscillation and is proportional to the density of neutrinos in the medium, and not the masses of the neutrinos.
Supernova:
- Any star that collapses under its own gravity after having run out of its fusion fuel is called a supernova. Usually stars more massive than eight times the Sun’s mass enter this phase of explosive death.
- Collisions lead to the high anisotropy conditions. In the presence of collisions, the fast oscillations take place.
India-based Neutrino Observatory (INO):
- INO Project is aimed at building a world-class underground laboratory with a rock cover to conduct basic research on neutrino.
- The Tata Institute of Fundamental Research is the nodal institution. The observatory is to be built jointly with the Department of Atomic Energy and the Department of Science and Technology. The observatory will be located underground so as to provide adequate shielding to the neutrino detector from cosmic background radiation.
- The operation of INO will have no release of e of radioactive or toxic substances
INCIDENCE OF CANCER SET TO RISE: LANCET STUDY
12, May 2019
Why in News:
- A study published in The Lancet, Oncology estimates that a steady growth curve of patients (eligible for chemotherapy) will be seen in low- and middle-income countries going from 63% in 2018 to 67% in 2040.
Background: / About cancer:
- Cancer is one of the most dreaded diseases of human beings and is a major cause of death all over the globe.
- More than a million Indians suffer from cancer and a large number of them die from it annually. The mechanisms that underlie development of cancer or oncogenic transformation of cells, its treatment and control have been some of the most intense areas of research in biology and medicine. In our body, cell growth and differentiation is highly controlled and regulated. In cancer cells, there is breakdown of these regulatory mechanisms.
- Normal cells show a property called contact inhibition by virtue of which contact with other cells inhibits their uncontrolled growth.
- Cancer cells appears to have lost this property of contact inhibition. As a result of this, cancerous cells just continue to divide giving rise to masses of cells called tumors.
Types of Tumors
- Tumors are of two types: benign and malignant.
- Benign tumors normally remain confined to their original location and do not spread to other parts of the body and cause little damage.
- The malignant tumors, on the other hand are a mass of proliferating cells called neoplastic or tumor cells. These cells grow very rapidly, invading and damaging the surrounding normal tissues.
- As these cells actively divide and grow, they also starve the normal cells by competing for vital nutrients.Cells sloughed from such tumors reach distant sites through blood, and wherever they get lodged in the body, they start a new tumor there. This property called Metastasis is the most feared property of malignant tumors.
Causes of Cancer:
- Transformation of normal cells into cancerous neoplastic cells may be induced by physical, chemical or biological agents. These agents are called carcinogens.
- Ionizing radiations like X-rays and gamma rays and non-ionizing radiations like UV cause DNA damage leading to neoplastic transformation.
- The chemical carcinogens present in tobacco smoke have been identified as a major cause of lung cancer. Cancer causing viruses called oncogenic viruses have genes called viral oncogenes. Furthermore, several genes called cellular oncogenes (c-onc) or proto oncogenes have been identified in normal cells which, when activated under certain conditions, could lead to oncogenic transformation of the cells.
Cancer Detection and Diagnosis
- Early detection of cancers is essential as it allows the disease to be treated successfully in many cases.
- Cancer detection is based on biopsy and histopathological studies of the tissue and blood and bone marrow tests for increased cell counts in the case of leukemias.
- In biopsy, a piece of the suspected tissue cut into thin sections is stained and examined under microscope (histopathological studies) by a pathologist.
- Techniques like radiography (use of X-rays), CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are very useful to detect cancers of the internal organs.
- Computed tomography uses X-rays to generate a three-dimensional image of the internals of an object. MRI uses strong magnetic fields and non-ionising radiations to accurately detect pathological and physiological changes in the living tissue.
- Antibodies against cancer-specific antigens are also used for detection of certain cancers.
- Techniques of molecular biology can be applied to detect genes in individuals with inherited susceptibility to certain cancers. Identification of such genes, which predispose an Individual to certain cancers, may be very helpful in prevention of cancers.
- Such individuals may be advised to avoid exposure to particular carcinogens to which they are susceptible (e.g., tobacco smoke in case of lung cancer).
Treatment of Cancer:
- The common approaches for treatment of cancer are surgery, radiation therapy and immunotherapy. In radiotherapy, tumor cells are Irradiated lethally, taking proper care of the normal tissues surrounding the tumor mass.
- Several chemotherapeutic drugs are used to kill cancerous cells. Some of these are specific for particular tumors. Majority of drugs have side effects like hair loss, anemia, etc.
- Most cancers are treated by combination of surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
- Tumor cells have been shown to avoid detection and destruction by immune system. Therefore, the patients are given substances called biological response modifiers such as a- interferon which activate their immune system and help in destroying the tumor.
KOLKATA RESEARCHERS USE NOVEL COMPOUND TO KILL CANCER CELLS
12, May 2019

why in News:
- Researchers at Kolkata’s the Indian Institute of Chemical Biology (CSIR-IICB) and the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS) have designed and synthesised about 25 quinoline derivatives that show potent anticancer activity.
Background:
- The compounds were tested in vitro against human Topoisomerase 1 (topo1) activity and their efficacy to kill cancer cells was carried out using breast, ovarian, cervical and colon cancer cell lines. The results of topo1 inhibition activity, cellular mechanisms and the cancer cell line studies carried out at IACS and the compounds designed and synthesised by IICB researchers were published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
Topoisomerase 1:
- Topoisomerase 1 is a fundamental enzyme that is essential for replication. DNA is in a supercoiled state and has to be unwound before replication can take place.
- For the DNA to uncoil, the topo1 enzyme has to first bind to the DNA and form a complex. Once the complex is formed, the topo1 enzyme cleaves one strand of the DNA thus allowing the DNA to uncoil. Once uncoiling is completed, the topo1 enzyme re-joins the cleaved DNA strand for replication to take place.
- Existing drugs and the quinoline derivatives synthesised by the IICB team have the ability to trap the complex thereby not freeing the topo1 to re-join the cleaved DNA strand. As the number of trapped complexes in the DNA increases, the amount of free topo1 enzyme available to repair the cleaved DNA strand reduces.
- Also, other enzymes involved in replication and transcription (where DNA is converted into RNA) come and collide with the trapped topo1 and this causes more DNA breaks.
- As a result, replication gets affected leading to DNA break and cancer cell death
India Facing Critical Shortage Of Healthcare Providers: Who
11, May 2019

Why in News:
- Despite the health sector employing five million workers in India it continues to have low density of health professionals.
Details:
- It is lower than those of Sri Lanka, China, Thailand, United Kingdom and Brazil, according to a World Health Organisation
- This workforce statistic has put the country into the “critical shortage of
- healthcare providers” category. Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh and
- Rajasthan are the worst hit while Delhi, Kerala, Punjab and Gujarat compare Southeast Asia needs a 50% increase in healthcare manpower to achieve universal health coverage by 2030. India faces the problem of acute shortages and inequitable distributions of skilled health workers as have many other low- and middle-income countries,’
New courses needed
- The need of the hour is to design courses for different categories of non-physician care providers.
- Competencies should be valued and reform must be brought in regulatory structures to provide flexibility for innovations,
- Data on the prevalence of occupational vacancies in the health care system in India overall is
- Government statistics for 2008, based on vacancies in sanctioned posts showed 18% of primary health centres were without a doctor, about 38% were without a laboratory technician and 16% were without a pharmacist,”
- The health workforce in India comprises broadly eight categories, namely: doctors (allopathic, alternative medicine); nursing and midwifery professionals; public health professionals (medical, non-medical); pharmacists; dentists; paramedical workers (allied health professionals); grass-root workers (frontline workers); and support
World Health Organization
- WHO is a specialised agency of UN
- It is concerned with international public health
- It acts as coordinating authority on international public health Established in 1948
- It succeeded the Health Organization, which was an agency of the League of HQ: Geneva, Switzerland
- India is a founder member of WHO.
- It is a member of UN Development Group (UNDP).
- WHO flag features the Rod of Asclepius as a symbol for healing
National Health Mission
- The National Health Mission (NHM) envisages achievement of universal access to equitable, affordable & quality health care services that are accountable and responsive to people’s needs. The National Health Mission seeks to ensure the achievement of the following indicators. Reduce Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) to 1/1000 live births
- Reduce Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) to 25/1000 live births Reduce Total Fertility Rate (TFR) to 1
- Prevention and reduction of anaemia in women aged 15–49 years
- Prevent and reduce mortality & morbidity from communicable, non-communicable; injuries and emerging Reduce household out-of-pocket expenditure on total health care expenditure. Reduce annual incidence and mortality from Tuberculosis by half
- Reduce prevalence of Leprosy to <1/10000 population and incidence to zero in all districts Annual Malaria Incidence to be <1/1000
- Less than 1 per cent microfilaria prevalence in all districts
- Kala-azar Elimination by 2015, <1 case per 10000 population in all blocks
Karnataka Law On Sc/St Promotion Quota Upheld
11, May 2019

Why in News:
- Jeff Bezos, who heads both Amazon and space company Blue Origin, unveiled a lunar lander and it would be used to transport equipment, and possibly human beings, to the south pole of the Moon by 2024
Details:
- He showed a mock-up of a huge vessel weighing many tons and able to carry four self- driving Mr. Bezos didn’t announce a specific date for the project’s first launch, but said the lander would be ready in time to make President Donald Trump’s announced timeline to return people to the Moon by 2024.
Generating water
- The vehicle has been under development for the past three years.
- It will be capable of carrying scientific instruments, the four small rovers, and also a future pressurized vehicle for humans. The goal is to land on the Moon’s south pole, where ice deposits were confirmed in 2018. Water can be exploited to produce hydrogen, which in turn could fuel future exploration of the solar Fully loaded with fuel, Blue Origin will weigh about 33,000 pounds (15,000 kilograms), which will decrease to around 7,000 pounds when it is about to land
Lunar colonies
- The broader vision to build an infrastructure that would sustain the colonisation of space by future generations of humans and shift polluting industries off the As space agencies prepare to return humans to the moon, top engineers are racing to design a tunnel boring machine capable of digging underground colonies for the first lunar inhabitants. The humans need to be shielded from radiation and freezing temperatures in structures which maintain atmospheric pressure in a vacuum.
- They also need protection from meteorite strikes.
India’s lunar mission
- Chandrayaan-2, India’s second lunar mission, has three modules namely Orbiter, Lander (Vikram) & Rover (Pragyan). The Orbiter and Lander modules will be interfaced mechanically and stacked together as an integrated module and accommodated inside the GSLV MK-III launch The Rover is housed inside the Lander. After launch into earth bound orbit by GSLV MK-III, the integrated module will reach Moon orbit using Orbiter propulsion module.
- Subsequently, Lander will separate from the Orbiter and soft land at the predetermined site close to lunar South
- Further, the Rover will roll out for carrying out scientific experiments on the lunar Instruments are also mounted on Lander and Orbiter for carrying out scientific experiments.
- All the modules are getting ready for Chandrayaan-2 launch during the window of July 09, to July 16, 2019, with an expected Moon landing on September 06,
Chandrayan -2 to Be Launched in July
11, May 2019

Why in News:
- Chandrayan-2, a fully indigenous mission to be launched during mid of July with 14 Indian payloads
Background:
- In October 2008, the space organisation had launched its orbiter mission Chandrayaan-1 on its PSLV The spacecraft had 11 payloads. One of the U.S. payloads shares credit with Chandrayaan-1 for confirming the presence of water ice on the moon.
- Before that, the Moon Impacter Probe carrying the Indian tricolour image was made to hard-land on the lunar south pole.
About Chandrayan -2:
- Launch vehicle: GSLV Mk III
- Lift off mass (approx.): 3,890 kg
- Launch from: Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh
- Orbiter: It will orbit the moon at a distance of 100 km from the lunar Payloads on the orbiter are: Large Area Soft X-ray Spectrometer, L and S band Synthetic Aperture Radar, Imaging IR Spectrometer, Neutral Mass Spectrometer and Terrain Mapping Camera-2. The structure of the orbiter was manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- Lander: The lander has been named Vikram after scientist Vikram The lander will detach from the orbiter, descend to a lunar orbit, before attempting to land on the surface.
- It will make a soft-landing and deploy the rover. It will also perform some scientific activities for about 15 days. Payloads on the lander are: seismometer, thermal probe, Langmuir probe and radio occultation.
- Rover: The 27 kg rover will operate on solar It will move on six wheels and conduct chemical analyses on-site. It will then transmit the data to the orbiter which will send this data back to the earth station. The rover payloads include Laser induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS) and Alpha Particle Induced X-ray Spectroscope (APIXS). Chandrayaan II is India’s second lunar mission after Chandrayaan I.
- The mission includes a lunar orbiter, rover and a The mission is developed by ISRO, India. Initially, the lander was supposed to have been developed by Russia. But, when Russia cited its inability to provide the lander by 2015, India decided to go solo. Now, the mission is entirely Indian. The launch vehicle would be a GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III).
Way Ahead:
- The mission is attempting to soft-land on the moon’s surface at a latitude of about 70° south, that would be on a high plain in between 2 If successful, this would be the
STRESS BUSTER SEROTONIN MAY HELP TREAT NEUROLOGICAL DECLINE
07, May 2019

Why in News:
- Researchers at TIFR say the chemical can impact the manner in which neurons grapple with stress and affect ageing
Details:
- researchers at the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) Mumbai have found a novel
- function for serotonin (a chemical that signals between neurons)
- The recent discovery establishes that serotonin is involved in the generation of new mitochondria (the powerhouse of the cell) in neurons, increased cellular respiration and fuel (ATP) in the cell.
Underlying mechanism
- At the level of an organism, serotonin is known to be involved in coping with stress
- The study provides insights into how serotonin generates more mitochondria thereby giving neurons the capacity to produce more energy and the ability to cope with stress better.
- It is found that serotonin reduces reactive oxygen species, thus providing neuroprotection against cellular stress. Serotonin can impact the manner in which neurons grapple with stress and affect the trajectory of ageing,
- Neuronal loss is a major cause of neurodegenerative diseases such as in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
Experimental proof
- Injecting serotonin directly into the brain of rats led to direct increase in mitochondria number and ATP level. This study paves way for further research into designing therapeutic interventions. This may help tackle mood disorders and age-associated neurological decline,
IIT KANPUR IDENTIFIES NOVEL MOLECULE TO CONTROL HYPER INFLAMMATION
05, May 2019

Why in News:
- Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur have identified and characterised a novel small protein molecule that can effectively control inflammation leading to better treatment outcomes.
Details:
- Hyper inflammation destroys the tissues surrounding the inflamed area leading to inflammation disorders such as sepsis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis.
- A small protein (C5a) that is a part of the innate immunity (immediate defence against pathogens that have never been encountered before) gets activated when a pathogen enters the body. The C5a protein then binds to a particular receptor (C5aR1) found on the surface of certain cells such as macrophages and neutrophils to begin the process of inflammation and pathogen clearance. Neutrophiles are already present in the body and circulate in the blood. Once the small protein binds to the C5aR1 receptor found on neutrophils, there is increased migration towards the site of infection leading to hyper inflammation. Binding of the small protein to the receptor on macrophages reduces the amount of a pro-inflammatory cytokine called interleukin-6 (IL-6) that is released, which is desirable to overcome inflammatory symptoms.
C5a protein:
- C5a is a protein fragment released from cleavage of complement component C5 by protease C5-convertase into C5a and C5b fragments.
- It leads to the formation of the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC), one of the most basic weapons of the innate immune system, formed as an automatic response to intrusions from foreign particles and microbial invaders. C5a is a chemotactic agent and an anaphylatoxin. It is essential in the innate immunity but it is also linked with the adaptive immunity. The increased production of C5a is connected with a number of inflammatory diseases.
Interleukin 6
- Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory cytokine and an anti-inflammatory myokine. In humans, it is encoded by the IL6 gene.
- In addition, osteoblasts secrete IL-6 to stimulate osteoclast formation.
- Smooth muscle cells in the tunica media of many blood vessels also produce IL-6 as a pro- inflammatory cytokine. IL-6’s role as an anti-inflammatory myokine is mediated through its inhibitory effects on TNF-alpha and IL-1, and activation of IL-1ra and IL-10.
GADCHIROLI NAXAL ATTACK: TROOP PULLOUT MAY HAVE LEFT A HOLE IN RED ZONE SECURITY GRID
05, May 2019
Why in News:
- The unceasing requisitioning of paramilitary forces for the elections in West Bengal may have weakened the security grid around Maharashtra’s Maoist heartland, where an IED blast killed 15 jawans
Details:
- Maoists torched 25 vehicles at a road
- construction site in Kurkheda of Gadchiroli early in the morning.
- A team of the Quick Response Team of the Gadchiroli police was on way to inspect this.
- While on road in a private vehicle, these fifteen policemen and their driver were killed by a powerful explosion set off by Maoists.
- An improvised explosive device (IED) blast was set off. The slain fighters were members of the elite C-60 wing.
- This is the fourth Maoist attack, since the national election began in April, 2019, in Gadchiroli which borders Chattisgarh.
Maoists:
- Maoists in India are anti-state rebellion groups spread in mainland country covering tribal areas of seven states. The insurgency began in 1967 in remote forests of West Bengal’s village ‘Naxalbari’. While Naxalism originated in India, Maoism in China. The common thread between the two is “armed resistance” and “violence”.
- The Maoists consider Parliamentary democracy to be tools of exploiting their rivers and natural resources by capitalists and politicians. They want to establish a ‘communist society’ through armed revolution against the government.
Measures taken to deal with Left Wing Extremism:
- In 2017, a security operations doctrine called ‘SAMADHAN’ was launched.
- The acronym SAMADHAN stands for Smart leadership, Aggressive strategy, Motivation and training, Actionable intelligence, Dashboard Based KPIs (key performance indicators) and KRAs (key result areas), Harnessing technology, Action plan for each theater, and No access to financing. The MHA suggested the use of trackers for weapons, and bio-metrics in smart guns. Unique Identification number (UID) for Gelatin sticks and explosives.
- At least one UAV or Mini UAV for each of the Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) battalions deployed in the Maoist hotbed. Joint Task Forces for operations along inter-State boundaries to be set up. Better inter-state coordination and intelligence sharing.
- 400 fortified police stations to be set up in Naxal belt.
- Resumption of Left-Wing Extremism (LWE) – specific schemes such as SRE, SIS, IAP/ACA, CIAT schools. Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) to be reviewed to ensure effective choking of fund flow to LWE groups. Fast tracking building infrastructure, with a focus on solar lights, mobile towers with 3G connectivity, and road-rail connectivity.
- Indian Army or specialized forces – such as Greyhounds – to train forces to take on naxals.
C-60 wing:
- The C-60 was created as a batch of 60 commandos to counter Maoist violence in Gadchiroli.
- As Naxal activities heightened in the coming years, a second branch was also created in 1994. They are similar to the Greyhound forces in Telangana and the SOG (Special Operation Group) units in Andhra Pradesh.
- The contribution of C-60 has been a notable one, and they have been alternatively referred to as ‘crack commandos’. The commandos were recruited from the same regions where the Naxals enlisted their own fighters.
- Having the same roots, the C-60 had operational advantages compared to other units of the state police. These include faster maneuvering, and the greater ability to converse with the local population. The C-60 is qualified for combat in difficult battlegrounds, such as dense forests and over hilly terrain. Apart from actual combat, the C-60’s task also includes facilitating Maoists to surrender and join the mainstream.
- For this, members of the unit meet the families of Maoists to apprise them of government schemes made for ex-Maoists.
Way Forward:
- The forces should be more proactive and aggressive in owning operations, rather than being reactive. To overcome the Maoist Challenge, there needs to be a comprehensive policy and not just a military or security centric approach.
IIT DELHI 3D PRINTS HUMAN SKIN
05, May 2019

Why in News
- Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Delhi have successfully 3D bioprinted human skin models
Details:
- 3D bioprinted human skin models that have certain
- anatomically relevant structural, mechanical and biochemical features similar to native human skin.
- The bioprinted skin produced in the lab by the team is already being used by ITC Ltd for experiments.
- The bioprinted skin model will have wide applications in testing cosmetics. It can also reduce and probably even replace testing on animals
- It can also be used for testing dermatology drugs on human skin and at a future date even help in testing drugs for personalised medicine.
Testing on animals:
- The European Commission has prohibited testing finished cosmetic products and cosmetic ingredients on animals.
- It even prohibits marketing of finished cosmetic products and ingredients in the European Union.
- The skin is composed of two important layers — the inner dermis (made of fibroblasts) and the outer epidermis (keratinocytes, melanocytes).
- The junction between the two layers is not flat but is undulatory or wavy.
- The undulatory morphology is important as it provides biochemical cues and mechanical support to the epidermis layer, provides structural stability to the skin by making the two layers adhere to each other, and not allow cells to cross the junction.
- Unlike the currently available tissue-engineered skin equivalents, the team was successful in creating this wavy junction in the bioprinted skin model.
No shrinkage
- The bioprinted skin also retained the original dimension without any shrinkage for up to three weeks. Traditionally, collagen used for developing skin constructs start shrinking within a few weeks thus affecting the morphology. gene and protein expression analysis showed 60% similarity in gene expression between bioprinted and native skin.
BioPrinting:
- Bioprinting is an extension of traditional 3D printing.
- Bioprinting can produce living tissue, bone, blood vessels and, potentially, whole organs for use in medical procedures, training and testing.
NOT KEEPING RECORD OF PRE-NATAL TESTS IS CRIMINAL: SC
04, May 2019

Why in News
- The Supreme Court upheld provisions in the anti-pre-natal sex determination law which ‘criminalises’ non-maintenance of medical records by obstetricians and gynaecologists and suspend their medical licence indefinitely.
Details:
- A Bench of Justices held that the particular provisions in the Pre-conception and Pre-natal Diagnostic Techniques (Prohibition of Sex Selection) Act of 1994 were necessary to prevent female foeticide in the country.
- The main purpose of the Act is to ban the use of sex selection and misuse of pre-natal diagnostic technique for sex selective abortions and to regulate such techniques.
- The court dismissed averments made by doctors that the provisions in the law criminalise even the smallest anomaly in paperwork which is in fact an inadvertent and unintentional error.
- The sections have made obstetricians and gynaecologists vulnerable to prosecution all over the country.
- “It is a responsible job of the person who is undertaking such a test i.e., the gynaecologist/medical geneticist/radiologist/ paediatrician/director of the clinic/centre/laboratory to fill the requisite information. In case he keeps it vague, he knows fully well that he is violating the provisions of the Act,
Pre-conception and Pre-natal Diagnostic Techniques (Prohibition of Sex Selection) Act
- The Pre-conception & Pre-natal Diagnostics Techniques (PC & PNDT) Act, 1994 was enacted in response to the decline in Sex ratio in India, which deteriorated from 972 in 1901 to 927 in 1991.
- The main purpose of enacting the act is to ban the use of sex selection techniques before or after conception and prevent the misuse of prenatal diagnostic technique for sex selective abortion.
- The Act was amended to bring the technique of pre conception sex selection and ultrasound technique within the ambit of the act.
- In 1988, the State of Maharashtra became the first in the country to ban pre-natal sex determination through enacting the Maharashtra Regulation of Pre-natal Diagnostic Techniques Act
AIDS DRUGS PREVENT SEXUAL TRANSMISSION OF HIV IN GAY MEN
04, May 2019
Why in News:
- A European study of nearly 1,000 gay male couples — who had sex without condoms where one partner had HIV and was taking anti-retroviral drugs to suppress it — has found the treatment can prevent sexual transmission of the virus.
Details:
- After eight years of follow-up of the so-called serodifferent couples, the study found no cases at all of HIV transmission within couples
- The study proves, the researchers said, that using anti-retroviral therapy to suppress the AIDS virus to undetectable levels also means it cannot be passed on via sex,
- The findings provide conclusive evidence for gay men that the risk of HIV transmission with suppressive ART is zero
- The study, published in the Lancet medical journal assessed the risk of HIV transmission between serodifferent gay male couples — where one partner is HIV-positive and one is HIV-negative — who do not use condoms.
- It also found zero risk.
AIDS
- The word AIDS stands for Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome. This means deficiency of immune system acquired during the lifetime of an individual indicating that it is not a congenital disease [disease or abnormality present from birth]. ‘Syndrome’ means a group of symptoms.
- AIDS was first reported in 1981 and in the last twenty-five years or so, it has spread all over the world.
antiretroviral therapy:
- AIDS is caused by HIV, a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. The virus destroys CD4+ T cells, a type of white blood cell that’s vital to fighting off infection. AIDS is treated with antiretroviral drugs. These drugs suppress HIV but don’t completely eliminate the virus from the body.
Government initiatives
- The Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare launched the National Strategic Plan 2017-24 aimed at eradicating HIV/AIDS by 2030. It was launched on the occasion of World AIDS Day (1st December).
- Mission SAMPARK was also launched to trace those who are Left to Follow Up and are to be brought under Antiretroviral therapy (ART) services.
- 90:90:90 Strategy It is a new HIV treatment narrative of UNAIDS programme which has set targets of 90% of all people living with HIV will know their HIV status (90% diagnosed), 90% of all people with diagnosed HIV infection will receive sustained antiretroviral therapy (90% on HIV treatment) and 90% of all people receiving antiretroviral therapy will have viral suppression (90% suppressed).
INDIAN ADULTS UNAWARE THEY ARE AILING FROM HYPERTENSION
04, May 2019
Why in News:
- Hypertension is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is a leading cause of death in India. First large-scale
study finds only 45% diagnosed, only 8% had BP under control
Details:
- Despite having a heavy burden of a hypertensive population, the proportion of adults with high blood pressure who are aware of their diagnosis, are treated and achieve control, is dismally low, only 3 out of 4 individuals with hypertension has ever had their blood pressure measured, only 45% had been diagnosed, and only 8% of those surveyed had their blood pressure under control. More than half the number of Indians aged 15-49 years with hypertension were not aware of their hypertension status. Awareness level was lowest in Chhattisgarh (22.1%) and highest in Puducherry (80.5%).
- Hypertension is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is a leading cause of death in India. “Researchers used the National Health and Family Survey (NFHS-4, 2015- 16) data
Hypertension
- Hypertension or high blood pressure is a serious health problem which currently affects nearly 1 billion people worldwide. According to the recent analysis by the World Health Organisation (WHO), this statistic might rise to around 1.57 billion by the year 2025.
- These patients suffering from this disorder will have their blood pressure reading greater than 140 over 90 mm.
National Family Health Survey (NFHS)
- The National Family Health Survey (NFHS) is a large-scale, multi-round survey conducted in a representative sample of households throughout India.
- All National Family Health Surveys have been conducted under the stewardship of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India, with the International Institute for Population Sciences, Mumbai, serving as the nodal agency.
- ICF International (formerly Macro International), Maryland, USA, provided technical assistance for all four surveys conducted as on date.
LOST LIVES: ON GADCHIROLI NAXAL ATTACK
03, May 2019

Why in News
- India must meet the Maoist challenge in a holistic manner
Details:
- The death of 15 security personnel in a landmine attack in Gadchiroli is another grim reminder of naxalism.
- a legislator and some security personnel lost their lives in a similar attack in the neighbouring State of Chhattisgarh ahead of polling.
- Despite the deployment of 30 companies of the Central Reserve Police Force shows not only the audacity of the perpetrators but also the unpreparedness of the security forces.
- The ease with which the extremists were able to torch so many vehicles is alarming, and the manner in which the response team blithely drove into an ambush is a shocking example of poor planning. the path of the voter to the polling booth in the naxal-dominated districts is still paved with disincentives.
Naxalism
- Naxalism the far-left radical communist organization though trace its origin to West Bengal in the early 1960s, gradually spread its wings towards the less developed areas of southern and eastern parts of the country.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs has been trying its hand in weakening the strength of the naxalites and other extremist groups who in the name of welfare for the downtrodden have done many heinous crimes resulting in deaths and harassment.
Government strategy
- The government has proposed a three-pronged strategy to combat Naxalism: Gain confidence of local people by taking up more welfare related activities. Build up infrastructure in naxal-affected areas and generate employment.
- Launch joint security operations with neighbouring states to eliminate left wing extremists.
What is a red corridor region?
- Red corridor region is demarcated by the union government to notify the districts which are affected by left wing extremism.
- It is spanning across 106 districts in 10 States, namely Bihar, Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Telangana, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
THE COST OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE
02, May 2019
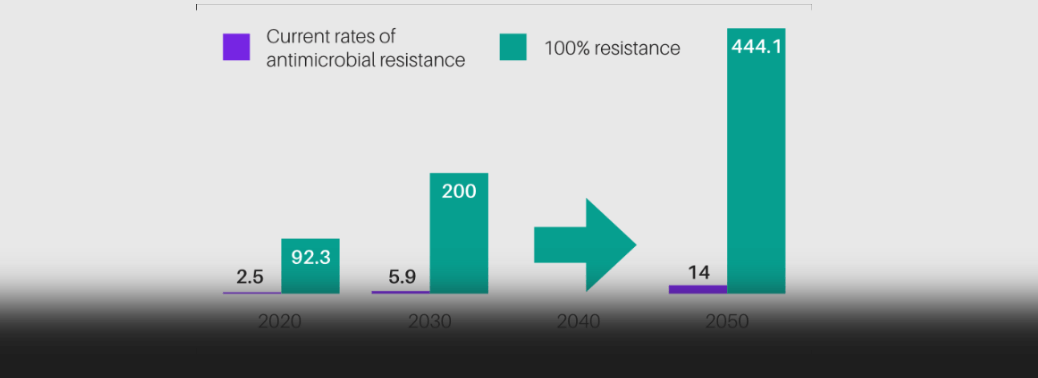
Why in News:
- India must brace for the economic shocks from uncontrolled antimicrobial resistance
Details:
- Even though antimicrobial resistance is acknowledged by policymakers as a major health crisis, few have considered its economic impact.
- a report from the Interagency Coordination Group on Antimicrobial Resistance (IACG) puts the financial fall-out in perspective.
- Titled “No Time to Wait: Securing The Future From Drug Resistant Infections”, it says in about three decades from now uncontrolled antimicrobial resistance will cause global economic shocks on the scale of the 2008-09 financial crisis.
- With nearly 10 million people estimated to die annually from resistant infections by 2050, health-care costs and the cost of food production will spike, while income inequality will widen.
- the world will lose 3.8% of its annual GDP by 2050, while 24 million people will be pushed into extreme poverty by 2030. many Indians still die of diseases like sepsis and pneumonia because they don’t get the right drug at the right time. On the other hand, a poorly regulated pharmaceutical industry means that antibiotics are freely available to those who can afford them. Some steps can be initiated right away, it says, such as phasing out critical human-use antibiotics in the animal husbandry sector, such as quinolones.
- Philanthropic charities must fund the development of new antibiotics, while citizen activists must drive awareness. the only way to postpone resistance is through improved hygiene and vaccinations. It is a formidable task as India still struggles with low immunisation rates and drinking water contamination. While the 2008-09 financial crisis caused global hardships, its effects began to wear off by 2011. Once crucial antibiotics are lost to humankind, they may be lost for decades.
Antimicrobial resistance:
- The WHO defines antimicrobial resistance as a microorganism’s resistance to an antimicrobial drug that was once able to treat an infection by that microorganism.
- The Union health ministry’s Anti-Microbial Resistance awareness campaign urges people not to use medicines marked with a red vertical line, including antibiotics, without a doctor’s prescription.
CHANDRAYAAN 2 GETS NEW LAUNCH WINDOW
02, May 2019
Why in News
- India’s much-delayed second lunar mission, Chandrayaan-2, has got yet another launch window.
Chandrayaan-2
- The mission is set to be launched any time in july
- The moon landing is likely to be around nearly two months after the launch, ISRO said.the second lunar mission of ISRO will have three modules — the Orbiter, Lander (Vikram) and Rover (Pragyan).
- The Orbiter and Lander will be interfaced mechanically and stacked together as an integrated module and accommodated inside the GSLV MK-III launch vehicle, ISRO said. “After launch into earth bound orbit by GSLV MK-III, the integrated module will reach the Moon orbit using Orbiter propulsion module. Subsequently, Lander will separate from the Orbiter and soft land at the predetermined site close to lunar South Pole. Further the Rover will roll out for carrying out scientific experiments on the lunar surface,
- The mission would land on the southern pole of the moon, which has not been explored much before by any of the countries. The landing of the craft near the lunar south pole would be historically significant as it would give ISRO the opportunity to name that site on the moon.
GSLV Mk III:
- GSLV Mk III is a three-stage heavy lift launch vehicle developed by ISRO. The vehicle has two solid strap-ons, a core liquid booster and a cryogenic upper stage.
- GSLV Mk III is designed to carry 4-ton class of satellites into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) or about 10 tons to Low Earth Orbit (LEO), which is about twice the capability of GSLV Mk II.
ARMY INVOKES EMERGENCY POWERS FOR MISSILE DEAL
30, Apr 2019

Why in News
- The Army set to procure Spike-LR Anti-Tank Missiles from Israel and Igla-S Very Short-Range Air Defence Systems (VSHORAD) from Russia through a set of new financial powers for emergency procurements sanctioned by the Defence Ministry
Details
- Under the latest emergency financial powers, armed forces have
- been given a free hand to procure equipment worth up to ₹300 crore on a priority basis. The Request For Proposal (RFP) for the two deals have been issued and negotiations are on process
- Under the emergency route, the Army is looking to procure about 12 launchers and around 250 missiles for each system.
Spike LR
- Spike is an Israeli fire-and-forget anti-tank guided missile and anti-personnel missile with a tandem-charge HEAT warhead currently in its fourth-generation. It was developed and designed by the Israeli company Rafael Advanced Defense Systems. It is available in man- portable, vehicle-launched, and helicopter-launched variants. Long range version. Maximum range is 4,000 m (2.5 mi) and it is used by infantry and light combat vehicles
VSHORAD deal
- The deal for VSHORAD, to replace the legacy Igla systems in service, began in 2010 and has since seen several trials and re-trials with three contenders in the fray
- While the benchmark price determined was just over $2 bn, Rosoboronexport’s bid was much lower at around $1.47 bn, while SAAB’s bid was at about $2.6 bn and MBDA around $3.68 bn.
- This led to a division within the Ministry on how to proceed given such low bid from the Russians compared to the benchmark price, but eventually Igla-S was declared the winner. “The deal is currently at the Contract Negotiation phase,” the source said.
- Officials said the emergency procurements were one of critical procurement and not related to the acquisitions through the regular route, in a bid to assure that these would not impact the regular deals. In the case of VSHORAD, the other two vendors lodged protests and wrote a series of letters to the Defence Ministry on several occasions alleging procedural violations favouring Igla-S which were rejected.
GENES OF CLIMATE-RESISTANT CHICKPEA VARIETIES IDENTIFIED
30, Apr 2019

Why in News
- ICRISAT study discovers important factors for heat and drought tolerance
Details:
- An international team led by the Hyderabad-based International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) has identified in chickpea four important genes for heat tolerance and three important genes for drought tolerance.
- With rising temperatures and increasing climatic fluctuations due to climate change, the identification of these climate-resistant genes will help in developing newer chickpea varieties which can tolerate temperatures up to 38°C. Also, the identification of other genes with important agromic traits will help in increasing the yield and providing better resistance to pests and diseases. The study was based on complete genome sequencing of 429 chickpea lines from 45 countries.
- More than 90% of chickpea cultivation area is in South Asia, including India. Globally, more than 70% yield is lost due to drought and increasing temperatures. Chickpea is a cool season crop, so in general any further increase in temperature is expected to further reduce the yield.
Timely Trial:
- By using such genomics-assisted breeding approach, the time taken to produce a new heat- and drought-tolerant chickpea variety can be halved from about eight to four years,” Currently, in India, chickpea does not face a major threat from increasing temperature.
- But we are already witnessing a slight warming during the months of January and February. So, a new variety with heat and drought tolerance will be highly useful to Indian farmers, When heat-tolerant chickpeas are developed in future, farmers in India may have a possibility to go in for a second round of cropping. Though the yield will be less for the second crop, farmers will still stand to gain.”
Diversity, domestication
- The study has found that chickpea originated in the Mediterranean/south-west Asia and migrated to south Asia.
- It reached India about two centuries ago, apparently through Afghanistan. In parallel, it migrated from the Mediterranean to east Africa and central Asia. The study provides insights into chickpea’s genetic diversity, domestication too
DRUG RESISTANT DISEASES COULD KILL 10 MILLION A YEAR BY 2050
30, Apr 2019

Why in News
- UN report calls for prudent use of antibiotics
Details:
- If no action is taken, drug-resistant diseases could cause 10 million deaths each year by 2050 and damage to the economy as catastrophic as the 2008- 2009 global financial crisis, warns a new report by United Nations (UN)
- The report released by Interagency Coordination Group on Antimicrobial Resistance (IACG) also finds that by 2030, antimicrobial resistance could force up to 24 million people into extreme poverty.
- UN, international agencies and experts demand immediate, coordinated and ambitious action to avert a potentially disastrous drug-resistance crisis.
- Antimicrobial resistance is a growing problem in India and is making it particularly hard to treat diseases like Tuberculosis (TB), childhood sepsis and malaria. It is estimated that annually at least 700,000 deaths occur from antibiotic-resistant infections in low- and middle-income countries. This includes 230,000 people who die from multidrug-resistant TB.
- More and more common diseases, including respiratory tract infections, sexually transmitted infections and urinary tract infections, are untreatable; lifesaving medical procedures are becoming much riskier, and our food systems are increasingly precarious.
- The world is already feeling the economic and health consequences as crucial medicines become ineffective. The report emphasises that without investment from countries in all income brackets, future generations will face the disastrous impacts of uncontrolled antimicrobial resistance.
- Antimicrobial resistance is one of the greatest threats we face as a global community. This report reflects the depth and scope of the response needed to curb its rise and protect a century of progress in health
Anti-Microbial Resistance (AMR)
- The Anti-Microbial Resistance (AMR) is an ability of a microbe to resist the effects of medication previously used to treat them. It is also known as the antibiotic resistance.
- The WHO defines antimicrobial resistance as a microorganism’s resistance to an antimicrobial drug that was once able to treat an infection by that microorganism.
International Conference on Antimicrobial Resistance
- India presided over the 68th session of the World Health assembly proceedings in Geneva (May 18-26, 2015) which adopted a Global Action Plan on AMR to prepare a blueprint with specific actions and timelines for WHO as well as member states to address the growing threat of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR).
What is a Red Line campaign?
- The Union health ministry’s Anti-Microbial Resistance awareness campaign urges people not to use medicines marked with a red vertical line, including antibiotics, without a doctor’s prescription. These medicines are called as the ‘Medicines with the Red Line’
- This campaign is aimed at discouraging unnecessary prescription and over-the-counter sale of antibiotics causing drug resistance for several critical diseases including TB, malaria, urinary tract infection and even HIV.
DELHI HC LIFTS CENTRE’S CURBS ON GI TAG FOR BASMATI RICE
29, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- The Delhi High Court has struck down the decision of the Central government restricting the famously aromatic basmati rice production to only seven States in the Indo-Gangetic plains.
Details:
- High Court’s verdict came on the Madhya Pradesh government’s plea to include 13 districts in the State under the Geographical Indications (GI) category for basmati rice.
Two memos
- The Ministry of Agriculture had through two Office Memorandums (OM) of May 2008 and February 2014 confined the GI certification for basmati to rice grown in the Indo-Gangetic plains in the States of Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and parts of Uttar Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir. GI certification gives recognition and several protections to a basmati rice producer and help in maintaining the specific qualities of the rice grown in that particular region. The Madhya Pradesh government contended that the two OMs were outside the scope of the Seeds Act, 1966. It additionally argued that the OMs encroach upon its power to pass laws in relation to agriculture, which is a State subject. The 2008 OM of the Ministry set forth the standards of the ‘basmati’ variety of rice.
Geographical indication (GI)
- A geographical indication (GI) is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin. In order to function as a GI, a sign must identify a product as originating in a given place.
Seeds Act 1966
- The parliament had passed to Seeds Act 1966 to provide legal framework around seed certification and make good quality seeds available to the cultivators. This act provided for establishment of a Central Seed Committee to advise the states in seed related matters. It also provided for establishment of Seed Certification Agencies in the states; Seed certification Boards and State Seed Testing Laboratories.
WHY CHRISTINA KOCH WILL STAY ON THE ISS FOR 11 MONTHS
29, Apr 2019

Why in News
- NASA wants to study the effects of spaceflight on a woman
Details:
- Astronaut Christina Koch will set a record for the longest single spaceflight by a woman when she completes her 11-month-long mission aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Her long stay on the ISS has to do with NASA’s preparation of human missions to the Moon and Mars.
Lack of data
- The mission became necessary as the majority of data available is on male astronauts. But male and female bodies respond differently, and health conditions occur at different rates in male and female populations. With this mission, researchers hope to better understand
- astronaut adaptability over long periods of space exposure and better support the development of effective countermeasures to maintain crew health.
- NASA last month accepted a challenge from the Donald Trump administration to return humans to the Moon by 2024, four years ahead of the U.S. space agency’s earlier set target.
- Ms. Koch’s stay on the space station will eclipse the previous mark set by Peggy Whitson of
- 288 days on Expeditions 50 through 52 in 2016-17.
- Meanwhile, NASA’s Human Research Programme continues to lay the groundwork for future one-year missions on the space station and has selected 25 proposals to investigate biological, physiological, and behavioural adaptations to spaceflight.
- NASA said it aims to address five hazards of human space travel — space radiation, isolation and confinement, distance from Earth, gravity fields (or lack thereof), and hostile/closed environments that pose great risks to the human mind and body in space.
International Space Station (ISS)
- The International Space Station (ISS) is a space station, or a habitable artificial satellite, in low Earth orbit. Its first component launched into orbit in 1998, and the ISS is now the largest human-made body in low Earth orbit.
- The ISS serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which crew members conduct experiments in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology, and other fields.
- Five different space agencies representing 15 countries built the $100-billion International Space Station and continue to operate it today. NASA, Russia’s Roscosmos State Corporation for Space Activities (Roscosmos), the European Space Agency, the Canadian Space Agency and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency are the primary space agency partners on the project.
COMFORT FOOD LEADS TO MORE WEIGHT GAIN DURING STRESS: STUDY
29, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- Indulging in high-calorie ‘comfort’ foods when stressed can lead to more weight gain than usual, scientists say.
Details:
- Researchers from the Garvan Institute of Medical Research in
- Australia discovered a molecular pathway in the brain, controlled by insulin, which drives the additional weight gain. Using an animal model, the team showed that a high-calorie diet when combined with stress resulted in more weight gain than the same diet caused in a stress-free environment. “This study indicates that we have to be much more conscious about what we’re eating when we’re stressed
- To understand what controls this ‘stress eating’, the team investigated different areas of the brain in mice. While food intake is mainly controlled by a part of the brain called the hypothalamus, another part of the brain — the amygdala — processes emotional responses, including anxiety. The study showed that when stressed over an extended period and high calorie food was available, mice became obese more quickly than those that consumed the same high fat food in a stress-free environment,”
NPY
- At the centre of this weight gain, the scientists discovered, was a molecule called NPY, which the brain produces naturally in response to stress to stimulate eating in humans as well as mice.
- Without NPY, the weight gain on a high-fat diet with stress was the same as weight gain in the stress-free environment,
- “This shows a clear link between stress, obesity and NPY,
- Under normal conditions, the body produces insulin just after a meal, which helps cells absorb glucose from the blood and sends a ‘stop eating’ signal to the hypothalamus feeding centre of the brain. The scientists discovered that chronic stress alone raised the blood insulin levels only slightly, but in combination with a high-calorie diet, the insulin levels were 10 times higher than mice that were stress-free and received a normal diet.
- The study showed that these prolonged, high levels of insulin in the amygdala caused the nerve cells to become desensitised to insulin, which stopped them from detecting insulin altogether. In turn, these desensitised nerve cells boosted their NPY levels, which both promoted eating and reduced the bodies’ normal response to burn energy through heat.
ADDRESS THE INNOVATION DEFICIT IN NEGLECTED DISEASES
28, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- The thrust in funding research should be followed up with policies that incentivise industry in drug development.
Details:
- India was reported to be the fourth largest funder of research and development (R&D) in neglected diseases as per the G Finder Survey which tracks global investments in R&D for the neglected diseases. Neglected diseases are mostly tropical infectious diseases, and the market size for
- drugs for such diseases is small due to their limited geographical incidence.
- To highlight the common problem of lack of innovation for drugs, diagnostics and vaccines for this basket of diseases, WHO started addressing these as neglected diseases from late 1980s. Some examples of neglected diseases are malaria, tuberculosis, leishmaniasis (kala azar), dengue, leprosy, lymphatic filariasis and diarrhoeal diseases.
- These diseases face an innovation deficit as they are neglected in R&D efforts of the pharmaceutical industry. However, it is not just the neglected diseases in the developing world that face this innovation deficit. Several rare diseases that affect the developed markets are called “orphan diseases.”
- These are called orphans because the pharmaceutical industry does not find it profitable to develop and market products intended for only a small number of patients suffering from rare diseases.
Innovation model
- This innovation deficit is caused by the prevailing model of pharmaceutical innovation.
- By the middle of the 20th century it became an endeavour that was largely driven by pharmaceutical companies. The second half of the 20th century saw consolidation of pharmaceutical entities leading to multinational pharmaceutical companies who drive innovation in the pharmaceutical sector. Orphan diseases comprise both rare diseases and neglected diseases. They are orphans of research focus, market interest and even public health policies. If the market size is not attractive, industry will not invest in such cases. This leads to market failures resulting innovation deficit.
Incentives:
- The thrust in funding research should be followed up with policies that incentivise industry to take up drug development.
- A sustained and long-term funding commitment to neglected diseases will address this issue. If the Prime Minister’s slogan of ‘Jai Anusandhan’ has to reach its benefits to the poor and neglected patients, there should be a comprehensive policy to address the innovation deficit in neglected diseases.
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs)
- A diverse group of communicable diseases that prevail in tropical and subtropical conditions in 149 countries – affect more than one billion people and cost developing economies billions of dollars every year. Populations living in poverty, without adequate sanitation and in close contact with infectious vectors and domestic animals and livestock are those worst affected.
JAMIA TEAM DEVELOPS ULTRASENSITIVE QUANTUM THERMOMETER
28, Apr 2019

Why in News
- Researchers at Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, have developed an ultrasensitive quantum thermometer using graphene quantum dots. The thermometer can measure micro Kelvin changes in temperature and has quick response time.
Sensitive device
- The thermometer can precisely measure a wide range of temperature: 27 degree C to –196-degree C. The thermometer has high sensitivity when measuring different temperatures and can measure very minute (micro Kelvin) changes in temperature.
- The thermometer also showed extremely quick response time of just about 300 milliseconds to register a change in temperature from 27 degree C to –196-degree C. And the time taken to return to its initial temperature value was as little as about 800 milliseconds.
- The thermometer showed excellent repeatability with negligible variation in sensing response when tested for over 50 cycles during a one-year period. The device can find widespread applications in cryogenic temperature sensing.
- Since the sensor has high sensitivity and ability to measure minute changes in temperature, it will be useful in the pharmaceutical industry, healthcare to measure the incubation temperature of biological cells and molecules and the automobile industry to measure the ignition temperature within the engine.
- The sensor can also be used for measuring high temperatures up to 100-degree C. Compared with low temperature, the high-temperature sensitivity is low but it is still much higher than currently available solid-state thermometers in terms of sensitivity, resolution, response and recovery timings,
Sensor Preparation
- The researchers first prepared graphene oxide and chemically made it reduced graphene oxide. “The physical and chemical properties of reduced graphene oxide are very close to monolayer graphene.
- So by using reduced graphene oxide it is easy to synthesise in large-scale materials having properties similar to graphene,”
- The synthesis process is extremely cost effective, has high yield and batch fabrication is possible. One of the main advantages is that this device can be made to any shape and dimension,” Scientists are working on making a prototype of this thermometer to be used in electronic devices, as on-chip thermometers that do not even require calibrations. they will replicate these achievements in single electron transistors (SETs) to miniaturise it for integration in integrated circuits.
Quantum thermometer
- The problem of normal thermometers are not accurate. They need to be calibrated, or adjusted, to some standard. To use the beam as a thermometer, researchers must be able to measure the tiniest possible vibrations in the beam. The amount that the beam vibrates is proportional to the temperature of its surroundings.
FBI Chief Tells us Congress that China Poses Bigger Security Threat Than Russia
27, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- China came under renewed criticism by US government officials and lawmakers on a range of issues, including charges of human rights violations against Chinese dissidents and minority groups and being a threat to US
background:
- FBI Director Chris Wray says Russia still poses a significant counterintelligence threat to the
- S. and continues to use social media campaigns to try and influence American politics. They use social media to try and spin us up and pit us against each other and to undermine Americans faith in democracy, Wray said at an event at the Council on Foreign Relations in Washington. Wray said Russia used those tactics in the 2018 midterms but that his agency saw “no material impact on election infrastructure or campaign infrastructure” during the election.
- Beyond the threats Russia poses to American elections, Wray said, the FBI was increasingly focused on the threats posed by China, especially in regard to its attempts to get its hands- on American technology and
- “No country poses a broader threat …. than China,” Wray said.
Cyber Security Issues in India:
- Emerging technologies and waves of digitisation have brought in their wake new challenges and exposed organisations to new
- It is estimated that cyber-attacks cost companies an estimated $500 billion in damages every year. The primary concern facing organisations is that security breaches to technology and physical infrastructure could lead to data loss, financial losses, regulatory sanctions, reputational damage, operational disturbances, among other
- Increasing global interconnectedness and the complexity of systems make large-scale cyber- attacks on financial market infrastructure even more pertinent and threaten the stability of financial
What measures are planned to address such issues?
- The strategies adopted for cyber risk management currently focus on reducing the risk of a cyber-attack and minimising the impact of a
- There are also plans for building resilience, that is, detecting and recovering quickly from the impact of a breach. Globally, organisations are investing in developing a comprehensive set of cyber risk management capabilities that cover the entire value chain and ensure the risk is efficiently managed across the
What measures were taken by government in this regard?
- Indian regulators have focused on cyber security as a core concern for several years now. Securities market regulator, the Securities and Exchange Board of India, issued guidelines on cyber security and cyber resilience to market infrastructure providers in 2015 and developed guidelines for registrars in 2017.
- In 2016, the RBI released a comprehensive set of requirements for internal cyber security frameworks. The government has also undertaken initiatives including the Information Technology Act, It has set up the nodal cyber security agency, CERT-In, to respond to computer security incidents.
- The National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre, is the central agency to facilitate safe, secure and resilient information infrastructure for critical sectors of the economy.
Proteins Hold Key to Healthy Babies
27, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- Bengaluru researchers estimate nutritional requirement for pregnant women
Details:
- A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition shows that a diet with relatively more protein is needed during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy for the growth and development of the
- To accurately estimate the daily protein requirement in pregnant Indian women, a whole- body potassium counting instrument was built at John’s Research Institute in Bengaluru, with financial support from the Centre’s Department of Biotechnology.
Month by month
- For a gestational weight gain of 10 kg, pregnant Indian women should eat an additional
- 6 grams and 17.6 grams of protein per day during the second (3 – 6 months) and third trimester (6-9 months) respectively, Extra food that a pregnant woman must eat should be high quality, in terms of its protein content such as milk and milk products, dals, rice and dal blends, eggs, fish and meat.
- It is important to meet these additional protein requirements during pregnancy directly from the diet, rather than to use high protein supplements, except in special situations where the diet is not able to meet the requirements for protein,”
- The Centre’s Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Scheme provides supplementary nutrition services for children (6 months – 6 years) and pregnant and lactating
- Rather than focussing on large amounts of cereals and calories, it is important to include combinations of high protein foods such as milk, dal and egg in the meals provided to the pregnant women.
The Integrated Child Development Service (ICDS)
- The Integrated Child Development Service (ICDS) Scheme providing for supplementary nutrition, immunization and pre-school education to the children is a popular flagship programme of the government. It is one of the world’s largest programs providing for an integrated package of services for the holistic development of the ICDS is a centrally sponsored scheme implemented by state governments and union territories.
Beneficiaries:
- Children in the age group of 0-6
- years Pregnant women and
- Lactating mothers
Services under ICDS
- The ICDS Scheme offers a package of six services, viz.
- Supplementary Nutrition, Pre-school non-formal education
- Nutrition & health education, Immunization
- Health check-up and Referral services
WHO SAYS ONE IN 10 CHILDREN DID NOT GET VACCINATED IN 2016
26, Apr 2019
Why in News?
- Worldwide, 12.9 million infants, nearly 1 in 10, did not receive any vaccinations in 2016, according to the most recent WHO and UNICEF immunization estimates.
Details:
- It means, critically, that these infants missed the first dose
- of diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis (DTP)-containing vaccine, putting them at serious risk of these potentially fatal diseases.
- Additionally, an estimated 6.6 million infants who did receive their first dose of DTP- containing vaccine did not complete the full, three dose DTP immunization series (DTP3) in 2016. Since 2010, the percentage of children who received their full course of routine immunizations has stalled at 86% (116.5 million infants), with no significant changes in any countries or regions during the past year. This falls short of the global immunization coverage target of 90%.
- These children most likely have also not received any of the other basic health services. If we are to raise the bar on global immunization coverage, health services must reach the unreached. Every contact with the health system must be seen as an opportunity to immunize.” Immunization currently prevents between 2–3 million deaths every year, from diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough and measles. It is one of the most successful and cost-effective public health interventions
Global immunization coverage levels
- According to the new data, 130 of the 194 WHO Member States have achieved and sustained at least 90% coverage for DTP3 at the national level – one of the targets set out in the Global Vaccine Action Plan.
- 4 million of them also live in just three countries – Afghanistan, Nigeria and Pakistan – where access to routine immunization services is critical to achieving and sustaining polio eradication
- Globally, 85% of children have been vaccinated with the first dose of measles vaccine by their first birthday through routine health services, and 64% with a second dose.
- Vaccination against both these diseases has the potential to substantially reduce deaths of children under 5 years of age, a target of the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Many middle-income countries are lagging behind in the introduction of these newer and more expensive vaccines. These countries often do not receive external support and their health budgets are often insufficient to cover the costs of procuring these vaccines
Inequities in immunization coverage
- National coverage estimates often mask large inequities in coverage within countries. The WHO report, State of inequality: Childhood immunization, highlights inequalities in childhood immunization coverage in low- and middle-income countries over the past 10 years. Efforts to reduce inequalities related to household economic status and mother’s education are needed in many countries if immunization coverage is to be improved. Additionally, more than half of the global population resides in urban areas, including in rapidly growing slums in Africa and Asia. The urban poor is a group at high risk of being un- or under-immunized.
- For the first time, WHO and UNICEF have collected disaggregated data on immunization coverage at the subnational level. Of 194 reporting countries, 125 reported on subnational coverage, covering nearly 20 000 districts and roughly two–thirds of the global infant population. These data will help shed more light on geographical disparities in access to vaccines.
SPEAK YOUR MIND: BRAIN IMPLANT TRANSLATES THOUGHT TO SPEECH
26, Apr 2019
Why in News:
- Scientists have developed a virtual prosthetic voice, a system that decodes the brain’s vocal intentions and translates them into mostly understandable speech, with no need to move a muscle, even those in the mouth.
Details:
- People unable to communicate due to injury or brain damage may one day speak again, scientists unveiled a revolutionary implant that decodes words directly from a person’s thoughts. Several neurological conditions can ruin a patient’s ability to articulate, and many currently rely on communication devices that use head or eye movements to spell out words one painstaking letter at a time. The new system decipher the brain’s motor commands guiding vocal movement during speech, the tap of the tongue, the narrowing of the lips and generates intelligible sentences that approximate a speaker’s natural cadence.
- Before operating, doctors must first locate the “hot spot” in each person’s brain where the seizures originate, this is done with electrodes that are placed in the brain, or on its surface, and listen for tell-tale electrical storms. Participants are recited hundreds of sentences; the electrodes recorded the firing patterns of neurons in the motor cortex. The researchers associated those patterns with the subtle movements of the patient’s lips, tongue, larynx and jaw that occur during natural speech. Then translated movements are changed into spoken sentences.
- A synthesized voice system based on one person’s brain activity could be used, and adapted, by someone else as an indication that off-the-shelf virtual systems could be available.
Problems:
- Strokes that disable a person’s speech often also damage or wipe out the areas of the brain that support speech articulation.
Illegal Cultivation Of BT Brinjal
26, Apr 2019
Why in News?
- The activists representing the Coalition for a GM-Free India (CGFI) have alleged that Bt brinjal is being cultivated illegally in
Highlights:
- Bacillus Thuringiensis Brinjal, popularly known as Bt brinjal, has been at the centre of controversy in
- Bt brinjal, a genetically modified strain created by India’s seeds company Mahyco in collaboration with American multinational Monsanto, claims to improve yields and help the agriculture
Side effects of Bt Brinjal:
- Brinjal is prone to attack from insect pests and diseases, the most serious and destructive of which is the fruit and shoot borer (FSB) Leucinodes
- It is said be fatal for lungs and
- Food safety and possible effects on organisms other than the pest insect (non-target organisms).
Genetically Modified Organisms:
- Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) can be defined as organisms (i.e. plants, animals or microorganisms) in which the genetic material (DNA) has been altered in a way that does not occur naturally by mating and/or natural
- The technology is called “recombinant DNA technology” or “genetic engineering”.
- It allows selected individual genes to be transferred from one organism into another and also between non-related
- GM crops are aimed at providing increased level of crop protection by introducing resistance against plant diseases caused by insects, viruses and from
- The resistance against insects in GM crops is achieved by incorporating into the food plant the gene for toxin production, which is currently used as a conventional insecticide in agriculture and is considered safe for human
- Virus resistance is achieved through the introduction of a gene from certain viruses which cause disease in plants. Virus resistance makes plants less susceptible to diseases caused by such viruses, resulting in higher crop
- Herbicide tolerance is achieved through the introduction of a gene from a bacterium conveying resistance to some In situations where weed pressure is high, the
MAGIC MILK: FIGHTING INFECTIONS WITH A CLUE FROM ECHIDNA
25, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- Scientists at the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research – Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CSIR-CCMB) have isolated an anti- microbial protein found in the milk of an egg-laying mammal.
Details:
- Echidnas, also known as spiny anteaters, are unique egg-laying mammals found only in Australia and New Guinea. Their young hatch from eggs at a very early stage of development and depend completely on mother’s milk. But the mammary glands of the echidnas are devoid of nipples, forcing the young ones to lick milk from the mother’s body surface and potentially making them vulnerable to micro-organisms.
- However, nature protects its own. The milk of the echidna has a protein that can puncture the cell membranes of multiple bacterial species, thus destroying the source of infection.
- Scientist Satish Kumar from the research team said that there are ways to produce the protein in large quantities using E. coli. It can then be used to fight infections.
- The scientist pointed out that there is a rise of superbugs due to the indiscriminate use of antibiotics by the animal husbandry industry to raise livestock.
- The superbugs can cause mastitis, an infection of the mammary gland, in dairy animals.
- “These studies give us novel approaches to fighting infectious diseases taking clues from nature. They are the best way forward in this emerging scenario of increased infectious disease burden and resistance to current treatments
Superbugs:
- Superbugs are bacteria that have acquired resistance to several types of antibiotic drugs either through genetic mutation or through build-up of resistance over time. That is, antibiotics will have no effect on such bacteria.
Echindas:
- Echidnas, also called spiny anteaters, are mammals
- Echidnas are one of the world’s oldest surviving mammals.
- They are egg-laying mammals.
- It is listed as ‘least concern’ in IUCN classification.
- However, the short-beaked echidna found only in Australia and Papua Guinea is threatened. The main threats are land clearing and habitat loss, traffic, feral cats and potentially the rapidly changing climate.
GHANA EYES WORLD RECORD ON MEDICAL DRONE DEVICE
25, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- Ghana launched a fleet of drones to carry medical supplies to remote areas, declaring it would become the “world’s largest drone delivery service.”
Details:
- The craft are part of an ambitious plan to leapfrog problems of medical access in a country with poor roads
- No one in Ghana should die because they can’t access the medicine they need in an emergency,” It represents a major step towards giving everyone in this country universal access to lifesaving medicine.” The drones have been flying test runs with blood and vaccines, but the project was officially inaugurated Wednesday at the main drone base in Omenako, 70 kilometres (40 miles) north of Accra. Operator Zipline, a US-based company, said the three other sites should be up and running by the end of 2019. Omenako is the first of four distribution centres which, when fully operational, will each have 30 drones serving 500 clinics within an 80-kilometre (50-mile) radius.
- The drones are planned to ferry 150 different medicines, blood, and vaccines to more than 2,000 clinics serving over 12 million people—roughly 40 percent of the population.
Bumpy roads
- Zipline first began delivering blood and medicine in East Africa in 2016, deploying drones in Rwanda, a country dubbed the “land of a thousand hills” where access to many villages by road is difficult. Now the company is expanding on the other side of the continent. “Millions of people across the world—in both developed and developing countries—die each year because they can’t get the medicine they need when they need it,” said Zipline boss Keller Rinaudo. For Ghana, a country of nearly 30 million people scattered across a land area about the size of former colonial ruler Britain, poor roads and a lack of ambulances are major challenges to health care access. Drones, not dependent on bumpy roads that can take hours to navigate, offer a way to get medical supplies to clinics before a patient bleeds to death, for example.
- Almost a third of maternal deaths are due to blood loss—easily preventable with a transfusion provided supplies are available.
Parachute drops:
- Medics can order blood or medicine by sending a message by mobile phone
- Each battery-powered flying machine has a delivery distance of 80 kilometres (50 miles), speeding at 100 kilometres (62 miles) an hour and carry up to 1.7 kilogrammes (3.7 pounds).
- Each drop can bring three units of blood, with deliveries made by parachute.
- The drones are stoked at their depot to ensure that vaccines and supplies are kept cold, cutting the need for expensive cold-chain storage systems in remote areas
- Once the programme is up and running, plasma deliveries can be made for the first time to Ghana’s most remote northern areas. The journey by road was too long, and the expiry date of plasma too short, to make this possible until now.
TUMMY TIMETABLES: WHO OFFERS LIFESTYLE ADVICE FOR CHILDREN
25, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- The United Nations released its first-ever recommendations on physical activity for children under five, with disputed advice on subjects ranging from screen time to “tummy time”.
Details:
- The guidelines from the World Health Organization
- may read to some parents like common-sense practices, including not exposing babies under one-year-old to screens.
- “This is about making the shift from sedentary time to playtime,” WHO’s point person for
- childhood obesity and physical activity, said in a statement.
- But several experts noted that WHO’s broad recommendations were based on thin
- evidence, and chastised the agency for adopting overly simplistic definitions of key terms, notably “sedentary screen time”. With obesity posing a rising public health threat and 80 percent of adolescents “not sufficiently physically active,” WHO said it was time to outline best practices for children under five — a crucial period for lifestyle development.
‘Tummy time’
- Despite acknowledging that its “strong recommendations” were based on “very low quality evidence,” the UN health agency said its advice could apply to all young children, regardless of gender, cultural background or socio-economic status.
- For infants under one, the WHO recommends at least 30 minutes of physically activity a day, including prone position — or tummy time — for those not yet mobile.
- Babies under one should also not be restrained in a pram, highchair or strapped to someone’s back for more than an hour at a time and should sleep between 12 and 17 hours a day, the agency said.
- For children between one and two years old, WHO recommends three hours of physical activity each day, with no more than an hour of “sedentary screen time” and at least 11 hours of sleep.
- And for children aged three to four, three hours of daily physical activity should include at least an hour of “moderate to vigorous” movement, while screen time should be kept under an hour.
‘Lots of science to do’
- By addressing the low quality of the evidence, WHO was simply being “transparent that there is still lots of science to do in emerging area of importance,”
- Director of research at the Oxford Internet Institute at Oxford University, agreed that while restricting young children’s screen time appeared to “make sense… in many ways the conclusions drawn about screens are out of step with scientific evidence of harm.”
- Not all screen time is created equal,” he added, urging further study on the various types of screen-based activities available to children and their impacts.
WHO
- The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health
- Established on 7 April 1948, it succeeded the Health Organization, which was an agency of the League of Nations. It is a member of the United Nations Development Group and its headquarters are located at Geneva. WHO flag features the Rod of Asclepius as a symbol for healing.
ARMY TO BUILD TUNNELS TO STORE AMMUNITION
25, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- Indian Army is planning to construct underground tunnels for storage of ammunition along the border with China and Pakistan
Details:
- The Army has also involved the National Hydroelectric Power Corporation Ltd (NHPC), a public sector undertaking, to construct the caves or tunnels and a memorandum of understanding (MoU) will soon be signed with the NHPC.
- The Army is also increasing its ammunition stockpile. Last year, it had finalised a Rs15,000 crore long-term plan to get domestic private sector players to manufacture seven different types. Army needs specialised areas to store them. The tunnels and caves would be constructed and NHPC was chosen for the task because of its best technical expertise, capability and capacity to construct them without any glitches. Major armies, including China and the U.S., already use underground ammunition storage.
- The tunnels will be built-in high-altitude areas in the Northern and Eastern borders. Number of caverns with storage capacity of 200 metric tonnes will be built in mountain folds in identified areas.
- Four pilot projects would be taken up at four different locations along the Northern border and in Jammu and Kashmir at a cost of 15 crore and are expected to be completed within two years. A range of ammunition used by the Army, ranging from bullets, rockets to anti- tank and surface to air missiles, can be stored in the caverns.
Advantages:
- It is cost-effective and each such cave or tunnel would have a capacity between 150 to 250 metric tonnes. Underground tunnel storage offers improved safety, easier camouflage from enemy observation and satellite imagery and protection from enemy strikes like Balakot air strike when Pakistan Air Force jets targeted Indian army installations along the Line of Control (LoC).
Way Forward:
- Even it had many advantages, it ensures better safety of sensitive ammunition minimising accidental explosions.
CHINA TO BUILD MOON STATION IN ‘ABOUT 10 YEARS’
25, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- Beijing plans to send a manned mission to the moon and to build a research station with the aim to achieve space superpower status and to became the first nation to land a rover on the far side of the moon.
Details:
- The Beijing plans to launch a Mars probe by 2020 and confirmed that a fourth lunar probe,
- the Chang’e-5, will be launched by the end of the year.
- The current Chang’e-4 moon lander carried equipment from Germany, the Netherlands and Sweden. Long March-5B rocket will make its maiden flight in the first half of 2020, carrying the core parts of a planned space station. It is planned to replace the International Space Station a collaboration between the United States, Russia, Canada, Europe and Japan, which is due to be retired in 2024.
- It is planned to build a scientific research station on the moon’s south pole within the next 10 years, China National Space Administration head Zhang Kejian said during a speech marking “Space Day”. China now spends more on its civil and military space programmes than Russia and Japan, and is second only to the United States.
Chang’e 4 craft,
- The Chinese National Space Administration has become the first space agency in the world to land its moon lander.
- Chang’e 4 craft, on the dark side of the moon that faces away from the Earth. Chang’e 4 craft opened up a new chapter in human lunar exploration.
- Before China, two nations – the United States, the former Soviet Union have sent spacecraft to the near side of the moon.
Key Highlights
- The relatively unexplored far side of the moon has a different composition than the near side, where previous missions have landed. Chang’e 4, a combined lander and rover, will make astronomical observations and probe the structure and mineral composition of the terrain above and below the surface.
Chang’e 5:
- Chang’e 5 is a robotic Chinese lunar exploration mission consisting of a lander and a sample-return vehicle. It is currently under development and it is scheduled for a launch in December 2019, after being postponed due to the failure of the Long March 5 launch vehicle in 2017. Chang’e 5 will be China’s first sample return mission, aiming to return at least 2 kilograms of lunar soil and rock samples back to the Earth.
- The spacecraft is named after its predecessors the Chinese moon goddess, Chang’e. This will be the first lunar sample-return mission since Luna 24 in 1976.
OUTER SPACE LESSONS
24, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) work toward ‘Mission Gaganyaan’, to send three Indian astronauts into space.
Details:
- The U.S objective, was to have a definite public-relations edge over the U.S.S.R. in the space race, which was marked by intense rivalry between two Cold War powers.
- A breakthrough in space was a matter of prestige.
- For ISRO’s plan, the prestige value of ‘Mission Gaganyaan’ is sky-high, ands same as the American National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s Apollo Mission to the moon.
Problems faced:
- If the mission, it would create certain problems which may affect India’s economic affairs. The programme of that scale and magnitude comes at a steep cost, monetary and non- monetary.
- It is the non-monetary loss that matters more than monetary loss. Failure indicates a waste of time and resources.
- A failed mission deeply hurts the image of the country in the eyes of the outside world.
- It raises doubts about the capability of the nation-state in question.
- Project development would play to the advantage of adversaries, politically and diplomatically. But, a failed mission of such magnitude could give voices in the opposition an opportunity to level criticism, perhaps weakening the incumbent domestically.
- The diplomatic costs arise from the fact that losses in space missions can seriously impact the future of cooperation between space powers.
Outer space
- Outer space is often referred to as the ‘final frontier’ by major world powers, with the prize for conquering it being more greatness on the world stage.
- India’s credentials were bolstered after the successful anti-satellite mission recently
- Success in ‘Mission Gaganyaan’ might provide India with that stamp of authority in outer space that it so keenly desires.
Mission Gaganyaan
- The Prime Minister of India in his Independence Day address announced that an Indian astronaut would go into space by 2022, when India celebrates her 75th year of Independence. In pursuance of this goal, India and France have announced a working group for Gaganyaan. ISRO and CNES, the French space agency, will work together in the fields of space medicine, astronaut health monitoring, life support, radiation protection, space debris protection and personal hygiene systems, etc.
The Mission
- Under the Gaganyaan schedule, three flights will be sent in orbit. Of the three, there will be two unmanned flights and one human spaceflight.
- The human space flight programme, called the Orbital Module will have three Indian astronauts, including a woman.
- It will circle Earth at a low-earth-orbit at an altitude of 300-400 km from earth for 5-7 days.
- The payload will consist of:
- Crew module – spacecraft carrying human beings.
- Service module – powered by two liquid propellant engines.
- It will be equipped with emergency escape and emergency mission abort.
- GSLV Mk III, also called the LVM-3 (Launch Vehicle Mark-3) the three-stage heavy lift launch vehicle, will be used to launch Gaganyaan as it has the necessary payload capability.
- The mission is expected to cost around Rs 10,000 crore.
FDI IN MEDICAL DEVICE DWINDLES, INDUSTRY BLAMES GOVERNMENT POLICY
24, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- India permitted 100 per cent foreign direct investment (FDI) through automatic route in medical devices sector.
Background:
- The government has just removed a clause from India’s foreign direct investment (FDI) policy to clear unintended obstacles which seemed to be delaying potential investments in several technologies, products and services that come under the broad definition of ‘medical devices’.
- The clause that is no longer applicable had earlier restricted the scope of ‘medical devices’ to what is defined in the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940. Now, with the delinking in place, the government has permitted a wide range of items that can attract up to 100 per cent FDI via the automatic route. These include any instrument, apparatus, appliance, implant, material or other articles, whether used alone or in combination, plus any software tool, intended by its manufacturer to be used especially for human beings or animals for diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, treatment or alleviation of any disease or disorder.
FDI:
- Foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment made by a firm or individual in one country into business interests located in another country. Generally, FDI takes place when an investor establishes foreign business operations or acquires foreign business assets, including establishing ownership or controlling interest in a foreign company.
Entry Routes for Investment / Procedure under Automatic Route
- FDI in sectors/activities permitted under automatic route does not require any prior approval either by the Government or RBI. The investors are only required to notify the Regional office concerned of RBI within 30 days of receipt of inward remittances and file the required documents with that office within 30 days of issue of shares to foreign investors.
Procedure under Government Approval
- FDI in activities not covered under the automatic route require prior Government approval. Such proposals are considered by the Foreign Investment Promotion Board (FIPB), a Government body that offers single window clearance for proposals on foreign investment in the country that are not allowed access through the automatic route.
Definition of Medical Devices In FDI:
- The definition of medical device for FDI purpose also includes accessories to such instruments, apparatus, appliance, material or other articles, a device which is reagent, reagent product, calibrator, control material, kit, instrument, apparatus, equipment or system, whether used alone or in combination, intended to be used for examination and providing information for medical or diagnostic purposes by means of in-vitro examination of specimens derived from the human body or animals.
Center eased several norms in FDI:
- Approval – In the single-brand retail, the Centre has allowed 100% FDI through the automatic route, from the 49% at present.
- 100% FDI is allowed in construction development relating to building townships, housing and infrastructure and real estate broking services.
- Local Sourcing – The mandatory 30% requirement could be relaxed for companies with ‘state-of-the-art’ or ‘cutting edge’ products, for which local sourcing was not possible.
- However, the absence of a definition for ‘state-of-the-art’ or ‘cutting edge’ technology has stalled the applications of global companies. The mandatory local sourcing is now relaxed for the first five years. Thereafter, single-brand retailers will be required to meet the 30 per cent local sourcing norm.
- Power sector- The government has removed the restrictions on investment in power exchanges through the primary market.
- This applies to foreign institutional investors and portfolio investors. Till now they could do so only through the secondary market.
Impact of foreign investment in hospitals in India:
- Such hospitals are likely to focus on more advanced procedures and specialty areas. They are more likely to focus on curative and intervention-oriented treatment than on preventive and long-term kind of treatment.
- They are likely to employ a higher ratio of technology to personnel in their healthcare delivery and thus involve a substitution of human resources with technology and equipment. They are likely to invest much more in medical equipment and devices and also in specialized and experienced medical personnel, thus involving a focus on high-end human resources and high-end technology.
- Such hospitals tend to have better systems and processes and usage of IT, which creates a more efficient and professional work environment.
- Foreign funded hospitals pay higher rates to staff at all levels and particularly to senior medical personnel.
- They are more likely to attract overseas doctors and specialists than other hospitals They are more likely to be accredited domestically and/or internationally.
- Their costs are likely to be comparable to or slightly higher than those of non-foreign funded large hospitals. Their costs will tend to be higher than for small and medium size nursing homes and hospitals but this is mainly due to greater capital intensity and focus on quality systems and processes and focus on hygiene
- There could be positive externalities in other areas, some of which could further drive foreign investment in hospitals
- Foreign funded hospitals could draw away medical personnel at all levels from other hospitals (both large non-foreign-funded and medium and small size hospitals/nursing homes, and public sector hospitals) and could adversely impact the quality of medical manpower available to competing institutions
- There is likely to be closure of substandard institutions, some consolidation of the hospital segment, and new kinds of arrangements could emerge between larger and smaller players as the healthcare sector evolves
- There could be greater segmentation between the public and private sector with resource flows towards the latter, greater wage disparity, unless innovative arrangements emerge between the two segments and reforms are undertaken in the public sector hospitals
Way ahead:
- While there are clearly concerns about the equity, affordability, and market segmentation implications of growing foreign investor presence in India’s hospital segment, it is evident
- that the root cause lies in structural problems that are already present in the healthcare sector, such as lack of affordable health insurance schemes or inappropriate regulations on medical education providers.
- Foreign investment and greater corporate presence in hospitals could aggravate such structural problems. The insights obtained from the discussions with stakeholders suggest that the solution lies in strengthening the public healthcare system, in amending certain regulations that affect all players, and in introducing schemes, which provide affordable access to healthcare for all and not in restricting foreign investment. The benefits of foreign investment in hospitals are likely to outweigh these adverse effects.
DOWN TO EARTH ON THE ASAT TEST
23, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- India has neither achieved a higher level of deterrence nor enabled a more stable strategic security environment
- India carried out a successful test of an Anti-Satellite (ASAT) weapon,launching an interceptor missile from the Balasore range in Odisha to hit a live satellite in Low Earth Orbit.
- It thus became the fourth country in the world to develop an ASAT capability.
ASAT test
- The significance of the test is that India has tested and successfully demonstrated its capability to interdict and intercept a satellite in outer space based on complete indigenous technology. With this test, the country joins an exclusive group of space faring nations consisting of USA, Russia, and China
Not a Game Changer
- An ASAT test is hardly a game-changer as far as space warfare is concerned
- several claims that India now had a “credible deterrence” against attacks on the country’s growing number of space assets seemed to suggest that India was not averse to weaponisation of outer space.
- India has, no doubt, sought to reassure the global community that it has not violated any international treaty or understanding with this test.
- India has also taken great pains to advertise the fact that the international community, especially the U.S., had not faulted India for carrying out this test, in marked contrast to what had happened when China had carried out an ASAT test in 2007. Nevertheless, it would be facile to think that the world endorses India’s claims regarding its peaceful intentions.
- India’s demonstration of ASAT capability comes a little more than a decade after China’s,
- and nearly six decades after that of the U.S. and Russia.
- An ASAT test is, undoubtedly, less threatening than a nuclear explosion, but the world is likely to ask why India decided to demonstrate its capability at this time, though it possessed the ability much earlier.
- The international community cannot be faulted if it were to think that India had deliberately breached an unwritten convention against weaponisation or militarisation of outer space.
- ASAT capabilities are generally perceived as integral to ballistic missile defence programmes.
- This clearly identifies an ASAT test as a military programme. In turn, it implies an intention to embark on weaponisation of outer space. It is, perhaps, for this reason that countries such as Israel and France, which are believed to have this capability, have so far refrained from carrying out such tests.
Does the Test Create Space debris?
- The test was done in the lower atmosphere to ensure that there is no space debris. Whatever debris that is generated will decay and fall back onto the earth within weeks.
Cold War Phenomenon
- ASAT was essentially a Cold War phenomenon whose strategic importance has declined over the years. Currently, none of the other three countries which possess an ASAT capability extol its strategic value and importance. The U.S., Russia and China, all seem to demonstrate less and less interest in pursuing ASAT weaponry.
- These countries are increasingly focussing on laser and cyber capabilities to achieve the objective of neutralising killer satellites. Countries are experimenting with directed-energy weapons, radio frequency weapons, etc. rather than concentrating on shooting down satellites in space. The last named also carries the danger of hitting satellites that may not be on an offensive mission, apart from the issue of space debris.
- It could well result in something very different. It is almost certain, as was the case with India’s nuclear test, that Pakistan will immediately try to acquire the same capability, in all likelihood with generous assistance from China. India has neither achieved a higher level of deterrence nor is it likely to lead to a more stable strategic security environment. Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) recently indicated that it has, of late, carried out certain new launchessuch as the Microsat-R and EMISAT satellites which are intended for ‘strategic use’.
Neighbourhood concerns
- The mere existence of such a situation could lead to heightened tensions. Based in one of the most dangerous neighbourhoods in the world, India needs to do everything in its power to convince other nations that space is not part of India’s overt defence calculations.
- India should highlight the fact that its enormously successful space programme,unlike those of many other countries, is notable for being conceived and implemented as a civilian programme, quite distinct and separate from any military programme or objective. ISRO was set up in 1969, and the Space Commission came into existence in the early 1970s.
- Vikram Sarabhai is credited with creating India’s vision for exploration of space and,
- following his untimely demise in 1971, the mantle fell on Satish Dhawan.
- ISRO launched its first Indian satellite, Aryabhatta, in April 1975. In April 1982, ISRO launched the first Indian National Satellite System (INSAT-1A). The first Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) took off from Sriharikota in 2001. In November 2013, ISRO launched the Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan) spacecraft.
- There is little strategic advantage accruing from an ASAT test; on the other hand the damage that could be caused to India’s image as a peaceful and responsible nation intent on, and committed to, peaceful uses of space could be immense.
CHINA DRAWS UP TIGHTER RULES ON HUMAN GENE AND EMBRYO TRIALS
22, Apr 2019
Why in News
- Medical and human tests would face closer scrutiny and stricter requirements
Details:
- China’s top legislature will consider tougher rules on research involving human genes and embryos, the first such move since a Chinese scientist sparked controversy last year by announcing he had made the world’s first “gene-edited” babies.
- He Jiankui, associate professor at Southern University
- of Science and Technology in Shenzhen, attracted condemnation from the global scientific community when he said he had used a technology known as CRISPR-Cas9 to alter the embryonic genes of twin girls born in November.
- Chinese authorities launched an investigation into Mr. He’s work and said they had halted the kind of research he was undertaking. Under the draft laws sent to China’s legislature for review on Saturday, medical and human trials would face closer scrutiny and stricter requirements, such as ensuring human subjects are properly briefed, State media outlet Xinhua reported. The rules would also require all future trials to be approved by administrative authorities as well as ethical committees, it said. The report did not specify a timeline for the approval of the regulations, or make specific mention of Mr. He’s research. In videos posted online and at the November 2018 conference, where Mr. He made his controversial presentation, the Chinese scientist said that he believed his gene editing would help protect the girls from infection with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
- Chinese authorities and institutions, as well as hundreds of international scientists, condemned him and said any application of gene editing on human embryos for reproductive purposes was against the law and medical ethics of China.
Gene editing
- Gene editing or genome editing is a way of making specific changes to the DNA of a cell or organism. An enzyme cuts the DNA at a specific sequence, and when this is repaired by the cell a change or ‘edit’ is made to the sequence.
What is CRISPR-Cas9?
- CRISPR is a dynamic versatile tool that allows us to target nearly any genomic location and potentially repair broken genes. It can remove, add or alter specific DNA sequences in the genome of higher organisms. CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) are sections of DNA and are sections of genetic code containing short repetitions of base sequences followed by spacer DNA segments.
- CAS-9 (CRISPR-associated protein 9) is an enzyme. It uses a synthetic guide RNA to introduce a double strand break at a specific location within a strand of DNA. It is a system used by bacterial cells to recognize and destroy viral DNA as a form of adaptive immunity.
MEDICINE LABELS IN REGIONAL LANGUAGE
22, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- In order to counter fake, sub-standard and expired drugs, the Union Health Ministry has said Hindi and regional language will be used in the tendering process.
Background:
- The Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB) recently recommended that government procurement agencies should take necessary steps in the tendering process to include the regional language, along with English, on the label of iron tablets and polio drops in government programmes.
DTAB:
- DTAB is highest statutory decision-making body on technical matters related to drugs in the country.
- It is constituted as per the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- It is part of Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) in the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
functions of DTAB:
- The Board (DTAB) deliberated the matter and agreed for the proposal to amend the provisions in Rule 64, making it identical for waiver of clinical performance evaluation of In-vitro Diagnostic medical devices in line with waiver given for medical devices under Rule 63 of the Medical Device Rules, 2017.
- The Board recommended that in case a medical device which already exists in the Indian market for use is brought in future under regulation, then such device shall not be a new medical device with condition that the applicant need to provide evidences of safety, performance & effectiveness.
- The Board deliberated the matter and agreed for the proposal for enabling NABL accredited laboratories or any hospital accredited by national accreditation board for hospitals and health care providers (NABH) for issuing performance evaluation report under Medical Devices Rules, 2017, to harmonize the requirements at par with the international rules and accordingly, the requirements specified in sub-clause (h) of clause of Part II of the Fourth Schedule may be The Board deliberated the matter and agreed for the proposal to include the following medical devices and other high end equipments under the purview of Section 3(b) (iv) of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940:
- All implantable medical devices
- CT scan equipment
- MRI equipment
- Defibrillators
- Dialysis Machine
- PET equipment
- X-Ray Machine
- The Board deliberated the matter and agreed for the proposal to incorporate pharmacy degree/ post-graduation as a qualification in Medical Devices Rules, 2017.
- The Board deliberated the matter and agreed for the proposal to accept the eIFU (electronic Instructions for Use) as an option in place of traditional paper IFU (Instructions for Use).
- The Board recommended the sale of Invitro Diagnostic products shall be undertaken by a valid, whole license holder to Hospitals, Pathology Laboratories, Blood Banks & other such institutions, based on requisition for such products, & the records of which shall be maintained. In case an In-vitro Diagnostic product is to be sold directly to the consumer, it shall be supplied through a valid license holder, for retail sale for such products.
- The Board deliberated the matter and agreed for the proposal for notification of bone marrow cell separator as a medical device under Section 3(b) (iv) of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- The Board deliberated the matter and agreed for the proposal for inclusion of medical devices approved by Licensing Authority under Drugs & Cosmetics Rules, 1945, to bear CDSCO logo on its labels.
WARMING UP TO THE HEAT FROM THE SUN
22, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- Use of solar thermal is yet to catch the imagination of investors and users; the key is to incentivise industry to use this less expensive method of heating
Background:
- Solar PV works by photons in sun’s rays knocking off electrons in the semi-conducting material in the panels and channels them through a wire—the stream of electrons is electricity. Solar PV, therefore, works best where there is lot of sunlight.
- Solar thermal systems, in contrast, suck up sun’s heat and conduct it to where it is needed – such as for drying of spices or fish or wet paint.
Smart Uses of Solar Thermal
- Solar thermal energy has been a popular choice for heating domestic hot water (DHW) over many decades now and as we know, solar power is an effective weapon in saving energy as well as reducing the electricity bill.
- Solar thermal energy uses Solar hot water panels, or collectors, and especially evacuated tube technology to increase the efficiency level of a solar heating system by absorbing and storing more heat for a longer time.
- Solar thermal energy systems convert the sun’s solar radiation directly into usable heat. Solar thermal energy is certainly not a new idea its been around as an alternative energy resource for hundreds of years heating up our water or drying our clothes. But domestic solar thermal technology has come a long way in the last 25 to 30 years as solar water heaters started to become more common place due to the fact these devices are useful, inexpensive and simple to install. Therefore in case you are searching for a different energy source to lower the ever increasing cost of electrical energy, you may want to think about a solar thermal water heating system.
- A solar powered hot water heating system, also known as a solar thermal energy or solar heating system, is really a very simple system that utilises the heat from the sun’s rays to heat up water for the home and domestic use.
- Compared with solar photovoltaics, the captured heat energy of the panel is not converted into electricity. Then a solar hot water heating system is nothing more than a large heater which is constructed to assist your present heating boiler by capturing the suns solar thermal energy.
Typical Solar Evacuated Tube Collector
- Solar hot water collectors do not boil your water to high temperatures, but instead pre-heat the water using the sun, meaning that your existing oil, gas, and electrical heater are utilized much less whilst still delivering the same amount of warmth and comfort. The big advantage of using the suns solar thermal energy to heat your water, is that no matter where you live, you are able to still produce totally free hot water just using the power of the sun.
- The immense heat generated by the sun is harnessed utilising either an evacuated tube collector, an integral collector storage (ICS) systems or even a simple solar flat plate collector (there are more designs but these three are the most common).
- These solar collectors, so referred to simply because they “collect” the sun’s energy, are generally located on a roof of the house or fixed to a wall oriented in the direction of the midday sun.
- A solar collector harnesses the solar thermal energy of the sun and subsequently uses this thermal energy to heat the water within the collector.
- Solar thermal collectors are generally made from glass fronted and fully insulated box having an absorber plate usually made from sheet aluminium or copper inside. Water is then pumped through a series of pipes in the collector and is heated. The hot water returns to a tank for storage, basically similar to a standard home heating system. Generally, a solar thermal collector can produce enough hot water for the average family, or could be used on its own to heat a swimming pool or used as space heating.
- Solar collectors are excellent for harnessing the suns solar thermal energy. Thermal collectors are usually classified into 3 different classes or types which include integral collector storage systems, flat plate collector, along with evacuated tube solar collector. The preferred solar powered water heater uses evacuated tubes as they are more effective when compared to flat plate collectors. This is because of their design, which allows evacuated tubes to provide much greater efficiencies and water temperatures while heating the water for long periods.
- As their name suggests, solar vacuum tube collectors are composed of a number of clear, glass solar vacuum tubes positioned together side by side, with each one containing a copper absorber tube.
- They work like a thermal flask by heating a special heat conducting material inside a tube encased in a outer evacuated tube. The suns light passes through the tubes glass body and heats up the copper absorber pipe inside, converting it to heat. This copper pipe has a heat transfer liquid, usually water, inside that absorbs the heat and transfers it by means of conduction to a storage tank via a heat exchanger.
- An evacuated tubes effectiveness comes from the fact that along with there being a vacuum inside, giving it its name “evacuated tube”, these glass tubes are totally sealed therefore the copper pipe and the liquid inside it lose very little heat outside, even during a freezing cold day. This process with modern solar technology is so efficient that over 80% efficiency is possible making it by far one of the best solutions for solar water heating as the heat energy goes in but doesn’t come out.
- As the tubes are totally closed and sealed, the small amounts of maintenance required, such as cleaning is an easy matter, as it’s straightforward to remove damaged glass tubes if required.
- Solar powered hot water heating systems are an excellent investment and smart way to greatly reduce your carbon footprint along with reducing your bills with a basic installation. Should you use natural gas or oil to heat your domestic hot water tank, possibly solar thermal energy is really a smart way to lower your bills.
- Whilst evacuated tube solar collectors tend to be more expensive compared to solar flat plate collectors, the enhanced performance, increased efficiency and reduced maintenance costs means a quicker payback period and higher return on investment.
Difference between solar PV and Solar thermal
| Comparison Parameter | Solar Thermal | Solar PV |
|---|---|---|
| What is the principle behind the technology? | Converts solar energy into heat. | Directly converts solar energy into electricity. |
| What is the process involved? | Solar thermal systems usually come with collectors that face the sun and absorb heat. This heat is then transferred to either water or another heating fluid. | Solar PV consists of arrays of cells made of semiconductor materials that are designed to convert sunlight into electricity. |
| What is the application of the technology? | Solar thermal systems are most commonly used for direct heating applications. Solar water heater is the most common application of solar thermal systems. These systems can also be used for power generation where a heated fluid is used to drive a generator to deliver electricity. | Solar PV systems are used for power generation as an alternative source of energy |
Disadvantage of Using Solar Thermal
- One disadvantage of using a solar thermal system is that you may need some kind of backup heating system, especially throughout the rainy period or overcast days when the solar collector experiences reduced thermal energy from the sun, or for those days when teenagers are in the home and the hot water usage increases significantly.
Advantages of Solar Thermal
- Solar thermal energy is a free and easy way to heat water but there are numerous other ways in which to heat water making use of the energy from the sun.
- it will lower your bills together with your carbon footprint, giving it many instant and long- lasting advantages. solar thermal is space-consuming
Way ahead
- A good first step would be to get the government to also pay solar thermal as much attention as solar PV.
MICRORNAS IN THE LIVER HELP REGULATE THE FEED-FAST CYCLE
21, Apr 2019
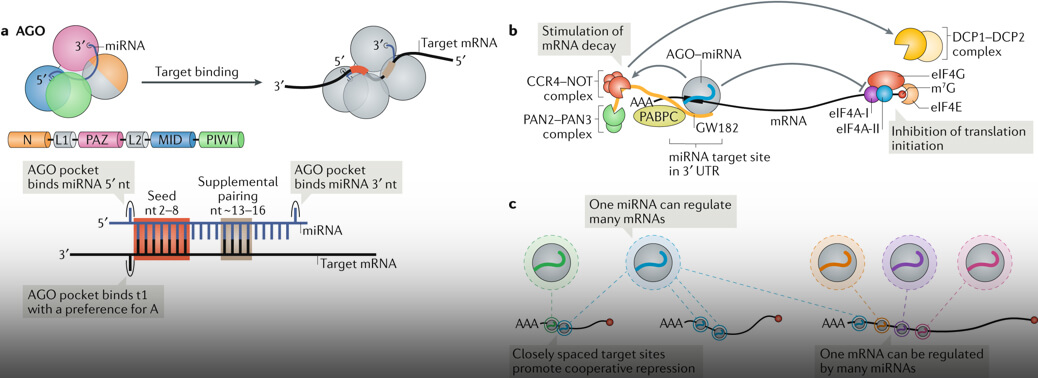
Why in News:
- Researchers from Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), Mumbai, have succeeded in identifying the mechanism that drives the feed-fast transition in the liver. They find that the oscillation in the levels of certain microRNAs in the liver drives this transition, and they inhibit the translation of the fasting responsive genes.
Details:
- The feed-fast cycle is an important aspect of our body metabolism.
- The four stages are fed state, post-absorptive state, fasting state, starvation state. Humans only experience the third stage and do not enter the fasting stage.
- Different organs in our body work to metabolise the food we consume, and they behave differently during each stage.The liver is a central organ in maintaining glucose and fat metabolism both under fed and fasted conditions. During a fasting state, liver produces glucose in a process which is critical for maintaining circulating glucose levels.
- An abnormality in either of these processes can lead to diabetes, obesity or other liver diseases. Aberrant molecular mechanisms that affect glucose and fat metabolism in the liver are the primary causes of several metabolic diseases and even ageing. Many of these occur due to aberrant gene expression and metabolic stress.
- fasting lasts from a few hours to days, feeding is a rapid process that takes from a few minutes to an hour. Therefore, when going from fasting to feeding, the liver functions must switch rapidly. This entails stopping the mRNA translation of fasting-induced genes in a fed state.
Mice Models
- Research is done by profiling microRNAs in the liver of mice models in a fed state in which identified that these fed microRNAs could control the expression of fasting-induced genes, thus controlling liver metabolism, mitochondrial functions and cellular respiration.
- By injecting molecular sponges that scavenged the microRNAs in the liver, it would reduce the level of fed microRNAs.
- The gene expression and metabolic pathways in the liver results in elevated glucose production and higher circulating blood glucose levels in the mice. The study is significant in having discovered changes in microRNA levels which constitutes an anticipatory mechanism and whose abrogation leads to a diabetic like state. Most of the mechanisms are conserved between humans and mice. So identifying such fed microRNAs in humans can aid in developing therapeutic interventions for tackling lifestyle disorders and ageing- associated loss in physiological fitness.
RNA:
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA), is quite similar to DNA. DNA molecules are typically long and double stranded, RNA molecules are much shorter and are typically single stranded.
- RNA molecules perform a variety of roles in the cell but are mainly involved in the process of protein synthesis (translation) and its regulation.
RNA Structure
- RNA is typically single stranded and is made of ribonucleotides that are linked by phosphodiester bonds. A ribonucleotide in the RNA chain contains ribose (the pentose sugar), one of the four nitrogenous bases (A, U, G, and C), and a phosphate group.
- The subtle structural difference between the sugars gives DNA added stability, making DNA more suitable for storage of genetic information, whereas the relative instability of RNA makes it more suitable for its more short-term functions. The RNA-specific pyrimidine uracil forms a complementary base pair with adenine and is used instead of the thymine used in DNA. Even though RNA is single stranded, most types of RNA molecules show extensive intramolecular base pairing between complementary sequences within the RNA strand, creating a predictable three-dimensional structure essential for their function
Functions of RNA in Protein Synthesis
- Cells access the information stored in DNA by creating RNA to direct the synthesis of proteins through the process of translation.
- Proteins within a cell have many functions, including building cellular structures and serving as enzyme catalysts for cellular chemical reactions that give cells their specific characteristics. The three main types of RNA directly involved in protein synthesis are messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA).
RNA Discovery:
- French scientists François Jacob and Jacques Monod hypothesized the existence of an intermediary between DNA and its protein products, which they called messenger RNA.
- The information from DNA is transmitted to the ribosome for protein synthesis using mRNA. If DNA serves as the complete library of cellular information, mRNA serves as a photocopy of specific information needed at a particular point in time that serves as the instructions to make a protein. The mRNA carries the message from the DNA, which controls all of the cellular activities in a cell. If a cell requires a certain protein to be synthesized, the gene for this product is “turned on” and the mRNA is synthesized through the process of transcription. The mRNA then interacts with ribosomes and other cellular machinery to direct the synthesis of the protein it encodes during the process of translation.
- mRNA is relatively unstable and short-lived in the cell, especially in prokaryotic cells, ensuring that proteins are only made when needed.
- rRNA and tRNA are stable types of RNA. In prokaryotes and eukaryotes, tRNA and rRNA are encoded in the DNA, then copied into long RNA molecules that are cut to release smaller fragments containing the individual mature RNA species. In eukaryotes, synthesis, cutting, and assembly of rRNA into ribosomes takes place in the nucleolus region of the nucleus, but these activities occur in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes. Neither of these types of RNA carries instructions to direct the synthesis of a polypeptide, but they play other important roles in protein synthesis.
- Ribosomes are composed of rRNA and protein. As its name suggests, rRNA is a major constituent of ribosomes, composing up to about 60% of the ribosome by mass and providing the location where the mRNA binds. The rRNA ensures the proper alignment of the mRNA, tRNA, and the ribosomes; the rRNA of the ribosome also has an enzymatic activity (Peptidyl transferase) and catalyzes the formation of the peptide bonds between two aligned amino acids during protein synthesis.
RNA as Hereditary Information
- Although RNA does not serve as the hereditary information in most cells, RNA does hold this function for many viruses that do not contain DNA. Thus, RNA clearly does have the additional capacity to serve as genetic information.
- Although RNA is typically single stranded within cells, there is significant diversity in viruses. Rhinoviruses, which cause the common cold, influenza viruses and the Ebola virus are single-stranded RNA viruses.
- Rotaviruses, which cause severe gastroenteritis in children and other immunocompromised individuals, are examples of double-stranded RNA viruses. Because double-stranded RNA is uncommon in eukaryotic cells, its presence serves as an indicator of viral infection
CASES OF MEASLES SHOWS ALARMING RISE-WHO
21, Apr 2019
Why in News:
- A team of researchers from the National Institute of Biomedical Genomics, Kalyani, West Bengal, has found Biomarkers for lymph node metastasis in oral cancer.
Background:
- By looking out for five biomarkers, it is now possible to tell in advance if a person with oral cancer of the gum and cheek has lymph node metastasis even before surgery is undertaken, a study has found.
- The ability to correctly predict absence/presence of lymph node metastasis in oral cancer patients is 80-90% based on the five biomarkers, a team led by Partha Majumder from the National Institute of Biomedical Genomics, Kalyani, West Bengal, has found.
- As a result, an oral cancer patient can be spared of a neck dissection to investigate if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in case the five biomarkers are absent. Lymph node dissection increases morbidity.
- However, if the patient tests positive for even one biomarker then an aggressive treatment would be required. An oral cancer patient with cancer spread to the lymph node has a 50% lower chance of survival for five years or more compared with patients in whom it has not spread to the lymph node.
Five Genomic Biomarkers:
- The team found that lymph node metastasis was associated with five genomic biomarkers. The results were published in International Journal of Cancer.
- There are five genomic features or biomarkers of lymph node metastasis in oral cancer patients. Two of these are rare, heritable DNA changes in BRCA2 and FAT1 genes. The remaining three are non-heritable (somatic) DNA alterations. The somatic DNA alterations can occur in genes belonging to three different pathways — mitotic G2/M cell-cycle pathway, homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) DNA- repair pathways.
About:
- Full name: The term biomarker is short for biological marker.
- Meaning: It generally refers to a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated to examine normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacologic responses to a therapeutic intervention.
Application:
- Biochemical biomarkers are often used in clinical trials, where they are derived from bodily fluids that are easily available to the early phase researchers.
- They are also used in pre-clinical work to identify compounds that appear to modulate disease in in vivo models and therefore might be tried in human clinicaltrials.
Disease-related biomarkers give an indication of the probable effect of treatment on patients.
CHEMISTS AND DRUGGISTS ARE PASSE; FROM NOW ALL WILL BE PHARMACIES
20, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- The words ‘chemist’ and ‘druggist’ are headed for a change, with the Union Health Ministry
- replacing them with ‘pharmacy’. The step is in keeping with international practice.
Details:
- Besides being a long-standing demand of the industry, a senior health official explained that the phrase ‘chemists and druggists’ was coined over seven decades ago, is quite old, and has lost its relevance in the current scenario.
- At present, the word ‘drug’ is looked upon as more clandestine, and as addiction to chemicals, and thus it’s not suitable while referring to a professional pharmacist,” he added. The matter was deliberated upon by the Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB), after repeated requests were made to amend the Rule 65(15)(b) and Rule 65(15)(c) so that medical shops can be called a ‘pharmacy’.
- After being cleared by DTAB, “This is now also in concurrence with the international practice of calling a medical shop selling medicines by this name [‘pharmacy’] and to also provide an identity and sense of value to the practising pharmacist at the outlets,” noted the Board. Meanwhile, the change was deliberated and recommended by the 55th Drug Consultative Committee meeting. “This will definitely give the profession better recognition. We always had a problem with the word ‘druggists’ as the meaning is negative.
- We welcome this change the government has made,” said Kailash Gupta of the All India
- Chemists and Distributors Federation.
- Meanwhile, according to the earlier Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, the description ‘Chemists and Druggists’ was to be displayed by those licensees who employ the services of a registered pharmacist but who do not maintain a ‘pharmacy’ for compounding (preparing a drug specifically for a buyer, based on a prescription from his or her doctor). The pharmacist mixes different ingredients together to create the individualised medication. “However, in the current scenario, the compounding of medicines by registered pharmacists hardly exists due to a capable pharma industry in place in the country,” noted the DTAB.
Drugs Technical Advisory board:
- DTAB is the highest statutory decision-making body on technical matters related to drugs in India. It was constituted under the provisions of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940. DTAB is part of the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) under the Ministry of Health and Family welfare.
TOP IT FIRMS UNDER THREAT OF CYBERATTACK
20, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- Criminals may be targeting Infosys and Cognizant, after Wipro, says security website Krebs on Security
Details:
- India’s leading tech players may be under serious threat from cyber criminals, according to cybersecurity investigation website KrebsOnSecurity.com.
- The website is run by former Washington Post staffer and cybersecurity writer, Brian Krebs. A fresh post on the website said the criminals responsible for launching phishing campaigns that netted dozens of employees and more than 100 computer systems last month at Wipro, India’s third-largest IT outsourcing firm, also appear to have targeted a number of other competing providers, including Infosys and Cognizant, as per new evidence available
- with the website. It appears the attackers in this case are targeting companies that in one form or another have access to either a tonne of third-party company resources, and/or companies that can be abused to conduct gift card fraud.’’
- Cognizant’s spokesperson from the U.S. told The Hindu: “We are aware of reports that our company was among many other service providers and businesses whose email systems were targeted in an apparent criminal hacking scheme related to gift card fraud.
- Since the criminal activity first surfaced earlier this week and following reports that another service provider’s email system was allegedly compromised, Cognizant’s security experts took immediate and appropriate actions including initiating a review.”
- It is not unusual for a large company like Cognizant to be the target of spear phishing attempts such as this. Infosys, in a statement said: “Infosys would like to assure all our stakeholders that we have not observed any breach of our network based on our monitoring and threat intelligence. This has been ascertained through a thorough analysis of the indicators of compromise that we received from our threat intelligence partners.”
- In addition, we are working with our threat intelligence partners to get more information on attack vectors and threat actors to further strengthen our IT and Cyber security controls,’’
Phishing
- It is the act of sending an email to a user falsely claiming to be an established legitimate enterprise in an attempt to scam the user into surrendering private information that will be used for identity theft.
- Phishing email will direct the user to visit a website where
- they are asked to update personal information, such as a password, credit card, social security, or bank account numbers, that the legitimate organization already has.
- The website, however, is bogus and set up only to steal the information the user enters on the page.
Phishing emails are blindly sent to thousands, if not millions of recipients.
By spamming large groups of people, the “phisher” counts on the email being read by a percentage of people who actually have an account with the legitimate company being spoofed in the email and corresponding webpage.
TRADERS AND POLITICIANS SLAM GOVERNMENT FOR SUSPENSION OF CROSS LOC TRADE
20, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- Traders and politicians in Kashmir have criticised the government over the sudden suspension of cross-Line of Control trade, which the government said had been triggered by issues including illegal trade,funneling of counterfeit currency, and the funding and promotion of terror groups and anti-India operations though the trade.
Details:
- The trade route has created 1.70 lakh job days so far.
- We hired services of 6,170 trucks and hundreds of labourers are involved directly. The move will only contribute to unemployment and desperation
- Sources in the Ministry of Home Affairs said the government
- was particularly alarmed by the case of U.S.-origin California almonds, which was not just a violation of the barter arrangement but also was under-invoiced to provide funds to anti- national elements and terrorist organisations in the Valley to fuel anti-India operations.
- Listing the reasons for the move, the MHA sources said they included the problem of goods being traded from other countries like the U.S., channelling of funds for terror groups like the Hizbul Mujahideen, drug trade, smuggling arms and ammunition and pumping in fake currency notes.
- The sources indicated that the trade was “only suspended and not cancelled permanently.” “The government will revisit the issue of resuming trade after stricter measures are put in place,
Line of control:
- LOC stands for Line of Control. It defines the boundary separating parts of Kashmir controlled by India and Pakistan
- LOC is a demarcated border marked by the militaries.
CASES OF MEASLES SHOWS ALARMING RISE-WHO
20, Apr 2019
why in news:
- The number of cases of measles — one of the world’s most contagious diseases — is climbing, warned the World Health Organisation (WHO), stating that preliminary global data shows that reported cases rose by 300% in the first three months of 2019, compared to the same period in 2018.
Background: / Measles:
- Measles is a highly contagious viral disease.
- It typically begins with a high fever. Several days later a characteristic rash appears on the face and then spreads over the body.
- Among serious complications, 1 in 20 patients gets pneumonia.
- 1 in 1,000 gets brain swelling, possibly leading to seizures, deafness or intellectual disability. Spread – Measles is transmitted via droplets from the nose, mouth or throat of infected persons. So, it spreads by coughing or sneezing, and someone can spread the virus for 4 days before the rashes appear.
- The virus can live for up to 2 hours in the air or on nearby surfaces.
- 9 of 10 unvaccinated people who come into contact with someone with measles will catch it. Vaccine – Known as the MMR vaccine, it protects against measles, mumps and rubella.
- Two shots are required, one around the first birthday and a second between age 4 and 6. Full vaccination is 97% effective at preventing measles.
Signs and symptoms:
- The first sign of measles is usually a high fever, which begins about 10 to 12 days after exposure to the virus, and lasts 4 to 7 days. A runny nose, a cough, red and watery eyes, and small white spots inside the cheeks can develop in the initial stage. After several days, a rash erupts, usually on the face and upper neck. Over about 3 days, the rash spreads, eventually reaching the hands and feet. The rash lasts for 5 to 6 days, and then fades. On average, the rash occurs 14 days after exposure to the virus (within a range of 7 to 18 days). Most measles-related deaths are caused by complications associated with the disease. Serious complications are more common in children under the age of 5, or adults over the age of 30. The most serious complications include blindness, encephalitis (an infection that causes brain swelling), severe diarrhoea and related dehydration, ear infections, or severe respiratory infections such as pneumonia. Severe measles is more likely among poorly nourished young children, especially those with insufficient vitamin A, or whose immune systems have been weakened by HIV/AIDS or other diseases.
Who is at risk?
- Unvaccinated young children are at highest risk of measles and its complications, including death. Unvaccinated pregnant women are also at risk. Any non-immune person (who has not been vaccinated or was vaccinated but did not develop immunity) can become infected. Measles is still common in many developing countries – particularly in parts of Africa and Asia. The overwhelming majority (more than 95%) of measles deaths occur in countries with low per capita incomes and weak health infrastructures. Measles outbreaks can be particularly deadly in countries experiencing or recovering from a natural disaster or conflict. Damage to health infrastructure and health services interrupts routine immunization, and overcrowding in residential camps greatly increases the risk of infection.
Transmission
- Measles is one of the world’s most contagious diseases. It is spread by coughing and
- sneezing, close personal contact or direct contact with infected nasal or throat secretions. The virus remains active and contagious in the air or on infected surfaces for up to 2 hours. It can be transmitted by an infected person from 4 days prior to the onset of the rash to 4 days after the rash erupts. Measles outbreaks can result in epidemics that cause many deaths, especially among young, malnourished children. In countries where measles has been largely eliminated, cases imported from other countries remain an important source of infection.
Treatment
- No specific antiviral treatment exists for measles virus.
- Severe complications from measles can be avoided through supportive care that ensures good nutrition, adequate fluid intake and treatment of dehydration with WHO- recommended oral rehydration solution. This solution replaces fluids and other essential elements that are lost through diarrhoea or vomiting. Antibiotics should be prescribed to treat eye and ear infections, and pneumonia.
- All children diagnosed with measles should receive two doses of vitamin A supplements, given 24 hours apart. This treatment restores low vitamin A levels during measles that occur even in well-nourished children and can help prevent eye damage and blindness. Vitamin A supplements have been shown to reduce the number of deaths from measles by 50%.
Prevention
- Routine measles vaccination for children, combined with mass immunization campaigns in countries with high case and death rates, are key public health strategies to reduce global measles deaths. The measles vaccine has been in use for over 50 years. It is safe, effective and inexpensive. It costs approximately one US dollar to immunize a child against measles. The measles vaccine is often incorporated with rubella and/or mumps vaccines. It is equally safe and effective in the single or combined form. Adding rubella to measles vaccine increases the cost only slightly, and allows for shared delivery and administration costs.
- In 2017, about 85% of the world’s children received 1 dose of measles vaccine by their first birthday through routine health services – up from 72% in 2000. Two doses of the vaccine are recommended to ensure immunity and prevent outbreaks, as about 15% of vaccinated children fail to develop immunity from the first dose. In 2017, 67% of children received the second dose of the measles vaccine.
- Of the estimated 20.8 million infants not vaccinated with at least one dose of measles vaccine through routine immunization in 2017, about 8.1 million were in 3 countries: India, Nigeria and Pakistan
WHO response
- In 2010, the World Health Assembly established 3 milestones towards the future eradication of measles to be achieved by 2015:
- increase routine coverage with the first dose of measles-containing vaccine (MCV1) by more than 90% nationally and more than 80% in every district;
- reduce and maintain annual measles incidence to less than 5 cases per million; reduce estimated measles mortality by more than 95% from the 2000 estimate; and
- In 2012, the Health Assembly endorsed the Global Vaccine Action Plan, with the objective of eliminating measles in four WHO regions by 2015 and in five regions by 2020.
- By 2017, the global push to improve vaccine coverage resulted in an 80% reduction in deaths. During 2000– 2017, with support from the Measles & Rubella Initiative and Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, measles vaccination prevented an estimated 21.1 million deaths; most of the deaths averted were in the African region and in countries supported by the Gavi Alliance.
- But without sustained attention, hard fought gains can easily be lost. Where children are unvaccinated, outbreaks occur.
- Because of low coverage nationally or in pockets, multiple regions were hit with large measles outbreaks in 2017, causing many deaths. Based on current trends of measles vaccination coverage and incidence, the WHO Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) concluded that measles elimination is greatly under threat, and the disease has resurged in a number of countries that had achieved, or were close to achieving, elimination.
- WHO continues to strengthen the global laboratory network to ensure timely diagnosis of measles and track international spread of the measles viruses to allow more coordinated country approach in targeting vaccination activities and reduce measles deaths from this vaccine-preventable disease.
India’s target:
- The following measures have been taken to achieve the target of measles elimination by 2020:
- Government of India introduced measles vaccine across the country in 1985 under the Universal Immunization Programme (UIP). To further reduce the measles burden, a second dose of measles vaccine was introduced in the country in the year 2010.
- With an aim to increase the full immunization coverage to 90% by December 2018 including improving measles vaccine coverage particularly in pockets with low immunization coverage, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has launched Intensified Mission Indradhanush on 8th October 2017.
- The Intensified Mission Indradhanush is being carried out in 173 districts and 17 urban areas across 24 states of the country and three rounds (Oct, Nov and Dec) have been completed since the launch.
- An India Expert Advisory Group on Measles & Rubella (IEAG-MR) has been established, comprising national and international experts, to provide technical guidance on the disease elimination efforts from time to time. The group has met twice since its formulation
GENOME SEQUENCING TO MAP POPULATION DIVERSITY
19, Apr 2019
Why in News:
- Youths from the length and breadth of India have their genomes which was sequenced by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR). The project aims at educating a generation of students on the usefulness of genomics.
Details:
- A large sample of Indians have undertaken genome sequencing of a sample of their citizens to determine unique genetic traits, susceptibility and resilience to disease.
- A part of genome-sample collections is representative of the country’s population diversity. In this case, the bulk of them will be college students, both men and women, and pursuing degrees in the life sciences or biology.
- Genomes will be sequenced based on a blood sample and the scientists plan to hold at least 30 camps covering most States.
- Every person whose genomes are sequenced will be given a report and the participants would be told if they carry gene variants that make them less responsive to certain classes of medicines.
- Having a certain gene makes some people less responsive to clopidogrel, a key drug that prevents strokes and heart attack.
- The project involves the Hyderabad-based Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB).
- The project would prove India’s capabilities at executing whole-genome sequencing. The human genome has about 3.2 billion base pairs and just 10 years ago cost about 10,000 dollars. Now prices have fallen to a tenth.
- Ever since the human genome was first sequenced in 2003, it opened a fresh perspective on the link between disease and the unique genetic make-up of everyone.
- Nearly 10,000 diseases including cystic fibrosis, thalassemia are known to be the result of a single gene malfunctioning.
Genome Sequencing
- Genome sequencing is figuring out the order of DNA nucleotides, or bases, in a genome— the order of As, Cs, Gs, and Ts that make up an organism’s DNA. The human genome is made up of over 3 billion of these genetic letters.
- Today, DNA sequencing on a large scale—the scale necessary for ambitious projects such as sequencing an entire genome—is mostly done by high-tech machines. Much as your eye scans a sequence of letters to read a sentence, these machines “read” a sequence of DNA bases. Genome sequencing is often compared to “decoding,” but a sequence is still very much in code. In a sense, a genome sequence is simply a very long string of letters in a mysterious language.
Why is genome sequencing so important?
- Sequencing the genome is an important step towards understanding it.
- The genome sequence will represent a valuable shortcut, helping scientists find genes much more easily and quickly. A genome sequence does contain some clues about where genes are, even though scientists are just learning to interpret these clues.
- Scientists also hope that being able to study the entire genome sequence will help them understand how the genome as a whole works, how genes work together to direct the growth, development and maintenance of an entire organism.
How to sequence a genome?
- The whole genome can’t be sequenced all at once because available methods of DNA sequencing can only handle short stretches of DNA at a time.
- Instead, scientists must break the genome into small pieces, sequence the pieces, and then reassemble them in the proper order to arrive at the sequence of the whole genome. Much of the work involved in sequencing lies in putting together this giant biological jigsaw puzzle.
- There are two approaches to the task of cutting up the genome and putting it back together again. One strategy, known as the “clone-by-clone” approach, involves first breaking the genome up into relatively large chunks, called clones, about 150,000 base pairs (bp) long. Scientists use genome mapping techniques where in the genome each clone belongs. they cut each clone into smaller, overlapping pieces the right size for sequencing—about 500 BP each. Finally, they sequence the pieces and use the overlaps to reconstruct the sequence of the whole clone.
- The other strategy, called “whole-genome shotgun” method, involves breaking the genome up into small pieces, sequencing the pieces, and reassembling the pieces into the full genome sequence.
N. KOREA CALLS FOR POMPEO TO BE DROPPED FROM TALKS
19, Apr 2019
Why in news:
- North Korea said, it no longer wanted to deal with U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo and said he should be replaced by someone more mature than him after the announcement of first weapons test.
Details:
- The statement came after North Korea announced the testing of a new tactical guided
- weapon, which has a “peculiar mode of guiding flight” and “a powerful warhead”.
- It was a short-range weapon rather than the long-range ballistic missiles that have been a threat to the United States.
Background:
- North Korea has improved its nuclear weapons capability, increasing tensions against the US and its allies. It has been threatening US and neighbour South Korea by successfully conducting intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBM) tests.
- US president Donald Trump has also responded back by tough words pointing that US can reply by its military solutions with fire and fury. These latest developments are also compared to the Cuban missile crisis (1962) between Soviet and US during the Cold War.
Historical Background:
- Korea was divided into two zones along the 38th parallel after the end of WW II in 1945, with the northern half of the peninsula occupied by the Soviet Union and southern half by the US. Before this it was under Japanese control since 1910 which had industrialised the peninsula and exploited Koreans mainly for benefiting Japan.
Analysis:
- North Korea-US relations are hostile till date that developed primarily during the Korean War. The two nations are separated by the Pacific Ocean. Since the Korean War, US has maintained a strong military presence in South Korea.
- North Korea (DPRK) is a one-party state under a totalitarian dictatorship. It maintains a huge number of military forces as per its ‘military-first’ policy. It has a military nuclear weapons program. Also, after US and Russia, it ranks 3rd in possessions of chemical weapons.
- North Korea has been conducting nuclear tests since 2006. As a result, several sanctions have been imposed by various countries and international bodies. Latest Resolution 2371, by UN in August 2017 tightened economic sanctions for the 6th time over DPRK in response to its July 2017 missile tests. The latest tests have resulted in missiles which flew over Japan and DPRK threatening Guam (US).
- US which has all three types of weapons of mass destruction, a very strong army, naval and air forces also responded with strong words. Trump has also warned of sending US Carl Winson super carrier and its carrier strike group to Korea.
- The use of any kind of weapons of mass destruction or armed conflicts on large scale will lead to:
- Causalities and losses as had occurred during the Korean War or the larger scale world wars which involved more countries of the
- Major economic problems in Korea and other countries like Japan, South Korea and
- Rise in debt levels of
- Severe effect on global supply
- South Korea is the biggest producer of liquid crystal displays in the world (40% of the global total) and the second biggest of semiconductors (17% market share). It is also a key automotive manufacturer and home to the world’s three biggest If South Korean production is badly damaged by a war there would be shortages across the world which would last for a few years.
- Migration of refugees from North Korea to China, Japan or nearby
FRANCE LAUNCHES GLOBAL CONTEST TO REPLACE NOTRE- DAME SPIRE
18, Apr 2019

Why in news:
- France announced that it would invite architects from around the world to submit designs for replacing the spire of Notre- Dame Cathedral after a devastating blaze.
Details:
- The contest would decide whether the monument should have a new spire and whether it should be identical to the fallen 19th-century model or be a wholly new design.
Notre-Dame de Paris
- Notre-Dame de Paris, also called Notre-Dame Cathedral, cathedral church in Paris. It is the most famous of the Gothic cathedrals of the Middle Ages and is distinguished for its size, antiquity, and architectural interest.
- Notre-Dame lies at the eastern end of the Ile de la Cite and was built on the ruins of two earlier churches, which were themselves predated by a Gallo-Roman temple dedicated to Jupiter. The cathedral was initiated by Maurice de Sully, bishop of Paris, who about 1160 conceived the idea of converting into a single building, on a larger scale, the ruins of the two earlier basilicas.
- The foundation stone was laid by Pope Alexander III in 1163, and the high altar was consecrated in 1189. The choir, the western facade, and the nave were completed by 1250, and porches, chapels, and other embellishments were added over the next 100 years.
- Notre-Dame Cathedral consists of a choir and apse, a short transept, and a nave flanked by double aisles and square chapels.
- Its central spire was added during restoration in the 19th century, replacing the original, which had been completely removed in the 18th century because of instability.
- The interior of the cathedral is 427 by 157 feet (130 by 48 metres) in plan, and the roof is 115 feet (35 metres) high.
- Two massive early Gothic towers (1210–50) crown the western facade, which is divided into three stories and has its doors adorned with fine early Gothic carvings and surmounted by a row of figures of Old Testament kings.
- The two towers are 223 feet (68 metres) high; the spires with which they were to be crowned were never added. At the cathedral’s east end, the apse has large clerestory windows (added 1235–70) and is supported by single-arch flying buttresses of the more daring Rayonnant Gothic style, especially notable for their boldness and grace. The cathedral’s three great rose windows alone retain their 13th-century glass.
- Notre-Dame Cathedral suffered damage and deterioration through the centuries.
- After the French Revolution it was rescued from possible destruction by Napoleon, who crowned himself emperor of the French in the cathedral in 1804. Notre-Dame underwent major restorations by the French architect Eugène-Emmanuel Viollet-le-Duc in the mid-19th century.
- The popularity of Victor Hugo’s historical novel Notre-Dame de Paris (1831), wherein the cathedral is the setting, was said to have inspired the renovations.
- During a restoration campaign in 2019, a fire broke out in the cathedral’s attic, and the massive blaze destroyed most of the roof, Viollet-le-Duc’s 19th-century spire, and some of the rib vaulting.
MARS BASE SIMULATOR UNVEILED IN GOBI DESERT
18, Apr 2019

Why in news:
- China’s Gobi Desert has a Mars base simulator, but instead of housing astronauts training to live on the red planet, full of teenagers on a school trip are allowed with the facility.
Details:
- It is surrounded by barren hills in north-western Gansu province.
- “Mars Base 1” is opened with the aim of exposing teens and soon tourists to show what life could be like on the planet.
- China is making progress in its efforts to catch up to the United States and become a space power, with ambitions of sending humans to the moon someday. The white-coloured base has a silver dome and nine modules, including living quarters, a control room, a greenhouse and an airlock. It is built at a cost of 50 million yuan, the base was constructed with help from the Astronauts Centre of China and the China Intercontinental Communication Centre, a state television production organisation. The teenagers are allowed to go on treks in the desert, where they explore caves in the Martian-like landscape. over 100 students from a nearby high school walked on the arid Gobi plains, dressed in suits like that of astronauts.
- The company behind the project is C-Space.
- By sending budding astronauts, they explore “Mars” on Earth
- China is planning to send a probe to the real red planet next year. Beijing is pouring billions into its military-run space programme, with hopes of having a crewed space station by 2022. The facility, composed of a “Mars community” and a “Mars camp”, will provide tourists with a unique scientific and cultural experience.
Mars:
- Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System after Mercury. In English, Mars carries a name of the Roman god of war. It is often referred to as the “Red Planet” because the reddish iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance that is distinctive among the astronomical bodies visible to the naked eye.
- Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere, having surface features like the craters of the Moon and the valleys, deserts, and polar ice caps of Earth.
SCIENTISTS REVIVE A FLICKER OF ACTIVITY IN BRAINS OF DEAD PIGS
18, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- Yale University scientists have succeeded in restoring basic cellular activity in pigs’ brains hours after their deaths in a finding that may one day lead to advances in treating human stroke and brain injuries, researchers reported on Wednesday.
Details:
- The scientists emphasised that their work did not even come close to reawakening consciousness in the disembodied pig brains.
- Still, the study raises a host of bioethical issues, including questions about the very definition of brain death and potential consequences for protocols related to organ donation.
- The research grew out of efforts to enhance the study of brain development, disorders and evolution. The main practical application is the
- prospect of allowing scientists to analyze whole brain specimens of large mammals in three dimensions, rather than through studies confined to small tissue samples, Yale said.
- Results of the experiment, to be published on Thursday in the journal Nature, run contrary to long-accepted principles of brain death, which hold that vital cellular activity ceases irreversibly seconds or minutes after oxygen and blood flow are cut off.
- The limited rejuvenation of circulatory function and cellular metabolism in pig brains, which were harvested from animals slaughtered at a meat-packing plant, was achieved four hours after death by infusing the brains with a special chemical solution designed to preserve the tissue.
Not a ‘LIVING BRAIN’
- Scientists stressed, however, that the treated brains still lacked any detectable signs of organized electrical activity associated with perception, awareness or consciousness. “Clinically defined, this is not a living brain, but it is a cellularly active brain,”
- While the study offers no immediate therapeutic benefits for humans, it creates a new research platform that may ultimately help doctors find ways to revive brain function in stroke patients or to test new treatments for restoring brain cells damaged by injury, the authors said. In the meantime, the research could spark new quandaries surrounding the determination of death itself, widely defined by one measure as the irreversible loss of all brain function. The blurring of that line has implications in turn for deciding when doctors are ethically bound to go from preserving a patient’s life to preserving their organs.
EARTH SIZED EXOPLANET FOUND
17, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- One year after its launch, NASA’s TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite) discovered its first Earth-sized exoplanet.
Details:
- Named HD21749c, the planet orbits a star just 53 light-years from Earth and is likely rocky but uninhabitable.
- The findings — published in Astrophysical Journal Letters– suggest TESS is capable of fulfilling its mission to catalog thousands of planet candidates, including more than 300 that are expected to be Earth-sized and super-Earth-sized exoplanets.
- This newly identified planet is the smallest world outside our solar system that TESS has spotted.
- And the spacecraft’s data shows HD21749c circles its star every 7.8 days, meaning it has a tight orbit that would lead to surface temperatures of up to 800 degrees Fahrenheit.
- TESS has now found 10 planets smaller than Neptune, and its ability to locate this one is a good indicator that it’s capable of finding other small planets — perhaps even some in the “Goldilocks” zone, close enough to their star to have liquid water but far enough to avoid being roasted.
- TESS, is eyeing planets much closer to us, so scientists can attempt, for instance, to determine their mass. Next, the team of astronomers behind this discovery, will try to do just that. If they’re successful, we could have the first mass measurement of an Earth-sized planet.
Exoplanet:
- Planets that orbit around other stars are called exoplanets.
- Exoplanets are very hard to see directly with telescopes. They are hidden by the bright glare of the stars they orbit. So, astronomers use other ways to detect and study these distant planets.
Light year
- A light-year is a unit of distance. It is the distance that light can travel in one year. Light moves at a velocity of about 300,000 kilometers (km) each second. So, in one year, it can travel about 10 trillion km. More precisely, one light-year is equal to 9,500,000,000,000 kilometers.
CHINA IS USING AI TO PROFILE UIGHUR MUSLIMS
16, Apr 2019
Why in news:
- Facial recognition technology being used by china to track and control the Uighurs. It is the first known example of a government intentionally using artificial intelligence for racial profiling,
Details:
- The facial recognition technology, which is integrated in China’s rapidly expanding networks of surveillance cameras, looks exclusively for Uighurs based on their appearance and keeps records of their comings and goings for search and review.
- The practice makes China a pioneer in applying next-generation technology to watch its people, potentially using technology for automated racism. Facial recognition technology uses aspects like skin tone and face shapes to sort images in photos or videos.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- It is a branch of computer science which deals with creating computers or machines as intelligent as human beings. The term was coined in 1956 by John McCarthy at the Dartmouth conference, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- It is a simulation of human intelligence processes such as learning (the acquisition of information and rules for using
- the information), reasoning (using the rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction by machines, especially computer systems. Nowadays it has become an umbrella term which encompasses everything from robotic process automation to actual robotics. It has become widely popular and gained prominence due to its multifaceted application ranging from healthcare to military devices.
Artificially Intelligent Technologies Applications:
- Robotic process automation: Automation is the process of making a system or processes function automatically. Robots can be programmed to perform high-volume, repeatable
- tasks normally performed by humans and further it is different from IT automation because of its agility and adaptability to the changing circumstances.
- Natural language processing (NLP) is the processing of human language and not computer language by a computer program. For Example, spam detection, which looks at the subject line and the text of an email and decides if it’s junk.
- Pattern recognition is a branch of machine learning that focuses on identifying patterns in data.
- Machine vision is the science of making computers visualize by capturing and analyzing visual information using a camera, analog-to-digital conversion, and digital signal processing.
- It is often compared to human eyesight, but machine vision isn’t bound by biology and can be programmed to see through walls. It is used in a range of applications from signature identification to medical image analysis.
- Machine learning: Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. Deep learning is a subset of machine learning and can be thought of as the automation of predictive analytics.
- Robotics is a field of engineering focused on the design and manufacturing of robots. Robots are often used to perform tasks that are difficult for humans to perform or perform consistently.
In Indian Context:
- The partnership between think tank in India NITI Aayog (National Institute for Transforming India) with Google to develop India’s artificial intelligence ecosystem will help to improve healthcare, education, agriculture, transportation, develop innovative governance systems and improve overall economic productivity. This will also help in promoting entrepreneurs associated with it, research in the field in premier institutions like IITs and providing crash course to students across India.
Disadvantages:
- Development in such advanced technologies affects employment opportunities also as machines can do the work of many labours. Whether they can compete with a human brain is also a question.
FIRST 3D PRINTED HEART HAS HUMAN CELLS, VESSELS
16, Apr 2019
Why in News?
- Scientists in Israel unveiled a 3D print of a heart with human tissue and vessels, calling it a first and a “major medical breakthrough” that advances possibilities for Transplants.
Details:
- The heart, about the size of a rabbit’s, marked “the first time anyone anywhere has successfully engineered and printed an entire heart replete with cells, blood vessels, ventricles and chambers.
- Until now, the Tel Aviv University said, scientists have been successful in printing only simple tissue without blood vessels. The printing process for the tiny heart took about three hours, journalists who were able to watch the entire process said. The importance of the heart’s being made with a patient’s own cells and biological materials in order to eliminate the risk of implant rejection was stressed.
- The next step for the researchers is to culture the printed hearts in a laboratory and “teach them” to behave like hearts. The current state of the primitive heart can be compared to the heart of an embryo. “The cells need to form a pumping ability; they can currently contract, but we need them to work together. Once they have achieved that, the scientists plan to transplant the hearts into small animals, such as rabbits or rats.
- “Larger human hearts require the same technology
- Maybe, in 10 years, there will be organ printers in the finest hospitals around the world, and these procedures will be conducted routinely
- The World health Organization said last year that ischaemic heart disease and stroke were the world’s biggest killers.
3D Bioprinting:
- 3D bioprinting uses a typical layer-by-layer 3D printing method, depositing bio inks or biomaterials, to create 3D tissues or structures used for medicine or tissue engineering.
- This technology is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and 3D printed organs for transplant
NSE AND BSE ACCOUNT FOR 96% OF CURRENCY TRADING IN THE ASIA-PACIFIC REGION
16, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- Even though India become one of the largest derivative trading centres globally, it has not stopped the bourses.
- Indian exchanges do not offer trading in exotic derivative instruments like their counterparts in the developed markets in the U.S. and Europe
Background:
- Three exchanges — Korea Exchange, NSE and the Moscow Exchange — accounted for 68% of the total single stock futures total volumes traded. Further, the NSE and Korea Exchange together accounted for 90.7% of the volume of index options in the Asia-Pacific region.
- In the currency derivatives segment, the NSE and the BSE together account for 96% of such derivatives volume in the Asia-Pacific region. The two Indian exchanges occupy the top two ranks with nearly 211 crore contracts traded in 2018. Further, the BSE registered the second-highest volume growth in the year at 70% — second only to 84% of Singapore Exchange.
- In commodities as well, an India exchange is featured among the top 10 globally. In 2018, the Multi Commodity Exchange of India (MCX) was ranked eighth globally with a little over 23 crore contracts traded while registering a 16% rise during the year. In India, MCX is the biggest commodity bourse with a market share of more than 90%.
NSE:
- NSE is an All India level stock exchange. It was incorporated in November 1992. It offers online trading system matching to international standards.
The Main features of National Stock Exchange are as follows
- It has nationwide coverage. The investor can make dealing through NSEI dealer.
- NSE is the first stock exchange in the world which uses communication technology for trading its securities. It is fully computerised, screen based and ringless system.
- It allows the investors to trade their securities from their offices or homes through the network with direct satellite link up. There are transparency dealings. The investor can check the exact price at which their transactions took place. National Stock Exchange is a company promoted BY IDBI, ICCI, LIC and GIC and its subsidiaries, commercial banks. SBI capital market limited. The establishment of the NSE is a major step in upgrading trading facilities for investors and bringing Indian Financial markets in line with international markets. The index of the NSE is called as the Broader 50 share – Nifty.
BSE:
- Bombay Stock Exchange Limited is the oldest stock exchange in Asia with a rich with a rich heritage popularly known as BSE. It was established as “The Native Share and Stock Brokers Association “in 1875. It is the first stock exchange in the country to obtain permanent recognition in 1956 from the government role of BSE in the development of the Indian capital market is widely recognised.
The strategic objective of Bombay stock exchange are as follows:
- To promote, develop and maintain a well-regulated market for dealings in securities.
- To safeguard the interest of members and the investing public having dealings on the exchange.
- To promote industrial development in the country through efficient resource mobilisation by way of investment in corporate securities.
- To establish and develop critical and fair practices in securities transactions.
Management of Bombay Stock Exchange
- The exchange is professionally managed under the overall direction of the board of directors., governing body, or executive committee. The board comprises of eminent, professionals, representatives of trading members and the managing director of the exchange. The day to day operations of the exchange are managed by the Managing
- Director and CEO and an expert management Team of professionals.
ASSANGE TRIED TO USE EMBASSY SAYS ECUADOR
16, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- Violation of asylum conditions and tried to use the Ecuador embassy in London.
Background:
- Julian Assange is the head of the anti-secrecy website WikiLeaks.
- Mr. Assange made international headlines in early 2010 when WikiLeaks published a classified U.S. military video.
- It showed a 2007 attack by Apache helicopters in Baghdad that killed a dozen people, including two Reuters news staff.
- Mr. Assange was facing charges related to theft of classified information from government computers, conspiring with former U.S. Army intelligence officer Chelsea Manning.
- In 2012, authorities from Sweden wanted to question him as part of a sexual assault investigation. To avoid being extradited to Sweden, Mr. Assange took refuge in Ecuador’s London embassy in June 2012. Sweden dropped that investigation in 2017, but Mr. Assange broke the rules of his original bail (2012) in London.
- Eventually, he had eluded authorities in the U.S. and the U.K. for nearly 7 years, to escape arrest. Now, Ecuador President Lenin Moreno withdrew his country’s grant of asylum to Mr. Assange that was on for 7 years.
- Ecuador had earlier limited Mr. Assange’s Internet access.
- Asylum was withdrawn after repeated violations to international conventions and daily-life protocols by Assange. Mr. Assange was thus arrested by British police and carried out of the Ecuadorean embassy, paving the way for his possible extradition to the U.S.
Cyber security issues:
- Cyber-Crime has been called one of the biggest risks to data and security.
- UNESCO says that the increased threat of cyber-attacks puts critical infrastructure, like the information systems of hospitals, air traffic control facilities, factories, police and military, of developing nations at risk.
- Developing nations which are in the throes of a technological revolution are catching up on modern technology, but the infrastructure for cyber security and cyber laws are either archaic or non-existent.
- Countries like India are bringing millions of people online, but the security infrastructure is just not ready.
- For emerging digital economies, another risk is that hacking attacks and online fraud can deter people from using e-commerce or e-payments.
- Added to that is the fact that Indian data protection laws are inadequate and only address some security, and privacy issues. Meanwhile cyber-crime in the country is on a rise.
- The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) said in its 2016 report, that 11,592 cases of cyber-crime were registered in India in 2015.
National Cyber Security Policy 2013:
- The National Cyber Security Policy 2013 aims at (1) facilitating the creation of secure computing environment (2) enabling adequate trust and confidence in electronic transactions and (3) guiding stakeholder’s actions for the protection of cyberspace.
- A vision and mission statement aimed at building a secure and resilience cyberspace for citizens, businesses and Government. Enabling goals aimed at reducing national vulnerability to cyber-attacks, preventing cyber-attacks & cyber-crimes, minimising response & recovery time and effective cybercrime investigation and prosecution.
- Focused actions at the level of Govt., public-private partnership arrangements, cyber security related technology actions, protection of critical information infrastructure and national alerts and advice mechanism, awareness & capacity building and promoting information sharing and cooperation.
- Enhancing cooperation and coordination among all the stakeholder entities within the country. Objectives and strategies in support of the National Cybersecurity vision and mission. Framework and initiatives that can be pursued at the Govt. level, sectoral levels as well as in public-private partnership mode.
- Facilitating monitoring key trends at the national level such as trends in cyber security compliance, cyber-attacks, cyber-crime and cyberinfrastructure growth.
Recent updates:
- A National and sectoral 24X7 mechanism has been envisaged to deal with cyber threats through National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC). Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) has been designated to act as a nodal agency for coordination of crisis management efforts. (CERT-In) will also act as an umbrella organisation for coordination actions and operationalization of sectoral CERTs.
- A mechanism is proposed to be evolved for obtaining strategic information regarding threats to information and communication technology (ICT) infrastructure, creating scenarios of response, resolution and crisis management through effective predictive, prevention, response and recovery action.
Recent Threats in India:
- Websites Hacked: Over 22,000 websites were hacked between the months of April 2017 and January 2018. As per the information presented by the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team, over 493 websites were affected by malware propagation including 114 websites run by the government. The attacks were intended to gather information about the services and details of the users in their network.
- ATM System Hacked in Kolkata: In July 2018 fraudsters hacked into Canara bank ATM servers and wiped off almost 20 lakh rupees from different bank accounts. The number of victims was over 50 and it was believed that they were holding the account details of more than 300 ATM users across India.
- The hackers used skimming devices on ATMs to steal the information of debit card holders and made a minimum transaction of INR 10,000 and the maximum of INR 40,000 per account. On 5 August 2018, two men were arrested in New Delhi who was working with an international gang that uses skimming activities to extract the details of bank account.
- SIM Swap Fraud: In August 2018, two men from Navi Mumbai were arrested for cybercrime. They were involved in fraudulent activities concerning money transfers from the bank accounts of numerous individuals by getting their SIM card information through illegal means.
WORLDS LARGEST PLANE MAKES FIRST FLIGHT TEST
15, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- The world’s largest aircraft took off over the Mojave Desert in California on Saturday, the first flight for the carbon-composite plane built by Stratolaunch Systems Corp.
Details:
- The mega jet carried out its maiden voyage over the Mojave Desert. It is designed to carry into space, and drop, a rocket that would in turn ignite to deploy satellites. It is supposed to provide a more flexible way to deploy satellites than vertical takeoff rockets because this way all you need is a long runway for takeoff.
- The aircraft is so big its wing span is longer than a football field, or about 1.5 times that of an Airbus A380 Specifically, the wing span is 117 meters; that of an Airbus A380 is just under 80. It hit a top speed of 304 kilometres per hour (189 mph) and reached an altitude of 17,000 feet, or 5,182 metres.
OIL CONSUMING BACTERIA FOUND AT SEA BOTTOM
15, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- Scientists have discovered a unique oil eating bacterium in the Mariana Trench, the deepest part of the earth’s oceans, a finding that may pave way for sustainable ways to clean up oil’s spills.
- In the samples, they found microorganisms that eat compounds similar to those in oil and then use it for fuel.
Background: / Causes of Oil Spills:
The common causes of oil spills are as following:
- Natural causes: Tsunami, Cyclone, Thunderstorm etc.
- Human Causes: War, attack, sabotage, human mistakes leading to a collision or some technical reasons.
What are the major impacts of Oil Spill?
On Marine life
- The most affected organisms are those which floats near the surface like turtles, fishes, crabs etc.
- Sea animals caught in an oil spill, on being exposed to toxic petroleum products often results in lower reproductive rates, organ damage, and death. The effects remain for a long period of time.
- Fishes die due to inability to swim or breath.
- Note: This time was core breeding period for olive ridley turtles and due to oil slick sticking to the gut mother turtles may find it difficult to lay the eggs.
On Birds
- Many birds die due to drowning or inability to eat due to oil sticking to their body.
On Humans
- Direct exposure can have varying effects depending on the toxicity and chemicals involved in the spill.
- Humans get exposed to toxicity through breathing gaseous oil compounds and/or oil compounds adsorbed on particulate matter (dispersed through the air). Exposure can also happen due to the activities in the contaminated ground (e.g., soil) or through skin absorption when touching spilled material.
- There is a huge economic cost attached with such disasters.
What are the problems faced in the oil-remedial processes?
The problems with oil-remedial processes are as following:
- Petroleum oils are complex mixtures of chemicals that are toxic, bio accumulative and persistent in the environment. Some, like benzene, are known human carcinogens.
- They enter the body through inhalation, ingestion and the skin.
- An oil spill clean-up is a hazardous waste remediation exercise. Many traditional methods of cleaning oil spills, such as breaking up the oil with dispersants or skimming it off the surface, are expensive, slow, and unsafe – and often don’t really work all that well anyway. During the recent disaster, authorities starting pumping oil sludge by city water pump but all in vain.
- Later on, volunteers skimmed off the oil using buckets in hand which can be very dangerous for individuals.
What are the available technological solutions?
- Oil Zapper is a cocktail of bacteria that feed on the oil and degrade the hydrocarbons. Newer methods and technologies like Nanosheets that could revolutionize oil spill clean ups and water purification needs to be deployed. It has following major benefits:
- Recyclable.
- absorb 33 times their weight in oil.
- One gram of nanosheets has the equivalent area as nearly 5.5 tennis courts – so a lot of surface for absorption. Saturated nanosheets can be simply heated in air for two hours for cleaning purpose. The absorbed oil burns off, leaving the nanosheets clean and free to absorb again. Easy to build and affordable.
LIPSTICK SEED’S GROWN BY TRIBAL’S
15, Apr 2019

Why in news:
- The coloured cosmetic that they adorn on their lips can be manufactured from the non- carcinogenic lipstick seed cultivated in the backyard of Adivasi habitations in Rampachodavaram, Chaparai, and Maredumilli in Andhra Pradesh.
Background: / Who are Adivasis?
- Adivasis are not a homogeneous group; there are over 200 distinct peoples speaking more than 100 languages, and varying greatly in ethnicity and culture. However, there are similarities in their way of life and generally perceived oppressed position within Indian society. According to the official Census held in 2001, Adivasis constitute 8 per cent of the nation’s total population, over 84 million people. Unofficial figures vary significantly but represent a much higher proportion of India’s population. Adivasis live throughout India but are primarily based in the mountain and hill areas, away from the fertile plains.
- According to the 2001 census, the greatest concentration is in Chattisgrah (38%), Jharkahand (26%) Madhya Pradesh (20%), Orisssa (22%), Andhra Pradesh (6%) Gujarat(15%) Rajasthan (12%), Maharashtra (9%) and Bihar (0.9%).
Problems Faced By Adivasis
- Many governments sign MoU’s with big mining corporations without the consent of the tribals who live on the land. Setting up mines and factories inside jungles requires displacing and relocating the tribal population. Most Adivasis do not want to relocate to a different place and prefer living in the jungles. They generally do not value money. Their refusal to vacate the land leads to the government deploying armed forces like the CRPF against them – often burning villages, harassing people, killing tribals – all in an attempt to get them to vacate. This conflict leads to Maoists leading an armed struggle against the government. They claim to be fighting for the rights of the tribals.
- Governments should make public all MoU’s signed with all the mining corporations. This information should be available publicly, with details like the exact location of the proposed mine/factory, which mineral is being mined, which corporation has been awarded the contract, how much money the government and the corporation stand to make etc Governments must take consent of the tribals living on the land before signing any MoU with any corporation. The method of consent must be transparent, without coercion and documented. The government must give up any proposed projects for minerals if tribals do not consent to the mining. The Tribals often are malnourished and lack access to basic healthcare. Anaemia is a common disease among the tribal populations.
- Tribals are often considered “low”, “dirty” by people from the towns, cities, upper castes. They lack social prestige in Indian society. India is a very racist country which is heavily judgmental.
Medicinal benefits of lipstick seeds:
The seeds have healing properties and used in
Treating digestive disorders, Weak bones, Headache, Neural tube defects, Eye ailments and respiratory problems.
Other Uses:
- The plant’s seed extract is used as a natural colouring agent in cheese, food preparations, bakery products and sweets across the world. These rare seeds have no fixed price as there is no organised trade in the tribal areas. The seeds command much higher value in the international market.
CAPTURING THE IMAGE OF BLACK HOLE
14, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- Recently astronomers have clicked a picture of one of the most secretive objects of the universe.
Black hole
- A black hole is an extremely dense object from which no light can escape. Anything that comes within a black hole’s “event horizon,” its point of no return, will be consumed, never to re-emerge, because of the black hole’s unimaginably strong gravity. By its very nature, a
- black hole cannot be seen, but the hot disk of material that encircles it shines bright.
Capturing Black Hole:
- Black holes are the result, mostly, of heavy stars collapsing in on themselves, radiation emitted by particles within the disc are heated to billions of degrees as they swirl around the black hole at close to the speed of light, before vanishing into them.
- A black hole and its shadow have been captured in an image for the first time, a historic feat by an international network of radio telescopes called the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT). EHT is an international collaboration whose support in the U.S. includes the National Science Foundation. The stunning new image shows the shadow of the supermassive black hole in the center of Messier 87 (M87), an elliptical galaxy some 55 million light-years from Earth. This black hole is 6.5 billion times the mass of the Sun.Catching its shadow involved eight ground-based radio telescopes around the globe, operating together as if they were one telescope the size of our entire planet.
YEAST STRAIN INCREASES ETHANOL PRODUCTION
14, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- yeast strain that can produce up to 15.5% more ethanol when glucose or lignocellulose biomass — rice and wheat straw — is fermented has been isolated by researchers from the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, DBT-ICGEB Centre for Advanced Bioenergy Research, Delhi.
Background:
- In India, ethanol production is mostly by fermenting molasses to meet the annual target of 5% blending of petrol with ethanol. But with India setting a target of blending petrol with 10% of biofuel by 2022, other sources such as rice and wheat straw have to be considered. Fermenting lignocellulose efficiently to generate more ethanol than what is currently possible is therefore necessary. To that end, the strain isolated by ICGEB becomes important.
Challenges:
- During the fermentation process, the temperature increases from about 30 degree C to 40- degree C. Since the commercially available yeast strains are good at fermenting at 30 degree C, the fermentor has to be cooled down when the temperature increases. This increases the cost of ethanol production.
- Second, lignocellulose biomass (rice and wheat straw) contains a mixture of hexose and pentose sugar.
- The pretreatment of lignocellulose (to breakdown the recalcitrant structure of the biomass) results in the production of three main inhibitors (furfural, 5-HMF and acetic acid). These inhibitors reduce the fermentation performance of yeast, leading to reduced ethanol production.
Uses of Ethanol:
- When Ethanol is mixed with petrol, such fuel is known as Ethanol Fuel / Gasohol (=Gasoline + Ethanol).
- It can be used with no modification to the vehicle’s engine. (if concentration of ethanol is
- upto 10%). Almost all vehicles of US and Brazil, use such ethanol fuel.
Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme:
- It was launched by the Government in 2003 on pilot basis which has been subsequently extended to the Notified 21 States and 4 Union Territories to promote the use of alternative and environmental friendly fuels.
- It aims at blending ethanol with petrol, thereby bringing it under the category of biofuels and saving millions of dollars by cutting fuel imports.
- Ethanol Blended Petrol Programme is being implemented by the Ministry or Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs).
- This intervention also seeks to reduce import dependency for energy requirements and give boost to agriculture sector.
Seeing Darkness: The First Image of a Black Hole
13, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- the Event Horizon Telescope collaboration showed the world the unseeable the very first image of a black
Details:
- The black hole itself could not be seen, because light cannot escape its intense gravitational attraction.
- Event horizon telescope that envelops the black hole is the point of no return and any object transgressing this boundary is lost. photon (light quantum) can orbit the black hole without falling
- This is called the ‘last photon ring’, The EHT imaged the effect of silhouette of a black hole. It had been after hundred years the black hole made its way into physics through Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity, the LIGO collaboration first directly observed the gravitational waves made by the merging of two black holes, the ‘dark star’ which had finally been imaged. The Higgs boson was detected 50 years after it had been postulated, and gravitational waves were after Einstein predicted them.
- A black hole marks the end of spacetime and nothing that enters it can escape from the tremendous gravitational attraction.
Two images of EHT
- The EHT set out to image two candidate supermassive black holes.
- Sagittarius A, which is 26,000 light years from the earth, at the centre of the Milky it was of more distant one. Another which is 55 million light years away at the centre of the Messier 87 galaxy in the Virgo galaxy cluster. The very long baseline interferometry technique linked radio dishes of telescopes across the world to produce a virtual telescope the size of the earth.
Challenges:
- Combining data from telescopes, each with different characteristics, was a separate challenge. In order to overcome this, Cutting-edge developments from computer science related to image recognition were efforts have been made to develop an algorithm to put the data together and create the image in a TEDx talk projects.
Black hole:
- A black hole is a region in space where gravity pulls to an extent that even light cannot escape. The gravity is so powerful because matter is compressed into a little space.
How Big Are Black Holes?
- Black holes may be either big or According to scientists, the smallest black holes are as small as an atom. These are very small but have the mass (amount of content in an object) of a mountain.
- A different type of black hole is stellar whose mass can be upto 20 times greater than mass of the There can be many stellar black holes in Earth’s galaxy which is known by the name Milky Way. The biggest black hole is known as ‘supermassive’, and their masses can be 1 million suns together. According to Scientists, every large galaxy includes a supermassive black hole in the center. This supermassive black hole which exists in the middle of the Milky Way galaxy is known as Sagittarius. Its mass is same as about 4 million suns.
How Do Black Holes Form?
- Primordial black holes are considered to have formed in the early universe soon after the big bang. Stellar black holes were produced when the middle of a massive star collapsed
Way forward:
This experiment endorses the diversity of collaboration, as it needs patience and good faith in the power of science.
FROM THEORY TO FACT
11, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- Scientists have revealed the first image ever made of black hole after assembling data gathered by network of Event Horizon Telescope.
Details:
- The term black hole was coined in mid-1960 by American physicist John Archibald Wheeler.
- The matter is so compressed as to create a gravity field from which even light could not escape called black hole.
- The more the mass, bigger the hole
- They were theorised by Albert Einstein in 1915 to explain the laws of gravity.
- The first image of a black hole in a galaxy called Messier 87 in the constellation Virgo. It is about 6 million times the mass of our sun.
Black Holes:
- A black hole is a region in space where gravity pulls to an extent that even light cannot escape. The gravity is so powerful because matter is compressed into a little space. This may occur when a star dies.
How Big Are Black Holes?
- Black holes may be either big or small. According to scientists, the smallest black holes are as small as an atom. These are very small but have the mass (amount of content in an object) of a mountain.
- A different type of black hole is stellar whose mass can be upto 20 times greater than mass of the sun. There can be many stellar black holes in Earth’s galaxy which is known by the name Milky Way. The biggest black hole is known as ‘supermassive’, and their masses can be 1 million suns together. According to Scientists, every large galaxy includes a supermassive black hole in the center.
- This supermassive black hole which exists in the middle of the Milky Way galaxy is known as Sagittarius. Its mass is same as about 4 million suns.
Event Horizon:
- It is one of the most violent place in the universe, and a point of no return beyond which anything such as stars, planets, gas, dusts, all types of electromagnetic radiation including lights gets sucked into it.
- The point within the black hole which nothing can escape from is called its event horizon.
Event Horizon Telescope:
- It is an international collaboration that aims to capture images of black hole areas by linking up various radio dishes from around the world that together create a virtual telescope roughly the size of planet Earth. The project began capturing data in 2006.
- the Event Horizon Telescope project aims to generate enough magnifying power to bring
ARMY GETS FIRST BATCH OF DHANUSH, HOME-MADE BOFORS ARTILLERY GUNS, FROM OFB
09, Apr 2019
Why in news
- The Ordnance Factory Board (OFB) handed over the first batch of six Dhanush artillery guns to the Army.
Dhanush artillery guns: / Features:
- Dhanush is an upgraded version, based on the original design of the Swedish 155-mm Bofors howitzers, which India procured in the mid-1980s. It is a 155-mm, 45- calibre gun with a maximum range of 40 km in salvo mode, compared to the 39-calibre, 27-km range of the original guns.
- Bofors, which had played a crucial role in targeting pakisthan.
- The gun is fitted with inertial navigation system with global positioning system- (GPS) based gun recording and auto-laying, an enhanced tactical computer for onboard ballistic computations, an onboard muzzle velocity recording, an automated gun sighting system equipped with camera, thermal imaging and laser range finder.
- This is the first long-range artillery gun to be produced in India.
RAFALE: GOVT GAVE UNPRECEDENTED WAIVERS IN OFFSET AGREEMENTS
09, Apr 2019

Why in News?
The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) gave exceptional and unprecedented waivers to
- The twin-engine Rafale combat jet is designed from the beginning as a multi-role fighter for air-to-air and air-to-ground attack is nuclear-capable and its on-board Electronic Warfare (EW) systems can also perform reconnaissance and radar jamming roles.
- Officials say that due to national security reasons, there is a confidentiality clause in the Rafale deal which bars the buyer and seller from talking about the pricing, making it impossible for any government to reveal any detail about the defence deals.
What are offset agreements?
- Offsets are kind of a quid pro quo between countries and defence companies. Basically, since a government spends a large part of its budget buying equipment from these companies, it asks these companies to invest a portion of the deal amount in their countries. The clause allows for economic growth of the country in the process of completing the deal. While some offset clauses may ask for investments, others may impose terms like onboarding of local suppliers in the process.
Two key issues of offset waivers
- The waivers concerned two key issues — the provisions to be made in the offset contracts for arbitration (Article 9) and access to books of accounts of the industrial suppliers (Article 12).
0% offsets in first three years
- According to the offset schedule, the two private French companies will discharge 0% of the value of the total offsets for ‘Make in India’ in the first three years and 4% in the fourth year. No less than 57% of the value of total offset obligations will be discharged in the seventh year.
French reluctance to mention ‘offsets
- The INT report reveals that the French negotiators were initially “not ready to mention the word ‘offsets’ in the IGA” but upon insistence by the Indian side, they “relented and added ‘Make in India’ initiative through Offsets at Article 12 of the IGA”. It was only after extended discussions that the two industrial suppliers agreed to provide their offset offer “as per the format specified in DPP-2013”.
Subject to France’s blocking statute
- There is France’s controversial blocking statute which criminalises the communication of economic, commercial, industrial, financial, or technical documents or information to foreign individuals or foreign legal entities. The blocking statute remains in place and can be invoked if needed.
Offsets are made for controversy
- Although the practice is often criticised for being trade-distorting, non-transparent, and riddled with corruption and has been generally prohibited by the World Trade Organisation (with an exception made for protection of the essential interests of a country’s national security), offsets are increasingly in vogue in the defence sector.
FUNGUS IMMUNE TO DRUGS IS SECRETLY SWEEPING THE GLOBE
08, Apr 2019
Why is it in news?
- The rise of Candida auris indicates that bacteria, germs are growing resistance.
Details:
- The germ, a fungus called Candida auris, preys on people with weakened immune systems, and it is quietly spreading across the globe. Leading federal Centers for
- Disease Control and Prevention added it to a list of germs deemed “urgent threats.” C. auris is so tenacious, in part, because it is impervious to major antifungal medications, making it a new example of one of the world’s most intractable health threats: the rise of drug-resistant infections.
Antibiotic resistant infections:
- Antibiotic resistant infections are not controlled or killed by antibiotics. They are able to survive and even multiply in the presence of an antibiotic. Overuse of antibiotics was reducing the effectiveness of drugs that have lengthened life spans by curing bacterial infections once commonly fatal.
- But lately, there has been an explosion of resistant fungi as well, adding a new and frightening dimension to a phenomenon that is undermining a pillar of modern medicine. The World Alliance against Antibiotic Resistance (WAAAR) — a conglomerate of 600 individuals from 50 countries and 96 professional groups — is concerned by the increasing incidence of antibiotic resistance.
SOON FIRST PHOTO OF BLACK HOLE
07, Apr 2019
Why in News:
- Scientists are expected to unveil the first photo of a black hole. US national science foundation has scheduled a news conference to announce “ground breaking result from the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) project.
Details Black holes:
- A black hole is a region in space where gravity pulls to an extent that even light cannot escape. The gravity is so powerful because matter is compressed into a little space. This may occur when a star die.
How Big Are Black Holes?
- Black holes may be either big or small. According to scientists, the smallest black holes are as small as an atom. These are very small but have the mass (amount of content in an object) of a mountain.
- A different type of black hole is stellar whose mass can be upto 20 times greater than mass of the sun. There can be many stellar black holes in Earth’s galaxy which is known by the name Milky Way.
- The biggest black hole is known as ‘supermassive’, and their masses can be 1 million suns together. According to Scientists, every large galaxy includes a supermassive black hole in the center. This supermassive black hole which exists in the middle of the Milky Way galaxy is known as Sagittarius. Its mass is same as about 4 million suns.
Event horizon:
- It is one of the most violent places in the universe, and a point of no return beyond which anything such as stars, planets, gas, dusts, all types of electromagnetic radiation including lights gets sucked into it. The point within the black hole which nothing can escape from is called its event horizon.
Event Horizon Telescope
- It is an international collaboration that aims to capture images of black hole areas by linking up various radio dishes from around the world that together create a virtual telescope roughly the size of planet Earth. The project began capturing data in 2006.
- the Event Horizon Telescope project aims to generate enough magnifying power to bring black hole environments into focus, allowing for the study of their characteristics. Because black holes do not emit light, they cannot be seen and are technically invisible.
- The Event Horizon Telescope looks to study areas surrounding a black hole, namely the gas which radiates around it due to its intensely strong gravity pull, in an attempt to capture images of its general dynamics.
How Do Black Holes Form?
- Primordial black holes are considered to have formed in the early universe soon after the big bang. Stellar black holes were produced when the middle of a massive star collapsed by itself. This collapse also created a supernova or an exploding star that blasts part of the star in the space
Is There Any Danger to Earth from Black Hole?
- Black holes do not move around in space swallowing planets, moons and stars. Earth will not drop into a black hole because no black hole is near enough to the solar system.
- Even if black hole of similar mass as sun were taken to the place of sun, Earth would not fall in. The gravity of black hole would be the same as sun and Earth would revolve the black hole as it orbits the sun.
MODERATE DRINKING MAY NOT BE GOOD FOR HEALTH: STUDY
07, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- One or two drinks a day might protect against stroke are not true, according to the results of a major genetic study.
Details:
- Previous researches claim that consuming one to two alcoholic drinks may prevent stroke development. The new study refutes this statement in a large collaborative investigation.
- Scientists discovered that alcohol itself, regardless of amount, can directly spike up blood pressure, and subsequently cause stroke.
- East Asians have common genetic variants that are known to lower alcohol tolerability due to the unpleasant flushing reaction that occurs after drinking. Such can be used for the study of alcohol effects because this is not connected to other lifestyle choices such as smoking. The researchers concluded that alcohol amps up the risk of stroke by about 35 percent for every four additional drinks per day, without any protective mechanism noted.
- Western people do not have the same genetic variant found in the East Asians involved in the study, but the researchers think their work is applicable worldwide. This large collaborative study has shown that stroke rates are increased by alcohol.
METEORITE SHEDS LIGHT ON THE SUN’S INFANT YEARS
07, Apr 2019

Why is it in news?
- By analysing the piece of Efremovka meteorite, researchers have envisaged how the sun behaved in its infancy and further deduced super flares could have been million times stronger than solar flares.
What is a Meteorite?
- A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon.
Super flare:
- Superflares are very strong explosions observed on stars with energies up to ten thousand times that of typical solar flares.
Solar flare
- A solar flare is a sudden flash of increased brightness on the Sun, usually observed near its surface and in close proximity to a sunspot group.
Pristine meteorite:
- Efremovka is one of the most pristine meteorites in the collections.
- Hence, there is a much greater probability of finding preserved isotopic records from the time of formation of the solar system. The first suggestion of irradiation by the Sun as a source of elements found in
- early solar system solids came from a study of the beryllium-10 radio nuclide in the Allende meteorite.
- This work, on the other hand, studies both beryllium-7 decaying to lithium -7 and beryllium-10 decaying to boron-10. This short half-life of beryllium-7 helps rule out the two competing theories and indicates that it is only irradiation by solar flares that led to the formation of the elements captured by the Calcium aluminium rich inclusions (CAI).
GUIDELINES FOR DOCTORS ON BOUNDARIES WITH PATIENTS
07, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- Recognising patients as a particularly vulnerable group and understanding the need for specific guidelines on sexual boundaries for doctors, the Indian Psychiatry Society (IPS) along with the Bangalore Declaration Group (a team of doctors across various medical specialties in India) have come up with a set of guidelines, for the first time, to direct doctors on what is ethically right and wrong.
In Detail:
15-point guidelines:
- The ethical duty of all doctors is to ensure effective care for their patients. This would mean that their own conduct should in no way harm their patient.
- Sexual relationships between doctors and patients invariably harm both the patient and the doctor. Trust, which is central to an effective doctor-patient relationship, is inevitably damaged.
- In view of the power gradient that invariably exists in the doctor-patient relationship, the onus is on the doctor to ensure he or she does not enter into a romantic or sexual relationship with a patient.” The guidelines, which aim to be gender neutral and serve both doctors and patients of all genders, further state, “Doctors are reminded that even a relationship with a former patient is discouraged and could be construed as unethical, as the previous professional relationship can influence the current relationship.”
- Doctors should use social media responsibly, the guidelines add.
MCI:
- It stands for Medical council of India. MCI is statutory body established in order to maintain uniform and high standards of Medical Education in India. Medical council of India was established in 1993. The MCI Headquarters is in New Delhi (National capital territory). Presently, Medical Council of India leader and president is Jayshreeben Mehta.
- MCI makes sure that in order to practise in India, doctors must be registered under MCI. In order to protect and promote the health and safety of the public, Medical council of India ensures that
- proper standards are maintained during the practice of medicine. MCI keeps a check on the establishment of new medical colleges offering different MBBS/BDS degree and their recognition by giving them permission.
- MCI also approves the number of students getting admitted in a college and also renews their licenses.
US REACHES H-1B VISA CAP FOR 2020
07, Apr 2019
Why in News?
- The US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) said it has reached Congressionally- mandated 65,000 H-1B visa cap for the fiscal year 2020, after it started receiving the applications for the most sought-after work visa among foreign, including Indian, professionals.
Background:
What is H-1B VISA:
- A citizen of a foreign country who wishes to enter the United States must first obtain a visa, either a non-immigrant visa for temporary stay, or an immigrant visa for permanent residence.
- Temporary worker visas are for persons who want to enter the US for employment lasting
- a fixed period of time, and are not considered permanent or indefinite.
- The H-1B visa is a non-immigrant visa that allows the US companies to employ foreign workers in speciality occupations that require theoretical or technical expertise. The technology companies depend on it to hire tens of thousands of employees each year from countries like India and China.
Whom will it benefit?
- There is a higher probability that advanced (U.S. masters and higher) degree holders will be selected in larger numbers than regular H1B applicants.
- It is aimed at awarding this popular work visa to the most skilled and highest paid foreign workers. The changes could also potentially bring down the costs for sponsoring companies, by reducing the paperwork of sponsors.
- Only those H1B sponsoring employers who get selected from the list of registered petitioners will be required to actually submit H1B petitions.
- This applies for both regular and advance degree categories. What are the implications for India?
- This will have a significant impact on Indians, as 74% of H1B petitions were on behalf of India-born workers in the fiscal year 2018.
The Two major H-1B beneficiary groups are:
- Indian employees that work for the big IT majors in the US
- Indian students who obtain a US Master’s/Ph.D. degree and then apply for H-1B visas at US-based companies
- The proposed rules, if implemented, will dramatically tilt this competition in favour of the students. The new process could increase the number of H-1B holders who have advanced degrees by up to 16%.
- So, the IT majors will lose heavily to a tune of over 10,000 visas each year.
IIT BOMBAY’S BACTERIA PREFERENTIALLY DEGRADE AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
07, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- A unique strain of bacterium isolated from soil contaminated with petroleum products, can selectively remove from the environment toxic, aromatic pollutants such as benzoate, benzyl alcohol and naphthalene, to name a few. What makes the bacterial strain (Pseudomonas putida CSV86) unique is its preference for
- aromatic compounds and organic acid as a food source even when glucose is available. The strain can degrade aromatics and organic acids simultaneously.
Uses of bacterial strain:
- The bacterial strain is a very good candidate for bioremediation or waste-water treatment. We can increase the metabolic diversity and capacity by genetically engineering the strain.
DEATH FROM C-SECTIONS HIGH IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES
06, Apr 2019

Why is it in News?
- WHO has said deaths from C sections are high in developing countries, and its overuse and underuse are a global concern?
Details:
- Maternal deaths following caesarean sections in low and middle-income countries are 100 times higher than in high-income countries, according to a new review published in The Lancet, which has considered 196 studies from 67 low and middle-income countries.
- Study shows that data from 1990 to 2017 show that a quarter of all women died while giving birth in low and middle-income countries had undergone caesarean section.
- Every year, 3 lakh women die during childbirth, 99% of whom are from low and middle- income countries.
What is C-section?
- Caesarean section, also known as C-section, or caesarean delivery, is the use of surgery to deliver babies. A caesarean section is often necessary when a vaginal delivery would put the baby or mother at risk.
Maternal mortality rate:
- MMR is defined as the proportion of maternal deaths per 1,00,000 live births.
- The causes could be related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management. Complications during pregnancy and childbirth are a leading cause of death and disability among women of reproductive age.
MMR in India:
- In the 2011-13 period, India’s MMR was 167. As per the recently released data, the MMR during 2014-16 period stands at 130.
- Significant decline (246 to 188) was seen in the so called Empowered Action Group (EAG) states and Assam. EAG states are those states where economic and development indicators are a particular concern. Among the southern states, the decline has been from 93 to 77 and in the other states from 115 to 93.
- National rural health mission: – Janani Suraksh Yojna (JSY) is one of the main strategies or policy shifts under NRHM. It is a conditional cash transfer scheme to motivate pregnant women for institutional deliveries. In better developed states of South India, it is limited to women below poverty line up to first two childbirths.
- But notably, maternal mortality steeply rises in grand multiparous women, delivering a child after third pregnancy onward.
- Web-based Mother and Tracking System tracked every pregnancy in the country since 2010. It sends messages to health workers and expectant mothers about ante-natal checkups, vaccinations etc. For Ceasarean sections, there are First referral units (FRUs)
- FRU (First Referral Unit) is a district or sub-divisional hospital or community health centre which has the facilities in this regard. NRHM also allowed auxiliary nurse midwives (ANMs). The Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA) attended to women who were not going to hospitals for deliveries. Besides these, the Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram (JSSK) was implemented. It entitles all pregnant women delivering in public health institutions to free delivery, including C-sections. Other initiatives include the Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan launched in 2016 for engaging the private sector to voluntarily provide free antenatal services on the 9th day of every month to pregnant women.
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana under which a cash incentive of ₹5,000 is provided to encourage antenatal check-ups for pregnant women and lactating mothers.
Concerns:
Regional inequalities
- Maternal mortality varies significantly within and between States. Kerala’s MMR, for instance, was 46 in 2016 compared to Assam’s 237.
Training and monitoring
- The shortage of trained human resources, especially doctors and auxiliary nurse midwives, remains a key challenge to improving maternal health outcomes.
- Human resource compensation packages for personnel working in remote and rural areas need to be made more attractive. Currently, haemorrhage is the leading cause of maternal mortality in the country followed by sepsis and abortion. This points to the need for urgently exploring the possibility of a national blood transfusion service network considering that India has a blood supply deficit of 25 per cent as against the prescribed reserve of 1 per cent of the population, according to the World Health Organisation.
- Strengthening of surveillance and monitoring systems such as the Mother and Child Tracking System and the Health Management Information System as well as the promotion of vital registration is required. Hypertensive disorders are a more important cause in south India and abortion-related deaths are higher in the EAG States and Assam, thereby necessitating the design of customised policy interventions.
OUTER CLARITY: ON ‘WEAPONISATION’ OF OUTER SPACE
05, Apr 2019
Why in News:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successful launch of the PSLV-C45 rocket that placed 29 satellites in three different orbits appears that the Indian space programme stands galvanised and poised for a giant leap.
Details:
- In February 2017, the PSLV-C37 placed 104 satellites, 96 of them from the U.S shows
- ISRO’s ability to launch satellites at a fraction of the cost that other countries incur.
- In February 2017 launch also placed the fifth of the Cartosat 2 series in orbit, an earth observation satellite with cameras that have a resolution of less than a metre.
- The PSLV-C45 placed EMISAT, which can, among other things, aid in electronic intelligence. In other words, India is achieving a great place in space military architecture.
- Over the next few months, as many as eight satellites are expected to be launched, which aims to strengthen the defence dimension.
PSLV-C37 / CARTOSAT -2 Series Satellite:
- India’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle, in its thirty ninth flight (PSLV-C37), launches the 714 kg Cartosat-2 series satellite for earth observation and 103 co-passenger satellites together weighing about 663 kg at lift-off into a 505 km polar Sun Synchronous Orbit (SSO). PSLV- C37 was launched from the First Launch Pad (FLP) of Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR, Sriharikota. This was the sixteenth flight of PSLV in ‘XL’ configuration (with the use of solid strap-on motors).
- The co-passenger satellites comprised of 101 nanosatellites, one each from Kazakhstan, Israel, The Netherlands, Switzerland, United Arab Emirates (UAE) and 96 from United States of America (USA), as well as two Nano satellites from India. The total weight of all these satellites carried on-board PSLV-C37 was about 1377 kg.
- PSLV-C37 also carried two ISRO Nano satellites (INS-1A and INS-1B), as co-passenger satellites. These two satellites carry a total of four different payloads from Space Applications Centre (SAC) and Laboratory for Electro Optics Systems (LEOS) of ISRO for conducting various experiments.
- The 101 International customer Nano satellites were launched as part of the commercial arrangements between Antrix Corporation Limited (Antrix), a Government of India company under Department of Space (DOS), the commercial arm of ISRO and the International customers.
PSLV C45:
- The PSLV-C45 is the 47th mission of the Indian Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) program.
- The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV)-C45 was launched on 1 April 2019 with a payload of 29 satellites, including one for electronic intelligence, along with 28 customer satellites from other countries.
- It placed the primary satellite, EMISAT, a piece of surveillance equipment to be used by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), to the 748 km sun-synchronous polar orbit.
- It then made one complete revolution around Earth, over the poles, while lowering its orbit to 504 km height, after which it deposited the 28 international customer satellites — 24 from the US, two from Lithuania, and one each from Switzerland and Spain.
- It then made a further round of Earth while attaining an even lower orbit of 485 km, where the fourth stage of the rocket will continue for some time. This operation took a little over three hours.
Significance of the Achievement:
- Reaching three different orbits gives ISRO a new technological edge.
- It demonstrated its capability to reuse the fourth-stage engines multiple times, and also showed that the guidance and navigation systems aboard the launch vehicle could be used for much longer times than in earlier missions
- it will help ISRO pack its future rockets with multiple satellites even if they require to be placed in very diverse but precise orbits. Currently, this could be done only in multiple missions.
Significance of Using the Fourth Stage as a Satellite:
- The rocket, or the launch vehicle, is only a carrier. Once it places its passenger, or satellite, to its designated orbit in space, it becomes practically useless, adding to the space debris.
- For the last few years, ISRO had been planning to give some life to the rocket — at least to the uppermost part, or the last stage — which remains with the satellite till the ejection.
- The lower parts of the rocket are in any case discarded in the earlier stages and become junk. There is no way to put them to any use.
- The uppermost stage, however, can be used, at least temporarily. Previously, they would end up in some orbit to wander aimlessly and endlessly.
What purpose will it serve?
- The fourth stage is carrying three kinds of equipment to carry out some measurements and experiments, and a solar panel to provide power to these equipment’s and enable communication with ground stations.
- One kind of instrument can be used to capture messages transmitted from ships, another can be used by amateur radio operators use for tracking and monitoring position data, and the third can study the structure and composition of the Ionosphere.
Way forward:
- The government should articulate much more clearly the doctrinal aspects of the space programme.
- India must communicate its peaceful intentions so as to contribute to a better understanding among countries and to reduce the chances of wrong inferences being drawn in crisis situations.
- New Delhi must take a bigger lead in forging a global and legally binding instrument to prevent militarisation of space
BALAKOT ATTACK
05, Apr 2019

Context:
- Twelve days after the Pulwama attack, the Indian Air Force bombed the Jaish-e- Mohammad’s “biggest” terror training camp in Pakistan’s Balakot early.
- The operation was carried out by 12 Mirage-2000 fighter jets, which unleashed five one- tonne bombs on the camp, based 70 km inside the Line of Control (LoC), in the Pakistani province of Khyber Pakthunkhwa.
Details of the attack:
- Senior officials citing intelligence inputs said the JeM facility was particularly crowded with 200-325 militants as many had abandoned launch pads and training camps closer to the LoC after the Pulwama attack in the expectation that India would not target Balakot.
- The aerial attack on a target inside Pakistani territory
- marks a major shift in India’s counter-terror responses,
- which have thus far been restricted to ground operations across the LoC in Pakistan- occupied Kashmir.
- Announcing the strikes, the government said it was a “non-military, pre-emptive” counter- terror operation against imminent threats from the JeM.
Pm-kisan (PM Kisan nidhi Yojana)
- PM-KISAN is aimed at boosting rural consumption and helping poor farmers recover from distress. PM Kisan nidhi Yojana is for small and marginal farmers for helping in financial condition for purchase of seed, fertilizers etc.
- PM Narender Modi inaugurated the scheme on 24 Feb 2019 under which Modi Ji transferred first installment money of Rs 2000 to few farmers directly via wire to their respective bank accounts.
- Total of Rs 6000 amount is to be distributed to farmer in 3 session. The government of India under the leader ship of PM Modi announced about this scheme in Budget 2019-20.
NYAY (Nyuntam Aay Yojana (NYAY) scheme):
- The Nyay scheme is targeted towards 5 crore families who are the poorest 20 per cent in India. Nyay scheme guarantees each family a cash transfer of R s. 72,000 a year and as far as possible the money will be transferred to a bank account of a woman in the family.
- There will a design phase (3 months) followed by pilot and testing phases (6-9 months) before the rollout of the plan. The scheme will be implemented in phases and the estimated cost will be less than 1 per cent of the GDP in the first year, and less than 2 per cent of the GDP in the second year.
- The Nyay scheme would be a joint scheme of the central and state governments.
- Nyay scheme will be funded through new revenues and rationalisation of expenditure. Current merit subsidy schemes that are intended to achieve specific objectives will be continued.
ORAL VACCINES FOR STRAY DOGS CAN HELP RABIES
05, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- Vaccines hidden in food for stray dogs could help curb the spread of rabies more effectively than injections, says UN scientists. Oral vaccination approach could help them reach the minimum 70% vaccine threshold needed to minimise the risk of rabies being passed on to people.
Background:
- With the recent increase in popularity among Indians of full breed dogs, more and more street dogs are abandoned pets or have bred with pet breeds.
- Although they are widely feared because some carry rabies, for the most part India’s street dogs are not aggressive and will only bite if provoked. Indeed, many are fearful of humans and sadly, the dogs’ fears are well founded.
- India’s street dog population is closely associated with municipal sanitation practices. Because these homeless dogs often survive by scavenging rubbish, exposed garbage means more healthy dogs – and more puppies.
- Ironically, this actually makes the dogs a boon to public sanitation. By scavenging garbage, they reduce perishable waste that could otherwise be a source of contamination for people. And their presence around garbage keeps away other potentially dangerous scavengers, such as rats and mice.
Why does India have a stray dog problem?
- A common characteristic of India’s cities encourages stray dog populations -open garbage. Stray dogs are scavengers, so they rely on garbage on the street as a source of food. India has fewer government and NGO services that deal with stray dogs.
- India has fewer large-scale interventions and organizations to deal with stray dogs. Organizations like People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals argue that one of the main causes of dog attacks is stray dog migration and breeding.
- Because of the number of dog attacks reported in the media, people often see strays as dangerous animals that should be killed. Prevalence of an incomplete and flawed understanding of street dogs, their interactions with people, and the risks that may emerge from these interactions. it is logistically and operationally challenging to sterilise 50 million dogs. Unsterilized dogs will always “spill over” into areas where sterilisation has been done. Infrastructure needed for such large-scale surgical interventions do not exist. India has never framed a rational, scientifically valid, and widely implementable dog ownership or population control strategy.
Rabies:
- Rabies is a zoonotic disease (a disease that is transmitted from animals to humans), caused by the rabies virus, of the Lyssavirus genus, within the family Rhabdoviridae.
- It is a viral disease that causes inflammation of the brain in humans and other mammals. Symptoms include fever, headache, excess salivation, muscle spasms, paralysis and mental confusion
What is Mission Rabies?
- Mission Rabies is a charity which was founded as a project of Worldwide Veterinary Service in 2013 with one aim, eliminate dog bite transmitted rabies through a research driven One Health approach. Since 2015, Mission Rabies is a charity in its own right.
How does Rabies spread through stray dogs? What should be done in the future?
- There are better ways to deal with India’s rabies epidemic than mass killings of stray dogs:
- many animal welfare organizations believe that the spay-and-neuter model — where both male and female dogs are taken from the street, sterilized, vaccinated, and returned to their original area.
- Since sterilized dogs are returned to their original area, dogs will not migrate to and fight over that territory.
- Sterilized females cannot breed, which decreases their aggressiveness.
- Organizations push for increased adoption, which is far less popular in India than in parts of the United States.
- Greece’s collective adoption, where communities and the Greek government collectively care for and treat local dogs.
- A key part of government’s work will be changing the public’s idea of stray dogs in India. promoting the adoption of stray dogs and ensuring that people do not support mass killings. National campaigns by the government can help create this systemic change in the public’s mindset.
- Thus, a multi-pronged approach that addresses these multiple factors is required, and not one that focuses narrowly on managing dog populations.
- effective public health programme to tackle dog bites and rabies will have to include:
- proper waste management underpinned by appropriate infrastructure
- public education and behaviour change with regard to live safely with free-living dogs and what to do when bitten
- systematic and carefully-designed neutering and vaccination programmes.
- Adequate facilities for post-exposure prophylaxis and treatment
- We need to call for holistic town planning. We have to plan for dog walking paths
SOUTH KOREA FIRST TO ROLL OUT 5G SERVICES, BEATING US AND CHINA
04, Apr 2019
Why in News:
- South Korea will become the first country to commercially launch fifth-generation (5G) services as it rolls out the latest wireless technology with Samsung Electronics.
5G Mobile Networks:
- 5G mobile networks, the next-generation standard for wireless communications are set to start taking over the mobile network environment in 2019.
- 5G delivers vastly increased capacity, lower latency, and faster speeds.
- 5G networks will operate in a high-frequency band of the wireless spectrum, between 28 GHz and 60 GHz. This range is known as the millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum. The sub-6 GHz range that LTE calls home will also be used. 5G is expected to add unlicensed frequencies such as the 3.5 GHz to its list of new frequencies for mobile use. This means a lot of bandwidth will be available to users.
- In addition to greater bandwidth, the new 5G networks will have a dense, distributed network of base stations in the small cell infrastructure. This will allow more processing to happen on the edge, leading to lower latencies.
- Smaller Cells for 5G Networks: Smaller cells are used for 5G networks as they provide the increased data capacity that 5G demands.
- They help providers reduce costs by eliminating expensive rooftop systems and installation costs.
- Users can expect improved performance and battery life of mobile handsets since less power is required to transmit data to something nearby.
- Small cells will also be important to the workability of 5G in the millimeter wave spectrum. At these mmWave frequencies, signals have trouble getting through walls.
5G Network Cooperation:
- A premier challenge of 5G network design has been to create a network architecture capable of supporting this kind of flexibility while meeting the multifaceted access demands of an Internet of Things (IoT) future.
- The new 5G networks will also need to incorporate seamless coexistence of LTE and 5G standards. This is mostly embodied in the spectrum sharing of frequencies used by both standards.
AIR POLLUTION SHORTENED LIFESPAN BY 30 MONTHS
04, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- The current high-level air pollution has shortened the average lifespan of a South Asian child by 20 months. Air pollution contributed to over 1.2 million deaths in India in 2017.
Details:
- State of Global Air 2019 published by Health Effect Institute said exposure to air pollution contributed to 1.2 million deaths in India.
- It also said that air pollution was responsible for more risk factors than malnutrition, alcohol abuse, and physical inactivity.
- In India air pollution the third highest cause of death among all healthy risks, ranking just above smoking, road traffic injuries, malaria.
- India and china are responsible for half of the total deaths from air pollution.
Initiatives taken by India:
- India had taken major steps to address pollution sources such as Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana Household LPG Programme, accelerated Bharat Stage VI clean vehicle standards and National Clean Air Programme.
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY): Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) aims to safeguard the health of women & children by providing them with a clean cooking fuel – LPG, so that they don’t have to compromise their health in smoky kitchens or wander in unsafe areas collecting firewood.
- Under this scheme, LPG connections will be provided to BPL families with a support of Rs.1600 per connection. The connection is provided in the name of the adult women of the family. Further, an option is provided to provide a loan at zero interest to bear the cost of the cooking stove and first refill which has to be paid by the beneficiary.
- The beneficiaries under the scheme were identified through socio economic caste census, now all the poor of the country are now eligible to get PMUY connection.
Bharat Stage (BS) VI:
- The Union Government in October 2016 had decided to skip one stage and migrate to BS- VI directly from BS-IV from April 2020 to fight the growing pollution.
- It was part of concerted efforts of Government to reduce vehicular emissions and improve fuel efficiency with an aim to reduce carbon footprints and keep environment healthy.
Benefits of Bharat Stage (BS) VI:
- The major difference in standards between the existing BS-IV and new BS-VI auto fuel norms is presence of sulphur. BS-IV fuels contain 50 parts per million (ppm) sulphur, while BS-V and BS-VI grade fuel will have 10 ppm sulphur. Thus, newly introduced BS VI fuel is estimated to reduce amount of sulphur released by 80%.
- It will also bring down the emission of NOx (nitrogen oxides) from diesel cars by nearly 70
- % and 25% from cars with petrol engines. It will also bring down cancer causing particulate matter emissions from diesel engine cars by 80%.
National Clean Air Programme (NCAP)
- The National Clean Air Programme is a mid-term, five-year action plan that includes collaborative, multi-scale and cross-sectoral coordination between relevant Central ministries, state governments and local bodies.
Objective:
- It is comprehensive mitigation actions for prevention, control and abatement of air pollution besides augmenting the air quality monitoring network across the country and strengthening the awareness and capacity building activities.
- Key features and highlights of the programme:
- The overall objective of the programme includes comprehensive mitigation actions for prevention, control and abatement of air pollution besides augmenting the air quality monitoring network across the country and strengthening the awareness and capacity building activities
- The Environment Ministry has announced a budget of Rs 300 crore for two years to tackle air pollution across 102 cities, which have been identified by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) for not meeting the pollution standards set by the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change.
- Also, city-specific action plans are being formulated for 102 non-attainment cities identified for implementing mitigation actions under NCAP.
- The Smart Cities programme will be used to launch the NCAP in the 43 smart cities falling in the list of the 102 non-attainment cities.
- The programme will be institutionalized by respective ministries and will be organized through inter-sectoral groups, which include, Ministry of Road Transport and Highway, Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Ministry of Heavy Industry, Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Ministry of Agriculture, Ministry of Health, NITI Aayog, CPCB, experts from the industry, academia, and civil society.
- Other features of NCAP include the increasing number of monitoring stations in the country including rural monitoring stations, technology support, emphasis on awareness and capacity building initiatives, setting up of certification agencies for monitoring equipment, source apportionment studies, emphasis on enforcement, and specific sectoral interventions.
DARK MATTER NOT MADE UP OF TINY BLACK HOLES
04, Apr 2019
Why in News?
- Dark matter is not made up of primordial black holes smaller than a tenth of a millimetre, say scientists who have put the theory put forward by the late Stephen hawking to its most rigorous test to date.
Dark matter:
- Dark matter is the hypothetical matter existing in space whose properties are unclear to scientists. The term ‘dark’ is used to mention the unknown. It only interacts by way of gravity and the weak atomic
- force. It does not interact through either the strong atomic force or electromagnetism, therefore, it cannot be seen and is hard to notice.
Background:
- Black holes are objects so dense that not even light can escape their gravity, and since nothing can travel faster than light, nothing can escape from inside a black hole. On the other hand, a black hole exerts the same force on something far away from it as any other object of the same mass would. For example, if our Sun was magically crushed until it was about 1 mile in size, it would become a black hole, but the Earth would remain in its same orbit.
Formation of black hole:
- After the death of star, it changes into one of these three forms according to its solar mass. White dwarf: stars below 1.4 solar mass lose their outer layer and their core cools down to form white dwarf. Later it changes into yellow dwarf and then to red dwarf. Finally, it becomes invisible by forming black dwarf which neither emits electric fields nor heat energy. Neutron star: the core of the star finishes up as Neutron start if the mass is greater than 1.4 but less than 5 solar mass
- Black hole: if the original mad of the star is greater than 5 solar mass the core does into black hole which is exactly not a hole but a curvature caused due to a high-density object.
Could a Black Hole Destroy Earth?
- Black holes do not go around in space eating stars, moons and planets. Earth will not fall into a black hole because no black hole is close enough to the solar system for Earth to do that.
- Even if a black hole the same mass as the sun were to take the place of the sun, Earth still would not fall in. The black hole would have the same gravity as the sun. Earth and the other planets would orbit the black hole as they orbit the sun now. The sun
- will never turn into a black hole. The sun is not a big enough star to make a black hole.
ENZYME TO CURB BACTERIA CELL GROWTH
03, Apr 2019
Why in News:
- Scientists at the Centre for Cellular & Molecular Biology (CCMB) have discovered a new enzyme which helps in breaking cell walls of bacteria and offers a potential for a new drug delivery route to arrest the anti-bacterial resistance through existing antibiotic drugs.
Details:
- Scientists all over the world are working on how e. coli bacteria cells function, divide and grow to cause diseases like cholera, leprosy, tuberculosis. Other bacteria too have the same enzyme working on cell division as the cell wall is fundamental for bacterial growth and division.
- By blocking the ‘scissors enzyme’ from functioning leads a new way to target microbes, leading to a new wave of antibiotic drugs.
Classical antibiotic drugs:
- It targets the last stage of cell synthesis to prevent cell growth like penicillin that hits the machinery that creates the cell wall — a mesh-like structure of cross-linked sugars and peptides.
Antibody:
- An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein produced mainly by plasma cells that is used by the immune system to neutralize pathogens such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
- The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen via the fragment antigen-binding (Fab) variable region.
Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCBR)
- The Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology or CCMB is an Indian biotechnology research establishment located in Hyderabad. It operates under the aegis of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- CCMB is a designated as ” Center of Excellence” by the Global Molecular and Cell Biology Network, UNESCO.
- The Centre for Cellular & Molecular Biology (CCMB) is a premier research organization in frontier areas of modern biology.
- The objectives of the Centre are to conduct high quality basic research and training in frontier areas of modern biology, and to promote centralized national facilities for new and modern techniques in the inter-disciplinary areas of biology.
POLL PANEL STEPS INTO ALLOW LAUNCH OF BOOK ON RAFALE DEAL
03, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- An election flying squad in Chennai banned the release of a book on the Rafale fighter aircraft scam, the publishing house managed to launch the book by obtaining the nod from the Election Commission of India.
Details:
- The book Nattai Ulukkum Rafale Bera Oozhal social activist S. Vijayan.
- The election flying squad told that the sale of the book could not be permitted under the model code of conduct.
Background:
India has a peculiar defence scenario as the country has one of the largest defence infrastructures and at the same time is one of the largest defence importers in the world.
To overcome the various hurdles of defence sector development and inorder to overcome import dependence, government introduced several measures including defence FDI and promotion of private sector participation.
A major policy is the defence offset policy which has become a chief instrument for India to develop its indigenous defence manufacturing sector. Defence offset means “a supplier places work to an agreed value with firms in the buying country, over and above what it would have brought in the absence of the offset.” Hence under defence offset, a foreign supplier of equipment agrees to manufacture a given percent of his product (in terms of value) in the buying country. This may take place with Technology Transfer.
Introduction:
ABOUT RAFALE FIGHTER AIRCRAFT:
India in September 2016 inked a direct deal with the French government to purchase 36 new Rafale fighter jets.
Rafale is a twin-engine medium multi-role combat aircraft, manufactured by French company Dassault Aviation. Dassault claims Rafale has ‘Omnirole’ capability to perform several actions at the same time, such as firing air-to-air missiles at a very low altitude, air- to-ground, and interceptions during the same sortie.
The aircraft is fitted with an On-board oxygen generation system (OBOGS) which suppresses the need for liquid oxygen re-filling or ground support for oxygen production.
It carry out a wide range of missions: Air-defence/air-superiority, Reconnaissance, close air support dynamic targeting, Air-to-ground precision strike/interdiction, anti-ship attacks, nuclear deterrence, buddy-buddy refuelling.
Rafale provides standoff capability when any country attacks India. An active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar which enables the pilot to look 200 to 400 kms away. It gives long range precision strike capability; the pilot can detect enemy aircraft and share the information and also destroy the targets.
The 4th generation Aircraft capabilities involve Situational awareness in which Aircraft has got those sensors which enable the pilot to be aware situationally and detect the enemy Aircraft for which the Rafale has AESA radar.
The weapons package includes Meteor radar guided Beyond Visual Range (BVR) missile considered the best in the class with range of over 150 km and Scalp long range air to ground missiles. The Rafale Aircraft will give India a superior Nuclear Strike capability and add to the existing nuclear strike capability of Sukhoi Su-30 and Mirage-2000.
CONTROVERSIES OF RAFALE:
Under the current agreement, the 36 Rafale procurement offset proposal supports the
‘Make in India’ initiative of the Indian Government through Article 12 of the Inter-
MISSION SHAKTI
03, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- NASA criticised India for the test, describing that it had endangered International Space Station.
Mission shakti:
- There are a large number of satellites currently in space, many of which have outlived their utility and orbiting aimlessly.
- The missile was launched from the Dr A P J Abdul Kalam island, struck a predetermined target which was a redundant Indian satellite that was orbiting at a distance of 300 km from the Earth’s surface.
NASA:
- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency of the United States Federal Government responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. It was established in 1958.
- Most US space exploration efforts have been led by NASA, including the Apollo space missions, the Space shuttle, etc.
International space station:
- The International Space Station (ISS) is a space station, or a habitable artificial satellite, in low earth orbit from 320 km (199 mi) to 400 km (249 mi) above the Earth’s surface.
- Its first component was launched into orbit in 1998, with the first long-term residents arriving in November 2000 and has been inhabited continuously since that date. The ISS is the largest human-made body in low Earth orbit and can often be seen with the naked eye from Earth. The ISS programme is a joint project between five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe) and CSA(Canada). The ISS serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which crew members conduct experiments in biology, human physiology, physics, astronomy and other fields.
Apogee and perigee:
- Apogee and perigee refer to the distance from the Earth to the moon. Apogee is the farthest point from the earth. Perigee is the closest point to the earth and it is in this stage that the moon appears larger.
Low earth orbit:
- The low earth orbit extends from 160km above Earth and ends at 2000km. More than 800 satellites are currently in orbit in the Low-Earth region. The most popular of these is the International Space Station and the Iridium network of communication satellites.
Problem of space debris:
- Anything launched into the space remains in space, unless it is specifically brought down or slowly disintegrates over decades or centuries.
- A satellite that is destroyed by a missile disintegrates into small pieces, and adds to the space debris. Satellites that are past their life and are no longer required also remain in space, orbiting aimlessly in some orbit. These included active and inactive satellites, rockets and their parts, and other small fragments. According to the NASA, there were 19,137 man-made objects in space that were large enough to be tracked. The threat from the space debris is that it could collide with the operational satellites and render them dysfunctional.
GLOBAL HEALTH AWARD
03, Apr 2019

Why in news:
- Vikram Patel, a psychiatrist and professor of global health at Harvard Medical School has won the prestigious John Dirks Canada Gairdner Global Health Award for the prevention and treatment of mental health problems in India with global impact.
Background:
- Mr. Patel has led research generating knowledge on the burden and determinants of mental health problems in low and middle-income countries and pioneered approaches which utilise community resources for the prevention and treatment of mental health problems in India with global impact, a press release said.
- Laureates receive a $100,000 cash honorarium and will be formally presented with their awards on October 24, 2019 at the annual Canada Gairdner Awards Gala in Toronto.
Global Health Award
- The John Dirks Canada Gairdner Global Health Award recognizes the world’s top scientists who have made outstanding achievements in Global Health Research. Since its inception eight years ago, the Global Health Award has grown significantly to become one of the world’s most prestigious awards recognizing excellence in global health research.
- Nominees should be individuals who have made major scientific advances with a significant impact on health outcomes in the developing world. The award is science-focused, and is not intended for those with primarily leadership and administrative accomplishments.
- Gairdner invites the scientific community to nominate qualified scientists from any branch of global health. The evaluation of the contributions of the nominees depends heavily on the quality of information supplied. Therefore, nominations should be accurate, detailed,
- current, complete, and with supporting letters reflecting the nominee’s accomplishments.
ISRO TO LAUNCH A STRING OF DEFENCE SATELLITES
03, Apr 2019
Why in News:
- The ISRO plans to send up atleast eight earth observatory satellites of varied hues and at the rate of almost a month between now and early 2020.
Background:
- Recently ISRO launched EMISAT, the country’s first electronic surveillance satellite. communication satellite GSAT-32 is also in the offing next year to replace GSAT-6A, which was lost in a failed launch.
Recently launched satellite for defence:
EMISAT:
- EMISAT was built by the Defence Research Development Organisation (DRDO).
- It will gather information on enemy radar positions from a sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of about 750km. EMISAT will achieve this through electromagnetic spectrum measurement. So, the spacecraft
- carries a payload of DRDO’s prestigious Kautilya system for electromagnetic intelligence (ELINT) gathering. Space-based electronic intelligence (ELINT) will add to the situational awareness of the Armed Forces. This will provide location and information of hostile radars placed at the borders.
- This will be another dimension to the current land or aircraft-based ELINT.
GSAT:
- The GSAT satellites are indigenously developed communication satellite, used for digital audio, data and video broadcasting. As of 5 December 2018, 20 GSAT satellites of ISRO have been launched out of which 14 satellites are currently in service.
CARTOSAT:
- The Cartosat series of satellites are a earth observation satellites, indigenously built by India. The Cartosat series is a part of India remote sensing programme. They were specifically launched for Earth’s resource management and monitoring.
RISAT:
- The RISAT series are the first all-weather earth observation satellites from ISRO. They provide all-weather surveillance using synthetic aperture radars (SAR).
INDIA LAUNCHES EMISAT INTELLIGENCE-GATHERING SATELLITE
02, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) launched the country’s first electronic surveillance satellite, EMISAT along with 28 small third party satellites from Sriharikota in coastal Andhra Pradesh.
EMISAT:
- The primary payload, EMISAT, is a 436-kilogram (961-pound) satellite to be operated by India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)
- EMISAT is based around the Indian Mini Satellite 2 (IMS-2) bus with solar panels providing 800 watts of power for the spacecraft.
- Its mission is officially stated as “electromagnetic spectrum measurement”.
- It is understood that EMISAT will be used for Electronic Signals Intelligence (ELINT).
- The satellite likely carries Kautilya, an ELINT package that India has been developing since at least 2014.
- EMISAT will operate in a circular sun-synchronous polar orbit, at an altitude of 749 kilometres (465 miles, 404 nautical miles) and an inclination of 98.4 degrees.
- Along with EMISAT twenty-eight smaller satellites were also put into space as secondary riders. These have all been built to CubeSat specifications.
CUBESAT:
- The CubeSat standard has become ubiquitous for small satellites and has played a significant role in their increased popularity in recent years. A single-unit CubeSat has a cubic shape with sides of ten centimetres (3.9 inches) – with larger satellites’ sizes based around multiples of this unit: for example, three-unit CubeSat measures ten centimetres along two axes and 30 centimetres (11.8 inches) along the third.
SPACE FOR CAMPAIGN
02, Apr 2019
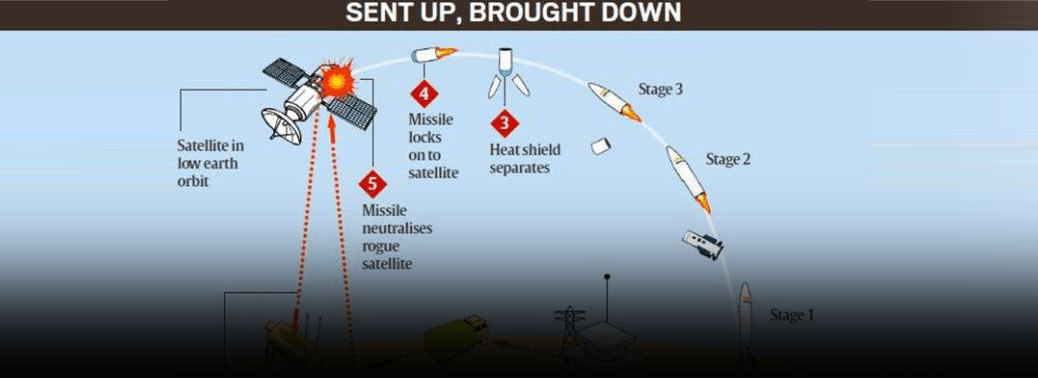
Why in News:
- Election commission announced that Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s address to the nation on the successful test-firing of an anti-satellite missile test (ASAT) did not violate the Model Code of Conduct (MCC).
Details:
- The EC took the decision based on the report of a 5-member committee of officers which found that the prime minister did not violate the provision of Part VII of the code covering the ‘party in power’ in the poll code. Part VII of the Code covering the “party in power” says that “the misuse of official mass media during the election period for the coverage of political news and publicity regarding achievements shall be scrupulously avoided”. The committee has concluded that there was no misuse of official mass media
Background:
What is Anti-Satellite Missile (ASAT)?
- They are missile-based systems to attack moving satellites. So far the United States, China and Russia were the only ones who’ve reported the ability to shoot down space objects from ground or airborne sources.
- The development of such systems was at the Cold War between the United States and the former Soviet Union
Why was the test done now?
- The test was done to verify that India has the capability to safeguard our space assets. It is the Government of India’s responsibility to defend the country’s interests in outer space.
- The tests were done after India acquired the required degree of confidence to ensure its success, and reflects the intention of the government to enhance India’s national security.
Steps taken by India to conduct the test:
- It is mandatory for any missile test, India did issue a Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) to airline authorities across the world informing them about an impending missile test. This notice does not have to specify the kind of missile being tested, only the flight path and the region affected are specified. NOTAM: It is a notice filed with an aviation authority to alert aircraft pilots of potential hazards along a flight route or at a location that could affect the safety of the flight
What is Mission Shakthi:
- Mission Shakti is a joint programme of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- India is only the 4th country to acquire such a specialised and modern capability, and Entire effort is indigenous. Till now, only the US, Russia and China had the capability to hit a live target in space. The test was carried out from the Dr A.P.J Abdul Kalam Island launch complex off the coast of Odisha by the DRDO. Since the test was done in the lower atmosphere, whatever debris that is generated will decay and fall back onto the earth within weeks. Mission Shakti does not violate the 1967 Outer Space Treaty of which India is a signatory. The treaty prohibits only weapons of mass destruction in outer space, not ordinary weapons.
Advantages:
- The ASAT test test was not directed against any country. India’s space capabilities neither
- threaten any country nor are they directed against anyone.
- The anti-satellite missile test provides deterrence against threats to our growing space- based assets from long-range missiles and proliferation in the types and numbers of missiles.
CORONARY STENTS
02, Apr 2019
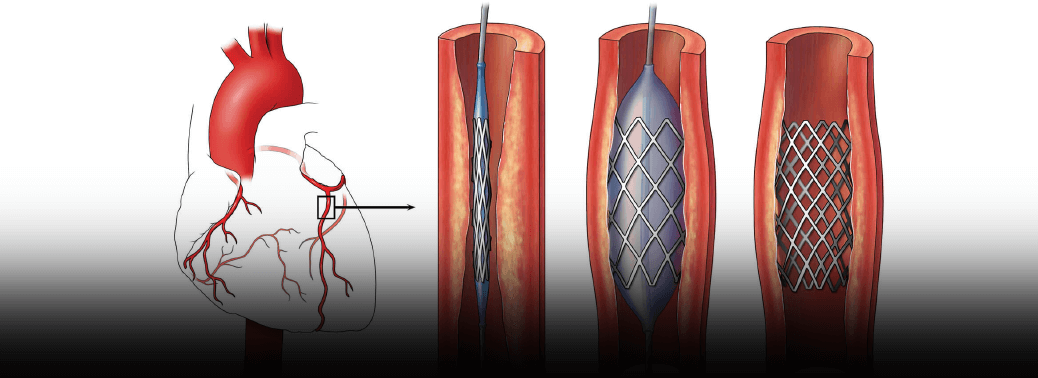
Why in News:
- National Pharmaceutical pricing authority has approved a hike in the price of coronary stents.
What is a stent?
- A stent is a tiny expandable metal scaffold inserted in the narrowed or weak arteries. The process of placing a stent in the artery is called angioplasty. A coronary artery stent is a small, metal mesh tube that expands inside a coronary artery. A stent is often placed during or immediately after angioplasty. It helps prevent the artery from closing up again.
Drug eluting stent:
- A drug-eluting stent has medicine embedded in it that helps prevent the artery from closing in the long term. It is often preferred over bare-metal stents because the latter carry a higher risk of restenosis, the growth of tissue into the stent resulting in vessel narrowing.
Bare Metal stent:
- Bare-metal stent is a stent without a coating or covering often made of stainless steel. More
- recent stents (‘2nd generation’) use cobalt chromium alloy.
- National pharmaceutical pricing authority:
- NPPA is an independent body under Department of Pharmaceuticals under the Union Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
Functions of NPPA:
- Fix/revise the controlled bulk drugs prices and formulations, enforce prices and availability of the medicines under the Drugs (Prices Control) Order, 1995/2013,
- recover amounts overcharged by manufacturers for the controlled drugs from the consumers
- monitor the prices of decontrolled drugs in order to keep them at reasonable levels. NPPA fixes ceiling price of essential medicines that are listed in Schedule I of DPCO, 2013 Medicines that are not under price control, manufacturers are allowed to increase the maximum retail price by 10% annually.
U.S MODIFIES ZIKA ADVISORY
02, Apr 2019
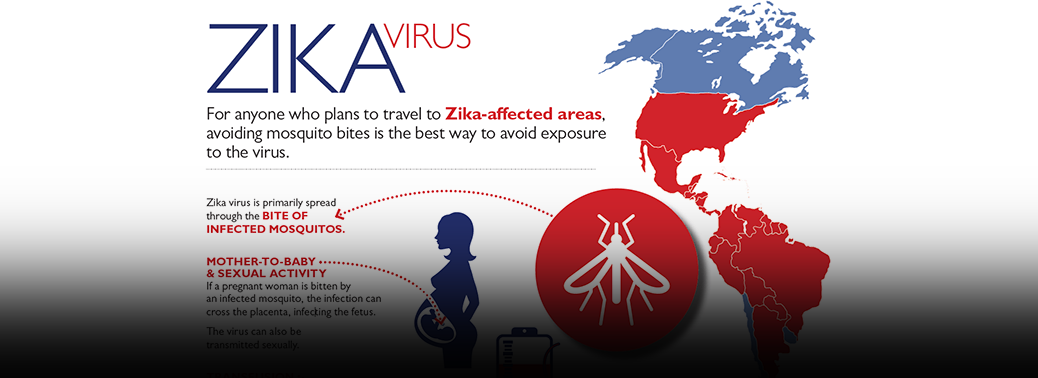
Why in news?
The US modified its Zika virus alert for travellers to India, changing the status from ‘ongoing outbreak’ to ‘current or past transmission but no current outbreak’ after the health ministry intervened.
Background:
India has asked the United States’ public health agency, the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, to “withdraw or modify” an advisory it issued on December 13 warning people against travelling to Rajasthan due to an outbreak of the Zika virus. The government took exception to the use of “endemic” in the advisory as Zika outbreaks in India have been contained within small areas.
CDC Report:
- The CDC had said the virus was endemic to India and pointed out “there is an unusual increase in the number of Zika cases in Rajasthan and surrounding states”.
- It cautioned pregnant women against travelling to such areas. This is because Zika infection during pregnancy can cause serious birth defects. The health agency classified its alert under Level 2, which requires “enhanced
- protection”. Level 1 advises “usual precautions” and Level 3 advises against “non-essential travel”.
What is CDC:
- The Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) serves as the national focus for developing and applying disease prevention and control, environmental health, and health promotion and health education activities designed to improve the health of the people of the United States.
How does the outbreak evolve?
- Zika virus was first identified in Uganda in 1947 and the outbreaks of Zika virus have been recorded in Africa, the Americas, Asia and the Pacific. The disease has been reported from across 86 countries.
- The carrier of this virus is the same day-biting Aedes aegypti mosquito that spreads dengue, chikungunya, and other vector-transmitted diseases and is present in hordes in most parts of the country.
- There is no available drug or vaccine against Zika, while the treatment is mainly supportive.
What should be done?
- Control – In the absence of any vaccine or specific drugs to cure zika, protection from mosquito bite and mosquito control are the only ways to combat this menace.
- This requires breaking the breeding cycle of the mosquitoes by destroying their eggs and larvae rather than just killing the adult mosquitoes as is usually done through fogging.
- revention – A nationwide mosquito control programme of the kind that had, in the past, helped in nearly eradicating malaria is needed once again.
- The option of using the highly effective pesticide DDT is no longer available on account of an ill-advised ban on it.
- Hence, alternate measures such as larvae-eating fish and mosquito predators would need to be deployed to check mosquito multiplication.
National vector disease control programme:
- The National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP) is a comprehensive programme for prevention and control of vector borne diseases namely Malaria, Filaria, Kala-azar, Japanese Encephalitis (JE), Dengue, Zika and Chikungunya which is covered under the overall umbrella of NRHM.
- Directorate of National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP) is the central nodal agency for the prevention and control of vector borne diseases.
Implementation
- The National Vector-Borne Diseases Control Programme has not been implemented properly and it is resurrected only during disease epidemics.
- If it is implemented on a regular basis on the lines of the polio control programme, it can help avert zika and also scourges such as malaria and Japanese encephalitis.
- However, Aedes mosquitoes breed even in small collections of fresh water in and around homes, schools and work sites. Hence door-to-door surveys to monitor the presence of larvae and suitable action against the defaulters are absolutely essential. The government should realise that the gains from spending resources on taming disease-dispensing vectors would far outweigh the cost of dealing with recurrent disease outbreaks and take measures accordingly.
GENERIC DRUGS
01, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- A petition has been filed to ensure that doctors prescribe generic medicines.
Why generic drugs:
- A generic drug is a pharmaceutical drug that is equivalent to a brand-name product in dosage, strength, route of administration, quality, performance, and intended use.
- The Medical Council of India (MCI), in an amendment to the Code of Conduct for doctors, has recommended that every physician “should prescribe drugs with generic names legibly, and shall ensure that there is a rational prescription and use of drug.
Pradhan Mantri Bharatya Janaushadhi Pariyojana:
- Pradhan Mantri Bharatya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP) is a campaign launched by the Department of Pharmaceuticals, to provide quality medicines at affordable prices to the masses.
- PMBJP stores have been set up to provide generic drugs, which are available at lesser prices but are equivalent in quality and efficacy as expensive branded drug.
- The Government of India has championed setting up Jan Aushadhis, which are pharmacies selling only generic name medicines to the extent possible, giving preference to pharmaceutical public sector undertakings (PSUs) too.
Drugs and cosmetics act:
- Drugs and cosmetics act 1940, regulates the import, manufacture and distribution of drugs in India.
- The act is to ensure that the drugs and cosmetics sold in India are safe, effective, and confirm to prescribed quality standards.
Medical council of India:
- Medical Council of India is a statutory body set up in 1934, under the Indian Medical Council Act, 1933.
- It establishes uniform and high standards of medical education in India , protects and promotes the health and safety of the public by ensuring proper standards in the practice of medicine.
- Recently, NITI Aayog has suggested the substitution of Medical Council of India (MCI) with the National Medical Commission (NMC).
MISSION SAKTHI
01, Apr 2019

Why in news:
- India carried an anti-satellite test using an interceptor missile to neutralise a target satellite in a Low Earth Orbit at an altitude of around 300km.India is the 4th country to acquire this ability after US, RUSSIA/USSR, CHINA.
About ASAT:
- An anti-satellite weapon or ASAT is anything that destroys or physically damages a satellite.
- The launch “Mission Shakti” likely struck an Indian satellite in low Earth orbit, turning the object into debris.
- ASATs can be used to intercept and jam communication or military satellites of enemy countries in the time of war and stop them from communicating with their soldiers.
- The range of an ASAT is limited and depends on where it is launched from. Satellites above the range of 20,000 kilometres are out of range. The US and Russia have the capabilities of launching an ASAT from the ship, land and space, while India, presently, has used a land installation.
Low earth orbit:
- A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with an altitude above Earth’s surface of 2,000 kilometers . Objects below approximately 160 kilometers (99 mi) will experience very rapid orbital decay and altitude loss.
Crowded space:
- since the sputnik was launched in 1957, more than 8000 satellites/manmade orbiting objects have been launched, of which 5000 remain in orbit; more than half are non-functional .US accounts for more than 800 of these, followed by china (280), Russia (150). India has an estimated 50 satellites.
Patchy International control:
- In 2008, Russia and China had proposed a draft to kick off negotiations on the Treaty of Prevention no Placement of Weapons in Outer Space and of the treat or use of force against outer space objects. It was rejected by the west.
- The European union, mindful of US allergy to any negotiations on this issue, began to develop a international code of conduct based on transparency and confidence building measures.
- The UN general assembly has called for a declaration of political commitment by all countries that they shall not be the first to place weapons in space.
Way ahead:
- while countries have developed and tested ASAT’S, they are not known to have stockpiled
IIT MADRAS CONVERTS PETROLEUM WASTE TOLUENE INTO USEFUL PRODUCT
31, Mar 2019

- Using platinum nanocatalyst, the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras has successfully converted petroleum waste-product toluene into benzoic acid.
Uses of Benzoic Acid:
- Benzoic acid is used as a food preservative (E210) and medicine for fungal/bacterial infection. Toluene is converted into benzoic acid through selective and controlled oxidation in the presence of a catalyst binaphthyl-stabilised platinum nanoparticles (Pt-BNP).
Green oxidant
- Organic reactions are carried out using organic solvents, which makes it expensive and also generates toxic waste.
- A green oxidant (70% aqueous tert-butyl hydroperoxide or TBHP) is used for converting toluene into benzoic acid.
The Chemistry Involved:
- When toluene is oxidised, it gives four products. But when we use the catalyst that we developed, only benzoic acid is produced. No alcohol, aldehyde or ester is produced.
- The yield of benzoic acid varied from 68-96% depending on whether the toluene used is electron-deficient or electron-rich. Toluene when oxidised gets converted into benzoic acid.
- Molecular oxygen when used alone does not oxidise toluene and so no benzoic acid is generated. So the researchers used TBHP as an oxidiser. The catalyst reacts with TBHP to initiate the oxidisation reaction where toluene gets converted into benzoic acid through a series of reaction steps.
Debris from anti-satellite test to disintegrate in 45 days: official
30, Mar 2019

The satellite targeted with an Anti-Satellite (ASAT) missile under Mission Shakti has broken up into at least 270 pieces, most of which are expected to disintegrate within 45 days.
The satellite has disintegrated into at least 270 pieces which has also been confirmed by the North American Aerospace Defence Command (NORAD). One of them is a large piece that has been deorbited and is estimated to be completely degraded by April 5. The rest of the pieces are estimated to disintegrate in less than 45 days.
Being in the Low Earth Orbit, the debris would fall towards earth and burn up as soon as they enter the atmosphere.
Imaging satellite:
The targeted satellite was Microsat-R, an imaging satellite that was launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on January 24 using a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle.
The satellite, weighing 740 kg, was placed in an orbit of 274 km above earth.
Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) shot down Microsat-R with a modified exo-atmospheric missile of the ballistic missile defence at an altitude of 300 km.
Being monitored:
The ASAT test was tracked by sensors of various agencies. Upon impact, data transmission from the satellite stopped and electro-optic systems confirmed an explosion.
Debris pose significant risk to satellites and other systems launched into orbit as they last for a long time especially in higher orbits. For instance, China’s 2007 ASAT test in an orbit of around 800 km created around 3,000 pieces of debris, of which 616 have decayed. The rest are still in orbit.
Humans can detect the earth’s magnetic fields
29, Mar 2019

Scientists have long known that turtles, birds, honeybees and even bacteria can sense the earth’s magnetic field and use them for navigation. But this magneto-reception has hardly been tested in humans and many studies have been inconclusive.
California Institute of Technology, U.S. and the University of Tokyo has shown that humans do indeed unconsciously respond to the changes in the earth’s magnetic fields. But they are yet to decode what our brains may be using this information for.
The Discovery:
34 volunteers, who sat with their eyes closed in a dark room. The room was wrapped with electrical coils, which helped simulate the earth’s natural magnetic field.
The participants were connected to an EEG set-up and their brain activity was monitored.
In the one-hour session, for a few minutes, the magnetic field around the chamber was shifted. They noticed that during this period, the alpha power of the brain began to drop.
When a human brain is unengaged, the alpha power is high. When something catches its attention, consciously or unconsciously, its alpha power drops.
The most interesting find was that the participants’ brain responded only to changes when the magnetic field pointed toward the floor.
This may be due to the fact that the study participants were people who live in the Northern Hemisphere. In this region, the natural geomagnetic field points downwards to the North.
First and most important is independent replication. Second, the drop in alpha-wave power is only one expression of the brain’s receiving magnetic information.
There may be many more magnetic fluctuations that trigger brain response, including variations in the total strength of the field.
U.S. tracking debris from ASAT test
29, Mar 2019
The United States has reacted to Prime Minister’s statement that India had successfully tested an anti-satellite (ASAT) missile in what he termed Mission Shakti.
As part of the strong strategic partnership with India, the US will continue to pursue shared interests in space and scientific and technical cooperation, including collaboration on safety and security in space- US in response to questions on the U.S. position on the ASAT test.
The U.S. is one of the now four (including India) countries that has demonstrated an ability to strike down an orbiting satellite. U.S. President Donald Trump has been pushing for the U.S. to have a ‘Space Force’ and has directed the administration to enhance America’s space-war fighting capabilities. This has been driven in part by the long-standing American concern that China and Russia were developing their ASAT systems, putting American GPS-based technology at risk.
Mission Shakti
In an incremental advance, India successfully conducted an Anti-Satellite (ASAT) missile test, named Mission Shakti, becoming the fourth country in the world to demonstrate the capability to shoot down satellites in orbit. So far, only the United States, Russia and China have this prowess.
About ASAT missile:
- The satellite downed by the ASAT missile was Microsat-R, an imaging satellite which was launched into orbit on January 24, 2019 using a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV).
- India has built the broad capabilities and building blocks to develop ASAT missiles for some time as part of its Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) programme.
- A BMD interceptor missile successfully engaged an Indian orbiting target satellite in LEO in a ‘hit to kill’ mode.
- The ASAT missile was a modified exo-atmospheric interceptor missile of the BMD. A LEO of 300 km was chosen to “minimise” debris and it also won’t last more than a few months.
- Anti-satellite weapons provide the capability to shoot down enemy satellites in orbit thereby disrupting critical communications and surveillance capabilities. ASAT missiles also act as a space deterrent in dissuading adversaries from targeting the country’s satellite network.
What is Space Debris?
- The term ‘space debris’ does not have a unanimously accepted legal definition. It is generally used to describe the collection of unwanted objects in the earth’s orbit which is either man-made or natural
- Natural Debris consists of natural bodies revolving around the sun, like, meteors and asteroids.
- Artificial Debris consists of man-made objects (usually non functional) which revolves around the Earth. (Therefore it is most commonly referred as Orbital Debris)
- According to the Report of Second U.N. Conference on Exploration and Peaceful Uses of Outer Space 1982, space debris consists of dead satellites, spent rocket motors, nuts and bolts etc.
SUCCESSFUL ANTI-SATELLITE MISSILE TEST PUTS INDIA IN ELITE CLUB
28, Mar 2019

- India successfully conducted an Anti-Satellite (ASAT) missile test, named Mission Shakti, becoming the fourth country in the world to demonstrate the capability to shoot down satellites in orbit. So far, only the
United States, Russia and China have this prowess
What is Anti-Satellite Weapons (ASAT)?
- Anti-satellite weapons are the space weapons that are designed to destroy satellites for military purposes. India tested this missile to target live satellite on low earth orbit (LEO). Most of the military satellites orbit up to 2,000 km above the earth’s surface on LEO
Anti-Satellite Weapons: History
- When USSR demonstrated its ability to attack satellites in space, the U.S Air Force began developing the air-launched anti-satellite missile (ASAT) to destroy enemy satellites. More importantly, at the top of this two-stage missile there was a Miniature Homing Vehicle (MHV). Once it separated from the missile, the MHV homed in and destroyed a satellite by direct collision, rather than by detonation of a warhead – a concept known as “hit-to-kill.”
Anti-Satellite Technologies and Policies: Timeline
- Nuclear-Tipped Interceptors and the Outer Space Treaty: 1950s to 1960s
- ASAT capabilities were earlier developed by the United States and Soviet Union as a dedicated systems and residual capabilities of systems developed for other purposes, notably defence against ballistic missiles.
- Due to the limitations of the interceptor guidance systems, U.S and Soviet missile interceptors were tipped with megaton-class nuclear weapons and would permit a successful ASAT or Anti-Ballistic-Missile (ABM) attack without precision guidance. And such interceptors were recognised as poor ASAT option.
- The United States and Soviet Union signed the Outer Space Treaty (OST) in 1967 which bans orbiting nuclear weapons and provides that all countries are free to use space for peaceful purposes.
Co-Orbital ASAT Weapons: 1960s to 1970s
- A co-orbital strategy was only used by Russia which was dedicated ASAT system. In this a weapon armed with conventional explosives is launched into the same orbit as the target satellite and moves near enough to destroy it.
- The 1,400-kilogram Russian Co-Orbital ASAT weapon was designed to approach a satellite within one or two orbits. Finally, the Soviet Union declared the system operational in 1973.
U.S.-Soviet Treaty: 1972
- The treaty on the limitation of Anti-Ballistic Missile Systems prohibited interfering with “national technical means of verification” of treaty compliance, which implicitly protected reconnaissance satellites.
- In 1976, the Soviet Union resumed testing of its Co-Orbital ASAT system. Testing continued until 1982 and the system remained operational until 1993.
Air-Launched ASAT Systems: 1980s
- The United State test the Air-Launched Miniature Vehicle (ALMV) in 1982 which is a two- staged missile launched from an F-15 aircraft flying at high altitude. This missile will target satellite in low earth orbit and destroy or disrupt it in a high-speed collision, a technique known as a “kinetic kill” or “hit-to-kill” strategy. Several tests were conducted and finally in December 1985, Congress there banned further testing of the system of satellites and The Air Force discontinued the ALMV program in 1987.
- In 1983, the Strategic Defense System (SDI) was expected to develop several types of space- based interceptors with intrinsic ASAT capabilities.
The U.S. and Soviet Laser ASAT System: 1980s to 1990s
- The Ground-based ASAT weapons based on directed electromagnetic energy like lasers which offer the potential to attack satellites with different levels of intensity and low powered lasers can temporarily or permanently damage parts of a satellite’s sensor where as high- powered lasers can disable, damage or destroy a satellite.
- During this period, the U.S. Army accelerated plans for its own ground-based ASAT system, known as the kinetic-energy ASAT (KE-ASAT).
Satellite Jamming: 2000
- Satellite jamming, interfering with radio communications between a satellite and users on the ground is another potential ASAT technology.
- In 2002, the United States deployed the ground-based Counter Communications System.
- In 2007, China used a mobile, ground-based missile to launch a homing vehicle that destroyed one of its aging weather satellites by direct impact, or “kinetic kill”
- In 2008, the U.S. demonstrated the ASAT capabilities of its sea-based Aegis missile defense interceptors by destroying a non-responsive U.S. satellite at an altitude of 240 km.
- In 2010, India announced its intentions to develop a hit-to-kill ASAT system and finally in 2019 India has successfully launched ASAT.
TECHNOFERENCE’ IS AFFECTING SLEEP, PRODUCTIVITY: STUDY
27, Mar 2019

- Excessive use of mobile phones is making people lose sleep and become less productive, according to an Australian study that found a jump in ‘technoference’ over the past 13 years.
1 in 5 women affected
- According to the survey, one in five women (19.5%) and one in eight men (11.8%) now lose sleep due to the time they spend on their mobile phone.
- About 12.6% of the men said their productivity decreased as a direct result of the time they spend on their mobile compared to none in 2005 and 14% of women have also noticed a productivity decline.
- Over 54% of women believe their friends will find it hard to get in touch with them if they do not have a mobile (up from 28.8%), and 41.6% of men thought this. About 8.4% of women and 7.9% of men have aches and pains they attribute to mobile phone use.
- The survey results also indicated that phones were being used as a coping strategy, with one in four women and one in six men saying they would rather use their phone than deal with more pressing issues.
The Good and Bad of Technology
- Rapid technological innovations over the past few years have led to dramatic changes in today’s mobile phone technology which can improve the quality of life for phone users but also result in some negative outcomes.
- These include anxiety and, in some cases, engagement in unsafe behaviours with serious health and safety implications such as mobile phone distracted driving.
Harmful Effects of Mobile Radiation
- Health effects of radiation can be classified into two categories: threshold effects and non- threshold effects. Threshold effects appear after a certain level of radiation exposure is reached and enough cells have been damaged to make the effect apparent. Non-threshold effects can occur at lower levels of radiation exposure. Here are few common health effects or harmful effects of radiation on human body.
Hair
- Loss of hair fall occurs when exposure to radiation is higher than 200 rems.
Heart and Brain:
- Intense exposure to radiation at 1000 to 5000 rems will affect the functioning of the heart. Radiation kills nerve cells and small blood vessels of heart which may cause immediate death. Brain cells are affected if the radiation exposure is greater than 5000 rems.
Thyroid
- Certain body parts are affected specifically when exposed to different types of radiation sources. The thyroid gland may be affected when exposed to radioactive iodine. If exposed to a considerable amount of radioactive iodine, whole or part of thyroid can be affected.
Blood System
- A number of lymphocytic cells present in the blood will be reduced if a person is exposed to 100 rems. This may cause several immune problems. This is termed as mild radiation sickness. As per the reports from Nagasaki and Hiroshima, symptoms may be present more than ten years from that exposure.
Reproductive Tract
- As the cells of reproductive tract divide fastly, these are more prone to be affected even if the exposure is not more than 200 rems.
POLITICAL PARTIES MOST DISTRUSTED, ARMY, JUDICIARY THE MOST TRUSTED’
27, Mar 2019

- Ahead of the Lok Sabha elections, a public opinion survey in 12 states has found that political parties are the most distrusted political institutions in India. It also found that one in five of those surveyed felt that unemployment is the single biggest issue facing the country today.
- The survey, Politics and Society between Elections 2019, found that political parties had a negative net trust rate of -55% (calculated as the percentage of respondent who trust them minus the percentage who do not). They are the only institutions with a negative net rate. On the other end of the scale, the Army is the
- most trusted institution in the country, with an effective trust rate of 88%, while the judiciary including the Supreme Court, High Courts and district court – enjoys an effective trust rate of more than 60%.
People’s perspective
- Apart from measuring institutional trust, the survey attempts to provide a glimpse into people’s views on governance, sexuality, gender, nationalism, populism, caste and religious identities. Other issues cited include development, growth and poverty (15%) and law, governance and corruption (13%).
- Indians across the country seem to have a deep distrust of elites, with a majority of respondents feeling that elites are a bigger hurdle to progress than minorities or migrants.
SHARP RISE IN H1N1 CASES
27, Mar 2019

- The number of influenza A (H1N1) cases and deaths in India has risen sharply by about 6,200 and over 225, respectively.
- Rajasthan continues to report the most number of cases and deaths, followed by Gujarat. Deaths from H1N1 in Rajasthan have increased from 137 to 178, while in Gujarat the increase as been from 88 to 125.
- Delhi has the third most number of cases; the number increased from 2,738 to 3,484. However, the number of H1N1 deaths in Delhi has remained constant at seven.
- The number of cases in Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra and Karnataka has nearly doubled in three weeks. Uttar Pradesh had 905 cases and nine deaths till February 24 but the numbers increased to 1,680 and 21, respectively.
What is swine flu?
- Swine flu, also known as the H1N1 virus, is a relatively new strain of an influenza virus that causes symptoms similar to the regular flu.
- The H1N1 infection was originally transmitted through contact with pigs, but now it can be spread from person to person.
- Its symptoms, which include fever, coughing, a sore throat, and body ache, are similar to the regular flu.
- But if not treated, the H1N1 infection can lead to more serious conditions, including pneumonia and lung infections.
- The risks are especially high for children under the age of five and the elderly.
PSLV C45 MISSION TO MARK SEVERAL FIRST FOR ISRO
26, Mar 2019

India’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), in its 47th mission (PSLV-C45), will launch EMISAT, the primary satellite and 28 international customer satellites.
EMISAT:
-
- Weighing about 436 kg, EMISAT based on ISRO’s Indian Mini Satellite -2 (IMS-2) bus platform. The satellite is intended for electromagnetic spectrum
- The PS4 orbital platform is envisaged to provide a microgravity environment for research organisations and academic institutes to perform
- In this mission, the PS4 hosts three payloads, namely,
- Automatic Identification System (AIS) from ISRO,
- Automatic Packet Repeating System (APRS) from AMSAT (Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation), India and
- Advanced Retarding Potential Analyzer for Ionospheric Studies (ARIS) from Indian Institute of Space Science and technology (IIST).
- 7. The 28 international customer satellites are from four countries, viz. Lithuania, Spain, Switzerland and USA. All these satellites are being launched under commercial arrangements.
Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle:
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is the third generation launch vehicle of India.
- It is the first Indian launch vehicle to be equipped with liquid stages.
- After its first successful launch in October 1994, PSLV emerged as the reliable and versatile workhorse launch vehicle of India with 39 consecutively successful missions by June 2017.
- During 1994-2017 period, the vehicle has launched 48 Indian satellites and 209 satellites
Vitamin deficiency high among urban adults, says NIN study
24, Mar 2019

Scientists at the ICMR-National Institute of Nutrition (NIN) screened the sub-clinical status of vitamins A, D, B1, B2, B6, B12 and folate among urban adults in the twin cities and they found several vitamin deficiencies and dietary inadequacies hidden under their apparently healthy exterior.
For the first time, explored the blood levels of major vitamins along with dietary intakes of urban adults and explored the homocysteine levels which amplify the chances of non-communicable diseases like heart diseases.
Vitamins:
- Vitamins are organic compounds that are required in small amounts in our diet but their deficiency causes specific diseases.
- Most of the vitamins cannot be synthesized in our body but plants can synthesize almost all of them, so they are considered as essential food factors.
- However, the bacteria of the gutcan produce some of the vitamins required by us.
- All the vitamins are generally available in our diet. Different vitamins belong to various chemical classes and it is difficult to define them on the basis of structure.
- They are generally regarded as organic compoundsrequired in the diet in small amounts to perform specific biological functions for normal maintenance of optimum growth and health of the organism.
- Vitamins are designated by alphabets A, B, C, D, etc. Some of them are further named as sub-groups e.g. B1, B2, B6, B12, etc.
- Vitamin A keeps our skin and eyes healthy.
- Vitamin C helps body to fight against many diseases. Vitamin C gets easily destroyed by heat during cooking.
- Vitamin D helps our body to use calcium for bones and teeth.
- Excess of vitamins is also harmful and vitamin pills should not be taken without the advice of doctor.
- The term “Vitamine” was coined from the word vital + amine since the earlier identified compounds had amino groups.
- Later work showed that most of them did not contain amino groups, so the letter ‘e’ was dropped and the term vitamin is used these days.
- Vitamins are classified into two groups depending upon their solubility in water or fat.
Fat soluble vitamins
- Vitamins which are soluble in fat and oils but insoluble in water are kept in this group. These are vitamins A, D, E and K. They are stored in liverand adipose (fat storing) tissues.
Water soluble vitamins
- B group vitamins and vitamin C are soluble in water so they are grouped together.
- Water soluble vitamins must be supplied regularlyin diet because they are readily excreted in urine and cannot be stored (except vitamin B12) in our body.
| S.No | Vitamin | Deficiency Diseases |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Night blindness | |
| Vitamin B1 | Beriberi | |
| Vitamin B2 | Ariboflavinosis | |
| Vitamin B3 | Pellagra | |
| Vitamin B5 | Paresthesia | |
| Vitamin B6 | Anemia | |
| Vitamin B7 | Dermatitis, enteritis | |
| Vitamin B9 & Vitamin B12 | Megaloblastic anemia | |
| Vitamin C | Scurvy, Swelling of Gums | |
| Vitamin D | Rickets & Osteomalacia | |
| Vitamin E | Less Fertility | |
| Vitamin K | Non-Clotting of Blood. |
Ooty’s muon detection facility measures potential of thundercloud
24, Mar 2019

For the first time in the world, researchers at the GRAPES-3 muon telescope facility in Ooty have measured the electrical potential, size and height of a thundercloud that passed overhead on December 1, 2014.
At 1.3 gigavolts (GV), this cloud had 10 times higher potential than the previous record in a cloud. This is not because clouds with such high potentials are a rarity, but rather, because the methods of detection have not been successful so far.
Cloud structure
- Clouds have negative charges along their lower side and positive charges on top and can be several kilometres thick.
- If balloons are used to measure the potential difference between the top and bottom, they will take hours to traverse the distance.
- Unfortunately, thunderstorms last only for about 15-20 minutes, and this method fails.
Threshold of detection
- Muons and other particles are produced when cosmic rays bombard air particles surrounding the earth.
- The muons produced can have positive or negative charge.
- When a positively charged muon falls through a cloud, it loses energy. If its energy falls below 1 giga electron volt (GeV), which is the threshold of detection of the GRAPES-3 muon telescope, it goes undetected.
- On the contrary, a negatively charged muon gains energy when falling through the cloud and gets detected.
- Since there are more positive than negative muons produced in nature, the two effects don’t cancel out, and a net change in intensity is detected.
Clue to puzzle
- This method can be used to solve a 25-year-old puzzle of terrestrial gamma ray bursts huge flashes of light that accompany lightnings, but which have not been explained in theory until now.
GRAPES-3 Experiment:
- The GRAPES-3 experiment at TIFR’s (Tata Institute of Fundamental Research) Cosmic Ray Laboratory in Ootacamund in Tamil Nadu is getting upgraded to detect solar storms.
- GRAPES-3 (Gamma Ray Astronomy PeVEnergieS phase-3) experiment had detected the effect of a solar storm that hit the earth in June 2015.
- GRAPES-3 has an important role in understanding the propagation of storms from the L1 point (Lagrange point 1) to its impact on the Earth.
- The upgraded detector will have an increased coverage and improved capacity to determine the direction of incident cosmic rays.
- It will play a major role in getting precise information about the propagation of storms in the last million miles (from the L-1 point) of their journey from the Sun to the earth.

muon
- The muon is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 e and a spin of 1/2, but with a much greater mass.
- It is classified as a lepton.
- As is the case with other leptons, the muon is not believed to have any sub-structure that is, it is not thought to be composed of any simpler particles.
- The muon is an unstable subatomic particle with a mean lifetime of 2.2 μs, much longer than many other subatomic particles.

End stigma and discrimination to end TB
24, Mar 2019

The years 2018 and 2019 have been landmark years in the fight against TB
- In the two years since, the team at REACH, an organisation working on TB since 1998, has witnessed similar scenes play out at other workshops around the country.
- Over 300 TB survivors from across India all of whom attended trainings to help them become powerful TB champions and advocates described stigma as an impenetrable barrier in accessing TB services.
Each TB survivor brought his/her own personal experience to the discussion the difficulties in getting a clear diagnosis, doctor-shopping, the lack of information on what the treatment involved, having to deal with side-effects, the loss of income, to name a few.
While TB had impacted each of their lives differently, they were all unanimous in identifying one cross-cutting barrier stigma and its assiduous companion, discrimination.
Landmark years
- The years 2018 and 2019 have been landmark years in the fight against TB, globally and in India, with the first ever High Level Meeting on TB held at the United Nations last year.
- In India, there is high political will and commitment to end TB, budgets are slowly increasing, new social support schemes have been announced and TB survivors are speaking up.
- There is a lot of talk of ‘ending TB’ and the ambitious phrase — TB elimination — has entered our lexicon.
India and TB
- TB is second only to HIV/AIDS as the greatest infectious killer disease worldwide
- India has the highest TB burden in the world, accounting for almost 25 per cent of global TB cases.
- According to the Global TB Report 2017 released by World Health Organisation (WHO), India has topped list of seven countries, accounting for 64% of the over 10 million new tuberculosis (TB) cases worldwide in year 2016.
- India’s domestic budget for fighting tuberculosis showed a dramatic jump from about ₹700 crore in 2015 to ₹2,500 crore last year.
- According to World Health Statistics 2018 released by World Health Organisation (WHO), India saw estimated 211 cases of tuberculosis (TB) per 1,00,000 people in 2016.
- India has pledged to eradicate tuberculosis by 2025, five years ahead of global target set by WHO.

Basics about TB:
Tuberculosis is an infectious, airborne disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It mainly affects the lungs. It can be transmitted from person to person through the air when people with TB cough, sneeze, laugh or speak, spit, propelling the germs into the atmosphere.
Why TB is an issue?
- With proper diagnosis and treatment, TB can be cured.
- However, too many people with TB don’t seek care for early symptoms and get properly diagnosed. Of those in whom the disease is detected, many do not complete their treatment.
- Despite global efforts to combat TB, which saved an estimated 53 million lives since 2000 and reduced TB mortality rate by 37%, the disease is still top infectious killer in 2016. The disease also has been reported to be main cause of deaths related to antimicrobial resistance and the leading killer of people with HIV.
- The biggest challenge was underreporting and underdiagnosis of TB cases, especially in countries with weak health systems and large unregulated private sectors.
‘90-90-90 target’ by 2035:
- The government has committed to achieve a ‘90-90-90 target’ by 2035 (90% reductions in incidence, mortality and catastrophic health expenditures due to TB).
- This is premised on improved diagnostics, shorter treatment courses, a better vaccine and comprehensive preventive strategies.
Moscow Declaration:
- The declaration calls for eliminating additional deaths from HIV co-infection by 2020 and achieving synergy in coordinated action against Tuberculosis
- and non-communicable diseases (NCDs). India is among signatories to the declaration. Moscow declaration emphasis need for fixing multi sectoral responsibility towards ending TB by 2035, the global target.
Steps Taken by Govt.:
- Indo-US partnership to free India of TB (see Indo-US relation).
- India has signed WTO’s call to end TB by 2030.
- USAID-India End TB Alliance.
IIT Guwahati’s bone graft aids extensive bone formation
24, Mar 2019

- A scaffold made of silk–bone cement composite doped with silicon and zinc metal ions has been found to regenerate new bone tissue in rabbits in three months.
- The newly formed bone forms a seamless joint with the existing bone and has blood vessels inside it.
- Tests carried out on rabbits with defective thigh bone (femur) showed extensive bone formation of 73% at the end of 90 days compared with 49% in the case of scaffold made only of silk fibre.
- Even at the end of 30 days, there was adequate bone regeneration and new blood vessel formation.

Superior graft
- The bone graft fabricated and tested is superior to currently available ones, affordable and does not require external use of growth factors for bone cells to grow.
- At the end of three months, the silk fibre had completely degraded leaving behind a homogeneous bone produced by rabbit bone cells.
- The newly formed bone had healed the defective femur. The bone cement made of calcium phosphate becomes a part of the bone while the biocompatible metal ions (silicon and zinc) get leached out at the end of 90 days.
The Chemistry behind:
- The scaffold is fabricated by first doping the bone cement with silicon and zinc and mixing the bone cement with chopped mulberry silk fibre.
- The bone cement gets adsorbed on the silk fibre. Liquid silk fibre is then added to bind the chopped fibre and bone cement; the liquid silk also makes the composite highly porous.
- The silk–bone cement composite has higher density and strength, more surface area and high surface roughness, closely resembling a native bone.
- The zinc and silicon ions get leached from the composite and activate bone and blood vessel cells.
- This leads to faster regeneration of the bone tissue and blood vessel formation.
- By doping with these metal ions we are doing away with external addition of growth factor and also making the graft affordable.
Bone regeneration
- The compressive strength of silk fibre is about 40 kPa, while it is nearly double in the case of the silk–bone cement composite.
- Though doping with the silicon and zinc metal ions reduces the mechanical properties, particularly the compressive strength, the bulk strength of the doped composite is sufficient to activate bone regeneration.
- Through in vitro studies carried out prior to experimentation with rabbits, the researchers realised that incorporation of bone cement and metal ion doped bone cement enhanced the bone tissue regeneration capacity.
- While the composite was seeded with bone cells for in vitro studies, in rabbits, the composite was used without adding any bone cells. Bone cells from neighbouring tissue migrate and bind to the scaffold and aid in bone regeneration.
Monkey birth a step in saving fertility of boys with cancer
23, Mar 2019

- Scientists are closing in on a way to help young boys undergoing cancer treatment preserve their future fertility and the proof is the first monkey born from the experimental technology.
- More and more people are surviving childhood cancer, but nearly 1 in 3 will be left infertile from the chemotherapy or radiation that helped save their life.
- When young adults are diagnosed with cancer, they can freeze sperm, eggs or embryos ahead of treatment. But children diagnosed before puberty can’t do that because they’re not yet producing mature eggs or sperm.
- Scientists froze a bit of testicular tissue from a monkey that hadn’t yet reached puberty. Later, they used it to produce sperm that, through a monkey version of IVF, led to the birth of a healthy female monkey named Grady.
Hope to families
- The technique worked well enough for human testing to begin in the next few years and It’s a huge step forward that should give hope to families.
- Boys are born with stem cells inside little tubes in the testes, cells that start producing sperm after puberty’s testosterone jolt Keep sperm-producing stem cells safe from cancer treatment by freezing small pieces of testicular tissue, and using them to restore fertility later in life.
- Boosted by hormones, the little pieces of tissue grew. Months later, the researchers removed them. Sure enough, inside was sperm they could collect and freeze.
Option for girls
- If the technique sounds a little bizarre, it’s similar to a female option.
- Girls’ eggs are in an immature state before puberty. Researchers have removed and frozen strips of ovarian tissue harbouring egg follicles from young women before cancer treatment, in hopes that when transplanted back later the immature eggs would resume development.
Evidence of water found on asteroid Bennu
21, Mar 2019

- Scientists have discovered evidence of abundant water-bearing minerals on the surface of the near-earth asteroid Bennu.
- Data from NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft that is currently orbiting the asteroid confirm presence of aqueously altered, hydrated minerals on its surface. Scientists say similar objects may have seeded the earth with water and organic materials.
Asteroid Bennu:
- So, analysis of returned sample from it could help to reveal key insights about early solar system and the origin of life on Earth.
- It can strike earth and cause massive destruction. According to experts, it has a only a one in 2,700 chances of hitting.
- This event will occur in year 2135
OSIRIS-REx Mission:
- Primary aim of the mission is to study asteroid 101955 Bennu, a carbonaceous asteroid.
- NASA’s project
- OSIRIS-Rex stands for Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer.
- OSIRIS-Rex will travel for two years on a journey to Bennu, a near-Earth asteroid about the size of a small mountain
- It will return with dirt samples from Bennu to Earth
- NASA scientists feel that the Bennu asteroid hold clues to the origin of the solar system and the source of water and organic molecules found on Earth
- The spacecraft is scheduled to reach small, roundish asteroid in 2018 and return to Earth after collecting some of its gravels by 2023. It was launched in 2016.
Moon samples to be unsealed for study
20, Mar 2019

- NASA will reveal never-before-seen morsels of the moon.
- The astronauts of the Apollo missions that landed on the moon from 1969 to 1972 collected 842 pounds (381 kg) worth of lunar rocks, core samples, pebbles, sand and dust. Many of those samples were later opened on the ground. But three have remained sealed their contents stashed away for nearly 50 years.
- They were intentionally saved for a time when more advanced technology would allow planetary scientists on earth to delve deeper into the moon’s mysteries.
- The technology available in the 1960s and 1970s wasn’t able to do what we can do now.
Apollo 8
- Apollo 8, the second manned spaceflight mission in the United States Apollo space program, was launched on December 21, 1968, and became the first manned spacecraft to leave low Earth orbit, reach the Moon, orbit it, and safely return.
- The three-astronaut crew—Frank Borman, James Lovell, and William Anders—became the first humans to travel beyond low Earth orbit, see Earth as a whole planet, and enter the gravity well of another celestial body. They were also the first humans to orbit another celestial body, see the far side of the Moon, witness and photograph an “Earthrise”, escape the gravity of another celestial body (the Moon), and reenter Earth’s gravitational well.
Alert after boy dies of West Nile fever
19, Mar 2019
A six-year-old in Kerala, who had tested positive for West Nile Virus (WNV), died in Kozhikode.
About West Nile Virus:
- West Nile virus (WNV) is an infectious virus spread by infected mosquitoes. It spreads from birds to humans with the bite of an infected Culex mosquito.
- The symptoms include a fever, headache, body aches, skin rash, and swollen lymph glands.
- The symptoms can lead to St. Louis encephalitis, Japanese encephalitis, meningitis and yellow fever.
- Humans, horses and other mammals can be infected.
Global spread:
- West Nile virus was first isolated in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
- WNV is commonly found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, North America and West Asia.
- The virus is now widely reported from Canada to Venezuela.
Spread in India:
- WNV is highly prevalent in India since 1970s. It had been reported from states like Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Tamilnadu, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat,Odisha.
- Presence of WNV was documented in north- eastern region of India during the year 2006 from four districts of Assam.
Treatment:
- There are no specific vaccines or treatments for human WNV disease.
- The best way to avoid WNV is to prevent mosquito bites.
A viable alternative to open-heart surgery
18, Mar 2019
The open heart surgery is a daring one to replace a failing heart valve where the cardiologists insert a mechanical replacement through a patient’s groin and thread it all the way to the heart, manoeuvring it into the site of the old valve.
The procedure, called transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), has been reserved mostly for patients so old and sick they might not survive open-heart surgery. Now, two large clinical trials show that TAVR is just as useful in younger and healthier patients.
About Transcatheter Aortic Valve Rreplacement (TAVR)
Percutaneous aortic valve replacement (PAVR), also known as transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) or transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), is the replacement of the aortic valve of the heart through the blood vessels (as opposed to valve replacement by open heart surgery).
The replacement valve is delivered via one of several access methods:
- Transfemoral (in the upper leg),
- Transapical (through the wall of the heart), subclavian (beneath the collar bone),
- Direct aortic (through a minimally invasive surgical incision into the aorta), and
- Transcaval (from a temporary hole in the aorta near the belly button through a vein in the upper leg), among others.
Second Scorpene submarine ready for induction
18, Mar 2019

- Indian Navy is set to induct the second Scorpene submarine Khanderi .
- Mazagon Dock Limited (MDL), Mumbai, is manufacturing six Scorpene submarines under technology transfer from Naval Group of France under a 2005 contract worth $3.75 bn.
- The first submarine of the class Kalvari joined service in December 2017. The entire project is expected to be completed by 2020.
- The third in the Scorpene series Karanj which was launched in January last year is in advanced stage of trials and could be ready for induction by year end.
- The last two submarines Vagir and Vagsheer are in advanced stages of manufacturing on the assembly line.
- Kalvari is the first modern conventional submarine inducted by the Navy in almost two decades.
Solar tsunami can trigger the sunspot cycle
17, Mar 2019

It is believed that the solar dynamo a naturally occurring generator which produces electric and magnetic fields in the sun is linked to the production of sunspots.
What kick-starts the 11-year sunspot cycle is not known.
The extreme temperature and pressure conditions that prevail some 20,000 km below the sun’s surface cause its material to form a plasma consisting primarily of hydrogen and helium in a highly ionized state.
The plasma is confined with huge magnetic fields inside the sun.
The sun’s toroidal magnetic field, from which sunspots get generated, wraps around the sun in the east-west direction.
Solar Dynamo
- It is believed that the “solar dynamo” a naturally occurring generator which produces electric and magnetic fields in the sun is linked to the production of sunspots.
- What kick-starts the 11-year sunspot cycle is not known.
- The extreme temperature and pressure conditions that prevail some 20,000 km below the sun’s surface cause its material to form plasma consisting primarily of hydrogen and helium in a highly ionised state.
- The plasma is confined with huge magnetic fields inside the sun.
What is Solar Tsunami?
- The sun’s magnetic field, from which sunspots get generated, wraps around the sun in the east-west direction.
- These magnetic fields behave like rubber bands on a polished sphere. They tend to slip towards the poles.
- Holding these fields in their place requires that there is extra mass (plasma mass) pushing at the bands from higher latitudes.
- Thus, a magnetic dam is formed which is storing a big mass of plasma.
- At the end of a solar cycle, this magnetic dam can break, releasing huge amounts of plasma cascading like a tsunami towards the poles.
- These tsunami waves travel at high speeds of about 1,000 km per hour carrying excess plasma to the mid-latitudes.
- There they give rise to magnetic flux eruptions.
- These are seen as the bright patches that signal the start of the next cycle of sunspots.
What are Sunspots?
- Sunspots are temporary phenomena on the Sun’s photosphere that appear as spots darker than the surrounding areas.
- They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic field flux that inhibit convection.
- Sunspots usually appear in pairs of opposite magnetic polarity.
Topical gel protects farmers from pesticides
17, Mar 2019

Using easily available, inexpensive natural polymers a gel for the skin to protect agricultural workers from harmful pesticide sprays has been developed. The gel does not just act as a simple physical barrier; it chemically deactivates pesticides.
Ripple effect
Organophosphate pesticides bring about the inhibition of important enzymes (AChE) of the body, which can, in turn, affect the functioning of nervous system, heart, immunity, and even the reproductive system
The base of the gel is chitosan, a natural substance extracted from the waste shells of crabs and shrimps, to which we added a nucleophile and few aqua reagents to get the consistency and desired pH.
The gel was found to cleave a wide range of commercially available pesticides before they enter the bloodstream, thus reducing the pesticide-induced enzyme inhibition
A gel to selectively remove oil or water
17, Mar 2019

A natural biopolymer, chitosan (a kind of polysaccharide obtained from a chitin shell such as the shrimp’s), which is water-soluble, has been chemically modified to selectively remove either an oil or water phase from an oil-water mixture.
Making of the Gel
To prepare the water or oil repelling chitosan, first converted the material into nanoparticles and then to a stable gel material by treating it with a chemical (5Acl).
This gel was found to have chemically active residues (amines and acrylate), which when treated with a small amine resulted in optimization of the two very different properties in the same material.
Chitosan in a different form
The chitosan which is converted into a stable gel — allows the researchers to selectively remove the oil or water phase from an oil-water mixture by making the material either superhydrophobic or super oleophobic, respectively.
For example, if the oil spill (in water) is less, the material can be made water-repelling to remove or collect the oil. In case the spill is huge and the water phase relatively less, the material can be made extremely oil-repelling to collect or remove water.
Superior performance
The biopolymer’s superhydrophobic property remained intact under diverse chemical conditions such as extreme pH (pH 1 and pH 13), sea and river water for seven days, and high (100º C) and low (10º C) temperatures.
Biopolymers:
Superior performance
The biopolymer’s superhydrophobic property remained intact under diverse chemical conditions such as extreme pH (pH 1 and pH 13), sea and river water for seven days, and high (100º C) and low (10º C) temperatures.
Biopolymers:
Biopolymers are polymers that are produced by living organisms. They are generally polymers of starch. These are composed of monomeric units. They can be classified based on the three main classes based on the formation of structure, length of the polymers that comprehends more than thirteen nuclei monomers or amino acids which are short lengthened amino acids.
Drug-resistant TB drug may cut treatment time
15, Mar 2019

A new drug cocktail reduces the length of treatment for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis from nearly two years to nine to 11 months with a similar effectiveness, according to a large clinical trial.
Nearly 6,00,000 people contract multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) every year.
Normal tuberculosis is treated with four antibiotics over a six-month period.
The new clinical trial, which included nearly 400 patients(all severely affected by the disease), compared the effectiveness of long-term treatment and that of a shorter therapy.
Tuberculosis
- TB is second only to HIV/AIDS as the greatest infectious killer disease worldwide
- India has the highest TB burden in the world, accounting for almost 25 per cent of global TB cases.
- According to the Global TB Report 2017 released by World Health Organisation (WHO), India has topped list of seven countries, accounting for 64% of the over 10 million new
- tuberculosis (TB) cases worldwide in year 2016.
- India’s domestic budget for fighting tuberculosis showed a dramatic jump from about ₹700 crore in 2015 to ₹2,500 crore last year
- According to World Health Statistics 2018 released by World Health Organisation (WHO), India saw estimated 211 cases of tuberculosis (TB) per 1,00,000 people in 2016.
- India has pledged to eradicate tuberculosis by 2025, five years ahead of global target set by
Basics about TB:
Tuberculosis is an infectious, airborne disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It mainly affects the lungs. It can be transmitted from person to person through the air when people with TB cough, sneeze, laugh or speak, spit, propelling the germs into the atmosphere
Why TB is an issue?
- With proper diagnosis and treatment, TB can be cured.
- However, too many people with TB don’t seek care for early symptoms and get properly diagnosed. Of those in whom the disease is detected, many do not complete their treatment.
- Despite global efforts to combat TB, which saved an estimated 53 million lives since 2000 and reduced TB mortality rate by 37%, the disease is still top infectious killer in 2016. The disease also has been reported to be main cause of deaths related to antimicrobial resistance and the leading killer of people with HIV.
- The biggest challenge was underreporting and underdiagnosis of TB cases, especially in countries with weak health systems and large unregulated private sectors.
‘90-90-90 target’ by 2035:
- The government has committed to achieve a ‘90-90-90 target’ by 2035 (90% reductions in incidence, mortality and catastrophic health expenditures due to TB).
- This is premised on improved diagnostics, shorter treatment courses, a better vaccine and comprehensive preventive strategies.
Moscow Declaration:
The declaration calls for eliminating additional deaths from HIV co-infection by 2020 and achieving synergy in coordinated action against Tuberculosis and non-communicable diseases (NCDs). India is among signatories to the declaration. Moscow declaration emphasis need for fixing multi sectoral responsibility towards ending TB by 2035, the global target.
Steps:
- Indo-US partnership to free India of TB (see Indo-US relation).
- India has signed WTO’s call to end TB by 2030.
- USAID-India End TB Alliance
Why does Anti-microbial Resistance occur?
The first rule of antibiotic use is that they are used to fight bacterial infections and they don’t work on viruses. A common cold or cough is most likely caused by a viral infection.
Excessive use of antibiotics is responsible for the alarming increase in antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in the country. Irrational use of drugs, overdosing or under-dosing, self-medication, misuse of drugs, and the inappropriate use of antimicrobials in a hospital setting are all cause for alarm.
Drug-resistant TB drug may cut treatment time
15, Mar 2019

- A new drug cocktail reduces the length of treatment for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis from nearly two years to nine to 11 months with a similar effectiveness, according to a large clinical trial.
- Nearly 6,00,000 people contract multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) every year. Normal tuberculosis is treated with four antibiotics over a six-month period. .
- The new clinical trial, which included nearly 400 patients(all severely affected by the disease), compared the effectiveness of long-term treatment and that of a shorter therapy.
Tuberculosis
- TB is second only to HIV/AIDS as the greatest infectious killer disease worldwide.
- India has the highest TB burden in the world, accounting for almost 25 per cent of global TB cases.
- According to the Global TB Report 2017 released by World Health Organisation (WHO), India has topped list of seven countries, accounting for 64% of the over 10 million new tuberculosis (TB) cases worldwide in year 2016.
- India’s domestic budget for fighting tuberculosis showed a dramatic jump from about ₹700 crore in 2015 to ₹2,500 crore last year.
- According to World Health Statistics 2018 released by World Health Organisation (WHO), India saw estimated 211 cases of tuberculosis (TB) per 1,00,000 people in 2016.
- India has pledged to eradicate tuberculosis by 2025, five years ahead of global target set by WHO.
Basics about TB:
- Tuberculosis is an infectious, airborne disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It mainly affects the lungs. It can be transmitted from person to person through the air when people with TB cough, sneeze, laugh or speak, spit, propelling the germs into the atmosphere
Why TB is an issue?
- With proper diagnosis and treatment, TB can be cured.
- However, too many people with TB don’t seek care for early symptoms and get properly diagnosed. Of those in whom the disease is detected, many do not complete their treatment.
- Despite global efforts to combat TB, which saved an estimated 53 million lives since 2000 and reduced TB mortality rate by 37%, the disease is still top infectious killer in 2016. The disease also has been reported to be main cause of deaths related to antimicrobial resistance and the leading killer of people with HIV.
- The biggest challenge was underreporting and underdiagnosis of TB cases, especially in countries with weak health systems and large unregulated private sectors.
‘90-90-90 target’ by 2035:
- The government has committed to achieve a ‘90-90-90 target’ by 2035 (90% reductions in incidence, mortality and catastrophic health expenditures due to TB).
- This is premised on improved diagnostics, shorter treatment courses, a better vaccine and comprehensive preventive strategies.
Moscow Declaration:
- The declaration calls for eliminating additional deaths from HIV co-infection by 2020 and achieving synergy in coordinated action against Tuberculosis.
and non-communicable diseases (NCDs). India is among signatories to the declaration. Moscow declaration emphasis need for fixing multi sectoral responsibility towards ending TB by 2035, the global target.
Steps:
- Indo-US partnership to free India of TB (see Indo-US relation).
- India has signed WTO’s call to end TB by 2030.
- USAID-India End TB Alliance
What is Anti-Microbial Resistance?
- Anti-microbial resistance (AMR) is the ability of micro-organisms that cause disease to withstand attack by anti- microbial medicines. From drugs used to treat common bacterial infections, to the complex combinations now fighting HIV infection, resistance is increasingly being detected and is spreading rapidly.
- Increasing resistance of pathogens to currently available antibiotics can lead to a situation where advanced techniques and procedures in the field of surgery and medicine become redundant and ineffective due to our failure to prevent the spread of infection.
Why does Anti-microbial Resistance occur?
- The first rule of antibiotic use is that they are used to fight bacterial infections and they don’t work on viruses. A common cold or cough is most likely caused by a viral infection.
- Excessive use of antibiotics is responsible for the alarming increase in antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in the country. Irrational use of drugs, overdosing or under-dosing, self-medication, misuse of drugs, and the inappropriate use of antimicrobials in a hospital setting are all cause for alarm.
First person on Mars may be a woman, says NASA
14, Mar 2019

NASA recently announced that it will have its first all-female spacewalk at the end of the month, when astronauts Anne McClain and Christina Koch will get to float around in space.
InSight Mission
- InSight is NASA’s Discovery Program mission dedicated to exploring the deep interior of Mars.
- It will place stationary lander equipped with seismometer and heat transfer probe on surface of Mars to study red planet’s early geological evolution.
- It is terrestrial planet explorer that will address one of most fundamental issues of planetary and solar system science.
- It will help in understanding processes that shaped rocky planets of inner solar system (including Earth) more than four billion years ago.
- The robotic lander will perform a radio science experiment to study internal structure of Mars by deploying seismometer and a burrowing heat probe.
- It will measure Mar’s vital signs such as pulse (seismology), temperature (heat flow probe) and reflexes (precision tracking).
- It will let scientists understand how different its crust, mantle and core are from Earth.
Is home test for Type 2 diabetes a waste of time and money?
12, Mar 2019

More than 30 million people in the U.S. have diabetes. The vast majority of them have Type 2 diabetes. Some of those are testing their blood sugar at home, but the best research is telling us that they do not need to — that in fact it is a waste of money.
For people with Type 1 diabetes, blood glucose monitoring and insulin administration is the standard of care. Patients need to check their blood sugar a number of times a day, then give themselves insulin to replace what would have been made in the pancreas. Treatment for Type 2 diabetes, however, does not involve these critical calculations of insulin. It is usually maintained with pretty regular administration of the same drugs on a set schedule.
Self-monitoring for blood glucose, therefore, may be unnecessary. This has been tested in well-designed studies.
Pragmatic study
The Monitor trial, published two years ago in JAMA , was a pragmatic trial that took place in 15 primary care practices in North Carolina. Patients with Type 2 noninsulin-treated diabetes were randomly assigned to one of three groups.
People in the first group were told to check their blood glucose once a day. People in the second were told to check their blood glucose once a day and then were given tailored advice depending on the results from the meter. The third group was told not to check blood sugar at all.
After one year (a pretty impressive length for a study like this), there were no differences in the hemoglobin A1C levels (the best way to monitor long-term blood glucose control) between the three groups. There were also no differences in the health-related quality of life measures for the patients. There were no differences in the number of times they experienced hypoglycemia, how much care they needed and how many progressed to the need for insulin.
In other words, there were no measurable differences in how patients fared, whether they checked blood sugar or not.
This evidence, while the best to date, confirmed what previous work had shown.
What critics say
Still, not everyone is on board. Critics said it did not prove that blood glucose monitoring could not help: It is possible that with better training, or more attention to detail, there might be ways to make this work.
The point of pragmatic comparative effectiveness trials like this, though, is to test how practices work in the real world. In these high-quality primary care practices, even with customised help in interpreting the measurements (which is more than most patients get), testing blood sugar did not make a difference.
But for most people with Type 2 diabetes not on insulin, testing is inappropriate most of the time. That message is not getting through. At the end of last year, another study was published in JAMA Internal Medicine that quantified the prevalence of glucose testing in adults. Researchers examined a database that contained data on more than 3,70,000 people who had Type 2 diabetes.
Of the more than 23% of patients who were using testing strips, more than half were probably doing so despite widespread recommendations that they shouldn’t. They were using a median of two testing strips a day at a cost of more than $325 per year per patient
| Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes |
|---|---|
| Type 1 diabetes is believed to be an autoimmune condition. | Type 2 diabetes starts as insulin resistance. |
| This means your immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the beta cells in your pancreas that produce insulin. | This means your body can't use insulin efficiently. |
| The damage is permanent. | That stimulates your pancreas to produce more insulin until it can no longer keep up with demand. |
NASA orbiter spots water molecules moving around the dayside of moon
11, Mar 2019
NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), have observed water molecules moving around the dayside of the moon, an advance that could help us learn about accessibility of water that can be used by humans in future lunar missions.
Measurements from the Lyman Alpha Mapping Project (LAMP) instrument aboard the LRO of the sparse layer of molecules temporarily stuck to the surface helped characterise lunar hydration changes over the course of a day.
Up until the last decade, scientists thought the Moon was arid, with any water existing mainly as pockets of ice in permanently shaded craters near the poles.
More recently, scientists have identified surface water in sparse populations of molecules bound to the lunar soil. The amount varies based on the time of day. This water is more common at higher latitudes and tends to hop around as the surface heats up.
These results aid in understanding the lunar water cycle and will ultimately help us learn about accessibility of water that can be used by humans in future missions to the Moon.
Lunar water can potentially be used by humans to make fuel or to use for radiation shielding or thermal management; if these materials do not need to be launched from Earth, that makes these future missions more affordable, Hendrix said in a statement.
Water molecules remain tightly bound to the regolith until surface temperatures peak near lunar noon.
A smart indicator to boost frozen food safety
10, Mar 2019

The temperature at which food products are stored is vital in ensuring their quality. For example, in retail outlets across India, power failure and repeated opening and closing of freezer storage units in which food products are stored can lead to temperature fluctuations. These in turn can affect the quality of food, especially perishable food, leading to microbial growth. Temperature fluctuations can also affect vaccines and drugs that are stored in cold storage or at below room temperature.
Researchers from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Institute of Fisheries Technology (ICAR-CIFT), Kochi, Kerala, in collaboration with the University of Wisconsin, Madison, U.S., have now found a way using gold nanoparticles that they synthesised to help tell if frozen food is still edible.
How it works
- The nanoparticles change colour in response to changes in temperature. They become ruby red (similar to the colour of red wine) at -18° C and turn purple when the temperature rises. At room temperature, their colour is dark grey.
- To synthesise the nanoparticles, the researchers used chitosan, a natural biodegradable polysaccharide that was extracted from marine waste such as shrimp and crab shell. A solution of chitosan and gold chloride solution was heated for about 30 minutes at 90° C. Though the sample preparation process was simple, care was taken to maintain proper conditions such as temperature, stirring and base concentration of the gold solution.
- The nanoparticles remained stable when tested at -18° C. Their colour and other physical properties remained intact even at the end of 30 days of testing at -18° C.
- The colour change of the nanoparticles is irreversible. So once they change from red to purple or grey when the temperature increases, the original colour cannot be regained even if the temperature is brought back to -18° C. They can be attached to the outer surface of the food or pharmaceutical packs as a visible indicator without coming in contact with the product.
Belle II: Chasing cousinly rivalry at the subatomic level
10, Mar 2019

Belle II, a particle accelerator experiment located in Tsukuba, Japan, is a unique facility in the world. Here, electrons and positrons (anti-electrons) collide to produce B mesons in order to study the breakdown of symmetry in these decays. As an international collaboration involving 26 countries, Belle II has an Indian link — a team led by physicists and engineers from the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai, have built the fourth layer of the vertex detector.
The focus at Belle II is on B-mesons — particles that contain the B-quark, also known as the beauty or bottom quark. Says Tom Browder from the University of Hawaii who is also the spokesperson for Belle II, In particular, we focus on the differences between the decay of the B-mesons and that of their antiparticles, the anti B-mesons. We are looking for the breakdown in the symmetry between matter and antimatter.
This broken symmetry between matter and antimatter is one of the most fundamental questions in particle physics.
Asymmetric universe
- At the time of the Big Bang some 13.7 billion years ago, the universe was in a fully symmetric state with equal quantities of matter and antimatter. Yet, today, we are in this extremely antisymmetric state. As soon as the first differences were discovered in particle physics between kaons and antikaons in 1964 at Brookhaven, Sakharov realised this was an important clue to understanding this asymmetry between matter and antimatter.” Sakharov suggested that we start with this symmetric state of the universe at the beginning, then decays of elementary particles that were asymmetric between particles and antiparticles amplified this difference. That led to the matter-dominated universe.
- The original CP violation, or asymmetry between matter and antimatter, which was discovered in 1964, was found in Kaons — particles containing the strange quark. The effects there were tiny — about one part in a thousand.
- For the particles containing the B quark, the effects of this matter-antimatter symmetry are large; they are of order 100%. The B quarks have much greater asymmetry. They are theoretically much easier to understand they are cleaner. That’s also the motivation for these machines.
- In addition to other experiments at CERN, the European Organisation for Nuclear Research, there’s one experiment that is devoted to B quark physics — the LHCb or the Large Hadron Collider beauty experiment. In this, two proton beams are collided at high energies and the results are observed.
- The facility in Japan uses electron-positron collisions. These are much cleaner, as the electron and positron are point-like particles. So, we will be in a competition with the LHCb as time proceeds.” He adds laughingly, At the LHCb, they throw two Swiss watches at each other and [a] lot of stuff comes out, while we have clean collisions of point-like particles.”
Anomalous interactions
In the Standard Model – the core theory of particle physics – there are generations of low mass particles (leptons); electrons, the muon and the relatively heavy cousin of the electron, the tau are the leptons. These particles are expected to have identical interaction strengths, the so-called couplings, in the Standard Model of weak interactions in physics. However, in particle decays where only leptons are produced (leptonic decays), it appears that the tau and muon particles have identical couplings. Specifically, interactions where a kaon particle decays to muon and a kaon decays to electron seem to have the same coupling to 1%. But B decays to tau leptons when compared to B decays to muon or electron are not on equal footing.
IIT-H’s device detects heart attack early
10, Mar 2019

A low-cost, ultra-sensitive device that is capable of detecting the cardiac biomarker troponin T protein has been fabricated by a research team from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Hyderabad. Troponin T is a cardiac protein that is released into the bloodstream after a heart attack.
Unlike the commercially available test that can detect the protein at nanogram per ml concentration, this device can detect the protein at an extremely low concentration of femto gram per ml. This could help pave the way for early diagnosis of a heart attack, increasing a patient’s survival rate. It even has the potential to be able to predict the onset of a heart attack.
Cost-effective fabrication
- Unlike electrodes that are available, it costs very little to fabricate this bioelectrode. This is because a commercially available substrate was used. Further, very little antibody was needed to coat the electrode.
- The electrode was fabricated by depositing perovskite (zinc tin oxide) material electrochemically onto the substrate (indium tin oxide coated polyethylene terephthalate). Glassy carbon electrode coated with the same perovskite material was then used as a control. Perovskite increases the volume-to-surface area of the electrode, thereby increasing its sensitivity.
- The electrodes coated with perovskite were then functionalised to attract proteins. To increase the specificity of the electrode to bind only to the troponin T protein, the electrodes were decorated or coated with the troponin T antibody.
Test findings
- The researchers added various concentrations of the biomarker (ranging from 1 femtogram per ml to 1 microgram per ml) to a buffer solution and measured the impedance (effective resistance in alternating current). Compared with the current limit of detection, the bioelectrode was able to detect troponin T even when it is 10,000 times less in concentration.
- When the troponin antigen binds to the antibody present on the electrode, the impedance increases. As more and more biomarker binds to the antibody, there is increased impedance, which is what we measure. After some time, the electrode is saturated with the troponin protein, so no change in impedance is seen.
- The researchers measured impedance using different concentrations of the protein. They plan to use these impedance values to know the concentration of the protein when testing actual blood samples. And by using a machine learning algorithm, we can measure the concentration of the biomarker in the sample.
- To test the selectivity of the bioelectrode to bind to the biomarker, the researchers tested it on bovine serum albumin (BSA) and human serum albumin (HSA).
- Only a slight change in relative resistance was observed in the case of HSA and BSA as only a small amount of proteins [from HSA and BSA] bind to the bioelectrode. This is unlike troponin where more protein gets bound to the bioelectrode, leading to more impedance.
Focus on miniaturisation
The team is now working on how to miniaturise the readout instrument, will soon be able to capture the signal using a circuit the size of a chip. This will be connected to [a] mobile phone with an app that has a machine learning algorithm for quantification of the troponin biomarker.
NASA captures images of supersonic shockwaves
09, Mar 2019

NASA has captured unprecedented photos of the interaction of shockwaves from two supersonic aircraft, part of its research into developing planes that can fly faster than sound without thunderous “sonic booms”.
When an aircraft crosses that threshold — around 1,225 km per hour at sea level — it produces waves from the pressure it puts on the air around it, which merge to cause the ear-splitting sound.
In an intricate manoeuvre by pilots at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, two supersonic T-38 jets flew just 30 feet apart below another plane waiting to photograph them with an advanced, high-speed camera.
The rendezvous — at an altitude of around 30,000 feet — yielded mesmerising images of the shockwaves emanating from both planes.
With one jet flying just behind the other, the shocks are going to be shaped differently. This data is really going to help us advance our understanding of how these shocks interact.
Sonic booms can be a major nuisance, capable of not just startling people on the ground but also causing damage like shattered windows and this has led to strong restrictions on supersonic flight over land in jurisdictions like the United States.
About NASA
- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is an independent agency of the United States Federal Government responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research.
- NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA).
- The new agency was to have a distinctly civilian orientation, encouraging peaceful applications in space science.
- Since its establishment, most US space exploration efforts have been led by NASA, including the Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and later the Space Shuttle. NASA is supporting the International Space Station and is overseeing the development of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle, the Space Launch System and Commercial Crew vehicles.
- The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management for unmanned NASA launches.
NASA science is focused on better understanding Earth through the
- Earth Observing System;
- Advancing heliophysics through the efforts of the Science Mission Directorate’s Heliophysics Research Program;
- Exploring bodies throughout the Solar System with advanced robotic spacecraft missions such as New Horizons; and
- Researching astrophysics topics, such as the Big Bang, through the Great Observatories and associated programs.
FOREST SURVEYS
08, Mar 2019

A high-power committee constituted by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has recommended that forest surveys the biennial exercise by the government to estimate forest cover explicitly demarcate trees grown in forests from those grown outside, that is, in plantations and private lands.
About:
- The panel has proposed that the trees in plantations, private lands should not come under survey.
- Currently, the government counts both towards estimating the portion of India’s geographical area covered by forest.
- Independent critics have for long pointed out that including both isn’t an ecologically sound principle but this is a first instance of government-constituted committee recommending so.
- India posted a marginal 0.21% rise in the area under forest between 2015 and 2017, according to the India State of Forest Report (SFR) 2017, which was made public in February 2018.
- The document says that India has about 7,08,273 sq. km. of forest, which is 21.53% of the geographic area of the country (32,87,569 sq. km.).
- Getting India to have at least 33% of its area under forest has been a long-standing goal of the government since 1988.
- Various editions of the SFR have over the years reported the area under forests as hovering around 21%. So the government also includes substantial patches of trees outside areas designated as forests, such as plantations or greenlands, in its assessment.
- The total tree cover, according to this assessment, was 93,815 sq. km. or a 2% rise from the approximately 92,500 sq. km. in 2015.
CCR5 Delta 32
07, Mar 2019

Context
- For just the second time since the global epidemic began, a patient appears to have been cured of infection with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
About the News:
- This is the second Patient to be cured of HIV AIDS
- Both milestones resulted from bone-marrow transplants given to infected patients. But the transplants were intended to treat cancer in the patients, not HIV.
- The transplants were from a donor with a mutation in a protein called CCR5, which rests on the surface of certain immune cells. HIV uses the protein to enter those cells but cannot latch on to the mutated version.
- CCR5 is the protein that He Jiankui, a scientist in China, claimed to have modified with gene editing in at least two children, in an attempt to make them resistant to HIV — an experiment that set off international condemnation.
About CCR5-Delta 32 Mutation:
- The remarkable research breakthrough that appears to have cured the anonymous “London Patient” of HIV is based on a stem cell transplant involving CCR5-delta 32 homozygous donor cells.
- This is the same treatment that cured Timothy Ray Brown, known as the “Berlin Patient” when he received two stem cell transplants in 2007 and 2008.
- HIV uses the CCR5 protein to enter immune cells, but it can’t latch on to cells that carry the delta 32 mutation. IciStem, a consortium of European scientists studying stem cell transplants to treat HIV infection, has a database of 22,000 donors with this HIV-resistant mutation. About 1% of people of Northern European descent, mainly Swedes, are born with a mutation known as CCR5-delta 32, which “locks ‘the door’ which prevents HIV from entering into the cell. This is only going to work if someone has a virus that really only uses CCR5 for entry. Patient would still be vulnerable to a form of HIV called X4, which employs a different protein, CXCR4, to enter cells.
Brown’s Case:
- Dr Hütter put Brown through an allogeneic stem cell transplant, which involved replacing his immune system with donor hematopoietic stem cells (usually found in bone marrow) so that his immune system could be regenerated, with no malignant cells. Importantly however, the donor he chose carried what is called a CCR5-delta 32 mutation.
F 16 Aircraft
02, Mar 2019

In News
- A day after India raked up contract details between the United States and Pakistan on the AMRAAM missile fired from an F-16 aircraft and shared the information with American interlocutors to bolster its case about the misuse of the fighter aircraft against India, the US sought more information on the matter.
About:
- US State Department was seeking more information on the potential misuse of American-made F-16 fighter jets by Pakistan against India in violation of the end-user agreement.
- Due to non-disclosure agreements in Foreign Military Sales contracts, it cannot discuss the specifics of end user-agreements contained within.
- There is enough evidence to show that F-16s were used in this mission and Pakistan is trying to hide this fact.
- Also, parts of AMRAAM air-to-air missile, which is carried only on the F-16s in PAF, were recovered east of Rajouri within Indian territory.
- Tthe contract details and the part of the missile show the use of F-16s in the air strike since the US, which sold the fighter jets to Pakistan, does not allow these platforms to be used in an offensive role.
- Previously Pakistan said that no F-16 fighter jets were used and denied that one of its planes had been downed by the Indian Air Force. It claimed that no F-16 was part of the operation any such admission would violate US sale conditions of not letting Pakistan use F-16s in an offensive role.
Background:
- The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is a single-engine supersonic multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force (USAF).
- Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it evolved into a successful all-weather aircraft.
- The F-16 is a single-engine, highly manoeuvrable, supersonic, multi-role tactical fighter aircraft with a maximum speed of over Mach 2.
- In 2016, India had strongly opposed the US decision to sell eight F-16s to Pakistan, which also could not pass the muster in US Congress for Foreign Military Funding. This meant that the order was never placed.
- The United States, which is the largest seller of high-tech defence equipment globally, and has a strong end-user monitoring agreement, as a matter of practice takes all allegations of misuse of defence articles very seriously.
- But before making any judgement or arriving at any conclusion, it needs to establish some facts on the ground, if there has been any violation by Pakistan to the F-16 end-user agreement it signed by the United States.
- F-16 jets were meant to be used to “enhance Pakistan’s ability to conduct counter-insurgency and counterterrorism operations. Publicly available documents reveal that the US has imposed nearly a dozen restriction on Pakistan related to its use of F-16.
- AMRAAM missiles allow a fighter pilot to target an enemy aircraft that is beyond visual range, in day or night, and in all-weather conditions. The AMRAAM has an autonomous guidance capability, which allows the pilot to manoeuvre immediately after the missile’s launch.
Qrsam Missile
27, Feb 2019

- India on Tuesday successfully test fired the short-range Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missile (QRSAM) from a test range along the coast of Odisha.
About:
- Developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), the QRSAM missile has a strike range of 25 km to 30 km and has a capability of engaging multiple targets. The sleek and highly mobile air defence system has been developed for the Indian Army.
- The indigenously developed QRSAM will replace the ‘Akash’ missile defence system which is on its way out due to technological obsolescence.
- A QRSAM is different from normal air defence system, as this is an all-weather, all-terrain missile with electronic counter measures against jamming by aircraft radars.
- The QRSAM, which has already been tested in the past, was test fired from a rotatable truck-based launch unit at Chandipur in Odisha’s Balasore district. According to sources, two missiles were tested from Integrated Test Range (ITR) at Chandipur.
Background:
- The missile was first tested on June 4, 2017 and this was followed by the second successful test on July 3.
- The test firing comes on a day when a dozen of Indian Air Force fighter jets blew up terror camps across the Line of Control in Pakistan. India launched an airstrike inside Pakistan territory early today in response to the Pulwama attack of February 14 that claimed the lives of 40 CRPF jawans.
- The jets dropped 1,000 kg laser-guided bombs on terrorist camps in Balakot in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, Muzaffarabad, and Chakothi. India’
INDIA’S FIRST INDIGENOUS SEMICONDUCTOR CHIPS FOR 4G/LTE AND 5G NR MODEMS
23, Feb 2019
GS 3: Science & Technology | Indigenization of technology & developing new technology
Why in News?
- A Bengaluru based company SIGNALCHIP has fabricated high performance and cost- efficient semiconductor chips.
- These would enable high-speed wireless communication.
Highlights:
• Four chips designed by SIGNALCHIP
SCBM3412: a single chip 4G/LTE modem including the baseband and transceiver sections in a single device
SCBM3404: a single chip 4X4 LTE baseband modem
SCRF3402: a 2X2 transceiver for LTE
SCRF4502: a 2X2 transceiver for 5G NR standards
Specifications:
- The RF sections cover all LTE/5G-NR bands upto 6 GHz.
- These chips also support positioning using India’s own satellite navigation system, NAVIC. The combined multi-standard system-on-chip (SoC) can serve as a base station chipset for a wide range of form factors from low-cost indoor small cells to high performance base stations. Through the IPs created for devices, the company now has the potential to design products for multiple related fields.
Significance:
- Currently, in India, all devices and infrastructure, whether imported or domestically manufactured, use imported silicon chips. Silicon chip design is a very challenging activity requiring high-cost R&D, deep knowhow and mastery of multiple complex domains.
- Hence, this technology is not available in most countries.
Impact:
- Data Security is the paramount concern in the World today and India cannot remain secure in terms of data, unless it manufactures its own chips.
- India is just breaking into the elite club of the world and this will have huge implications for India’s data security and data sovereignty, besides the positive economic implications.
- At present only 8 companies and a few countries can design and build semiconductor chips.
BRAHMOS
22, Feb 2019

- A sleeker, more lethal version of the supersonic cruise missile BrahMos is under development and the prototype should be ready for testing in about three years.
About:
- The idea is to have a smaller missile with the same capabilities. So the missile will fly at 3.5 times the speed of sound instead of 2.8 Mach. The range will remain at 300 km.
- For this several mechanical components in the missile are being replaced with electrical components which will also reduce the size. A structural study has been carried out and several sub-systems have already been developed.
- BrahMos is a joint venture between India and Russia and named after Brahmaputra and Moscowa rivers. It is capable of being launched from land, sea, sub-sea and air against surface and sea-based targets. The development trials of an anti-shipping variant began in 2003 and combat trials began in 2005.
- The reduced weight enables the NG variant to be carried by the indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA). An LCA can carry two missiles while a Su-30MKI can carry five of them.
Tejas – FOC
21, Feb 2019

- More than three-and-half decades after the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) or Tejas was conceived, the programme got a shot in the arm as it was accorded the Final Operational Clearance (FOC) by aviation certifying authorities, raising the hope of the Indian Air Force (IAF) that has been grappling to cope with its ageing fleet.
About:
- The release to service document, known as FOC, was handed over at the ongoing Aero India in Bengaluru. The LCA, that began as an ambitious programme in 1983, had proved that it could not just sustain a very high sortie rate but also carry out accurate weapon delivery of both air-to-air and air-to-ground targets.
- The FOC coming at a time when several defence procurements of successive governments have been held to public scrutiny over alleged scams and kickbacks, especially in the run up to the parliamentary elections, scheduled to be held later this year.
- Procedural delays among other hurdles has had a crippling effect on the Indian armed forces who are forced to continue using outdated technology, weapons and systems despite the consistently swelling defence budget.
- The IAF’s interests in acquiring more Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) developed products raising the hope for the cash strapped public sector unit, whose fortunes and order books have slimmed down in recent years.
AERO India – 2019
21, Feb 2019

Asia’s biggest air show Aero India-2019 will open Yelahanka air force station in Bengaluru, showcasing aerospace majors and their technologies and products, which include helicopters, fighter jets and transport aircraft.
About:
- The 12th edition of Asia’s premier show will be a five-day-long biennial event, exhibiting India’s defence prowess will also have aerobatic teams like India’s Sarang (ALH-Dhruv) and UK-based Yakovlevs will engross the audience present at the show.
- The will also be a platform for aviation companies to forge new alliances and contracts.
- Aero India 2019 endeavours to put India as the global runway of a billion opportunities as invitees includes Ministers, heads of global defence aerospace companies, corporate and government policymakers, military brass, entrepreneurs, delegates and exhibitors from across the world were at the event. After many years, the edition brings civil aviation back to a largely military show. The Ministry said it was the biggest so far, with 403 exhibitors and 61 aircraft in static or flying displays. 61 metal birds, including HAL’s indigenous products Light Combat Aircraft Tejas will soar high in the city’s skies. On static display will be HAL’s Light Utility Helicopter (PT-1), Light Combat Helicopter (TD-2), Advanced Light Helicopter (Rudra) and ALH MICU (Medical Intensive Care Unit).
- However, the event will be shrouded by the tragic death of an Indian Air Force (IAF) pilot from its aerobatic team Surya Kiran during the rehearsal earlier. Two British-origin Hawk advanced jet trainers collided and crashed mid-air during a rehearsal session.
- Another controversy surrounding this edition of the event were reports that it has been shifted to Uttar Pradesh, leading the state government to lash out at the central government for the alleged move.
- According to the Aero India official website, a total of 61 aircraft will be put on display and 403 exhibitors will be a part of the 5-day event.
Study Magnitude of Substance use in India
20, Feb 2019
- An estimated 16 crore Indians in the age group of 10-75 are consumers of alcohol and around 4.6 lakh children are addicted to inhalant drugs.
About:
- The first countrywide survey commissioned by the Union government on the extent of substance abuse has found that these children are in dire need of help.
- The study Magnitude of Substance Use in India revealed that close to 15 in every hundred Indians consume alcohol band more than five per cent needed medical help to tackle dependence on substance. The survey was conducted by the National Drug Dependence Treatment Centre (NDDTC) under the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, and were released
- The study defines users who have used substances in nine categories, namely — alcohol, cannabis, opioids, cocaine, sedatives, inhalants and hallucinogens – at least once in past 12 months.
Findings
- The study said that 14.6 per cent Indians were found to be alcohol users while 5.2 per cent wanted help. Close to 1.6 crore people in Uttar Pradesh have been found to suffer from alcohol dependence or consumed it in a harmful way. In Bengal, 27 lakh people have consumed alcohol while the figure for Odisha stands at 21 lakhs.
- The number assigned to a state is the extrapolated figure to match the population share of the state. Hence Utter Pradesh is found to have the highest number of harmful and dependent users of alcohol and other substances.
- Tripura (13.7 per cent), Arunachal Pradesh (7.2 per cent) and Chhattisgarh, Punjab and Andhra Pradesh (around 6 per cent each) were the states with highest prevalence of alcohol dependence. The survey found that alcohol dependence is lesser in states where prohibition in in force. For example, only 0.9 per cent of the population in Bihar and 3.9 in Gujarat were found to be alcohol users.
- According to the study, cannabis users number around 3.1 crore; opioid users 2.25 crore; sedative users 1.18 crore; hallucinogen users 12.6 lakh and cocaine users 10 lakh.
- The states which have recorded use of cannabis more than the national average include Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, Sikkim, Chhattisgarh, and Punjab.
- In terms of percentage of population affected, the top states in the country are those in the Northeast — Mizoram, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Manipur.
- The current survey also points that heroin use prevalence is higher than 2004 and has, in fact, surpassed the opium use. Currently, the prevalence of heroin use is twice as much of opium use in total population.
- Nationally, it is estimated that there are about 8.5 lakh people who inject drugs.
The Last of the Elusive Pangolins
19, Feb 2019

- Obsession for its supposedly medicinal scales in China is believed to have made the ant-eating Chinese Pangolin, one of two species found in South Asia, extinct in India.
- The pangolin is the most trafficked mammal in the world.
- Though hunted for its meat across the north-eastern States and in central India
- The Demand for its scales in China has made it the most critically endangered animal in less than a decade.
- On World Pangolin Day, wildlife experts mourned the “possible extinction” of the Chinese Pangolin in the northeast and the likelihood of the Indian Pangolin found elsewhere in India of being wiped out in a decade or so. The third Saturday of February is observed as the day of the scaly nocturnal ant-eater, which activists say is an animal very few even forest officials know about.
- The Chinese Pangolin was officially categorised as critically endangered in 2014, but it is extinct today. The Indian Pangolin, marked endangered that year, is now critically endangered and disappearing fast,”
- The STF had busted one of the biggest international gangs of wildlife body parts smugglers. It arrested 159 people across 14 States and registered 12 cases, mostly for pangolin scale smuggling.
Northeastern gateway:
- Investigations by wildlife crime sleuths have revealed that almost 90% of smuggling of pangolin and pangolin scales is through the northeast.
- From elsewhere in India, the scales are smuggled out to China via Myanmar at Moreh in Manipur and Champhai in Mizoram. But there are numerous gateways along the border with Myanmar. This is why checking the smuggling network in the northeast is crucial for the survival of the last of the pangolins.
- Smaller animals like pangolins get indirect benefit of the focus on larger ones such as rhino, tiger, and elephant.
Killed Cruelly:
- Sadly, there is no survey of pangolin, which get smoked out of their burrows and killed cruelly by being thrown into boiling water. The animal used to be killed for meat until people learnt there was illegal money in its scales.
- The Chinese Pangolin has not gone the way of the dodo. Conservation policies have to look beyond major species, but the world needs to tell China that pangolin scales – like rhino horns – are made of keratin that produces human hair and nails and has no medicinal value.
DRDO Looking for Partnership
19, Feb 2019

- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is looking for potential partners to co-develop an engine for its planned Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) and five other future technologies.
About:
- It is on the lookout for collaborators to realise the other military technologies that it hopes to have in around five years Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicles (UCAVs) and UAVs, materials, sensors, avionics, and artificial intelligence, he said at the inauguration of a two-day international seminar connected with Aero India 2019.
- In all six areas, DRDO looking for partners with the capability and experience, within the country or outside. An aeroengine of the 110-kilo Newton type that we want for the AMCA is not available. Materials development is another very important area for making aircraft or missiles light and stealthy [or undetected]..
- Industry would be enlisted at the beginning of a project so that it can begin production as a natural partner. At present, the focus is on consolidating ongoing R&D activities and ensuring they reach the logical end.
- Indigenous technologies were being given a push. Minor innovators and startups are also being tapped for new concepts that the DRDO can try out. The new time-bound ‘Dare to Dream’ challenge has received 1,000 responses from individuals and startups.
Obesity Linked Cancers on Rise in Young Adults
05, Feb 2019

Study says diet, exercise is key to reducing body weight:
- The risk of developing obesity-related cancer is increasing in successive generations, along with increasing rates of obesity.
- The incidence of 30 of the most common cancers, including 12 that are obesity related, from 1995 to 2014 in people ages 25-84 — more than 14.6 million cases. The study was published is in Lancet Public Health.
- Using five-year age cohorts, they found that for six of the 12 obesity-related cancers (multiple myeloma, colorectal, uterine, gallbladder, kidney and pancreatic) the risk for disease increased in adults in the 25- 49 age bracket, with the magnitude of the increase’s steeper with younger age.
- For example, compared with people born in 1950, those born in 1985 had a risk of multiple myeloma 59% higher, and a risk of pancreatic cancer more than twice as high at comparable ages. At the same time, incidence decreased for smoking-related and infection-related cancers.
- Diet and exercise are of course essential in reducing obesity rates, but that interventions by health care professionals are also needed and only a third of obese patients actually get a diagnosis of and counselling for obesity.
Microbial Fuel Cell treats Textile Wastewater
03, Feb 2019

The Power Generated in degradation Can be used to Sustain the Process:
- Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are fast emerging as an option for several specific requirements.
- The principle of using the MFC to degrade wastewater is simple. A carefully selected cohort of bacteria is made to act on the textile wastewater placed in the fuel cell.
- These bacteria are isolated from the very wastewater they are meant to degrade. They feed on the organic material in the water and break it down under anaerobic (without oxygen) conditions, releasing electrons in the process. The electrons are collected at the anode which results in a current in the circuit. Because the bacteria form a biofilm on the anode, the electrons are collected easily by it.
- “After a period, when the thickness of the biofilm exceeds a limit, it will automatically detach and bring back the thickness to optimal level. A nanotech filter is required to improve this process. “This is like a ‘trickling filter’ – where after thickness exceeds a limit, and it is difficult to sustain that thickness, the excess tears off. When it falls off, it shouldn’t get mixed up with the water. That’s where the nanotechnology filter will come in, to remove the bacteria and get clean water.
- The bacteria take turns to act on the wastewater and purify it: There are many species of bacteria. If a dye is present in the water, it is broken to a simpler form by one species; this, in turn, is acted on by another species and so on. “It has a cascading effect.
- Using MFC to process wastewater was an idea that the two used in the Carbon zero challenge, a competition hosted by IIT Madras when they were students there. They used the funding obtained through the event to develop the 200 litre prototype within the few months they were given. “We spoke to some people [in the textile industries] at Tiruppur, and they said that if it is cheaper and more energy efficient than current technologies, we will use it.
- While now, with the prototype, they can generate power of around 1 watt per square-metre, they aim to get to about 5 watts per square-metre. This power can be used to sustain the process. However, scaling up has challenges. The size of the chamber and its geometry and design remain to be worked out. All the power produced must be captured so that it is not wasted. “For that, we will work with some electrical engineers.
Nilavembu Kudineer Kills Dengue Virus, Protects from Chikungunya
03, Feb 2019

The siddha drug showed significant antiviral activity, Immuno-Modulation:
- Under in vitro conditions, nilavembu kudineer (a Siddha medicine) was found to provide protection against chikungunya virus while it was effective as a treatment during acute phase of dengue infection. Dengue subtype-2, which is the most prevalent subtype in India, was used for testing the formulation.
- There was significant antiviral activity of the formulation at 3% of human dose onwards. Currently, there is no treatment for dengue and chikungunya.
Mode of Action:
- A team of researchers from the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB), Delhi found that thenilavembu kudineer formulation was modulating the host response in the case of both chikungunya and dengue virus but in a different manner.
- The mode of action of the concoction is antiviral in the case of dengue while immuno-modulatory in chikungunya infection. “The reason why we say the formulation is immuno-modulatory is because of the way nilavembu kudineer acts upon viral infections in different types of cells. However, the mode of action of the formulation on immuno-modulation is yet to be understood.
- To study the antiviral activity, the researchers tested the formulation on monocytes and macrophages in the case of dengue and epithelial kidney cells for chikungunya virus. “The monocytes and macrophages are the primary sites of infection in the case of dengue.
- And kidney is the secondary site of infection by chikungunya virus. The primary site of infection of chikungunya virus is fibroblasts before the virus enters the blood stream and then to different organs.
- The joints are the worst affected due to chikungunya virus infection. But we don’t have primary joint cell lines to test the formulation at this point.
Safety studies:
- Safety studies showed that nilavembu kudineer concoction was non-toxic starting from 3% (about 1.8 milligram per millilitre) of human dose. However, the researchers found that andrographis, which is the active ingredient ofnilavembu kudineer, when used alone was extremely toxic at 3% of human dose.
- Human dose is prepared by mixing 5 grams of nilavembu kudineer in 240 ml of water. It is then boiled and reduced to 30 ml and consumed.
- “This shows that nilavembu kudineer as a formulation is safe for use in humans. The cytotoxicity of andrographis reduces drastically when given as a concoction with other ingredients of nilavembu kudineer. The nilavembu kudineer herbal concoction is made by mixing nine ingredients in equal measure.
- “The importance of herbal medicines lies in the fact that they use plant as a whole. This is important because if the modern concepts are used in alternative medicine and only active component is separated, then it will cease to act as a herbal medicine and will plainly act as a chemical drug which can be highly toxic/hazardous to the human body.
- “Based on the results of our study we see the formulation working well for dengue and chikungunya infections especially during outbreak conditions.
- Based on the positive results from in vitro studies, the researchers are in the process of studying the safety and mode of action of the formulation using mice models.
Non-Communicable Disease are top killers in SE Asia
29, Jan 2019

Context:
- As per the WHO report the non-communicable diseases like Diabetes, cancer and heart disease responsible for over 70% of deaths worldwide.
Details:
- Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) — mainly cardiovascular diseases, chronic respiratory diseases, diabetes and cancer — continue to be the top killers in the South-East Asia Region, claiming 8.5 million lives each year.
WHO Goal:
- Containing the NCDs has been listed by the WHO as its health goal for this year along with reducing mortality related to air pollution and climate change, global influenza pandemic etc.
The Cause for Concern:
- “One third of these deaths are premature and occur before the age of 70, affecting economically productive individuals. This results in the lost of loved one and people serving our Nation. The NCDs disproportionately affect the poor, impoverish families, and place a growing burden on health care systems.
- Non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, cancer and heart disease, are collectively responsible for over 70% of all deaths worldwide, or 41 million people. These include 15 million people dying prematurely, aged between 30 and 69.
Causes:
- The four ‘major’ NCDs are caused, to a large extent, by four modifiable behavioural risk factors: tobacco use, unhealthy diet, insufficient physical activity and harmful use of alcohol.
Way Forward for Humanity:
- Consuming fibre and whole grains can reduce health risks from non-communicable diseases such as heart disease.
- Eating fibre-rich foods reduces the incidence of coronary heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes and colorectal cancer by 16% to 24%. A higher fibre intake is also associated with lower bodyweight, systolic blood pressure and total cholesterol when compared with lower intake.
- Doctors then recommend — eat less and enjoy your food by eating slowly, fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables, avoid oversized portions which causes weight gain, at least half of your grains should be whole grains, limit consumption of food high in trans fats.
ISRO EYES KEROSENE TO BOOST GSLV MK3
28, Jan 2019

In News
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is working on upgrading its heavylifter GSLV Mk III where the upper stage of the rocket will have highly refined form of kerosene as fuel in order to increase its payload capability.
Explained
- To increase the payload capability of GSLV Mk III from 4 tonnes to 6 tonnes, we are in the process of making some improvements in rocket stages.
- According to ISRO, First, ISRO is working on enhancing the cryogenic stage fuel loading from 25 tonnes to 30 tonnes. Second, ISRO is also working on changing the core stage L110 — which has 110 tonnes of unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) and dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4)
- ISRO want to replace L110 stage with semi cryogenic engine that will carry liquefied oxygen and highly refined kerosene called kerolox (aka RP-1) instead of liquefied hydrogen.
- The rocket with the semicryogenic stage won’t be used for the Gaganyaan mission. The current GSLV Mk III with L110 stage will only be used for the manned mission with some modifications.The advantage of using kerolox is that it is 10 times dense— meaning the same volume of kerolox will generate more thrust than the same volume of hydrolox. It is also cheaper, more stable at room temperature and less hazardous than hydrolox. Elon Musk-promoted Space X currently uses kerolox in its Falcon 9 rocket for launching heavy payloads.
- With increase in payload capacity, the advanced GSLV MK III will help Isro cut expenses and save time. Currently, India uses the services of Arianespace to launch its heavy satellites weighing over 4 tonnes. Last year on December 4, ISRO had used the services of Arianespace for launching its heaviest satellite Gsat-11 weighing over 5.7 tonnes from French Guiana.
GSLV Mk III
- GSLV Mk III is a three-stage heavy lift launch vehicle developed by ISRO. The vehicle has two solid strap-ons, a core liquid booster and a cryogenic upper stage. GSLV Mk III is designed to carry 4-ton class of satellites into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) or about 10 tons to Low Earth Orbit (LEO), which is about twice the capability of GSLV Mk II.
Technical Specifications
Payload to GTO: 4,000 kg
- GSLV Mk III will be capable of placing the 4 tonne class satellites of the GSAT series into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbits.
Payload to LEO: 8,000 kg
- The powerful cryogenic stage of GSLV Mk III enables it to place heavy payloads into Low Earth Orbits of 600 km altitude.
Cryogenic Upper Stage: C25
- The C25 is powered by CE-20, India’s largest cryogenic engine, designed and developed by the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre.
Solid Rocket Boosters: S200
- SLV Mk III uses two S200 solid rocket boosters to provide the huge amount of thrust required for lift off. The S200 was developed at Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre.
Core Stage: L110 Liquid Stage
- The L110 liquid stage is powered by two Vikas engines designed and developed at the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre.
Monkey Fever Cases Confirmed in Wayanad
24, Jan 2019

Context:
- A case of Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD), a viral disease transmitted to humans through a species of ticks usually found on monkeys, has been reported from the Aranappara hamlet at Appapara, near Tirunelly, in Wayanad district after an interval of two years.
Details:
- The 36-year-old patient, who is at the District Hospital, Mananthavady, is reportedly out of critical condition. The samples collected from the patient were sent to the Manipal Centre for Virus Research and it had been confirmed as a case of KFD, District Medical Officer R. Renuka told The Hindu.
- Meanwhile, a 27-year-old from the area was referred to the Government Medical College Hospital, Kozhikode, with symptoms of the disease. They were working in a farm at Bairakuppa in Karnataka and admitted to the District Hospital on January 20 with symptoms of the disease, Dr. Renuka said. Surveillance have been stepped up in forest areas on the Wayanad- Karnataka border, district surveillance officer Noona Marja said.
- Meanwhile, the district administration, in association with the Health Department, has intensified preventive measures, including a vaccination drive, to combat KFD.
Medicine Stock:
- “Though we have stocked 350 doses of KFD vaccine, the drive is facing a setback in villages on the fringes of forests as many are not ready to accept vaccination,” Dr. Noona Marja said.
- “However, we advised them to use personal protection measures, including gloves and gumboots as well as repellent lotions, before they enter forest.” The first case of the disease was reported in the district in 2013. The virus wreaked havoc in the district in 2015 when 102 cases were reported and 11 persons died of the disease. Nine cases were reported in 2016. Though two suspected cases were reported in 2017, not a single case was reported last year, Dr. Renuka said.
ISRO to Launch Military Satellites
24, Jan 2019

Context:
- Just before midnight on Thursday, Indian Space Research Organisation’s first mission of 2019 will put into space a 740-kg military imaging satellite, Microsat-R.
Details:
- ISRO has shied away from sharing details of the spacecraft or its uses as it does routinely each time during its missions; except to say the satellite would be placed within 15 minutes after take-off in a polar orbit 274 km away from Earth.
- This is much lower than any of its civil Earth observation spacecraft, which fly pole to pole over the globe at between 400 km and 700 km.
- According to information obtained from different sources Microsat-R and its payload come assembled from a handful of laboratories of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and is meant for military use. The satellite was “assembled outside and ISRO only interfaced it” with its own systems and the launch vehicle, just as it treats any customer satellite.
- C-44 will be launched around 11.30 p.m. from the older First Launch Pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
- For its part, ISRO is experimenting on two aspects of the vehicle. One is to reuse a waste stage. “For us, the excitement is about reusing the spent fourth stage [PS4] of the rocket as an orbiting platform for future experiments,” an official said. Kalamsat, a small student payload, will be the first to use PS4 as an orbital platform.
- Amid the 28-hour countdown for the launch, ISRO Chairman K.Sivan said the PS4-Kalamsat experiment would be short-lived. It would start about 1.5 hours from take-off and last about 14 hours until Friday midday. Later experiments with PS4 will be improved gradually, he said.
- For the third time in ISRO’s recent history, the mission team is slated to cut off and restart the PS4 engine twice over a flight lasting around 100 minutes.
- ISRO’s pre-launch brochure said, “In PSLV-C44, the fourth stage (PS4) of the vehicle will be moved to higher circular orbit so as to establish an orbital platform for carrying out experiments.” The other experiment with the launcher PSLV-C44 vehicle will be a new third variant having two strap-on boosters. Called the PSLV-DL, D standing for demonstration, it ranges between the older two variants.
Chinese Doctor Who Gene – edited Babies for ‘FAME’ to face Probe
22, Jan 2019
In News:
- A researcher who claimed to have created the world’s first genetically-edited babies will face a Chinese police investigation, State media said, as authorities confirmed that a second woman fell pregnant during the experiment.
Explained:
- He Jiankui shocked the scientific community last year after announcing he had successfully altered the genes of twin girls born in November to prevent them from contracting HIV.
- The provincial government probe found He had “forged ethical review papers” and “deliberately evaded supervision
- He had “privately” organised a project team that included foreign staff and used “technology of uncertain safety and effectiveness” for illegal human embryo gene-editing,
- But such gene-editing work is banned in most countries, including China. Mr. He will be “dealt with seriously according to the law,” and his case will be “handed over to public security organs for handling
- He said the twins’ DNA was modified using CRISPR, a technique which allows scientists to remove and replace a strand with precision.
What is Gene Editing?
- Genome editing (also called gene editing) is a group of technologies that give scientists the ability to change an organism’s DNA.
- These technologies allow genetic material to be added, removed, or altered at particular locations in the genome. Several approaches to genome editing have been developed.
- A recent one is known as CRISPR-Cas9, which is short for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats and CRISPR-associated protein 9. The CRISPR-Cas9 system has generated a lot of excitement in the scientific community because it is faster, cheaper, more accurate, and more efficient than other existing genome editing methods
- CRISPR-Cas9 was adapted from a naturally occurring genome editing system in bacteria. The bacteria capture snippets of DNA from invading viruses and use them to create DNA segments known as CRISPR arrays. The CRISPR arrays allow the bacteria to “remember” the viruses (or closely related ones).
- If the viruses attack again, the bacteria produce RNA segments from the CRISPR arrays to target the viruses’ DNA. The bacteria then use Cas9 or a similar enzyme to cut the DNA apart, which disables the virus.
Human Genome editing:
- Genome editing is of great interest in the prevention and treatment of human diseases. Currently, most research on genome editing is done to understand diseases using cells and animal models. Scientists are still working to determine whether this approach is safe and effective for use in people.
- It is being explored in research on a wide variety of diseases, including single-gene disorders such as cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, and sickle cell disease. It also holds promise for the treatment and prevention of more complex diseases, such as cancer, heart disease, mental illness, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection.
- Ethical concerns arise when genome editing, using technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9, is used to alter human genomes. Most of the changes introduced with genome editing are limited to somatic cells, which are cells other than egg and sperm cells.
- These changes affect only certain tissues and are not passed from one generation to the next. However, changes made to genes in egg or sperm cells (germline cells) or in the genes of an embryo could be passed to future generations.
- Germline cell and embryo genome editing bring up a number of ethical challenges, including whether it would be permissible to use this technology to enhance normal human traits (such as height or intelligence). Based on concerns about ethics and safety, germline cell and embryo genome editing are currently illegal in many countries.
NAIR Rues delay in Human spaceflight Plan
14, Jan 2019

What’s in the news?
- Former ISRO chief attributes delay to political factors and changed priorities
- India could have put an astronaut in space in 2015 had the original plan for the human spaceflight programme worked out, former ISRO chairman G. Madhavan Nair has said.
- Madhavan Nair, who headed the space agency from 2003 to 2009, attributed the delay to political factors and the changed priorities of the subsequent ISRO management.
- “But it’s never too late. ISRO now has a strong chairman in K. Sivan. The human spaceflight mission will be a turning point in the Indian space programme,” he told The Hindu on Friday, responding to ISRO’s formal announcement that it plans to put three Indians in space in December 2021.
- According to Madhavan Nair, it was in 2005 that ISRO decided that it was time to think beyond the grand vision of Dr. Vikram Sarabhai. “Dr. Sarabhai wanted India to achieve self-reliance in satellite building, launch vehicle technology and, more importantly, ensure that the common man benefited from these technologies. We took a review in 2005. The question was, what next?” recalls Mr. Nair.
Natural choice:
- The human spaceflight programme was a natural choice as a target for the future, he said.
- “Human access to space had become very important for various reasons. One, ISRO had improved in terms of launch vehicle technology. Second, if we are to send humans to the Moon and Mars, we have to make a beginning,” he said.
- In 2008, ISRO prepared a project report and submitted it to Space Commission. The same year, a small team was formed at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) to study various aspects of spaceflight and the technologies that such a venture called for. It was headed by S. Unnikrishnan Nair, who was appointed project director, Human Spaceflight Programme (HSP). The team consisted of 10 to 12 people.
Green light:
- “In 2009, the Planning Commission gave the green light for the programme.
- “In 2009, the plan was to have the mission in six years. So, by 2015, we would have been flying in earth orbit. But unfortunately, due to various political factors and probably, the attitude of the subsequent management in ISRO it was put in cold storage,” he said.
About India’s Human spaceflight:
- Prime Minister announced that India will send an astronaut to space in the year 2022. He was addressing the nation on India’s 72nd Independence Day. “I make this announcement today, before 2022, an Indian astronaut – son or daughter – will be in space. One of us will carry the tricolour to the space to commemorate the 75th year of India’s Independence.”
- The name of the mission is Gaganyaan and it is a crewed orbital spacecraft expected to carry 3 members on board.Gaganyaan joins Chandrayaan-1, India’s first lunar probe, and Mangalyaan, the Mars Orbiter Mission project, orbiting Mars.With this, India could potentially become the fourth country to send a man to space, after the erstwhile USSR, the US and China. Denmark also has a manned space flight scheduled for 2022.
- The total programme is expected to be complete before 2022. Two unmanned Gaganyaan missions will be undertaken prior to sending humans. As per ISRO schedule, the first and second unmanned flights would be sent in orbit within 30 and 36 months beginning from August 2018.
- GSLV Mk III, the three-stage heavy lift launch vehicle, will be used to launch Gaganyaan as it has the necessary payload capability. The mission is estimated at Rs 9,000 crore.
AI beats Doctors at detecting early stage Cervical Cancer
12, Jan 2019
Context:
- Artificial intelligence may be poised to wipe out cervical cancer, after a study showed on Thursday that computer algorithms can detect pre-cancerous lesions far better than trained experts or conventional screening tests.
Details:
- According to the World Health Organization, cervical cancer is the fourth most frequent cancer in women with an estimated 570,000 new cases globally in 2018.
- Despite major advances in screening and vaccination, which can prevent the spread of human papillomavirus which causes most cases of cervical cancer, those gains have mainly benefited women in rich nations.
- Some 266,000 women died of cervical cancer globally in 2012, 90% of them in low-and middle-income nations, according to the WHO.
- This is has much linked the disease cervical cancer with the economic status of the patient.
- Hence there raises a necessity to find extremely cheap, easy and yet accurate method to detect and wipe out cervical cancer.
- According to a report, the AI technique, called automated visual evaluation, found precancerous cells with 91% accuracy.
- The goal is to roll out the technology in the next three to five years, enrolling more patients in clinical trials worldwide, says the study.
About AI:
- An intelligence exhibited by machines
- It is a branch of computer science which deals with creating computers or machines as intelligent as human beings. It is a simulation of human intelligence processes such as learning (the acquisition of information and rules for using the information), reasoning (using the rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction by machines, especially computer systems.
- Nowadays it has become an umbrella term which encompasses everything from robotic process automation to actual robotics.
Areas of AI technologies:
- Robotic process automation: Automation is the process of making a system or processes function automatically. Robots can be programmed to perform high-volume, repeatable tasks normally performed by humans and further it is different from IT automation because of its agility and adaptability to the changing circumstances.
- Natural language processing (NLP) is the processing of human language and not computer language by a computer program. For Example, spam detection, which looks at the subject line and the text of an email and decides if it’s junk.
- Pattern recognition is a branch of machine learning that focuses on identifying patterns in data. Machine vision is the science of making computers visualize by capturing and analyzing visual information using a camera, analog-to-digital conversion, and digital signal processing. It is often compared to human eyesight, but machine vision isn’t bound by biology and can be programmed to see through walls. It is used in a range of applications from signature identification to medical image analysis.
- Machine learning: Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. Deep learning is a subset of machine learning and can be thought of as the automation of predictive analytics.
- Robotics is a field of engineering focused on the design and manufacturing of robots. Robots are often used to perform tasks that are difficult for humans to perform or perform consistently.
National Strategy on Artificial intelligence:
- It is unveiled by NITI Aayog and it has identified five sectors – healthcare, agriculture, education, smart cities and infrastructure and transportation and hence to to focus its efforts towards implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) to serve societal needs.
- AI refers to the ability of machines to perform cognitive tasks like thinking, perceiving, learning, problem solving and decision making
- This strategy helps to focus on to leverage the transformative technologies to ensure social and inclusive growth in line with the developmental agenda of the government
ISRO Cranks up GAGANYAAN Project
12, Jan 2019

Context:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) said work on ‘Gaganyaan’, the project to send a manned mission to space by 2022, would start soon at the newly created Human Space Flight Centre (HSFC).
Details:
- According to ISRO, Gaganyaan has taken high priority now and the Human Space Flight Centre would carry out all activities related to the human programme, under which Gaganyaan project would function.
- The project has also got government approval and budget for putting three astronauts in space for seven days.
About the Gaganyaan Mission:
- It will be India’s first manned space mission.
- Under it, India is planning to send three humans (Gaganyatris) into space in low earth orbit (LEO) by 2022 i.e. by 75th Independence Day for a period of five to seven days.
- The mission was announced by Prime Minister during his 72nd Independence Day speech.
- Under this mission, crew of three astronauts will conduct experiments on microgravity in space.
- The crew will be selected jointly by Indian Air Force (IAF) and ISRO after which they will undergo training for two-three years.
- India will be fourth nation in the world after USA, Russia and China to launch a human spaceflight mission.
- Enhancement of science and technology levels in the country, serve as national project involving several institutes, academia and industry, improve of industrial growth, inspire youth, develop technology for social benefits and improve international collaboration.
Satellite Images help Assess Poverty
10, Jan 2019

Details:
- High-resolution satellite data can precisely assess the status of poverty at household level in rural areas of developing countries, according to a study.
- According to a study, if countries are to achieve the U.N. sustainable development goals, it is particularly important to track the living conditions in poor nations around the world where the future population growth is highest.
- Based on high-resolution satellite images, the status of poverty at household level in rural areas in developing countries can be precisely assessed.
Applications of Satellites:
- The reconnaissance satellites are used to spy on other countries, they provide intelligence information on the military activities of foreign countries, they can detect the missile launches or the nuclear explosions in space.
- The ocean surveillance satellites are used to search for the ships or the submarines, they can spot the nuclear vessels, and new advancements may allow them to scan the depths of the ocean.
- The satellites provide the meteorologists with the ability to see the weather on a global scale The satellites are used in the field of oceanography, use the satellites to detect the oceans affect on environment; they can analyze the wave patterns.
- The satellites are the best sources of data for the climate change research, they monitor the ocean temperatures and the prevailing currents, the data acquired by the satellite-borne radars were able to show the sea levels have been rising by three mm a year over the last decade.
- Imaging satellites can measure the changing sizes of the glaciers which is difficult to do from the ground due to the remoteness and darkness of the Polar Regions, the satellites can determine the long-term patterns of the rainfall, the vegetation cover, and the emissions of the greenhouse gases.
- Earth observation satellites can monitor the ocean and the wind currents, the extent of the forest fires, the oil spills, and the airborne pollution, this information helps organize the emergency responders and the environmental clean-up.
NASA’S Probe Discovers a New Planet
09, Jan 2019

Context:
NASA’s latest planet-hunting probe has discovered a new world outside our solar system, orbiting a dwarf star 53 light years away.
Details:
- This is the third new planet confirmed by the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) since its launch in April last year.
- The planet, named HD 21749b, orbits a bright, nearby dwarf star about 53 light years away, in the constellation Reticulum, and appears to have the longest orbital period of the three planets so far identified by TESS.
About Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite
- The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is a space telescope for NASA’s Explorers program, designed to search for exoplanets using the transit method in an area 400 times larger than that covered by the Kepler mission.
- It was launched on April 18, 2018 atop a Falcon 9 rocket. During its 2-year primary mission, it is expected to find more than 20,000 exoplanets, compared to about 3,800 exoplanets known when it launched.
- The primary mission objective for TESS is to survey the brightest stars near the Earth for transiting exoplanets over a two-year period.
- The TESS satellite uses an array of wide-field cameras to perform a survey of 85% of the sky. With TESS, it is possible to study the mass, size, density and orbit of a large cohort of small planets, including a sample of rocky planets in the habitable zones of their host stars.
Navy to set up New Air base in Port Blair
08, Jan 2019

Context:
- The Navy to commission a new airbase 100 miles north of Port Blair in the strategically located Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Details:
- Upon commission, this will be India’s fourth air base and the third naval air facility in the archipelago, which are closer to Southeast Asia than to the Indian mainland, overlooking key sea lanes of communication and strategic choke points. According to the officials, the base will initially operate choppers and Dornier short-range surveillance aircraft and will have a runway of about 3,000 m which will in phases be extended to 9000 m to support all kinds of aircraft including fighter jets.
- As part of the upgrade, the base will feature staging facilities, a fuel dump and maintenance and repair facilities.
Scientists Boost Plant Yield by 40%
07, Jan 2019

Context:
- Researchers have found a way to boost the plant growth genetically.
Details:
- Scientists have confirmed 40% increase in tobacco plant productivity using their genetic shortcut.. The same mechanism could be replicated in other plants such as wheat or soy beans in order to meet demand.
- According to the research, the enzyme ‘Rubisco’, which is a key to carbon fixation process (converting atmospheric carbon into an organic compound, consumed by plants), also acts to fix atmospheric oxygen, converting it into toxic compounds that the plant expends considerable energy eliminating it. This competing process is called photorespiration. The scientists have discovered that implanting bits of algae DNA into the tobacco plant’s cells to create a type of biological shortcut would speed up the process of photorespiration.
- According to them, when a plant uses less energy on photorespiration, it will be able to take that energy and put it into plant growth and plant productivity, rather than using it to metabolise this toxic compound.
Chinese Lunar Rover Named as ‘YUTU 2’
05, Jan 2019

Context:
- China has named the lunar rover, successfully deployed to carry out a string of experiments on the unexplored far side of the moon, as ‘Yutu 2’.
Details:
- It is said that China’s lunar probe is part of its ‘Made in China-2025’ project, which focuses on advanced technology, including space applications.
- The lunar rover follows the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System — China’s homegrown Global Positioning System that started worldwide service last month. Next year China plans to launch its Mars explorer mission. In 2022, it hopes to complete its own earth-orbiting space station. The rover has been programmed to launch ground penetration radar that would help map the moon’s inner structures. It would also analyse soil and rock samples for minerals, apart from activating a radio telescope to search for possible signals from deep space.
About Lunar Rover:
- The lunar rover has been launched to experiment the far side of the moon.
- The robotic spacecraft is carrying instruments to analyse the unexplored region’s geology and will conduct biological experiments.
- This is the pioneering achievement as earlier moon missions that have landed only on the Earth-facing side, this is the first time any craft has landed on the unexplored and rugged far side of the moon.The scientific tasks of the mission include low-frequency radio astronomical observation, surveying the terrain and landforms, detecting the mineral composition and shallow lunar surface structure, and measuring the neutron radiation and neutral atoms to study the environment on the far side of the moon.
Improved Light combat Aircraft gets green Light for Production
04, Jan 2019

Context:
- Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas progressed towards manufacture in an enhanced, battle standard format.
Details:
- The LCA is being designed and developed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) in Bengaluru.
- A new limited clearance from military airworthiness certifier CEMILAC for the Indian fighter green-lights its production in a superior lethal version.
- HAL aims to get the first aircraft out in late 2019.
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) has asked Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) to make 40 LCA aircraft.
- Of this, 20 will be in the advanced Final Operational Clearance (FOC) format. Another 20 are in the earlier Initial Operational Clearance (IOC) version.
- The IAF has modified and upgraded its trainer requirement in its old package order of 40 LCA aircraft.
Light Combat Aircraft:
- A Light combat aircraft is a light multirole military aircraft most coming from advanced trainers that have been modified or designed for engaging in light combat missions, either in light strike or attack missions, reconnaissance or interdiction roles while some keeping its trainer role.
- They are also slower than their bigger counterparts capable only of subsonic speed though some are capable of reaching mach 1+.
- Although equipped with either guns or short range air-to-air missiles it is usually for self-defense purpose or anti-hostile aircraft/helicopter missions not for air defense as lightweight fighters do, though some are capable of air combat or point air defense missions due to integrated or have variants capable of carrying powerful multi-mode radar systems, most LCAs don’t have such due to their small limited design or are less powerful.
- However, they can still be used to patrol the skies and implement border patrol or air policing.
China’s Change – 4 Lunar Rover Lands on Moon’s far side, sends back images
04, Jan 2019

Context:
- China’s Chang’e-4 lunar rover scripted history on January 3 when it made the first-ever soft landing on the far side of the moon and sent back close-up images of the previously unexplored region, a giant leap for cosmic exploration and a major boost to the China’s quest to become a space superpower.
Details:
- China National Space Administration said that Chang’e-4, named after a Chinese moon goddess and comprising a lander and a rover, touched down at the preselected landing area at 177.6 degrees east longitude and 45.5 degrees south latitude on the far side of the moon.
- The lunar explorer has shared its first pictures from the surface.
- The robotic spacecraft is carrying instruments to analyse the unexplored region’s geology and will conduct biological experiments.
- This is the pioneering achievement as earlier moon missions that have landed only on the Earth-facing side, this is the first time any craft has landed on the unexplored and rugged far side of the moon.
- The scientific tasks of the Chang’e-4 mission include low-frequency radio astronomical observation, surveying the terrain and landforms, detecting the mineral composition and shallow lunar surface structure, and measuring the neutron radiation and neutral atoms to study the environment on the far side of the moon
- Chang’e-4 mission has four scientific payloads developed by scientists from the Netherlands, Germany, Sweden and Saudi Arabia. Chang’e 4 is the fourth lunar probe launched by China since the country’s lunar programme was opened in 2004.
- China has now joined the U.S. and the former USSR as the only countries to have made a “soft landing” on the moon. But beyond underlining China’s technological advances, Chang’e-4 could herald a new chapter in lunar exploration.
- The country also further aims to land a crewed flight on the moon in the coming decade.
Background:
- Tidal forces on Earth slow the moon’s rotation to the point where the same side always faces Earth. The other side, most of which is never visible from Earth, is the far side of the moon. Direct communication with the far side of the moon, however, is not possible, which is one of the many challenges for the Chang’e-4 lunar probe mission.
- China launched a relay satellite, named Queqiao, in May, to set up a communication link between the Earth and Chang’e-4 lunar probe.
- This is the first time an attempt is made to explore the far side of the moon. Since the moon’s revolution cycle is the same as its rotation cycle, the same side always faces Earth.
- The far side of the moon is the hemisphere that never faces Earth, due to the moon’s rotation.
- It is sometimes mistakenly referred to as the “dark side of the moon,” even though it receives just as much sunlight as its Earth-facing side.
- The Chang’e-4 mission will be a key step in revealing the moon’s mysterious side.
NASA Spacecraft Zips Past Ultima Thule
02, Jan 2019

Context:
- A NASA spacecraft ‘New Horizons’ flew past the most distant world ever studied by humankind, Ultima Thule, a frozen relic of the early solar system that could reveal how planets formed.
Details:
- Ultima Thule is located in the Kuiper belt in the outermost regions of the Solar System, beyond the orbit of Neptune. Ultima Thule is unique because it is a relic from the early days of the Solar System and could provide answers about the origin of the other planets. The spaceship was to collect 900 images over the course of a few seconds as it shaved by at a distance of about 2,000 miles (3,500 kilometres).
- These photographs would help in better understanding of the Solar System
About New Horizons:
- New Horizons is an interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA’s New Frontiers program. It aims to understand worlds at the edge of our solar system by making the first reconnaissance of the dwarf planet Pluto and by venturing deeper into the distant, mysterious Kuiper Belt – a relic of solar system formation.As part of an extended mission, the spacecraft head farther into the Kuiper Belt, to study MU69 another
of the ancient, icy mini-worlds in that vast region, at least a billion miles beyond Neptune’s orbit.
SETTING UP OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY PARK AND MUSEUMS
01, Jan 2019
GS 3: Science & Technology | Developments and their applications and effects in everyday life
Why in News?
The ISRO (Department of Space) has planned to set up Space Galleries in various parts of the country.
Highlights:
The Space Galleries are expected to disseminate the knowledge about space science and technology amongst the citizens of our country.The Gallery will consist of interactive methods/ models describing the principles of Space science and technology. Space Galleries are planned to be established at Birla Science Centre at Hyderabad, Nehru Science Centre at Mumbai and National Science Centre at Pragati Maidan in New Delhi.ISRO has taken initiatives to establish space gallery in all the national museums/science centres (under Ministry of Culture) across the country in a phased manner.ISRO is also planning to establish Knowledge centres, mobile exhibitions, competitions amongst students and various talks/ lectures on Space Science/ technology related aspects.
Bepicolombo Mission
21, Dec 2018

- A European-Japanese spacecraft set off on a treacherous seven-year journey to Mercury to examine the solar system’s smallest and least-explored planet.
About:
- The BepiColombo mission, only the third ever to visit Mercury, blasted off from Europe’s spaceport in French Guiana aboard an Ariane 5.
- It is the Europe’s first mission to Mercury, built in cooperation with the Japanese space agency JAXA. Europe’s Mercury Planetary Orbiter (MPO) and Japan’s Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter (MMO) have different roles. The BepiColombo mission includes two spacecraft, a planetary orbiter and a magnetospheric orbiter, which, according to the European Space Agency, will need to deal with temperatures above 350°C during their year-long mission around the closest planet to the sun.
- When it arrives, BepiColombo will release two probes Bepi and Mio that will independently investigate the surface and magnetic field of Mercury.
- Newly developed electrical ion thrusters will help nudge the spacecraft, which is named after Italian scientist Giuseppe ‘Bepi’ Colombo, into the right orbit.
- The MMO will make as its priority the study of the planet’s magnetic field. It will investigate the field’s behaviour and its interaction with the “solar wind”, the billowing mass of particles that stream away from the Sun. This wind interacts with Mercury’s super-tenuous atmosphere, whipping atoms into a tail that reaches far into space.
- Europe’s MPO will map the terrain, generate height profiles, sense the interior, and collect data on the surface structure and composition.
Background:
- It is the second recent cooperation between the Europeans and JAXA after the Japanese agency’s Hayabusa2 probe dropped a German-French rover on the asteroid Ryugu earlier this month.
- The Americans have already been there, briefly with the Mariner 10 probe in the 1970s, and with the Messenger orbiter earlier this decade.
- The latter provided remarkable new insights that included the amazing discoveries that water-ice is held inside some of baking Mercury’s shadowed craters, and that its crust contains a lot of graphite (pencil lead).
- Bepi will build on Messengers’ investigations. The new mission carries twice as much instrumentation and will get closer for longer, giving scientists much more detailed information.
Significance:
- Beyond completing the challenging journey, this mission will return a huge bounty of science. Helps to understand how Earth was formed, how all rocky planets formed.
- BepiColombo mission is one of the most challenging in its history given Mercury’s extreme temperatures, the intense gravity pull of the sun and blistering solar radiation make for hellish conditions. The first spacecraft to visit Mercury was NASA’s Mariner 10 that flew past the planet in the mid-1970s. Mercury, which is only slightly larger than Earth’s moon, has a massive iron core about which little is known. Researchers are also hoping to learn more about the formation of the solar system from the data gathered by the BepiColombo mission.
ISRO’S GSLV-F11/GSAT-7A Mission Successful
20, Dec 2018

Context:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) sucessfully placed GSAT-7A, the second communication satellite meant primarily for military applications in orbit.
Details:
- GSLV-F11 (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle) carrying the satellite lifted off from the second launch pad of Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
- It was the 13th flight of GSLV Mark II and the seventh flight with an indigenous cryogenic engine.
- Around 19 minutes after take-off, the three-stage launcher ejected the satellite into a geosynchronous transfer orbit.
- In the coming days, the satellite will be moved to its final geostationary orbital slot at an altitude of around 35,000km by firing its onboard chemical propulsion system.
- Gsat-7A, the 39th communication satellite of Isro, has communication capabilities to users in Ku-band over the Indian region.
- Gsat-7A is expected to interlink all ground-based radars, airbases and airborne early warning and control aircraft for surveillance, maintain air superiority, gather intelligence by detecting aircraft, vessels and other vehicles in long range.
About the satellite:
- GSLV – F11 is ISRO’s fourth generation launch vehicle with three stages. The four-liquid strap-ons and a solid rocket motor at the core form the first stage. The second stage is equipped with high thrust engine using liquid fuel. The Cryogenic Upper Stage forms the third and final stage of the vehicle.
- The GSAT-7A incorporates chemical propulsion system to provide an operational mission life of a minimum of eight years.
- Chemical propulsion will be used for orbit raising as well as for on orbit attitude correction operations.
- Sufficient redundancy is built into the Spacecraft for continued service.
- It is an advanced military communications satellite meant exclusively for the Indian Air force.
- GSAT-7A is similar to Indian navy’s GSAT-7 and the Indian Air Force will be the sole operator of the satellite.
- It will qualitatively unify its assets and improve combined, common intelligence during operations
- GSAT-7A will enable IAF to interlink different ground radar stations, ground airbase and Airborne early warning and control (AWACS) aircraft such as Beriev A-50 Phalcon and DRDO AEW&CS.
- The satellite will enhance Network-centric warfare capabilities of the Indian Air Force and therefore enhance its global operations. The satellite will also be used by Indian Army’s Aviation Corps for its helicopters and UAV’s operations.
- It will support aerial activities of the Army and the Navy wherever required
NSG Must Have its own AIR WING
13, Dec 2018

Context:
- A Parliamentary panel has recommended that the Centre urgently take steps to ensure that the National Security Guard (NSG) — the country’s premier counter-terrorist and contingency force — is equipped with its own dedicated air wing.
Reason for this measure:
- Non-availability of dedicated aircraft has at times hampered NSG’s rapid reaction capabilities. For example, the NSG’s delay in reaching Mumbai during the November 2008 terrorist attacks on the city had come under severe criticism
- The 215th Parliamentary Standing Committee Report on Home Affairs tabled in the Rajya Sabha on Wednesday recommended that the “Ministry of Home Affairs should make urgent and sincere efforts to commission a dedicated Air Wing of NSG and provide requisite types and number of air assets to strengthen the aviation capability of the force.”
About National Security Guard:
- The National Security Guard (NSG) is an Indian special forces unit under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- It was raised in 1984, following Operation Blue Star and the assassination of Indira Gandhi, “for combating terrorist activities with a view to protect states against internal disturbances”.
- NSG is under the authority of Ministry of Home Affairs. However, it is not categorized under the uniform nomenclature of Central Armed Police Forces.
- It has a special forces mandate, and its core operational capability is provided by the Special Action Group (SAG) which is drawn from the Indian Army.
- The Special Rangers Group (SRG), the police component of NSG, which also handles VIP security, is composed of personnel on deputation from other Central Armed Police Forces and State Police Forces
- The NSG personnel are often referred to in the media as Black Cats because of the black outfit and black cat insignia worn on their uniform.
India Gets Submarine Rescue System
13, Dec 2018

Context:
- The Indian Navy joined a select group of naval forces in the world on Wednesday when it inducted its first non-tethered Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicle (DSRV) system at the Naval Dockyard in Mumbai.
Details:
- With this, India joins a select league of navies with the sovereign capability in fly away configuration to search, locate and rescue crew from a disabled submarine.
- The second vehicle that is out for delivery, is expected to reach Visakhapatnam soon. It will be operational by April next year.
Need of DSRV:
- The nature of operations undertaken by submarines expose them to high degree of inherent risk. In such an eventuality, traditional methods of search and rescue at sea are ineffective for a disabled submarine. To overcome this capability gap, the Navy has acquired a third generation, advanced Submarine Rescue System considering of a non-tethered DSRV and its associated equipment.
Details of DSRV:
- Using a third-generation system, the DSRV is considered to be the most advanced system currently in operation globally.
- The DSRV is used to rescue crew members from submarines stranded under water in the high seas.
- The DSRV can be operated at a depth of 650 meters and can rescue 14 people at a time.
- The state-of-the-art system is also equipped with a decompression chamber that can accommodate submariners and a remotely operated vehicle (ROV), which can be used to beam images and provide immediate assistance.
- The Western Naval Command had recently successfully held trials with actual simulations with different classes of submarines.
- The DSRV can also be transported by air, enabling it to conduct rescue operations across the globe
- The induction of the DSRV marks the culmination of years of effort of the Navy in acquiring this niche submarine rescue capability. It is the latest in terms of technology and capability.
About Deep-submergence vehicle:
- A deep-submergence vehicle (DSV) is a deep-diving manned submarine that is self-propelled. Several navies operate vehicles that can be accurately described as DSVs.
- DSVs are commonly divided into two types: research DSVs, which are used for exploration and surveying, and DSRVs (Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicle), which can be used for rescuing the crew of a sunken navy submarine, clandestine (espionage) missions (primarily installing wiretaps on undersea cables), or both.
- DSRVs are equipped with docking chambers to allow personnel ingress and egress via a manhole.
Insight Mars Lander Takes its First Selfie
13, Dec 2018

Details:
- The spacecraft used a camera on its robotic arm to take its first selfie—a mosaic made up of 11 images. This is the same imaging process used by NASA’s Curiosity rover mission, in which many overlapping pictures are taken and later stitched together. Visible in the selfie are the lander’s solar panel and its entire deck, including its science instruments.
About NASA’s InSight:
- The Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) mission is a robotic lander designed to study the deep interior of the planet Mars.
- It was manufactured by Lockheed Martin and is managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
- It has to place ‘seismometer’, on the surface to measure the seismic activity and provide accurate 3D models of Mars’s interior and measure heat flow and transfer within Mars using a heat probe to study the planet’s early geological evolution
Voyager 2 Probe Reaches Interstellar Space: NASA
12, Dec 2018
Context:
- NASA’s Voyager 2 has become the second human-made object in history to reach the edge of our solar system, after the spacecraft exited the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun.
Details:
- Voyager 2 is the only probe ever to study Neptune and Uranus during planetary flybys.
- Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to have visited all four gas giant planets — Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune
- Its twin, Voyager 1, crossed this boundary in 2012, but Voyager 2 — launched 41 years ago — carries a working instrument that will provide first-of-its-kind observations of the nature of this gateway into interstellar space.
- Their observations complement data from NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX), a mission that is remotely sensing that boundary.
Interstellar space:
- In simple terms, it is a part of space that exists between stars
- Scientists define the beginning of interstellar space as the place where the sun’s constant flow of material and magnetic field stop affecting its surroundings. This place is called the heliopause. It marks the end of a region created by our sun that is called the heliosphere. The sun creates this heliosphere by sending a constant flow of particles and a magnetic field out into space at over 670,000 miles per hour. This stream is called the ‘solar wind.’
India Successfully Test-Fires Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile Agni-5
11, Dec 2018

In News:
- The indigenously built Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile Agni-V has been test-fired successfully from Abdul Kalam island under Chandipur Interim Test Range.
- This is the fourth successful test of this missile. Previously the test of Agni 4 was unsuccessful. It can carry both nuclear and traditional weapons.
Agni V Missile – Important Facts:
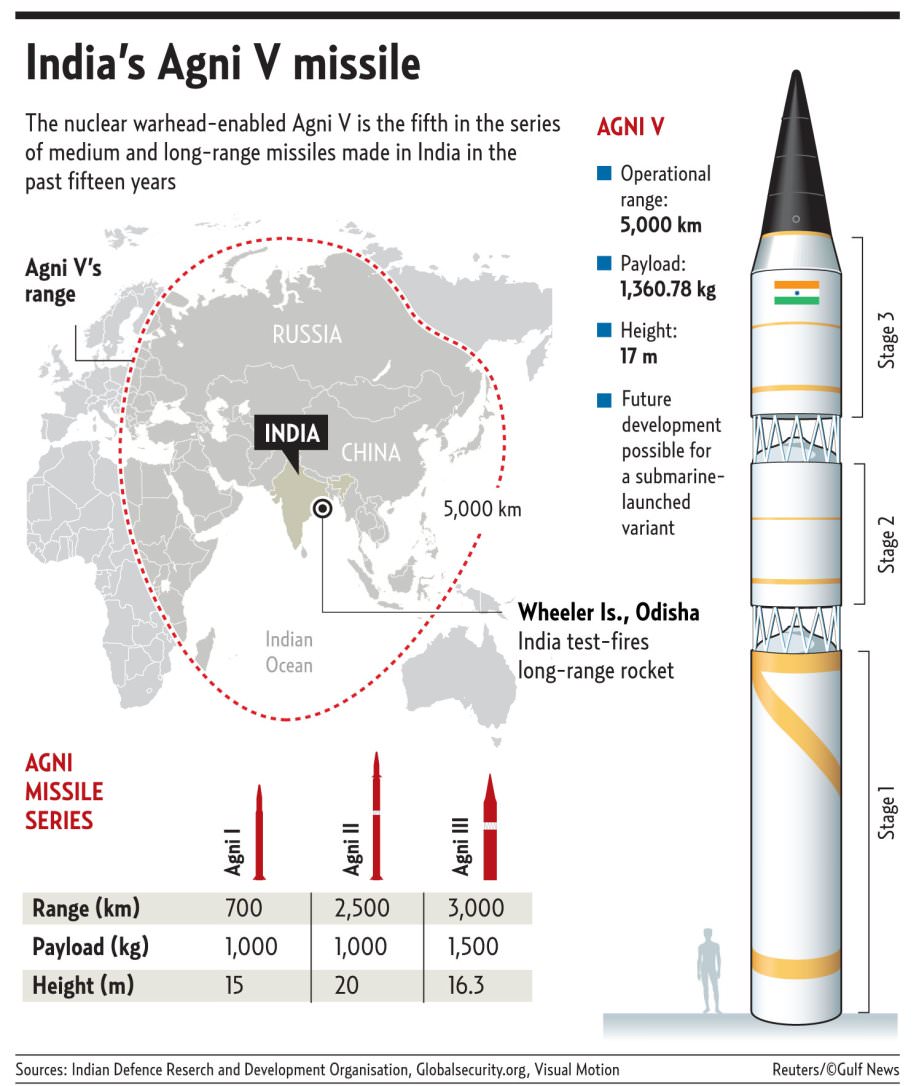
- Agni V ballistic missile is the brainchild of Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). It is the most advanced in the series.
- Agni-V is a nuclear capable long-range missile with new technologies in terms of navigation and guidance, warhead and engine.
- The three stage, 17- meter tall, two-meter wide Agni-V missile has a range of 5000 km.
- It can carry a nuclear warhead weighing up to 1.5 tonnes.
- Agni-V uses Ring Laser Gyro based Inertial Navigation System RINS. It is the most modern and gives very high accuracy.
- The Micro Navigation System or MINS helped the missile reach its target with precision.
- Other features of Agni- V missile include a high speed on- board computer, fault tolerant software and a robust reliable bus.
- The advanced computer and the inertial navigation system are the highlights of the missile as they aid in precision of the path.
- The missile is highly reliable, has longer shelf life and enhanced mobility compared to the other versions.
Nuclear-Capable Agni-V Successfully Test-Fired Off Odisha
11, Dec 2018

Context:
- India successfully test-fired nuclear-capable long-range ballistic missile Agni-V. The missile was launched from a canister on a road mobile-launcher from Dr. Abdul Kalam Island off Odisha.
Details:
- This is the third successful launch of Agni-V this year and the fifth launch of the missile in a canisterised form
- The mission critical avionics were indigenously designed and developed by Research Centre Imarat (RCI), Hyderabad
- All the mission objectives were successfully achieved. This launch comes after a series of successful launches of the missile. It further strengthens the country’s deterrence capability, which has been developed indigenously by assiduous efforts of scientists
About Agni V:
- Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) with a strike range of over 5,000 km and can reach most parts of China.
- It is three-stage solid propellant nuclear-capable missile
- It is a surface-to-surface missile. Capable of carrying nuclear warheads of over one tonne
- It carries Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicles (MIRV) payloads. A single MIRV equipped missile that can deliver multiple warheads at different targets.
- It is also a fire and forget missile, which once fired cannot be stopped, except by interceptor missile which only US, Russia and Israel have.
- The missile has been designed to hit the designated target point accurately, guided by the on-board computer with the support of a Ring Laser Gyro-based Inertial Navigation System, the Micro Inertial Navigation System, fully-digital control system and advanced compact avionics.
EX AVIAINDRA 2018
11, Dec 2018

Why in News?
- The second edition of the service-specific exercise AVIAINDRA between Indian Air Force (IAF) and Russian Federation Aerospace Force (RFAF), has been commenced at Air Force Station Jodhpur in Rajasthan on December 10, 2018. This bi-annual air-service exercise will conclude on December 22, 2017.
Highlights:
- The primary objective of this bi-annual air service exercise is to strengthen both of the air forces for anti-terrorist operations.
- Besides strengthening air forces, it also seeks to increase cooperation and build understanding between IAF and RFAS. This air service exercise takes place in two phases.
- This exercise allows foreign partners to participate without their assets. Indian Air Force pilots and Russian Federation Aerospace Force pilots flew aircraft when this air exercise was held at Lipetsk, Russia in September 2018.
- Similarly, RFSAF and IAF pilots will fly aircraft during in this 12-day long service specific exercise.
- Russia has been a major partner of India in the defence sector and the cooperation has been steadily growing further.
- In October 2017, India and Russia held a 10-day mega war game involving their armies, navies and air forces for the first time ramp up military ties.
- The exercise Indra, which took place in Russia, primarily focused on achieving coordination between forces of the two countries in tri-services integrated theatre command scenario.
- It was the first time, India participated in tri-services exercise with a foreign country with large scale participation by the Navy, the Army and the Air Force.
Indian Institute of Skills
21, Oct 2018

- The Union Cabinet gave its approval for setting up of Indian Institute of Skills at different locations across the country. The IISs will be set up in public private partnership mode.
About:
- The setting up of IISs will help augment the global competitiveness of key sectors of Indian economy by providing high quality skill training, applied research education and a direct and meaningful connection with industry.
- It will provide opportunity to aspiring youth across the country to have access to highly skilled training, and enhance the scope of accountability through its linkage with industry and global competitiveness across sectors, the release added.
- The institute shall be equipped with state-of-the-art facility to impart skill development courses to the trainers and assessors along with training of candidates in new age courses catering to the needs of the industry, designed keeping in mind the youth of the institutes’ catchment areas. Skill India is a demand driven program which trains people in job roles which are market relevant and of current industry needs and standards
Significance:
- Skills and knowledge are the driving forces of economic growth and social development for any country. Countries with higher and better levels of skills adjust more effectively to the challenges and opportunities of world of work.
- The skill development initiatives support the supply of trained workers who are adjustable dynamically to the changing demands of employment and technologies. This policy will promote excellence and will meet the requirements of knowledge economy.
- Skill development will help actualize the potential of huge demographic dividend.
- Bringing the PPP institute will make equitable access to all who are deprived of skill training. Creating effective convergence between school education, various skill development efforts of government and between government and Private Sector initiative.
- It helps in achieving India’s target of creating 500 million skilled workers by 2022.
- Improving productivity and living standards of the people. Strengthening competitiveness of the country which will attract investment in skill development.
Phosphorous Origin
19, Oct 2018

- The new study pointed out that most of the phosphorus on Earth was generated in outer space and reached Earth via meteorites and comets.
About:
- University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa researchers, in collaboration with colleagues in France and Taiwan, provide compelling new evidence that this component for life was found to be generated in outer space and delivered to Earth in its first one billion years by meteorites or comets. The team replicated interstellar icy grains coated with carbon dioxide and water, which are ubiquitous in cold molecular clouds, and phosphine.
- When exposed to ionizing radiation in the form of high-energy electrons to simulate the cosmic rays in space, multiple phosphorus oxoacids like phosphoric acid and diphosphoric acid were synthesized via non-equilibrium reactions.
- On Earth, phosphine is lethal to living beings but in the interstellar medium, an exotic phosphine chemistry can promote rare chemical reaction pathways to initiate the formation of biorelevant molecules such as oxoacids of phosphorus, which eventually might spark the molecular evolution of life as we know it.
- According to the study, phosphates and diphosphoric acid are two major elements that are essential for these building blocks in molecular biology.
Phosphorus:
- Phosphorus is a chemical element with symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth’s crust of about one gram per kilogram. With few exceptions, minerals containing phosphorus are in the maximally oxidized state as inorganic phosphate rocks.
- All living beings need cells and energy to replicate. Without these fundamental building blocks, living organisms on Earth would not be able to reproduce and would simply not exist. The phosphorus compounds were then incorporated in biomolecules found in cells in living beings on Earth. They are the main constituents of chromosomes, the carriers of genetic information in which DNA is found.
- Together with phospholipids in cell membranes and adenosine triphosphate, which function as energy carriers in cells, they form self-replicating material present in all living organisms.
Chandra Observatory
19, Oct 2018

In News:
- NASA’s Chandra X-ray telescope which observes galaxies from the Earth’s orbit is back in action after suffering a technical glitch and going into safe mode.
- The Glitch occurred in one of Chandra’s gyroscopes, scientists said.
Background:
- The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space observatory launched on STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999
- NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory is a telescope specially designed to detect X-ray emission from very hot regions of the Universe such as exploded stars, clusters of galaxies, and matter around black holes.
- Because X-rays are absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere, Chandra must orbit above it, up to an altitude of 139,000 km (86,500 mi) in space.
- Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources 100 times fainter than any previous X-ray telescope, enabled by the high angular resolution of its mirrors.
- Since the Earth’s atmosphere absorbs the vast majority of X-rays, they are not detectable from Earth-based telescopes; therefore space-based telescopes are required to make these observations.
- Chandra is an Earth satellite in a 64-hour orbit, and its mission is ongoing as of 2018. The Smithsonian’s Astrophysical Observatory in Cambridge, MA, hosts the Chandra X-ray Center which operates the satellite, processes the data, and distributes it to scientists around the world for analysis. Although nothing can escape the incredible gravity of a black hole, not even light, the Chandra X-ray Observatory will be able to study particles up to the last millisecond before they are sucked inside. The Chandra X-ray Observatory’s resolving power is 0.5 arc-seconds — equal to the ability to read the letters of a stop sign at a distance of 12 miles. Put another way, Chandra’s resolving power is equivalent to the ability to read a 1-centimeter newspaper headline at the distance of a half-mile.
What makes Chandra Unique?
- Chandra has outstanding imaging precision; its mirrors are the largest, the most perfectly aligned, and smoothest ever built.
- The images Chandra makes are 25 times sharper than the best previous x-ray telescope.
Bio – Bank for Drug Resistant Microbes
17, Oct 2018
- India’s battle against “superbugs” has just got more teeth with the Government setting up a bio-repository for resistant microbes, the first of its kind bio-bank in the country at the Pune-based National Centre for Microbial Resource (NCMR).
About:
- The bank is part of the Union Science and Technology Ministry’s Mission programme on Anti-microbial resistance (AMR) initiative with the vision to develop indigenous and cost-effective therapies against the superbugs like bacteria and fungi.
- Though India has many bio-repositories, a dedicated facility for superbugs at the NCMR is the first such unit in the country.
- The bio-bank — a storage place for biological materials that collects, processes and distributes biospecimen catalogs, and keeps samples of material, such as urine, blood, tissue, cells, DNA, RNA and protein from humans, animals or plants to support future scientific investigations — is expected to be a boon to clinicians and researchers in the field of AMR as they could deposit or obtain samples of infective agents for scientific investigation. Currently, the National Centre for Disease Control and the Indian Council of Medical Research carry out anti-microbial resistance surveillance in various geographical regions and settings. But these two bodies only collect data and not microbe samples. The DBT has already given green signal to the NCMR to collect, preserve and characterise drug-resistant microbes in the bio-bank. The NCMR would take necessary steps to facilitate clinicians, scientists and others to handle multidrug-resistant microbe samples.
- The DBT is also working to share the information regarding National AMR-specific Pathogen list which will be available very soon including a landscaping report on existing rapid and cost-effective diagnostic kits to identify AMR-specific pathogens, the official added.
- AMR is one of the major threats to human health in the 21st century, with some bacterial pathogens acquiring resistance to all clinically available antibiotics. Worldwide, infections caused by multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacteria are now a major cause of morbidity and mortality and have markedly enhanced healthcare costs.
- Considering AMR as a national priority, under National Action Plan endorsed by the Government the Department of Biotechnology has initiated the fight against AMR in a mission mode envisaging needed measures.
Background:
- Antimicrobial resistance is resistance of a microorganism to an antimicrobial drug that was originally effective for treatment of infections caused by it.
- Anti-microbial resistance has serious implications for a country like India where misuse of “last-resort” antibiotics for common health conditions is rampant. Many microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi have an exceptional capacity to survive in adverse surroundings. According to health experts, the situation in India is alarming on AMR front. A study has pointed that a intensive care units of 20 tertiary care hospitals showed that 7 per cent of critically ill patients are resistant to antibiotics.
- Drug resistance to first-line antibiotics also results in 58,000 neonatal deaths each year.
Cell Sized Robots
13, Oct 2018
- MIT scientists have developed a method to mass produce robots no bigger than a cell that could be used to monitor conditions inside an oil or gas pipeline, or to search out disease while floating through the bloodstream by using Auto perforation technique.
About:
- Tiny robots no bigger than a cell could be mass-produced using a new method developed by researchers at MIT called autoperforation.
- The microscopic devices, called “syncells” (short for synthetic cells), might eventually be used to monitor conditions inside an oil or gas pipeline, or to search out disease while floating through the bloodstream.
- The system uses a two-dimensional form of carbon called graphene, which forms the outer structure of the tiny syncells. One layer of the material is laid down on a surface, then tiny dots of a polymer material, containing the electronics for the devices, are deposited by a sophisticated laboratory version of an inkjet printer. Then, a second layer of graphene is laid on top.
- • Embedded inside these pockets are electronic circuits and materials that can collect, record, and output data.
- • These tiny objects “behave like a living biological cell” which can be used in variety of applications.
Chandra X-RAY Observatory enter safe mode
10, Oct 2018

- The Chandra X-ray Observatory, which has been observing the universe in high-energy light since 1999, entered a protective “safe mode”. The cause of the safe mode transition (possibly involving a gyroscope) is under investigation.
About:
- During the safe mode, the observatory is put into a safe configuration, critical hardware is swapped to back-up units, the spacecraft points so that the solar panels get maximum sunlight, and the mirrors point away from the Sun.
- Analysis of available data indicates the transition to safe mode was normal behaviour for such an event. All systems functioned as expected and the scientific instruments are safe.
- Gyroscopes help spacecraft maintain proper orientation. If a faulty gyroscope is to blame for Chandra’s current plight, the observatory would be in good company: A gyroscope failure knocked NASA’s iconic Hubble Space Telescope into safe mode last week.
Safe mode:
- Safe mode is an operating mode of a modern spacecraft during which all non-essential systems are shut down and only essential functions such as thermal management, radio reception and attitude control are active.
- Safe mode is entered automatically upon the detection of a predefined operating condition or event that may indicate loss of control or damage to the spacecraft. Usually the trigger event is a system failure or detection of operating conditions considered dangerously out of the normal range.
- Cosmic rays penetrating spacecraft electrical systems can create false signals or commands and thus cause a trigger event.
- While in safe mode the preservation of the spacecraft is the highest priority. Typically, all non-essential systems, such as science instruments, are shut down. The spacecraft attempts to maintain orientation with respect to the Sun for illumination of solar panels and for thermal management.
Background:
- The Chandra X-ray Observatory previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility is a Flagship-class space observatory launched by NASA on July 23, 1999.
- Chandra is one of the Great Observatories, along with the Hubble Space Telescope, Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (1991–2000), and the Spitzer Space Telescope.
- The telescope is named after the Nobel Prize-winning Indian-American astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar.
- Its mission is similar to that of ESA’s XMM-Newton spacecraft, also launched in 1999.
- Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources 100 times fainter than any previous X-ray telescope, enabled by the high angular resolution of its mirrors.
- Since the Earth’s atmosphere absorbs the vast majority of X-rays, they are not detectable from Earth-based telescopes therefore space-based telescopes are required to make these observations.
- Chandra focuses on the powerful X-ray emissions from violent cosmic phenomena such as supernovae and black holes.
- It is well beyond the original design lifetime of 5 years. In 2001, NASA extended its lifetime to 10 years. It is now well into its extended mission and is expected to continue carrying out forefront science for many years to come.
- It continues to work towards resuming science operations of the Hubble Space Telescope. On October 5, Hubble entered safe mode after one of the three gyroscopes (gyros) being used to point and steady the telescope failed.
- Gyroscopes help spacecraft maintain proper orientation.
Dark Microbial Matter
08, Oct 2018

- Dark microbial matter uncultured microbes whose characteristics have never been described could be dominating nearly all the environments on the earth, scientists found.
About:
- The study, published in the journal M-Systems, is the first time to estimate the population of microbes that have not yet been grown in a lab culture.
- Researchers collected every DNA sequence deposited in public databases by researchers all over the world, totalling 1.5 million, and compared them to 26,000 DNA sequences of microbes and bacteria that have already been cultured. As many as a quarter of the microbes on earth could come from the roughly 30 phyla a taxonomic classification between kingdoms and classes of microbes that have never been cultured.
Significance:
- Scientists have long been aware of this mass of uncultured microbes, also known by scientists as microbial dark matter. However, counting them one by one would be an impossible task and, up until now, researchers have not been able to even estimate how many of them there are.
- The study and characterisation of uncultured microbes can be a particularly valuable tool in specific fields such as in medicine, where scientists have described cases of culture-resistant pathogens. It is also possible that these microbes can’t grow on their own in culture because they die if they are removed from their intricate relationships with each other or their particular environment. Uncultured microbes are so vastly different than cultured ones that they might be doing unusual things, like surviving on extremely low energy or growing extraordinarily slowly.
- Since these microbes provide many ecosystem services such as helping crops grow and battling climate change solving the considerable puzzle they’ve presented us is a crucial challenge for modern microbiology.
Background:
- Microbes comprise 60% of the earth’s biomass and they are everywhere. They are abundant in the oceans and in soil there are more microbes in a teaspoon of soil than there are humans on earth they live in deserts, on mountains in Antarctica, near boiling hydrothermal vents at the seafloor, and in the acid stomachs of mammals including us humans.
- Life as we know it on our planet would not be possible without microbes. Much of the oxygen we breathe is produced by microbes, they are necessary to create our food such as yogurt, and cheese.
- Also, beer and wine would not exist without their ability to ferment sugar to alcohol, and in industry microbes are used as tiny living factories, for example to produce human insulin for people with diabetes. Scientists are very curious to learn more about this microbial world, but there is one big problem. We can only study about 1% of all the microbes in our laboratory, since most of the little critters just don’t grow on artificial substrates in the lab.
- Traditionally one would grow the microbes millions of them to get enough DNA for sequencing, because one cell has so little DNA. Since we can’t do this for the majority of microbes, they remained a mystery to us and are known as the Microbial Dark Matter (MDA).
- The inability to culture this microbial dark matter has led to a very skewed view of the microbial world. The two largest groups of microbes (Bacteria and Archaea) have many members which are only known because we found a small piece of DNA, the 16S rRNA gene, in environmental samples. We have almost no genomic information about those microbes, so we don’t know what they are doing or what they are capable of
- We apply a method, called single cell genomics, which omits the culturing step and allows to amplify the DNA of a single microbial cell a billion-fold, more than enough to sequence its genome.
- The first step is to take an environmental sample and to sort individual cells into tiny droplets. This is done on a cell sorter which detects the cells by a laser and separates them into droplets by electrostatic forces, similar to how an ink-jet printer directs individual droplets of ink to print a letter on a page. Next, we break open the cell envelope, very carefully so we don’t damage the DNA.
- Then we add a cocktail with the enzyme phi29 which has the ability to amplify very long stretches of DNA, and after several hours we have billions of copies from the microbial genome and can start sequencing.
Bharat – WI-FI project
08, Oct 2018

- The Indian telecom industry will rollout 10 lakh Wi-Fi hotspots in the country by December,2019.
About:
- The project has been named as Bharat Wi-Fi, which is a country-wide common inter-operable platform of one million Wi-Fi Hotspots, owned and operated by Telecom Service Providers, Internet Service Providers and Virtual Network Operators.
- This initiative allows consumers to access Wi-Fi Hotspots of any of the partnering operators, it is believed that it will help generate 5 lakh employment opportunities.
- The move is part of the infrastructure called Bharat Wi-Fi, and is believed to be a fresh step in Prime Minister’s Digital India initiative.
- Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Communications announced it in India Mobile Congress (IMC), one of the biggest marquee Mobile, Internet, and Technology event for South and South-East Asia.
- The need for data hungers drastically rises in India, even more, when Jio creates the Data Revolution in India. It also provoked the rural areas as well for data. So, the Government considers deploying some of these hotspots across rural areas or not.
- One thing was sure about, if the Government completes this Project successfully then, India will become the highest data usage country in the World.
- India’s data-led growth and digital revolution would help realise four ambitious goals of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, namely – doubling farmers’ income, Ayushman Bharat Scheme, quality education and employment generation.
- With world-class digital infrastructure in place India is now ready to not only embrace but actually lead the Fourth Industrial Revolution. This will make each one of the 130-crore people of India can now productively participate in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
India Mobile Congress:
- India Mobile Congress was a first of its kind event in the Indian Subcontinent, bringing together Mobile, Internet, and Technology companies on one platform, under the theme, “Connecting the Next Billion”.
- The event was attended by more than 2,000 delegates, 32,000 visitors, 150 Speakers, 100 Exhibitors and 100 start-ups. IMC 2017 firmly established the India Mobile Congress platform as South Asia’s largest digital forum where voice, data and a billion people converge.
- This year, IMC 2018, is envisaged to be an even bigger event with its theme “New Digital Horizons. Connect. Create. Innovate.”. This technology mega event will be held from 25th to 27th October 2018, at Aerocity, New Delhi, organized by the Department of Telecommunications, Government of India and Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI). The second edition of IMC expects to bring together the largest congregation of global professionals from the digital ecosystem, encompassing 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Smart Cities, Start-ups in the technology space and allied industry sectors.
- The platform will see a greater International presence with the participation of policy makers and regulators from partner countries in the ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) and BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) regions.
Carrots make Concrete Stronger and Greener
07, Oct 2018

- A group of researchers at Britain’s Lancaster University has been using a household food blender to mix particles from the root vegetable with concrete to see if they can produce a stronger and more environmentally sound product.
About:
- There is a chemical reaction happening between the fibres and the cement. That a carrot is made up nearly entirely of water but still stays rigid and crunchy because of cellulose, a fibrous substance found in all plants. Those fibres have strength characteristics in them. It’s the building blocks of the strength of a vegetable
- The potential of the vegetable-composite concretes lies in the ability of the Nano platelets to increase the amount of calcium silicate hydrate in concrete mixtures, which is the main substance controlling structural performance. The knock-on effect means smaller quantities of concrete would be needed for construction.
- Cellulose is also found in wood, but is easier to extract from vegetables. With large amounts of vegetable waste available as a by-product of agriculture, it is a cheap and environmentally friendly source of the fibres.
- Only a tiny amount of cellulose is needed to alter the properties of cement because it changes the way water behaves during the process when cement hardens
Significance:
- It increases the strength of concrete by 80 percent by using a small amount of this new material, the addition of carrots prevents any cracks in the concrete. It also means less cement is required, therefore lowering the global carbon dioxide (CO2) output. As cement is responsible for seven percent of total global CO2 emissions, according to International Energy Agency estimates.
- The vegetable-composite concretes, have structurally and environmentally out-performed all commercially-available cement additives, such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, doing so at a much lower cost.
Type 2 Polio Virus Contamination
06, Oct 2018
In News:
- The Union Health Ministry has ordered an inquiry into the type-2 polio virus contamination detected in the vials used for immunisation in Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra and Telangana
Indian Scenario:
- The last case due to type-2 wild poliovirus globally was reported from Aligarh in India in 1999
- India was declared polio free in 2014 and the last case was reported on 13 January 2011, when a person from Howrah was infected with type-1 polio virus.
- India eliminated the type-2 strain in 2016, and the type-2 containing poliovirus vaccine (ToPV) was phased out in April 2016. Children born after April 2016 in India have no immunity to type-2 polio virus.
- Traces of polio type-2 virus were found in some batches of oral polio vaccine (OPV) manufactured by a Ghaziabad-based pharmaceutical company. The Drugs Controller General of India has also asked the company to stop manufacture, sale or distribution till further orders
- According to a Health Ministry source, the contamination came to light after surveillance reports from Uttar Pradesh showed signs of the virus in stool samples of some children.
- The government, which has stepped-up surveillance after the breach
- The continued occurrence of polio cases caused by type 2 vaccine-derived poliovirus is the reason to implement the switch from trivalent OPV to bivalent OPV in routine immunization programmes, even before the remaining strains of wild poliovirus are eradicated
Polio virus:
- Poliomyelitis is a crippling disease that results from infection with any one of the three related poliovirus types (referred to as types P1, P2, and P3), members of the enterovirus (picornavirus) family. Humans are the only natural host and reservoir of polioviruses.
- Poliovirus is transmitted from one person to another by oral contact with secretions or faecal material from an infected person.
- Once viral reproduction is established in the mucosal surfaces of the nasopharynx, poliovirus can multiply in specialized cells in the intestines and enter the blood stream to invade the central nervous system, where it spreads along nerve fibres.
- When it multiplies in the nervous system, the virus can destroy nerve cells (motor neurons) which activate skeletal muscles.
- These nerve cells cannot regenerate, and the affected muscles lose their function due to a lack of nervous enervation – a condition known as acute flaccid paralysis (AFP).
- Typically, in patients with poliomyelitis muscles of the legs are affected more often than the arm muscles.
Polio Vaccines:
- Poliovirus infection can provide lifelong immunity against the disease, but this protection is limited to the serotype involved.
- Infection with one type does not protect an individual against infection with the other two types.
Two different kinds of vaccine are available:
- A inactivated (killed) polio vaccine (IPV) and
- A live attenuated oral polio vaccine (OPV).
- A inactivated (killed) polio vaccine (IPV) is produced from wild-type poliovirus strains of each serotype that have been inactivated (killed) with formalin. As an injectable vaccine, it can be administered alone or in combination with other vaccines
- A live attenuated oral polio vaccine (OPV) consists of a mixture of the three live attenuated poliovirus serotypes (Sabin types 1, 2 and 3), selected for their lower neurovirulence and reduced transmissibility.
Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI):
- In 1999, the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) scored an unequivocal victory: It wiped one of three serotypes of wild poliovirus, type 2, off the face of the earth, except for samples stored in labs for study or vaccine creation
Global scenario:
- Niger too has showed this similar kind of type 2 polio virus resurfacing.
Sphere to Fight Water Pollutants
05, Oct 2018

- Rice University researchers have enhanced micron-sized titanium dioxide particles to trap and destroy bisphenol A (BPA), a water contaminant with health implications.
About:
- BPA is commonly used to coat the insides of food cans, bottle tops and water supply lines, and was once a component of baby bottles. While BPA that seeps into food and drink is considered safe in low doses, prolonged exposure is suspected of affecting the health of children and contributing to high blood pressure.
- The reactive oxygen species (ROS), hydroxyl radicals are bad for BPA. Inexpensive titanium dioxide releases ROS when triggered by ultraviolet light. But oxidating molecules fade quickly, BPA has to be close enough to attack.
- The spheres reveal themselves as flower-like collections of titanium dioxide petals. The supple petals provide plenty of surface area to anchor cyclodextrin molecules.
- Cyclodextrin is a benign sugar-based molecule often used in food and drugs. It has a two-faced structure, with a hydrophobic (water-avoiding) cavity and a hydrophilic (water-attracting) outer surface.
- BPA is also hydrophobic and naturally attracted to the cavity. Once trapped, ROS produced by the spheres degrades BPA into harmless chemicals.
- In the lab, the researchers determined that 200 milligrams of the spheres per litre of contaminated water degraded 90 percent of BPA in an hour, a process that would take more than twice as long with unenhanced titanium dioxide.
- Cyclodextrin molecules on the surface trap BPA, which is then degraded by reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced by the light-activated particles.
- Most of the processes reported in the literature involve nanoparticles. The size of the particles is less than 100 nanometres. Because of their very small size, they’re very difficult to recover from suspension in water. The Rice particles are much larger. Where a 100-nanometer particle is 1,000 times smaller than a human hair, the enhanced titanium dioxide is between 3 and 5 microns, only about 20 times smaller than the same hair. That means we can use low-pressure microfiltration with a membrane to get these particles back for reuse. Because ROS also wears down cyclodextrin, the spheres begin to lose their trapping ability after about 400 hours of continued ultraviolet exposure but once recovered, they can be easily recharged.
- This is an example of how advanced materials can help convert academic hypes into feasible processes that enhance water security.
Current Problem:
- This new material helps overcome two significant technological barriers for photocatalytic water treatment. First, it enhances treatment efficiency by minimizing scavenging of ROS by non-target constituents in water. Here, the ROS are mainly used to destroy BPA.
- Second, it enables low-cost separation and reuse of the catalyst, contributing to lower treatment cost.
Mehar Baba Prize
05, Oct 2018
- The Indian Air Force has announced India’s first competition in the defence sector, the Mehar Baba Prize. The competition, in line with Make in India, is spread over three phases, from ideation to production.
About:
- In the wake of floods, cyclones and other natural disasters across the country, the IAF is holding a competition for participants to build a swarm of 50 drones to lead Humanitarian Aid and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
- The IAF will pick up to three winners, each of whom will get Rs 10 lakh in prize money and an opportunity to co-produce a Rs 100 crore order for induction of the drones to the Force.
- The competition is divided into three phases.
Bacteria to Degrade Toluene
04, Oct 2018
- Researchers from the University of Delhi and Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Varanasi, have successfully degraded toluene into less-toxic by-products using bacteria isolated from soil and effluents near an oil refinery.
About:
- The researchers also tested the bacterial strain for the degradation of benzene, phenol, and xylene and they showed effective results towards degradation of these compounds both individual compounds and their mixtures.
- In laboratory conditions, the bacteria were able to degrade these petrochemical wastes in both soil and water samples. More studies are needed to design industrial-scale bioreactors for taking up large-scale degradation of petrochemical waste.
- The bacteria were isolated from the samples, identified and studied for their toluene-degrading abilities. To the soil and effluent samples containing some bacteria 100 mg/L of toluene was added and incubated for four weeks.
- They isolated eight to 10 strains of bacteria and found that a particular bacteria Acinetobacter junii showed good degrading potential about 80% of toluene (50 ppm) in a liquid medium was degraded within 72 hours.
- A consortium of A. junii bacteria was found to be more effective than using a single strain. Different bacterial strains have different characteristic potential to degrade intermediate by-products formed during the degradation process and, hence, increase the efficiency.
- The bacteria use up this toluene as their carbon source in the presence of oxygen. Though most of the waste degradation studies have involved the use of bacteria that grow in an anaerobic environment, we tried an aerobic one and succeeded.
Toluene:
- Toluene also known as aromatic hydrocarbon. It is a colourless, water-insoluble liquid with the smell associated with paint thinners. Toluene is predominantly used as an industrial feedstock and a solvent.
- Toluene is one of the petrochemical wastes that get released without treatment from industries such as refineries, paint, textile, paper and rubber. Toluene occurs naturally at low levels in crude oil and is a by-product in the production of gasoline by a catalytic reformer or ethylene cracker. It is also a by-product of the production of coke from coal.
- Toluene has been reported to cause serious health problems to aquatic life, and studies point that it has genotoxic and carcinogenic effects on human beings. Sometimes used as a recreational inhalant and has the potential of causing severe neurological harm.
New Antibody for Cancer Treatment
03, Oct 2018

- A team of researchers in Spain, Switzerland and the U.S. has homed in on a specific antibody, called the p95HER2-T cell bispecific antibody (TCB), that can successfully guide immune cells, known as lymphocytes, directly to cancerous ones for their targeted killing.
About:
- The immune system has the natural capacity to fight against disseminated disease. To do so more effectively, it must be better equipped to recognize and act against malignant cells. While bispecific antibodies are designed to do just that, they often signpost T cells to healthy ones.
- Among the key hurdles in cancer immunotherapy an emerging approach to cancer medicine is to ensure that these therapeutics only target cancerous cells and not healthy tissue.
- This direct delivery is achieved by p95HER2 protein, which is only located in tumour cells. Not only are they highly specific but they can also hone in on one protein among tens of thousands, in this particular case, p95HER2.
- The study represents a new therapeutic avenue and fresh hope for patients who have ceased to respond to current therapies.
- This novel immune-based approach, can be used to tackle certain HER2+ breast cancers through its exclusive targeting of cancerous cells.
- Each antibody molecule has a bipartite structure containing two protein-binding sites. This means that they can simultaneously attach to immune cells and cancerous ones as well as take the lymphocytes hand-in-hand directly to the malignant cells for their subsequent destruction.
- It is an important step towards ensuring that the immune system can successfully deliver its powerful anti-cancer blows.
- Approximately 10% of patients with HER2-positive breast cancers expressing p95HER2 could stand to benefit from this novel strategy who no longer responded to standard therapies.
- By more precisely matching novel therapy to a particular patient population, we are getting closer to delivering on the true promise of precision medicine.
MASCOT – New Robot on Asteroid
02, Oct 2018
- A Japanese probe launched a new observation robot towards an asteroid, as it pursues a mission to shed light on the origins of the solar system.
About:
- The French-German Mobile Asteroid Surface Scout, or MASCOT, launched from the Hayabusa2 probe, landed safely on Ryugu asteroid’s surface.
- MASCOT’s launch comes 10 days after the Hayabusa2 dropped a pair of MINERVA-II micro-rovers on the Ryugu asteroid.
- The 10-kilogram box-shaped MASCOT is loaded with sensors. It was the first time that moving, robotic observation devices have been successfully landed on an asteroid.
- MASCOT is expected to collect a wide range of data on the asteroid which is some 300 million kilometres from Earth.
- It can take images at multiple wavelengths, investigate minerals with a microscope, gauge surface temperatures and measure magnetic fields.
- The rover will take advantage of Ryugu’s low gravity to jump around on the surface – travelling as far as 15 metres (49 feet) and staying above the surface for as long as 15 minutes.
- It will do this to better survey the asteroid’s physical features with cameras and sensors. The rovers will spend several months on the asteroid, the MASCOT has a maximum battery life of just 16 hours, and will transmit the data it collects to the Hayabusa2 before running out of juice.
Significance:
- Jaxa’s Hayabusa Two probe is on a mission to study the ancient asteroid Ryugu in a bid to help scientists better understand the origins of the universe.
- Hayabusa -Two is studying soil and rock samples using several pieces of equipment. The probe will then hover over the artificial crater and collect samples using an extended arm.
- The probe is loaded with four surface landers, an array of cameras and even an explosive device that will dig out subsurface rock samples.
- Ryugu, a Type C asteroid, contains traces of water and organic material and it is hoped that analysing this material will reveal what the early conditions were like at the time the solar system formed around 4,6 billion years ago.
- Hayabusa Two is expected to return to Earth in late 2020 carrying samples for further analysis.
RYUGU Asteroid:
- Ryugu was discovered on 10 May 1999 by astronomers with the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the Lincoln Lab’s ETS near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States. The asteroid was officially named “Ryugu”. The name refers to Ryūgū (Dragon Palace), a magical underwater palace in a Japanese folktale.
Centre Launches two Schemes to Promote Higher Education Research
01, Oct 2018

Why in News?
The Centre announced two schemes to promote higher education research in India:
- IMPRESS, dealing with social science research projects and coordinated by the ICSSR.
- SPARC, involving foreign collaboration mainly in science research, coordinated by IIT Kharagpur.
IMPRESS:
- The Union Minister for Human Resource Development launched the web portal of the Scheme “Impactful Policy Research in Social Sciences (IMPRESS)”. Indian Council of Social Science and Research (ICSSR) will be the project implementing agency.
- Under the Scheme, 1500 research projects will be awarded for 2 years to support the social science research in the higher educational institutions and to enable research to guide policy making.
- The broad objectives of the scheme are:
- To identify and fund research proposals in social sciences with maximum impact on the governance and society.
- To focus research on (11) broad thematic areas such as: State and Democracy, Urban transformation, Media, Culture and Society, Employment, Skills and Rural transformation, Governance, Innovation and Public Policy, Growth, Macro-trade and Economic Policy, Agriculture and Rural Development, Health and Environment, Science and Education, Social Media and Technology, Politics, Law and Economics. The Sub-Theme areas will be decided on the basis of Expert Groups’ advice before notifying the scheme and calling for applications.
- To ensure selection of projects through a transparent, competitive process on online mode.
- To provide opportunity for social science researchers in any institution in the country, including all Universities (Central and State), private institutions with 12(B) status conferred by UGC.
- e) ICSSR funded/recognised research
SPARC:
- The Minister of Human Resource Development, Shri Prakash Javadekar launched the web portal of the Scheme “Scheme for Promotion of Academic and Research Collaboration (SPARC)”. SPARC scheme aims at improving the research ecosystem of India’s higher educational institutions by facilitating academic and research collaborations between Indian Institutions and the best institutions in the world.
- Salient Features of SPARC are : This scheme will improve research ecosystem of India’s higher educational institutions by facilitating academic and research collaborations between Indian Institutions [overall top-100 or category-wise top-100 in NIRF ( including such Private Institutions which are recognized under 12(B) of UGC Act)] and the best institutions in the world (top-500 overall and top-200 subject-wise institutions listed in QS World University Ranking) from 28 selected nations [Australia, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, China, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Hong Kong, Israel, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Portugal, Russia, Singapore, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, United Kingdom(UK), United States of America(USA)] to jointly solve problems of national and international relevance. As per the criteria mentioned above, 254 top Indian Institutes and 478 top ranked global Institutes have been already identified.
- A set of 5 Thrust Areas (Fundamental Research, Emergent Areas of Impact, Convergence, Action-Oriented Research and Innovation-Driven) and sub-theme areas in each thrust area has been identified for collaboration under SPARC based on emergent relevance and importance for the nation.
- Each Thrust Area will have a Section Chair. The role of Section Chair of each Thrust Area is to review shortlist and recommend the potential joint-proposals submitted under SPARC scheme.
- A set of Nodal Institutions (NI), from India, for each participating foreign country has been identified. The role of a NI is to help, handhold and coordinate with willing Participating Indian (PI) Institutions to forge alliance with the Institutions of concerned participating foreign country, for academic and research collaboration. 25 such reputed Institutions have been notified as Nodal Institutions.
- SPARC proposes to enable productive academic cooperation by supporting the following critical components that can catalyse impact making research : i) Visits and long-term stay of top international faculty/researchers in Indian institutions to pursue teaching and research , ii) Visits by Indian students for training and experimentation in premier laboratories worldwide , iii) Joint development of niche courses, world-class books and monographs, translatable patents, demonstrable technologies or action oriented research outcomes and products , iv) Publication , Dissemination and Visibility through a high profile annual international conference in India .
- This Scheme is expected to have a major impact in providing the best international expertise to address major national problems, expose Indian academicians to the best collaborators abroad, enable international faculty to stay in India for a longer duration, provide Indian students an opportunity to work in the world class laboratories, to develop strong bilateral relationships in research, and improve the international ranking of Indian Institutes.
WITH GENETIC TWEAK, MOSQUITO POPULATION MADE EXTINCT
18, Sep 2018
Why in news?
- Scientists said that they had succeeded for the first time in wiping out an entire population of malaria-carrying mosquitoes in the lab using a gene editing tool to programme their extinction.
Background:
- Gene drive technology works by forcing evolution’s hand, ensuring that an engineered trait is passed down to a higher proportion of offspring—across many generations—than would have occurred naturally.
- In experiments with the species Anopheles gambiae, scientists at Imperial College London tweaked a gene known as double sex so that more females in each generation could no longer bite or reproduce.
- After only eight generations, there were no females left and the population collapsed due to lack of offspring.
- This breakthrough shows that gene drive can work, providing hope in the fight against a disease that has plagued mankind for centuries. The next step will be to test the technology in a confined laboratory setting that mimics a tropical environment.
- It will be at least five-to-ten years before we consider testing any mosquitoes with gene drive in the wild.
- The double sex gene targeted in the experiments is deeply “conserved”, meaning that is formed tens or even hundreds of millions of years ago and is today shared by many insects with only minor variations.
- This suggests the technology could be used in the future to specifically target other disease-carrying insects.
- Traditional approaches to controlling mosquitoes — especially the use of insecticides — is becoming less effective,” mainly due to the build-up of resistance
Negatives:
- The ability to eradicate species and natural populations at will with synthetic gene drive is not to be celebrated but should rather sound an alarm.
- There are ecological risks from manipulating and removing natural populations, such as destroying food webs and shifting the behaviour of diseases, as well as social risks of disrupting agriculture and enabling new weapons.
- The issue will be squarely on the agenda in November in Egypt at a UN Biodiversity summit, which has mandated one of its technical committees to assess gene drive’s potential risks and benefits.
- Governments, farmers, indigenous peoples and civil society will be pressing for a full moratorium.
MITRA CLIP
17, Sep 2018

Mitra clip is a tiny device may be effective in treatment of heart failure.Patients with severe heart failure often are gravely ill, too sick to have open-heart surgery to have mitral valves replaced.But the new procedure is much less invasive than open-heart surgery.A cardiologist threads the device to the heart through a blood vessel in the groin. Once it reaches the heart, the MitraClip is guided to the valve, and the device is used to clip the two flaps together.
ELECTRIC VEHICLES DO NOT NEED PERMITS
17, Sep 2018

Why in news?
- Electric vehicles and vehicles that run on alternative fuels such as compressed natural gas (CNG) and ethanol will not require permits to ply on roads.
>Background:
- Gadkari said that all states have given their support to Centre’s move to end permits for such vehicles. He was speaking at the annual convention of Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM).
- While the minister did not specify the timeline of the decision’s implementation, it may happen within three months.
- A permit is an instrument issued by a state or regional transport authority, allowing the use of a vehicle as per provisions of the Motor Vehicle Act. Various permits required by commercial vehicles include contract carriage bus permit, goods carrier permit and cab permit, among others.
- The move to end permit era for eco-friendly vehicles will result in saving time and money and is also likely to encourage fleet owners to add more green vehicles.
- Giving any additional incentives on electric vehicles for personal use, saying there is already a GST benefit extended on them. GST on electric vehicles has been kept at 12%.
- There was no need to further subsidise electric vehicles, but ministry was preparing non-fiscal measures to have at least 15% EVs in the country in five years.
- Electric vehicles imported for testing will be exempted from duties. The exemption will be limited and enable manufacturers to evaluate if these vehicles can be made locally.
- The government was considering removing speed governors from the roads since the emphasis is on better infrastructure and cleaner roads.
Electric vehicles:
- An electric vehicle, also called an EV, uses one or more electric motors or traction motors for propulsion.
- An electric vehicle may be powered through a collector system by electricity from off-vehicle sources, or may be self-contained with a battery, solar panels or an electric generator to convert fuel to electricity.
- EVs include, but are not limited to, road and rail vehicles, surface and underwater vessels, electric aircraft and electric spacecraft.
Advantages of electric vehicles:
- Cheaper to run – the cost of charging an EV is equivalent to paying around 30 cents per litre for petrol.
- Charge up at home – EVs can be charged anywhere there is a power point, just like charging your cell phone. You can wake up to a ‘full tank’ every morning by plugging in at home, and never have to go out of your way to a petrol station again.
- Pollution-free driving – BEVs don’t have a tailpipe and produce no exhaust emissions that cause local air pollution.
- Noise reduction – EVs are quieter than petrol or diesel vehicles.
- 80% reduction in CO2 emissions in New Zealand – this significant reduction in emissions is because 80% of New Zealand’s electricity is generated from renewable sources. There are also many other advantages to using this home-grown energy compared with using imported fossil fuels.
- Fewer lifecycle emissions – even when you take into account raw material extraction, battery manufacture, vehicle manufacture and shipping, BEVs emit 60% fewer climate change emissions over their full life cycle than for petrol vehicles.
- More efficient – EVs can convert well over 90% of energy from their batteries into moving the car. This compares to 20% – 30% energy conversion for a petrol or diesel vehicle.
Challenges of electric vehicles:
- Price – new EVs tend to cost more to buy than equivalent conventional cars, but much lower running costs will help offset the initial higher price tag.
- Range – most EVs don’t travel as far on a full-charge as petrol or diesel vehicles travel on a full tank.
- Battery re-use and recycling – if an EV battery reaches the end of its vehicle life, it may still have a useful second life, for example storing electricity from solar PV panels. EV manufacturers already have recycling programmes in place.
New Akash Missiles Get Green Light
16, Sep 2018

Why in news?
- The Army, which is inducting the indigenously developed Akash short-range surface-toair missile (SRSAM) system, will get an upgraded variant. The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) gave its procedural approval to the variant.
About the missile:
- Akash missiles are designed to be launched from static or mobile platforms such as battle tanks and wheeled trucks, providing flexible deployment.
- It can handle multiple targets and destroy manoeuvring targets, including unmanned aerial vehicles, fighter aircraft, cruise missiles and missiles launched from helicopters. Deployment of Aakash significantly improves defence capabilities from incoming air attacks.
- Akash missile system is an indigenously developed supersonic short-range surface-to-air missile system with the capability to engage a wide variety of aerial threats like aircraft, helicopters and unmanned aerial vehicles up to a maximum range of 25 km and up to an altitude of 20 km.
- This approval is for the procurement of an upgraded version of Aakash missiles which are much sleeker and more accurate compared to previous versions already in operation.
- Each Akash battery includes four 3D passive electronically scanned array (PESA) radars and four self-propelled launchers with three missiles each, all of which are interconnected. It also has battery level radar known as Rajendra, as well as a battery control centre. It can track and attack multiple targets concurrently.
- The Akash SAM system was produced by Bharat Electronics (BEL). Bharat Dynamics (BDL) serves as nodal agency for Akash SAM production for the army.
- The missile is guided by a phased array fire control radar called ‘Rajendra’ which is termed as Battery Level Radar (BLR) with a tracking range of about 60 km.
- The tracking and missile guidance radar configuration consists of a slew able phased array antenna of more than 4000 elements, spectrally pure TWT transmitter, two stage super heterodyne correlation receiver for three channels, high speed digital signal processor, real time management computer and a powerful radar data processor.
- The Akash is powered by Ramjet-rocket propulsion system which renders thrust for the missile to intercept the target at supersonic speed without any retardation.
- The engine is ‘on’ throughout the flight. The thrust is on till the missile intercepts the target. Most other surface-to-air missiles, including the U.S. Patriot and the Russian S-300 series, use solid-fuel rocket propulsion.
Predatory Bacteria
16, Sep 2018
PREDATORY BACTERIA
Predatory bacteria are the one that feeds on other bacteria, such as those that cause diseases. Dubbed “living antibiotics,” this group of carnivorous fauna have caught researchers’ attention, for their properties. It helps to fight back against antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
GERMANY ROLLS OUT WORLD’S FIRST HYDROGEN TRAIN
16, Sep 2018

Why in news?
- Germany on Monday rolled out the world’s first hydrogen-powered train, signalling the start of a push to challenge the might of polluting diesel trains with costlier but eco-friendly technology.
Background:
- Hydrogen trains are equipped with fuel cells that produce electricity through a combination of hydrogen and oxygen, a process that leaves steam and water as the only emissions.
- Excess energy is stored in ion lithium batteries on board the train.
- The Coradia iLint trains can run for around 1,000 km on a single tank of hydrogen, similar to the range of diesel trains. Alstom is betting on the technology as a greener, quieter alternative to diesel on non-electrified railway lines — an attractive prospect to many German cities scrambling to combat air pollution.
- Two bright blue Coradia iLint trains, built by French TGV-maker Alstom, began running a 100 km (62-mile) route between the towns and cities of Cuxhaven, Bremerhaven, Bremervoerde and Buxtehude in northern Germany — a stretch normally plied by diesel trains.
- Alstom has said it plans to deliver another 14 of the zero-emissions trains to Lower Saxony by 2021, with other German States also expressing an interest.
Advantages of hydrogen fuel:
- It’s a renewable energy source and bountiful in supply
- It practically a clean energy source
- Hydrogen energy is non-toxic
- It’s far more efficient than other sources of energy
- Used for powering space ships
Disadvantages of hydrogen fuel:
- Hydrogen energy is expensive
- Storage complications
- Tricky to move around
- It is highly flammable
- It is not easy to replace existing infrastructure.
Surgical Strike Day- Parakram Parv
14, Sep 2018

Why in news?
- Union Minister of Human Resource Development Prakash Javadekar said that the celebration of September 29 as Surgical Strike Day in universities was not compulsory but claimed that it was decided on the advice of many students.
Surgical strike:
- On 29 September 2016, border skirmishes between India and Pakistan began following reported “surgical strikes” by India against militant launch pads across the Line of Control in Pakistani-administered Azad Kashmir.
- The operations began at 12.30 am when the commandos of Indian Army were dropped at Line of Control (LoC) in the region of Pakistan controlled and administered Kashmir. The surgical operations were conducted in Bhimber, Holspring, Kel and Lipa sectors across the LoC in Pakistan. As claimed by India, during the surgical strike, 7 military launch pads were destroyed and 38 terrorists and 2 Pakistani soldiers were killed. Before the attack, the army forces walked for 1-3 km destroying terrorist bases. All the Indian soldiers returned safely, except one who accidently stepped on a land mile.
- Pakistan rejected India’s reports of any other casualties. Pakistani sources reported that at least 8 Indian soldiers were killed in the exchange, and one was captured. India confirmed that one of its soldiers was in Pakistani custody.
- The Indian operation was said to be in retaliation for a militant attack on the Indian army at Uri on 18 September in the Indian-administered state of Jammu and Kashmir that left 19 soldiers dead.
- In the succeeding days and months, India and Pakistan continued to exchange fire along the border in Kashmir, resulting in dozens of military and civilian casualties on both sides.
After Effect of Surgical Strike:
- Pakistan claimed that there had been no surgical strike conducted at LoC by India. It also increased the terrorist activities in India and strained the relations shared by both the countries.
- It also had a negative impact on the film industry, encountering a significant uprising amongst the citizens on the issue of casting Pakistani actors despite the tension across the border.
- It also saw the formation of allied groups as Pakistan feared of another attack on a larger scale. The Modi government began gathering support from the neighbouring countries like Japan and Germany whereas Pakistan tried to improve their relationship with China.
- In today’s political scenario, every country is trying to strengthen their powers hoping against the odds.
LITHIUM-CARBON-DIOXIDE BATTERIES
14, Sep 2018

- Researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have developed a new battery made partly from carbon dioxide captured from power plants.
About:
- Researchers combined the prior knowledge from two different areas, metal-gas battery electrochemistry and carbon-dioxide capture chemistry, and succeeded in increasing both the energy density of the battery and the efficiency of the carbon-dioxide capture,
- Rather than attempting to convert carbon dioxide to specialized chemicals using metal catalysts, which is currently highly challenging, this battery could continuously convert carbon dioxide into a solid mineral carbonate as it discharges.
- The battery is made from lithium metal, carbon, and an electrolyte, where the captured gas(C02) could then be used during the discharge of the battery to provide a power output. This approach is different from releasing the carbon dioxide back to the gas phase for long-term storage, as is now used in carbon capture and sequestration, or CCS.
Significance:
- The new battery formulation could open up new avenues for tailoring electrochemical carbon dioxide conversion reactions, which may ultimately help reduce the emission of the greenhouse gas to the atmosphere.
- Currently, power plants equipped with carbon capture systems generally use up to 30 percent of the electricity they generate just to power the capture, release, and storage of carbon dioxide. Anything that can reduce the cost of that capture process, or that can result in an end product that has value, could significantly change the economics of such systems,
- Carbon capture is widely considered essential to meeting worldwide goals for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but there are not yet proven, long-term ways of disposing of or using all the resulting carbon dioxide.
- Underground geological disposal is still the leading contender, but this approach remains somewhat unproven and may be limited in how much it can accommodate. It also requires extra energy for drilling and pumping.
GOVERNMENT DEVELOPS ONLINE GAME TO COUNTER CYBER CRIMES AGAINST CHILDREN
14, Sep 2018

- The government has launched its own game application for children in a bid to counter incidents of cyber-crimes against children due to dangerous games like ‘blue whale’ and ‘momo’ challenges.
Background:
- Known as the ‘cyber trivia’ app, it would include a set of multiple-choice questions which will help the kids learn ways to deal with strangers on the internet, the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) said.
- It is an attempt to teach these children in a fun way, what should be done if they are contacted by a stranger on the Internet who might ask for their pictures or ask them to do things
- The game has been developed amid rising cases of suicide by children due to challenges like ‘blue whale’ and ‘momo’. It will soon be available on online stores.
- The children these days outsmart even their parents. They do not understand the dangers the cyber world poses and online games would be really effective. That is the reason we decided to develop this game
- A child psychologist, said that the app is based on behaviour modification technique. “We use a system of rewards and punishments to encourage positive behaviour and discourage negative behaviour. It is a standard technique of behaviour modification therapy”. She said the game might interest younger children but to capture the interest of teenagers it needs to evolve.
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR):
- The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) emphasizes the principle of universality and inviolability of child rights and recognizes the tone of urgency in all the child related policies of the country.
- For the Commission, protection of all children in the 0 to 18 years age group is of equal importance. Thus, policies define priority actions for the most vulnerable children. This includes focus on regions that are backward or on communities or children under certain circumstances, and so on.
- The NCPCR believes that while in addressing only some children, there could be a fallacy of exclusion of many vulnerable children who may not fall under the defined or targeted categories.
India’s DRDO test fires
13, Sep 2018

Why in news?
- India’s Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) has conducted the first successful test firing of a new indigenously designed and developed man portable antitank guided missile (MPATGM) at the Ahmednagar test range in the western Indian state of Maharashtra.
MPATGM:
- The MPATGM is a third-generation anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), which has been under development by DRDO in partnership with Indian defence contractor VEM Technologies Ltd. since 2015.
- Fitted with a high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead, the MPATGM reportedly boasts a top attack capability and has a maximum engagement range of about 2.5 kilometres.
- The man-portable missile is said to be a derivative of the NAG weapon system, and will be the third iteration of the missile following the baseline vehicle-launched version and air-launched version HELINA.
- The Indian Army finally opened its doors to the baseline NAG missile earlier this year after the MoD cleared an inaugural $70 million deal for 300 NAG missiles across 25 tracked launcher vehicles.
- The MPATGM program was sanctioned in January 2015, envisaging modifications to the NAG missile along with a launch tube and launcher system. Design configurations were frozen by the end of 2015.
- In 2016, the DRDO conducted eight static tests of the rocket motor to monitor ballistic performance for shoulder launch.
- India has a large requirement of anti-tank guided missiles running into more than 40,000 missiles for its hundreds of infantry and mechanised Army units.
- It has in the past turned down offers of the U.S.-built Javelin system and has oscillated over the Israeli SPIKE system.
- The indigenous MPATGM is finally off the ground, but has a journey ahead, including an unforgiving user trial phase (that endlessly bedevilled the original NAG system) following the current phase of development launch tests.
- The DRDO has been involved in researching man-portable anti-tank infantry weapons for years now. In 2009, it unveiled a separate light-weight 84mm anti-tank system
JAPAN TO TEST MINI ‘SPACE ELEVATOR’
13, Sep 2018

A Japanese team has developed a “space elevator” and will conduct a first trial this month, blasting off a miniature version on satellites to test the technology.
Mini Space Elevator:
- It’s the world’s first experiment to test travel between two mini satellites in space
- The test equipment, produced by researchers at Shizuoka University, will hitch a ride on an H-2B rocket being launched by Japan’s space agency
- The test involves a miniature elevator stand-in a box just 6 cm long, 3 cm wide, and 3 cm high.
- The mini-elevator will travel along the cable from a container in one of the satellites.
- If all goes well, it will provide proof of concept by moving along a 10-metre cable suspended in space between two mini satellites that will keep it taut.
- The movement of the motorised “elevator” box will be monitored with cameras in the satellites.
- It is still a far cry from the ultimate beam-me-up goals of the project, which builds on a long history of “space elevator” dreams.
- The idea was first proposed in 1895 by Russian scientist Konstantin Tsiolkovsky after he saw the Eiffel Tower in Paris.
- But technical barriers have always kept plans stuck at the conceptual stage.
- Japanese construction firm Obayashi, which is collaborating with the Shizuoka university project, is also exploring other ways to build its own space elevator to put tourists in space in 2050.
- it could use carbon nanotube technology, which is more than 20 times stronger than steel, to build a lift shaft about 96,000 km above the earth
India’s First Missile tracking ship is readying for sea trials
12, Sep 2018
Why in news?
- Hindustan Shipyard Limited (HSL) is gearing up to undertake sea trials of India’s first missile tracking ship by the first week of October.
Background:
- Once ready, it will be India’s first, a force multiplier and cruise the country into a global elite club. The keel of the ship, is being built for the National Technical Research Organisation, the technical intelligence agency working directly under the supervision of the Prime Minister’s Office and the National Security Adviser.
- This will be the first of its kind ocean surveillance ship being built as part of the efforts under the NDA government to strengthen the country’s strategic weapons programme.
- Considered a “topmost secret project”, a lot of confidentiality is being maintained in executing the project costing about ₹750 crore.
- It will be named after its induction into the Indian Navy. For now, it is simply referred as VC 11184.
- It has the capacity to carry 300-strong crew with hi-tech gadgets and communication equipment, powered by two 9000 KW diesel engines, and a large deck capable of helicopter landing.
- 14 MW power is needed to activate the tracking radars.
- The ship can be move at an average speed of 21 knots.
Hindustan Shipyard Limited:
- HSL, set up in 1941, it is poised to get orders for construction of five fleet support ships costing ₹9,000 crore and finalise request for proposal for design collaborator for construction of two Special Operation Vessels called mini submarines.
- It is also banking on the order for medium refit of Russia-made third Sindhughosh class submarine INS Sindhuratna for which it has submitted technical bids.
Ship Building Centre:
- Visakhapatnam is considered a strategic location on the East Coast for the Indian defence forces as it is home for Ship Building Centre to build nuclear powered submarine INS Arihant class.
- Naval Alternate Operational Base at Rambilli, the second naval base after Eastern Naval Command headquarters, training centre for Marine Commandos and headquarters of the submarine arm.
INDIA -RUSSIA COLLABRATION ON GAGANYAAN
12, Sep 2018

- India has sought assistance from Russia in its manned space programme in the area of training the astronauts, life support systems and crew modules.
About:
- The talk of Russia assisting India in the manned space mission came up during the meeting in Moscow between external affairs minister Sushma Swaraj and Russia’s deputy prime minister for defence and space industry a week ago.
- A proposal was made about Russian specialists’ assistance in conducting various stages of selection of candidates for the flight, as well as (the candidates) passing a training course in Russia and assistance in the subsequent training of Indian astronauts in India,
- In 2015, India and Russia signed an agreement to pursue joint programmes in a few areas of space research. Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Russian Federal Space Agency (ROSCOSMOS) signed a new Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on expansion of cooperation in the field of the exploration and use of outer space for peaceful purposes.
- This new MoU provides scope for developing joint activities in areas of mutual interest, including satellite navigation, launch vehicle development, critical technologies for human spaceflight programme, remote sensing of Earth, space science and planetary exploration, and use of ground space infrastructure.
- India will become the fourth country after Russia, US and China to send a human to space on its own, if it successfully completes the mission.
Gaganyaan:
- Gaganyaan is an Indian crewed orbital spacecraft intended to be the basis of the Indian Human Spaceflight Programme.
- The spacecraft is being designed to carry three people, and a planned upgraded version will be equipped with rendezvous and docking capability.
- In its maiden crewed mission, Indian Space Research Organisation’s largely autonomous 3.7-tonne capsule will orbit the Earth at 400 km (250 mi) altitude for up to seven days with a three-person crew on board. The crewed vehicle is planned to be launched on ISRO’s GSLV Mk III in 2022
International Co-operation:
- India has always recognised that space has dimension beyond national considerations, which can only be addressed along with international partners.
- Over the years, as ISRO has matured in experience and technological capabilities, the scope for cooperation has become multifaceted.
- ISRO has the benefit of International cooperation since inception. Establishment of Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS), conduct of Satellite Instructional Television Experiment (SITE) and Satellite Telecommunication Experiment Project (STEP), launches of Aryabhata, Bhaskara, Ariane Passenger Payload Experiment (APPLE), IRS-IA, IRS-IB satellites, INSAT series of satellites, Mission to Moon, Human Space flight Programme Initiatives, etc., have the components of international cooperation.
- ISRO is pursuing bilateral and multilateral relations with space agencies and space related bodies with the aim of building and strengthening existing ties between countries; taking up new scientific and technological challenges; refining space policies and defining international frameworks for exploitation and utilisation of outer space for peaceful purposes.
- Specifically, the developing countries look to India for assistance in building up their capabilities to derive benefits of space technology. The scope of international cooperation has become wider and diverse, as ISRO has made tremendous progress in recent time.
- The data products generated from recently launched OCEANSAT-2 and Scatter meter is made available globally in near-real-time for global applications through an arrangement with EUMETSAT.
- India continues to play active role in deliberation on Scientific and Technical and Legal sub-committees of the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (UN-COPUOS) and others.
ISRO-Russia:
- Russia has played an important role in India’s space journey, and space remains one of the key pillars of the strategic partnership between the two countries. Over the years India’s indigenous space programme has benefited from Russian technical and scientific assistance.
- The first man to travel to space, Russian cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin predicted a future collaboration between the two nations, back in 1961, when he spent 8 days in India. Two decades later, Rakesh Sharma made the nation proud, becoming the first Indian to travel to outer space, on board the Soyuz T-11 spacecraft with a Russian commander and a Russian flight engineer.
- India and Russia have a four-decade strong relationship in the field of space. The former Soviet Union launched India’s first two satellites, Aryabhata and Bhaskar, into orbit from Baikonur Cosmo drome. Aryabhata was launched on the Soviet launch vehicle Soyuz.
- Even today, both countries cooperate on lunar and Mars exploration missions. India will be using Russian isotope products in its lunar mission Chandrayaan-2, which will be launched in 2018.
Logistic deal with Russia
11, Sep 2018

- India and Russia are in the process of concluding a logistics agreement, with both sides targeting to conclude consultations before the annual summit.
Logistics agreement with other countries:
- India signed the Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Understanding (LEMOA), with the U.S. in August 2016 after a decade of negotiations.
- Since then it has concluded several such agreements with France, Oman, Philippines, Singapore and for access to the Sabang port in Indonesia.
Importance with Russia:
- India has longstanding and wide-ranging cooperation with Russia in the field of defence. India-Russia military technical cooperation has evolved from a simple buyer-seller framework to one involving joint research, development and production of advanced defence technologies and systems.
- It increases operational flexibility
- Logistics agreements are administrative arrangements facilitating access to military facilities for exchange of fuel and provisions on mutual agreement simplifying logistical support and increasing operational turnaround of the military when operating away from India.
NASA’s ICESAT- 2
11, Sep 2018

- NASA mission that will use a laser to track changing ice levels on Earth soared into space. Lifting ICESat-2 on a quest to explore the polar ice sheets of our constantly changing home planet.
About:
- The satellite will reveal new insights into the ice in the deep interior of Antarctica, which is area of mystery to scientists.
- The new laser will fire 10,000 times in one second, compared to the original ICE Sat which fired 40 times a second.
- Measurements will be taken every 2.3 feet (0.7 meters) along the satellite’s path.
- “The mission will gather enough data to estimate the annual elevation change in the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets even if it’s as slight as four millimetres – the width of a No. 2 pencil.
- Importantly, the laser will measure the slope and height of the ice, not just the area it covers, also will allow ice sheet modelers to make better predictions of the future,
- It is launched in the background of urgent need of data about ice melt since global average temperatures have climbed year after year, with four of the hottest years in modern times all taking place from 2014-2017.
- The launch marks the first time in nearly a decade that NASA has had a tool in orbit to measure ice sheet surface elevation across the globe.
- The preceding mission, ICE Sat, launched in 2003 and ended in 2009.
- The first ICE Sat revealed that sea ice was thinning, and ice cover was disappearing from coastal areas in Greenland and Antarctica.
- In the intervening nine years, an aircraft mission called Operation Ice Bridge, has flown over the Arctic and Antarctic, taking height measurements of the changing ice.
- But a view from space especially with the latest technology should be far more precise.
S-300 Missile
10, Sep 2018

- Russia will transfer two to four S-300 air defence missile systems to Syria. It is a long-range, multi-channel anti-ballistic missile defence system which provides war fighters with enhanced combat capabilities.
- Venezuela received two S-300VM air defence systems in April 2013. Russia has also offered the missile system to Turkey and Saudi Arabia.
ISRO incubation centre
10, Sep 2018

- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) launched a space technology incubation centre in Tripura capital Agartala. The incubation centre will be located in the National Institute of Technology, Agartala.
About:
- The Centre was launched at the first edition of ‘Spacetronics’ organised by the India Electronics and Semiconductor Association (IESA). ISRO’s first Space Technology Incubation Centre
- It is the first of six such centres planned nationally to build capacity in new locations. More such space research activities will be splashed in a big way across small cities to tap their talent and include them in the space footprint
- The space agency’s new Capacity Building Programme directorate will invest ₹2 crore. Within the next six months, ISRO plans to set up five more space technology incubation centres at Jalandhar in Punjab, Bhubaneswar in Odisha, Nagpur in Maharashtra, Indore in Madhya Pradesh and Tiruchirapalli in Tamil Nadu.
- The centres will bring out prototypes and innovations for ISRO in electronics, propulsion and others. ISRO will buy the innovations back if we can use them in our programmes.
- It is to incubate start-ups which would build applications, offer services and products which can be used internally and exploit opportunities globally given enough help to scale up. It is put in place policies and framework to ensure that the ecosystem is favourable to more partnerships, access to funds, ease of business, networking in the domestic and international market and more importantly, inculcating this new initiative – ISRO Space Technology Incubation Centre of the NIT, Agartala.
- This facility, with active support from the state government of Tripura and IESA, the Ecosystem Partner, will be a big boost for the process in every sense.
- The state is working to emerge as a prominent place in Indian technology map by nurturing innovation, entrepreneurship and invention.
- This is a kind of process to develop start-ups by ISRO and the government initiative of Transforming India.
Significance:
- ISRO will also provide the necessary mentorship and guidance to individuals and businesses at the incubation centres.
- Those locations to set up incubation centres where there is no space activity happening, but there is a presence of strong academic institutions and industry, so as to spur research and innovations in the country.
- If the prototypes developed by the start-ups along with the industry meet the standards required, ISRO will acquire the technologies and components for use in its future space missions.
- The incubation centre will provide Tripura with an opportunity to steer ahead in the Information Technology (IT) and manufacturing sectors.
- The space agency aims to make use of the brightest minds across the length and breadth of the country.
- With India forced to import over 75 % of its electronics needs, there is a huge opportunity for Indian industry to expand their businesses
SMART Fencing of India Borders
09, Sep 2018

- Union Home Minister Rajnath Singh on Monday inaugurated the first phase of hi-tech ‘smart fencing’ of a 11 km stretch on the International Border (IB) in Jammu as the system would prevent the infiltration of terrorists and will reduce the casualties of security forces at the border.
- He also mentioned a future plan of covering more than 2000 km of ‘vulnerable’ and unfenced areas through CIBMS.
About:
- The launch of two pilot projects of ‘smart fencing’ along India’s International Border with Pakistan, is being implemented at a 60 km patch. A part of the project is functional.
- The smart fencing project will initially be implemented to cover gaps in the physical fencing. Eventually, this technology will be implemented across the entire border, which is planned to be launched by December.
- The BSF had taken up the initiative as part of the comprehensive integrated border management system. Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS) would provide for round-the-clock laser-guided surveillance of the borders.
- The CIBMS- a concept and nomenclature written by Commandant Jagdish Maithaniintegrates different sensors to maintain surveillance over an area. The data collected is sent to a command and control centre, from where operations can be directed.
- It consists of five types of sensors- radar, electro optics, unattended ground sensors, OFC based sensors and mini aerostat.
In Assam:
- A similar setup that was planned border along the Brahmaputra river in Dhubri later this month has hit rough weather.
- Due to its geographical features, no outpost could be erected in the area which often led to incidents like illegal migrations going unchecked. The smart fencing can be a solution for this problem.
- The Border Security Force (BSF), which is implementing this project in Assam, says that it is facing a few challenges such as setting up technological equipment on the riverbed with the river changing course regularly, finding sensors that can work in water and shortage of power and data connectivity.
- The Dhubri project was supposed to have technical issues, if someone is infiltrating through the riverine stretch, the problem is that there is so much ambient noise that it requires a software of the capability of a sonar to bring out the characteristic signature. For example, cattle could be crossing or a boat is passing by, the software should be able to differentiate each one of them.
- The river changes course and a whole installation can get washed away. It is important to make a project which is dynamic, so that even if the river changes course it should still work.
- Only a few sensors can work in rivers such as sonars and getting them is another challenge. There is also no power and data connectivity in these areas, so have to setup these things ourselves.
Border Fencing:
- India’s geostrategic location, its relatively sound economic position vis-à-vis its neighbours and its liberal democratic credentials have induced the government to undertake proper management of Indian borders, which is vital to national security.
- India shares 15,106.7 km of its boundary with seven nations Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, Bangladesh and Afghanistan. These land borders run through different terrains, managing a diverse land border is a complex task but very significant for security point of view.
- What further increase the complexity and criticality are the varied climatic conditions and relationship with some of the neighbouring countries.
- The traditional approach to border management, i.e. focussing only on border security, has become inadequate. India needs to not only ensure seamlessness in the legitimate movement of people and goods across its borders but also undertake reforms to curb illegal flow
- With the adoption of new technologies for border control and surveillance and the development of integrated systems for entering, exchange and storage of data, will facilitate the movement of people and products without endangering security.
- Smart border management is an attempt to identify and implement controls which aim to improve border security by
- Enabling effective communication and coordination among all security agencies
to arrive at a common entity picture. - Neutralising threats linked to terrorism and organised crime.
- Checking illegal migration.
- Enabling effective communication and coordination among all security agencies
Current system:
- A variety of measures are taken to safeguard land borders. These measures are grouped
into three categories people, process and technology.- Comprises the various types of forces and manpower deployed for safeguarding
our borders. - Outlines a few initiatives taken by the Government of India to streamline the
process of border control. - Lists the technological controls into which the Government of India continues to
invest in order to strengthen border management.
- Comprises the various types of forces and manpower deployed for safeguarding
Indo-Pak Border Challenges:
- Critical issues like the Pakistan occupied Kashmir, Sir Creek dispute, cross-border terrorism and ceasefire violation are key challenges plaguing this part of the Indian border and our armed forces.
- The harsh and varied climatic conditions along this 3,323-km of border compound the challenges faced by our armed forces in securing these areas.
- An increase in ceasefire violation and infiltration amount have been observed during the pre-winter season, when vigilance becomes extremely tough due to snowfall along the mountainous terrain.
- Other factors like the political instability and crisis in Pakistan also lead to an upsurge in cross-border tension along the border areas.
Data localisation
29, Aug 2018

Why in news?
- S. technology giants plan to intensify lobbying efforts against stringent Indian data localisation requirements, which they say will undermine their growth ambitions in India.
What is data localisation?
- Data localization is the act of storing data on any device that is physically present within the borders of a specific country where the data was generated.
Advantages of data localisation:
- The main advantages of securing citizen’s data, data privacy, data sovereignty, national security, and economic development of the country.
- It acts as a solution for the advent of cloud computing that raises important questions on accountability of service providers who store Indian users’ data outside of the country’s boundaries, leading to a conflict of jurisdiction in case of any dispute.
- Also, minimal or deregulated governance on critical data, due to absence of localisation requirements, could be detrimental to India’s national security as data would be outside the purview of existing data protection legislation. This shall be avoided in in case of data localisation.
- In addition to these, India also aspires to become a global hub for, among others, cloud computing, data hosting and international data centres, all of which are prompting the government to enact data localisation requirements for accelerating the nation’s economic growth, especially in the sphere of digital technologies.
Delhi Government Official Bags WHO Award
29, Aug 2018

- Delhi government’s additional director of health S.K. Arora has been awarded the prestigious WHO World No Tobacco Day 2018 Award for his extraordinary contribution towards tobacco control.
National Tobacco Control Programme:
- India is the second largest tobacco consuming country in the world with 27 crore users.
- The National Tobacco Control Programme (NTCP) was launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW), Government of India in 2007- 08, during the 11th five year plan, with the following objectives:
- To bring about greater awareness about the harmful effects of tobacco use and about the Tobacco Control Laws.
- To facilitate effective implementation of the Tobacco Control Laws.
- The key activities undertaken under the National Tobacco Control Programme include:
- National Level Public awareness campaigns
- Monitoring, Evaluation and Research.
- Advocacy and inter-sectoral linkages
- Training and capacity building of multiple stakeholders.
- Enforcement of the Tobacco Control Act (COTPA, 2003)
- School Awareness Programmes
- Setting up and expansion of cessation services.
WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC)
- The WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) is the first global public health treaty. It is an evidence-based treaty that reaffirms the right of all people to the highest standard of health.
- The WHO FCTC was developed by countries in response to the globalization of the tobacco epidemic.
- The Treaty was developed by countries in response to the globalization of the tobacco epidemic.
- There are currently 180 Parties to the Convention.
- India has been the forerunner in ratification of this public health treaty and was the 7th Country to ratify the Convention in 2004.
- India provided a leadership role in the negotiations of FCTC and was also the Regional Coordinator for the South-East Asia Region.
- The Conference of the Parties (COP) is the Governing Body of the WHO FCTC and is comprised of all Parties to the Convention.
- It keeps under regular review the implementation of the Convention and takes the decisions necessary to promote its effective implementation, and may also adopt protocols, annexes and amendments to the Convention.
Outcomes:
- As a result of various measures taken by the government, NGOs and civil society organizations, the tobacco use in the country is estimated to have reduced by 81 lakhs and youth consumption of tobacco has also seen marked decrease.
- A 54% relative reduction in prevalence of tobacco use among minors (15-17 years) and 28% reduction in the age group of 18-24 years has been reported
5g Technology
29, Aug 2018

TRAI gives nod for sale of 5G spectrum
About:
- It is a mobile network connectivity that would ensure fast broadband Speeds along with capacity to perform well without barrier’s
Characteristics:
- Fast speed compared to previous generation
- Reliability
- Higher Bandwidth
- How Latency ratio
- Can increase the number of interconnected devices
Challenges Faced:
- Infrastructure : Lack of infrastructure for 5G services and lack of allocation of spectrum.
- Communication, Navigation and sensing : It requires large radio spectrum to transmit signals and we lack this infrastructure
- Security and privacy : 5G has to define the uncertainties related to security threats including, trust, privacy, cybersecurity which are growing across globe.
- Legislation : Cybercrime and online Fraudent activities will increase with increase in technology. Therefore a good Cybersecurity initiative is mandatory
Impact of 5G Technology:
- It makes data sharing, enabling and transfer and processing more quickly which will result in enhanced application like internet of things even more faster and larger.
- This Technology will be a short in the arm for sister technologies like artificial intelligence and cloud computing
- This Technology will gather all networks in one platform and provide a huge broadcasting data.
- Will make possible to provide uninterrupted connectivity with uniform high speeds across the world.
- It will boost the ambitious project of ‘Digital India’ by making possible the last mile connectivity whereby enhancing the governance.
Centre wants supreme court to get tough with FB, YouTube
28, Aug 2018

- The efforts by Internet giants to curb circulation of online videos of sexual violence against women and children inadequate, the government is likely to seek “stricter directions” to service providers, such as Facebook and YouTube, from the Supreme Court.
Directions sought:
- Reducing the time taken by the intermediary to comply with content removal requests under certain Sections of the IT Act to less than 10 hours from about 36 hours at present.
- The service providers be asked to employ agencies for identification and removal of sexually violent content, particularly videos relating to child pornography and rape.
- Intermediaries should be asked to keep a complete trail of forwarding of unlawful content and verify and maintain identifiers of the users that can help attribute information to the users.
- The centre also wants service providers to be able to identify the origin of such content.
Congo Cube
28, Aug 2018

- The Alliance for International Medical Action, or ALIMA, in collaboration with Securitec, has developed a self-contained treatment unit or a bio-secure emergency room called CUBE, or Cudor Chambre d’Urgence Biosécurisée.
- It allows for quality care with minimal contamination risks, having been developed in the aftermath of the 2014 Ebola outbreak.
Advantages:
- The primary objective is to confine the start of an outbreak by creating a first line of treatment close to a patient’s home.
- As a transportable unit that can be assembled in 90 minutes, its main advantage is that health workers no longer need personal protective equipment as protection is centred around the patient.
- With its transparent walls and external arm entries, medical teams can comfortably ensure continuous monitoring of an infected patient and also adapting treatment from the outside, reducing the risk of contamination.
- The patient also benefits from the transparent walls which allow them to remain in contact with the outside world, again without the risk of contamination.
- As the unit includes air conditioning and air filtration units, it can also be configured as an operating theatre and ‘P4-level’ laboratory for diagnostics and research.
LIGO-India
27, Aug 2018

- The Environment Ministry has allowed scientists to test the suitability of land in Maharashtra’s Hingoli district to host the India wing of the ambitious Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory (LIGO) project.
About:
- The first of its kind in Asia to study gravitational wave.
- The LIGO-India project is an international collaboration between the LIGO Laboratory and three lead institutions in the LIGO-India consortium: Institute of Plasma Research, Gandhinagar; IUCAA, Pune; and Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology, Indore.
- The proposed LIGO-India project aims to move one Advanced LIGO detector from Hanford to India.
- The LIGO-India consortium, made up of physicists from several institutes, had submitted a proposal to “prospect” 121 hectares of forest land in Dudhala village, Hingoli.
- The project, piloted by the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and Department of Science and Technology (DST), is expected to be ready by 2025.
Project:
- An astronomical observatory, the LIGO detector will increase the ability and accuracy of localizing gravitational wave sources in the sky.
- The project involves constructing a network of L-shaped arms, each four kilometres long, which can detect even the faintest ripples from cosmic explosions millions of light years away.
- The construction of such a large, sensitive device — there are only three of its kind in the world — requires an extremely flat surface.
Background:
- Gravitational waves were predicted by Albert Einstein a century ago as part of his theory of general relativity, but the first hard evidence of their existence came only in 2015, when two U.S. detectors found the first such signal.
- Gravitational waves are ripples in the otherwise tough, stiff fabric of spacetime produced by the most violent phenomena the cosmos can offer—things like exploding stars and collisions between ultra-dense neutron stars or merging black holes.
- These ripples would travel at the speed of light through the Universe, carrying with them information about their cataclysmic origins, as well as invaluable clues to the nature of gravity itself.
- The strongest sources of gravitational waves are among the enigmatic objects in our universe: black holes, neutron stars, supernovae, even the Big Bang.
- The LIGO facility consists of two identical L-shaped detectors in Washington state and Louisiana, each of which employs lasers and mirrors to measure the tiny changes in spacetime made by passing gravitational radiation.
- Known as interferometers, these high-tech underground stations do not rely on light in the sky like a telescope does, but instead sense vibrations in space and can pick up the “chirp” created by a gravitational wave.
- Extracting the information carried by the waves to address questions in both physics and astronomy depends on our ability to identify where the individual sources are on the sky. This requires a network of detectors spread widely over the Earth.
- LIGO operates two sites in the United States and collaborates with a similar detector in Italy (Virgo). Together they can triangulate sources over part of the sky. LIGO-India will enable scientists to locate sources over the entire sky.
- The discovery of gravitational waves earned three U.S. scientists the Nobel for physics in 2017.
Need of it:
- Gravitational waves are so hard to detect. By the time gravitational waves reach us from the distant events that spawn them, they distort spacetime by an utterly minuscule amount. The distortion is many times smaller than the width of a proton, one of the particles in an atom’s nucleus. Measuring such minute changes in length is pretty much impossible for most instruments.
Significance:
- Previously, scientists have relied primarily on observations with electromagnetic radiation (visible light, x-rays, radio waves, microwaves, etc.) to learn about and understand objects and phenomena in the Universe.
- But it is completely different phenomenon, it carry information about cosmic objects and events that is not carried by usual electromagnetic radiation .
- Detecting and analysing the information carried by gravitational waves will allow us to observe the Universe in a way never before possible.
- It will open up a new window of study on the Universe, give us a deeper understanding of these cataclysmic events, and usher in cutting-edge research in physics, astronomy, and astrophysics.
- More importantly, since gravitational waves interact very weakly with matter (unlike electromagnetic radiation), they travel through the Universe virtually unimpeded giving us a clear view of the gravitational-wave Universe.
- Measuring the gravitational-wave background will allow us to study populations of black holes at vast distances.
- Hosting such a detector in India will improve the odds of detecting more such phenomena. The first detection of gravitational waves will be one of the highest profile scientific discoveries of our time. Engaging the Indian scientific community in this quest will raise the visibility and appeal of experimental science in India.
- The presence of a world-leading facility in India can be used to attract students and inspire them to pursue technical careers.
- The physical measurements required for gravitational wave detection are arguably the most precise ever made, and they involve cutting edge technologies that have many non-military applications.
- The LIGO Laboratory will provide the hardware for a complete LIGO interferometer, technical data on its design, installation and commissioning, training and assistance with installation and commissioning, and the requirements and designs for the necessary infrastructure
- The LIGO project operates three gravitational-wave (GW) detectors. Two are at Hanford in the State of Washington, north-western USA, and one is at Livingston in Louisiana, south-eastern USA.
- However, there are more than 100,000 gravitational wave events every year too faint for LIGO and Virgo to unambiguously detect due to less coverage. Thus by establishing LIGO in India makes it possible to detect it.
A New, Robust form of Gold
26, Aug 2018

- Researchers from Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR), Bengaluru, have developed a new type of gold in the form of very small crystals — micro crystallites.
Robust Form of Gold:
- The microcrystal gold has been found to be nobler than gold — it do not dissolve in mercury and Aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), and showed the least interaction with copper.
- The microcystallites were synthesised by decomposing an organic complex containing gold and other ions under controlled conditions.
- The newly formed microcystallites, about 3 micrometre in length were found to be of a different crystal structure.
- Normal gold has a (face-centered) cubic structure, while the new ones exhibit deformed cubic structure — tetragonal and orthorhombic cells.
- The researchers then examined copper growth on these gold crystals when subjected to plating without the use of electrodes.
- Electron microscopy images revealed that thick copper got deposited on normal gold within minutes, while no detectable copper was seen on the central portion of the new crystals even after an hour.
- It is found that deposition of copper only on the tips of the new crystallites while the rest of the crystal surface was devoid of copper. This may be due to the different arrangement of the new facets.
- The researchers then investigated the stability of the gold microcystallites using corrosive agents like mercury and Aqua regia. While normal gold disappeared in a matter of minutes when immersed in mercury and also in aqua regia, the gold crystallites remained intact. Microscopy imaging showed that the surface was undamaged.
As a catalyst:
- All these properties make new crystallites an ideal candidate for catalytic purposes.
- Gold in itself is not a catalyst but the new gold microcystallites have very active surfaces.
- Compared with other catalysts like palladium and ruthenium, gold is cheaper and it can also be easily recovered.
- Though the production cost of the crystallites is a little high,
researchers are optimising it to bring down the cost. More studies are needed to understand them fully in the context wide range of applications in the offing,” he added.
India’s First Biofuel flight
26, Aug 2018

Why in news?
- SpiceJet today operated India’s first test flight powered biojet fuel, marking a new chapter in the fast-growing domestic sector. The flight was tested from Dehradun to Delhi.
Biofuel blend ATF:
- A blend of oil from Jatropa seeds and aviation turbine fuel propelled the country’s first ever bio jet fuel powered flight.
- A blend of 25%of bio jet fuel and 75% of aviation turbine fuel (ATF) was carried in one of the two engines of the plane, while the other engine carried only ATF. International standards permit a blend rate of up to 50% biofuel with ATF.
- It has the potential to reduce fuel costs by 15-20%
- The indigenously developed fuel has been nearly 8 years in the making by the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) lab based in Dehradun along with the Indian Institute of Petroleum (IIP).
- The institute started its experiment on biofuel soon after Virgin Atlantic carried out the first test flight globally in 2008.
Jatropa:
- Jatropha oil has been used in India for several decades as biodiesel for the diesel fuel requirements of remote rural and forest communities. It is a second generation-based biofuel.
- Jatropha oil can be used directly after extraction (i.e. without refining) in diesel generators and engines.
- Jatropha has the potential to provide economic benefits at the local level since under suitable management it has the potential to grow in dry marginal non-agricultural lands, thereby allowing villagers and farmers to leverage non-farm land for income generation.
- Since no food producing farmland is required for producing this biofuel (unlike corn or sugar cane ethanol, or palm oil diesel), it is considered the most politically and morally acceptable choice among India’s current biofuel options; it has no known negative impact on the production of the massive amount’s grains.
DNA Reveals First Inter-Species Child
26, Aug 2018

Why in news?
- Denny’s mother was a Neanderthal, but her father a Denisovan, a distinct species of primitive human
About Denny:
- Her mother was a Neanderthal, but her father was Denisovan, a distinct species of primitive human that also roamed the Eurasian continent 50,000 years ago, scientists reported.
- Nicknamed by Oxford University scientists, Denisova 11 — her official name — was at least 13 when she died, for reasons unknown.
First direct link:
- There was earlier evidence of interbreeding between different hominin, or early human, groups, said lead author Viviane Slon of Evolutionary Anthropology. But this is the first time that they have found a direct, first-generation offspring.
- Denny’s surprising pedigree was unlocked from a bone fragment unearthed in 2012 by Russian archeologists at the Denisova Cave in the Altai Mountains of Siberia.
- Analysis of the bone’s DNA left no doubt: the chromosomes were a 50-50 mix of Neanderthal and Denisovan, two distinct species of early humans that split apart between 4,00,000 to 5,00,000 years ago.
Early humans:
- Worldwide, fewer than two dozen early human genomes from before 40,000 years ago — Neanderthal, Denisovan, Homo sapiens — have been sequenced, and the chances of stumbling on a half-and-half hybrid seemed vanishingly small.
- The very fact that we found this individual of mixed Neanderthal and Denisovan origins suggests that they interbred much more often than we thought.
- A 40,000-year-old Homo sapiens with a Neanderthal ancestor a few generations back, recently found in Romania, also bolsters this notion. But the most compelling evidence that inter-species hanky-panky in Late Pleistocene Eurasia may not have been that rare lies in the genes of contemporary humans.
- About 2% of DNA in non-Africans across the globe today originate with Neanderthals, earlier studies have shown.
- Denisovan remnants are also widespread, though less evenly. We find traces of Denisovan DNA — less than 1% — everywhere in Asia and among native Americans. “Aboriginal Australians and people in Papua New Guinea have about 5%.”
- Taken together, these facts support a novel answer to the hotly debated question of why Neanderthals — which had successfully spread across parts of western and central Europe — disappeared some 40,000 years ago.
Gaganyaan
26, Aug 2018

- Gaganyaan, the human space flight Programme green-flagged and set for 2022. State-run Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will fly an Indian astronaut into space for the first time by 2022.
About:
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to develop and launch a two-person crew to low Earth orbit.
- Most of the critical technologies and hardware required for the project are ready or have been demonstrated by its centres.
- When it achieves the mission, India would be the fourth nation to circle Earth after the Soviets, the Americans and the Chinese.
- Previously in 1984, Rakesh Sharma became the first Indian cosmonaut to fly into space on-board Russian Soyuz spacecraft.
Timeline for Human Space Programme:
- ISRO revealed the first germ of an HSP in November 2004 and got incremental funds for supporting projects over the next few years.
- In the last few years, it did a lot of groundwork as part of R&D at our centres. ISRO have developed most of the critical technologies needed for a human mission.
- It could not go ahead mainly because the GSLV Mark III vehicle was not ready until last year.
- ISRO demonstrated the flight of a crew module and its re-entry in 2014.
- On July 5 this year, ISRO conducted an experiment for emergency escape of astronauts called the Pad Abort Test. It will be repeated at higher distances.
- The rest of the technologies are getting ready and will be realised in time.
- The most critical elements of the human mission are the Environment Control and Life Support Systems that make the crew capsule liveable and the flight safe for the astronauts, food and hygiene are other aspects. These technologies are getting ready while space suits are being developed at ISRO.
- ISRO will set up a full-fledged training facility in Bangalore for training Vyomanauts. centre will train the selected Vyomanauts in rescue and recovery operations, operate in zero gravity environment, and monitoring of the radiation environment.
- ISRO is planning to build a third launch pad at Sriharikota for manned missions with extra facilities like entry into the crew capsule and an escape chute.
Positive:
- Describing it more as a national mission than ISRO’s alone, It would raise scientific and technological temper across the country and inspire youngsters.
- Manned flights is in keeping with India’s emergence as an economic and technological power house.
- Space research is truly inter-disciplinary and has enabled true innovations at the intersection of multiple areas of science and engineering.so by launching manned mission will make multiplier effect in other field.
- Human spaceflight has enabled the emergence of new research: physical and life sciences in space.in the area of fundamental and applied research.
- By exploiting the unique conditions in space, particularly microgravity, scientists have begun to examine many fundamental processes in physics, chemistry and biology that would normally be masked by Earth’s gravity.
- Experiments that have flown on the Space Shuttle and on space stations have already contributed to the development of new theories and the discovery of new phenomena. Such fundamental research offers good prospects for applications that will benefit society as a whole, notably in the areas of biotechnology, new materials, combustion, fluid physics and medical science.
- This will further improve scientific knowledge and create new industrial applications for the benefit of society
- But it is fantasy of competing with the economically advanced nations in the exploration of the moon or the planets or manned spaceflight. we must develop advanced technologies to the real problems of man and society which we find in our country.
Chandrayan – I
26, Aug 2018

- The first Indian planetary mission to moon, Chandrayaan-1 with a suite of Indian
- And International payloads on board, collected very significant data over its mission duration of close to one year.
- This mission was a huge success.
- The observations made by Chandrayan – 1 are as follows
- Discovery of hydroxyl (-OH ) and water molecule in sunlit lunar surface region around the poles
- exposure of large anorthositic blocks confirming the global lunar magma hypothesis
- signature of sub surface ice layers in permanently shadowed regions near the lunar north pole evidence for a new refractory rock type
- mapping of reflected lunar neutral atoms and identification of mini-magnetosphere
- mapping of reflected lunar neutral atoms and identification of mini-magnetosphere
- preserved lava tube that may provide site for future human habitation.
New Radio Galaxy Discovered Using Indian Telescope
25, Aug 2018

Why in news?
- Astronomers have made use of the Indian telescope “Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope” to discover the most distant radio galaxy ever known.
The Radio galaxy:
- Radio galaxies are very rare objects in the universe. They are colossal galaxies with a supermassive black hole in their centre that actively accretes gas and dust from its surroundings.
- It is located at a distance of 12 billion light-years.
- The radio galaxy belongs to a time when the universe was only seven per cent of its current age.
- This activity initiates the launch of high-energy jet streams, which are capable of accelerating charged particles around the supermassive black hole to almost the speed of light.
Significance:
- The discovery of such galaxies at extremely large distances is important for our understanding of the formation and evolution of galaxies.
- The researchers are of the view that analysing and studying these galaxies at length also reveals the formation of primordial black holes.
- These black holes have driven and regulated the growth of galaxies.
Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope:
- National Centre for Radio Astrophysics has set up a unique facility for radio astronomical research using the metre wavelengths range of the radio spectrum, known as the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT).
- It is located at a site about 80 km north of Pune. GMRT consists of 30 fully steerable gigantic parabolic dishes of 45m diameter each spread over distances of upto 25 km.
- GMRT is one of the most challenging experimental programmes in basic sciences undertaken by Indian scientists and engineers.
- GMRT is a very versatile instrument for investigating a variety of radio astrophysical problems ranging from nearby Solar system to the edge of observable Universe.
Hemochromatosis- Iron Overload Disease
24, Aug 2018
- Researchers at the Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology (CSIR-IGIB) have successfully discovered a pathway that regulates hepcidin hormone production by Gene mutations.
About:
- The hepcidin hormone which is released by the liver, is a central regulator of iron in the body.
- Dysregulation of the hormone leads to anaemia on one hand and excess iron accumulation in organs such as liver and heart leading to multi-organ failure.
- Hepcidin hormone is low in the hemochromatosis patients, and that this causes iron overload.
- Mutations in about six genes are known to cause reduction in hepcidin hormone production thereby causing excess iron accumulation.
- This is the first time that researchers have been able to identify and tell that the NFkB pathway regulates liver hepcidin production.
- In India, Hemochromatosis is still not commonly seen, perhaps because of our underlying iron deficiency. But Thalassemia, is a serious problem where iron overload is very common.
Hemochromatosis:
- Hemochromatosis causes your body to absorb too much iron from the food you eat. Excess iron is stored in your organs, especially your liver, heart and pancreas.
- Too much iron can lead to life-threatening conditions, such as liver disease, heart problems and diabetes.
Cause:
- Hereditary hemochromatosis is caused by a mutation in a gene that controls the amount of iron your body absorbs from the food you eat.
- The genes that cause hemochromatosis are inherited, but only a minority of people who have the genes ever develop serious problems.
Symptoms:
- Early symptoms include Joint pain, Abdominal pain, Fatigue, Weakness Later symptoms include Diabetes, Loss of sex drive, Impotence, Heart failure, Liver failure.
- Some people with hereditary hemochromatosis never has symptoms. Hereditary hemochromatosis is present at birth. But, most people don’t experience signs and symptoms until later in life usually between the ages of 50 and 60 in men and after age 60 in women. Women are more likely to develop symptoms after menopause, when they no longer lose iron with menstruation and pregnancy.
Treatment:
- Treatment includes regularly removing blood from your body. Because much of the body’s iron is contained in red blood cells, this treatment lowers iron levels.
Chandrayan – 2
23, Aug 2018

- India’s second mission to the Moon is a totally indigenous mission comprising of an Orbiter, Lander and Rover.
- The payloads will collect scientific information on lunar topography, mineralogy, elemental abundance, lunar exosphere and signatures of hydroxyl and water-ice.
- Chandrayaan-2 will be ISRO’s first time attempt to land a rover, on the Moon. The rover, will be made to land near the yet-unexplored south pole of the moon.
- It is also ISRO’s first mission to land on any celestial body.
Orbiter:
- The orbiter is physically similar to Chandrayaan-1.
- It is three-axis stabilized with reaction wheels.
- The orbiter carries five science instruments and two supporting instruments.
Terrain Mapping Camera 2 (TMC-2):
- It will perform 3D mapping of the lunar surface using two cameras.
Collimated Large Array Soft X-ray Spectrometer (CLASS):
- It will map abundance of major rock-forming elements on the Moon including Mg, Al, Si, Ca, Ti, and Fe.
- Assisting it is the Solar X-ray Monitor (XSM), which measures solar x-ray emission.
Chandra’s Atmospheric Composition Explorer(ChACE-2)
- It is a neutral mass spectrometer that is based upon CHACE
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)
- It will perform radar mapping of the surface in both L and S bands of the radio spectrum.
- It has heritage from MiniSAR on Chandrayaan-1 but will be the first L-band radar mapper to orbit the Moon.
Imaging Infra-Red Spectrometer (IIRS)
- It is sensitive to light with wavelengths between 0.8 and 5 microns and has the specific goal of mapping the abundance of hydroxl ions and molecular water.
Orbiter High Resolution Camera (OHRC):
- It will perform high-resolution imaging of the landing site prior to the lander mission.
Lander:
- The lander will have a throttleable engine for performing a soft landing.
- A special radar altimeter will help the Lander orient itself while it lands on the moon surface safely.
Rover:
- The rover has been designed in such a way that it will have the power to spend a lunar day or 14 Earth days on the moon’s surface and walk up to 150-200 metres.
- It will do several experiments and on-site chemical analysis of the surface.
- The rover will then send data and images of the lunar surface back to the Earth through the orbiter within 15 minutes.
- After spending 14 earth days, the rover will go into sleep mode.
- ISRO is hopeful that the rover will again come alive whenever that part of the moon (where the rover will land) gets sunlight and recharges the rover’s solar cells.
Significance of Moon:
- Scientists and space planners have long acknowledged that extended human residence on the Moon would be greatly aided by the use of local resources.
- Lunar soil could be used for shielding habitats against the radiation environment.
- More advanced uses of lunar resources are clearly possible, but how advantageous they would be is presently unknown.
- Most lunar rocks are about 40 percent oxygen, and chemical and electrochemical methods for extracting it have been demonstrated in laboratories.
- The solar windhas implanted hydrogen, helium, and other elements in the surfaces of fine grains of lunar soil. Though their amounts are small they constitute about 100 parts per million in the soil they may someday serve as a resource.
- Helium-3, a helium isotope that is rare on Earth and that has been deposited on the Moon by the solar wind, has been proposed as a fuel for nuclear fusion reactors in the future.
- One natural resource uniquely available on the Moon is its polar environment. Water molecules are found in their strongest concentrations at the lunar poles.
Chandrayan – I
- The first Indian planetary mission to moon, Chandrayaan-1 with a suite of Indian
- And International payloads on board, collected very significant data over its mission duration of close to one year.
- This mission was a huge success.
- The observations made by Chandrayan – 1 are as follows
- Discovery of hydroxyl (-OH ) and water molecule in sunlit lunar surface region around the poles
- exposure of large anorthositic blocks confirming the global lunar magma hypothesis
- signature of sub surface ice layers in permanently shadowed regions near the lunar north pole evidence for a new refractory rock type
- mapping of reflected lunar neutral atoms and identification of mini-magnetosphere
- mapping of reflected lunar neutral atoms and identification of mini-magnetosphere
- preserved lava tube that may provide site for future human habitation.
AI Can Adjust Dosage For Cancer Patients
22, Aug 2018

- MIT researchers are using an artificial intelligence (AI) model that would help determine the correct drug dosage and, in turn, reduce debilitating side effects for brain cancer patients.
About:
- Powered by a “self-learning” machine-learning technique i.e ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENT, the model looks at treatment regimens currently in use, and iteratively adjusts the doses.
- Eventually, it finds an optimal treatment plan, with the lowest possible potency and frequency of doses that should still reduce tumour sizes to a degree comparable to that of traditional regimens.
- Glioblastoma is a type of cancer – malignant tumour that appears in the brain or spinal cord, and prognosis for adults is no more than five years. There is no cure for it.
- Generally, administer maximum safe drug doses to shrink the tumour as much as possible. However, these strong pharmaceuticals still cause debilitating side effects in patients.
- Patients must endure a combination of radiation therapy and multiple drugs taken every month.
- This system provides alternate for it. Can help reduce toxic chemotherapy dosing for the most aggressive form of brain cancer, potentially improving the quality of life for patients.
ISRO Set to Launch its Tv Channel
22, Aug 2018

India will soon launch a dedicated space and science television channel to make their benefits reach people across the country
ISRO TV:
- The channel will telecast science programmes and highlight the benefits of the space agency’s missions in regional languages as well as English, so that it reaches people across the country. This makes people aware of the benefits of the space programme.
- The space agency also aims to develop scientific temper among India’s children and youth through this channel.
Capacity Building:
- ISRO will also be setting up a module for students from Classes 8-10 to be trained at the space agency for a month.
- In order to inculcate scientific temper among students, ISRO officials will mentor them for 25-30 days and allow them to visit ISRO’s labs and launch facilities.
- The students will be allowed to make their own small satellites at the end of the programme.
- ISRO will also be opening up its spaceport at Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh to public.
- The Indian public will soon be able to pay visits to the launch facility at Sriharikota on the lines of American space agency NASA.
ISRO Telemedicine Nodes for Soldiers in High-Altitude Areas
20, Aug 2018

- The Integrated Defence Staff of the Defence Ministry and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) signed a memorandum of understanding to set up telemedicine nodes in critical places across the country.
Telemedicine:
- The delivery of healthcare services, where distance is a critical factor, by all healthcare professionals using information and communication technologies for the exchange of valid information for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of disease and injuries, research and evaluation and for the continuing education of healthcare providers, all in the interests of advancing the health of individuals and their communities.”
- Telemedicine Consulting Centre is the site where the patient is present.
- The Telemedicine system consists of an interface between hardware, software and a communication channel to eventually bridge two geographical locations to exchange information and enable tele consultancy between two locations.
- The hardware consists of a computer, printer, scanner, videoconferencing equipment etc. The software enables the acquisition of patient information (images, reports, films etc.). The communication channel enables the connectivity whereby two locations can connect to each other.
- Telemedicine is one of the unique applications of Space Technology for societal benefit. ISRO Telemedicine programme started in 2001 has been connecting remote/rural/medical college hospitals and Mobile Units through the Indian satellites to major specialty hospitals in cities and towns.
Significance:
- Easy access to remote areas
- Using telemedicine in peripheral health set-ups can significantly reduce the time and costs of patient transportation
- Improves communications between health providers separated by distance
- Critical care monitoring where it is not possible to transfer the patient
- Continuing medical education and clinical research
- A tool for public awareness
- A tool for disaster management
- Second opinion and complex interpretations
- The greatest hope for use of telemedicine technology is that it can bring the expertise to medical practices once telecommunication has been established.
- Tele mentored procedures-surgery using hand robots
- Disease surveillance and program tracking
- It provides an opportunity for standardization and equity in provision of healthcare, both within individual countries and across regions and continents.
Oxytocin
20, Aug 2018

Why in news?
- Setting aside its ban on the sale of oxytocin, the Health Ministry has allowed private retail stores to sell the life-saving hormone oxytocin.
Background:
- Recently government banned imports of the hormone oxytocin to stop its misuse in the livestock industry, where activists say it causes hormonal imbalances and shortens the lives of milch animals.
- Later it says that State-owned Karnataka Antibiotics Pvt Ltd will be the only company to manufacture and distribute oxytocin in India from September 1.
Why oxytocin was restricted to other producers?
- The reason for the ban is the misuse of oxytocin in dairy animals, like buffaloes, to increase milk production.
- Daily oxytocin injections would make cattle barren and reduce their lifespans.
- In addition, it claimed that drinking milk from oxytocin-treated cattle led to male impotence, early puberty among women and cancers.
Was the ban the only solution?
- No, the Drugs Technical Advisory Board recommended against a ban, advocating better surveillance instead. A ban might lead to scarcity and high drug prices.
Russia, China Set To Launch Joint Military Exercises
19, Aug 2018

Why in news?
- China will join Russia in a giant military exercise, sending a message of deterrence to the U.S. which has designated Beijing and Moscow as “revisionist powers”.
5-day Exercise Vostok 2018:
- The five-day Vostok 2018 exercises, to be held from September 11, will be bigger than Zapad 81 — the mammoth manoeuvres carried out in Eastern Europe by the former Soviet Union in 1981.
- Mongolia will be the third country participating in the drills.
- The Vostok-2018 will involve 300,000 troops. They will engage in tri-service mock-operations, involving 1,000 military aircraft, two of Russia’s naval fleets and all its airborne units.
- Nearly 36,000 military vehicles will participate in the drills that will take place at Russia’s Tsugol training range in the trans-Baikal region.
- China will dispatch about 3,200 troops, along with more than 900 pieces of weaponry, as well as 30 fixed-wing aircraft and helicopters state-run Xinhua.
- These exercises are taking place amid Washington’s growing friction with Russia and China, which include mounting sanctions and a trade war.
- The Pentagon’s national defence strategy unveiled in January focused on Russia and China as principle strategic challenges to the U.S. In presenting the new strategy, U.S. Defence Secretary called China and Russia “revisionist powers” that “seek to create a world consistent with their authoritarian models”.
- China quoted that exercise as a response to the intentions of “hegemonic powers”. Some hegemonic powers target China and Russia as their biggest threats, giving heavy blows to the two countries in political, economic and military areas.
- Such actions have severely threatened regional and even global peace and stability. Therefore, the China-Russia alliance is a reasonable stance against the hegemonic impulse and for safeguarding peace and stability of the region and the world.
- Since last year, China and Russia have begun joint missile defence exercises — a signal that Beijing and Moscow “foresee that any strategic nuclear conflict that embroils one would, naturally, involve both”.
European Wind Survey Satellite Launched
18, Aug 2018

- Europe put a satellite into orbit which will track global winds, allowing for improved weather forecasting,
- The “Aeolus” satellite named after the guardian of wind in Greek mythology will be placed at an altitude of 320 kilometres (200 miles) above the Earth.
- It is part of the Copernicus project, a joint initiative of the European Union and the European Space Agency (ESA) to track environmental damage and aid disaster relief operations.
- Aeolus is equipped with a single instrument: a Doppler wind lidar an advanced laser system designed to accurately measure global wind patterns from space.
- This mission will thus provide much-needed data to improve the quality of weather forecasting as well as contributing to long-term climate research.
- It described the satellite as the world’s first space mission to acquire profiles of Earth’s wind on a global scale.
- The Doppler lidar transmits short, powerful pulses of laser light toward Earth in the ultraviolet spectrum.
- Particles in the air moisture, dust, gases scatter a small fraction of that light energy back to the transceiver, where it is collected and recorded.
- The delay between the outgoing pulse and the so-called backscattered signal reveals the wind’s direction, speed and distance travelled.
- Once per orbit, data is downloaded to a ground station in Svalbard, Norway.
Anti-Runway and Anti-Tank Missiles Tested Successfully
18, Aug 2018

- The defence ministry announced the success of two major new indigenous weapon systems developed by the Defence R&D Organisation (DRDO).
Missiles that are tested:
- Smart anti-airfield weapon (SAAW)
- Helina (Helicopter launched Nag missile)
SAAW:
- The SAAW is an accurate bomb and is termed a long-range precision-guided munition (PGM).
- After its release from an aircraft, a sophisticated “inertial navigation system” on the bomb guides it precisely to its target — typically an enemy airfield up to 100 km away.
Advantages of SAAW:
- Striking the airfield’s runway precisely with one bomb is more economical than using traditional free-fall bombs, which are less accurate and must therefore be released in large numbers to be assured of incapacitating the target airfield.
- Another advantage of SAAW is that, after releasing it at a distance from the enemy airbase, the aircraft can return without exposing itself to anti-aircraft defences surrounding most air bases.
- It is capable of destroying runways, bunkers, aircraft hangers and other reinforced structures.
- The bomb, which is said to have higher precision and much cheaper compared with missiles, can be carried on IAF’s various aircraft like Jaguar and MiG
Helina:
- Indigenous Dhruv helicopter launched a HELINA anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) at a tank target seven kilometres away, successfully striking and destroying it.
- The missile is one of the most advanced anti-tank weapons in the world.
- It is a heavier and longer-range version of the vehicle mounted Nag missile with a 4-km range.
- The Missile is guided by an Infrared Imaging Seeker (IIR) operating in the Lock on Before Launch mode.
Lynching: Social Media sites to be held responsible
16, Aug 2018

Why in news?
- A panel headed by Union Home Secretary Rajiv Gauba, which deliberated on measures to check incidents of lynching, submitted its report to a Group of Ministers headed by Home Minister Rajnath Singh.
- In May and June, more than 20 people were lynched based on fake posts or rumours floating on various social media platforms.
- The panel discussed such incidents and is learnt to have come to the conclusion that social media platforms needed to act in a “time-bound” manner.
Panel Members:
- The panel report will first be discussed by the GoM, whose members are External Affairs Minister Sushma Swaraj, Transport Minister Nitin Gadkari, Law Minister Ravi Shankar Prasad and Social Justice and Empowerment Minister Thawar Chand Gehlot.
Background:
- According to the sources, the panel is learnt to have suggested that the existing provisions in the Indian Penal Code (IPC) and criminal procedure code (CrPC) should be tightened by inserting new clauses.
- Social media platforms — Facebook, WhatsApp, YouTube and Twitter — would be made accountable for not blocking malicious posts and videos when brought to their notice and an “FIR could be lodged against their country heads” for not complying with government orders and they could be prosecuted under law.
- The committee of secretaries held consultations with a cross-section of society and other stakeholders before submitting its report to the Group of Ministers.
- They suggested that some countries employ non-governmental organisations and volunteers who proactively surf the Internet.
- They have created a portal where people can report such videos and content and that can be forwarded by the National Crime Records Bureau [the nodal body] to the States concerned for appropriate action
- The Centre asked to appoint an officer in each district at the level of Superintendent of Police, set up a special task force to gather intelligence, and closely monitor social media contents to prevent mob attacks on people on the suspicion of being child-lifters or cattle smugglers.
Aspirin May Help Prevent HIV
16, Aug 2018
- An affordable, globally available drug — low-dose aspirin — could help prevent HIV transmission.
Study:
- Researchers tested the effect of aspirin and other anti-inflammatory drugs on HIV target cells in a group of Kenyan women who were at low risk for HIV.
- Transmission of the virus requires a susceptible target cell in the human host. Activated immune cells are more susceptible to HIV infection than resting cells. It is known that inflammation brings activated HIV target cells to the female genital tract.
- The researchers found that Aspirin was the most effective anti-inflammatory drug. It reduced the number of HIV target cells in the female genital tract by 35 per cent.
Impacts:
- This could be a strategy for HIV prevention that is not only inexpensive, but easily accessed globally.
- This could be a affordable and immediately available prevention approach.
- This helps in providing a new tool in the HIV prevention arsenal that would be used together with other approaches to reduce HIV transmission in high-risk populations.
India Science Technology And Innovation Portal
12, Aug 2018

Why in news?
- The Union science ministry’s communication wing, Vigyan Prasar, has launched the India Science Technology and Innovation portal.
About the portal:
- The portal can be queried for information about the status of the technology, organisations carrying out research, those funding them, international collaborations, the scientists involved in the research, the states in which they are being carried out, their achievements and impact.
- A major thrust of the portal is to reach out to students, researchers, scholars, scientists both from India and abroad, so that they can choose from the mineof fellowships, scholarships and funding and start up opportunities that India puts on their plate.
- The portal follows a launch this week of India Science (indiascience.in), an Internet-based science channel, to showcase the developments in science and technology in India.
- Both the portal and the channel are part of a push by the Science Ministry to improve its public outreach.
Vigyan Prasar:
- Vigyan Prasar (VP) is an autonomous organization under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India.
- Vigyan Prasar is focused on enabling access to appropriate information in a timely manner aligned with India’s developmental imperatives so that her citizens will be able to acquire the necessary scientific insights to improve their core strengths in all sectors of learning with implications for sustainable development.
- The logical framework of science communication, therefore, emphasizes enriched learning and enhanced abilities for well-informed action.
- The principal objective of VP is to serve India’s science popularization agenda.
Exercise Peace Mission 2018
08, Aug 2018

- Exercise Peace Mission 2018, the joint military exercise of Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), ended in Russia
- The eight-member states undertaking joint training on combating terrorism.
Significance:
- It will play a positive role in enhancing the ability of all member states to work together to cope with new threats and challenges, promoting the SCO’s defence and security cooperation to go further both in substance and depth, and safeguarding regional peace and stability.
- The joint exercise will strengthen mutual confidence, interoperability and enable sharing of best practices among armed forces of the SCO nations.
- The scope of the exercise includes professional interaction, mutual understanding of drills & procedures, establishment of joint command and control structures and elimination of terrorist threat in urban counter terrorist scenario.
- This is the first time India and Pakistan participated in the exercise which brings stability between the two countries which was significant to the peace and development of the region and the whole world.
SCO:
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a permanent intergovernmental international organisation
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation Charter was signed during the St. Petersburg SCO Heads of State meeting in June 2002, and entered into force on September 2003
- The status of a full member of the Organization was granted to the Republic of India and the Islamic Republic of Pakistan during the Astana summit
- The SCO’s main goals are as follows: strengthening mutual trust and neighbourliness among the member states; promoting their effective cooperation in politics, trade, the economy, research, technology and culture, as well as in education, energy, transport, tourism, environmental protection, and other areas; making joint efforts to maintain and ensure peace, security and stability in the region; and moving towards the establishment of a democratic, fair and rational new international political and economic order.
Member States:
- The Republic of India
- The Republic of Kazakhstan
- The People’s Republic of China
- The Kyrgyz Republic
- The Islamic Republic of Pakistan
- The Russian Federation
- The Republic of Tajikistan and
- The Republic of Uzbekistan
Ebola Virus
30, Jul 2018
Recently new type of Ebola virus has been found in the continent of Africa (Sierra Leone). Researchers found the new virus in the northern Bombali Region.
Background:
It is not yet known whether the new Bombali species of the virus which reserachers say could be transmitted to humans can develop into the deadly Ebola Diseases. The Ebola Outbreak which happen during 2013 in west Africa continent was most devastating and claimed around more than 11,000 Life’s
About Ebola:
- Ebola virus disease (EVD), also known as Ebola Haemorrhagic Fever (EHF) or simply Ebola, is a viral Haemorrhagic fever of humans and other primates caused by ebolaviruses.
- Signs and symptoms typically start between two days and three weeks after contracting the virus with a fever, sore throat, muscular pain, and headaches. Vomiting, Diarrhoea and rash usually follow, along with decreased function of the liver and kidneys. At this time, some people begin to bleed both internally and externally.
- The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids, such as blood from infected humans or other animals. Spread may also occur from contact with items recently contaminated with bodily fluids.
- Spread of the disease through the air between primates, including humans, has not been documented in either laboratory or natural conditions.
- Semen or breast milk of a person after recovery from EVD may carry the virus for several weeks to months.
- Fruit bats are believed to be the normal carrier in nature, able to spread the virus without being affected by it. Other diseases such as malaria, cholera, typhoid fever, meningitis and other viral Haemorrhagic Fevers may resemble EVD. Blood samples are tested for viral RNA, viral antibodies or for the virus itself to confirm the diagnosis.
Indian Scenario:
The Ebola Outbreak was first recorded in New Delhi and followed by Death which was inevitable so far in Indian Subcontinent Ebola is not a threat.
Formalin
29, Jul 2018

Samples of fish species tested from Chennai have shown positive for formalin. It is a cancer-inducing chemical used illegally to preserve fish.
Why it is used:
- In Fish industry ,formalin or formaldehyde is sprayed on the fish or injected into the fish or the fish is dipped into the solution. This helps keep the fish fresh for a longer time.
- When formalin is used the gills remain red for longer periods.
Formalin:
- A solution of 35 to 40 per cent of water in formaldehyde.
- Formalin is a colourless strong-smelling, toxic, flammable, explosive liquid substance usually used in industry of textiles, plastics, papers, paint, construction, and well known to preserve human corpse.
- It is also used as raw material for organic combination, formaldehyde resin, plastic production, organic material synthesis, disinfection, and anatomic preparation conservation, as fungicide.
- Effective against viruses.
- Effective against mycobacteria so used as an antiseptic in sterilising surgical instruments.
- It’s vapour together with air form explosive compounds.
- Exposure from its gas or vapor can cause irritation to the eyes, nose and respiratory tract, causing sneezing, sore throat, larynx constriction, bronchitis and pneumonia. Multiple exposures can lead to asthma. It can also affect the skin, causing dermatitis or allergic reaction.
- Formalin that was recently found in food, might not give such obvious reactions. However, this substance is known to be a carcinogenic substance, can precipitate cancer. Some other studies also show formalin will cause kidney, liver, and lung problems.
- Formalin will make the fish become stiff, whitish and odourless. Even when cooked, i.e. fried, it will still be stiff.
- Formalin must be disposed though the hazardous chemical waste disposal program.
Auto Immune Disease
29, Jul 2018

- It is a condition in which the immune system of our body mistakenly attacks our blood cells, joints skin etc.,
- Generally immune system can differentiate foreign cells and own cells.
- In this condition, it mistakenly attacks your parts of the body
Causes:
- Exact causes are unknown
- There are 80 different Auto-immune Diseases.
Brahmos Missile
28, Jul 2018

Why in News?
India achieved another milestone in its defence preparedness by successfully test firing BrahMos supersonic cruise missile amidst extreme weather conditions at sea state 7 (waves as high as 9 meter with strong wind) at Balasore, odisha.
The missile was tested as part of the service life extension program for the Indian Army as it is the first missile whose life has been extended from 10 years to 15 years.
About the Missile:
Brahmos is a supersonic (app. thrice the sound of the speed) cruise missile.
It is a joint venture of DRDO of India and NPOM of Russia which has been named after two rivers Brahmaputra and Moskva (river in western Russia).
Technical specification:
- It is two stage missile where first stage is being a solid and second stage is ramjet liquid propellent.
- It is self-propelled guided missile which operates on “fire and forget principle”.
- It has low radar signature along with pin point accuracy.
- It is capable of being launched from land, sea, sub-sea and air against sea and land targets. • It carry both conventional and nuclear warhead weighing Upto 300 kg.
- It has unique feature of quicker engagement time and non-interception by any known weapon system in the world. • Its Airforce version is under developmental tests, the missile has already been inducted in the Army and the Navy. • Initially, developed for 299 km, the strike range of the weapon system has been increased to 450 km after India’s full membership to the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), which removed caps on range of cruise missiles.
Border Connectivity
28, Jul 2018

Why in News?
- Connectivity issues are troubling people living in areas bordering china in the Ladakh region, which was discussed during the BADP meeting chaired by Union Home Minister.
- The Ladakh region, which has high significance from strategic considerations, remains cut-off for almost half of the year throughout the winter season from the rest of India.
Geographical features of Ladakh:
- Ladakh is the highest plateau of the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir with much of it being over 3,000m.
- Ladakh (“land of high passes”) is a region that currently extends from the Kunlun mountain range to the main Great Himalayas to the south, inhabited by people of Indo Aryan and Tibetan descent.
Border Area Development Program:
- Connectivity is one of the major hinderance which limits the development prospectus in border areas.
- In order to improve infrastructure, Border area development program along with India-Pakistan border was initiated in 1987 during the seventh five year plan period.
- It is implemented by the department of border management, Ministry of Home affairs through state government.
Objective:
- The objective was to meet the special development in socio-economic conditions of the people living in inaccessible and remote areas near the international border.
- The funds under BADP are provided to the States as a 100% non-lapsable Special Central Assistance.
Areas covered under BADP:
The programme has been expanded since to cover the border blocks of the 17 States (including 8 North Eastern States), which have international land borders with Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar and Bangladesh.
BADP Guidelines:
- Coverage of BADP has been extended to cover all the villages which are located within the 0-10 Km of the International Border
- The list of schemes permissible under BADP has been expanded to include schemes/ activities relating to Swatchhta Aabhiyan , Skill Development programmes, Promotion of sports activities in border areas , Promotion of Rural Tourism/ Border Tourism, Protection of heritage sites.
- Construction of helipads in remote and inaccessible hilly areas, which do not have road connectivity, Construction of toilets in schools, public places particularly for women; Skill development training to farmers for the use of modern/ scientific technique in farming, Organic farming, etc.
- Provision for Third Party Inspection and Quality Control Mechanism under MHA for random inspections of the BADP schemes.
- Warehouses for food grains and fodder in hilly areas particularly in snow bound areas of Jammu & Kashmir Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh and, E-chaupals, Agri shops, mobile media vans etc. have been made.
- Special/Specific area schemes such as composite development of at least one village of sizeable population surrounded by five-six or more villages close to the border as Model Village.
Reason for the hinderance of the program:
- Difficult terrain
- Political interference
- Corruption
- Faulty implementation
- Poor planning and lack of coordination
- Fund diversion.
Blood Moon
27, Jul 2018

The month of July is set to witness a rare astronomical spectacle as a blood moon, the second of the year, will appear on the intermediary night of July 27-28.
The ‘Marathon’ Eclipse:
According to space experts, the eclipse will last one hour and 43 minutes – nearly 40 minutes longer than the January 31 Super Blue Blood Moon.
Why will the moon turn red?
- The blood moon, or the ‘full buck moon’ as it is being called, will turn blood red during the eclipse due to the way light bends around Earth’s atmosphere.
- During a blood moon, the moon takes on a deep red to orange colour, rather than completely disappearing when it passes through the shadow cast by Earth.
- This bizarre effect known as ‘Rayleigh scattering’ filters out bands of green and violet light in the atmosphere during an eclipse.
Why will this lunar eclipse be longer?
- The full buck moon will last longer than normal as it will pass almost directly through Earth’s shadow during the eclipse.
- At the same time, it will be at the maximum distant point from earth. Therefore, it will take longer to cross Earth’s shadow.
Rayleigh scattering:
The dispersion of electromagnetic Radiation by particles that have a radius less than approximately 1/10 the wavelength of the radiation. The angle through which sunlight in the atmosphere is scattered by molecules of the constituent gases varies inversely as the fourth power of the wavelength; hence, blue light, which is at the short wavelength end of the visible spectrum, will be scattered much more strongly than will the long wavelength red light.
LEG up for the Private sector Participation
27, Jul 2018

- Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) has approved the Implementation of strategic partnership guidelines.
- Objective: To Enhance defence industries (Domestic) and progressively build indigenous capability in private sector and to develop complex weapon systems for the army.
- It has four components
SUBMARINES SINGLE ENGINE FIGHTER AIRCRAFT HELICOPTERS ARMOURED CARRIES - Under this policy one Indian Private Company would be selected in each segment mentioned above and will tie-up with their foreign counterpart and work with technology transferred by them.
- DAC also approved acquisition of Eight Fast Patrol Vessels which will be indigenously designed and manufactured.
What is strategic model and why do we need private sector participation?
- Strategic model in defense simply means a struct set of regulations to enhance procurement process.
- In a time when PSU’s are stressed and fiscal deficit has widened, we need more investment from private sector, so we to build ‘Make in India’ Initiative
- Broad based eligibility criteria for selection of private partner’s
1. Financial capability – Profitability net worth
2. Financial Prudence – Credit Ratings
3. Technical Capability – Domain of specialisation
4. Research and Development Capability – Track Record
5. Capacitive infrastructure – Global Benchmarks
6. Executive track record – Timely deliveries
7. Ownership structure – Private, Public or Promoter
Pitch Black
27, Jul 2018

For the first time, the Indian Air Force will be participating in Exercise Pitch Black 2018 (PB-18), a three-week multinational drill scheduled from 24 July in Australia.
- The Exercise Pitch Black which was first started in the year 1981 for different RAAF units, takes place every two years in the Australian continent.
- The last exercise in 2016, was attended by France, Indonesia, New Zealand, Thailand, Canada, Germany, Netherlands, Singapore, and the United States.
- Singapore was the first nation to be included in the exercise in the year 1990 following with the Australian administration opened the exercise to other countries too Background:
- Through the exercise the countries aim to practice OCA and DCA, more commonly known as the offensive and defensive counter air combat.
- The exercise takes place in New South Wales’ Glenbrook region, at the Australian Air Force base in a simulated environment.
- The other joint exercise between India and Australia which includes the AUSINDEX from 2015.
Eat Right Movement
22, Jul 2018

To improve public health in India and combat negative nutritional trends to fight lifestyle diseases FSSAI launched ‘EAT RIGHT MOVEMENT’.
About:
- ‘The Eat Right Movement’, built on two broad pillars of ‘Eat Healthy’ and ‘Eat Safe’, aims to engage, excite and enable citizens to improve their health and wellbeing.
- ‘The Eat Right Movement’ is a holistic and collaborative approach, with stakeholders on both the demand and supply-side.
- On the demand side, the Eat Right Movement focuses on empowering citizens to make the right food choices.
- On the supply side, it nudges food businesses to reformulate their products, provide better nutritional information to consumers and make investments in healthy food as responsible food businesses.
- The Safe and Nutritious Food Initiative – Focused on social and behavioural change around food safety and nutrition at home, school, workplace and on-the-go.
- The Eat Healthy Campaign – focused on reduction of high fat, sugar and salt foods in the diet.
- Food Fortification – focused on promoting five staple foods-wheat flour, rice, oil, milk and salt that are added with key vitamins and minerals to improve their nutritional content.
- The edible oil industry, bakeries and ‘halwais’ committed to phase out trans-fats by 2022 as voluntary commitments.
- Major food companies voluntarily committed to reformulate packaged foods to reduce the level of salt, sugar and saturated fat.
- The food services sector promised to provide healthier food options and introduce menu-labelling.
- The Eat Right Movement Website is an interface between food safety and nutrition experts and citizens. It provides credible and authentic nutrition information including health tips by experts, nutritious recipes, and exciting tools to get a peek into one’s nutritional needs, body indices, learning about nutrition labels, and other resources.
- An AI Powered Chatbot for citizens to answer all questions related to food is part of the website.
- The Eat Right Toolkit to reach out to people at the grass roots level includes a training manual for frontline health workers such as Health and Wellness Centre workers, ASHA and Anganwadi workers etc and engagement material for citizens in rural and aspirational areas, with a special focus on children.
- Resource books on safe and nutritious food such as the Pink Book for homes, The Yellow Book for schools, The Orange Book for workplaces, The Purple Books for eating out, vetted by domain experts are also in place.
The Eat Right Movement brings together three ongoing initiatives of FSSAI
Background:
- In the last 25 years, a major transition in the disease patterns has taken place in India.
- In 1990, more than 60% of all diseases were either infectious (like TB and diarrhoeal diseases), lack of nutrition (like anaemia). These afflictions now account for just 33% of the disease burden.
- Conversely, the contribution of non-communicable diseases like cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, neurological diseases, cancers, etc, has increased from 30% to 55%. The maximum increase has happened in diseases that are linked to an unhealthy diet and lifestyle.
- The country has more people with type-2 diabetes than any other nation.
- There is now an emerging body of scientific studies linking junk food with childhood obesity and the diabetes epidemics.
- In order to combat this draft Food Safety and Standards (Labelling and Display) Regulations, 2018 has been released for comments by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) in April, 2018. • It mandate compulsory labelling of salt and introduced a special red labelling for high in fat, sugar. But it was opposed by food industries due to low consumer base for sugar and fat free items.
So FSSAI launched The Eat Right Movement as an awareness generation and voluntary commitment of food industries to give heathy food to consumers.
World First Melanoma Blood Test
22, Jul 2018
Australian researcher have developed a blood test for melanoma in its early stages .
- Melanoma is a cancer that begins in the melanocytes. Other names for this cancer include malignant melanoma and cutaneous melanoma. Most melanoma cells still make melanin, so melanoma Tumours are usually brown or black.
- This test could help doctors detect skin cancer before it spreads through a person’s body.
- The early detection of melanoma in patients have a five-year survival rate between 90% and 99% whereas the rates fell to less than 50% if the cancer spread in the body.
Super Conductivity at Ambient Temperature
22, Jul 2018

Researchers from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bengaluru have been able to achieve superconductivity at ambient temperature and pressure.
Superconductor:
- A superconductor is a material that can conduct electricity or transport electrons from one atom to another with no resistance.
- This means no heat, sound or any other form of energy would be released from the material when it has reached “critical temperature” (Tc), or the temperature at which the material becomes superconductive.
- A large number of materials have been found to undergo normal to superconducting transitions.
- But such transitions require extremely low temperature and/or extremely high pressure.
- A type I superconductor consists of basic conductive elements that are used in everything from electrical wiring to computer microchips.
- A type II superconductor is composed of metallic compounds such as copper or lead. They reach a superconductive state at much higher temperatures when compared to type I superconductors.
Applications:
- Power transmission cables.
- Transformers.
- Motors and generators.
- Fault current limiters.
- Superconducting magnets including MRI and research magnets.
- SQUID (superconducting quantum interference device) – sensitive sensors to detect magnetic field and Josephson junctions.
- Magnetic Levitation including magnetic suspension, contactless bearings, linear motors and trains.
- Shielding of magnetic fields.
- Superconducting electronics and quantum computers.
- SMES (superconducting magnetic energy storage).
- Maglev (magnetic levitation) trains. Large hadron collider or particle accelerator.
- The USA is developing “E-bombs”. These are devices that make use of strong, superconductor derived magnetic fields to create a fast, high-intensity electromagnetic pulse that can disable an enemy’s electronic equipment.
Deep Ocean Mission
21, Jul 2018

The Centre has drawn up a five-year plan to explore the deep recesses of the ocean. The mission proposes to explore the deep ocean similar to the space exploration started by ISRO.
About the mission:
- The mission is to explore and harness mineral resources beneath the ocean floor which intended to harness ocean resources in a “responsible way” and could turn out to be a transformative step for the prosperity and security of the nation.
- The focus will be on technologies for deep-sea mining, underwater vehicles, underwater robotics and ocean climate change advisory services, among other aspects.
- This will improve India’s position in ocean research field.
- The Exclusive Economic Zone allotted to India in the international waters will be covered under the Deep Ocean Mission.
- The Union Earth Sciences Ministry tasked with coordinating the exercise.
Resources from Ocean:
Energy from the Ocean:
Ocean can produce two types of energy: thermal energy from the sun’s heat, and mechanical energy from the tides and waves. The fact that the marine renewable sector is less developed than other energy sectors.
Tidal Energy:
- Tidal power converts the energy from the natural rise and fall of the tides into electricity.
- Since India is surrounded by sea on three sides, its potential to harness tidal energy has been recognized by the Government of India.
The most attractive locations for tidal energy are:
- Gulf of Cambay
- Gulf of Kachchh
- Ganges Delta in the Sunder bans
Problems Faced in Exploiting Tidal Energy:
- The altering of the ecosystem at the bay
- Only provides power for around 10 hours each day, when the tide is actually moving in or out.
- Present designs do not produce a lot of electricity, and barrages across river estuaries can change the flow of water and, consequently, the habitat for birds and other wildlife
- Limited construction locations
- Barrages affect fish migration and other wildlife- many fish like salmon swim up to the barrages and are killed by the spinning turbines.
- Barrages may affect the tidal level – the change in tidal level may affect navigation, recreation, cause flooding of the shoreline and affect local marine life
- Tidal plants are expensive to build
Wave Power:
- Wave power systems convert the motion of the waves into usable mechanical energy which in lump can be used to generate electricity.
- The potential along the 6000 Km of coast is about 40,000 MW. This energy is however less intensive than what is available in more northern and southern latitudes.
- Primary estimates indicate that the annual wave energy potential along the Indian coast is between 5 MW to 15 MW per meter, thus a theoretical potential for a coast line of nearly 6000 KW works out to 40000-60000 MW approximately. However, the realistic and economical potential is likely to be considerably less.
- Offshore desalination plants powered by renewable energies are being proposed as an alternative for a coastal desalination facility, for those locations where the lack of suitable land makes a land-based desalination plant inadequate
- The sole energy source of a reverse osmosis (RO) plant is utilised through wave or tidal energy in order to produce drinkable water, which is then transported offshore (through pipes, water tank ships, or bladders
Problems in wave energy generation:
- Depends on the waves – variable energy supply
- Needs a suitable site, where waves are consistently strong
- Must be able to withstand very rough weather
- Poses a possible threat to navigation from collisions due to the low profile of the wave energy devices above the water, making them undetectable either by direct sighting or by radar May interfere with mooring and anchorage lines with commercial and sport-fishing
- May degrade scenic ocean front views from wave energy devices located near or on the shore, and from onshore overhead electric transmission lines.
Ocean Thermal Energy:
- The main objective of ocean thermal energy or Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) is to turn the solar energy trapped by the ocean into useable energy.
- OTEC has a potential installed capacity of 180,000 MW in India
Barriers in OTEC:
- OTEC-produced electricity at present would cost more than electricity generated from fossil fuels at their current costs.
- OTEC plants must be located where a difference of about 40 degrees Fahrenheit occurs year round.
- Ocean depths must be available fairly close to shore-based facilities for economic operation.
- Construction of OTEC plants and laying pipes in coastal waters may cause localized damage to reefs and near-shore marine ecosystems.
Mineral Resources:
- Exploration for offshore petroleum and Natural gas also has been under way in the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, both of which are believed to have large reserves.
- The sea offers a variety of minerals, many of which are considered to be alternative sources of metals in the future.
- Among these are the placer deposits, which are mechanically concentrated minerals that originate from eroded onshore rocks. The near-shore waves separate the minerals brought by rivers and glaciers into heavy and light minerals, and concentrate heavy minerals on the beaches and estuaries.
- Elements in native state (diamond, gold, and platinum) or minerals such as ilmenite, rutile, magnetite, zircon, monazite, garnet, and corundum are some examples of placer deposits.
- Oolites are the inorganic chemical precipitates of calcium carbonate that form in hyper-saline, shallow marine environment (<10 m). Oolites are found on the continental shelf off Mumbai, Visakhapatnam, and Chennai. Zeolites, Phosphorites or sedimentary phosphate, Barite are the other minerals.
- Ferro-manganese deposits form in the deep ocean basins (4-5 km depth) in areas away from the influence of terrigenous (from land) fluxes. They occur as nodules (round objects upto 10 cm in size) and encrustations (as layers on rocks exposed on the seafloor). They have copper, nickel, and cobalt (total 2.5%) content.
- Manganese nodules grow at a rate of 1-3 mm per million years and occur on the ocean floor or a few centimetres below it. Crusts with high cobalt content (0.25% – 1%) usually occur on seamounts, elevated marginal areas, and mid-ocean ridges.
- Hydrothermal deposits are formed by the interaction of seawater with submarine volcanic activity.
- Gas hydrates are compounds where gas molecules are physically trapped inside an expanded lattice of water molecules. They can be present below the ocean floor on the continental slopes and deeper areas of high rate of deposition of sediments with moderate organic content (0.5%).
- Seabed gas hydrates could be an energy source of the future.
Living Resources:
- The Indian Ocean’s living resources represent one of the region’s most significant assets. According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), catches from Indian Ocean marine capture fisheries have soared from less than 900,000 tonnes in 1950 to 11.3 million tonnes in 2010, about 14.6 percent of the world catch.
- Aquaculture – farming fish, shellfish, and other aquatic animals in captivity – has expanded equally rapidly, growing twelve-fold globally since 1980.
- In 2010, six Indian Ocean nations – India, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Thailand, Egypt, and Myanmar – counted among the top ten producers worldwide, supplying over 11.3 million tonnes of fish between them, as much as all the region’s capture fisheries combined.
NEU Print Skin (Neuromorphic Printed Tactile Skin)
19, Jul 2018
- Project on creating a robotic hand covered in so-called “brainy skin” that mimics the human sense of touch.
- Brainy Skin reacts like human skin, which has its own neurons that respond immediately to touch rather than having to relay the whole message to the brain.
- This electronic “thinking skin” is made from silicon-based printed neural transistors and graphene – an ultra-thin form of carbon that is only an atom thick, but stronger than steel. The new version in the making is said to be more powerful, less cumbersome and would work better than earlier prototypes.
- Inspired by real skin, this project will harness the technological advances in electronic engineering to mimic some features of human skin, such as softness, bendability and now, also sense of touch.
- Brainy Skin is critical for the autonomy of robots and for a safe human-robot interaction to meet emerging societal needs such as helping the elderly.
Stem Cells Trial to Flight Parkinson’s
16, Jul 2018
Japanese researchers announced the first human trial using a kind of stem cell to treat Parkinson’s disease.
About the Research:
- The research team plans to inject five million induced Pluripotent Stem (iPS) cells, which have the potential to develop into any cell in the body, into patient brains.
- The iPS cells from healthy donors will be developed into dopamine-producing brain cells, which are no longer present in people with Parkinson’s disease.
- iPS cells are created by stimulating mature, already specialised, cells back into a juvenile state — basically cloning without the need for an embryo.
- The primates with Parkinson’s symptoms regained significant mobility after iPS cells were inserted into their brains.
Parkinson’s Disease:
- Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects predominately dopamine-producing (“dopaminergic”) neurons in a specific area of the brain called substantia nigra.
- Symptoms generally develop slowly over years.
- The progression of symptoms is often a bit different from one person to another due to the diversity of the disease. People may experience:
- Tremor.
- Bradykinesia(slowed movement).
- Limb rigidity.
- Gait and balance problems.
- Loss of automatic movements.
- Speech changes.
- Writing changes.
The cause remains largely unknown. Although there is no cure, treatment options vary and include medications and surgery.
Stem Cell Therapy:
- Stem cells are a class of undifferentiated cells that are able to differentiate into specialized cell types. Commonly, stem cells come from two main sources
- Embryos formed during the blastocyst phase of embryological development (embryonic stem cells) and Adult tissue (adult stem cells).
- Both types are generally characterized by their potency, or potential to differentiate into different cell types (such as skin, muscle, bone, etc.).
- Stem Cell Therapy (SCT) is the treatment of various disorders, non-serious to life threatening, by using stem cells.
- These stem cells can be procured from a lot of different sources and used to potentially treat more than 80 disorders, including neuromuscular and degenerative disorders.
Applications of Stem Cell Therapy:
- Brain and spinal cord injury
- Generation of heart muscle cells
- Stimulating growth of new blood vessels to repopulate damaged heart tissue
- Secretion of growth factors
- Blood-cell formation
- Re growing teeth
- Cochlear hair cell regrowth
- Wound healing
- Blindness and vision impairment
Adult Versus Embryonic Stem Cells:
- Embryonic stem cells are present only in very early embryos whereas adult stem cells are present in tissues of children and adults.
- Since the embryonic cells are unspecialized cells, they have the potential to develop into any cell type. In contrast, the adult stem cells are only capable of producing into tissue specific cell types.
- The adult stem cells are difficult to grow in culture. The Embryonic stem cells, in contrast, can be easily grown in culture.
- Unlike the adult stem cells, the embryonic stem cells can multiply indefinitely resulting in a very large number of daughter cells.
- The Embryonic cells can be easily obtained from the early embryos while the adult cells are very rare so that they are difficult to obtain from the body.
- The Embryonic stem cells have more potential to become cancerous while the adult stem cells have less potential to be so.
Alzheimer Disease
16, Jul 2018

For The First time a drug was able to reduce the Plaques the brain of Patients and slow the progression of Dementia.
Alzheimer’s versus dementia:
- Dementia is an umbrella term for a range of conditions that involve a loss of cognitive functioning.
- Alzheimer’s is the most common type of dementia. It involves plaques and tangles forming in the brain. Symptoms start gradually and are most likely to include a decline in cognitive function and language ability.
- Other types of dementia include Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. People can have more than one type of dementia.
Symptoms:
- Reduced ability to take in and remember new information
- Impairments to reasoning, complex tasking, and exercising judgment
- Impaired visuospatial abilities that are not, for example, due to eye sight problems
- Impaired speaking, reading and writing Changes in personality and behavior
Stages:
The progression of Alzheimer’s can be broken down into three main stages:
- Preclinical, before symptoms appear
- Mild cognitive impairment, when symptoms are mild
- Dementia
Fast facts on Alzheimer’s disease
- Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia.
- It happens when plaques containing beta amyloid form in the brain.
- As symptoms worsen, it becomes harder for people to remember recent events, to reason, and to recognize people they know.
- Eventually, a person with Alzheimer’s is likely to need full-time assistance.
Treatment:
- There is no known cure for Alzheimer’s. The death of brain cells cannot be reversed.
However, there are therapeutic interventions that can make it easier for people to live with the disease
E-Census Date
16, Jul 2018

- The data collected during the 2021 Census will be stored electronically. first time since the decennial exercise was conducted in 1951 in Independent India.
- Till now census data being stored in a physical form at the government’s storehouse in Delhi, the data is preserved for 10 years and then it is destroyed.
- For this census rules 1990 was amended & electronic record(data) linked to Information Technology Act,2000.
- If any tampering with the data will invite punishment under the Information Technology Act, 2000
Census in INDIA:
- It is an decennial operation.
- Still now 15 census was conducted (prior to independence conducted from 1865 to 1947)
- 1865-first proper census conducted but it covered only some parts of India
- 1872-only British administrative area was censused.
- 1881-First decennial all India census conducted.
- Post-Independence Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India was created under ministry of Home Affairs which take census.
- Census data was collected in 16 languages and the training manual was prepared in 18 languages.
Task Force on Artificial Intelligence
16, Jul 2018

A Multi stakeholder task force chaired by N. Chandrasekaran appointed in February to with mandate to
- Studied the level of AI development in India in general and specific in the context of defence needs.
- Made recommendations of making India a significant power of AI in defence specifically in the area of aviation, naval, land systems, cyber, nuclear, and biological warfare;
- Made recommendations for policy and institutional interventions that are required to regulate and encourage a robust AI based technologies for defence sector in the country.
- Considering that most AI work is happening in private sector, made recommendations to work with start-ups/commercial industry in the field of use of AI for defence purposes.
- Artificial Intelligence: Artificial intelligence (AI) is an area of computer science that emphasizes the creation of intelligent machines that work and react like humans.
Some of the activities computers with artificial intelligence are designed for include:
- Speech recognition
- Learning
- Planning
- Problem solving
DNA Profiling
15, Jul 2018

Why in News?
India’s proposed DNA databank, to be used during investigation into crimes or to find missing persons, will not permanently store details of people.
What is DNA Profiling?
DNA profiling is process of utilizing DNA to identify certain individuals. DNA is a unique biological map that points to a specific person and his or her close consanguinity. It is widely used in law enforcement today for the resolution of crimes and the identification of criminals, as well as in proving or disproving consanguinity claims.
Procedure for DNA Profiling:
The process of DNA fingerprinting involves gathering of samples. Scientists don’t need so much biological samples – only about 100 micrograms – to map the biological information of a specific individual.
- A smudge of saliva on a drinking straw is more than enough for DNA sampling.
- The next step is amplifying tell-tale regions.
- Researchers use the very potent Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) to make several copies of the sample’s tell-tale regions including Short Tandem Repeats (STRs), which varies from person to person.
- After amplifying the STRs, scientists then start counting the repeats. This is done by attaching fluorescent dyes onto the STR copies, and then running the mixture of STRs through a capillary electrophoresis machine that sizes various DNA fragments.
- After knowing the size of the repeats, it becomes easier to identify the length of each STR and the number of repetitive units.
- The final step in DNA profiling is looking for a match. A person whose STR repeats matches those of the sample at all 13 STR regions is at risk of conviction
Pros of DNA Profiling:
- It is simple, less intrusive testing.
- It can reduce innocent convictions.
- It can help solve crimes and identity issues.
The Cons of DNA Profiling:
- There is a lack of privacy.
- It raises concerns over third-party access.
- It can be used the wrong way to convict innocents.
- The data could be hacked.
Parker Solar Probe
12, Jul 2018
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe a seven-year mission aiming to get the closest ever to the sun has got its revolutionary heat shield permanently attached to the spacecraft.
That heat shield should, in theory, prevent the space craft from being burned by the sun made of reinforced carbon-carbon composite, which is designed to withstand temperatures outside the spacecraft nearly 2,500 F (1,377 C).
About Mission:
It is a planned NASA’s robotic spacecraft to probe the outer corona of the sun. Humanity’s first mission to the Sun’s corona, on its journey to explore the Sun’s atmosphere and the solar wind. It will probe
- Determine the structure and dynamics of the magnetic field at the sources of solar wind.
- Trace the flow of energy that heats the corona and accelerates the solar wind.
- Determine what mechanisms accelerate and transport energetic particles.
- Explore dusty plasma near the Sun and its influence on solar wind and solar energetic particles formation.
It will also hold more than 1.1 million names submitted by the public to go to the Sun. Parker Solar Probe is powered by two solar arrays. Unlike solar-powered missions that operate far from the Sun and are focused only on generating power from it, we need to manage the power generated along with the substantial heat that comes from being so close to the Sun.
Significance:
It will also make critical contributions to our ability to forecast changes in Earth’s space environment that affect life and technology on Earth. Parker Solar Probe will employ a combination of in situ measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and expand our knowledge of the origin and evolution of the solar wind.
Sun’s structure:
- About 73% of the Sun’s mass is hydrogen, and another 25% is helium and 2% other gasses.
- The Sun’s layers are different from each other, and each plays a part in producing the energy that the Sun ultimately emits
Core:
The site of thermonuclear fusion, which is the engine of the sun. Temperatures here approach 15,000,000 K and pressures exceed 250,000,000,000 atmospheres. The core makes up 50% of the sun’s mass but only 1/64th of the Sun’s volume. All of the energy that emits from the Sun is produced in the core.
Radiative Zone:
The region where energy from the core begins its journey outward, but the material is too dense and hot for heat transfer, and therefore the energy radiates out by creating alternating parallel magnetic and electrical fields, thus moving outward as electromagnetic radiation.
Convective Zone:
A region of less dense material, the energy is primarily carried toward the surface by heat convection currents which carry hot gases toward the surface before they cool and fall back inward
The Sun doesn’t behave the same way all the time. It goes through phases of its own solar cycle. Approximately every 11 years, the Sun’s geographic poles change their magnetic polarity. When this happens, the Sun’s photosphere, chromosphere and corona undergo changes from quiet and calm to violently active. The height of the Sun’s activity, known as solar maximum, is a time of solar storms: sunspots, solar flares and coronal mass ejections. These are caused by irregularities in the Sun’s magnetic field and can release huge amounts of energy and particles, some of which reach us here on Earth. This space weather can damage satellites, corrode pipelines and affect power grids.
Why study Sun:
- The Sun is the only star we can study up close. By studying this star we live with, we learn more about stars throughout the universe.
- The Sun is a source of light and heat for life on Earth. The more we know about it, the more we can understand how life on Earth developed.
- The Sun also affects Earth in less familiar ways. It is the source of the solar wind; a flow of ionized gases from the Sun that streams past Earth at speeds of more than 500 km per second (a million miles per hour).
- Disturbances in the solar wind shake Earth’s magnetic field and pump energy into the radiation belts, part of a set of changes in near-Earth space known as space weather.
- Space weather can change the orbits of satellites, shorten their lifetimes, or interfere with onboard electronics. The more we learn about what causes space weather – and how to predict it – the more we can protect the satellites we depend on.
- The solar wind also fills up much of the solar system, dominating the space environment far past Earth. As we send spacecraft and astronauts further and further from home, we must understand this space environment just as early seafarers needed to understand the ocean.
India to Expand Polar Research to Arctic:
11, Jul 2018

The government is refocusing priorities to the Arctic because of opportunities and challenges posed by climate change
Background:
- Sea ice at the Arctic has been melting rapidly — the fastest in this century. That means several spots, rich in hydrocarbon reserves, will be more accessible through the year via alternative shipping routes.
- This month, India has renamed the National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research (NCAOR) charged with conducting expeditions to India’s base stations to the continent as the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research.
India’s Artic Expedition:
- India’s interests in the Arctic region are scientific, environmental, commercial as well as strategic.
- India has no published “Arctic policy”. India’s Arctic work comes under the ambit of the National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research (NCAOR), an autonomous research institute under the umbrella of the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- India has one Arctic observation station near Norway. India opened an Arctic research base at Ny-Alesund, Svalbard, Norway -“Himadri” – to pursue research in Glaciology, Atmospheric Sciences, and Biological Sciences.
- India began its engagement with the Arctic region when it signed the Svalbard Treaty in February 1920.
- In 2007 India began its Arctic Research Program, focusing on climate change.
- The Indian Arctic research team hopes to understand the relation between the Arctic climate and the Indian monsoon by analysing sediment and ice core records from Arctic glaciers and the Arctic Ocean.
- In 2002, the state-owned ONGC Videsh (OVL) bought a 20 percent stake in the Sakhalin-I project on Sakhalin Island in the Russian sub-Arctic North Pacific.
- Scientists across the world are reporting that the rapid ice-melt in the Arctic is leading to large quantities of fresh water into the seas around the poles. This impedes the release of heat from the water and directs warm water into the seas around India, the theory goes, and eventually weakens the movement of the monsoon breeze into India. Therefore we need more observations and stations in the Arctic countries to improve understanding of these processes.
BIMSTEC Military Exercise
05, May 2018

India will host the first military exercise of the BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) group focussing on counter terrorism.
About:
- In a first such initiative, militaries of BIMSTEC member nations barring Nepal today began a week-long anti-terror exercise at Aundh near Pune to enhance cooperation in dealing with the challenge of terrorism in the region.
- The exercise is focused on boosting inter-operability among the forces and exchanging best practices to contain terror related activities, training in search-and-cordon operations and handling and neutralisation of improvised explosive devices (IEDs) among other things.
- The exercise is taking place nearly two weeks after leaders of the BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) countries, in their summit talks in Kathmandu, resolved to join hands to combat the scourge of terrorism effectively.
- India had organised the BIMSTEC Leaders’ Retreat in Goa in October 2016 during which the grouping had endorsed New Delhi’s effort to corner Pakistan on terror.
- special “tactical level” anti-terror operations will be practiced in semi urban setting.
- India has been pushing for making the BIMSTEC a vibrant form for regional collaboration as cooperation under the SAARC (South Asian Association of Regional Cooperation) framework was not moving forward visit topjuegos.net/. As BIMSTEC excludes Pakistan.
BIMSTEC:
- The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is an international organisation of seven nations of South Asia and South East Asia, The BIMSTEC member states are Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Bhutan, and Nepal are among the countries dependent on the Bay of Bengal.
- Leadership is rotated in alphabetical order of country names. Sri Lanka is the current chair. The permanent secretariat is in Dhaka.
- The main objective of BIMSTEC is technological and economic cooperation among south Asian and southeast Asian countries along the coast of the Bay of Bengal. Commerce, Investment, Technology, Tourism, Human Resource Development, Agriculture, Fisheries, Transport and Communication, Textiles, Leather etc. have been included in it.
- BIMSTEC Free Trade Area Framework Agreement (BFTAFA) has been signed by all member nations to stimulate trade and investment in the parties, and attract outsiders to trade with and invest in BIMSTEC at a higher level.






