Category: India Bilateral Cooperation
USA’S BLUE DOT NETWORK
26, Feb 2020

Why in News?
- During Trump’s visit, India and the US will discuss the Blue Dot network, a new proposal to cover infrastructure and development projects across the region and other countries.
Highlights:
- The BDN was formally announced on 4th November, 2019 at the Indo-Pacific Business Forum in Bangkok, Thailand. It will be led by the US along with Japan and Australia.
BDN:
- The Blue Dot network is a multi-stakeholder initiative to bring together governments, the private sector and civil society to promote high-quality, trusted standards for global infrastructure development.
- The proposal, which is part of the US’s Indo-Pacific strategy, is aimed at countering Chinese President Xi Jinping’s ambitious One Belt One Road initiative.
- The initiative will evaluate projects on various parameters, including level of public consultation, transparency in funding, debt traps and basic environment norms.
- Projects that meet the norms will get a “blue dot”, which will enable them to attract private funding and not have to depend on state-funding alone. Blue Dot will be about supporting alternatives to predatory lending by facilitating foreign investment in projects that come under this network.
- Under BRI, China’s government and state-owned enterprises finance international projects by providing logistical support, from concrete and steel to workers and cash. This approach, however, has been labelled by some experts as “debt-trap diplomacy”.
- The new Blue Dot Network is seen as part of the USA’s strategy of trying to persuade developing countries in Asia-Pacific not rely on Chinese funds for infrastructure.
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI):
- BRI is an ambitious project that focuses on connectivity and cooperation among multiple countries spread across the continents of Asia, Africa, and Europe.
- The stated objectives are to construct a unified large market and make full use of both international and domestic markets, through cultural exchange and integration, to enhance mutual understanding and trust of member nations, ending up in an innovative pattern with capital inflows, talent pool, and technology database.
- The initial focus has been infrastructure investment, education, construction materials, railway and highway, automobile, real estate, power grid, and iron and steel.
INDIA, AFRICAN COUNTRIES RESOLVE TO FIGHT TERROR
07, Feb 2020

Why in News?
- The first India-Africa Defence Ministers’ Conclave which was recently held in Lucknow has adopted the ‘Lucknow Declaration’.
About Lucknow Declaration:
- Acknowledges contribution of Indian defence forces in humanitarian assistance and disaster relief operations in Africa.
- It appreciates initiation of Africa India Field Training Exercises with the first ever AFINDEX in March 2019 and agree that it will further strengthen cooperation in defence preparedness and security.
- The vision is to achieve ‘a conflict-free Africa, prevent genocide, make peace a reality for all and rid the continent of wars, violent conflicts, human rights violations, and humanitarian disasters.
- It calls for deeper cooperation in the domain of defence industry including through investment, joint ventures in defence equipment software, digital defence, research & development etc.
- It recognizes the common security challenges such as terrorism and extremism, piracy, organised crime including human trafficking, drug trafficking, weapon smuggling and others.
- The members endorsed initiatives such as African Peace and Security Architecture (APSA), Silence the Guns in Africa and Agenda 2063.
- It calls for strengthening the UN Counter-Terrorism mechanisms and to ensure strict compliance with the UN Security Council sanctions regime on terrorism.
- It urged the international community to envisage the adoption of Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism in the UNGA.
- The members recognized the importance of the oceans and seas to the livelihoods of our peoples and that Maritime security is a pre-requisite for the development of Blue or Ocean economy.
- It sought to increase cooperation in securing sea lines of communication, preventing maritime crimes, disaster, piracy, illegal, unregulated and unreported fishing through sharing of information and surveillance.
INDIA AND BRAZIL TO SIGN STRATEGIC ACTION PLAN
23, Jan 2020

Why in News?
- India and Brazil will upgrade their strategic partnership with an action plan and sign a Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) when Brazilian President Jair Bolsonaro visits as the Chief Guest of the Republic Day celebrations.
Highlights:
- The two countries hope to take their partnership to the next level and build on the relationship between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and President Bolsonaro.
- The Strategic Partnership Action Plan will serve as an “umbrella agreement”, for plans between the two countries to increase defence cooperation, technology sharing and a logistics agreement. Brazil and India will also exchange a Social Security Agreement (SSA), first signed in March 2017, to allow investments in each other’s pension funds, to help business processes and encourage the flow of investment.
- Among about 20 agreements set to be exchanged, are the Strategic Partnership Action Plan, along with the BIT, a Mutual Legal Assistance Agreement (MLAT) on crime, agreements on double taxation avoidance, bio-energy or ethanol production, cybersecurity, health, mining, oil and gas exploration and investment, and animal husbandry.
Bilateral Investment Treaty:
- A bilateral investment treaty (BIT) is an agreement establishing the terms and conditions for private investment by nationals and companies of one state in another state. This type of investment is called foreign direct investment (FDI).
- BITs are established through trade pacts. Most BITs grant investments made by an investor of one Contracting State in the territory of the other a number of guarantees, which typically include fair and equitable treatment, protection from expropriation, free transfer of means and full protection and security.
- The distinctive feature of many BITs is that they allow for an alternative dispute resolution mechanism, whereby an investor whose rights under the BIT have been violated could have recourse to International Arbitration.
INDUSTRIAL SECURITY ANNEX (ISA)
20, Dec 2019

Why in News?
- The Industrial Security Annex (ISA) was recently signed between India and the U.S. at the second 2+2 dialogue in Washington.
About 2+2 Dialogue:
- It is a format of dialogue where the defense and foreign ministers or secretaries meet with their counterparts from another country.
- India holds such talks with Japan andAustralia, at the foreign secretary and Defense secretary level.
- India holds ministerial-level talks only with the US. Apart from India, the United Statesholds such ministerial dialogues with Australia and Japan
- The talks were announced when Prime Minister Narendra Modi met US President Donald Trump in June 2017.
- The “2+2” dialogue has replaced the Strategic and Commercial Dialogue between the foreign and commerce ministers of the two countries that were held during the previous Obama administration.
Outcomes of the Summit:
- Industrial Security Annex (ISA): The Industrial Security Annex (ISA) to the India-U.S. General Security of Military Information Agreement (GSOMIA)will provide a framework for exchange and protection of classified military information between the U.S. and Indian defence industries.
- Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI): United States has announced its commitment to being the founding member of the CDRI whose headquarters will be located in India.
- Finalisation of Defense Technology and Trade Initiative (DTTI) Standard Operating Procedure (SOP): This will harmonise the two side’s processes for identification, development and execution of projects under the DTTI.
- S&T Agreement: The new Science and Technology (S&T) Agreement concluded and implemented updates and replaces the 2005 Agreement and provides a framework for collaboration between the two countries in all fields of science, technology and innovation.
- The Young Innovators Internship Programme (YIIP): This Programme will create short-term internship opportunities in the U.S. for Indian students at post-secondary level or recent graduates, in key areas of scientific and economic endeavour.
- Tiger Triumph Exercise: It has been decided to hold the India-U.S. joint tri-services and amphibious exercise ‘Tiger Triumph’ on an annual basis. It was first held in November 2019 as a Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) Exercise.
- Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement (BECA): Both countries have agreed to continue discussions on BECA. It will enable exchange of geo-spatial information between the two countries, enhancing the operational efficiency of the U.S. platforms currently being operated by India.
- MRO facilities in India: In line with GOI’s efforts to build defence industry ecosystem in India, both countries have agreed to explore collaboration for establishment of Maintenance Repair and Overhaul (MRO) facilities in India.
Other Defence Agreements between India and US:
- There are four foundational agreements that help the U.S. to intensify its defence cooperation with a partner nation such as India.
- India has already signed three pacts such as Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement (LEMOA), General Security of Military Information Agreement (GSOMIA) and Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA).
- LEMOAgives both nations access to each other’s military facilities. But it does not make it automatic or obligatory.
- GSOMIA paved the way for greater technology cooperation in the military sector.
- COMCASAfacilitates transfer of encrypted communications systems.
- It helps in sharing high-tech military hardware, especially armed drones which the U.S. is willing to supply to India.
- The other pact which India yet to ratify is Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement for Geo-spatial Cooperation (BECA).
- BECAfacilitates exchange of Geospatial Information.
INDIA – JAPAN: 2+2 DIALOGUE
02, Dec 2019

- India and Japan held their first ever Foreign and Defence Ministerial Dialogue (2+2), to discuss on the issues relating to defence and security, and other issues of mutual interest. The 2+2 ministerial dialogue is seen as an upgrade of the meeting between foreign and defence secretaries of the two countries, which is in place since 2010.
- The upgrade is said to be the outcome of the 13th India-Japan Annual Summit held in Japan, in October 2018, between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and his Japanese counterpart Shinzo Abe. Japan is only the second country (after the US) with which India has such a dialogue format.
- Quad, as one of the elements of Indo-Pacific strategy for “a free, open and rules-based order” in face of an aggressive and expansionist China in the region, should eventually evolve into a ministerial-level dialogue imbued with a strong military dimension.
India- Japan Relations:
- In spite of having ‘close-to-littoral’ policies of the past, India, realizing the importance of far reaching maritime ties with other Indo-Pacific nations, has had a close relation with Japan.
- The India-Japan 2+2 dialogue is an endorsement of the special strategic partnership between New Delhi and Tokyo. The dialogue, mainly, has been driven by the mutual desire to take forward Asia as a multi-polar region and ensuring a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific realm.
- India and Japan continue to enjoy healthy maritime ties underscored by amity and trust with the two nations conducting annual bilateral naval exercise-JIMEX since 2012 and the formal inclusion of Japan into the MALABAR exercise in 2015 (India, US and Japan).
- The defence exercises between the two nations include the Dharma Guardian land exercise and the Shinyu Maitr air exercise.
India and its Sphere of Influence in the Indo-Pacific:
- The rise of China, the realignment of US’ global strategy, the new approach adopted by Japan, ASEAN, France and other key players have further underlined the importance of the Indo-Pacific region.
- China has increasingly active presence in the Indian Ocean region and also extends its efforts to expand its geopolitical reach in Asia and beyond, by the use of trade and military.
- India, also has a significant presence in the Indian Ocean and it is emphasizing regional connectivity and growth through – Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR). This has made India, an option to counter the threat of unipolarity posed by China.
- India, in recent years, understanding the salience of the region has moved from being a reluctant maritime power to a conscious one. It has sought to align its Indo-Pacific strategy with national maritime interests, and has developed partnerships accordingly.
- India, also has created a nexus of common goals amongst different nations in South East Asia. And exercising its role as net security provider, is expanding its current sphere of influence. India’s quick response to humanitarian disasters, piracy issues, evacuating civilians from conflict zones, and securing SLOCS, have displayed its capabilities as the net provider of security.
- The US believes the Quad (Japan, India, United States and Australia), as one of the elements of its larger Indo-Pacific strategy for “a free, open and rules-based order” in face of an aggressive and expansionist China in the region.
India – Japan: Defence Trade:
- The sale of the ShinMaywa US-2 amphibious aircraft for the Indian Navy, is yet to be concluded. India’s purchase of the aircraft could see enhance India’s capability of the humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HADR)
- Further, the two have established a working group to study the possibilities in Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) Based Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Augmentation Technology for UGV/robotics.
- The Acquisition and Cross-Servicing Agreement (ACSA), which will enhance the strategic depth of bilateral security and defence cooperation between the two nations, is still in its development stage.
- Opportunities in the areas of technology collaboration is significant. With India’s domestic defence electronic manufacturing segment still at a nascent stage, it has to partner with its strategic partners in building a domestic capability base.
- Japan is also pushing for India to join the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) and is making talks with other countries that are part of the deal to ensure that India’s concerns are addressed.
What stops Japan?

- Article 9 of the Japanese Constitution declares that “the Japanese people forever renounce war as a sovereign right of the nation and the threat or use of force as means of settling International Disputes”.
- The Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, wants to change the provisions to make Japan just as normal as other democratic countries. But any attempt to revise the constitution would be politically risky. And these amendments require approval of two-thirds of both houses of parliament and a majority in a referendum.
- Overall, the India-Japan ministerial level 2+2 strategic dialogue is an important initiative emphasizing the deep interest in both India and Japan to further strengthen their security and strategic engagements. The two countries have built a strong strategic partnership in the last decade. But India and Japan also need to build a larger coalition if they are to balance China effectively.
INDO-SWEDISH JOINT COMMISSION FOR ECONOMIC, INDUSTRIAL AND SCIENTIFIC COOPERATION
22, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- The Commerce and Industry Minister will attend the 19th Session of the Indo-Swedish Joint Commission for Economic, Industrial and Scientific Cooperation in Stockholm, Sweden.
Indo-Swedish Joint Commission for Economic, Industrial and Scientific Cooperation:
- It is the leading institutional mechanism of inter-governmental dialogue between India and Sweden at the level of the Ministers of Commerce and Industry in India and the Swedish Minister for Foreign Trade and EU Affairs.
- MoUs are signed in these sessions.
- Currently, the 19th session will happen in Stockholm. The previous session was held in May 2017 at New Delhi.
Indo-Sweden Business Relations:
- Sweden has a long history of investments in India.
- As of 2017, there are more than 170 Swedish joint ventures and wholly-owned subsidiaries in India.Sweden is the 20th largest foreign investor in India.
- The existing Swedish MNCs are now expanding not only in manufacturing but also increasingly on offshore IT operations and R&D in India.
- The sectors that have received the largest share of investments from Sweden are:
- Automobile (33%)
- Industrial machinery (15%)
- Miscellaneous mechanical & engineering industries (10%)
- Over the last decade, Indian investment in Sweden has also increased.
- There are over 70 Indian companies including IT companies currently present in Sweden.
- Indian pharmaceutical and biotech companies have formed collaborative relations in Sweden.
Chief Indian exports to Sweden:
- Articles of Apparel
- Clothing Accessories
- Textiles Yarn
- Fabrics
- Manufactures of metals
- Road vehicles
- General industrial machinery and Equipment
- Chief Indian imports from Sweden:
- Pulp and waste paper
- Road vehicles
- Paper board
- General industrial machinery and Equipment
- Iron and steel
- Power generating machinery & Equipment.
INDIA DECIDES TO PUT OFF PM MODI’S VISIT TO TURKEY
21, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- The government has decided to put off a proposed visit by Prime Minister Narendra Modi to Ankara as part of a number of measures showing its displeasure with Turkey.
Issue:
- Turkish President Recip Tayyip Erdogan’s speech at the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) last month, in which he criticised its move on Article 370 in Jammu & Kashmir. India considers it an internal issue.
- India’s expected decision to cancel the selection of Turkey’s Anadolu Shipyard for building naval support ships for India. While the sources noted that rules for local procurement and security concerns over Anadolu’s work for the Pakistan navy were reasons for the likely cancellation, diplomatic sources said Turkey’s recent statements and its support for Pakistan at the Financial Action Task Force on terror financing were also considered.
- India’s sharp criticism of Ankara’s unilateral military offensive against Syria. However turkey defending its Operation Peace Spring along its border with Kurdish-held parts of northeast Syria claimed that all operations were on “legitimate terrorist targets” and claimed “zero civilian casualties”.
INDIA-PHILIPPINES BUSINESS CONCLAVE
20, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- The President of India, Shri Ram Nath Kovind, addressed the India-Philippines Business Conclave and the 4th ASEAN-India Business Summit in Manila, Philippines.
Agreements between India and Philippines:
- India and Philippines have entered into four agreements which includes
- Science and Technology
- Maritime
- exchanging of white shipping data that includes identification and information about the movement of commercial and non-military vessels
- Tourism
- Culture
Significance:
- The president’s visit coincides with the 70th anniversary of the establishment of diplomatic relations between the two countries.
- Agreements between both countries will not only strengthen the bilateral relations but also put an impact on China and its dominating image in the region.
- The Philippines can emerge as one of the most focused countries for India’s corporate business expansion. India and Philippines economic-ties can achieve new heights.
- India is hoping to get defence cooperation and participation in weapon modernization of Philippines.
- Several Indian companies are looking for investment opportunities in the health, innovation and pharma sectors.
INDIA-CHINA FACE-OFF AT PANGONG TSO LAKE
13, Sep 2019

Why in News?
- According to a PTI report Indian and Chinese soldiers had a heated exchange in Ladakh near the Pangong Tso lake and the issue has now been resolved. The report said the exchange happened after Chinese Army personnel objected to patrolling by Indian soldiers. Differing perceptions about the Line of Actual Control (LAC) was responsible for the incident.
- The incident recalls a similar incident almost exactly two years ago, in the same area in Eastern Ladakh. Differing perceptions of where exactly the LAC lies has often been the reason for such incidents.
About Pangong Tso:
- In the Ladakhi language, Pangong means extensive concavity, and Tso is lake in Tibetan.
- Pangong Tso is a long narrow, deep, endorheic (landlocked) lake situated at a height of more than 14,000 ft in the Ladakh Himalayas.
- The western end of Pangong Tso lies 54 km to the southeast of Leh. The 135 km-long lake sprawls over 604 sq km in the shape of a boomerang, and is 6 km wide at its broadest point.
- The brackish water lake freezes over in winter, and becomes ideal for ice skating and polo.
- The legendary 19th century Dogra general Zorawar Singh is said to have trained his soldiers and horses on the frozen Pangong lake before invading Tibet.
Strategic Location of Pangong Tso Lake:
- The LAC cuts through the lake, but India and China do not agree on its exact location. As things stand, a 45 km-long western portion of the lake is in Indian control, while the rest is under China’s control. Most of the clashes between the two armies occur in the disputed portion of the lake.
- By itself, the lake does not have major tactical significance. But it lies in the path of the Chushul approach, one of the main approaches that China can use for an offensive into Indian-held territory. Indian assessments show that a major Chinese offensive, if it comes, will flow across both the north and south of the lake.
- During the 1962 war, this was where China launched its main offensive — the Indian Army fought heroically at Rezang La, the mountain pass on the southeastern approach to Chushul valley.
- Over the years, the Chinese have built motorable roads along their banks of the Pangong Tso. At the People’s Liberation Army’s Huangyangtan base at Minningzhen, southwest of Yinchuan, the capital of China’s Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, stands a massive to-scale model of this disputed area in Aksai Chin. It points to the importance accorded by the Chinese to the area.
The Dispute:
- The difference in perception over where the LAC lies on the northern bank of the lake, makes this contested terrain.
- In 1999, when the Army unit from the area was moved to Kargil for Operation Vijay, China took the opportunity to build 5 km of road inside Indian territory along the lake’s bank. The August 2017 skirmish took place in this area.
- The 1999 road added to the extensive network of roads built by the Chinese in the area, which connect with each other and to the G219 Karakoram Highway. From one of these roads, Chinese positions physically overlook Indian positions on the northern tip of the Pangong lake.
- The mountains on the lake’s northern bank jut forward in major spurs, which the Army calls “fingers”. India claims that the LAC is coterminous with Finger 8.
Induction of High-Speed Boats by India:
- On the water, the Chinese had a major advantage until a few years ago, but India purchased better boats some seven years ago, leading to a quicker and more aggressive response.
- Although there are well-established drills for disengagement of patrol boats of both sides, the confrontations on the waters have led to tense situations in the past few years.
- The induction of high-speed boats has ostensibly provoked the Chinese, who have responded by increasing the number of transgressions in this area in recent years.
INS TARKASH AT BERGEN
10, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- Indian Naval Ship Tarkash, a front-line warship of the Indian Navy, entered the port of Bergen, Norway, for a three-day visit as part of Western Fleet Overseas Deployment.
Highlights:
- The ship is part of the Indian Navy’s Western Fleet and is under the operational Command of Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief/ Western Naval Command, based at Mumbai.
- The port call by Tarkash at Bergen is a demonstration of India’s warm ties with Norway. INS Tarkash, commanded by Captain Sathish Vasudev, is one of the most potent frontline frigates of the Indian Navy equipped with a versatile range of weapons and sensors.
- During the port call, various dignitaries and government officials of Norway are scheduled to visit the ship.
- Professional interactions are planned with the Royal Norwegian Navy and Coast Guard towards further enhancing co-operation between the two countries.
- In addition to social engagements and sports event, best practices will also be shared between the Indian and Royal Norwegian Navies.
India and Norway Ties:
- India has cordial and friendly relations since 1947 with Norway. Bilateral cooperation between the two countries is progressed through the India-Norway Joint Commission Meetings. The inaugural ‘Bilateral Discussion’ between the Royal Norwegian Navy and IN was held in February 2017 at New Delhi.
- Indian Navy ships are regularly deployed as part of Indian Navy’s mission of building ‘bridges of friendship’ and strengthening international cooperation with friendly countries.
- The ship visit to Norway comes amidst growing importance and convergence of national goals towards shared maritime interest and deepening of ties between both the countries.
ISRO TECHNICAL LIAISON UNIT
01, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- The Union Cabinet has approved the setting up of ISRO Technical Liaison Unit (ITLU) at Moscow, Russia.
Highlights:
- Department of Space has instituted technical Liaison Units, namely ISRO Technical Liaison Units (ITLU) at Washington, USA and Paris, France with the prime objective to liaise with various Government and space agencies in USA and Europe, respectively.
- Space cooperation has been one of the major links between India and Russia almost from the beginning of the space era and currently both sides are actively pursuing interactions in diversified areas of space programme
- Apart from intensifying cooperation with Russia, India has expanded its space cooperation with countries near to Russia.
- This calls for extensive uninterrupted coordination & interface support for increased level international technical collaboration.
ISRO Technical Liaison Unit (ITLU):
- The ISRO Technical Liaison Unit (ITLU) at Moscow will enable effective technical coordination for timely interventions on diversified matters with Russia and neighbouring countries for realization of the programmatic targets of ISRO.
- The Liaison Officer, deputed at ITLU from ISRO provides technical information about the developments in research and technology and inputs arising from their meetings with researchers, government agencies and industries in the respective countries.
- They also support the ongoing bilateral programmes of cooperation in space technology and act on behalf of ISRO on the matters referred.
Advantages:
- ISRO will be able to collaborate with Space agencies/industries in Russia and neighbouring countries for mutually synergetic outcomes.
- ISRO’s Gaganyaan programme requires development of some of the key technologies and establishment of specialized facilities, which are essential to support life in space.
- Keeping in view the 15th August, 2022 timeline for realization of the Gaganyaan human space programme, it is prudent to avail technical cooperation from International space agencies, who have already demonstrated their technical capabilities in specific areas.
- Russia, being one of the space-faring nations, it is envisaged to collaborate with Russia extensively in various fields of relevance.
INDIA AND BENIN RELATIONSHIP
30, Jul 2019

Why in News?
- The President of India, Shri Ram Nath Kovind, reached Cotonou, Benin on the first leg of his state visits to three West African nations – Benin, Gambia and Guinea.
- This visit is the first-ever visit of Head of State/Head of Government of India to each of the three countries.
MOUs/agreements:
- MOUs exchanged between India and Benin:
- Cultural Exchange Programme between the two countries for the years 2019-2023
- MOU on Cooperation in the field of Export Credit and Investment Insurance
- MOU between Benin & Telecommunications Consultants India Limited (TCIL) for participation in the e- VBAB Network Project (Technology upgradation of Pan Africa e-Network Project (PAeNP)- Phase-I) of Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India. Agreement on mutual exemption from the visa requirement for holders of Diplomatic, Official/Service Passports
India and Benin:
- India is keen to strengthen economic partnership with Benin. India has emerged as the largest trading partner of Benin with two-way trade crossing US$ 800 million.
- Around 100 Indian or Indian-owned companies are operating in Benin. More Indian companies are interested to enter the Benin market, especially in mining. India seeks Benin’s support to help them grow their business.
- President announced fresh Line of Credit worth US$ 100 million for developmental projects in Benin. He also announced extension of e-visa facility to Benin.
- India also offered to extend free tele-education courses to 15,000 Beninese students and tele-medicine courses to 1000 doctors and paramedics in Africa.
- In addition, the two sides discussed defence and security cooperation and India offered further training assistance to Benin to expand its anti-piracy capacity.
- India thanked Benin for its support for India’s candidature for permanent membership of the UN Security Council. Both countries reiterated their commitment to stand together in the global fight against terrorism and piracy.
LOOK EAST AGENDA
21, Jul 2019

Act East Policy:
- India’s Act East Policy focusses on the extended neighbourhood in the Asia-Pacific region. The policy which was originally conceived as an economic initiative, has gained political, strategic and cultural dimensions including establishment of institutional mechanisms for dialogue and cooperation.
Objective:
- The Objective of” Act East Policy” is to promote economic cooperation, cultural ties and develop strategic relationship with countries in the Asia-Pacific region through continuous engagement at bilateral, regional and multilateral levels thereby providing enhanced connectivity to the States of North Eastern Region including Arunanchal Pradesh with other countries in our neighbourhood.
- The North East of India has been a priority in our Act East Policy (AEP).
- The focus has been on the development and prosperity of the North Eastern states by improving connectivity, access and facilities to the region through various initiatives including improving connectivity of North East Region with Bangladesh, improving access to North East from Myanmar to facilitate tourism and cross border connectivity, promotion of Land Border Crossing Agreement and Integrated Check Post at Moreh and infrastructure projects like India-Myanmar-Thailand trilateral highway, Kaladan Multi Modal Transit Transport Project in Myanmar.
Initiatives undertaken by the Govt:
- ASEAN-India Plan of Action (2016-20) adopted at the 13th ASEAN-India Foreign Ministers’ Meeting held in Kuala Lumpur in 2015 and endorsed by Leaders at the 13th ASEAN-India Summit held in Kuala Lumpur in 2015, provides for a road map for cooperation between ASEAN and India across three pillars.
- Political security
- Economic and Socio-cultural.
- A number of activities are held under the Plan of Action (2016-20) in all three spheres to promote ASEAN-India relations.
- Various projects are undertaken from Indo-Pacific Division’s budget, and ASEAN-India Fund (AIF), ASEAN-India Green Fund (AIGF) and ASEAN-India Science & Technology Development Fund (AISTDF) which have been set up by Government of India for undertaking joint projects with ASEAN Member States. These Funds are rolling funds and are replenished on need basis.
- Under the 3 Lines of Credit worth about USD 8 billion extended by India to Bangladesh, GoI has undertaken several projects to enhance connectivity with our North East Region through Bangladesh.
- India has disbursed around US $ 1.04 billion in grant projects, and has extended concessional loans of US $ 478.9 million from India’s LOC amount of around US $750 million to Myanmar.
- Projects on grant funding include connectivity infrastructure projects like Kaladan Multi Modal Transit Transport Project, upgradation of 69 bridges and building the Kalewa Yargi road segment on the Trilateral Highway.
- On the Civilizational front, Buddhist and Hindu links could be energized to develop new contacts and connectivity between people.
SAGARDHWANI EMBARKS ON SAGAR MAITRI MISSION-2
21, Jul 2019

Why in News?
- Oceanographic research vessel of Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), INS Sagardhwani, embarked on a two-month long SAGAR MAITRI
SAGAR MAITRI:
- SAGAR MAITRI is a unique initiative of DRDO which promote closer co-operation in socio-economic aspects as well as greater scientific interaction especially in ocean research among Indian Ocean Rim (IOR) countries.
- INS Sagardhwani has been designed and developed by Naval Physical and Oceanographic Laboratory (NPOL), Kochi, a premier systems laboratory of DRDO.
- It conducts ocean research experiments in the Indian waters and spearheads NPOL’s at-sea data collection activities
- SAGAR MAITRI Mission-2 commemorates the Golden Jubilee Celebrations of India’s lone research ship INS Kistna’s missions as part of the historic International Indian Ocean Expeditions (IIOE), which took place during 1962-65.
- The prime objectives of the SAGAR MAITRI Mission are data collection from the entire North Indian Ocean, focussing on the Andaman Sea and adjoining seas and establishing long-term collaboration with eight IOR countries in the field of ocean research and development.
- The other IOR countries, include Oman, Maldives, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia and Myanmar.
- The programme also aims at establishing long term scientific collaboration with these countries in the field of ‘Ocean Research & Development’ and data collection with a focus in the Andaman Sea.
INTER-INSTITUTIONAL AGREEMENT BETWEEN INDIA AND USA
19, Jul 2019
Why in News?
- The Union Cabinet has given approval to the Inter-Institutional Agreement between India and the USA in the areas of regenerative medicine and 3D bioprinting, new technologies, exchange of scientific ideas/information and technologies.
Benefits:
- The joint research projects, training programmes, conferences, seminars etc. under this Agreement will be open to all qualified scientists and technologists, and will be supported on the basis of scientific merit and excellence.
- Scientific research and technology development in the areas of regenerative medicine and 3D bio-printing will have potential for generation of new Intellectual Property, processes, prototypes or products.
- Both institutes anticipate the general academic exchange contemplated under the Agreement will lead to the development of specific projects, each of which may have academic, clinical and commercial implications.
Objectives:
- The objective of the Agreement is to contribute towards the development of research and education of both the Institutions through academic collaboration.
- The general areas of common interest where collaboration and exchange of knowledge are intended for both include:
- Exchange of faculty members and students for training, study and research especially in the areas on 3D Bioprinting;
- Execution of joint research projects; and
- Exchange of information and academic publications.
India, France to Deepen Cooperation
25, Jun 2019

- India and France have decided to deepen cooperation in the cyber security sector.
- They will jointly work towards curbing the use of the Internet for terrorist purposes and online radicalisation.
- The third Indo-French cyber dialogue was held in Paris on 20 June 2019.
- France and India have reaffirmed their commitment to open, reliable, secure, stable and peaceful cyberspace.
India Granted USD15 Million to Niger for holding African Union Summit
23, Jun 2019

- India has extended USD 15 million assistance to Niger for organising the African Union (AU) summit scheduled to be held in Niamey from July 7-8.
- The support of grant assistance was in response to a specific request made by the Niger government.
- This year, Niger is hosting an AU summit for the first time.
- In this AU summit, the historic African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) is likely to be launched.
Background:
- Bilateral ties between India and Niger have expanded significantly since the opening of the Indian Resident Diplomatic Mission in Niamey in 2009.
- India has provided Lines of Credit worth USD 96.54 million to Niger for projects in transport, electrification, solar energy, and potable drinking water.
- India is also establishing the Mahatma Gandhi International Convention Centre (MGICC) in Niamey under grant assistance.
GREAT THINGS ARE IN STORE FOR BILATERAL TIES, SAYS TRUMP
24, May 2019

Why in News:
- Reacting to Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s victory the U.S. House [of Representatives] Foreign Affairs Committee issued a statement congratulating “the Indian people”.
Details:
- Listing the of priorities for the India-U.S. partnership mentioned human rights first. It also referred to climate change.
- U.S. Congress looks forward to continue working with India, on a host of issues, including human rights, defense, trade and economic growth, and climate change.
Why India Matters to the USA?
- India is an indispensable partner for the United States. Geographically, it sits between the two most immediate problematic regions for U.S.
national interests. The arc of instability that begins in North Africa goes through the Middle East, and proceeds to Pakistan and Afghanistan ends at India’s western border. - With the rise of Asian economies, the Indian Ocean is home to critical global lines of communication, with perhaps 50 percent of world container products and up to 70 percent of ship-borne oil and petroleum traffic transiting through its waters.
- India’s growing national capabilities give it ever greater tools to pursue its national interests to the benefit of the United States. India has the world’s third-largest Army, fourth-largest Air Force, and fifth largest Navy.
- India is an important U.S. partner in international efforts to prevent the further spread of weapons of mass destruction.
- India’s broad diplomatic ties globally (most importantly in the Middle East), its aspirations for United Nations (UN) Security Council permanent membership, and its role in international organizations such as the International Atomic Energy Agency makes New
U.K. to Test Immigration proposals in India
10, Jan 2019

Context:
- The immigration plans aim to create a level-playing field for EU and non-EU workers, basing immigration opportunities on skills levels rather than which part of the world workers have come from.
Details:
- The government has positioned the new planned immigration system as a positive one for partners such as India.
- Among the changes proposed are the removals of the current annual cap on the number of Tier 2 visas for skilled workers, as well as the requirement that employers demonstrate that they attempted to fill the role domestically before bringing in a person from abroad (the resident labour market test)
- The government will also allow international students six months after they graduate to find permanent skilled work and work temporarily during that period, while PhD graduates will have a whole year to do so
- The government has also said it is to consult on the salary threshold for the skilled visas which has been the subject of much debate in the U.K.
- These moves would immensely benefit Indian students and skilled workers looking for employment opportunities in the UK and also helps in strengthening India-UK relationship.
ISRO’S New Station in Bhutan to Counter China’s Tibet Facility
02, Jan 2019

In News:
- India is setting up a satellite tracking and data reception centre in the Himalayan state of Bhutan that will also strategically serve to counter a similar Chinese facility in the region.
Explained:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation’s ground station in Bhutan is likely to double up as “a strategic asset” for the country, given its location between India and China, China has already established an advanced satellite tracking centre and astronomical observatory at Ngari in Tibet Autonomous Region, about 125 km away from the Line of Actual Control, which serves as the de-facto border between India and China. The facility
in Tibet is so advanced that apart from tracking Indian satellites, it can also “blind” them - This strategy is significant in the backdrop of the Doklam crisis, when the Chinese tried to construct a road at a tri-junction between India, Bhutan and China. Bhutan stood firmly with India during the 72-day face-off between the Indian army and the Chinese People’s Liberation Army at Doklam in western Bhutan in June-August, 2017.
India-Bhutan:
- Although ISRO’s ground station in Bhutan is intended to help the Himalayan state take advantage of the South Asia Satellite, it is also India’s way of counterbalancing the Chinese station in Tibet
- With the completion of this project, Bhutan will get help in tasks such as weather information, tele-medicine and disaster relief in the far-flung areas of the country.
- India also pledged Rs 4,500 crore as assistance to Bhutan to support the Himalayan state’s 12th five-year plan for development.
Gandhi Statue Removed in Ghana
15, Dec 2018

Context
- A statue of Mahatma Gandhi has been removed from Ghana’s most prestigious university after complaints that “he was racist against black Africans”.
Details
- India’s former president Pranab Mukherjee had unveiled the statue of the global peace icon at the University of Ghana in Accra two years ago as a symbol of close ties between the two nations.
- But lecturers soon began a petition calling for its removal, citing passages written by Mahatma Gandhi claiming that Indians were “infinitely superior” to black Africans.
- The online protest was one among many on university campuses in Africa and beyond about the enduring symbols of the continent’s colonial past.
- The other side mentioned that it was removed on the note of ‘self-respect’
India, China Join Hands to Promote Tea Globally
14, Dec 2018

In News
- Two apex industry organizations, Indian Tea Association (ITA) and China Tea Marketing Association (CTMA), have signed a memorandum of understanding to promote green and black tea consumption in major tea markets in Europe, the U.S., Russia and West Asia, besides India and China. The pact could also involve organization of joint events.
Background:
- China imported 30 million kg of black tea annually amid its rising popularity in the country where green tea had earlier held sway.
- Indian exports stood at about 8.7 million kg in 2017 with the market being dominated by Sri Lanka and Kenya.
- An export of 15 million kg to china was being targeted next year. It may be mentioned that Tea Board and ITA had organised a tea delegation to China in October to boost trade between the two countries where the trade deficit between two countries stand almost 60 billion in favor of china
- According to China that it would not look to India as a major market as prices were more attractive in their domestic market. China was the world’s third largest exporter (mainly of green tea).
- Asia had taken the lead role in forging this alliance which, it felt, would promote sustainable development of the tea industry in the two countries, including that of the small tea sector.
- The MoU (memorandum of understanding) covers the areas of trade promotion, intellectual property protection and technology exchange
- It may be attributed to “Wuhan spirit” between India and china
TEA:
Conditions of Growth:
1.Tea bush is a tropical and sub-tropical plant and thrives well in hot and humid climate. There is a very close relation between climate, the yield and the quality of tea.
2.The ideal temperature for its growth is 20°-30°C and temperatures above 35°C and below 10°C are harmful for the bush.
3.It requires 150-300 cm annual rainfall which should be well distributed throughout the year. While prolonged dry spell is harmful for tea, high humidity, heavy dew and morning fog favour rapid development of young leaves.
4.Alternate waves of warm and cool winds are very helpful for tea leaves. Tea is a shade-loving plant and develops more vigorously when planted along with shady trees.
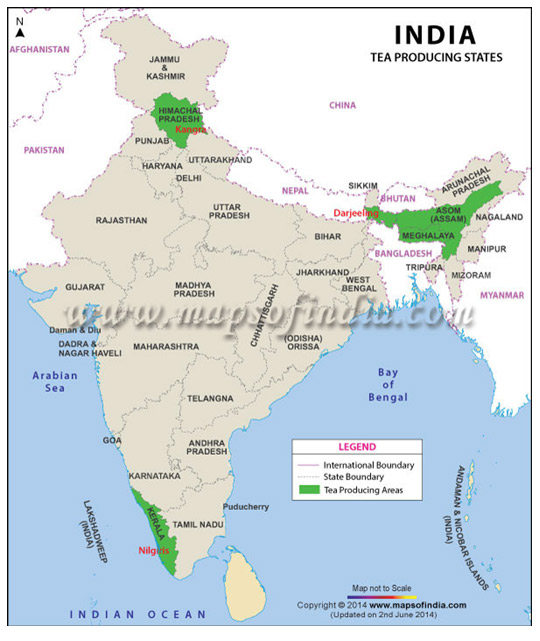
5.Tea cultivation in India is highly concentrated in a few selected pockets. Following three areas of tea cultivation are identified according to their importance as tea producers and their location.
- North-Eastern India
- South India
- North-West India.
- This is the most important tea producing region of India accounting for about three-fourth production and about the same percentage of area under tea production.
1. Assam (Surma Valley, Brahmaputra valley),
2. West Bengal -The Duars in Koch Bihar and Jalpaiguri districts, Darjeeling district - In South India tea is produced in Nilgiri, Cardamom, Palni and Anaimalai hills in Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Karnataka states
- Some of tea is produced in Dehra Dun, Almora and Garhwal districts of Uttaranchal and in Kangra Valley and Mandi district of Hiamchal Pradesh.
- Green tea is produced in Kaangra valley of Himachal Pradesh.
North-Eastern India:
South India:
North West India:
Rajya Sabha TV – India’s World President Kovind’s Visit To Myanmar
12, Dec 2018

In News:
- President Ram Nath Kovind will be on a four-day visit to Myanmar. During his stay, the President will visit capital Nay Pyi Taw and Yangon, and interact with his counterpart U Win Myint and State Counsellor Aung San Suu Kyi. A high-level delegation is also accompanying Mr Kovind.
- In the past three years, India’s political, economic and defence ties with Myanmar have grown rapidly. Through this visit, the President will reaffirm India’s commitment to developing an important partnership with Myanmar.
Significance of India Myanmar relationship:
- Myanmar is one of India’s strategic neighbours and shares a 1,640-km-long border with a number of north eastern states. Myanmar is at the heart of Indian government’s Act East policy with the India-Myanmar-Thailand Asian Trilateral Highway, the Kaladan multimodal project, a road-river-port cargo transport project, and BIMSTEC.
- India is also working closely with the security forces of Myanmar to target the insurgents operating in the country’s northeast.
- Myanmar is expected to act as the bridge between India and ASEAN, has risen in much significance in the context of India’s Act East Policy, and good neighbourhood policy.
- Better relations with Myanmar have become crucial for India with China gradually gaining confidence of countries in the region.
- Further India’s completion of the projects with Myanmar would also prove India to be a responsible regional player, thus improving its reliability.
- Myanmar is on India’s energy security radar on account of its abundant oil and natural gas reserves.
- Good relations with Myanmar can help boost the development of North Eastern India through growth in trade and business opportunities, border haats, communication and physical connectivity infrastructure to promote people to people connectivity.
- Capacity building in Myanmar as India has been actively involved in capacity building in Myanmar through Myanmar Institute of Information Technology, Advanced Centre for Agriculture Research and Education
Important projects by India in Myanmar:
- Kaladan multi-modal corridor
- Repair of 69 bridges on the Tamu-Kalewa road
- The construction of the 120-km KalewaYargyi corridor both of which are part of the India-Myanmar-Thailand trilateral highway
- The Rhi-Tiddim road in the Chin state bordering Mizoram
Issues in the relationship:
- The Rohingya crisis: India does not directly engage with the issue of Myanmar’s treatment of its Rohingya Muslim minority. Peace and stability in the Rakhine state is important for India’s strategic and economic point of view though but the Rohingya crisis is posing a security challenge to the South and Southeast Asia. As China’s profile continues to rise in India’s vicinity, India would like to enhance its presence by developing infrastructure and connectivity projects in the country. India has found it difficult to counter Chinese influence in Myanmar. India is losing friends because of widespread discontent over continuing delay in completion of flagship projects such as Kaladan and the India-Myanmar-Thailand trilateral highway.
- Despite mutual consensus on the value of people-to-people exchanges, actual progress is negligible due to the absence of an enabling instrument.
Way Ahead:
- It is crucial for India to focus on timely delivery of projects to improve its legitimacy.
- It is essential that the two countries immediately start negotiating transit and other agreements for the smooth movement of goods and vehicles for optimal use of the infrastructure.
- There is a strong need to expand, diversify and upgrade commercial ties in ways that also contribute to Myanmar’s development needs and meet India’s $3 billion trade target set in 2012. Indian businesses could look for avenues to invest in the power, steel, automobiles and even textile sectors in Myanmar.
- India can certainly help in improving the socio-economic conditions in the area facing violence and also create employment opportunities.
Check Your Understanding:
- Despite the increasing cooperation between India and Myanmar, there are many roadblocks which need to be solved. Analyse the statement and provide suggestions for future initiatives.
President Kovind holds Delegation-Level Talks with Myanmar Leadership
12, Dec 2018

In News:
- President Ram Nath Kovind held delegation-level talks with the Myanmar leadership. He was given a grand ceremonial reception and guard of honour at Myanmar president house in the morning.
- President’s visit to Myanmar aims to continue India’s high-level engagements with Myanmar under the rubric of ‘Act East Policy’ and ‘Neighbourhood First Policy’.
MoUs Signed between the countries:
- After wide-ranging talks with Myanmar President and the State counsellor, India and Myanmar signed two MOUs.
- First one is for the training of Myanmar judicial officers in India, in the field of civil law, criminal law, environmental and medical jurisprudence.
- The second one is to enhance cooperation in science and technology, especially for the research in industry, agriculture and other fields.
- India has also handed over first 50 housing units, built for people of Myanmar, under the India-Myanmar friendship project.
Bangladesh to provide key point
10, Sep 2018

Why in news?
- Bangladesh’s Cabinet approved the draft of a proposed agreement with India to allow it to use the Chittagong and Mongla sea ports for transporting goods to and from the north eastern States.
- The agreement will be effective for five years.
Importance of the Chittagong port:
- Plan prepared by the BJP-led government for the development of North Eastern states by providing the landlocked region direct access to Bangladesh’s Chittagong port instead of shipping the goods all the way from Mumbai and Chennai ports.
- North-East is a special focus area for government. So, connecting Tripura with Chittagong port which is about 90 miles.
- Through Chittagong port entire North East is connected with ocean trade.
- Right now, goods to North East are to be taken by rail and road from Mumbai or Chennai through Kolkata to Guwahati. If there is a connection to Chittagong port, it will be an excellent connectivity.
- The Chittagong port is the busiest seaport on the coastline of the Bay of Bengal. North East connects with five countries, Bangladesh, Bhutan Nepal, Myanmar and China through Tibet.
- Opening up of Chittagong and Mongla ports in Bangladesh to bilateral commerce will give immense boost to relations between two countries
- The agreements seek to reduce not only the time in shipping goods but also costs.
Mauritius tops India’s chart
10, Sep 2018

Mauritius remained the top source of foreign direct investment (FDI) into India in 2017-18 as per the RBI report. FDI from Mauritius totalled $13.41 billion as against $13.38 billion in the previous year, inflows from Singapore rose to $9.27 billion from $6.52 billion. FDI from the Netherlands declined marginally to $2.67 billion as against $3.23 billion a year earlier.
India signs landmark, defence fact with us
09, Sep 2018

Why in news?
- India and the United States sealed the landmark Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA) that will lead to a new generation of bilateral military partnership. It comes into force immediately and is valid for 10 years.
What is COMCASA?
- COMCASA is one of the three foundation agreements that signed by a country with the United States to share high-end encrypted communication and satellite data.
- India has already signed two of them – General Security of Military Information Agreement (GSOMIA) in 2002 and the Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement (LEMOA) in 2016.
- Discussions have not even begun on the agreement, Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement for Geo-spatial Cooperation (BECA).
- This agreement permits Indian military to function on high-end secured and encrypted communication equipment that are installed on American platforms obtained by Indian Armed Forces.
- These platforms include C-130 J, C-17, P-8I aircraft, and Apache and Chinook helicopters. This facilitates greater interoperability between forces and military hardware of the two countries, and also possibly with other countries that operate on US-origin platforms. Due to non-signing of COMCASA, these platforms were using commercially available communication systems
How it helps India?
- The agreement is meant to provide a legal framework to allow transfer of encrypted communication security equipment from the US to India, which is said to be safer and more secure than the system that India uses right now.
- Currently, Indian military reportedly uses a locally-sourced platform to communicate between various weapons systems, which also includes the platforms that India has acquired from the US.
- The US government will be able to give the go-ahead to install the best communication equipment on relevant platforms being sold to India.
- As a complement to COMCASA, a hotline will also be established not only between the countries’ defence and foreign ministers but also between the US Naval Forces Central Command (NAVCENT) and the Indian Navy in the interest of security in the Indian Ocean.
- Though Russia remains the biggest defence partner of India, the US has become India’s second-largest arms supplier; the two countries have closed $15 billion worth of deals in the last The meeting also saw the two sides agreeing to step up their counter terrorism cooperation.
Role for Private Sector:
- Sitharaman and Secretary of Defence James N. Mattis also announced their readiness to begin negotiations on an Industrial Security Annex (ISA) that would allow Indian private sector to collaborate with the U.S. defence industry.
- The GSOMIA allows sharing of classified information from the S. government and American companies with the Indian government and defence Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) but not with Indian private companies.
- To further defence innovation, a Memorandum of Intent was signed between the S. Defense Innovation Unit (DIU) and the Indian Defence Innovation Organization – Innovation for Defence Excellence (DIO-iDEX), which will look into joint projects for co-production and co-development projects through the Defense Technology and Trade Initiative (DTTI). Ahead of the 10th anniversary of the 26/11 terror strikes in Mumbai, India and the U.S. resolved to combat international terrorism and asked Pakistan to bring those responsible for recent acts of terrorism against India to justice.
Bangladesh Pipeline
07, Sep 2018

- India will build pipelines to carry diesel and natural gas to Bangladesh as the world’s third largest energy consumer looks to strengthen ties with the neighbour.
About:
- Prime Minister of Bangladesh and her Indian counterpart jointly inaugurated the construction work of 130km Bangladesh-India Friendship Pipeline between Shiliguri in West Bengal and Parbatipur in Dinajpur.
- The start of works for Bangladesh-India Friendship Pipeline is going to add a new chapter in the friendship of the two countries. It will play a huge role in the mega project taken up by the Bangladesh government.
- The pipeline, would specially contribute to fuel supply in a cheaper rate in Bangladesh’s northern part while after its construction with Indian financing, the infrastructure would be handed over to Bangladesh government.
- This will be the first such pipeline through which refined diesel will be supplied to Parbatipur depot from Numaligarh of Assam in India.
- The 131-km pipeline will be laid from from Siliguri in West Bengal to Parbatipur in northern Bangladesh to transport diesel, a line from Dattapulia in West Bengal will take natural gas to Khulna, the third-largest city of Bangladesh
- The pipelines are part of a non-binding Framework of Understanding (FoU) which India will enter into with Bangladesh for cooperation in the hydrocarbon sector.
- India will supply 2.5 lakh tonnes of diesel for the first three years through the pipeline and the amount will be increased to 4 lakh MT in the last five years.
- The import of fuel will be further raised in future through the pipeline as per the requirements of The NRL will distribute diesel for 15 years through the pipeline and the time could be expanded following the consent of both sides.
Significance:
- The Indian prime minister said that the two countries implemented a number of projects within a short time which are the symbols of good relations.
- Bangladesh-India bilateral cooperation had reached to a new height in the past few years while prospects for economic development would substantially be enhanced through such bilateral projects as ‘economic development is the biggest challenge for South Asian countries. These projects are very important for people-to-people contact between the two countries.
India Rejects U.K. Proposal on DNA Tests for ‘Illegal Migrants’
08, Aug 2018

- India rejected a proposal by the U.K. to use DNA sampling to establish the nationality of illegal migrants living there citing “privacy issues”.
MoU:
- In January, Union Cabinet approved the contents of a MoU on “return of illegal migrants” to be signed with U.K.
- MoS Home Kiren Rijiju, who led a delegation to U.K the same month, signed the MoU.
- As per the original MoU, the security agencies in India were to verify the antecedents of document less illegal migrants in the U.K within 72 days and those with documents within 15 days.
- If no report was given within the stipulated time frame, the illegal migrant would be deported automatically.
- In April, the pact was expected to be signed during the visit of Prime Minister Narendra Modi to London, but it was not included in the official list of business.
- The agreement was put on indefinite hold after National Security Adviser conveyed that the 15-day limit was unworkable.
Unethical:
- The U.K. authorities suggested that the nationality of document-less illegal migrants suspected to be Indians could be established by matching DNA samples of their family members living here.
- India raised objections that this was a breach of privacy and unethical.
DNA Testing:
- DNA testing is basically comparative testing, which allows for two DNA samples to be sequenced and compared to see if two people are biologically related.
- Most developed nations use DNA testing on a routine basis when assessing immigration applications.
- DNA testing is a relatively straightforward process to ensure that accurate evidence is provided. Although applicants are not forced to undergo DNA testing in relation to their immigration application, it is in their best interests to do so, assuming they have been truthful about a claimed familial relationship.
- This type of testing also ensures that international applicants who are dishonest about a relationship or show false and forged documentation can be identified and prevented from entering the country. With DNA testing, a more fair and accurate system of immigration can be supported.
India Designated as sta-1 country
07, Aug 2018

- India has become the first south Asian to get the Strategic Trade Authorisation-1 (STA-1) status. India became the third Asian country after Japan and South Korea to get the Strategic Trade Authorization-1 (STA-1) status.
- India is also the 37th country to be designated the STA-1 status by the United States.
- India so far was listed in STA-2 category along with Albania, Hong Kong, Israel, Malta, Singapore, South Africa and Taiwan.
- It was significance as the Trump Administration made an exception for India, which is yet to become a member of the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG).
- The US has placed only those countries in the STA-1 list who are members of the four export control regimes: Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), Wassenaar Arrangement (WA), Australia Group (AG) and the NSG.
Strategic Trade Authorisation:
- STA is the licence exemption that allows a set of items on the Commerce Control List to be exported from the US under defined conditions without a transaction-specific licence.
- The STA exception is relevant to exports, re-exports and transfers for which a licence is required under the Export Administration Regulations – one of the two important US export control laws that affect the manufacturing, sales and distribution of technology.
Impact:
- This commitment has been realised in the two countries mutually agreed upon steps to expand cooperation in civil space, defence, and other high-technology sectors.
- This status will ease export control of high-technology product sales to India will help getting critical and latest technology, particularly in civil space and defence sectors.
- This would allow the transfer of more sensitive defence technologies and dual use technologies to India and without the risk of any proliferation by this certain equipment & devices are given which are avoided for long.
- STA-1 status reduces the number of licenses required for equipment purchase and increases the number of license exceptions available.
- This regulatory change will enhance the bilateral defence trade relationship and result in a greater volume of US exports to India.
- This recognition facilitates and supports India’s military modernisation efforts.
- Provides India greater supply chain efficiency, both for defence and for other high-tech products, that will increase activity with US systems, the interoperability of the systems.
Strategic:
- By placing India in the STA-1 list, the United States has acknowledged India as a special allay even Israel not got that tag.
- This tells other country which are blocking India’s membership of NSG like china that India meet all requirement of NSG.
- This rule is another in the series of rules that implement reforms to which the US and India mutually agreed to promote global non-proliferation, expand high technology cooperation and trade, and ultimately facilitate India’s full membership in the four multilateral export control regimes.
- Help India to emerge as global power & help in Make in India by increasing defence manufacturing.
- This is an acknowledgement of the security as well as the economic relationship between India and the USA it fleshes out our defence partnership in a big way.
India UGANDA
20, Jul 2018

News
The Prime Minister Narendra Modi made a two-day visit to Uganda – the first bilateral tour by an Indian prime minister since 1997.
MOU’s:
List of MoUs signed between India and Uganda are
- MoU on Defence Cooperation
- MoU on Visa exemption for Diplomatic and official passport holders.
- MoU on Cultural Exchange Programme.
- MoU on Material Testing Laboratory
Areas of Engagement
PM Modi announced several areas of engagement with Uganda. These included
- Two Lines of Credits for construction of electricity lines and Substations worth US$141 million.
- Agriculture and Dairy production US $ 64 million.
- India’s contribution for establishment of Mahatma Gandhi Convention/Heritage centre at Jinja where the ashes of Mahatma Gandhi were immersed in the Nile.
- Training of Uganda People’s Defence Force (UPDF) in various Indian Army training institutions as well as the deployment of Indian Military Training Team in Uganda’s Senior Command and Staff College (SCSC) in Kimaka.
- Keeping in mind Uganda’s role in East Africa, Prime Minister also announced a financial support of US $ 929,705 for East African Community (EAC) which is currently chaired by Uganda.
- India also announced donation of 88 vehicles, 44 each for the Ugandan Peoples Defence Forces (UPDF) and for the civil use by the Ugandan Government.
- Bhabhatron Cancer Therapy machine to Uganda Cancer Institute.
- 100,000 NCERT books for school going children of Uganda.
- 100 solar-power irrigation pumps to help in development of agriculture.
India Uganda Relationship:
Relationship
- The bilateral relations between India and Uganda are characterised by historical cultural linkages, extensive economic and trade interests, and a convergence on major bilateral and international issues.
- A common and deep respect for universal values like democracy and peace reinforce the architecture of India-Uganda bilateral relations.
- Trade and economic interests brought several Indians to the shores of East Africa as early as the 17th century in dhows laden with their wares.
- India’s freedom struggle inspired the early Ugandan activists to fight colonization and Uganda eventually achieved Independence in 1962.
- India established it diplomatic presence in Uganda in 1965. Except for the era of Idi Amin’s reign in early 70’s when nearly 55,000 Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs) and 5000 Indian nationals were expelled and their properties confiscated, relations between the two countries have since been cordial.
- The anti-Indian policies of Amin were reversed when the current President Yoweri Kaguta Museveni came to power in 1986.
- The current Government’s progressive policies ensured that the India-Uganda relations were restored to erstwhile levels. Uganda remains an important partner in Africa. India and Uganda closely cooperate at regional and international fora.
Capacity Building and Development Partnership
- Government of India is setting-up a Food-Processing Business Incubation Centre (FPBIC) in Uganda.
- The centre will provide support to the local entrepreneurs to enhance their skills in food processing and also create additional jobs for the rural youth.
Education and Healthcare
- A Tele-medicine centre and a tele-education centre have been set up under the Pan African e-Network Project in 2009.
- India is a preferred destination for affordable and quality health care for Ugandans.
- India is also seen as a destination for quality and affordable education by Ugandan students.
- The Government of India offers scholarships and fellowships to Ugandans from the public and private sector to enable them to pursue under-graduate, graduate, post-graduate and research courses in India under ITEC, ICCR, CV Raman Fellowship and Special Agricultural Scholarship.
Defence Cooperation
- India cooperation with Uganda in the sectors of Security and Defence is increasing.
- Each year, several Ugandan defence officers are trained in India at state-of-the-art training facilities, including the prestigious National Defence College (NDC).
Trade and Commerce
- India remains one of the leading FDI investors in Uganda. India has consistently been among the top three FDI sources.
- It is estimated that Indians/PIOs have invested more than USD 1 billion in the country during the last decade.
Geography
Uganda is a land locked country bounded by
- South Sudan
- Democratic Republic of Congo
- Kenya
- Rwanda
- Tanzania
The Great lakes of Africa which are in Uganda are
- Lake Victoria
- Lake Edward
- Lake Albert
India & Africa
19, Jul 2018

Recently Prime Minister Visited the continent of Africa and visited Rwanda, Uganda and South Africa
Importance of Africa
- From the Backdrop of Chinese penetration in the African Continent and their ability to invest more in Africa remains a concern for India.
- Africa remains as a good market for Indian Goods and services especially health care and it has also promoted medical tourism.
- ‘Make in India’ success depends upon the markets internationally, so Africa being a young continent has enormous growth potential could be a boost for us.
- Africa is home for a large number of Indian Diaspora and the political stability in Africa is substantial as our diaspora play a pivotal role in determining the political condition • We have more number of educational institution which is preferred by many African nation’s (Students)
- Maritime stability and trade route (Suez Canal) Ultimately depends on African Nations, as we plan to expand our ports to secure Indian ocean and trade in Atlantic
Takeaway from the visit
- PM has sponsored 200 cows to the villages of Rwanda as it is seen as a sign of helping neighbour in Africa
- China’s focus is so far on improving infrastructure which ultimately helps the elite. This leads long-term debt trap as these investment are in the form of loan, which ultimately makes Africa subordinate in long term. India’s focus on Human resource development and training to impart skills.
Why China and India is Important to Africa
- Africa being a young continent, especially countries like Rwanda which encountered political turmoil has now a stable political condition.
- Hence it require investment from other economies, china and India being major player’s and Europe and U.S.A being in a political turmoil such as rise in Protectionist policies






