Category: GS-II
Andhra Pradesh can’t change capital, says HC
06, Mar 2022

Why in News?
- The Andhra Pradesh High Court has recently directed the State government to construct and develop Amaravati, the capital city of the State, and the capital region within six Months.
About the News:
- In a significant observation, the High Court held that the State legislature lacked the competence to make any legislation for shifting, bifurcating or trifurcating the capital.
- A three-judge Bench, gave the final verdict after hearings in a case relating to a bunch of writ petitions filed by landowners of Amaravati to declare that the State government had no legislative competence to change the capital or remove Amaravati from being the capital of the three civic wings — legislature, executive and judiciary — of the State.
What is the Issue?
- Counsel for the petitioners contended that the State has failed to deliver on its promise to return the developed plots as per the final master plan within a period of three years even after the deadline expired on January 20.
- The High Court directed the government and the Capital Region Development Authority (CRDA) to discharge their duties enshrined under the A.P. Capital Regional Development Authority (CRDA) Act and Land Pooling Rules.
- It directed the State to develop the reconstitutional plots belonging to landowners and hand them over to landowners within three months.
- The HC held the view that the agreement signed between the farmers and the CRDA in Form-9.14 is a Development Agreement-cum-Irrevocable General Power of Attorney and it is a statutory contract, and the violation of terms and conditions by the respondents —
State and APCRDA — warrants interference of this court, while exercising power under Article 226 of the Constitution.
- The State was also directed to pay costs of ₹50,000 to each of the petitioners for having forced the filing of the case to perform their statutory obligations.
What are the provisions in the 2014 Act regarding the Capital of Andhra Pradesh?
- It may be noted that Section 5 (2) of the 2014 Act says that after the expiry of 10 years, Hyderabad shall be the capital of the State of Telangana and there shall be a new capital for the State of Andhra Pradesh.
- Significantly, Section 6 of the 2014 Act says that the Central Government shall constitute an expert committee to study various alternatives regarding the new capital for the successor State of Andhra Pradesh and make appropriate recommendations.
- Further, Section 94 (3) of the Act says that the Central Government shall provide special financial support for the creation of essential facilities in the new capital of the successor State of Andhra Pradesh including the Raj Bhawan, High Court, Government Secretariat, Legislative Assembly, Legislative Council, and such other essential infrastructure.
- It also says that the Central Government shall facilitate the creation of new capital for the successor State of Andhra Pradesh, if considered necessary, by denotifying degraded forest land.
What are the other Examples of Multiple Capital Cities?
- In Sri Lanka, Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte is the official capital and seat of national legislature, while Colombo is the de facto seat of national executive and judicial bodies.
- Malaysia has its official and royal capital and seat of national legislature at Kuala Lumpur, and Putrajaya is the administrative centre and seat of national judiciary.
Among Indian states:
- Maharashtra has two capitals– Mumbai and Nagpur (which holds the winter session of the state assembly).
- Himachal Pradesh has capitals at Shimla and Dharamshala (winter).
- The former state of Jammu & Kashmir had Srinagar and Jammu (winter) as capitals.
India’s abstention on UNSC vote over Russia’s invasion of Ukraine
03, Mar 2022

Why in News?
- India recently abstained on a US-sponsored UN Security Council resolution that “deplores in the strongest terms” Russia’s “aggression” against Ukraine.
Who moved the Resolution?
- The UN Security Council voted on the draft resolution presented by the US and Albania, and co-sponsored by several other nations, including Australia, Estonia, Finland, Georgia, Germany, Italy, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Romania and the United Kingdom.
What was the Resolution About?
- The Council’s resolution reaffirmed its commitment to the sovereignty, independence, unity and territorial integrity of Ukraine within its internationally recognised borders.
- The resolution “deplores in the strongest terms Russia’s aggression against Ukraine” and decides that Russia “shall immediately cease its use of force against Ukraine and shall refrain from any further unlawful threat or use of force against any UN member state”.
- The resolution added that Russia “shall immediately, completely, and unconditionally withdraw all of its military forces from the territory of Ukraine within its internationally recognised borders”. It also asked Moscow to “immediately and unconditionally reverse the decision related to the status of certain areas of Donetsk and Luhansk regions of Ukraine”.
- In UN Security Council meeting on #Ukraine today, India abstained on the vote on draft resolution.
Why did India Abstain?
- India did not endorse the harsh language used in the resolution condemning Russia’s actions.
- It wants to maintain a balance between the Western bloc led by the US, and Russia, since it has strategic partners on both sides.
- India’s past record has been maintaining balance between the West and Russia. On January 31, India abstained on a procedural vote on whether to discuss the issue of Ukraine. New Delhi had then articulated its position on “legitimate security interests” that echoed with a nuanced tilt towards the Russian position, and had abstained along with Kenya and Gabon.
So, what was the Fate of this Resolution?
- While Russia — which chaired the meeting of the UNSC since it holds the presidency for the month of February — vetoed the resolution, China, too, abstained along with the United Arab Emirates.
- Despite the remaining 11 members of UNSC, including US, UK, France, voting in favour of the resolution, it did not pass since Russia vetoed it.
- China’s abstention is a surprise since it had opposed the vote on January 31, and was seen echoing Russia’s position.
How did India Explain its vote?
- First, it said that it is “deeply disturbed”, but did not name Russia at all. India is deeply disturbed by the recent turn of developments in Ukraine.
- Second, it reiterated its appeal for “cessation of violence”. India urge that all efforts are made for the immediate cessation of violence and hostilities. This was conveyed by Prime Minister Narendra Modi to Russian President Vladimir Putin as well during the phone call.
- Third, it flagged its core concern about Indian nationals in Ukraine — about 16,000 are still stuck, most of whom are students. “India is also deeply concerned about the welfare and security of the Indian community, including a large number of Indian students, in Ukraine.
- Fourth, it touched upon “territorial integrity and sovereignty”, which was a new theme. The contemporary global order has been built on the UN Charter, international law, and respect for the sovereignty and territorial integrity of states. All member states need to honour these principles in finding a constructive way forward.
- Fifth, it advocated diplomacy. Dialogue is the only answer to settling differences and disputes, however daunting that may appear at this moment. It is a matter of regret that the path of diplomacy was given up. We must return to it. For all these reasons, India has chosen to abstain on this Resolution.
Was India under Diplomatic Pressure?
- Before the United Nations Security Council took up the draft resolution condemning the Russian invasion, India was caught in a diplomatic bind between the Western powers and Russia.
- Ambassadors of European countries in India got together in New Delhi and expressed solidarity with their Ukrainian counterpart and strongly condemned Russia’s “unprovoked and unjustified” military attack on Ukraine.
- British and EU Foreign ministers had also called up Jaishankar, while ambassadors of G-7 countries had expressed support for the Ukrainian ambassador.
So, is this good for India’s Diplomatic Space?
- Experts said that India maintained its “consistent, steadfast and balanced position on the matter”.
- “India has been in touch with all sides, urging the parties concerned to return to the negotiating table. By abstaining, India retained the option of reaching out to relevant sides in an effort to bridge the gap and find a middle ground with an aim to foster dialogue and Diplomacy,” a source said.
- An earlier draft of the resolution had proposed moving the resolution under Chapter VII of the UN Charter, which provides the framework within which the Security Council may take enforcement action, the sources added. However, this was dropped in the final version that was put to vote.
INS TARKASH
20, Jul 2019

Context:
- INS Tarkash, a frontline warship of the Indian Navy, made a port call at Karlskrona, Sweden
- This marks the first visit of an Indian Naval Ship to Swedish shores after a gap of more than 15 years.
About:
- INS Tarkash (F50) is the second Teg-class frigate constructed for the Indian Navy. She is part of the second batch of Teg-class frigates ordered by the Indian Navy.
- Operation Raahat
- v In March 2015, Tarkash was deployed with INS Mumbai and INS Sumitra as part of Operation Raahat to provide protection and support to Indian ships and aircraft involved in the evacuation of Indian citizens from Yemen during the military intervention.
Indian Navy and Sweden Navy:
- The visit is part of Indian Navy’s mission of building ‘Bridges of Friendship’ and strengthening international cooperation with friendly countries.
- The current visit seeks to underscore India’s peaceful presence and solidarity with friendly countries, thereby allowing both India and Sweden to meet the growing challenges of the maritime environment.
- India and Sweden have had a number of high-level bilateral visits and interactions resulting in a rapid growth in relations across a broad spectrum.
- The two navies have also been regular contributors to the global operations against piracy.
WHAT IS A WHIP? WHAT DOES IT DO?
20, Jul 2019

What is a WHIP?
- A whip in parliamentary parlance is a written order that party members be present for an important vote, or that they vote only in a particular way.
- The term is derived from the old British practice of “whipping in” lawmakers to follow the party line.
- In India all parties can issue a whip to their members.
- Parties appoint a senior member from among their House contingents to issue whips — this member is called a Chief Whip, and he/she is assisted by additional Whips.
Kinds of WHIPS:
- The importance of a whip can be inferred from the number of times an order is underlined.
- A one-line whip, underlined once, is usually issued to inform party members of a vote, and allows them to abstain in case they decide not to follow the party line.
- A two-line whip directs them to be present during the vote.
- A three-line whip is the strongest, employed on important occasions such as the second reading of a Bill or a no-confidence motion, and places an obligation on members to toe the party line.
Defiance of WHIP:
- The penalty for defying a whip varies from country to country.
- In the UK, MPs can lose membership of the party, but can keep their House seats as Independents.
- In India, rebelling against a three-line whip can put a lawmaker’s membership of the House at risk. The anti-defection law allows the Speaker/Chairperson to disqualify such a member
- The only exception is when more than a third of legislators vote against a directive, effectively splitting the party.
ARANI SILK SAREE
20, Jul 2019

Context:
- Information about Arani Silk Saree was given by the Union Minister of Textiles in a written reply to the Lok Sabha
About:
- Arani Silk Saree produced on handloom is of high quality and in good demand.
- Arani Sari is a traditional sari made in Arani, Tamil Nadu
Handloom Marketing Assistance (HMA) scheme:
- For providing marketing facility to all the handloom products including Arani Silk, Government of India is implementing Handloom Marketing Assistance (HMA) scheme,
- It is a component of National Handloom Development Programme (NHDP), all across India. The scheme provides marketing platform to the handloom weavers/organisations to sell their products directly to the consumers.
- Under the scheme, financial assistance is provided to National Level Handloom Organisations and nominated handloom agencies of the State Governments to organize the marketing events like National Handloom Expos (NHEs), Special Handloom Expos (SHEs) and District Level Events (DLEs).
Other Programmes;
- Central Silk Board through Silk Mark Organisation of India is organising “Silk Mark Expo” in various towns and cities including Chennai near Arani.
- Silk Mark Expos provide excellent platform to promote silk products of different silk clusters of India including Arani cluster.
- under Section 8 of the Companies Act 2013, Arani Master Weavers have created and registered a non-profit company “Arani Handloom Silk Park” and a MoU have been signed with the Government of Tamil Nadu in 2015.
Schemes related to Textile:
- Scheme For Integrated Textile Park (SITP)
Objective
- To provide financial assistance to a group of entrepreneurs to establish state-of-the-art
- infrastructure facilities in a cluster for setting up their textile units, conforming to international environmental and social standards and thereby mobilize private investment in the textile sector and generate fresh employment opportunities
Features:
- The Scheme targets industrial clusters and locations with high growth potential, which require strategic interventions for developing world-class infrastructure support.
- An ITP under the scheme should preferably have 25 integrated units with components like Land (registered under the name of SPV), common infrastructure (compound, road, drainage, electricty, etc), buildings for common facilities (creche, canteen, laboratories, etc), and factory buildings for production purposes.
- The total project cost shall be funded through a mix of Equity/Grant – from the Ministry of Textiles, State Government, State Industrial Development Corporation, Industry, Project Management Consultant and Loan – from Banks/ Financial Institutions.
- The Government support under the Scheme by way of Grant or Equity will be limited to 40% (90% for first two projects in N.E states and J&K) of the project cost subject to a ceiling of Rs. 40 crore.
- The combined equity stake of GOI/State Government/State Industrial Development Corporation, if any, should not exceed 49%.
- The release of GoI assistance to the SPV shall be done in 3 (three) installments in the ratio of 30:40:30 depending upon fulfillment of terms and conditions.
- Each project will normally be completed in 3 years from the date of release of the first installment of government grant. (Delays can lead to cancellation of project and imposition of penalty).
- The ITPs can also get benefits from Amended Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme (ATUFS), SAMARTH, etc.
Integrated Scheme for Development of Silk Industry:
Objective:
- To improve the productivity and quality of silk through R&D intervention.
- To promote improved cross-breed silk and the import substitute
- Bivoltine silk so that Bivoltine silk production in India enhances to such a level that raw silk imports become nil by 2022 thereby making India self-sufficient in silk.
- To increase productive employment from 85 lakhs to 1 crore persons by 2020.
Powertex India Scheme:
- To provide financial assistance to economically weaker low-end powerloom units for their modernisation and Infrastructure development.
- To improve quality and productivity of the fabrics being produced and enable them to face the competition in domestic and international markets.
- To boost development cluster-based
- Organize Buyer-Seller Meets and Reverse Buyer-Seller Meets to promote market for powerloom product.
- To avoid middle man/local supplier brokerage charge on sales of yarn.
- To give thrust to renewable energy (solar).
Amended Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme (ATUFS):
- To promote Ease of doing Business in the country and to achieve the vision of general employment and promoting exports through Make in India and Zero Effect and Zero Defect in manufacturing.
- To facilitate augmentation of investment, productivity, quality, employment, exports along with import substitution in textile industry and to indirectly promote investment in the textile machinery manufacturing.
Scheme for Capacity Building In Textile Sector (SAMARTH):
- To provide demand driven, placement oriented NSQF (National Skills Qualification Framework) Compliant skilling programme to incentivize organized textile and related sectors excluding Spinning and Weaving.
- To promote skilling and skill up-gradation in the traditional sectors of Handlooms, Handicrafts, Sericulture and Jute
- To provide Sustainable livelihood to all sections of the society across the country via wage or self-employment.
RESTRUCTURED NATIONAL BAMBOO MISSION
20, Jul 2019

Why in News?
- The restructured National Bamboo Mission (NBM) has been launched in 2018-19 to focus on the development of complete value chain of bamboo sector and link growers with markets.
Objectives of the Mission:
- To increase the area under bamboo plantation in non-forest Government and private lands to supplement farm income and contribute towards resilience to climate change as well as availability of quality raw material for industries.
- To improve post-harvest management through establishment of innovative primary processing units near the source of production, primary treatment and seasoning plants, preservation technologies and market infrastructure.
- To promote product development keeping in view market demand, by assisting R&D, entrepreneurship & business models at micro, small and medium levels and feed bigger industry.
- To rejuvenate the under developed bamboo industry in India.
- To promote skill development, capacity building, awareness generation for development of bamboo sector from production to market demand.
- To re-align efforts so as to reduce dependency on import of bamboo and bamboo products by way of improved productivity and suitability of domestic raw material for industry, so as to enhance income of the primary producers.
INDIA AGAIN ABSTAINS AT U.N. VOTE ON SEXUAL MINORITIES
13, Jul 2019

Context:
- India abstained at the vote for extending the mandate of an important UN official who reports on violence and discrimination against sexual minorities.
Issue:
- Human Rights Council (HRC) celebrated the United Nations Human Rights Council’s vote to renew for a second three-year term the mandate of the U.N. Independent Expert on protection against violence and discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity.
- India’s abstention at the resolution for term renewal of the Independent Expert on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity in the UN Human Rights Council.
- Indian delegation had supported some amendments brought by countries that opposed the work of the Independent Expert.
U.N. Independent Expert on Protection Against Violence and Discrimination Based on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity (IE SOGI):
- Established in 2016 by the U.N. Human Rights Council, the IE SOGI.
- working collaboratively with U.N. and regional leaders, has helped nations develop policies and actions to protect people from discrimination and violence based on sexual orientation and gender identity.
- The Independent Expert oversees the implementation of international human rights law, raises awareness, engages in dialogue with stakeholders and provides advisory and technical assistance.
Connecting Dots in India
- Indian Supreme Court struck down Section 377 and decriminalised the LGBTQ community.
CCTV IN CLASSROOMS- ANALYSIS
13, Jul 2019

- Context– Project to install CCTV cameras inside all classrooms in Delhi state schools.
Delhi Government Stand:
Empowering Parents
- In private schools, parents are empowered by their own education and economic leverage due to the fees they pay. Parental oversight has been the bedrock of effective school management. CCTV surveillance would bring empowerment to parents.
Parent Participation
- School Management Committees (SMCs), parent bodies mandated by the Right to Education Act. They have been empowered to monitor and supervise basic deliverables of schools, such as teacher attendance, healthy mid-day meals, clean washrooms, drinking water, etc. The CCTV in classrooms project is the next step towards increasing accountability of schools.
Accountability:
- By sharing feeds with parents, it is actually ensuring that the crores of public money invested into CCTVs are not wasted.
- Often, CCTVs fail to serve their purpose for lack of motivated monitoring.
- Outsourcing of the monitoring to an invested stakeholder like parents is actually a smart innovation.
Child Care:
- The CCTV feeds can aid parents to identify several problems their children may be facing, including bullying, corporal punishment, inadequate attention spans, teacher absenteeism and even student truancy. It will empower them to not just raise their children better but also to ask the right questions to their child’s school.
Issue of Privacy Breach
- Classrooms cannot be classified as private by any stretch of imagination.
- feed being provided to parents is highly restricted.
- Only the feed for their own children will be provided to parents.
- The feed does not include audio, and can only be accessed live.
Deterrence for Crimes
- If CCTVs can be deterrents to crime outside schools, they can be deterrents within too.
Argument Against CCTV Installation in Schools:
The Aim of Education Isn’t Just Disciplinary:
- While a school is meant to teach discipline, it is also the space where students can make mistakes and subsequently learn from them.
- Creating panopticons inside schools instils fear, not values.
Classrooms Aren’t Public Spaces Either:
- Classrooms cannot be classified as private.
- However, schools are not as public as a footpath.
- The expectation of relative privacy is what allows students the freedom to express themselves, make mistakes, and inculcate creativity and imagination.
- The Delhi government cannot assume that constant surveillance of every activity will improve the learning environment.
Lack of digital infrastructure:
- Internet penetration in urban India still stands at 64.84%, including multi-SIM usage. In cases where parents don’t have smartphones and internet access, what does the government intend to do?
Phone sharing:
- Shared access to a phone is a common habit, and the Delhi government has still not clarified, despite our repeated queries, how they intend to verify a parent’s identity on the DGS Live app.
Access to Videos:
- Creating a massive repository of video footage of children is a phenomenally bad idea, and a violation of their privacy.
- In the absence of any legislative and judicial oversight, it can be easily abused.
Conclusion:
- There should be proper white paper published by Delhi Government regarding CCTV installation so that public understands the motives and undue activity can be restricted.
THE AADHAAR AND OTHER LAWS (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2019
13, Jul 2019

- Context: Recently the Parliament passed the Aadhaar and Other Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2019.
Key Changes in the Aadhar:
- The existing Act on Aadhaar provides for the use of Aadhaar number as proof of identity of a person, subject to authentication. the Bill replaces this provision to state that an individual may voluntarily use his Aadhaar number to establish his identity, by authentication or offline verification.
- Enabling offline verification is another key change brought about by the Bill. Under the exiting Aadhaar Act, verification of identity requires authentication, which, in turn, requires an individual to submit their Aadhaar number and biometric or demographic information to the Central Identities Data Repository.
- The latest Bill amends the Act to additionally allow offline verification of a person’s identity through modes specified by the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI). The existing Act allowed State or a corporate entity under any law to use Aadhaar. The Bill replaces this bit and allows the UIDAI to decide whether an entity can use Aadhaar.
- The UIDAI can do so once it has satisfied itself that the entity is allowed to do so under law or conforms to requisite privacy and security standard, or indeed, is obtaining Aadhaar in the interest of the State. the Bill has also strengthened the disclosure norms relating to Aadhaar.
- It has also provided for a dedicated Unique Identification Authority of India Fund, which will receive all fees and revenue collected by the UIDAI. Under the Act, these go to the Consolidated Fund of India. The Bill also makes it possible for individuals to file complaints under certain circumstances such as impersonation instead of just allowing the UIDAI to file complaints.
- Lastly, the Bill also lays down a federated structure for deciding penalties in case an entity fails to play by the rules.
ANTI-DEFECTION LAW
13, Jul 2019

- Context: In the light of the Karnataka Assembly crisis, the Anti-Defection Law is being debated nationally.
About Anti-Defection Law:
- Anti-Defection law is contained in the Tenth Schedule of the Constitution, which was introduced by the 52nd Amendment in 1985 During tenure of Rajiv Gandhi.
- Definition of Defection: Defection is defined as” to abandon a position or association, often to join an opposing group” which essentially describes a situation when a member of a particular party abandons his loyalty towards that party and provide his support (in the form of his vote or otherwise) to another party.
When was the Anti-Defection Law instituted and what was the Trigger?
- For a long time, the Indian political scene was besmirched by political defections by members of the legislature. This situation brought about greater instability in the political system.
- The infamous “Aaya Ram, Gaya Ram” slogan was coined against the background of continuous defections by the legislators. Legislators used to change parties frequently, bringing about chaos in the legislatures as governments fell. In sum, they often brought about political instability.
- This caused serious concerns to the right-thinking political leaders of the country.
- Several efforts were made to make some law to curb defections. Starting from private members’ efforts, Bills were brought in by the government at different times.
- No Bill could be passed because of one reason or the other. However, the most important reason was that there was no consensus on the basic provisions of an anti-defection law.
- Members of Parliament were concerned about the freedom of speech in Parliament and other legislatures as they had a fear that too stringent a law on defection would likely curb the freedom of speech (which is a constitutional right) of the legislators. A lot of time was taken before a consensus could be reached on this issue.
- Finally, in 1985, the Rajiv Gandhi government brought a Bill to amend the Constitution and curb defection.
- The 10th Schedule of the Constitution, which contains the anti-defection law, was added to the Constitution through this amendment.
What is the purpose of the anti-defection law? What are the grounds of disqualification?
- The purpose of the law is to curb political defection by the legislators.
- There are two grounds on which a member of a legislature can be disqualified:
-
- If the member voluntarily gives up the membership of the party, he shall be disqualified. Voluntarily giving up the membership is not the same as resigning from a party. Even without resigning, a legislator can be disqualified if by his conduct the Speaker/Chairman of the concerned House draws a reasonable inference that the member has voluntarily given up the membership of his party.
- If a legislator votes in the House against the direction of his party and his action is not condoned by his party, he can be disqualified. These are the two grounds on which a legislator can be disqualified from being a member of the House.
- However, there is an exception that was provided in the law to protect the legislators from disqualification. The 10th Schedule says that if there is a merger between two political parties and two-thirds of the members of a legislature party agree to the merger, they will not be disqualified.
Exceptions:
- If a Person is elected as speaker or chairman then he could resign from his party, and rejoin the party if he demitted that post. No Disqualification in this case.
- A Party could be merged into another if at least one – thirds of its party legislators voted for the merger. The Law initially permitted splitting of parties, but that has now been made two – third. As Soon as this law was passed, it was met with severe oppositions on logic that it impinged on right to free speech of legislators. A PIL was filed in the supreme court in the form of famous Kihoto Hollohon vs Zochillhu and others (1992). This PIL had challenged the constitutional validity of the law.
- But SC upheld the constitutional validity of 10th Schedule. Court also decided that the law does not violate any rights of free speech or basic structure of the parliamentary democracy.
- However, Supreme Court also made some observations on section 2(1) (b) of the Tenth Schedule, Section 2(1) (b) reads that a member shall be disqualified if he votes or abstains from voting contrary to any direction issued by the Political party.
- The Judgement highlighted the need to limit disqualifications to votes crucial to the existence of the government and to matters integral to the electoral programme of the party, so as not to ‘unduly impinge’ on the freedom of speech of members.
91st Amendment Act, 2003
- When it was enacted first, there was a provision under which if there occurs a split in the original political party and as a result of which one-third of the legislators of that party forms a separate group, they shall not be disqualified.
- This provision resulted in large scale defections and the lawmakers were convinced that the provision of a split in the party was being misused.
- Therefore, they decided to delete this provision.
- Now at least two-thirds of the members of a party have to be in favor of a “merger” for it to have validity in the eyes of the law.
- The 91st Amendment also makes it mandatory for all those switching political sides – whether singly or in groups – to resign their legislative membership. They now have to seek re-election if they defect.
Is the law, as it stands now, open to interpretation?
- The first ground for disqualifying a legislator for defecting from a party is his voluntarily giving up the membership of his party. This term “voluntarily giving up the membership of his party” is susceptible to interpretation.
- As has been explained earlier, voluntarily giving up the membership is not the same as resigning from a party.
- Then what exactly it means? How can one decide that a member of a legislature has voluntarily given up the membership of his party? The Supreme Court has clarified this point by saying that the presiding officer, who acts as a tribunal, has to draw a reasonable inference from the conduct of the legislator.
How far has the law succeeded in achieving its goal?
- The law certainly has been able to curb the evil of defection to a great extent. But, of late, a very alarming trend of legislators defecting in groups to another party in search of greener pastures is visible.
- The recent examples of defection in state Assemblies and even in Rajya Sabha bear this out. This only shows that the law needs a relook in order to plug the loopholes if any. But it must be said that this law has served the interest of the society.
- Political instability caused by frequent and unholy change of allegiance on the part of the legislators of our country has been contained to a very great extent. That is a story of success of one of the most important legislation that the Indian Parliament has enacted
Jal Shakti Abhiyan
04, Jul 2019

Why in News?
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan for Water Conservation Launched.
Highlights:
- It is a time-bound, mission-mode campaign that would focus on 1,592 “water-stressed” blocks in 257 districts. The campaign will run through citizen participation during the monsoon season, from 1st July, 2019 to 15th September, 2019.
- The 1,592 blocks, identified as “water-stressed” as per the Central Ground Water Board’s 2017 data, include 313 critical blocks, 1,000-odd over-exploited blocks and 94 blocks with least water availability (for states without water-stressed blocks).
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan is a collaborative effort of various Ministries of the Government of India and State Governments, being coordinated by the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation.
- The focus of the campaign is on water stressed districts and blocks. The teams of officers from the central government will visit and work with district administration in 1592 water stressed blocks in 256 districts, to ensure five important water conservation interventions.
- The Five Important Water Conservation Interventions are:
- Water conservation and rainwater harvesting,
- Renovation of traditional and other water bodies/tanks,
- Reuse of water and recharging of structures,
- Watershed development and
- Intensive afforestation.
- The water conservation interventions will also be supplemented with special interventions including the development of block and district water conservation plans, promotion of efficient water use for irrigation and better choice of crops through Krishi Vigyan Kendras.
- A large-scale communications campaign has also been planned alongside the JSA involving mass mobilisation of different groups including school students, college students, swachhagrahis, Self Help Groups, Panchayati Raj Institution members, youth groups (NSS/NYKS/NCC), defence personnel, ex-servicemen and pensioners, among various others.
Cabinet NOD to Better Pay Benefits for CAPF Officers
04, Jul 2019

Context:
The Cabinet has approved the proposal to grant Organised Cadre Status to Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) officers.
- The move comes after a Supreme Court order asked the government to extend the benefit already available to IPS, IAS, IRS and IFS officers — to CAPF officers
Significance:
- This will make them eligible for several benefits, including Non-Functional Financial Upgradation (NFFU).
- The move will benefit thousands of serving officers and many others who have retired since 2006 from the five primary CAPFs or paramilitary forces — CRPF, BSF, CISF, ITBP and SSB.
- The officers will now get better deputation chances as they will be eligible to get empanelled under the central staffing scheme, get enhanced facilities of transportation, house rent allowance, travelling and dearness allowance.
- Besides the pay hike, the demand for NFFU also encapsulates a long-standing tussle between CAPF cadre officers and IPS officers who come on deputation to the forces.
- Most top positions in these forces are occupied by IPS officers.
The Dentist (Amendment) Bill, 2019
04, Jul 2019

Context:
The Dentist (Amendment) Bill, 2019 was recently passed in the monsoon session of the Parliament.
About the Bill:
- The Bill amends the Dentists Act, 1948.
- The Act regulates the profession of dentistry and constitutes:
- The Dental Council of India,
- State Dental Councils and
- Joint State Dental Councils.
- A register of dentists is maintained under the Act in two parts, Part A and Part B. Persons possessing recognised dental qualifications are registered in Part A and persons not possessing such qualifications are registered in Part B.
- The persons in Part B are Indian citizens who have been practicing as dentists for at least five years prior to a registration date notified by the state government.
Composition of the Dental Councils:
- Under the Act, composition of the Dental Council of India, State Dental Councils, and Joint State Dental Councils includes representation from dentists registered in Part B.
- The Bill seeks to remove the mandatory requirement of the representation of dentists registered in Part B in these Councils.
Osaka Declaration
30, Jun 2019

Context– India refused to become a signatory to the Osaka declaration on digital economy.
About–
- It was signed by 24 countries and groupings.
- It was a sign of resistance against developed countries led by the US and Japan, which are pushing for free flow of data across borders.
- It is an overarching framework promoting cross-border data flow with enhanced protections.
- Apart from India, South Africa and Indonesia also stayed away from signing the Osaka declaration.
- The declaration is aimed for the creation of international rules enabling free movement of data across borders.
- India believes that discussions and negotiations pertaining to data should be held within the context of the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
MEITY reported that 2.22 crore villagers are given Digital Education under Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA)
29, Jun 2019

CONTEXT:
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology reported that 2.22 crore villagers are given Digital Education under Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA).
BACKGROUND:
- To increase the Digital Literacy rate in India, Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyaan (PMGDISHA) was launched as an integral part of the ‘Digital India’
- The vision of this scheme is that one person in every household becomes digitally literate
- Train them to operate digital devices such as Tablets, Smartphones et cetera.
- Bridge the digital divide, specifically targeting the rural population
- It also ensures high-speed internet access for all, though a secure ecosystem.
World Bank Chief Urges Reforms To Attract Investment Amid Trade Uncertainty
29, Jun 2019

- The World Bank in its annual Global Economic Prospects report earlier this month forecast that slowing trade and investment flows would cut global growth this year to 2.6 percent, down 0.3 percentage point from previous forecasts.
- Uncertainty from trade tensions and slowing global growth is increasing the need for developing countries to pursue reforms that make them more attractive to private investment.
- The Bank will urge countries to take bolder steps to improve their business climates to allow private firms to compete better with state-owned companies and generate more profitable growth, innovation and jobs.
- The International Monetary Fund has forecast a similar slowdown, driven primarily by increased tariffs, primarily between the United States and China.
- The bank’s private-sector arm, the International Finance Corp, is doing a deep diagnostics dive into obstacles to private-sector firms in various countries on issues like customs facilitation, stronger bankruptcy regimes and legal changes to bring more women into workforces.
Fortified Ration
29, Jun 2019

Why in News?
- Department of Food & Public Distribution has approved the “Centrally Sponsored Pilot Scheme on Fortification of Rice & its distribution through Public Distribution System”. Financial Assistance up to 90% in case of North-Eastern, Hilly and Island States and up to 75% in case of rest of the States has been extended.
Fortified Ration
- Under the scheme, milled rice will be mixed with a premix containing vitamins and minerals post-harvest.
- As per the Food Fortification Resource Centre (FFRC) of the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) under Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, iron, Vitamin B12, and Folic acid are the mandatory nutrients for the fortification of rice, the kernels of which are added into the regular rice kernels in 1 to 100 ratio.
- Iron and folic acid are the two main ingredients that will be added to the food grains.
- Fortification norms will be in accordance with the specifications laid down by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI).
- Further, Government of India has also advised all States/UTs especially those States/UTs that are distributing wheat flour through Public Distribution System (PDS), to distribute fortified wheat flour through PDS Fortified Edible oils is also supplied to certain states through PDS
GENERALIZED SYSTEM OF PREFERENCE
26, Jun 2019

- The Generalized System of Preference (GSP) is the largest and oldest US trade preference programme and is designed to Promote Economic Development by allowing duty-free entry for thousands of products from designated beneficiary countries.
- On March 4, Trump announced that the US intends to terminate India’s designations as a beneficiary developing country under the GSP programme. The 60-day notice period ended on May 3. Under the GSP programme, nearly 2,000 products including auto components and textile materials can enter the US duty-free if the beneficiary developing countries meet the eligibility criteria established by Congress.
- India was the largest beneficiary of the programme in 2017 with USD 5.7 billion in imports to the US given duty-free status and Turkey the fifth largest with USD 1.7 billion in covered imports. The GSP criteria includes, among others, respecting arbitral awards in favour of the US citizens or corporations, combating child labour, respecting internationally recognised worker rights, providing adequate and effective intellectual property protection, and providing the US with equitable and reasonable market access.
DEFENCE POLICY GROUP
26, Jun 2019

- India and the US are planning to revive the Defense Policy Group (DPG) between the two countries after a four-year gap.
- The last DPG, co-chaired by India’s defense secretary and US Under-secretary of defense for policy, was held in 2015.
- The decision to revive the DPG was taken in the Two-Plus Two meeting between the foreign and defense ministers of the two countries.
- DPG will review the reports of existing sub-groups — Military Cooperation Group, Joint Technology Group, Senior Security Technology Group and the Defense Procurement and Production Group. DPG will also only lay the future roadmap for joint advanced exercises between two countries, and look at the prospect of technological cooperation in building military hardware under Make in India.
GEO-SPATIAL COOPERATION AGREEMENT (BECA)
26, Jun 2019

- Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement
- BECA will allow India to use US geospatial maps to get pinpoint military accuracy of automated hardware systems and weapons such as cruise and ballistic missiles.
- Along with Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA), and Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement (LEMOA), BECA is one of the foundational military communication agreements between the two countries.
- BECA is an important precursor to India acquiring armed unmanned aerial vehicles such as the Predator-B from the US.
- The Pentagon in 2018 was ready to supply Predator-B, which uses spatial data for accurate strikes on enemy targets, to India.
DNA TECHNOLOGY (USE AND APPLICATION) REGULATION BILL
26, Jun 2019

- The Bill seeks to create a Regulatory Framework for Obtaining, storing and testing of DNA samples of human beings, mainly for the purposes of criminal investigations, and with the objective of establishing the identity of a person.
- The proposed law seeks to bring in a supervisory structure to oversee these practices, and frame guidelines and rules so that the DNA technology is not misused.
- Bill proposes to set up two institutional structures — a DNA regulatory board, and a DNA data bank — at the national level. Regional centers of the board as well as the data bank can be set up at the state level as well.
- The Bill proposes that testing of DNA samples can be carried out only at laboratories that are authorized to do so by the regulatory board. It also specifies the circumstances under which a person can be asked to submit DNA samples.
- Police can ask for DNA samples of the person accused of an offence to facilitate their investigation. But unless the offence is of a very serious nature, punishable by death or by imprisonment for at least seven years, the DNA sample can be obtained only on the written consent of the accused. It can be also be obtained if an authorized magistrate is satisfied that a DNA test is absolutely necessary for investigation of the crime.
- People who are witness to a crime, or want to locate their missing relatives, or in similar other circumstances, can volunteer to give their DNA samples, again through written consent.
Issues:
- Whether the DNA technology is foolproof?
- Whether the provisions adequately address the possibility of abuse of DNA information, and whether the privacy of the individual is protected.
- Critics of the Bill have been claiming that collecting and storing such intrusive information could lead to abuse, besides being violative of a person’s privacy.
Government Stand:
- Since DNA tests are already happening, and frequently used as the most reliable tool to establish identity, it would be better to have regulatory safeguards so that it is carried out only in prescribed manner and by authorized personnel and Institutions.
LITCHI AND ACUTE ENCEPHALITIS SYNDROME
26, Jun 2019

- Litchi is being most commonly blamed for the Acute Encephalitis Syndrome (AES) outbreak in Bihar.
- Research paper By Jacob states:
- Its main finding was that this fruit contains a toxin called Methylene cyclo propyl glycine (MCPG).
- But the authors never blamed litchi for AES.
- The causal Factor is Malnutrition and not Litchi.
- The luscious fruit is only a triggering factor for malnourished children as the toxin MCPG can lead to hypoglycaemia (fall in sugar levels).
- So, if a healthy child eats litchi, s/he will not suffer from AES.
How Malnutrition Cause Hypoglycaemia?
- Malnourished children have depleted glycogen store in the liver.
- So if there is no glycogen reserve, the glycogen breaks into glucose.
- When the shortage further increases, even fats start burning. This process produces by products like ketones and amino acids which are neurotoxic.
- So, if a child sleeps without food, this whole physiological process gets completed by wee hours of the day and then the kid gets fever with convulsions and at times s/he loses consciousness.
How does MCPG Interplays with Malnourishment:
- When malnourished kids are exposed to toxins like MCPG present in litchi, which is grown in these months, the chemical triggers hypoglycaemia.
- It’s so much that sugar levels fall up to 30 milligrams per deciliter and sometimes even nil. This leads to complications. The fact that only malnourished children are at risk is also proven by the reasoning that all the vulnerable children belong to the poorest of poor class.
- No child eating litchi, who belongs to a well-to-do family and gets adequate food, suffers from AES.
Why is AES Caused due to Hypoglycaemia so Fatal?
- Most of these deaths are preventable.
- Within four hours of onset of symptoms like convulsions, high fever if a child is administered dextrose (glucose), s/he can be saved.
- Only glucose administration is required. However, most of the patients come from far off villages where the peripheral medical facilities, much against the government’s claims, don’t even have facilities to administer it intravenously.
- They take a lot of time to arrange for conveyance and so the golden time is lost. Only last week, Hospitals saved a child whose glucose level was nil when he was brought to Hospital.
FOOD AND NUTRITION SECURITY ANALYSIS REPORT
26, Jun 2019

- Prepared by Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation & The UN World Food Programme.
- 31.4% of Indian children will be stunted by 2022
- Food grain yields have risen 33% over the last two decades, but are still only half of 2030 target yields
- The Indian farmer is producing more food grains than ever before, making the country Self Sufficient. The Consumer’s access to rice, wheat and other cereals has not increased at the same rate, due to population growth, inequality, food wastage and losses, and exports
- Average Per Capita Consumption of energy among the poorest 30% of the population is 1811 kilo calories, much lower than the norm of 2155 kilo calories per day.
- There are high rates of stunting among children in the poorest wealth quintile (51.4%), Scheduled Tribes (43.6%) and Scheduled Castes (42.5%), and children born to mothers with no education (51%).
HEALTHY STATES, PROGRESSIVE INDIA’-NITI Aayog
26, Jun 2019

- Is a Report on Health published by NITI Aayog
- Report on Rank of States and UTs’ has ranked states in three categories — larger States, smaller States and UTs “to ensure comparison among similar entities”.
- The report ranks states and Union territories innovatively on their year-on-year incremental change in health outcomes, as well as, their overall performance.
- It ranks states and union territories on their year on year incremental change in health outcomes, as well as, their overall performance with respect to each other.
- Kerala, Andhra Pradesh & Maharashtra ranked on top in terms of overall performance. Haryana, Rajasthan and Jharkhand ranked top three States in terms of annual incremental performance.
CENTRAL BOARD OF FILM CERTIFICATION (CBFC)
26, Jun 2019

- It is a Statutory Body under Union Ministry of Information and Broadcasting.
- It grants certificate to regulate the public exhibition of films in India under the provisions of the Cinematograph Act 1952.
- Films can be publicly exhibited in India only after they have been certified by the Central Board of Film Certification.
- The Certification process is in accordance with The Cinematograph Act, 1952, The Cinematograph (certification) Rules, 1983, and the guidelines issued by the Central government u/s 5 (B).
EASTERN ECONOMIC FORUM
25, Jun 2019

- The Eastern Economic Forum was established by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation Vladimir Putin in 2015. In accordance with the Decree, the Eastern Economic Forum takes place each year in Vladivostok.
- Every year, the Eastern Economic Forum serves as a platform for the discussion of key issues in the world economy, regional integration, and the development of new industrial and technological sectors, as well as of the global challenges facing Russia and other nations.
Objectives:
- Strengthening ties between the international investment community, Russian business, and federal, regional, and local government bodies
- Conducting a comprehensive expert assessment of the economic potential of the Russian Far East and improving the region’s competitiveness and attractiveness to investors both nationally and internationally
- Showcasing new investment and business opportunities such as advanced special economic zones, Vladivostok Free Port, and state support for high-potential investment projects
- India and China will meet along with Russia in the side-lines of Easter Economic Forum apart from a trilateral meeting during the G20 summit. Such a meeting would add weightage to the global significance of Eurasian region.
REGIONAL COMPREHENSIVE ECONOMIC PARTNERSHIP (RCEP)
25, Jun 2019

- The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a mega-regional economic agreement being negotiated since 2012 between the 10 ASEAN (Association of South-East Asian Nations) governments and their six FTA partners: Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand and South Korea.
- The agreement’s contents, the proposed RCEP would cover almost every aspect of economy such as goods, services, investment, economic and technical cooperation, intellectual property rights (IPR), rules of origin, competition and dispute settlement.
- The negotiations have missed several deadlines repeatedly, even though they have gained momentum since 2016.
Issues of concern for India:
- Japan and South Korea are channelling demands by big pharma for longer patent terms and for monopoly rights over clinical trial data. These provisions could undermine access to price-lowering generic medicines, and thus, life-saving treatment for millions of people in the developing world.
- The RCEP would threaten livelihoods in sectors like dairy, meat and other agricultural products by allowing duty free imports of subsidised products from Japan, New Zealand and Australia. India, with 100 million small scale dairy producers, and Vietnam are among the countries that will be most affected.
- One of the provisions proposed in RCEP will allow governments to treat foreign investors as they treat locals. This means that large corporations will be able to grab land, displacing local subsistence farmers.
- India’s trade deficit [annual] with RCEP nations is about $100 billion, and half of this is with China alone even without an FTA with China. Post India’s FTA with ASEAN, Japan and Korea [who are all RCEP members], our trade deficit with them have increased, and the government needs to take this into account during RCEP negotiations.
- Visa Norms– India’s push for easier norms on movement of professionals across borders for short-term work in 16 Asia-Pacific nations, including itself, under a proposed mega Free Trade Agreement (FTA) — is learnt to have found favour with some ASEAN-bloc members. To date, no official text has been made public, even though the agreement would affect several billion people. This continues to fuel concerns.
India, France to Deepen Cooperation
25, Jun 2019

- India and France have decided to deepen cooperation in the cyber security sector.
- They will jointly work towards curbing the use of the Internet for terrorist purposes and online radicalisation.
- The third Indo-French cyber dialogue was held in Paris on 20 June 2019.
- France and India have reaffirmed their commitment to open, reliable, secure, stable and peaceful cyberspace.
RESERVE BANK OF INDIA (RBI)
25, Jun 2019

Context
- Viral Acharya’s resignation as Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank of India
About:
- The Reserve Bank of India was established on April 1, 1935 in accordance with the provisions of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- Though originally privately owned, since nationalisation in 1949, the Reserve Bank is fully owned by the Government of India.
Composition:
Central Board
- The Reserve Bank’s affairs are governed by a central board of directors. The board is appointed by the Government of India in keeping with the Reserve Bank of India Act.
- Appointed/nominated for a period of four years
Constitution:
Official Directors
- Full-Time: Governor and not more than four Deputy Governors
Non-Official Directors
- Nominated by Government: ten Directors from various fields and two government Official
- Others: four Directors – one each from four local boards
Functions:
Monetary Authority:
- Formulates, implements and monitors the monetary policy.
- Objective: maintaining price stability while keeping in mind the objective of growth.
Regulator and supervisor of the financial system:
- Prescribes broad parameters of banking operations within which the country’s banking and financial system functions.
- Objective: maintain public confidence in the system, protect depositors’ interest and provide cost-effective banking services to the public.
Manager of Foreign Exchange
- Manages the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999.
- Objective: To facilitate external trade and payment and promote orderly development and maintenance of foreign exchange market in India.
Issuer of currency:
- Issues and exchanges or destroys currency and coins not fit for circulation.
- Objective: to give the public adequate quantity of supplies of currency notes and coins and in good quality.
Developmental Role:
- Performs a wide range of promotional functions to support national objectives.
Regulator and Supervisor of Payment and Settlement Systems:
- Introduces and upgrades safe and efficient modes of payment systems in the country to meet the requirements of the public at large.
- Objective: maintain public confidence in payment and settlement system.
Related Functions
- Banker to the Government: performs merchant banking function for the central and the state governments; also acts as their banker.
- Banker to Banks: maintains banking accounts of all scheduled banks.
DRAFT NATIONAL EDUCATION POLICY 2019
25, Jun 2019

Context:
- The Committee for Draft National Education Policy (Chair: Dr. K. Kasturirangan) Report discussed in Parliament.
- The report proposes an education policy, which seeks to address the challenges of:
- Access
- Equity
- Quality
- Affordability, and
- Accountability faced by the current education
School Education:
Early Childhood Care and Education:
- Curriculum that doesn’t meet the developmental needs of children,
- Lack of qualified and trained teachers, and
- Substandard pedagogy
The Right to Education Act, 2009 (RTE Act):
- Currently, the RTE Act provides for free and compulsory education to all children from the age of six to 14 years. The draft Policy recommends extending the ambit of the RTE Act to include early childhood education and secondary school education.
- This would extend the coverage of the Act to all children between the ages of three to 18 years.
School Exam Reforms:
- The Committee noted that the current board examinations:
- Force students to concentrate only on a few subjects
- Do not test learning in a formative manner, and
- Cause stress among
- To track students’ progress throughout their school experience, the draft Policy proposes State Census Examinations in classes three, five and eight.
- it recommends restructuring the board examinations to test only core concepts, skills and higher order capacities.
Teacher Management:
- The Committee noted that there has been a steep rise in teacher shortage, lack of professionally qualified teachers, and deployment of teachers for non-educational purposes.
- The draft Policy recommends that teachers should be deployed with a particular school complex for at least five to seven years.
- Teachers will not be allowed to participate in any non-teaching activities (such as cooking mid-day meals or participating in vaccination campaigns) during school hours that could affect their teaching capacities.
- The Ministry of Human Resources and Development must be renamed as the Ministry of Education in order to bring focus back on education.
Financing Education:
- The Draft Policy reaffirmed the commitment of spending 6% of GDP as Public Investment in Education.
Janani Suraksha Yojana
24, Jun 2019

- Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY) is a safe motherhood intervention under the National Rural Health Mission (NHM).
- It is being implemented with the objective of reducing maternal and infant mortality by promoting institutional delivery among pregnant women.
- The scheme is under implementation in all states and Union Territories (UTs), with a special focus on Low Performing States (LPS).
- It was launched in April 2005 by modifying the National Maternity Benefit Scheme (NMBS).
- The NMBS came into effect in August 1995 as one of the components of the National Social Assistance Programme (NSAP).
- The scheme was transferred from the Ministry of Rural Development to the Department of Health & Family Welfare during the year 2001-02.
Various Measures under JSY:
- The scheme focuses on the poor pregnant woman with special dispensation for States having low institutional delivery rates namely the States of UP, Uttaranchal, Bihar, Jharkhand, MP, Chhattisgarh, Assam, Rajasthan, Orissa and J&K.
- While these States have been named as Low Performing States (LPS), the remaining States have been named as High performing States (HPS).
- Exclusion criteria of age of mother as 19 years or above and up to two children only for home and institutional deliveries under the JSY have been removed.
- Eligible mothers are entitled to JSY benefit regardless of any age and any number of children.
- BPL pregnant women, who prefer to deliver at home, are entitled to a cash assistance of Rs 500 per delivery regardless of age of women and the number of children.
- States are encouraged to accredit private health facilities for increasing the choice of delivery care institutions.
NITI AAYOG
24, Jun 2019

Issue in economy now that can be handled by NITI Aayog:
- There is horizontal and vertical imbalance revenues of centre and states. Vertical Imbalance mainly allocates more money to Centre.
- Horizonal imbalance involves two types of imbalances.
- Type I is to do with the adequate provision of basic public goods and services, while the second,
- Type II, is due to growth accelerating infrastructure or the transformational capital deficits.
- We need another institution to tackle the horizontal imbalance of the Type II; for this the NITI Aayog is the most appropriate institution.
- NITI Aayog should be engaged with the allocation of “transformational” capital in a formulaic manner, complete with incentive• compatible conditionalities.
- NITI Aayog should also mandated to create an independent evaluation office which will monitor and evaluate the efficacy of utilisation of grants.
Features of NITI Aayog:
- Not Constitutional Body nor statutory body
- NITI Aayog is essentially an advisory body that seeks to provide critical directional and strategic inputs across spectrum of key elements of policy to the centre as well as states.
- It also seeks to put an end to the slow and tardy implementation of the policy by fostering inter-ministry, inter-state and centre-state coordination.
- It has been envisaged to follow the bottom-top development approach.
Composition of NITI Aayog:
- Chairperson -Prime Minister Governing Council –
- Its members are Chief Ministers and Administrators of the Union Territories Regional Councils. These would be created as per need and its members would be chief ministers and administrators of UTs of respective regions. Vice-Chairperson.
- The Vice-chairperson of the NITI Aayog will be appointed by Prime Minister.
Leader of opposition made Minister in Government of State.
24, Jun 2019

Context:
- Rtd. High Court Judge Thipsay questions appointment of Vikhe• Patil (Leader of Opposition), Kshirsagar as ministers.
- Leader of Opposition of Maharashtra has reigned from his party and joined party in government and sworn as minister
Issues:
- By the Constitution (91st Amendment) Act, 2003, Clauses (1A) and (1B) were inserted in Article 164, which provide for appointment of Chief Minister and other ministers. Clause (1B) states that a member of either House of the legislature of a State, belonging to a political party, who is disqualified to be appointed as a minister for duration of the period commencing from the date of his disqualification.
- ‘‘Disqualification on ground of defection.
-
- Clause (a) of paragraph 2 is “if he has voluntarily given up his membership of such political party.
-
- Apart from this, Article 164(4) only permits a person to be a minister for a maximum period of six consecutive months without being a member of the legislature.
Removal of the Judge of a High Court
24, Jun 2019
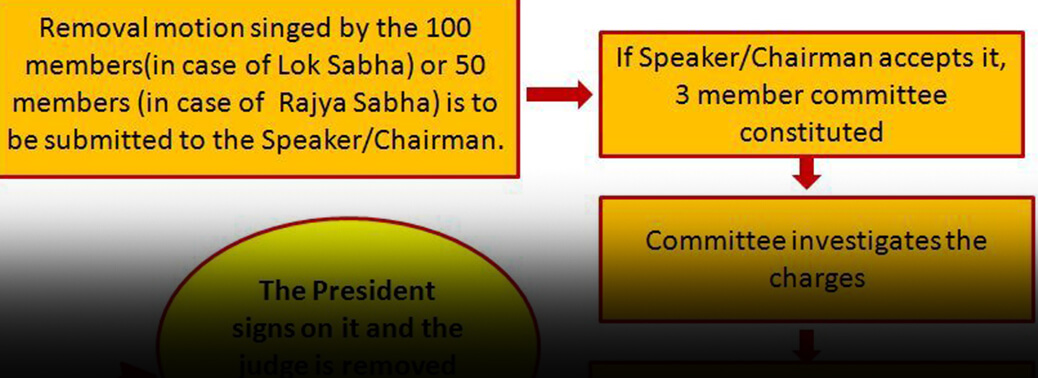
Context:
- In•house panel found an Allahabad High Court judge, Justice S.N. Shukla, guilty of misconduct, Chief Justice of India Ranjan Gogoi has written to Prime Minister Narendra Modi to initiate a motion for his removal.
- A Judge of the High Court can be removed from office only for proven misbehaviour or incapacity and only in the same manner in which a Judge of the Supreme Court is removed. The President of India can remove a Judge of the High Court, from his office only if each house of the parliament passes a resolution by a two third majority of its members present and voting in each house requesting him to remove the judge.
Appointment of the Judges of High Courts:
- As per article 217, the chief Justice of the high court is appointed by the President in consultation with the Chief justice of India as well as the Governor of the state in question. A collegium system has evolved over the years in which a Collegium headed by the CJI makes recommendation to the government for appointment of judges.
Inner Line Permit
24, Jun 2019
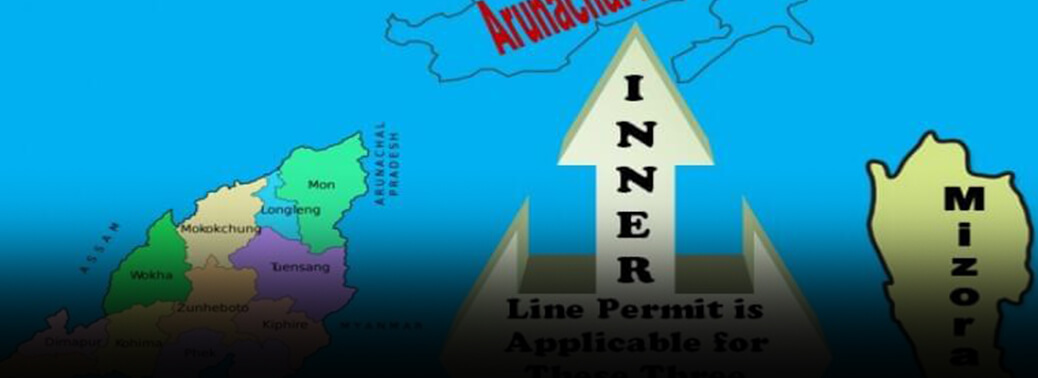
Context:
- A petition filed has sought a direction to the Centre and the Nagaland government to take appropriate steps for the protection of life and liberty, properties and other fundamental rights of nonNagas living in the commercial hub of Dimapur following the imposition of the Inner Line Permit.
- (PIL) petition, has challenged certain sections of the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation, 1873 which gives unbridled power to a State to prescribe ILP.
- Section 2 of the Regulation empowers a State government to prescribe ‘Inner Line’ to prohibit citizens of India or any class of such citizens going beyond the prescribed line without a pass.
- The Inner Line Permit (ILP) is an official travel document issued by the Government of India to grant inward travel of an Indian citizen into a protected area for a limited period. It is obligatory for Indians residing outside those states to obtain permission prior to entering the protected areas. Currently, the Inner Line Permit is operational in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram and Nagaland. The document has been issued under the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation, 1873 and the conditions and restrictions vary from state to state.
- It can be issued for travel purposes solely. Visitors are not allowed to purchase property in these regions. However, there might be a different set of rules for long term visitors, though they are not valid for central government employees and security forces.
Chikungunya Disease
24, Jun 2019
Context:
- The Institute of Life Sciences (ILS), which functions under the Department of Biotechnology, has entered into a non•exclusive license for product commercialisation after having successfully developed antibodies against the Chikungunya viral (CHIKV) infection.
Symptoms:
- Symptoms usually begin 3–7 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. The most common symptoms are fever and joint pain.
- Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, or rash.
- Chikungunya disease does not often result in death, but the symptoms can be severe and disabling.
- Most patients feel better within a week. In some people, the joint pain may persist for months.
- People at risk for more severe disease include newborns infected around the time of birth, older adults (≥65 years), and people with medical conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart disease.
- Once a person has been infected, he or she is likely to be protected from future infections.
Diagnosis:
- The symptoms of chikungunya are similar to those of dengue and Zika, diseases spread by the same mosquitoes that transmit chikungunya.
- See your healthcare provider if you develop the symptoms described above and have visited an area where chikungunya is found.
- If you have recently traveled, tell your healthcare provider when and where you traveled. Your healthcare provider may order blood tests to look for chikungunya or other similar viruses like dengue and Zika.
Treatment:
- There is no vaccine to prevent or medicine to treat chikungunya virus. Treat the symptoms:
- Get plenty of rest.
- Drink fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Take medicine such as acetaminophen (Tylenol®) or paracetamol to reduce fever and pain.
- Do not take aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS until dengue can be ruled out to reduce the risk of bleeding).
- If you are taking medicine for another medical condition, talk to your healthcare provider before taking additional medication.
- If you have chikungunya, prevent mosquito bites for the first week of your illness.
- During the first week of infection, chikungunya virus can be found in the blood and passed from an infected person to a mosquito through mosquito bites.
- An infected mosquito can then spread the virus to other people.
Report on International Religious Freedom
24, Jun 2019

- The International Religious Freedom Report – describes the status of religious freedom in every country.
- The report covers government policies violating religious belief and practices of groups, religious denominations and individuals, and U.S. policies to promote religious freedom around the world.
- The U.S. Department of State submits the reports in accordance with the International Religious Freedom Act of 1998.
Report States that:
- An Annual Report on International religious freedom released by US Secretary of State Pompeo said Hindu groups had used “violence, intimidation, and harassment” against Muslims and low-caste Dalits in 2017 to force a religion-based national identity.
- Groups claiming to protect cows – considered sacred by Hindus – have attacked Muslims and Dalits. Christians have also been targeted for proselytizing since Modi came to power in 2014.
- National Register of Citizenship in north-eastern state Assam, which could land millions of minorities stateless, also got noticed in the report.
- Indian Stand- MEA rejects U.S. report on state of religious freedom in India A foreign govt. has no locus standi to pronounce on the rights of our citizens
India Granted USD15 Million to Niger for holding African Union Summit
23, Jun 2019

- India has extended USD 15 million assistance to Niger for organising the African Union (AU) summit scheduled to be held in Niamey from July 7-8.
- The support of grant assistance was in response to a specific request made by the Niger government.
- This year, Niger is hosting an AU summit for the first time.
- In this AU summit, the historic African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) is likely to be launched.
Background:
- Bilateral ties between India and Niger have expanded significantly since the opening of the Indian Resident Diplomatic Mission in Niamey in 2009.
- India has provided Lines of Credit worth USD 96.54 million to Niger for projects in transport, electrification, solar energy, and potable drinking water.
- India is also establishing the Mahatma Gandhi International Convention Centre (MGICC) in Niamey under grant assistance.
QS World University Ranking 2020: IIT Bombay tops among Indian Institutions
23, Jun 2019

- MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) has made a history by topping the 2020 QS World University Rankings for the eighth consecutive year.
- Stanford University, Harvard University and California Institute of Technology (Caltech) — all retain their positions at second, third and fourth in the world, respectively.
- Only three Indian institutes — IIT-Bombay, IIT-Delhi and IISc-Bangalore making it to top 200 in 2020 QS World University Rankings.
- The Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay (IIT-Bombay), has emerged as India’s best institution in the Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) World University Ranking 2020. IIT Bombay which was at 162nd rank last year has moved up to 152nd rank.
- IIT-Delhi has bagged 182th position and IISc Bangalore has secured 184th rank.
IIIDEM (ECI) organises capacity building program on Electoral Technology
23, Jun 2019

- India International Institute of Democracy and Election Management (IIIDEM) (ECI) organized a five-day training program
- The program on Use of Technology in Elections for Election Officials of Union Election Commission of Myanmar.
- The Capacity Building Programs on Electoral technology is the 7th program of 09 programs scheduled across 2018-2019.
- Election Commissioner of India Sushil Chandra shared the need of sharing best practices of Elections among Election Management Bodies
- Their aim is to strengthen the democracy around the world and create transparency
Background:
- India International Institute of Democracy and Election Management (IIIDEM) conducted training on Election Management of SAARC Countries.
- It is conducted by Election Commission of India (ECI) and sponsored by the Union Ministry of External Affairs.
Bill Passed for 16% Maratha Quota in PG Course
23, Jun 2019

- The Maharashtra Legislative Council cleared a bill to provide 16% reservation to the Maratha
- community students in post-graduate (PG) medical courses.
- This comes a day after the bill was unanimously passed in the Legislative Assembly.
- As both the Houses of the Legislature have cleared the bill, it will now be sent to the Governor for his approval.
Modi voted ‘World’s Most Powerful Leader 2019
23, Jun 2019

- PM Narendra Modi was voted the ‘World’s Most Powerful Person 2019’ in the reader’s poll conducted by UK-based British Herald magazine.
- PM Modi received 30.9% of total votes to beat US President Donald Trump, Russian President Vladimir Putin, and Chinese President Xi Jinping.
- PM Modi will feature on the cover page of the July 15 edition of the magazine.
Central Equipment Identity Register (CEIR)
23, Jun 2019

Why in News?
- In a bid to curtail the rampant cloning and theft of mobile phones across the country, the Telecom Ministry is ready to roll out a Central Equipment Identity Register (CEIR) — a database of IMEIs, the 15-digit numbers that uniquely identify each mobile device.
Central Equipment Identity Register:
- The concept of a central identity register is advocated by the GSM Association (GSMA), a body representing mobile operators, equipment manufacturers, and software and internet companies, among other stakeholders in the telecom ecosystem.
- In India, the plan to prepare the registry of mobile identification numbers was first conceived in the National Telecom Policy-2012.
- A pilot for the project was developed and conducted by state-owned BSNL’s IT Project Service unit in Pune. In the interim budget for 2019-20, the government allocated Rs 15 crore to the DoT for the CEIR project.
Significance:
- The theft and cloning of mobile phones have become a serious problem.
- The theft of mobile phones is not just a financial loss but also a threat to personal life of the citizens as well as national security.
How will Database work?
- In line with global practices, DoT’s identity register will be a database of IMEI numbers that will consist of three lists – white, grey and black.
- Mobile phones with IMEI numbers in the white list will be permitted for use, while those in the blacklist will be the ones that are reported stolen or lost and will not be allowed to access the network.
- Devices with IMEI numbers in the grey list will be the ones that do not conform to standards but will be permitted to connect under supervision.
Utility of CEIR:
- Once implemented in the coming weeks, consumers in India whose mobile phones are lost or stolen can inform the Department of Telecom (DoT) via a helpline number after filing a report with police. The DoT can then blacklist the IMEI number, effectively blocking the mobile device from accessing any cellular network in the future.
- The CEIR will have access to GSMA’s global IMEI database, allowing comparison of IMEI numbers to identify counterfeit devices.
IMEI:
- The International Mobile Equipment Identity or IMEI is a number, usually unique to identify 3GPP and mobile phones, as well as some satellite phones.
- GSM networks use the IMEI number to identify valid devices, and can stop a stolen phone from accessing the network.
- For example, if a mobile phone is stolen, the owner can have their network provider use the IMEI number to blacklist the phone.
- This renders the phone useless on that network and sometimes other networks, even if the thief changes the phone’s subscriber identity module (SIM).
- The IMEI only identifies the device and has no particular relationship to the subscriber. The phone identifies the subscriber by transmitting the International mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number, which it stores on a SIM card that can, in theory, be transferred to any handset. However, the network’s ability to know a subscriber’s current, individual device enables many network and security features.
NATIONAL ACCREDITATION BOARD FOR CERTIFICATION BODIES (NABCB)
22, Jun 2019

Why in News?
- The National Accreditation Board for Certification Bodies (NABCB), India’s national accreditation body, secured international equivalence for its accreditation programme for personnel certification bodies in the annual meetings of the Asia Pacific Accreditation Cooperation in Singapore today.
Highlights:
- NABCB has currently accredited one certification body for Personnel Certification and has 4 applicants.
- This programme will help professionals to get certified based on their competence in any required field.
- NABCB is already supporting Ministry of AYUSH and has accredited a certification body for certification for Yoga professionals. This would promote Yoga certification scheme internationally.
Significance:
- With the above recognition, NABCB hopes to facilitate export of Indian services and skills into the world market by attesting that persons are certified following international standards by the certifying bodies.
- Personnel Certification would support many professionals in India, especially those who do not have formal education or certificate programme.
- Any person carrying ISO/IEC 17024 certificate with NABCB logo will be recognized internationally.
- It can also be used by regulators for establishing confidence in certified personnel for different activities.
- This signifies that the accreditation of personnel certification bodies by NABCB is now accepted as equivalent at international level
NABCB:
- NABCB, a constituent Board of the Quality Council of India provides accreditation to Certification and Inspection Bodies based on assessment of their competence as per the Board’s criteria and in accordance with International Standards and Guidelines.
- NABCB is internationally recognized and represents the interests of the Indian industry at international forums through membership and active participation with the objective of becoming a signatory to international Multilateral / Mutual Recognition Arrangements (MLA / MRA).
INDIA TO RAISE TERROR, FINANCIAL CRIMES AT G20 SUMMIT
22, Jun 2019

Theme “Human Centered Future Society”
- Issue to be taken up:
-
- Digital economy
- Artificial Intelligence
- Global Health
- Ageing
- Marine Plastic
What is DFFT or Data Free Flow with Trust?
- This is a new principle emerging among the global economies where they wish unrestricted, yet accountable flow of data over a localized data.
- It underlying principles are:
- Rather than tell firms where they can store or process data, policymakers should hold firms accountable for managing data they collect, regardless of where they store or process it.
- Countries should revise the inefficient processes and outdated legal agreements that govern law enforcement requests for access to data stored in another country’s jurisdiction.
- Countries should develop the legal and administrative frameworks (with respective checks and balances) that allow Internet service providers to block data flows that involve the illegal distribution and use of unlicensed content.
- Countries should support and not undermine encryption’s role in securing data flows and digital technologies.
Money-laundering and its prevention:
Terror Funding:
What is FATF?
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an inter-governmental body
- established in 1989 by the Ministers of its Member jurisdictions.
- The objectives of the FATF are to set standards and promote effective implementation of legal, regulatory and operational measures for combating money laundering, terrorist financing and other related threats to the integrity of the international financial system.
- The FATF currently comprises 36 member jurisdictions and 2 regional organisations, representing most major financial centres in all parts of the globe.
- In June 2018, Pakistan was placed in the ‘grey list’ and given a 27 point action plan.
What does this mean for the Country?
- Pakistan’s banking channel could be adversely affected as it is inevitably linked with the international financial system.
- Foreign financial institutions may carry out enhanced checking of transactions with Pakistan to avoid risk of violations pertaining to money laundering and financing of terrorism.
- Another affected is the sentiment of foreign investors.
Which are the other countries in the grey list?
- The other countries on the list, in alphabetical order, are Ethiopia, Serbia, Sri Lanka, Syria, Trinidad and Tobago, Tunisia and Yemen.
What is Black List?
- Black list makes more stringent restrictions on the countries in the list. This black list comprises Iran and North Korea.
Other Facts:
- The FATF implements UN designations, which do not warrant arrest.
- They ask only to freeze funds, denial of access to weapons and travel embargo
OPERATION BANDAR CODE
22, Jun 2019

- Operation Bandar’ code name of Balakot strike
Air Strike:
- 12 Mirages having taken off from multiple air bases crossed over into the Pakistani air space and carried out missile attacks in Balakot town of Khyber Pakhtunwa province
GROWING HORNS’ WITH PHONE OVERUSE
22, Jun 2019

- New research in biomechanics suggests that young people are developing hornlike spikes at the back of their skulls — bone spurs caused by the forward tilt of the head, which shifts weight from the spine to the muscles at the back of the head, causing bone growth in the connecting tendons and ligaments.
- Smartphones and other handheld devices are contorting the human form, requiring users to bend their heads forward to make sense of what’s happening on the miniature screens.
TRIPLE TALAQ
22, Jun 2019

Context:
- Triple Talaq bill again introduced by NDA government in Lok Sabha.
About:
- The Bill makes all declaration of talaq, including in written or electronic form, to be void (i.e. not enforceable in law) and illegal.
- It defines talaq as Talaq-e-biddat or any other similar form of talaq pronounced by a Muslim man resulting in instant and irrevocable divorce.
- Talaq-e-biddat refers to the practice under Muslim personal laws where pronouncement of the word ‘talaq’ thrice in one sitting by a Muslim man to his wife results in an instant and irrevocable divorce.
Offence and Penalty:
- The Bill makes declaration of talaq a cognizable offence, attracting up to three years’ imprisonment with a fine. (A cognizable offence is one for which a police officer may arrest an accused person without warrant.)
- The offence will be cognizable only if information relating to the offence is given by:
- (i) The married woman (against whom talaq has been declared), or
- (ii) Any person related to her by blood or Mariage
Feature:
- The Bill provides that the Magistrate may grant bail to the accused. The bail may be granted only after hearing the woman (against whom talaq has been pronounced), and if the Magistrate is satisfied that there are reasonable grounds for granting bail.
- Allowance: A Muslim woman against whom talaq has been declared, is entitled to seek subsistence allowance from her husband for herself and for her dependent children. The amount of the allowance will be determined by the Magistrate.
- Custody: A Muslim woman against whom such talaq has been declared, is entitled to seek custody of her minor children. The manner of custody will be determined by the Magistrate
ANTI DEFECTION LAW
22, Jun 2019

Context:
- 5 TDP members of Rajya Sabha defected in BJP party.
About:
- The Anti-Defection law sought to prevent such political defections which may be due to reward of office or other similar considerations.
- 10th Schedule
- Power to disqualify bears with Speaker/ Chairman of House.
- A legislator is deemed to have defected if he either voluntarily gives up the membership of his party or disobeys the directives of the party leadership on a vote.
Background:
- Anti-Defection Law was passed in 1985 through 52nd amendment of constitution.
Disqualification Grounds:
- If member of house belonging to a political party
- Voluntary gives membership of his political
- Votes or does not vote contrary to directions of his party. If an independent candidate joins a political party after
- Nominated member is allowed to join a political party provided he joins such political party of his choices within a period of six months. After that period, joining a political party would lead to defection and disqualification.
Disqualification Authority:
- The question whether a member is subject to disqualification in all other matters except under 10th Schedule (disqualification) is Decided by President. However, President should obtain the opinion of the election commission before taking such decision.
- The Question of Disqualification under Anti-defection / Tenth Schedule is decided by the Chairman in the case of Rajya Sabha {i.e. Vice-President} and Speaker in the case of Lok Sabha.
When Defection is not Applied:
- Person shall not be disqualified if his political party merger with another party.
- Person and other members do not accept the merger and opt to function as a separate group.
- This exception shall operate only if not less than two third of the members of party in house have agreed to the agreed to the merger.
Epistocracy
19, Jun 2019

- Epistocracy is a system in which the votes of people who can prove their political knowledge count more than the votes of people who can’t.
- In other words, it’s a system that privileges the most politically informed citizens.
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN)
19, Jun 2019

Objective:
- With a view to Augment the Income of the Small and Marginal Farmers (SMFs), the Government has launched a new Central Sector Scheme, namely, “Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN)” in the current financial year.
- The PM-KISAN scheme aims to supplement the financial needs of the SMFs in Procuring Various Inputs to ensure proper Crop Health and appropriate yields, commensurate with the anticipated farm income at the end of each crop cycle.
- This would also Protect them from Falling in The Clutches of Moneylenders for meeting such expenses and ensure their continuance in the farming activities
Definition of Families:
- The SMFs landholder farmer family is defined as “a family comprising of husband, wife and minor children who collectively own cultivable land upto 2 hectare as per land records of the concerned State/UT”
Fund:
- Financial year 2018-19, a budget provision of Rs. 20,000 crores has been kept.
Benefit to Eligible SMFs:
- Under the Scheme, a Direct Payment of Rs. 6000 per year will be transferred in three equal instalments of Rs. 2000 Every Four Months into the Aadhar ceded bank accounts of eligible landholding SMFs families.
Monitoring of the Scheme:
- For effective review and monitoring of the scheme, a Project Monitoring Unit (PMU) at Central level will be set up in DAC & FW.
National Company Law Tribunal
19, Jun 2019

- The statutory body has constituted National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) under section 408 of the Companies Act, 2013
- It is a quasi-judicial body in nature.
Significance:
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (Bankruptcy Code), also provides wide powers to the NCLT to adjudicate upon the ‘insolvency resolution process’ and liquidation of corporate debtors.
- NCLAT is also the Appellate Tribunal to hear and dispose of appeals against any direction issued or decision made or order passed by the Competition Commission of India.
Speaker
19, Jun 2019

Context:
- MP Om Birla named as choice for Speaker’s post.
- He is presiding officer of Lok sabha.
- He is the guardian of powers and privileges of members and committees of Lok Sabha
Duration in Office:
- Speaker remains in office during the life of Lok Sabha (he needs to remain member of Lok Sabha).
- When the office of Lok Sabha speaker falls vacant, the members elect another speaker on a date fixed by the President.
- Whenever Lok Sabha is dissolved, the Speaker continues to remain in office until immediately before the first meeting of Lok Sabha after it is reconstituted.
Resignation:
- Disqualified if ceases to be the member of House Addressing a resignation letter to Deputy Speaker
Removal:
- Speaker can be removed by the members of Lok Sabha by a resolution passed by Absolute Majority {Majority of the Total Members of the House} of Lok Sabha.
- 14 days advanced notice must be given for such resolution.
- The Motion of Removal can be considered and discussed only when it has the support of at least 50 Members.
- If resolution is under consideration of the house, Speaker Cannot Preside the Meeting, but can participate in the house and vote in the first instance though not in the case of an equality of votes.
Powers and Functions:
- The Guardian of powers and privileges of members and committees of Lok Sabha. To Maintain order and decorum in Lok Sabha
- His interpretations of constitutional provisions, rules and regulations related to Lok Sabha are final.
- Adjournment of Lok Sabha is done by Speaker
- During voting in the house on a bill or other matters, he does not vote in the first instance. However, if there is a tie due to equal votes, speaker exercises the casting vote
- Joint sittings of both the houses of parliament are although called by President but presided by Lok Sabha speaker.
- On the request of the Leader of the House, Speaker may allow a secret meeting.
- Whether a bill is money bill or not, is decided by Speaker and his decision in this matter is final.
- Disqualification of Members of House-
- Speaker decides the question of disqualification of Lok Sabha members in matters of tenth schedule / anti-defection law. This decision is subject to judicial
- He is the Ex-Officio Chairman of Indian Parliamentary Group of the Inter- parliamentary Union.
- Chairman of all the parliamentary committees of Lok Sabha are appointed by Speaker, provided such committees does not need an elected chairman
- Speaker himself is the chairman of
- Business Advisory Committee,
- Rules Committee and
- General Purpose
- The Secretary General of the Lok Sabha is appointed by the Speaker.
Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha:
- If Speaker of Lok Sabha is not available, his duties are carried out by Deputy Speaker Election– A Deputy Speaker is elected by the Lok Sabha members from amongst themselves.
- Election of Deputy Speaker is done after election of Speaker.
- Deputy speaker is not subordinate to the Speaker and is directly responsible to Lok Sabha.
- If Deputy Speaker is also not present, a person appointed by President will discharge the duties.
Pro Tem Speaker:
- President appoints a speaker Pro Tem for the first meeting of the newly elected Lok Sabha. He is appointed to administer oath to the new members and enable the house to elect a new speaker (Before Oath they cannot be member of house and participate in proceeding).
UN CONVENTION ON HATE SPEECH
18, Jun 2019

- United Nations (UN) Committee on the Elimination of Racial Discrimination (the CERD) conducts discussion on “Hate Speech” in the context of the International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination (the Convention) to enhance understanding of the causes and consequences of racist hate speech.
- The Universal Declaration of Human Rights both prohibits discrimination and protects freedom of expression. It is well-established in international human rights law that the right to freedom of expression, though not absolute, is a fundamental right which may only be restricted in certain limited circumstances.
- The conditions in which restrictions are allowed are set out in Article 19(3) and 20 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), as well as numerous regional treaties also ratified by many States parties to the Convention.
NATIONAL HUMAN RIGHTS COMMISSION (NHRC)
18, Jun 2019

- It is a Statutory Body the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) of India was established on 12 October, 1993.
- It is in conformity with the Paris Principles, Section 2(1)(d) of the PHRA defines Human Rights as the rights relating to life, liberty, equality and dignity of the individual guaranteed by the Constitution or embodied in the International Covenants and enforceable by courts in India.
Composition:
- NHRC comprises of a chairman and four members. The chairman should be a retired chief justice of India.
- The other members should be
-
- One Member who is, or has been, a Judge of the Supreme Court of India
- One Member who is, or has been, the Chief Justice of a High Court
- Two Members to be appointed from among persons having knowledge of, or practical experience in, matters related to human
Members appointed by committee consist of:
- Prime Minister (chairperson) Home Minister
- Speaker of the Lok Sabha
- Leader of the Opposition in the Lok Sabha Deputy Chairman of the Rajya Sabha Leader of the Opposition in the Rajya Sabha
Functions of NHRC:
- Inquire suo motu or on a petition presented to it, by a victim, or any person on his be into complaint of violation of human rights or negligence in the prevention of such violation by a public servant.
- Intervene in any proceeding involving any allegation of violation of human rights before a Court with the approval of such Court.
- Visit any jail or detention places to study the living conditions of the inmates and make recommendations thereon
- Review the safeguards provided by or under the constitution of any law for the time being in force for the protection of human rights and recommend measures for their effective implementation.
- Review the factors, including acts of terrorism that inhibit the enjoyment of human rights and recommend appropriate remedial measures.
- Undertake and promote research in the field of human rights.
- Spread human rights literacy among various sections of society and promote awareness of the safeguards available for the protection of these rights.
- Encourage the efforts of Non-Governmental organizations and institutions working in the field of human rights.
- Undertake such other functions as it may consider necessary for the promotion of human rights.
BHARATMALA PROJECT
17, Jun 2019

Why in News?
- Bharatmala is a name given to road and highways project of Government of India.
Highlights:
- The total investment for the Bharatmala plan is estimated at Rs10 trillion, which is the largest ever outlay for a government road construction scheme.
- Bharat Mala will provide easier access to border areas for armed forces and boost trade via the land route.
- Roads will be built along borders with Bhutan and Nepal.
- Road connectivity to small industries will be ensured and manufacturing centres will be connected with national highways.
- The project will be executed through Ministry of Road, Transport and Highways (MoRTH), NHAI, National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL) and State Public Works Department (PWDs). Bharatmala is the largest highways project after the National Highways Development Programme.
KIMBERLEY PROCESS
17, Jun 2019

Why in News?
Intersessional meeting of the Kimberley Process (KP) is being hosted by India in Mumbai.
Highlights:
- India is currently the Chair of Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) since 1st January 2018. It was handed Chairmanship by the European Union during KPCS Plenary 2018, which was held in Brussels, Belgium.
- India is founding member of KPCS.
Kimberley Process:
- The Kimberley Process is an international certification scheme that regulates trade in rough diamonds. It aims to prevent the flow of conflict diamonds, while helping to protect legitimate trade in rough diamonds.
- The Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) outlines the rules that govern the trade in rough diamonds.
- The KP is not, strictly speaking, an international organisation: it has no permanent offices or permanent staff. It relies on the contributions – under the principle of ‘burden-sharing’ of participants, supported by industry and civil society observers.
- Neither can the KP be considered as an international agreement from a legal perspective, as it is implemented through the national legislations of its participants.
Kimberley Process Certification Scheme:
- The Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) imposes extensive requirements on its members to enable them to certify shipments of rough diamonds as ‘conflict-free’ and prevent conflict diamonds from entering the legitimate trade.
- Under the terms of the KPCS, participating states must put in place national legislation and institutions; export, import and internal controls; and also commit to transparency and the exchange of statistical data.
- Participants can only legally trade with other participants who have also met the minimum requirements of the scheme, and international shipments of rough diamonds must be accompanied by a KP certificate guaranteeing that they are conflict-free.
BIMAL JALAN COMMITTEE ON THE QUANTUM OF RESERVES
17, Jun 2019

Constituted on 26 December 2018, to decide upon the appropriate level of reserves the regulator should hold. This committee has been appointed in the backdrop of a deadlock between the RBI and the Government. The government feels that RBI’s reserves exceeded its limits and that these could be used for productive purposes such as recapitalizing public sector banks.
What are RBI Reserves?
RBI holds reserves in currency and gold inorder to:
- Absorb potential losses that it may incur while holding foreign
- Shield the economy from monetary and financial
- Carry monetary burden during unstable
- Perform price and exchange
- Perform its functions independently of the government
- RBI holds 25.6 % of its assets as reserves while the global median is 16%. Under Section 47 of RBI Act, RBI transfers the excess funds to the Government after accounting for contingency reserves.
PUBLIC PROCUREMENT LEGISLATION
17, Jun 2019

Context:
- Supreme Court expressed its growing concern over the award of tenders being challenged in writ proceedings almost as a matter of routine.
Why:
- Need the Central government must pass legislation on Public Procurement.
- Nearly, 30% of GDP is contributed by this public procurement which has a fiscal significance in public policy.
Previous bills:
- United Progressive Alliance introduced the Public Procurement Bill in the Lok Sabha in 2012, The National Democratic Alliance, in 2015, revamped the provisions of the earlier Bill to come up with the Public Procurement Bill, 2015
- Both the bill were not passed in parliament.
Constitutional Provision:
- There is absence of Any Constitutional Provision regarding such Public procurement. Reason- Article 282 gives financial autonomy in public spending for executive.
State take on Public procurement:
- State public procurement is regulated by a State Act only in five states Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh and Assam.
- There is absence of grievance redress mechanisms in above states.
Judiciary Stand:
- Courts have imposed such stringent Self-Imposed Restrictions in the area of judicial review regarding tendered and power to interfere.
Conclusion:
- Absence of Legislation would only encourage the growth of other negative aspects of public procurement.
- In such a depressing legal scenario, it is no surprise that public procurement tender awards are often challenged in constitutional courts.
- Passing a roboust legislation in Public procurement will Reduce Litigations in Court Regarding Procurement Help Fiscal Consolidation
- Accountability in procurement. Boost MSME further.
LEADER OF OPPOSITION
17, Jun 2019

Context:
- Like 2014 leader of opposition no political party is qualifying that mark of 55 MPs in Lok Sabha to get Leader of opposition.
- UPSC Question Prelims – Leader of Opposition in 2018
About:
- Lop is leader of largest non-government party.
- Source of Lop- ‘the salary and allowances of leaders of opposition in Parliament Act, 1977’ which only says that the largest opposition party should get the post securing 10%(at least a strength equal to the quorum) of seats.
- This act for LoP is extended to both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.
- The Leaders and Chief Whips of Recognised Parties and Groups in Parliament (Facilities) Act, 1998 also refers to a recognised party in the Lok Sabha as a party that has not less than 55 members.
Constitutional Provision:
- There is no provision in the Constitution or even in the Lok Sabha Rules of Procedure in regard to the recognition of the LoP.
- Since there is no constitutional provision, the 1977 law does not provide for the requirement of 55 members as an essential pre requisite. As it all depends on the Speaker’s directions and discretion.
Importance of LoP:
- To Democracy to survive there is need of effective and strong opposition.
- It is said that if no Opposition exists, one may have to be created. Also, if there is no Opposition outside, there is every danger that it may grow within.
History:
- First officially recognized LoP was after breakup of congress in 1969, The Leader of INC(O), Ram Subhag Singh, became the first LoP in Lok sabha.
Hint for Way Ahead:
The simple way out is to substitute ‘pre -poll alliance’ for ‘party’ or say ‘party or pre- poll alliance’. and get that number of 55 MPs.
LABOUR ISSUES
16, Jun 2019

- Indian Staffing Federation has asked the government to completely scrap the archaic labor laws.
- ISF is an apex body of staffing or the outsourcing industry. It is yet to be recognized by the government. India has 463 million workforces, of which 94% are in informal sector employed with small and micro firms.
- Such enterprises tries to remain small since they enjoy tax benefits in India as they employ less than 20 people. Therefore, such a ceiling on the number of employees has restricted the growth of the industries as well as the growth of employment in the country.
- Once a company employs more than 20 labourers it is subjected to unrealistic labour laws and compliances. Labour laws in India is framed by both the Central government and the State government as it comes under the Concurrent list of the constitution.
- This has created lot of ambiguity in laws and confusion in its implementation. For example, existing labour laws define worker and wage in 17 different ways.
- This has made India a hostile place for investments.
- The ISF recommends new labour laws that suits the modern times and needs of an emerging economy.
CHINA – PHILLIPINES CONFLICT IN S. CHINA SEA
16, Jun 2019

Issue:
- South China Sea is a significant area in the Pacific Ocean.
- It is the major trade route connecting South East Asia to the Pacific Ocean, China and Japan.
- China has been claiming the sovereignty over the South China Sea. This has led to the tensions among the nations surrounding the South China Sea.
- China has been aggressively building artificial island in the area to further their claims in the region and also to establish their military and naval bases in the region. This act has been widely condemned by the
- Western world and also by India.
- India’s stand: The dispute over the Sea should be resolved through International laws and consensus. Especially the laws that govern the sea under the UNCLOS.
- On 15th June a Chinese vessel hit a Phillipino fishing boat which escalated the ongoing tensions.
- It happened near Reed Bank over which Phillipines claims sovereignity as it falls within 200 nautical miles exclusive economic zone of the country. However, Beijing also claims the ownership of Reed bank.
Exclusive Economic Zone:
- It is a law formulated under the UNCLOS or the United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea. It is an area beyond and adjacent to the territorial area; maximum 200 nautical miles from the baselines.
- -Within the EEZ, the coastal state has the sovereignity over the natural resources.
Within an EEZ a state is allowed to do the following:
- Create artificial islands. Marine scientific research.
- Protection and preservation of Marine Environment.
IRAN – US NUCLEAR ISSUE
16, Jun 2019

Context:
- U.S withdrawn from JCPOA after Donald Trump had become the President of the country.
What is JCPOA?
- Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action is an agreement reached between Iran and P5+1 nation on the issue of nuclear enrichment process happening in Iran.
- It was adopted on July 14, 2015 and later endorsed by the United Nations Security Council Resolution 2231 on July 20, 2015.
Who are the Members?
- Iran and (P5= U.S, Britain, Italy, China, Russia) + Germany
Who is the Implementing Agency?
- Iran’s compliance with the nuclear related provisions will be verified by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
- Core Issue: The Western nations suspect Iran is enriching uranium to the levels required to make nuclear bombs. Such an action by Iran could trigger an all-out war in the Gulf region as Iran is a hostile nation to most of the Sunni dominated Gulf region and the Western countries.
- Arak Reactor: JCPOA demands Iran to shut down the Arak nuclear reactor. Replace the core of the Arak reactor to reduce the weapons grade plutonium output.
- Fordow: For 15 years no introduction of Uranium to this facility. However, after the U.S withdrawal from the deal, Iran has decided to scale back compliance with a nuclear deal unless the signatories to the JCPOA show positive response.
- CAATSA: Countering America’s Adversaries through Sanctions Act. This law has used by the U. S government to impose sanctions on Iran, Russia and N.Korea.
ESSENTIAL SERVICES MAINTENANCE ACT (ESMA)
16, Jun 2019

Context:
- Doctors Strike in West Bengal regarding assault on doctors by public. Esma is Central law.
- ESMA enables the Government to ban strikes and demand conciliation or arbitration in certain “essential” industries.
- Act also allows states to choose the essential services on which to enforce Esma.
- Its implementation is entirely on discretion of State Government.
Provisions of Act:
- Esma gives police the right to arrest, without a warrant, anybody violating the Act’s provisions. “Any person who commences a strike…or otherwise takes part in… any such strike shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to six months, or with fine which may extend to two hundred rupees, or with both,” the Act reads.
- “Any person who instigates…a strike which is illegal under this Act shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to one year, or with fine which may extend to one thousand rupees, or with both.”
Mains Perspective:
- Provisions that need to be brought to assure that there is no disruption in vital services like Health. Reasons for recent attacks on doctors by public across the country and what are solution to avoid the same?
Hints;
- Poor Doctor patient ratio,
- Infrastructural bottle necks of health sector. Accessibility of quality health care for poor.
- Right to strike for people in essential service such as health sector?
SOUTH ASIA IS TOP PRIORITY: JAISHANKAR
08, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Building connectivity in the South Asian region and coordinating economic issues will be top priorities of the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), said S. Jaishankar.
Background: / More in News
- Jaishankar is on a two-day tour to Thimphu on June 7-8 to meet with the King of Bhutan, Prime Minister Lotay Tshering, and Foreign Minister Tandi Dorji
- Speaking at the event organised by the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), Ananta Centre and Smadja and Smadja, S Jaishankar highlighted three trends being witnessed in the world which include
- Globalisation under stress especially in terms of market access and mobility of labour, Growth of nationalism and
- Global rebalancing.
On South Asia:
BIMSTEC
- Mr Jaishankar indicated that the government had chosen to invite leaders of BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) rather than leaders of SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation), because there was a higher likelihood of making progress with BIMSTEC, as it doesn’t include Pakistan.
Regional Connectivity:
- He highlighted the importance of regional connectivity. South Asia is among the least inter-connected regions in the world, but efforts are being made to make the region more integrated.
- Mr Jaishankar emphasised the need for more regional exchanges, saying India needed to “incentivise cooperation in the neighbourhood” by being “generous” to smaller neighbours.
On Economy:
- Jaishankar also spoke on the need for more coordination between the MEA and economic ministries.
- The comments reflect the economic challenges the government faces immediately, given the United States decision to withdraw India’s ‘GSP’ preferential trade status, and the emerging costs of replacing Iranian oil after sanctions.
- He also said that a large part of India’s economy has been externalised and there is a need for India’s foreign policy and the diplomatic machinery to help Indian companies gain better access to overseas markets.
SUDAN CRISIS
08, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Sudan is in the midst of a political crisis after security forces opened fire on pro-democracy protesters in the capital, Khartoum.
Background: / More in News:
- When Sudanese dictator Omar al-Bashir was toppled on April 11 after a months-long popular uprising, the generals had two options before them
- One was the Tunisian model in which the army allowed a smooth transition of power to a civilian government after Zine El Abidine Ben Ali was removed from power in 2011.
- The other was the Egyptian model in which the army, after losing power to a civilian ruler following Hosni Mubarak’s ouster as President in 2011, staged a coup in 2013 and reinstalled itself at the helm. Sudanese generals chose the Egyptian Model, setting the stage for a prolonged showdown. The protesters had demanded a transfer of power to a transitional civilian government, followed by free and fair elections. But the generals used the crisis to concentrate more powers in their own hands. Later military generals established a military council which took over governance, while angry protesters continued a sit-in in front of the Defence Ministry in Khartoum.
- As talks between pro-democracy activists and the military rulers collapsed, paramilitary groups unleashed deadly violence this week to break the sit-in, killing at least 100 people and injuring hundreds.
Global Response:
- The US condemned what it called a “brutal attack” and the UK said the military council bore “full responsibility”. The African Union (AU) has suspended Sudan from its membership until a civilian led transitional authority is established.
- However, The UN Security Council couldn’t even condemn the violence as China, backed by Russia, blocked the move. Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, which offered financial aid to the junta as soon as Mr. Bashir was removed from power, also support the generals.
Impact of Crackdown:
- After the crackdown, General Abdel Fattah al-Burhan, the military ruler, has offered to hold elections in nine months, upturning an earlier plan of a two-year transition. But there is no immediate plan to transfer power to a civilian transitional government, a key demand of the protesters.
Conclusion:
- Military must resume talks with the protesters and facilitate a quick and orderly transition to civilian rule. The choice the generals make will determine the future of Sudan.
HOME MINISTRY WARNS NGOS
08, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- The Home Ministry has warned of taking penal action against NGOs which change office bearers without taking its approval.
Background: / More in News
- In a notification, the home ministry said incidents have come to light that some NGOs, having registered under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), have changed their office bearers without its approval and without updating this data on a real-time basis through the online application meant for a change of these details.
- All NGOs and associations registered under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), 2010, which makes them eligible to receive foreign funds and donations, have to submit an online application for addition, deletion and change of details about office- bearers and key functionaries within one month.
- The ministry told the NGOs to submit applications for addition/ deletion/change of details about office bearers/ key functionaries by July 7, failing which penal action will be initiated against them. Since 2014, the central government has started scrutiny of the activities of NGOs leading to the cancellation of their FCRA registration, which allows them to get foreign funding.
- There was a total of 23,176 FCRA registered NGOs in 2016-17, which has now come down to around 12,000.
Regulation of NGO under FCRA:
- The Home Ministry monitors foreign funds donated to NGOs and organisations through the FCRA. The FCRA was brought into force to regulate the flow of foreign funds to voluntary organisations with the objective of preventing any possible diversion of such funds to anti-national activities.
- However, there are many NGOs which are registered under FEMA and continue to disburse foreign funds to various associations. NGOs under FEMA is regulated by the Finance Ministry, there are many occasions when the Home Ministry failed to monitor the flow of funds effectively.
- International donors such as the Ford Foundation, the U.K.’s Department for International Development and Canada’s International Development Research Centre are registered under FEMA but not the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), 2010.
- Funds flowing to NGOs can be used for an anti-national activity such as economic security. Hence regulation of NGO receiving fund is necessary.
- NGO is used by vested interest to halt the developmental project in India as reported by the Intelligence Bureau. This was witnessed in kudankulam protest.
- Earlier, the Home Ministry wants the Finance Ministry to surrender its to monitor non- governmental organisations (NGOs) under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) for effective and better monitoring.
DRAFT NATIONAL EDUCATION POLICY MOOTS ALL-INDIA ENTRANCE TESTS FOR UG COURSES
08, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Admission to undergraduate courses in all government-funded universities and colleges will soon be through all-India entrance tests, if the draft National Education Policy is approved.
Background: / More in News
- Private institutes will also be strongly encouraged to make use of the common admission tests, which will be available from 2020. Both aptitude and subject knowledge-based tests will be offered.
- According to draft policy,
- This seems to indicate that the NTA assessment will replace Class 12 marks as the criteria for admission to these government funded institutions.
- The NTA tests will aim to assess essential concepts, knowledge, and higher order skills from the national common curriculum as per the NCF in each subject, for the purpose of aiding colleges and universities in their admissions decisions.
- This will help to eliminate the intensity, stressfulness, and wasted time of the Grade 12 examination season faced by students every year as well as by so many higher educational institutions and employers
- The system seems to have some similarities to the SAT, a standardised aptitude test widely used for admissions to colleges and universities in the United States. The SAT, however, is used as a criterion alongside school grades.
- In India, the common entrance test has largely been the domain of aspirants to professional or post-graduate courses, but that is already changing.
- The new National Testing Agency (NTA) has already conducted premier professional entrance tests — JEE, NEET, and CMAT — this year.
- NTA will also conduct admission tests for applicants to more than 170 Delhi University (DU) courses, including 12 undergraduate programmes.
National Testing Agency:
- National Testing Agency (NTA) is an Indian government agency that has been approved by the Union Council of Ministers and established in November 2017 to conduct entrance examinations for higher educational institutions
- It also helps individual colleges and universities in the field of testing and to provide training and advisory services to the institutions in India. It provides quality testing services to the academic institutions in India.
- It undertakes the reforms and training of school boards as well as other bodies where the testing standards should be comparable with the entrance examinations.
Jal Shakti’ Ministry to deal with integrated water issues
01, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- A new ‘Jal Shakti’ Ministry, in which the erstwhile Ministries of Water Resources and Drinking Water and Sanitation will be merged, has been formed
Details:
- Mr. Shekhawat took charge of the Ministry
- The remit of the Ministry will encompass issues ranging from international and inter-State water disputes, the Namami Gange project, the flagship initiative to clean the Ganga, its tributaries and sub-tributaries and the provision of clean drinking water.
- Mr. Shekhawat said that the priority would be to provide clean drinking water to everyone.
India to lose preferential trade terms with U.S.
01, Jun 2019

Why in news
- India will lose access to preferential trade terms with the U.S. under the latter’s Generalised System of Preferences (GSP) programme.
Details:
- Trump had written to the U.S. Congress on stating his intention to withdraw GSP benefits for India, saying India had failed to assure Washington that it would provide “equitable and reasonable access to the markets of India”.
- GSP can and is expected to be terminated via a Presidential proclamation. Indian exports to the U.S. worth $5.6 billion are covered by GSP, although India gets only $190 million in tariff savings. Nevertheless, the programme impacts crucial Indian sectors including textiles, leather, engineering goods, gems and jewellery.
GSP:
- Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) is an umbrella that comprises the bulk of preferential schemes granted by industrialized nations to developing countries.
- It involves reduced Most Favored Nations (MFN) Tariffs or duty-free entry of eligible products exported by beneficiary countries to the markets of donor countries.
Saudi Arabia is sowing division’
01, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Tehran accused Riyadh of “sowing division” in the region to Israel’s advantage, after the Kingdom hosted summits of Gulf and Arab leaders to rally support against the Islamic republic.
Details:
- Saudi Arabia has “continued to sow division between Islamic countries and in the region, which is the wish of the Zionist regime,” Foreign Ministry spokesman said.
- Saudi Arabia’s King Salman ratcheted up the rhetoric against arch-rival Iran, calling on Arab states to confront its “criminal” actions after attacks on oil installations sparked fears of a regional conflagration.
- Tehran dismissed the accusation as “laughable” and accused the U.S. of pursuing “evil desires for chaos in the region.”
Oil price:
- The ruler of the world’s top crude exporter said Shia Iran’s development of nuclear and missile capabilities and its threats on world oil supplies posed a risk to regional and global security. Riyadh accused Tehran of ordering the drone strikes. The attacks were claimed by the Iran-aligned Houthi group, which has been battling a Saudi-led military coalition in Yemen for four years. “The Kingdom is keen to preserve the stability and security of the region, to spare it the scourge of war and to realise peace and stability,”
Nuclear deal:
- Tensions have risen between the U.S. and Iran after President Donald Trump a year ago withdrew Washington from a 2015 international nuclear deal with Iran, re-imposed sanctions and boosted its military presence in the Gulf. The final communiqué said regional stability required the establishment of an independent Palestinian state along 1967 borders to include Gaza, the West Bank and East Jerusalem.
U.S. to hit Mexico with tariffs over migration
01, Jun 2019

Why in news
- Washington will impose a 5% tariff on all goods from Mexico — increasing to as much as 25% — until “illegal migrants” stop coming through the country into the U.S., President Donald Trump said.
Details:
- The Tariff will gradually increase until the Illegal Immigration problem is remedied, at which time the Tariffs will be removed,” Tariffs will permanently remain at the 25% level unless and until Mexico substantially stops the illegal inflow of aliens coming through its territory,” the statement said. The tariffs would have severe consequences on Mexico, which sends 80% of its exports to the U.S.
Mexico’s response
- Mexican President Andrés Manuel López Obrador struck a conciliatory tone in a letter to Mr. Trump following the tariff announcement. “I express to you that I don’t want confrontation,” The announcement came a day after border agents in El Paso, Texas detained the largest single group of migrants they had ever encountered — 1,036 people.
Recent Cases of Migration
- Syria is focal point of ‘global refugee crises’. Lot of people migrate from the country. People crossing Mediterranean Sea from Libya to Italy.
- Rohingya Muslims in Myanmar fleeing to Bangladesh and India. Thousands of Dominicans and Stateless in Caribbean.
Drawbacks
- It is often seen that immigrants are exploited for their cheap labour.
- Developing countries may suffer ‘Brain Drain’ as the limited resources they spend in educating their students would amount to very little if that talent gets enticed to another country. Immigration also attracts criminal elements from drug and people traffickers to other forms of crime and corruption. Immigration sometimes also becomes social or political issue; racism is used to exploit feelings or as an excuse for current woes of the local population.
TAIWAN LEGALIZES SAME-SEX MARRIAGE IN HISTORIC FIRST FOR ASIA
18, May 2019

Why in News:
- Lawmakers in Taiwan have approved a bill legalizing same-sex marriage, a landmark decision that makes the self-ruled island the first place in Asia to pass gay marriage legislation.
Details:
- Lawmakers comfortably passed part of a bill that would allow gay couples to enter into “exclusive permanent unions” and apply for marriage registration with government agencies.
What is Section 377?
- Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code dating back to 1860, introduced during the British rule of India, criminalises sexual activities “against the order of nature”, including homosexual sexual activities. Prior to that, sexual activities, including amongst homosexuals, were not penalised in India.
- Though it textually applies to all persons, homosexual and heterosexual, it has been targeted at Transgender men.
Courts judgement on Section 377
- The Delhi High Court in Naz Foundation v. Government of NCT of Delhi (2009) rightly held that criminalising sexual activities with consent in private not only impairs the dignity of those persons targeted by the law, but it is also discriminatory and impacts the health of those people.
- The top court had set aside a historic Delhi High Court judgment that had decriminalized homosexuality.
- Supreme Court, in Suresh Kumar Koushal v. Naz Foundation (2013) case, set aside the Delhi High Court judgment and said that homosexuality or unnatural sex between two consenting adults under Section 377 of IPC is illegal and will continue to be an offense. The court said that Section 377 did not suffer from any “constitutional infirmity”.
- The astounding claim made in Koushal case that there was no need to challenge Section 377 because the LGBT community constitutes only a minuscule minority has been completely discredited. It was unreasonable to advance the view that constitutional protection is available to a group based on its size.
CHARTING A CLEAR COURSE IN THE INDO-PACIFIC
18, May 2019

Why in News:
- Indo-Pacific has been gaining traction in Indian policy and has achieved operational clarity after the Indian vision was presented by Prime Minister Narendra Modi at the Shangri-La Dialogue.
Details:
- India has been an active participant in mechanisms like the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), in ASEAN-led frameworks like the East Asia Summit, the ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting Plus, the ASEAN Regional Forum as well as the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi- Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation and the Mekong-Ganga Economic Corridor.
- India has also been convening the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium, in which the navies of the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) participate.
- India has boosted its engagements with Australia and New Zealand and has deepened its cooperation with the Republic of Korea.
- India is stepping up its interactions with the Pacific Island countries.
- India’s growing partnership with Africa can be seen through the convening of mechanisms
like the India-Africa Forum Summits. - India’s multi-layered engagement with China as well as strategic partnership with Russia underlines its commitment to ensuring a stable, open, secure, inclusive and prosperous Indo-Pacific.
Background:
Shangri-La Dialogue
- The Shangri-La Dialogue (SLD) is an intergovernmental security forum held annually by an independent think tank, the International Institute for Strategic Studies in Singapore.
- The Shangri-La Dialogue has evolved into a key strategic gathering of the Asia-Pacific region. It is attended by defense ministers, permanent heads of ministries and military chiefs of Asia-Pacific states.
East Asia Summit
- The East Asia Summit (EAS) is a forum held annually by leaders of 18 countries established in the year 2005. Initially, 16 countries in the East Asian, Southeast Asian and South Asian regions were the members of the forum.
- The membership expanded to 18 countries including the United States and Russia at the Sixth EAS in 2011. EAS meetings are held after the annual Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) leaders’ meetings.
- The first summit was held in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia on 14 December 2005.
- The East Asia Summit includes India, China, Japan, Republic of Korea, Australia, New Zealand, The United States, and Russia apart from the 10 ASEAN Member States.
- India is a founding member of the East Asia Summit.
- Eleven East Asia Summits have been held so far. Though the ASEAN is at the core of the EAS, its vision is beyond the ASEAN and is seen by India as an alternative to the APEC, in which India doesn’t enjoy the membership.
- Within the framework of the East Asia Summit, there are six priority areas of regional cooperation. These are
- Environment and Energy
- Education
- Finance
- Global Health Issues and Pandemic Diseases
- Natural Disaster Management
- ASEAN Connectivity.
- EAS is an initiative of ASEAN and is based on the premise of the centrality of ASEAN.
- It has evolved as a forum for strategic dialogue and cooperation on political, security and economic issues of common regional concern and plays an important role in the regional architecture.
- Trade is also an important focus for the summit.
Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)
- The Indian Ocean Rim Association was set up with the objective of strengthening regional cooperation and sustainable development within the Indian Ocean Region
- The IORA is a regional forum, tripartite in nature, bringing together representatives of Government, Business and Academia, for promoting co-operation and closer interaction among them.
- It is based on the principles of Open Regionalism for strengthening Economic Cooperation particularly on Trade Facilitation and Investment, Promotion as well as Social Development of the region.
- India, Australia, Iran, Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, South Africa, Mozambique, Kenya, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, Bangladesh, Singapore, Mauritius, Madagascar, UAE, Yemen, Seychelles, Somalia, Comoros and Oman are among the members of IORA.
BIMSTEC:
- BIMSTEC stands for Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation. It is an international organisation involving a group of countries in South Asia and South East Asia. 7 members are Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Bhutan, Nepal
- Established in 1997 in Bangkok
- Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand were founding members HQ: Dhaka, Bangladesh
- The main objective of BIMSTEC is technological and economic cooperation among south Asian and south east Asian countries along the coast of the Bay of Bengal. Commerce, investment, technology, tourism, human resource development, agriculture, fisheries, transport and communication, textiles, leather etc. have been included in it
- BIMSTEC uses the alphabetical order for the Chairmanship Bhutan has never been chairman
- Current chairmanship: Sri Lanka
Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC)
- The MGC is an initiative by India and five ASEAN countries, Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam for cooperation in tourism, culture, education, as well as transport and communications. It was launched in 2000 at Vientiane, Laos. It is named after Ganga and the Mekong which both are civilisational rivers. MGC initiative aims to facilitate closer contacts among the people inhabiting these two major river basins.
TRUMP COULD MEET XI ON SIDELINES OF G20 MEET
13, May 2019

Why in News:
- President Donald Trump and China’s Xi Jinping could meet on the sidelines of the G20 summit to hash out their differences on trade, but no new talks are scheduled.
Details:
- The world’s top two economies ended two days of negotiations in Washington with no deal The G20 summit is scheduled to take place in Osaka on June 28-29.
- Mr. Trump ordered new punitive duties, on $200 billion worth of Chinese imports, raising them to 25% from 10%.
- He then ordered a tariff hike on almost all remaining imports — $300 billion worth
Group of 20:
- The G20 (Group of 20) is an international forum which includes 19 of the world’s largest
- economies and the European Union.
- G20 is a forum for economic, financial and political cooperation. It addresses the major global challenges and seeks to generate public policies that resolve them.
Significance of G20:
- Together, the G20 members represent
- Two thirds of the world population. 85% of the global gross product.
- 75% of international trade.
- 80% of global investments in research and development.
DEAL IN DANGER: ON IRAN AND NUCLEAR DEAL
13, May 2019

Why in News:
- Iran’s decision to reduce its commitments under the 2015 Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, which sought to curtail its nuclear capabilities, is more of a warning than a move to break the nuclear deal
Details:
- Iran has been under economic and political pressure since President Donald Trump pulled the U.S. out of the deal a year ago. The U.S. has since amped up its anti-Iran rhetoric and reimposed sanctions.
- With the U.S. having ended the sanctions-waiver it had given to certain countries, including India, on purchasing Iranian oil, the Iranian economy has come under more pressure.
- Iran will immediately stop shipping out excess enriched uranium and heavy water. Mr. Rouhani has given 60 days to other signatories to find solutions to shield Iran’s banking and oil sectors from U.S. sanctions. The big threat is that it will resume higher levels of enrichment to build weapons unless its grievances are addressed in 60 days
- Iran’s move to put the remaining signatories on notice could be the start of the formal unravelling of the deal. If Europe doesn’t do enough in 60 days and Iran sticks to its threat, the deal will collapse, giving more reason to the U.S. to escalate hostilities
- A collapse of the deal would not only exacerbate the Iran nuclear crisis but also set a bad precedent in international diplomacy.
Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA)
- The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) known commonly as the Iran deal, is an international agreement on the nuclear program of Iran reached in Vienna on 14 July 2015 between Iran, the P5+1 (the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council—China, France, Russia, United Kingdom, United States—plus Germany),and the European Union.
Way Forward:
- With this decision President Trump is risking U.S. national security, recklessly upending foundational partnerships with key U.S. allies in Europe and gambling with Israel’s security.
- Withdrawal from the JCPOA makes it more likely Iran will restart its nuclear weapons program in the future
- The U.S. stands isolated in its decision. Europe and other powers (UN permanent members) should stick together to respect the mandate of an international agreement. Any sanctions imposed by U.S. will hurt the global economy and may force Iran to stock nuclear weapons, further complicating the situation.
- Thus, the need of the hour is to standby with the agreement even after the U.S. has withdrawn.
SUBSTANTIVE EQUALITY: ON SC/ST GOVERNMENT STAFF
13, May 2019

why in news:
- The Supreme Court on Friday upheld the validity of a new Karnataka law granting reservation in promotions to Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe (SC/ST) employees.
Background: / Various judgements related to SC/ST reservations in promotion:
-
Indhira Sawhney Case (1992):
- In Indira Sawhney case, where it was held that once SCs and STs were part of the Presidential List under Articles 341 and 342 of the Constitution, and there was no need to prove backwardness.
- Hence, SC ruled that States need not collect quantifiable data on the backwardness of SC/ST for giving quota in job promotion to SC/ST employees.
- It had not made any changes to application of ‘creamy layer’ principle in reservation in promotion of SC/STs.
2. Nagaraj Case (2006):
- The Supreme Court had held that the state was not bound to provide reservation in promotions to SCs/STs.
- But in case any state wished to make such a provision, it was required to –
- Collect quantifiable data on backwardness of the
- Prove its inadequate representation in public
- Show no compromise on efficiency of
- Additionally, the state was also required to ensure that the reservation does not breach the 50% ceiling.
- The ruling also said that the ‘creamy layer’ concept applies to SCs and STs for promotions in government jobs.
3. Jarnail Singh Case (2018):
- The court set aside the requirement to collect quantifiable data that was stipulated by its 2006 verdict in M. Nagaraj v. Union of India as it ignored the reasoning of a nine-judge bench in Indra Sawhney (1992) that any discussion on creamy layer “has no relevance” in the context of SC/STs.
- The court has taken more than a decade to correct an anomaly in the Nagaraj case which brought in a creamy layer filter for promotions for SC/ST employees. This resulted in thousands of employees being denied their due promotions.
Way Ahead:
- The court said special measures need to be adopted for considering the claims of SCs and STs in order to bring them to a level playing field. Centuries of discrimination and prejudice suffered by the SCs and STs in a feudal, caste-oriented societal structure poses real barriers of access to opportunity, it pointed out.
IMF TO LOAN FOR PAKISTAN
13, May 2019
why in news:
- Pakistan will get loan of $6 billion for 3 years-IMF.
Background: / How strained is Pakistan’s economy?
- Pakistan’s economy has been ruined in the last 8 months, and almost every indicator has deteriorated substantially.
- It is marked since Imran Khan became Prime Minister and his party, the Pakistan Tehreek- e-Insaf (PTI), formed the government.
IMF:
- Inflation, at 9.4%, is at its highest level in five-and-a-half years and is likely to rise to double digits for the months ahead.
- The rupee continues to lose value every other day, which adds to further inflation especially with the oil price on the way up.
- The fiscal deficit is about to hit more than 6% of GDP.
- Even a cut in development expenditure will not stop this trend, as defence spending and interest payments continue to rise. Pakistan’s exports, stuck at around $26 bn for years, despite the 35% devaluation of the rupee over one year, have barely recovered.
- Besides, the government owes power producing companies huge amounts of money and the debt continues to accumulate. Interest rates are also going up making the cost of business even more uncompetitive. The GDP grew by 5.8% in the last fiscal year, the highest in 13 years.
- But the State Bank of Pakistan recently lowered the expectations of GDP growth for the current fiscal year to an 8-year low, to around 3.5%.
- This was reduced further by the IMF and the World Bank to a dismal 2.9% for the current fiscal year. It is expected to fall further over the next 3 years. By all accounts, Pakistan’s economy is in a dismal state.
HQ – Washington
- Official language – Chinese, English, French, Russian, Spanish, Arabic Formally created in 1945 by 29 member countries
- Stated goal was to assist in the reconstruction of world’s international payment system post World War II. Countries contribute funds to a pool through a quota system from which countries with payment imbalances temporarily can borrow money and other resources.
Organization’s objectives as stated in the Articles of Agreement:
- To promote international economic co-operation,
- To promote international trade,
- To promote employment and exchange-rate stability,
- Make financial resources available to member countries to meet balance of payments needs.
Upon initial IMF formation, its two primary functions were:
- To oversee the fixed exchange rate arrangements between countries To provide short-term capital to aid balance of payments
For A Full Bench: On Recommendations For Judicial Appointments
11, May 2019

Why in News:
- The government and the Supreme Court collegiums disagree on recommendations for judicial appointments.
Details:
- The latest concerns Jharkhand High Court Chief Justice Aniruddha Bose and Gauhati High Court Chief Justice A.S. Bopanna, who were recommended for elevation to the Supreme
- The government had sought a reconsideration of the two names.
- The collegium has now repeated its recommendations, emphasising that there is nothing adverse against the two judges in terms of their “conduct, competence and integrity” and that there is no reason to agree with the government. Under the present procedure, the government is now bound to accept the
- The Supreme Court is keen to fill up the current
- It has also recommended two more judges, Justice B.R. Gavai of the Bombay High Court and Chief Justice Surya Kant of the Himachal Pradesh High Court, for appointment to the apex court. If all these four recommendations go through, the court will have its full complement of 31
- The filling up of vacancies is a continuous and collaborative process involving the executive and the judiciary, and there cannot be a time frame for
- It is time to think of a permanent, independent body to institutionalise the process.
Collegium system
- Collegium system in India is the system by which the judges are appointed by the judges
- only also referred to as “Judges- selecting- Judges”.
- It is the system of appointment and transfer of judges that has evolved through judgments of the Supreme Court, and not by an Act of Parliament or by a provision of the Constitution.
- The Supreme Court collegium is headed by the Chief Justice of India and comprises four other senior most judges of the A High Court collegium is led by its Chief Justice and four other senior most judges of that court.
- Names recommended for appointment by a High Court collegium reaches the government only after approval by the CJI and the Supreme Court
- The government is bound to appoint a person as a Supreme Court judge if the collegium reiterates its recommendation.
Karnataka law on Sc/St Promotion Quota upheld
11, May 2019

why in news:
- The Supreme Court upheld the constitutional validity of a 2018 Karnataka law, granting reservation in promotion and consequential seniority to the Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe employees in the state.
Background:
- The Karnataka law grants reservation to non-IAS cadre government employees who belong to SC/ST The issue dates back to 2002 when the Karnataka government had enacted a similar law that was later upheld by a constitutional bench in 2006.
- However, it was challenged in 2011 and in 2017 the apex court had said it was necessary for the government to provide material that there was “compelling necessity” for exercise of such powers that eventually resulted in 3,799 SC/ST employees, promoted earlier, to be The state government had constituted a committee under then chief secretary K.Ratna Prabha to study the backwardness of these communities. The Karnataka government took the ordinance route in August 2017 to circumvent an apex order in February earlier that year that struck down reservations on promotions to SCs/STs by the Karnataka government and had also set a deadline of three months to reverse the promotions.
Controversy:
- In the Indira Sawhney case, the Supreme Court held that the “test or requirement of social and educational backwardness cannot be applied to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, who indubitably fall within the expression ‘backward class of citizens
Judicial Appointment Contraversy
11, May 2019

Why in News:
- Supreme Court Collegium, led by Chief Justice of India Ranjan Gogoi, recommended the names of two judges to the court and rejected the government’s disapproval of the elevation of two others.
Background:
- Collegium refused the government’s request to reconsider its April 12 recommendation to elevate Jharkhand High Court and Gauhati High Court Chief Justices Aniruddha Bose and
- S. Bopanna as Supreme Court judges.
- The Collegium said their names were recommended after all parameters were The Collegium said there was no reason to agree with the government as there was
- nothing adverse found in the two judges’ conduct, competence or integrity. Now, the government is bound to appoint Justices Bose and Bopanna to the court.
What is the Collegium System?
- The Collegium System is a system under which appointments/elevation of judges/lawyers to Supreme Court and transfers of judges of High Courts and Apex Court are decided by a forum of the Chief Justice of India and the four senior-most judges of the Supreme Court.’ There is no mention of the Collegium either in the original Constitution of India or in successive
- The recommendations of the Collegium are binding on the Central Government; if the Collegium sends the names of the judges/lawyers to the government for the second
How Collegium System Works?
- The Collegium sends the recommendations of the names of lawyers or judges to the Central Government. Similarly, the Central Government also sends some of its proposed names to the Collegium. The Central Government does the fact checking and investigate the names and resends the file to the Collegium.
- Collegium considers the names or suggestions made by the Central Government and resends the file to the government for final approval. If the Collegium resends the same name again then the government has to give its assent to the names. But time limit is not fixed to reply. This is the reason that appointment of judges takes a long time.
N. Korea fires missiles as U.S. envoy visits Seoul
10, May 2019

Why in news
- North Korea fired two short-range missiles, the South’s military said, less than a week after its leader, Kim Jong-un, oversaw the test-firing of multiple rockets and a missile
Details:
- The launches came as U.S. special envoy for North Korea Stephen Biegun was in Seoul for talks with Foreign Minister Kang Kyung-wha and his counterpart, nuclear envoy Lee Do-hoon.
- South Korea’s President said the tests seemed to be a protest by the North after Mr. Kim and U.S. President Donald Trump failed to reach agreement on the North’s nuclear weapons and missile arsenal at a February summit. “North Korea seemed to be discontented it could not reach a deal in Hanoi,
- The two missiles were fired from the northwest area of Kusong, in an easterly direction, They covered distances of 420 km and 270 km and reached an altitude of about 50 km before falling into the sea,
- South Korea’s presidential Blue House called the missile launches “very worrisome” and unhelpful for efforts to reduce tensions on the peninsula and improve Korean relations.
- even if the missiles were short range, they could still violate UN resolutions barring North Korea from developing its ballistic missile force.
About Missile Test Objective:
- The purpose of drill was to test operating ability and accuracy of multiple rocket launchers and tactical guided weapons and also to increase country’s combat ability. This could be North Korea first short range missile launch after more than a year since it is in talk with US for nuclear disarmament
- Pressure tactics of test: The attempt seeks to put pressure on US in aftermath of deadlocked nuclear talks between leader Kim Jong-un and US President Trump in their second meeting held at Vietnam.
- Importance for US: As US heads into 2020 presidential election, this move by North Korea may threaten signature diplomatic initiative by President Trump depriving him of opportunity to declare that he brought peace with Island Nation (which his predecessors failed). But, in reality peace never got very far as even suspension of all nuclear and missile testing hangs in balance. As per USA’s intelligence agencies report to Congress North Korea in 2018 produced more nuclear material and fabricating an unknown quantity of it into new weapons.
Loud and clear: on India-U.S. discord on market access
10, May 2019

Why in news
- New Delhi must snap out of its denial on the discord with the U.S. on market access
Details:
- U.S. Commerce Secretary Wilbur Ross lashed out at what he called India’s unfair trade practices and “overly restrictive market access barriers”. His comments followed a series of measures by the U.S. that have affected India.
- These include a refusal to revoke or waive tariff increases made last year on steel and aluminium, an ultimatum that India “zero out” oil imports from Iran even without securing comparable alternatives, and the decision to withdraw India’s GSP (Generalised System of Preferences) trade status.
- India is a “tariff king”, and threatened India with “consequences” if it responded to U.S. tariffs with counter-tariffs,
- New Delhi and Washington need to make a more determined attempt to sort out issues, starting from scratch if required, with tariffs.
- While the 50-60% duties on motorcycles and cars and 150% duties on American liquor that India imposes need a second look, the U.S. must see that average tariffs imposed by India (13.8%) are not much higher than those levied by economies such as South Korea and Brazil.
- In addition, the government will need to revisit some of its decisions like data localisation requirements and new e-commerce regulations, which were declared suddenly, while the U.S. must show some flexibility on India’s price caps on coronary stents and other medical devices
- The U.S. must understand the cultural differences over the labelling of non-vegetarian dairy products
- New Delhi will have to work closely with other countries to build alternative financial structures to avoid U.S. sanctions.
Why the United States matters to India?
- America remains the critical stabilizing force in Asia through its military and diplomatic power projection and commitments to the region
- India will be better able to protect its national interests in Pakistan and Afghanistan in coordination with the United States.
- The United States has also remained one of the top sources of foreign direct investment in India, bringing important managerial expertise, capital, and technology with it to the dynamic Indian market.
Assam NRC: Supreme Court frowns on foreigners’ tribunals plan
10, May 2019

Why in news
- The Supreme Court questioned a proposal by the Assam government to quickly throw open 1,000 foreigners’ tribunals all over the northeastern State to try suspected illegal immigrants.
Details:
- A Bench led by Chief Justice Ranjan Gogoi said it looked like the State government hatched the plan without bothering to conduct a “basic study” of how to carry it out.
- A 1,000 tribunals means a 1,000 judicial officers to preside over them.
- The CJI hinted at the possible flood of petitions which would hit the foreigners’ tribunals once the final NRC was published
- These petitions would be from people who had not been able to prove their Indian citizenship.
- The court, which is also examining the plight of 900-odd illegal immigrants languishing in Assam’s detention centres for years, said it was in favour of releasing them.
What is National Register of Citizens (NRC)?
- National Register of Citizens, 1951 is a register prepared after the conduct of the Census of 1951 in respect of each village, showing the houses or holdings in a serial order and indicating against each house or holding the number and names of persons staying therein.
Who is a citizen in Assam?
- The Citizenship Act of 1955 was amended after the Assam Accord for all Indian-origin people who came from Bangladesh before January 1, 1966 to be deemed as citizens. Those who came between January 1, 1966 and March 25, 1971 were eligible for citizenship after registering and living in the State for 10 years while those entering after March 25, 1971, were to be deported.
Impact
- An updated NRC is likely to put an end to speculations about the actual number of illegal migrants in Assam in particular and the country in general.
- It will provide a verified dataset to carry out meaningful debates and implement calibrated policy measures.
- Publication of an updated NRC is expected to deter future migrants from Bangladesh from entering Assam illegally.
- The publication of the draft NRC has already created a perception that staying in Assam without valid documentation will attract detention/jail term and deportation.
- More importantly, illegal migrants may find it even more difficult to procure Indian identity documents and avail all the rights and benefits due to all Indian citizens.
- Inclusion of their names in the NRC will provide respite to all those Bengali speaking people in Assam who have been, hitherto, suspected as being Bangladeshis.
Way Forward
- India, as a country which follows the ideology of ‘VasudhaivaKutumbakam’, should not be hasty in taking decisions that can disenfranchise her citizens – contradicting its centuries-followed values.
- The need of the hour is that Union Government should clearly chart out the course of action regarding the fate of excluded people from final NRC data and political parties should refrain from coloring the entire NRC process through electoral prospects that may snowball in to communal violence.
- There is a need for a robust mechanism of legal support for the four million who have to prove their citizenship to India with their limited means.
Europe rejects Iran’s ‘ultimatum’ but stands by nuclear agreement
10, May 2019

Why in news:
- European powers denounced Iran’s threat to resume nuclear work but vowed to save a landmark deal with Tehran despite U.S. pressure.
Details:
- Iran said it would defylimits under the 2015 agreement, and threatened to go further if Europe, China and Russia fail to deliver sanctions relief within 60 days.
- Tehran says it is responding to unilateral U.S. sanctions imposed after President Donald Trump called a “horrible” deal, dealing a severe blow to the Iranian economy.
Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA)
- It is informally called as ‘Iran nuclear deal’. It is multilateral nuclear deal signed between Iran and P5 +1 (five permanent members of United Nations Security Council- US, China, France, Russia, and UK), plus Germany and European Union (EU), in Vienna.
- The JCPOA is aimed at preventing Iran from building nuclear weapon, involved lifting of international sanctions in return for Tehran curbing its nuclear programme.
- This plan ensured that Iran will drastically reduce its uranium enriching capacity and levels, enriched stockpiles and centrifuges and will allow for stringent inspection and monitoring by international agencies including International International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
- In exchange for Iran compliance to deal, economic sanctions that had kept Iran away from international banking and the global oil trade were lifted.
- It allowed Iran to make business deals and also unfroze billions of dollars Iran had overseas before multilateral sanctions were imposed on Iran over its nuclear programme.
Why did Iran agree to the deal?
- It had been hit with devastating economic sanctions by the United Nations, United States and the European Union that are estimated to have cost it tens of billions of pounds a year in lost oil export revenues. Billions in overseas assets had also been frozen.
Impact on India
- Energy trade
- Implications in West Asia
- Chabahar port
U.S. THREATENS TO IMPOSE MORE SANCTIONS ON IRAN
09, May 2019

Why in News:
- USA advises European countries against doing business with Tehran; Russia, China reiterate opposition to punitive steps
Details:
- The U.S. threatened to impose more sanctions on Iran “very soon” and warned Europe against doing business with Tehran via a system of non-dollar trade to circumvent U.S. sanctions.
- It is the time for the community of nations to strongly condemn Iran’s nuclear misconduct and increase pressure on the regime to comply with U.S. demands,” US said, adding that Washington was not “done” with sanctions on Iran. “
Special Purpose Vehicle
- U.S. would move quickly against any attempt by European countries to undermine Washington’s sanctions pressure on Iran
- US advised them against using the so-called Special Purpose Vehicle to facilitate non-dollar trade to get around U.S. sanctions.
- Washington’s European allies opposed Mr. Trump’s decision to withdraw from the agreement and have failed so far to find ways to blunt the economic impact of new U.S. sanctions, which include an all-out effort to block Iran’s oil exports to starve its economy.
- Russia remained committed to the Iran nuclear deal and denounced “unreasonable pressure” that led Tehran to suspend some of its commitments under the agreement.
- China called on all parties to uphold the nuclear pact. “Maintaining and implementing the comprehensive agreement is the shared responsibility of all parties
US-Iran Relations:
- United States and Iran established diplomatic relations in 1883.
- US-Iran wasn’t very complex before World War II, but it soon turned chaotic when the US’s CIA helped stage a coup to overthrow Iranian Prime Minister Mohammad Mossadegh in 1953. Later after several years the US offered Iran a nuclear reactor and weapons-grade nuclear fuel in 1967
- Once again, the diplomatic crisis erupted in 1988, When a US Navy ship was shot down an Iranian passenger plane, killing 290 people who were onboard.
- Hassan Rouhani was elected president in Iran. US-Iran Nuclear Deal was signed.
- US President Donald Trump pulled the U.S. out of the deal in 2018 and gets ready to impose sanctions over its nuclear program and claims the country is supporting militant groups in the gulf.
TAKING TENSIONS SERIOUSLY: INDIA AND THE U.S.
09, May 2019

Why in News:
- A true strategic partnership remains elusive between India and the U.S.
Details:
- The U.S.’s decision to not extend Iran sanctions waivers, including the one provided to India, has notable implications for India-
- U.S. relations, given the importance of New
- Delhi’s energy relationship with Tehran.
- It comes on the heels of many other deleterious developments for bilateral ties including the U.S.’s decision to withdraw GSP benefits for Indian exports and the Trump administration’s discontent deepening over India’s policies on e-commerce, intellectual property rights and data localisation.
- the non-security dimension of the relationship has long lagged behind the fast-growing defence side. India will scale up oil imports from other top producers; the GSP withdrawal will have minimal impact on India’s economy; the two capitals are working actively on high levels, most recently through the U.S.-India CEO Forum and the India-U.S. Commercial Dialogue, to ease tensions; and above all the strength of the bilateral relationship can easily withstand all these headaches.
- India-U.S. relations extend well beyond security.
- joint statements have dwelt on the potential for cooperation on initiatives ranging from clean energy to innovation. And despite the problems, bilateral trade in goods and services has increased over the last decade
India-USA: Five Pillars of Strategic Partnership
- Strategic Issues
- Energy and Climate
- Change Science and Technology
- Health and Innovation Education and Development
Why the United States matters to India?
- America remains the critical stabilizing force in Asia through its military and diplomatic power projection and commitments to the region
- India will be better able to protect its national interests in Pakistan and Afghanistan in coordination with the United States.
- The United States has also remained one of the top sources of foreign direct investment in India, bringing important managerial expertise, capital, and technology with it to the dynamic Indian market.
KOLAM TRIBE
09, May 2019

Why in News:
- Four children belonging to the aboriginal Kolam tribe from Narnoor mandal in Adilabad district died after food poisoning
Details
- Kolam are a designated Scheduled Tribe in the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh Chhattisgarh Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.
- They belong to the sub-category Particularly vulnerable tribal group, one of the three belonging to this sub-category.
- They speak the Kolami language, they are an agricultural community. The Kolam are an endogamous group.
- They have a high rate of returning positive to the Naked eye single tube red cell osmotic fragility test (NESTROFT) test, making them prone to high incidence of Thalassaemia.
Government initiative for tribes:
- The Tribal Sub Plan (TSP) strategy is a Government of India initiative aimed for the rapid socio-economic development of tribal people.
- The National Commission for Scheduled Tribes is vested with the duty to participate and advise in the planning process of socio-economic development of STs, and to evaluate the progress of their development under the Union and any State.
IRAN SAYS IT WILL NOT HONOUR NUCLEAR CURBS
09, May 2019

Why in News
- Iran said it had stopped respecting limits on its nuclear activities agreed under a 2015 deal with major powers
Details:
- The announcement came as Washington stepped up its rhetoric against Tehran, accusing it of planning “imminent” attacks and deploying an aircraft carrier strike group with several nuclear-capable B-52 bombers to the region
- Iran said it was responding to the sweeping unilateral sanctions that Washington has reimposed since it quit the agreement one year ago, which have dealt a severe blow to the Iranian economy. Iran’s Supreme National Security Council said that it no longer considered itself bound by the agreed restrictions on stocks of enriched uranium and heavy water.
What did Iran do over the deal and why?
- It suspended two parts of the deal, known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), namely the sale of surplus enriched uranium and heavy water. Under the deal, Iran is required to sell its surplus enriched uranium – which can be used in the manufacture of nuclear weapons – abroad, rather than keep it.
Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA)
- The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) known commonly as the Iran deal, is an international agreement on the nuclear program of Iran reached in Vienna on 14 July 2015 between Iran, the P5+1 (the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council—China, France, Russia, United Kingdom, United States—plus Germany),and the European Union.
What is Instex?
- It’s a new payments mechanism set up by the UK, France and Germany to allow businesses to trade with Iran without being subject to sanctions. It is supposed to focus on “legitimate trade” in goods “where the immediate need of the Iranian people is greatest”, for example food, pharmaceutical products and consumer goods not subject to sanctions. Oil, Iran’s main source of foreign exchange, is at the moment not covered and Tehran wants the Europeans to give the system more bite.
- But that could put traders at loggerheads with the US sanctions.
IRAN TO REDUCE COMMITMENTS TO NUCLEAR DEAL
08, May 2019

Why in News:
- Iran is expected to announce plans to scale back compliance with a landmark nuclear deal on the anniversary of the United States decision to withdraw from the international accord.
Details:
- The US unilaterally withdrew on 2018, from the 2015 multilateral deal known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) under which Iran agreed to curb its nuclear programme in exchange for the lifting of biting sanctions.
- Iran will convey details of the “decision to reduce its commitments” to ambassadors of the five countries still party to the agreement – Britain, China, France, Germany and Russia.
- The US also blacklisted Iran’s elite Revolutionary Guard Corps as “terrorists”, and announced it was deploying a naval strike group to the Middle East because of indications of a “credible threat from Iranian regime forces”.
- Iran dismissed the move as “psychological warfare”
Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA)
- The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) known commonly as the Iran deal, is an international agreement on the nuclear program of Iran reached in Vienna on 14 July 2015 between Iran, the P5+1 (the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council—China, France, Russia, United Kingdom, United States—plus Germany),and the European Union.
B2B TECH START-UPS TREBLE IN 5 YEARS: STUDY
08, May 2019

Why in News:
- Business-to-business (B2B) technology start-ups have more than trebled in the last five years driven by the spurt in the need for digital transformation of enterprises, financial institutions, hospitals, government and small and medium enterprises (SMEs), among others.
Details:
- While the number of such ventures has increased from 900 to over 3,200, the investment in such start-ups touched $3.7 billion in 2018, a rise of 364% from $797 million in 2014, as per a study
- According to the study, 70% of the B2B start-ups are in the area of enterprise technology, financial technology and health technology.
Growth of B2C
- However, the growth in the number of B2C technology start-ups has been comparatively slower since there were 2,200 such B2C ventures in 2014.
- Within the B2B technology segment, ‘advanced tech start-ups’ have grown at a higher pace when compared to the entire technology start-up segment.
- Advanced B2B tech start-ups typically deal in 3D printing, blockchain and robotic process automation.
Bengaluru leads
- Bengaluru is the top city for B2B technology start-ups followed by Delhi NCR and Mumbai, with the three cities accounting for about 60% of all B2B technology start-ups.
- Further, Hyderabad, Pune and Chennai are poised to be the growing start-up hubs on account of flexible economic policies, State government support and access to various industries.
- There are over 50 corporate accelerators and incubators in the country, focussing on technologies such as AI/ML, Big Data, Cloud, Blockchain, Cybersecurity, among others,”
Different types of e-commerce
- Business-to-business (B2B)
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- Business-to-government (B2G)
- Consumer-to-consumer (C2C)
- Government to consumer (G2C)
- Government-to-business (G2B)
BELT AND ROAD 2.0
08, May 2019

Why in News:
- With the second Belt and Road Forum, a paradox is now apparent at the heart of the initiative.
Details:
- Six years after it was unveiled, China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) assumes another avatar. In its initial form, it was all things to all people, a catch-all for China’s international engagement. The first concerned domestic economics: exporting surplus industrial capacity and cash reserves overseas to keep China’s economy humming, its industrial output flowing, and its employment levels high.
- The second concerned domestic politics: a signature foreign initiative to associate with Chinese President Xi Jinping. The third concerned security: stabilising Western provinces
- and the Eurasian hinterland. And the fourth concerned strategy: leveraging China’s new- found economic heft for political objectives in Asia, Africa, Europe, and the Indian and Pacific Oceans, and creating new standards and institutions in a bid to challenge U.S. leadership. As the second Belt and Road Forum (BRF) concludes, a paradox has become apparent at the heart of its ambitious initiative. On the one hand, there has been a strong backlash. The economic viability of Chinese projects is now viewed with considerable scrutiny.
- security concerns have begun to predominate as far afield as in the European Union, the South Pacific and Canada.
The Belt and Road Initiative
- The Belt and Road Initiative is a Chinese foreign policy initiative promoted by president Xi Jinping in 2013. Initially the idea of Silk Road Economic Belt (SREB) and Maritime Silk Road (MSR) was put forward. Subsequently, the two projects together came to be known as ‘One Belt One Road’ (OBOR) Initiative. Later, it came to be known as Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). Aim of BRI. Build a trade, investment, and infrastructure network connecting Asia with Europe and Africa along the ancient trade routes. The Communist Party of China (CPC) has incorporated Belt and Road Initiative into the Chinese Constitution.
India and BRI
- India has opposed the BRI and did not attend the 2017 BRI Summit held in Beijing. It cited issues of sovereignty, transparency and unilateral decision making.
SC TURNS DOWN OPPOSITION PLEA FOR INCREASED VVPAT VERIFICATION
08, May 2019
Why in News:
- The Supreme Court on Tuesday dismissed a plea by 21 Opposition parties to review its judgment rejecting 50% random physical verification of Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) using Voter-Verified Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT).
Details
- On April 8, a Bench led by Chief Justice Ranjan Gogoi had directed the Election Commission of India (ECI) to increase physical counting of VVPAT slips to five random EVMs in each Assembly segment/constituency.
Fool-proof’ polls
- Its April verdict, the court had assured the petitioners, would ensure a ‘fool-proof’ Lok Sabha polls 2019.
- The Opposition had found the Supreme Court’s April 8 verdict a far shot from what it
- wanted — VVPAT verification in 50% or 125 polling booths in each constituency.
- The physical scrutiny of slips in five EVMs has increased the VVPAT verification percentage from .44% to less than 2%.
VVPAT
- Voter-verified paper audit trail (VVPAT) is a device which dispenses a slip with the symbol of the party for which a person has voted for. The slip appears on a small window for seven seconds and then drops in a box. The voter cannot take it home. VVPAT displays
- candidate’s serial number. Name of the candidate and Corresponding symbol for whom the vote has been cast.
Advantages in VVPATs:
- Enables to verify vote: Instant feedback to voter that vote polled has been allocated to the intended candidate.
- Enables authorities to count the votes manually if there is a dispute in the electronically polled votes.
- Operates under a Direct Recording Election system (DRE) which detects fraud and existent malfunctions.
- Will ensure greater transparency in voting process. Gives both the voters and political parties an assurance.
M3 EVMs
- M3 EVMs are the third generation EVMs. The M3 EVMs can keep data of 384
- candidates. M3 EVMS also has added features like Tamper Detection and Self Diagnostics. The tamper detection feature makes an EVM inoperative the moment anyone tries to open the machine. The Self diagnostic feature checks the EVM fully every time it is switched on. Any change in its hardware or software will be detected.
CJI SEXUAL HARASSMENT CASE: HAVE A RIGHT TO COPY OF BOBDE PANEL REPORT, SAYS COMPLAINANT
08, May 2019

Why in News:
- The former apex court staffer wrote to the in-house panel, which found “no substance” in her sexual harassment allegations against the CJI.
Details:
- If a copy of the report is being given to the CJI directly or indirectly, I am entitled to a copy thereof in any case,” the woman appealed to the committee.
- The Sexual Harassment of Women at the Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013, in Section 13 provides that both parties have a right to receive a copy of the report.
- Not providing a copy to the complainant while holding her complaint to be unfounded would be a violation of the principles of natural justice and a complete travesty of justice,” the Supreme Court is relying on a judgment which pre-dates the Right to Information (RTI) Act of 2005 which mandates the fundamental right to information.
Under RTI:
- The complainant she quoted a full-bench judgment of the Delhi High court in the case of disclosure of assets of judges, saying “the full bench had held that even assets of judges would be accessible under RTI to any citizen”
- The complainant said she had been treated as an “outsider” from the very beginning of the inquiry process.
What were the earlier Vishaka guidelines?
- The Vishaka guidelines were laid down by the Supreme Court in Vishakha and others v State of Rajasthan judgment in 1997.
- It imposes three key obligations on employing institutions – prohibition, prevention, and redress. The institutions are mandated to establish a Complaints Committee.
- This was to look into matters of sexual harassment of women at the workplace. These guidelines are legally binding
Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace
- Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Actwas passed in 2013. It broadens the Vishaka guidelines, which were already in place.
- An aggrieved victim is a woman “of any age whether employed or not”, who “alleges to have been subjected to any act of sexual harassment”.
- The Act thus covers the rights of all women working or visiting any workplace, in any capacity. Sexual harassment is any one or more of “unwelcome acts or behaviour”, committed directly or by implication.They include:
- Physical contact & advances
- A demand or request for sexual favours Sexually coloured remarks
- Showing pornography
- Any other unwelcome physical, verbal or non-verbal conduct of sexual nature






