Category: Newer Invention
SEISMIC NOISE
17, Apr 2020
Why in News?
- Amid this coronavirus lockdown, British Geological Survey (BGS) scientists have reported a change in the Earth’s seismic noise and vibrations.
- Few weeks ago, the Royal Observatory in Belgium observed a 30-50% fall in levels of seismic noise since schools and businesses were closed during this lockdown.
What is Seismic Noise?
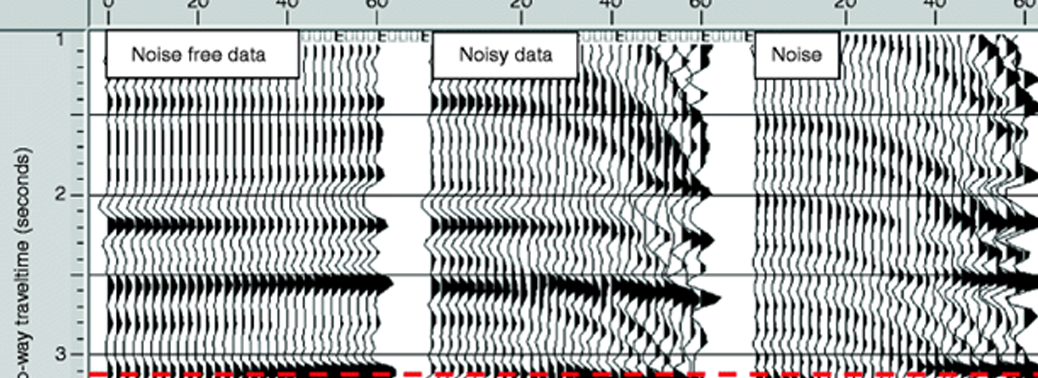
- Seismic noise refers to the relatively persistent vibration of the ground due to a multitude of causes. This noise includes vibrations caused due to human activity, such as transport and manufacturing.
- It is the unwanted component of signals recorded by a seismometer and makes it difficult for scientists to study seismic data that is more valuable.
- Scientists first observed this seismic noise everything recorded on seismograms that cannot be attributed to earthquakes at the end of the 19th
Advantages of Reduced Seismic Noise:
- Usually, to measure seismic activity accurately and reduce the effect of seismic noise, geologists place their detectors 100 metres below the Earth’s surface.
- Because, the seismic noise vibrations caused by human activity are of high frequency (between 1-100 Hz), and travel through the Earth’s surface layers.
- However, since the lockdown, researchers have said that they were able to study natural vibrations even from surface readings, owing to lesser seismic noise.
- Due to lower noise levels, scientists are now hoping that they would be able to detect smaller earthquakes and tremors that had slipped past their instruments so far.
What is a Seismometer?
- Seismometer is the scientific instrument that records ground motions, such as those caused by Earthquakes, volcanic Eruptions, and Explosions.
- These are incredibly sensitive so they also pick up other sources of vibration too, including human activity, such as road traffic, machinery and even people walking past.
ROLE OF GLUCOSE IN REGULATING LIVER FUNCTIONS
16, Mar 2020
Why in News?
- The recent study by researchers from the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai (TIFR) has revealed that glucose in the body controls the function of SIRT1 directly.
What is SIRT1?
- SIRT1 is an enzyme that de-acetylates (removal of acetyl) proteins and contribute to cellular regulation (reaction to stressors, longevity).
Functions:
- In normal healthy individuals, SIRT1 protein levels are known to increase during fasting and decrease during the feed, which is essential to maintain a balance between glucose and fat metabolism.
- The glucose controls the functions of a protein SIRT1 which in turn maintains everyday feed-fast cycles and is also associated with longevity.
- The feed-fast cycle is a basic pattern and the metabolism-related to this is largely taken care of by the liver.
- Thus, the study shows that both over-activation and under-activation of SIRT1 can lead to diseases.Glucose puts a check on the activity of SIRT1 in the fed state. In the absence of this check, SIRT1 activity increases and results in hyperglycemia in a fasted state, mimicking diabetic state.
- The constant feeding or high-calorie intake that leads to a sustained reduction in the levels of SIRT1 (by glucose) is associated with ageing and obesity.
Significance of the Study:
- A shortage or absence of the control of SIRT1 by glucose may lead to a diabetic-like state, while excess feeding and sustained low levels of SIRT1 can lead to obesity and enhanced ageing.
- This study paves the way might be beneficial in tackling lifestyle disorders and ageing-Related Diseases.
LI-ION BATTERIES
10, Feb 2020

Why in news?
- Recently, India has quadrupled its imports of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries.
Key Points:
- Indian manufacturers source Li-ion batteries from China, Japan and South Korea.
- India is the largest importers in the world. China dominates the LI-ion batteries market.
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) manufactures such batteries but volumes are limited and they are restricted for use in space application.
- To promote indigenous development of such batteries, the union Cabinet in 2019 approved a programme called National Mission on Transformative Mobility and Battery Storage, under the NITI Aayog.
About National Mission on Transformative Mobility and Storage:
- The Mission will have an Inter-Ministerial Steering Committee chaired by Chief Executive Officer (CEO), NITI Aayog to promote clean, connected, shared, sustainable and holistic mobility initiatives.
- The Mission will launch the Phased Manufacturing Programmes (PMP) for Batteries and for Electric Vehicle components.
About Li-ion Battery:
- A lithium-ion battery or Li-ion battery (abbreviated as LIB) is a type of rechargeable battery.
- It is commonly used for portable electronics and electric vehicles and are growing in popularity for military and aerospace applications.
- It is the lightest metal on the periodic table, and the one most willing to donate its electrons (The Most Powerful Reducing Agent).
- From portable electronics like the smartphone to high performance electric cars like the Tesla Model S, lithium ion batteries are currently the most promising chemistry on the market for meeting our renewable energy storage needs.
Advantages of Lithium Ion batteries:
- High energy density – potential for yet higher capacities.
- Does not need prolonged priming when new. One regular charge is all that’s needed.
- Relatively low self-discharge – self-discharge is less than half that of nickel-based batteries.
- Low Maintenance – no periodic discharge is needed; there is no memory.
- Specialty cells can provide very high current to applications such as power tools.
VIRTUAL AUTOPSY
09, Dec 2019

Why in News?
- India will be the first country in South and Southeast Asia to carry out these “virtual autopsies
Virtual Autopsy:
- An autopsy (Postmortem Examination, Autopsia Cadaverum, or Obduction) is a highly specialized surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse to determine the cause and manner of death and to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present.
- Virtopsy is a word combining ‘virtual’ and ‘autopsy’ … for the purpose of autopsy and to find the cause of the death. Virtopsy can be employed as an alternative to standard autopsies for broad and systemic examination of the whole body as it is less time consuming, aids better diagnosis, and renders respect to religious sentiments.”
- In a virtual autopsy, doctors use radiation to examine the innards to reach a conclusion about the cause of death. A CT or an MRI machine could be used, in the same way that they are used to scan a living human’s body.
Need:
- According to a paper in The Lancet, the advent of virtual autopsy owes to the “Longstanding public objection to dissection of cadavers (that) re-emerged in the UK as a major issue after organ retention scandals in the late 1990s.
- Some groups —notably Jewish and Muslim communities — have religious objections to autopsy, and demand for a minimally-invasive alternative has increased.” (‘Post-mortem imaging as an alternative to autopsy in the diagnosis of adult deaths: a validation study’: 2012, Ian S D Roberts et. al)
- A virtual autopsy is also faster than a traditional one — 30 minutes against 2½ hours, and more cost-effective.
International Examples:
- Virtual autopsy began in Sweden, but is now a “standard technique” in major centres in Japan, the US, Australia, and many European countries.
Accuracy of Virtual Autopsy:
- In 2018, in an article in the Journal of Pathology Informatics, Russian and Italian scientists compared the results of virtual autopsy and Traditional Post-Mortem.
- “Out of 23 cases for which the traditional post mortem examination found a cause of death, 15 (65%) were diagnosed correctly using virtual autopsy, these cases were considered as true positives.
- For one case for which the cause of death was unascertained, the same result was also obtained during the virtual autopsy.
- This case was considered as true negative. Overall, in 16/25 (64%) cases, virtual autopsy results matched that of the traditional autopsy,” they concluded.
RADIATION TECHNOLOGY FOR SEWAGE TREATMENT
27, Jul 2019

Why in news?
Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) in collaboration with Amdavad Municipal Corporation (AMC), Ahmedabad has set up a Technology Demonstration Pilot Project “Sewage Sludge Hygienisation Plant” at Shahwadi, Ahmedabad.
Highlights:
- Large amount of sewage sludge is produced in India every day. The sludge is infectious and can spread diseases. It also has essential micro and macro nutrients, especially carbon, useful for soil and crop production.
- Radiation Technology can be used to hygienise the sludge reliably and affordably and protect health and environment. Addition of useful microorganisms to the hygienised sludge can convert it to a value-added manure
Radiation Technology:
- Ionizing radiation emitted by radiation source such as Cobalt-60 interacts with the critical molecules like DNA, proteins and water present in the cell and result in the inactivation of microorganisms.
- As a result of Irradiation, besides pathogens, other unwanted constituents like weeds, chemicals, etc. are also degraded, making the sludge safer for use
- Based on microbiological inactivation, Radiation Technology is already established world over for sterilizing medical products, food safety and food preservation. Sludge hygienisation can be carried out in the similar manner
Advantages of Radiation Technology:
- Process is simple, economic, effective, reproducible and scalable.
- Easy to integrate with conventional sewage treatment facilities.
- Process is fully automatic to avoid manual handling of contaminated sludge.
- Based on the process of radiation sterilization which is well established world over and in India.
- Degrades chemical contaminants and makes sludge safer for use.
Benefits To The Farmers/People:
- Increased crop yield – direct benefit to the farmers.
- Improved soil conditions – soil conservation & restoration.
- Reduced health risks associated with sludge, reduces costs of health care system.
- Reduced demand of water due to higher water holding capacity of the sludge.
- Radiation technology has sound scientific basis and is a practical technology to economically hygienise sewage sludge for agriculture application.
- The technology and radiation source both are available in our country. Irradiation facility can be utilised to treat whole city sludge at one place in a fully automatic process.
- The hygienised sludge can benefit farmers and protect environment and human health. The technology has high potential in contributing towards meeting the objectives of Clean India Mission (the Swachh Bharat mission).
BLACK GOLD
10, Jul 2019

Why in News?
- Using gold nanoparticles Indian scientists have developed a new material called “black gold”, which can potentially be used for applications ranging from solar energy harvesting to desalinating seawater, according to a study.
Black Gold:
- To develop the material, the team from Mumbai-based Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) rearranged size and gaps between gold nanoparticles.
- It has unique properties such as capacity to absorb light and carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Gold does not have these properties therefore ‘black gold’ is being called a new material.
- In appearance it is black, hence the name ‘black gold’, according to the findings published in Chemical Science. The researchers varied inter-particle distance between gold nanoparticles using a cycle-by-cycle growth approach by optimizing the nucleation-growth step. They used dendritic fibrous nano silica; whose fibres were used as the deposition site for Gold Nanoparticles.
Features of Black Gold:
- One of the most fascinating properties of the new material is its ability to absorb the entire visible and near-infrared region of solar light.
- It does so because of inter-particle plasmonic coupling as well as heterogeneity in nanoparticles size. Black gold could also act as a catalyst and could convert CO2 into methane at atmospheric pressure and temperature using solar energy.
- If we develop an artificial tree with leaves made out of back gold, it can perform artificial photosynthesis, capturing carbon dioxide and converting it into fuel and other useful chemicals. The efficiency of conversion of CO2 into fuel, at present, is low but researchers believe it could be improved in future. The material can be used as a nano-heater to covert seawater into potable water with good efficiency, the researchers said.
Mendeleev and his Periodic Table of Elements
18, Jun 2019
The Modern Periodic Table:
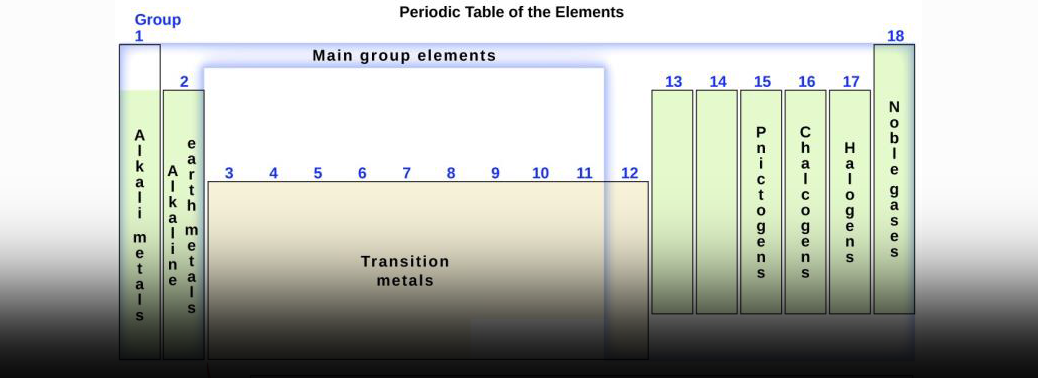
- The periodic table is an arrangement of all the elements known to man in accordance with their increasing atomic number and recurring chemical properties.
- They are assorted in a tabular arrangement wherein a row is a period and a column is a group. Until 1863, the world was aware of only 56 known elements.
- The rate of scientific progress was such that every year, a new element was being discovered. It was during this time that Mendeleev came up with the idea of the Periodic Table.
- He published the Periodic Table in his book– The Relation between the Properties and Atomic Weights of the Elements.
- Mendeleev said that he arrived at the idea in his dream, where he saw all chemical elements falling into place on a table according to their chemical properties.
- Mendeleev had found a definitive pattern following which, each element could be placed according to their atomic weight.
- He had also predicted the qualities of the ‘missing’ (yet to be discovered) elements and gave them Sanskrit names.
Evolution of the Table:
- The noble gases including helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn) were added to the table between 1895 and 1901.
- Likewise, additions have been made to the periodic table as new elements have been discovered in the last hundred years.
- In 1914, English physicist Henry Gwyn-Jeffries Moseley found out that each atomic nucleus can be assigned a number, according to the number of protons in that atom. This changed the way the periodic table worked. The table was redesigned according to the atomic number of elements rather than their atomic weight. Rare-earth elements, including the elements in the Lanthanide series, were included in the atomic table in the late 19th century.
TAWANG YIELDS A NEW SPECIES OF DUNG BEETLE
02, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- A new species of dung beetle has been discovered in Tawang district of Arunachal Pradesh.
Details:
- The species, Enoplotrupes tawangensis, is shining dark blue in colour and, measuring up to 27 mm, is relatively bigger than most of the dung beetles.
- Dung beetles belong to the super family scarabaeoidea, having clubbed antennae and pro- tibiae (pro-legs) modified for burrowing dung inside the soil.
- This group of insects are considered beneficial to the environment as they help in nutrient cycling of the soil. Often referred to as little recyclers, these scavenger beetles require mammalian dung to survive. “Insects comprise almost 65% of all animal species on the planet. From India, approximately 65,000 species of insects are known, of them, more than 22,000 species are beetles.
- Dung beetles are the one of the fascinating group of insects because of their ability to bury dung deep in the soil and are indicators of the ecological health of an ecosystem,”
- Other than the relatively large size and distinct blue colour, another important distinguishing characteristic of this species is the strong sexual dimorphism, with the fronto-clypeal horn shorter in females than males.
SCIENTISTS GIVE THE THUMBS-UP FOR ANTHROPOCENE EPOCH
29, May 2019

Why in News:
- Experts say human impact on Earth so profound that Holocene must give way to epoch defined by nuclear tests, plastic pollution and domesticated chicken
Background:
- A team of scientists have voted to declare “Anthropocene” as a new chapter in the Earth’s geological history- the new epoch. The result builds on an informal vote taken at the 2016 International Geological Congress in Cape Town, and lays the groundwork for a formal proposal by 2021 to the International Commission on Stratigraphy.
What is it?
- Coined by Paul Crutzen and Eugene Stoermer in 2000 to denote the present geological time interval, Anthropocene has been used to describe humanity’s large impact on the environment. Implications: The move signals the end of the Holocene epoch, which began 12,000 to 11,600 years ago.
Evidence of the Anthropocene
- Human activity has: Pushed extinction rates of animals and plants far above the long-term average. The Earth is on course to see 75% of species become extinct in the next few centuries if current trends continue. Increased levels of climate-warming CO2 in the atmosphere at the fastest rate for 66m years, with fossil-fuel burning pushing levels from 280 parts per million before the industrial revolution to 400ppm and rising today.
- Put so much plastic in our waterways and oceans that microplastic particles are now virtually ubiquitous, and plastics will likely leave identifiable fossil records for future generations to discover. Doubled the nitrogen and phosphorous in our soils in the past century with fertiliser use. This is likely to be the largest impact on the nitrogen cycle in 2.5bn years. Left a permanent layer of airborne particulates in sediment and glacial ice such as black carbon from fossil fuel burning.
IISC TEAM CONFIRMS BREAKTHROUGH IN SUPERCONDUCTIVITY AT ROOM TEMPERATURE
26, May 2019

Why in News:
- Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru confirms that material exhibits major properties of superconductivity at ambient temperature and pressure.
Details:
- A material is said to be a superconductor if it conducts electricity with nil resistance to the flow of electrons.
- Superconductors will help build very highly efficient devices leading to huge energy savings. Till now, scientists have been able to make materials super conduct only at temperatures much below zero degree C and hence making practical utility very difficult.
- Superconductivity at ambient temperature has been a holy grail in physics for about a century. If this [result] is correct, it would be the greatest work done in India since the discovery of Raman effect,” The material they have made is unbelievable — a tiny sphere of gold, placed 10-20 tinier spheres of silver inside it…This [material] they found shows a sharp drop in resistivity [reflecting superconducting state].
The proof:
- “Two of the most important properties of superconductivity are dimagnetism and zero resistance. These two were seen in the material.
- At 286 K there is clear transition from a normal state to a superconducting state.
What is Raman Effect?
- Some part of light beam after passing through a transparent medium gets scattered.
- This phenomenon of scattering of light is termed as Raman Scattering and the cause of scattering is called the Raman Effect.
- The wavelength of these scattered rays is different from that of the incident rays of light.
- This phenomenon was explained/discovered by Indian physicist Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (CV Raman) on February 28, 1928.
- This discovery was awarded with the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930.
India Gets Submarine Rescue System
13, Dec 2018

Context:
- The Indian Navy joined a select group of naval forces in the world on Wednesday when it inducted its first non-tethered Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicle (DSRV) system at the Naval Dockyard in Mumbai.
Details:
- With this, India joins a select league of navies with the sovereign capability in fly away configuration to search, locate and rescue crew from a disabled submarine.
- The second vehicle that is out for delivery, is expected to reach Visakhapatnam soon. It will be operational by April next year.
Need of DSRV:
- The nature of operations undertaken by submarines expose them to high degree of inherent risk. In such an eventuality, traditional methods of search and rescue at sea are ineffective for a disabled submarine. To overcome this capability gap, the Navy has acquired a third generation, advanced Submarine Rescue System considering of a non-tethered DSRV and its associated equipment.
Details of DSRV:
- Using a third-generation system, the DSRV is considered to be the most advanced system currently in operation globally.
- The DSRV is used to rescue crew members from submarines stranded under water in the high seas.
- The DSRV can be operated at a depth of 650 meters and can rescue 14 people at a time.
- The state-of-the-art system is also equipped with a decompression chamber that can accommodate submariners and a remotely operated vehicle (ROV), which can be used to beam images and provide immediate assistance.
- The Western Naval Command had recently successfully held trials with actual simulations with different classes of submarines.
- The DSRV can also be transported by air, enabling it to conduct rescue operations across the globe
- The induction of the DSRV marks the culmination of years of effort of the Navy in acquiring this niche submarine rescue capability. It is the latest in terms of technology and capability.
About Deep-submergence vehicle:
- A deep-submergence vehicle (DSV) is a deep-diving manned submarine that is self-propelled. Several navies operate vehicles that can be accurately described as DSVs.
- DSVs are commonly divided into two types: research DSVs, which are used for exploration and surveying, and DSRVs (Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicle), which can be used for rescuing the crew of a sunken navy submarine, clandestine (espionage) missions (primarily installing wiretaps on undersea cables), or both.
- DSRVs are equipped with docking chambers to allow personnel ingress and egress via a manhole.
Phosphorous Origin
19, Oct 2018

- The new study pointed out that most of the phosphorus on Earth was generated in outer space and reached Earth via meteorites and comets.
About:
- University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa researchers, in collaboration with colleagues in France and Taiwan, provide compelling new evidence that this component for life was found to be generated in outer space and delivered to Earth in its first one billion years by meteorites or comets. The team replicated interstellar icy grains coated with carbon dioxide and water, which are ubiquitous in cold molecular clouds, and phosphine.
- When exposed to ionizing radiation in the form of high-energy electrons to simulate the cosmic rays in space, multiple phosphorus oxoacids like phosphoric acid and diphosphoric acid were synthesized via non-equilibrium reactions.
- On Earth, phosphine is lethal to living beings but in the interstellar medium, an exotic phosphine chemistry can promote rare chemical reaction pathways to initiate the formation of biorelevant molecules such as oxoacids of phosphorus, which eventually might spark the molecular evolution of life as we know it.
- According to the study, phosphates and diphosphoric acid are two major elements that are essential for these building blocks in molecular biology.
Phosphorus:
- Phosphorus is a chemical element with symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth’s crust of about one gram per kilogram. With few exceptions, minerals containing phosphorus are in the maximally oxidized state as inorganic phosphate rocks.
- All living beings need cells and energy to replicate. Without these fundamental building blocks, living organisms on Earth would not be able to reproduce and would simply not exist. The phosphorus compounds were then incorporated in biomolecules found in cells in living beings on Earth. They are the main constituents of chromosomes, the carriers of genetic information in which DNA is found.
- Together with phospholipids in cell membranes and adenosine triphosphate, which function as energy carriers in cells, they form self-replicating material present in all living organisms.
Carrots make Concrete Stronger and Greener
07, Oct 2018

- A group of researchers at Britain’s Lancaster University has been using a household food blender to mix particles from the root vegetable with concrete to see if they can produce a stronger and more environmentally sound product.
About:
- There is a chemical reaction happening between the fibres and the cement. That a carrot is made up nearly entirely of water but still stays rigid and crunchy because of cellulose, a fibrous substance found in all plants. Those fibres have strength characteristics in them. It’s the building blocks of the strength of a vegetable
- The potential of the vegetable-composite concretes lies in the ability of the Nano platelets to increase the amount of calcium silicate hydrate in concrete mixtures, which is the main substance controlling structural performance. The knock-on effect means smaller quantities of concrete would be needed for construction.
- Cellulose is also found in wood, but is easier to extract from vegetables. With large amounts of vegetable waste available as a by-product of agriculture, it is a cheap and environmentally friendly source of the fibres.
- Only a tiny amount of cellulose is needed to alter the properties of cement because it changes the way water behaves during the process when cement hardens
Significance:
- It increases the strength of concrete by 80 percent by using a small amount of this new material, the addition of carrots prevents any cracks in the concrete. It also means less cement is required, therefore lowering the global carbon dioxide (CO2) output. As cement is responsible for seven percent of total global CO2 emissions, according to International Energy Agency estimates.
- The vegetable-composite concretes, have structurally and environmentally out-performed all commercially-available cement additives, such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, doing so at a much lower cost.
Sphere to Fight Water Pollutants
05, Oct 2018

- Rice University researchers have enhanced micron-sized titanium dioxide particles to trap and destroy bisphenol A (BPA), a water contaminant with health implications.
About:
- BPA is commonly used to coat the insides of food cans, bottle tops and water supply lines, and was once a component of baby bottles. While BPA that seeps into food and drink is considered safe in low doses, prolonged exposure is suspected of affecting the health of children and contributing to high blood pressure.
- The reactive oxygen species (ROS), hydroxyl radicals are bad for BPA. Inexpensive titanium dioxide releases ROS when triggered by ultraviolet light. But oxidating molecules fade quickly, BPA has to be close enough to attack.
- The spheres reveal themselves as flower-like collections of titanium dioxide petals. The supple petals provide plenty of surface area to anchor cyclodextrin molecules.
- Cyclodextrin is a benign sugar-based molecule often used in food and drugs. It has a two-faced structure, with a hydrophobic (water-avoiding) cavity and a hydrophilic (water-attracting) outer surface.
- BPA is also hydrophobic and naturally attracted to the cavity. Once trapped, ROS produced by the spheres degrades BPA into harmless chemicals.
- In the lab, the researchers determined that 200 milligrams of the spheres per litre of contaminated water degraded 90 percent of BPA in an hour, a process that would take more than twice as long with unenhanced titanium dioxide.
- Cyclodextrin molecules on the surface trap BPA, which is then degraded by reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced by the light-activated particles.
- Most of the processes reported in the literature involve nanoparticles. The size of the particles is less than 100 nanometres. Because of their very small size, they’re very difficult to recover from suspension in water. The Rice particles are much larger. Where a 100-nanometer particle is 1,000 times smaller than a human hair, the enhanced titanium dioxide is between 3 and 5 microns, only about 20 times smaller than the same hair. That means we can use low-pressure microfiltration with a membrane to get these particles back for reuse. Because ROS also wears down cyclodextrin, the spheres begin to lose their trapping ability after about 400 hours of continued ultraviolet exposure but once recovered, they can be easily recharged.
- This is an example of how advanced materials can help convert academic hypes into feasible processes that enhance water security.
Current Problem:
- This new material helps overcome two significant technological barriers for photocatalytic water treatment. First, it enhances treatment efficiency by minimizing scavenging of ROS by non-target constituents in water. Here, the ROS are mainly used to destroy BPA.
- Second, it enables low-cost separation and reuse of the catalyst, contributing to lower treatment cost.
ELECTRIC VEHICLES DO NOT NEED PERMITS
17, Sep 2018

Why in news?
- Electric vehicles and vehicles that run on alternative fuels such as compressed natural gas (CNG) and ethanol will not require permits to ply on roads.
>Background:
- Gadkari said that all states have given their support to Centre’s move to end permits for such vehicles. He was speaking at the annual convention of Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM).
- While the minister did not specify the timeline of the decision’s implementation, it may happen within three months.
- A permit is an instrument issued by a state or regional transport authority, allowing the use of a vehicle as per provisions of the Motor Vehicle Act. Various permits required by commercial vehicles include contract carriage bus permit, goods carrier permit and cab permit, among others.
- The move to end permit era for eco-friendly vehicles will result in saving time and money and is also likely to encourage fleet owners to add more green vehicles.
- Giving any additional incentives on electric vehicles for personal use, saying there is already a GST benefit extended on them. GST on electric vehicles has been kept at 12%.
- There was no need to further subsidise electric vehicles, but ministry was preparing non-fiscal measures to have at least 15% EVs in the country in five years.
- Electric vehicles imported for testing will be exempted from duties. The exemption will be limited and enable manufacturers to evaluate if these vehicles can be made locally.
- The government was considering removing speed governors from the roads since the emphasis is on better infrastructure and cleaner roads.
Electric vehicles:
- An electric vehicle, also called an EV, uses one or more electric motors or traction motors for propulsion.
- An electric vehicle may be powered through a collector system by electricity from off-vehicle sources, or may be self-contained with a battery, solar panels or an electric generator to convert fuel to electricity.
- EVs include, but are not limited to, road and rail vehicles, surface and underwater vessels, electric aircraft and electric spacecraft.
Advantages of electric vehicles:
- Cheaper to run – the cost of charging an EV is equivalent to paying around 30 cents per litre for petrol.
- Charge up at home – EVs can be charged anywhere there is a power point, just like charging your cell phone. You can wake up to a ‘full tank’ every morning by plugging in at home, and never have to go out of your way to a petrol station again.
- Pollution-free driving – BEVs don’t have a tailpipe and produce no exhaust emissions that cause local air pollution.
- Noise reduction – EVs are quieter than petrol or diesel vehicles.
- 80% reduction in CO2 emissions in New Zealand – this significant reduction in emissions is because 80% of New Zealand’s electricity is generated from renewable sources. There are also many other advantages to using this home-grown energy compared with using imported fossil fuels.
- Fewer lifecycle emissions – even when you take into account raw material extraction, battery manufacture, vehicle manufacture and shipping, BEVs emit 60% fewer climate change emissions over their full life cycle than for petrol vehicles.
- More efficient – EVs can convert well over 90% of energy from their batteries into moving the car. This compares to 20% – 30% energy conversion for a petrol or diesel vehicle.
Challenges of electric vehicles:
- Price – new EVs tend to cost more to buy than equivalent conventional cars, but much lower running costs will help offset the initial higher price tag.
- Range – most EVs don’t travel as far on a full-charge as petrol or diesel vehicles travel on a full tank.
- Battery re-use and recycling – if an EV battery reaches the end of its vehicle life, it may still have a useful second life, for example storing electricity from solar PV panels. EV manufacturers already have recycling programmes in place.
GERMANY ROLLS OUT WORLD’S FIRST HYDROGEN TRAIN
16, Sep 2018

Why in news?
- Germany on Monday rolled out the world’s first hydrogen-powered train, signalling the start of a push to challenge the might of polluting diesel trains with costlier but eco-friendly technology.
Background:
- Hydrogen trains are equipped with fuel cells that produce electricity through a combination of hydrogen and oxygen, a process that leaves steam and water as the only emissions.
- Excess energy is stored in ion lithium batteries on board the train.
- The Coradia iLint trains can run for around 1,000 km on a single tank of hydrogen, similar to the range of diesel trains. Alstom is betting on the technology as a greener, quieter alternative to diesel on non-electrified railway lines — an attractive prospect to many German cities scrambling to combat air pollution.
- Two bright blue Coradia iLint trains, built by French TGV-maker Alstom, began running a 100 km (62-mile) route between the towns and cities of Cuxhaven, Bremerhaven, Bremervoerde and Buxtehude in northern Germany — a stretch normally plied by diesel trains.
- Alstom has said it plans to deliver another 14 of the zero-emissions trains to Lower Saxony by 2021, with other German States also expressing an interest.
Advantages of hydrogen fuel:
- It’s a renewable energy source and bountiful in supply
- It practically a clean energy source
- Hydrogen energy is non-toxic
- It’s far more efficient than other sources of energy
- Used for powering space ships
Disadvantages of hydrogen fuel:
- Hydrogen energy is expensive
- Storage complications
- Tricky to move around
- It is highly flammable
- It is not easy to replace existing infrastructure.
LITHIUM-CARBON-DIOXIDE BATTERIES
14, Sep 2018

- Researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have developed a new battery made partly from carbon dioxide captured from power plants.
About:
- Researchers combined the prior knowledge from two different areas, metal-gas battery electrochemistry and carbon-dioxide capture chemistry, and succeeded in increasing both the energy density of the battery and the efficiency of the carbon-dioxide capture,
- Rather than attempting to convert carbon dioxide to specialized chemicals using metal catalysts, which is currently highly challenging, this battery could continuously convert carbon dioxide into a solid mineral carbonate as it discharges.
- The battery is made from lithium metal, carbon, and an electrolyte, where the captured gas(C02) could then be used during the discharge of the battery to provide a power output. This approach is different from releasing the carbon dioxide back to the gas phase for long-term storage, as is now used in carbon capture and sequestration, or CCS.
Significance:
- The new battery formulation could open up new avenues for tailoring electrochemical carbon dioxide conversion reactions, which may ultimately help reduce the emission of the greenhouse gas to the atmosphere.
- Currently, power plants equipped with carbon capture systems generally use up to 30 percent of the electricity they generate just to power the capture, release, and storage of carbon dioxide. Anything that can reduce the cost of that capture process, or that can result in an end product that has value, could significantly change the economics of such systems,
- Carbon capture is widely considered essential to meeting worldwide goals for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but there are not yet proven, long-term ways of disposing of or using all the resulting carbon dioxide.
- Underground geological disposal is still the leading contender, but this approach remains somewhat unproven and may be limited in how much it can accommodate. It also requires extra energy for drilling and pumping.
A New, Robust form of Gold
26, Aug 2018

- Researchers from Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR), Bengaluru, have developed a new type of gold in the form of very small crystals — micro crystallites.
Robust Form of Gold:
- The microcrystal gold has been found to be nobler than gold — it do not dissolve in mercury and Aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), and showed the least interaction with copper.
- The microcystallites were synthesised by decomposing an organic complex containing gold and other ions under controlled conditions.
- The newly formed microcystallites, about 3 micrometre in length were found to be of a different crystal structure.
- Normal gold has a (face-centered) cubic structure, while the new ones exhibit deformed cubic structure — tetragonal and orthorhombic cells.
- The researchers then examined copper growth on these gold crystals when subjected to plating without the use of electrodes.
- Electron microscopy images revealed that thick copper got deposited on normal gold within minutes, while no detectable copper was seen on the central portion of the new crystals even after an hour.
- It is found that deposition of copper only on the tips of the new crystallites while the rest of the crystal surface was devoid of copper. This may be due to the different arrangement of the new facets.
- The researchers then investigated the stability of the gold microcystallites using corrosive agents like mercury and Aqua regia. While normal gold disappeared in a matter of minutes when immersed in mercury and also in aqua regia, the gold crystallites remained intact. Microscopy imaging showed that the surface was undamaged.
As a catalyst:
- All these properties make new crystallites an ideal candidate for catalytic purposes.
- Gold in itself is not a catalyst but the new gold microcystallites have very active surfaces.
- Compared with other catalysts like palladium and ruthenium, gold is cheaper and it can also be easily recovered.
- Though the production cost of the crystallites is a little high,
researchers are optimising it to bring down the cost. More studies are needed to understand them fully in the context wide range of applications in the offing,” he added.
India’s First Biofuel flight
26, Aug 2018

Why in news?
- SpiceJet today operated India’s first test flight powered biojet fuel, marking a new chapter in the fast-growing domestic sector. The flight was tested from Dehradun to Delhi.
Biofuel blend ATF:
- A blend of oil from Jatropa seeds and aviation turbine fuel propelled the country’s first ever bio jet fuel powered flight.
- A blend of 25%of bio jet fuel and 75% of aviation turbine fuel (ATF) was carried in one of the two engines of the plane, while the other engine carried only ATF. International standards permit a blend rate of up to 50% biofuel with ATF.
- It has the potential to reduce fuel costs by 15-20%
- The indigenously developed fuel has been nearly 8 years in the making by the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) lab based in Dehradun along with the Indian Institute of Petroleum (IIP).
- The institute started its experiment on biofuel soon after Virgin Atlantic carried out the first test flight globally in 2008.
Jatropa:
- Jatropha oil has been used in India for several decades as biodiesel for the diesel fuel requirements of remote rural and forest communities. It is a second generation-based biofuel.
- Jatropha oil can be used directly after extraction (i.e. without refining) in diesel generators and engines.
- Jatropha has the potential to provide economic benefits at the local level since under suitable management it has the potential to grow in dry marginal non-agricultural lands, thereby allowing villagers and farmers to leverage non-farm land for income generation.
- Since no food producing farmland is required for producing this biofuel (unlike corn or sugar cane ethanol, or palm oil diesel), it is considered the most politically and morally acceptable choice among India’s current biofuel options; it has no known negative impact on the production of the massive amount’s grains.
World First Melanoma Blood Test
22, Jul 2018
Australian researcher have developed a blood test for melanoma in its early stages .
- Melanoma is a cancer that begins in the melanocytes. Other names for this cancer include malignant melanoma and cutaneous melanoma. Most melanoma cells still make melanin, so melanoma Tumours are usually brown or black.
- This test could help doctors detect skin cancer before it spreads through a person’s body.
- The early detection of melanoma in patients have a five-year survival rate between 90% and 99% whereas the rates fell to less than 50% if the cancer spread in the body.
Super Conductivity at Ambient Temperature
22, Jul 2018

Researchers from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bengaluru have been able to achieve superconductivity at ambient temperature and pressure.
Superconductor:
- A superconductor is a material that can conduct electricity or transport electrons from one atom to another with no resistance.
- This means no heat, sound or any other form of energy would be released from the material when it has reached “critical temperature” (Tc), or the temperature at which the material becomes superconductive.
- A large number of materials have been found to undergo normal to superconducting transitions.
- But such transitions require extremely low temperature and/or extremely high pressure.
- A type I superconductor consists of basic conductive elements that are used in everything from electrical wiring to computer microchips.
- A type II superconductor is composed of metallic compounds such as copper or lead. They reach a superconductive state at much higher temperatures when compared to type I superconductors.
Applications:
- Power transmission cables.
- Transformers.
- Motors and generators.
- Fault current limiters.
- Superconducting magnets including MRI and research magnets.
- SQUID (superconducting quantum interference device) – sensitive sensors to detect magnetic field and Josephson junctions.
- Magnetic Levitation including magnetic suspension, contactless bearings, linear motors and trains.
- Shielding of magnetic fields.
- Superconducting electronics and quantum computers.
- SMES (superconducting magnetic energy storage).
- Maglev (magnetic levitation) trains. Large hadron collider or particle accelerator.
- The USA is developing “E-bombs”. These are devices that make use of strong, superconductor derived magnetic fields to create a fast, high-intensity electromagnetic pulse that can disable an enemy’s electronic equipment.






