EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT
29, Jan 2020

Prelims level : European Union
Mains level : GS-II Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Context:
- The EU Parliament is taking steps to debate and vote on a resolution asking India to repeal the Citizenship Amendment Act. The Indian government, on its part, says the CAA is an internal Indian matter and a law adopted through democratic means.
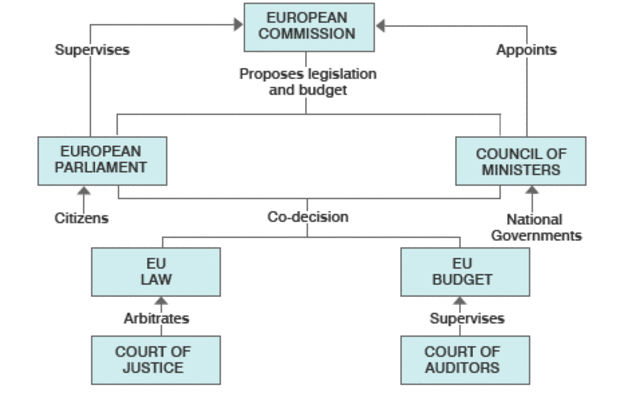
The European Union has Seven Institutions:
- 1.The European Parliament,
- 2.The Council of the European Union,
- 3.The European Commission,
- 4.The European Council,
- 5.The European Central Bank,
- 6.The Court of Justice of the European Union
- 7.The European Court of Auditors.
European Parliament:
- The European Parliament is an important forum for political debate and decision-making at the EU level.
- It is the EU’s law-making body, and shares its power with the EU Council.
- It is directly elected by EU voters every 5 years.
- The European Parliament allows the citizens of the EU to participate directly in European political affairs.
What does the Parliament do?
- The Parliament has 3 Main Roles:
- Legislative :
-
- Passing EU laws, together with the Council of the EU, based on European Commission proposals
- Deciding on international agreements
- Deciding on enlargements
- Reviewing the Commission’s work programme and asking it to propose legislation.
-
- Supervisory –
- Democratic scrutiny of all EU institutions
- Electing the Commission President and approving the Commission as a body. Possibility of voting a motion of censure, obliging the Commission to resign
- Granting discharge, i.e. approving the way EU budgets have been spent
- Examining citizens’ petitions and setting up inquiries
- Discussing monetary policy with the European Central Bank
- Questioning Commission and Council
- Election observations
- Budgetary:
- Establishing the EU budget, together with the Council
- Approving the EU’s long-term budget, the “Multiannual Financial Framework”








