FINDING CURE FOR CORONAVIRUS
14, Mar 2020

Prelims level : Science& Technology - Biotechnology
Mains level : GS-III Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, Robotics, Nano-Technology, Bio-Technology and issues relating to intellectual property Rights.
Why in News?
- Scientists across the world are trying to develop a line of treatment and a possible vaccine for COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, which has infected over 100,000 people and claimed over 4,000 lives.
Highlights:
- A global effort is on to collect and analyse the genetic composition of the new virus, which would be key to developing a cure and a vaccine.
- Laboratories in various countries have been isolating and sharing the genome sequences of the virus on an international platform.
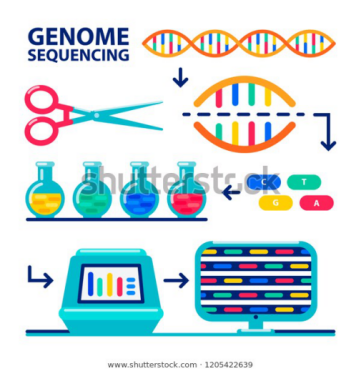
- Whole genome sequencing is the process of determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism’s genome at a single time.
Significance of COVID-19 Genome Sequencing:
- Genome sequence is the unique code of genetic material of any organism, and determines the characteristic of any organism.
- The gene composition of novel coronavirus, for instance, is different from that of the influenza virus.
- India has so far reported two sets of genome sequences, both of which are very similar to the original sequences collected from patients in Wuhan.
- When viruses multiply, or reproduce, there is a copying mechanism that transfers the gene information to the next generation.
- When the virus multiplies, there will be small changes, which are called mutations. These mutations accumulate over time, and after prolonged periods, are responsible for evolution into new organisms.
- The small changes could provide scientists with information about the origin, transmission, and impact of the virus on the patient.
- It could also hold clues to the differing effects the virus could have on patients with different health parameters.
- Patients with existing medical conditions could be candidates from where genome sequences of this virus could be isolated. This could help scientists to look for clues to possible impact of virus amidst those existing medical conditions.
- New technological tools have made it easier to isolate full genome sequences. Traditional techniques used to take weeks for the extraction, but new machines are able to do it within two to three days.
- Right now, drugs are being repurposed, meaning old drugs for similar diseases are being checked for their efficacy against COVID-19. These drugs, if they work, will require clinical trials, and then can be made widely available for people.
Genome Sequencing:
- Genome:It is an organism’s complete set of DNA, including all of its genes.
- Each genome contains all of the information needed to build and maintain that organism. In humans, a copy of the entire genome—more than 3 billion DNA base pairs—is contained in all cells that have a nucleus.
- Genome sequencing: It is figuring out the order of DNA nucleotides, or bases, in a genome—the order of As, Cs, Gs, and Ts that make up an organism’s DNA. The human genome is made up of over 3 billion of these genetic letters.
- Sequencing the genome doesn’t immediately lay open the genetic information of an entire species. Even with a rough draft of the human genome sequence in hand, much work remains to be done. Scientists still have to translate those strings of letters into an understanding of how the genome works.