FIRST 3D PRINTED HEART HAS HUMAN CELLS, VESSELS
16, Apr 2019
Prelims level : Science & Technology
Mains level : GS-III Technology, Economic Development, Bio diversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management
Why in News?
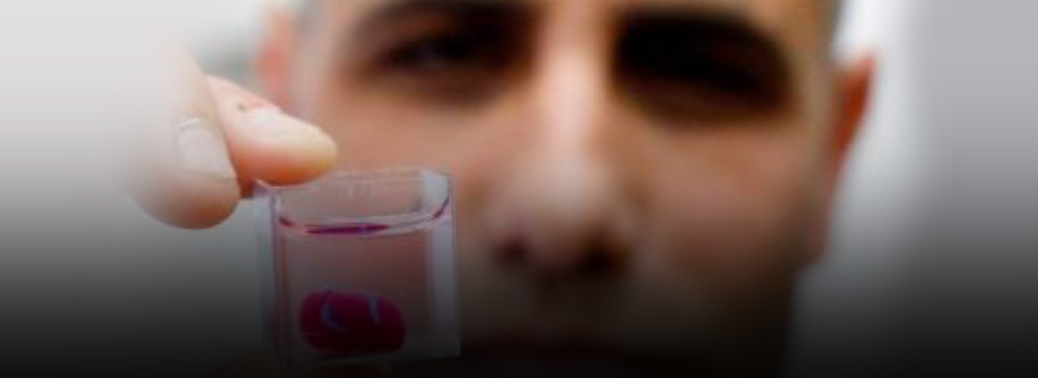
- Scientists in Israel unveiled a 3D print of a heart with human tissue and vessels, calling it a first and a “major medical breakthrough” that advances possibilities for Transplants.
Details:
- The heart, about the size of a rabbit’s, marked “the first time anyone anywhere has successfully engineered and printed an entire heart replete with cells, blood vessels, ventricles and chambers.
- Until now, the Tel Aviv University said, scientists have been successful in printing only simple tissue without blood vessels. The printing process for the tiny heart took about three hours, journalists who were able to watch the entire process said. The importance of the heart’s being made with a patient’s own cells and biological materials in order to eliminate the risk of implant rejection was stressed.
- The next step for the researchers is to culture the printed hearts in a laboratory and “teach them” to behave like hearts. The current state of the primitive heart can be compared to the heart of an embryo. “The cells need to form a pumping ability; they can currently contract, but we need them to work together. Once they have achieved that, the scientists plan to transplant the hearts into small animals, such as rabbits or rats.
- “Larger human hearts require the same technology
- Maybe, in 10 years, there will be organ printers in the finest hospitals around the world, and these procedures will be conducted routinely
- The World health Organization said last year that ischaemic heart disease and stroke were the world’s biggest killers.
3D Bioprinting:
- 3D bioprinting uses a typical layer-by-layer 3D printing method, depositing bio inks or biomaterials, to create 3D tissues or structures used for medicine or tissue engineering.
- This technology is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and 3D printed organs for transplant






