Inner Line Permit
24, Jun 2019
Prelims level : Polity Governance- Parliament
Mains level : GS2B - Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, Issues and Challenges Pertaining to the Federal Structure, Devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein
Context:
- A petition filed has sought a direction to the Centre and the Nagaland government to take appropriate steps for the protection of life and liberty, properties and other fundamental rights of nonNagas living in the commercial hub of Dimapur following the imposition of the Inner Line Permit.
- (PIL) petition, has challenged certain sections of the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation, 1873 which gives unbridled power to a State to prescribe ILP.
- Section 2 of the Regulation empowers a State government to prescribe ‘Inner Line’ to prohibit citizens of India or any class of such citizens going beyond the prescribed line without a pass.
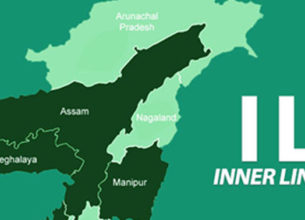
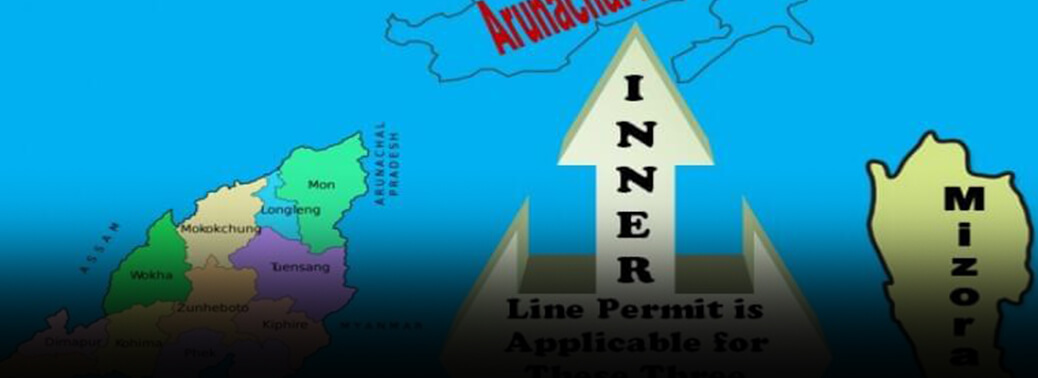
- The Inner Line Permit (ILP) is an official travel document issued by the Government of India to grant inward travel of an Indian citizen into a protected area for a limited period. It is obligatory for Indians residing outside those states to obtain permission prior to entering the protected areas. Currently, the Inner Line Permit is operational in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram and Nagaland. The document has been issued under the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation, 1873 and the conditions and restrictions vary from state to state.
- It can be issued for travel purposes solely. Visitors are not allowed to purchase property in these regions. However, there might be a different set of rules for long term visitors, though they are not valid for central government employees and security forces.