MINIMUM WAGE SYSTEM
05, Jul 2019
Prelims level : Governance- Policies
Mains level : Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, Institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these Vulnerable Sections.
Background
- In India, labour is included in the concurrent list which implies that both the central government and state governments can make laws regarding this subject.
- The Second National Commission on Labour (2002) had recommended that existing labour laws should be classified into broader groups for easier compliance, such as
- (i) industrial relations, (ii) Wages, (iii) Social Security, (iv) Safety, and (v) welfare and working conditions.
- This would also allow for uniformity in the coverage of various labour laws that are in force.2
- The Code on Wages replaces four existing laws:
1. The Payment of Wages Act, 1936
2. The Minimum Wages Act, 1948
3. The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965 and
4. The Equal Remuneration Act, 1976.
Who Determines Minimum Wages?
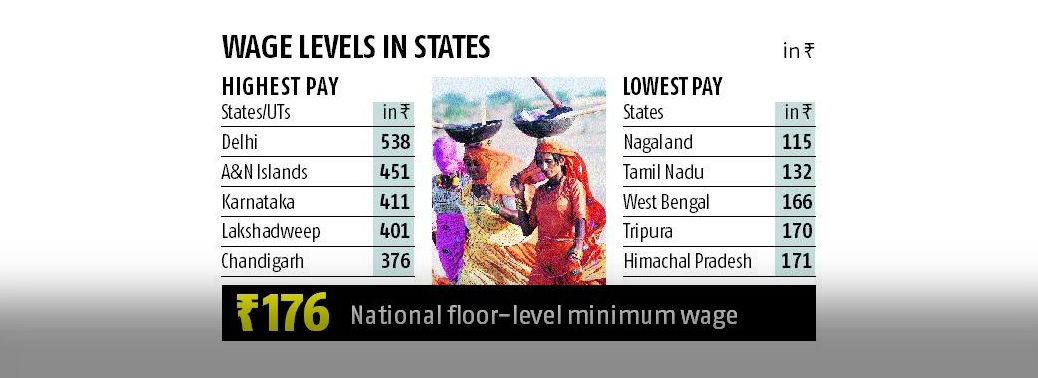
- The Code provides that a National Minimum Wage may be set by the Central Government. States cannot set minimum wages lower than the national minimum wage.
- The Central Government may set separate national minimum wages for different states or regions of the country. Minimum wages must be revised by the central or state governments at an interval of Five Years.
Key Issues:
- Central government may set a national minimum wage. Further, it may set separate national minimum wages for different states or regions.
- 1. The rationale for a national minimum wage, and
- 2. Whether the central government should set one or multiple national minimum wages.
- States have to ensure that minimum wages set by them are not lower than the national minimum wage. If existing minimum wages set by states are higher than the national minimum wage, they cannot reduce the minimum wages.
- This may affect the ability of states to reduce their minimum wages if the national minimum wage is lowered.
Gender Discrimination:
- The Equal Remuneration Act, 1976, prohibits employers from discriminating in wage payments as well as recruitment of employees based on gender.
- While the Code prohibits gender discrimination on wage-related matters, it does not include provisions regarding discrimination during recruitment.
Advisory boards:
- The central government and state governments will constitute the Central Advisory Board
- and State Advisory Boards respectively.
- These boards will consist of:
- 1. Employers,
- 2. Employees in equal number as the employers, and
- 3. Independent Persons (Not Exceeding One Third of the Total Members of the Board).
- They will advise the central or state governments on issues such as setting and revision of minimum wages and increasing employment opportunities for women, among others.
Advantages of A National Minimum Wage:
- National minimum wage is to ensure a uniform standard of living across the country.
- The introduction of a national minimum wage may help reduce these differences and provide a basic standard of living for all employees across the country.
Disadvantages of A National Minimum Wage:
- It may be argued that the ability of state governments to adjust minimum wage levels may be affected, if the central government sets a national minimum wage.
- These adjustments may be required for variations, across the country, in costs of living such as prices of essential goods and housing.
- The Code does not provide for consultation between the central and state governments while determining the national minimum wage.






