Prelim Snippets 16-07-2019
VPM1002’ and MIP Vaccines for TB
- Context: ICMR launches third phase trial for adult anti-TB vaccine
- India has the highest number of TB cases in the world and aims to eliminate TB by 2025.
- ICMR is undertaking this first vaccine clinical trial after the BCG vaccine trial undertaken decades ago
- Two vaccines- ‘VPM1002’ and MIP had been shortlisted for the phase III trial among the healthy household contacts of a sputum smear positive patient
- While the neonatal BCG vaccination is partially efficacious at protecting infants and young children, particularly from the most severe consequences of TB disease
- The WHO End TB Strategy aims at a 95 per cent reduction in TB mortality and a 90 per cent reduction in TB incidence worldwide by 2035
- About TB:
- Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria.
- Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body.
- Tuberculosis is Spread through the Air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze.
APOLLO 11 MISSION

- Context: The anniversary of one of the most important launches of all time is on July 16, 2019. Tuesday marks 50 years since the launch of the Apollo 11 mission.
About APOLLO 11 mission:
- Apollo 11 was the Fifth Crewed Mission of NASA’s Apollo program.
- It was the spaceflight that first landed humans on the Moon.
- Commander Neil Armstrong and lunar module pilot Buzz Aldrin, both American, landed the Apollo Lunar Module
- It was launched by a Saturn V rocket from Kennedy Space Center on Merritt Island, Florida
- The Apollo spacecraft had three parts:
- A command module
- A service module
- A lunar module
MULTIDIMENSIONAL POVERTY INDEX (MPI)
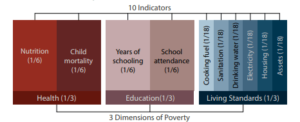
- Context: About 1.3 billion people are ‘multi-dimensionally poor’, says UN report
About MPI:
- It is released by the Oxford Poverty & Human Development Initiative and the United Nations Development Programme.
- It uses different factors to determine poverty beyond income-based lists.
- It replaced the previous Human Poverty Index
- It is an international measure of acute multidimensional poverty covering over 100 developing countries.
- It defines poor not only on the basis of income, but on other indicators, including poor health, poor quality of work and the threat of violence
- The MPI assesses poverty at the Individual Level.
- If someone is deprived in a third or more of ten (weighted) indicators, the global index identifies them as ‘MPI poor’
- The number of poor people in India fell by more than 271 million within ten years
- Among states, Jharkhand had the greatest improvement, with Arunachal Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, and Nagaland only slightly behind.
- However, Bihar was still the poorest state in 2015- 16, with more than half of its population living in poverty.
- In 2015-16, the four poorest states – Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh – were home to 196 million multidimensional poor people – over half of all the people living in multidimensional poverty in India.
‘The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World’- UN Report
- Context: A UN report has said, more than 821 million people suffered from hunger worldwide last year.
- It is the third year in a row that the number has risen.
Report Highlights:
- The report named, ‘The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World’, produced by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization and other UN agencies, including WHO, was released on June 15, 2019
- It noted that the number of people without enough to eat had risen from 811 million in 2017
- The report said, after decades of decline, malnutrition began to increase in 2015, mainly because of climate change and war.
- Reversing the trend is one of the 2030 targets of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals which aim to improve the planet and its people.
JALYUKTA SHIVAR ABHIYAN
- Context: Jalyukta Shivar key for Maharashtra, but still has a long road ahead
About Jalyukta Shivar Abhiyan:
- Jalyukta Shivar is the flagship programme of the Maharashtra government launched in December 2014.
- Aim:
- It aims to make 5,000 villages free of water scarcity.
- Objectives:
- The scheme targeted drought-prone areas by improving water conservation measures in order to make them more water sustainable.
- Under the scheme, decentralised water bodies were installed at various locations within villages to enhance the groundwater recharge.
- Besides, it also proposed to strengthen and rejuvenate water storage capacity and percolation of tanks and other sources of storage.
- Dedicated committees were formed to assist in construction of watersheds like farm ponds, cement nullah bunds alongside rejuvenating the existing water bodies in the villages.
- A mobile-app developed by the Maharashtra Remote Sensing Application Centre (MRSAC) for quick monitoring of the scheme is functional in this respect.
NEW LIZARD SPECIES: INDRASAURUS WANGI

- Context: A Team of researches has discovered a new specimen of a microraptor with the remains of a nearly complete lizard preserved in its stomach.
About Indrasaurus Wangi:
- The Lizard is unlike any previously know from the Cretaceous period and represents a new species: Indrasaurus wangi.
- The name Indrasaurus was inspired by a Vedic legend in which Hindu God Indra was swallowed by a dragon during a great battle.
- The Lizard was also named after Prof. Wang Yuan from the Institute of vertebrate Palaeontology and palaeoanthropology of the Chinese academy of sciences.
- The New Lizard had teeth unlike any other previously known from the Jehol Biota.
- The Jehol Biota includes all the Living Organisms of north-eastern China Between 133 and 120 million years ago.
SEVA BHOJ SCHEME
- Context: Recently, Ministry of Culture launched a new scheme “Seva Bhoj Yojna”.
About Scheme:
- It is a central sector scheme to reduce financial burden of Charitable Religious Institutions.
- It envisages reimbursing the CGST and IGST of such Charitable Religious Institutions who provide
- Food
- Prasad
- Langar
- Bhandara free of cost without any discrimination to Public/Devotees.
- It is applicable to all Charitable Religious Institutions such as
- Temples,
- Gurudwara,
- Mosque,
- Church,
- Dharmik Ashram,
- Dargah, Monasteries etc. which follows following norms:
- Which have been in existence for preceding five years before applying for financial assistance/grant.
- Which have been distributing free food, langar and prasad to public for at least past three years on the day of application.
- Which serve free food to at least 5000 people in a Month
ORCHIDS
- Context: According to the first comprehensive survey, India is home to 1,256 species of orchids
- Orchids of India: A Pictorial Guide, a publication detailing all the species of India was unveiled earlier this month by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
Key highlights:
- The 1,256 species or taxa of orchids belong to 155 genera and 388 species are endemic to India.
- Out of 388 species, one-third (128) endemic species are found in Western Ghats.
- The publication points out that Kerala has 111 of these endemic species while Tamil Nadu has 92 of them
- Among the 10 bio geographic zones of India, the Himalayan zone is the richest in species concentration followed by North east, the Western Ghats, Deccan Plateau and Andaman &Nicobar Islands
- The highest number of orchid species is recorded from Arunachal Pradesh with 612 species, followed by Sikkim 560 species and West Bengal.
- Among the 10 bio geographic zones of India, the Himalayan zone is the richest in terms of orchid species followed by Northeast, Western Ghats, Deccan plateau and Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
About Orchids:
- Marked by extremely beautiful flowers with unique shape and ornamentation, orchids have complex floral structure that facilitates biotic cross-pollination and makes them evolutionarily superior to the other plant groups.
- Orchids can be broadly categorised into three life forms:
- Epiphytic
- Terrestrial and
- Mycoheterotrophic
- About 60% of all orchids found in the country are epiphytic, 447 are terrestrial and 43 are mycoheterotrophic.
- The entire orchid family is listed under Appendix II of CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) and hence any trade of wild orchid is banned globally.









