Prelim Snippets 11-11-2019
1.Samudra Shakthi
Why in News?
- A joint bilateral maritime exercise between India and Indonesia was held recently.
About:
- It is a bilateral maritime exercise between India and Indonesia.
- The latest edition is being held in Bay of Bengal.
- The joint exercises include manoeuvres, surface warfare exercises, air defense exercises, weapon firing drills, helicopter operations and boarding operations.
2.Dhrupad
Why in News?
- Padma Shri awardee and renowned Dhrupad vocalist Ramakant Gundecha passed away in Bhopal.
About Dhrupad:
- The word Dhrupad is derived from Dhruva, the steadfast evening star that moves through the galaxy, and Pada meaning poetry.
- Traditionally, the dhrupad style of singing was performed with a tanpura and pakhawaj.
- The lyrics sung in Dhrupad are in a medieval form of Hindi and typically heroic in theme, or praise of a particular deity.
- It is a form of devotional music that traces its origin to the ancient text of Samveda.
- One significant characteristic of Dhrupad is the emphasis on maintaining the purity of the Raga.
- Hindustani classical music is primarily vocal-centric. The primary vocal forms associated with Hindustani music are the Khayal, Ghazal, Dhrupad, Dhammar, Tarana and Thumri.
3.COCSSO
Why in News?
- Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) is organizing 27th Conference of Central and State Statistical Organizations (COCSSO) in Kolkata.
Highlights:
- The Conference, a major national annual event, provides a platform for discussion and improved coordination between the Central and State Statistical agencies for enhancing the efficiency of the Indian Statistical System.
- The theme of this year’s Conference “Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)”. It has been chosen for intensive and focused discussions aimed at filling the data gaps and improvement of timelines/quality in SDG monitoring.
- The next important step on SDGs is preparation of the State Indicator Framework (SIF) so that monitoring of progress in respect of SDGs can take place at the State and sub-State levels.27th COCSSO assumes greater Significance for proposing the way forward for evolving SIF through a wider consultation with State Governments/Uts and other stakeholders.
National Indicator Framework (NIF):
- MoSPI, which is responsible for monitoring the progress of SDGs, has developed the National Indicator Framework (NIF) for monitoring country’s progress on SDGs.
- NIF has been developed in consultations with Central Ministries and State/UT Governments.MoSPI has also released the NIF Baseline Report 2015-16 setting the benchmark for measuring SDGs progress up to 2030.
4.“National Capital Region – 2041”
Why in News?
- The Inaugural Conclave “NCR-2041” with the theme “Planning for Tomorrow’s Greatest Capital Region” will be held in the national capital.
- The Regional Plan-2041 for NCR will be among the key instruments to address various issues related to harmonious development of the largest metropolitan region of the world.
National Capital Region Planning Board (NCRPB):
- The National Capital Region (NCR) is a distinct federal setup having the National Capital Territory of Delhi as its core. It is a unique example of inter-state regional planning and development.
- The constituent areas of the National Capital Region are as under:
- Entire National Capital Territory of Delhi.
- Districts from Haryana sub-region.
- Districts from Rajasthan sub-region.
- Districts from Uttar Pradesh Sub-region.
- For the development of above, the National Capital Region Planning Board (NCRPB) was constituted by the Act of Parliament in 1985, as a statutory body under the Ministry of Housing & Urban Affairs.
- The NCRPB is tasked to evolve harmonized policies for the control of land-uses and development of infrastructure in the region so as to avoid any haphazard development.
- The success rate of these experiments in inducing rains is about 60 to 70 per cent, depending on local atmospheric conditions, the amount of moisture in the air and cloud characteristics.
- Apart from IITM, some private companies also offer cloud-seeding services.
- It is these companies that have been engaged by Maharashtra and Karnataka in the last few years. These also received mixed success.
5.Kartarpur Corridor
Why in News?
- The Prime Minister of India will inaugurate the Integrated Check Post at Kartarpur Corridor.
Highlights:
- India and Pakistan have signed an agreement to operationalise the Kartarpur corridor that will facilitate pilgrims from India to visit the Gurdwara Kartarpur Sahib in Pakistan.
The Highlights of the Agreement are:
- Indian pilgrims of all faiths and persons of Indian origin can use the corridor;
- The travel will be Visa Free;
- Pilgrims need to carry only a valid passport;
- Persons of Indian Origin need to carry OCI card along with the passport of their country;
- The Corridor is open from dawn to dusk. Pilgrims travelling in the morning will have to return on the same day;
- The Corridor will be operational throughout the year;
- Pilgrims will have a choice to visit as individuals or in groups, and also to travel on foot;
- India will send the list of pilgrims to Pakistan 10 days ahead of travel date. Confirmation will be sent to pilgrims 4 days before the travel date.
6.Very Severe Cyclonic Storm ‘Bulbul’
Why in News?
- A meeting of the National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC), chaired by the Cabinet Secretary, was held to review the preparedness to deal with severe cyclone ‘Bulbul’ over the Bay of Bengal that is likely to affect coastal districts of West Bengal and Odisha.
Highlights:
- Cyclone Bulbul is the seventh named storm of the unusually active 2019 North Indian Ocean cyclone season.
- The season has seen Cyclone Pabuk (South China Sea-Andaman Sea), Cyclone Fani (Bay of Bengal), Cyclone Vayu (Arabian Sea), Cyclone Hikka (Arabian Sea), Cyclone Kyarr (Arabian Sea) and Cyclone Maha (Arabian Sea).
- Bulbul was named by Pakistan.
- Cyclone Bulbul comes around seven months after Cyclone Fani struck Odisha. Cyclone Fani was the strongest storm to hit the state since the devastating 1999 Super Cyclone that killed thousands of people.
National Disaster Response Force:
- The National Disaster Response Force or the NDRF is a specialized paramilitary force formed under the Disaster Management Act of 2005 with the objective of having a specialized response to an impending disaster situation or disaster.
- Its purpose is to direct and implement a specialized response to both man-made and natural disasters.
- It was constituted in 2006 and is headed by a Director-General, who is a senior IPS officer.
- The NDRF operates on the basis of ‘proactive availability’ and ‘pre-positioning’ to the states.
- Its parent ministry is the Ministry of Home Affairs.
National Crisis Management Committee:
- A Standing National Crisis Management Committee, called the National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC) was set up by the Government of India with Cabinet Secretary as Chairman for effective implementation of relief measures in the wake of natural calamities.
- At the national level, Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) and National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC) are the key committees involved in the top-level decision-making wart Disaster Management (DM).
- It oversees the Command, Control and Coordination of the disaster response and gives direction to the Crisis Management Group (CMG) as deemed necessary.
7.Indian Railways Launches Three Online Applications
Why in News?
- Indian Railways launched three applications for all-India rollout to strengthen the IT enablement of railways which will help ensure proper monitoring of projects being undertaken by Indian Railways and will boost the vision of Digital India.
Highlights:
- The details and the salient features of these three applications are as under:
CRS Sanction Management System:
- CRS Sanction is an important aspect in construction, maintenance and up-gradation of railway assets.
- Benefits:
- Expeditious preparation and processing of cases for CRS Sanction.
- Effective monitoring of compliance of observations raised by the CRS.
- On-Line Repository of circulars/check-lists/guidelines related to CRS Sanction.
- Managerial reports to monitor the cases, comparative performance.
Rail-road crossing GAD Approval System:
- This project for online e-Governance platform was developed to expedite preparation, processing & approval of General Agreement Drawings (GADs) related to construction of Road Over Bridges (ROB)/Road Under Bridges (RUB).
- Benefits:
- Accountability of Railways and State Governments/Uts is fixed to each stage for approval of proposals.
- Better and real time coordination between the stakeholders (Railways/States).
- Facilitates users to get proposal status through mail and SMS at each stage.
- Complete proposal is targeted to be approved in a maximum of 60 days.
- All information related to the proposal and contact person is available within the proposal.
TMS for Construction:
- This application has been developed for new assets being constructed by the construction/project organisation.
- Benefits:
- Data validation at source.
- Easy checking/verification of Data Entry.
- For every data ownership and responsibility is defined and fixed in the Application Design.
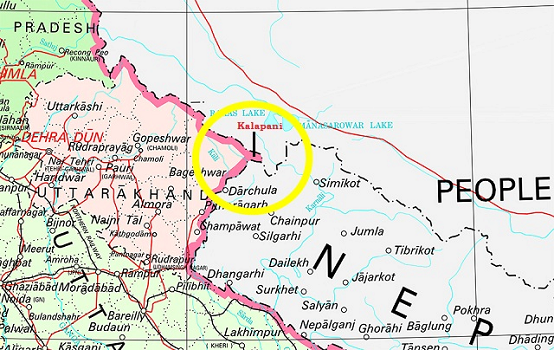
8.Kalapani
Why in News?
- The new political map of India, recently released by the government to account for the bifurcation of Jammu and Kashmir, has triggered fresh protests over an old issue in Nepal.
About:
- Kalapani is a 372-sq km area mapped within Uttarakhand, bordering far-west Nepal and Tibet.
- While the Nepal government and political parties have protested, India has said the new map does not revise the existing boundary with Nepal and accurately depicts the sovereign territory of India.
Timeline:
- Nepal’s western boundary with India was marked out in the Treaty of Sugauli between the East India Company and Nepal in 1816. Nepali authorities claim that people living in the low-density area were included in the Census of Nepal until 58 years ago.
- Nepal claims that the late King Mahendra had “handed over the territory to India” in the wake of India-China War of 1962.
- The Prime Ministers of the two countries discussed the issue in 2000, with Atal Bihari Vajpayee assuring Nepal that India would not occupy even an inch of Nepal. Five years ago, the matter was referred to a new mechanism comprising foreign secretaries of both sides.
- Apart from Kalapani, another unresolved issue involves a vast area along the Nepal-Uttar Pradesh border. During his visit to Nepal in 2014, Prime Minister Modi had said that the Susta and Kalapani issues would be sorted out.