Prelim Snippets 11-12-2019
1. BIS to Set Standards for Piped Water Quality
Why in News?
- Union government has recently stated that it is working with BIS to create standards for Piped water delivered by government for people.
About:
- Government stated that the Bureau of Indian Standards is preparing the ground for enforcement of piped water quality standards – IS 10500:2012, in cooperation with state departments.
- However, it is not clear whether the Centre’s own flagship mission (Jal Jeevan Mission) to provide piped water to all households by 2024 will implement the BIS standard.
- Unlike the BIS standard for bottled water, which is mostly produced by private companies, the standard for piped water — largely supplied by government agencies is not yet mandatory.
- Jal Shakti is the nodal Ministry for the Jal Jeevan Mission to provide functional household tap connections to 14.6 crore rural households by 2024.
About Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS):
- It is a statutory body established in 1987 under the BIS Act 1986. It replaced the Indian Standards Institution (ISI), a body set up under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- It works under the guidance of Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.
- The objective of BIS is to achieve harmonious development of the activities of standardization, certification marking and quality certification of goods.
- BIS is involved in various activities such as Standards Formulation, Product Certification Scheme, Hall Marking Scheme, Laboratory Services etc.
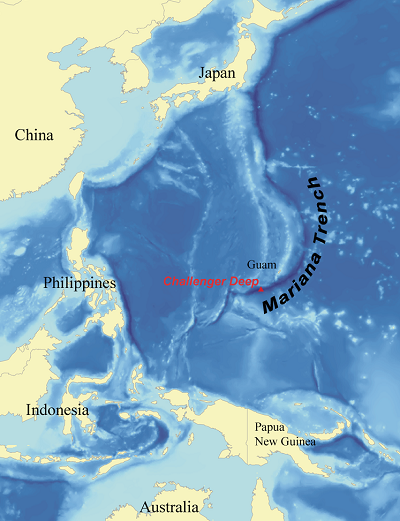
2. Marina Trench
Why in News?
- Recently, Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC) have identified plastic waste generated by human activity in Earths deepest point, Mariana Trench.
About Mariana Trench:
- It is Located in the western Pacific Ocean.
- It is considered to be the deepest part of the Earth’s surface.
- It is the Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench that is known as the deepest point.
- It appears as a crescent-shaped scar, the trench measures around 2,550 km long, 69 km wide on average and has a maximum depth of 10.91 km at the Challenger Deep.
- It is formed due to the collision of converging plates of oceanic lithosphere.
- During the collision, one plate descends into the mantle and the downward flexure forms a trough at the line of contact between the plates.
- At the bottom of the Marina Trench, the density of water is increased by 4.96% due to the high pressure at the seabed.
3. TCV Vaccine
Why in News?
- Recently, Hyderabad-based Bharat Biotech has developed a typhoid vaccine (Typbar TCV).
About Typbar TCV:
- It is a type of conjugate vaccine which has already been pre-qualified by the World Health Organisation’s Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (WHO-SAGE).
- It consists of two typhoid vaccines viz. Polysaccharide Typhoid Vaccine and Live, Weakened Typhoid Vaccine are used in India. However, their efficacy is lower than the conjugate vaccine as they offer 60-70% protection, unlike the conjugate vaccine which confers nearly 82% protection.
- It is a type of conjugate vaccine, which is made using a combination of two different components.
- It can be given to babies as young as six months, while the other two typhoid vaccines — polysaccharide typhoid vaccine and live, weakened typhoid vaccine cannot be given to children below two years of age.
- In it, an antigen is chemically linked to a carrier protein to create more powerful combined immune response.
- Its single dose is effective in preventing typhoid in children aged 9 months to 16 years. It confers protection two-three weeks after the administration.
- It is the world’s first clinically proven conjugate Typhoid vaccine.
- Typhoid bacteria can be treated with antibiotics but the microbes have developed resistance against multiple antibiotics.
- Extensively drug-resistant (XDR) typhoid outbreaks have been found in India, Bangladesh, and Pakistan.
- Bharat Biotech is been supplying the typhoid conjugate vaccine to Pakistan since 2017.
- Pakistan is also the first country to introduce the typhoid conjugate vaccine as part of its national immunisation programme.
About Typhoid:
- It is fever caused by the highly contagious Salmonella Typhi bacteria.
- It spread through contaminated food or water.
- It is often non-specific and clinically non-distinguishable from other febrile illnesses.
- Symptoms are prolonged fever, headache, nausea, loss of appetite, and constipation or sometimes diarrhoea.
- In severe cases that may lead to serious complications or even death.
- According to the WHO, a large proportion of severe typhoid fever cases occur in children aged below two years.
- Extensively drug-resistant TB, XDR-TB, is a form of multidrug-resistant TB with additional resistance to more anti-TB drugs that therefore responds to even fewer available medicines.
4. White Island Volcano
Why in News?
- Recently, a volcanic eruption took place at White Island in New Zealand.
About White Island volcano:
- It is also known as Whakaari, is located about 50 km from the eastern coast of North Island in a region known as the Taupo Volcanic Zone.
- It is located in the Bay of Plenty, about 48km from the east coast of New Zealand’s North Island.
- It is most active cone volcano which has been built up by continuous volcanic activity over the past 1,50,000 years.
- It is characterized by conical shape and its layers are built up by years of lava flow and hardening.
- It is actually, the tip of a sub-marine volcano which rises from the seabed to a height of 1,600m. It is noted for its near continuous emission of volcanic gases since 1760.
- It is monitored by the Deep earth Carbon Degassing Project.
- It caused injury to several persons and also resulted in 5 fatalities.
Deep Carbon Observatory (DCO):
- It is a global research program to outreach carbons role on Earth.
- It is a community of scientists including physicists, biologists, geo – scientists and chemists working across several traditional disciplinary lines.
- It explores High pressure and Extreme temperature organic synthesis, complex interactions between organic molecules and minerals, conducts field observations of deep microbial eco systems, constructs theoretical models of lower crust and upper mantle carbon sources and conducts observations of anomalies in petroleum geochemistry
5. Antibiotics in Crops
Why in News?
- The Union Minister for Agriculture gave information about certain antibiotics in crops in the Lok Sabha.
Antibiotics in Crops:
- Aureofungin, Kasugamycin, Validamycin and Streptomycin+ Tetracycline combination are antibiotics that are registered under the Insecticide Act 1968 for use as pesticides to combat certain fungal and bacterial diseases in plants.
- Pesticides are toxic substances but they do not pose any adverse effect on human beings, animals and the environment if they are used as per the label and leaflet approved by the Central Insecticide Board and Registration Committee.
- Pesticides are registered for use in the country by the Registration Committee only after being satisfied about their efficacy and safety to human health, animals and environment.
- However, the indiscriminate use of antibiotics is worrying as the practice may lead to the development and spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), already a pressing concern worldwide; at least 10 million people are likely to die of AMR every year by 2050.
- When used in crops, unspent antibiotics find their way into the surrounding environment.
- Microorganisms exposed to this increasing load of antibiotics in soil and water can develop resistance to it.
- The resistance can spread to other bacteria through transfer of genetic material. When humans or animals get infected by such resistant microorganisms, their treatment becomes difficult as well as expensive.
- There is a possibility that traces of antibiotics remain in the edible parts of the plant.
Central Insecticide Board and Registration Committee (CIBRC):
- The CIBRC is the country’s apex body that approves the use of pesticides.
- The use of pesticides and insecticides in India are regulated by the following two:
- Insecticides Act, 1968
- Insecticides Rules, 1971
- In the Act and the Rules framed thereunder, there is compulsory registration of the pesticides at the Central level and licence for their manufacture, formulation and sale are dealt with at the State level.
- With the enforcement of the Insecticides Act in the country, pesticides of very high quality are made available to the farmers and the general public for household use, for protecting the agricultural crops from the ravages of their pests, humans from diseases and nuisance caused by public health pests and the health hazards involved in their use have been minimised to a great extent.
- The CIBRC functions under the Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare.
6. NAVARMS-19
Why in News?
- The fourth edition of the International Seminar cum Exhibition on Naval Weapon Systems ‘NAVARMS-19’ will be held in New Delhi.
NAVARMS-19:
- NAVARMS is the only international seminar and exhibition on naval weapon systems conducted in India to invite all the stakeholders in life cycle management of naval weapons and provide a common platform to share their views and concerns.
- The theme for this year’s exhibition is: “Make in India – Fight Category: Opportunities and Imperatives”.
- The 2-day event will provide an opportunity for the exchange of ideas, create awareness and identify emerging prospects for Indian/International defence industry in the domain of naval weapon systems.
- The previous three editions were held in 2007, 2010 and 2013.







