Prelim Snippets 17-12-2019
1. Government Instant Messaging System (GIMS):
Why in News?
- The government has started testing its Government Instant Messaging System (GIMS):
About Government Instant Messaging System (GIMS):
- Designed and developed by National Informatics Centre (NIC).
- It is being packaged for employees of Central and state government departments and organisations for intra and inter organisation communications.
- It is an Indian equivalent of popular messaging platforms, such as WhatsApp and Telegram, for secure internal use.
- It is being developed as a secure Indian alternative without the security concerns attached with apps hosted abroad or those owned by foreign entities.
- Like WhatsApp, GIMS employs end-to-end encryption for one-to-one messaging.
Value addition for Mains:
Need for and significance:
- The launch of the new app comes amid the recent controversy over the WhatsApp breach. Some Indian users’ mobile devices were targeted through a spyware called Pegasus recently.
- GIMS is being touted as a safer bet as the platform has been developed in India, the server hosting it is installed within the country and the information stored would be in government-based cloud — NIC-operated data centres that are only meant for captive use by the government and its Departments.
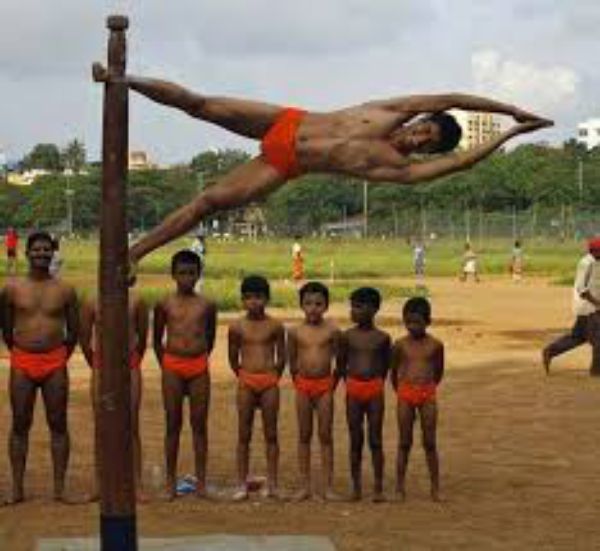
2. Mallakhamba
Why in News?
- Mallkhamba art form is recently displayed in the “The Fitness Arts Festival” of Maharashtra.
About Mallakhamba:
- Mallakhamba is a traditional sport, in which a gymnast performs aerial yoga postures and wrestling grips on a hanging wooden pole, cane, or rope.
- Mallakhamb (‘malla’ meaning ‘wrestler’ and ‘khamb’ meaning ‘pole’).
- It is performed as an art form, especially during national festivals.
- The pole is usually made from Indian rosewood polished with castor oil.
- This traditional sport is more prevalent in Maharashtra and adjacent regions.
- In 2013, Madhya Pradesh declared Mallakhamba the state sport.

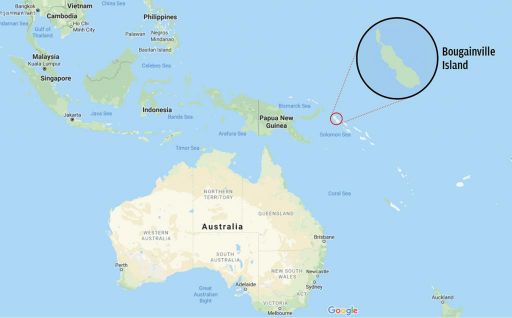
3. Bougainville – A new country in the Pacific
Why in News?
- The Autonomous Region of Bougainville, a chain of islands that lie 959 kilometres northwest of Papua New Guinea’s (PNG) capital, Port Moresby, has recently voted for its independence.
China’s interest in Bougainville:
- For the broader region, an independent Bougainville has a number of implications.
- Firstly, it sends a strong signal for other self-determination movements across the Pacific, including in New Caledonia which will hold a second referendum for independence in 2020.There are also geopolitical implications. The referendum has taken place during a period of heightened strategic anxiety among the Pacific’s so-called traditional partners — Australia, NZ and the US, as well as the UK, France and Japan.
- There have long been concerns China will seek to curry influence with an independent Bougainville.
- Beijing’s interest in Bougainville is two-fold: First, it is seeking to shore up diplomatic support in the Pacific Islands region, thereby reducing support for Taiwan which lost a further two Pacific allies this year.
- And second, to access to resources, namely fisheries and extractive minerals.
- The current strategic prism of China is about debt-trap diplomacy to undermine the importance of local dynamics and the resilience of Bougainville people.
Bougainville Referendum:
- The referendum marks an important part of a peace agreement signed almost 20 years ago.The 2001 Bougainville Peace Agreement ended the deeply divisive nine year conflict (1988-1997) that lead to the deaths of approximately 20,000 people, or about 10 per cent of Bougainville’s population. The referendum, however, is non-binding.
- The ultimate outcome will be determined by a vote in Papua New Guinea’s National Parliament following negotiations between the Papua New Guinean government and the Autonomous Bougainville Government.
4. Crystal award:
Why in News?
- Recently, 26thAnnual Crystal Award for the year 2020 have been announced.
About Crystal Award:
- It is awarded by the World Economic Forum (WEF)
- It is an annual award hosted by World Economic Forum’s World Arts Forum.
- It recognises the achievements of leading artists and cultural figures whose leadership inspires inclusive and sustainable change.
5. Article 6 of The Paris Agreement (CARBON MARKETS)
Why in News?
- Recently, Madrid climate talks finally setting up a new carbon market under the Paris Agreement.
About Carbon Market:
- It allows the buying and selling of carbon credits. It existed under the 1997 Kyoto Protocol as well but that regime is coming to an end next year.
About Article 6 of Paris Agreement:
- It describes provisions relating to setting up a new carbon market.
- It allows for two different approaches of carbon trading.
- It enables bilateral arrangements for transfer of emissions reductions, while ensuring that they do not double-count the reductions.
- It talks about a wider carbon market in which reductions can be bought and sold by anyone.
- It also provides for making ‘non-market approaches’ available to countries to achieve targets.
- It includes any cooperative action, like collaboration on climate policy or common taxation, that are not market-based.
- Countries like India, China and Brazil want their unsold carbon credits to be valid in the new market while the developed countries are opposing it on the ground that many of these credits were bogus and did not represent actual emission reductions.
6. Chief of the Army Staff
Why in News?
- Recently, Lt Gen MN Naravane named as next Chief of Army Staff.
About Chief of the Army Staff:
- It is created through the Commanders in Chief Act of the Indian parliament in 1955.
- Its appointment is made by the Appointments Committee of Cabinet (ACC).
- The tenure of office is three years or at the age of 62, whichever is earlier.
About ACC
- The composition of ACC has Prime Minister and Minister of Home Affairs.
- Initially, Minister of concern ministry is also a part of the committee.
- After the new notification on 2016 the minister of concern ministry is been excluded from the committee.
7. Evidence found for the existence of River Saraswati
Why in News?
- A study by Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad, and IIT Bombay, has recently divulged few details about the mystic River Saraswati.
Details of the study regarding River Saraswati:
- PRL has shown that the ancient counterpart of modern Ghaggar River was a perennial river, fed by glacial rivers in the past.
- This reaffirms the belief that the focus of Early Harappan civilization was not the Indus but the Saraswati River and its tributaries which flowed between the Indus and the Ganga.
- A number of researchers for this reason call Indus Valley Civilization as Indus-Saraswati civilization.
Background info:
- The NadiSukta hymn of Rig Veda makes a mention of 21 rivers including a perennial snow-fed river Saraswati.
- This mythological river is believed to be the life-blood of the Harappans.
- Besides more than 1500 archeological sites of the Harappan Civilization are found near the dried-up banks of the Ghaggar River.
- Thus, the study has concluded that River Saraswati was nothing but the ancient counterpart of the modern Ghaggar-Hakra








