Prelim Snippets- 28.02.2020
1. Market Intelligence and Early Warning System (MIEWS) Portal
Why in News?
- Recently, Union Minister of Food Processing Industries has launched the– Market Intelligence and Early Warning System (MIEWS) Web Portal.
About the Portal:
- It will provide real time monitoring of prices of tomato, onion and potato (TOP) and simultaneously generate alerts for intervention under the terms of the Operation Greens (OG) scheme.
- It would also disseminate all relevant information related to TOP crops such as Prices and Arrivals, Area, Yield and Production, Imports and Exports among others.
About Operation Greens:
- It is announced by the Union government in the Budget 2018-2019 with an outlay of Rs.500 crores.
- It aims to contain the annual price distress of tomatoes, onions and potatoes (TOP) in regions with high production.
- It aspires to increase the income of the farmers as in line with an ambition of doubling the farmer’s income by 2022.
- Their goals are to be achieved through interventions by encouraging farmer producers’ organisations, agri-logistics, processing facilities and Professional Management.
2. State of India’s Birds Report 2020
Why in News?
- The State of India’s Birds 2020 Report was recently released at the 13thCOP Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals, Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
Highlights:
- The report has been prepared with the help of a massive database of more than 10 million observations uploaded by 15,000 birdwatchers on the ‘e-bird’ platform.
- It is India’s first of its kind report that highlights observations by birdwatchers form the basis of the analyses.
- The project was started in May 2018 as a means to collect the actual data of birds in India.
- The final report was released on February 17, 2020, at 13thCOP to the convention on migratory species held in Gujarat.
Report:
- The report suggests that about 867 birds were assessed which made it clear that almost all the species are declining.
- The report categorises 101 species as of High Conservation Concern, 59 based on their range size and abundance trends, and an additional 42 based on their IUCN Red List status.
- According to the report, India has witnessed a big decline in migratory shorebirds, raptors, Indian Vulture, Large-billed Lea Warbler, Curlew Sandpiper, Richard’s Pipit and While-rumped Vulture.
- The report also highlights that some species have increased in numbers such as Glossy Ibis, Rosy Starling, Ashy Prinia, and Feral Pigeon.
- Birds were divided into different categories – 101 birds as a high concern, 319 birds as moderate concern and 442 birds as low concern species.
Growth of Indian Peacock:
- The State of India’s Birds 2020 Report said that numbers of Indian Peacock have increased.
- The report also highlights that good growth has been observed in Indian Peacock’s population.
- IUCN: Least concern
Status of House Sparrow:
- The report said that the number of India’s domestic or house sparrow has decreased in large cities but almost stable overall.
- House Sparrow is a commonly found birth across the country. It can be seen in small towns, villages also in markets.
- Its population is currently stable but more attention is required.The report said that there are certain reasons for decreasing numbers of house sparrows such as lack of suitable nesting sites and lack of insect (a key part of sparrow’s diet) population.
Suggestions:
- The report suggests that it is important to promote collaborations between public initiatives and researchers.
- It also suggests that the government should support the monitoring and conservation efforts by citizens and researchers.
- The report also suggests that there should be a dedicated fund for high concern species so that scientists and researchers can save those birds.
3. ICoSDiTAUS-2020
Why in News?
- ICoSDiTAUS-2020 a two-day International Conference on Standardisation of Diagnosis and Terminologies in Ayurveda, Unani and Siddha Systems of Medicine was concluded in New Delhi.
ICoSDiTAUS-2020:

- The conference was jointly organized by the Ministry of AYUSH and the WHO at New Delhi
- It adopted the “New Delhi Declaration on Collection and Classification of Traditional Medicine (TM) Diagnostic Data”.
- The New Delhi declaration emphasised the commitment of the countries to Traditional Medicine (TM) as a significant area of health care.
- It further sought the opportunity for including traditional systems of medicine like Ayurveda, Unani and Siddha in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) of WHO which is the standard diagnostic tool for health management across the world.
4. InSights Mission
Why in News?
- It’s now more than a year since NASA’s InSight lander mission touched down on Mars on November 26, 2018. This week, NASA published a set of six papers to reveal a planet alive with quakes, dust devils and strange magnetic pulses.
Highlights:
-
- The InSight mission is part of NASA’s Discovery Program.
- It is being supported by a number of European partners, which include France’s Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and the United Kingdom Space Agency (UKSA).
- InSight is the first mission dedicated to looking deep beneath the Martian surface. Among its science tools are a seismometer for detecting quakes, sensors for gauging wind and air pressure, a magnetometer, and a heat flow probe designed to take the planet’s temperature.
- Mars trembles more often than expected, but also more mildly. This emerged from readings of the ultra-sensitive seismometer, called the Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS).
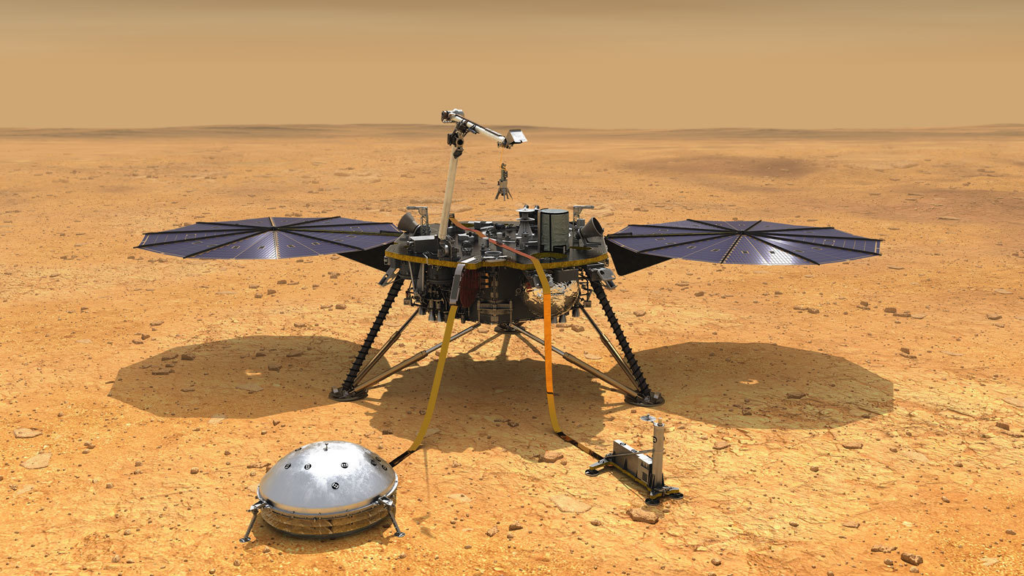

- The instrument enables scientists to hear multiple trembling events from hundreds to thousands of miles away.
- Mars doesn’t have tectonic plates like Earth, but it does have volcanically active regions that can cause rumbles. SEIS has found more than 450 seismic signals to date, the majority of which are believed to be quakes (as opposed to data noise created by environmental factors, like wind).
- Billions of years ago, Mars had a magnetic field. Although it is no longer present, it left behind magnetised rocks that are now between 61 m to several km below ground. InSight is equipped with a magnetometer, which has detected magnetic signals.
- InSight measures wind speed, direction and air pressure nearly continuously. Weather sensors have detected thousands of passing whirlwinds, which are called dust devils when they pick up grit and become visible.
- InSight has two radios. One is for regularly sending and receiving data. The other radio is designed to measure the “wobble” of Mars as it spins. This X-band radio, also known as the Rotation and Interior Structure Experiment (RISE), can eventually reveal whether the planet’s core is solid or liquid.
- A solid core would cause Mars to wobble less than a liquid one would.
5. Early Human Habitat in Northern India
Why in News?
- An archaeological excavation carried out in the trenches at Dhaba in the upper Son river valley in central India has found evidence of human occupation in this area almost 80,000 years ago.
Highlights:
- The international team of researchers found evidence of the continuous presence of humans in this region between 80,000 years ago and 65,000 years ago.
- The lithic industry (stone tools) from Dhaba strongly resembles stone tool assemblages from the African Middle Stone Age (MSA) and Arabia, and the earliest artefacts from Australia, suggesting that it is likely the product of Homo sapiens as they dispersed eastward out of Africa.
- This finding is important in the face of competing theories on the first presence of human populations in different regions of the world and on human dispersal from Africa.
- About 74,000 years ago, the Toba volcanic super-eruption, centred around Sumatra, is believed to have caused an almost decade-long spell of cold weather across many parts of the Earth.
- There is an argument that this induced winter not only led to the cooling of the Earth’s surface for almost a thousand years since the eruption, but also destroyed huge populations of hominins.
- The hypothesis is that the ‘volcanic winter’ caused a bottleneck in the gene pool of humans, because only a few survived who were in Africa at the time. Later, this population is believed to have emerged from Africa and colonised different parts of the world.
- However, the present study rules out this hypothesis as it implies that a population of early humans inhabited northern India even before the date of the eruption (74,000 years ago) and continued through the period of the devastation and until much later.
- The excavation unearthed a large tool industry spanning the period of the Toba super-eruption.
- The large Megalithic tools were dated between approximately 80,000 years and 65,000 years and the small tools were dated at approximately 50,000 years suggesting a continuous inhabiting of this region by humans undisturbed by the super-eruption.
- The fact that we find these before and after the Toba eruption with no apparent change in technology indicates that major eruptions like Toba appear not to have had a catastrophic effect on small hunter-gatherer bands living in India at the time.
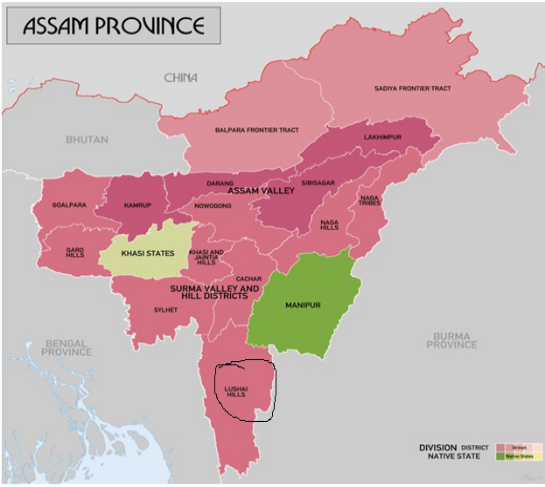
6. Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation (BEFR)
Why in News?
- The Mizoram government has sought the revision of the boundary with Assam, based on the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation (BEFR), 1873 and the Inner Line of the Lushai Hills Notification of 1993.
About:
- The BEFR allows Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Mizoram and Nagaland not to let non-resident Indians in without an inner-line permit for a temporary stay.
- Mizoram used to be the Lushai Hills district of Assam before being made a Union Territory in 1972 and a State in 1987.
- Mizoram shares a 123-km border with southern Assam and has been claiming a 509-square mile stretch “occupied” by the neighbouring State.
7. Light Combat Helicopter
Why in News?
- Recently, the Defence Minister inaugurated Light Combat Helicopter production at the HAL complex in Bengaluru. It is a part of the “Make in India” initiative.
About Light Combat Helicopters:
- It is completely designed by HAL. It has the capacity to carry 500 kg of load.
- It is powered by two Shakti engines and inherits many technical features of the Advanced Light Helicopter.
- It has the distinction of being the first attach helicopter to land in Forward Bases at Siachen, 4,700 mts above sea level.









