Prelim Snippets- 29.02.2020
1. Pigmentary Disorders
Why in News?
- A Rs. 3.6 crore grant has been given to promote research on pigmentary disorders.
Highlights:
- The grant in the form of an Intermediate Fellowship Award was given to an Assistant Professor at Faridabad-based Regional Centre for Biotechnology by the Wellcome Trust/DBT India Alliance.
- The award consists of a grant of Rs 3.60 crore for a period of five years.
Pigmentary Disorders:
- Physiological pigmentation is a critical defense mechanism by which skin is protected against harmful UV radiations.
- Inefficient pigmentation predisposes to skin cancers, which are one of the leading causes of cancer-associated deaths worldwide.
- Further, pigmentary disorders (both hypo and hyper pigmentary) are considered a social stigma and therefore they impart long-term psychological trauma and tremendously hamper mental well-being of patients.
- The current therapeutic strategies are not efficient in alleviating pigmentary disorders.
- The research project to be taken up under the award would seek to identify novel targetable molecular players that critically regulate pigmentation process. Further, the researchers would try to repurpose commercially available drugs for the treatment of pigmentary disorders.
- In the long run, this project is expected to have a two-pronged benefits for society – protection from UV-induced skin cancers and potential treatment options for pigmentary disorders.
- So far, the focus in the pigmentation biology field has been to understand the enzymes regulating melanin synthesis and on the melanosome proteins involved in their biogenesis and maturation. However, melanosome biogenesis and melanin synthesis are complex phenomena and other cellular organelles could potentially regulate this process.
2. Biofuels
Why in News?
- Researchers at the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB) are developing a method to improve the growth rate and sugar content of a marine microorganism called Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002.

Highlights:
- Most biotechnological processes, including biofuel production, are dependent on the availability of low-cost and sustainable supply of sugars and a nitrogen source.
- The sugars typically come from plants. Plants utilize light energy through the process of photosynthesis to convert carbon dioxide in the atmosphere into biological components such as sugars, proteins and lipids.
- However, some bacteria, such as the cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae), too can perform photosynthesis and produce sugar by fixing the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Using Cyanobacteria:
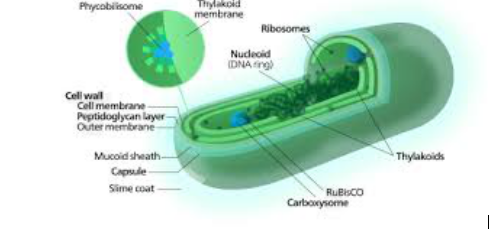
- The yield of sugars from cyanobacteria could potentially be much higher than that of land-based crops.
- Further, unlike plant-based sugars, cyanobacterial biomass provides a nitrogen source in the form of proteins.
- Cyanobacteria are found in both fresh and marine waters.
- Using marine cyanobacteria could be better as freshwater is increasingly getting scarce.
- However, there is a need to significantly improve their growth rates and sugar content in order to improve the economic feasibility of marine cyanobacteria-based sugar production.
- A team from the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology has achieved this. This could give the biofuel sector a boost.
- They have successfully engineered a marine cyanobacterium called Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 which showed a higher growth rate and sugar (glycogen) content. When grown on air, the growth was doubled and the glycogen content of the cells increased by about 50%.
- The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) sponsored the research.
3. ADIP Scheme
Why in News?
- The PM will distribute assistive aids and devices to senior citizens (under the Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana-RVY) and the physically challenged (Under ADIP Scheme) at a mega distribution camp at Prayagraj.
Highlights:
- This is said to be the biggest ever distribution camp being conducted in the country in terms of the number of beneficiaries covered, number of appliances distributed and value of aids and appliances distributed.
- In the mega camp, over 56,000 assistive aid and devices of different types will be distributed free of cost to over 26,000 beneficiaries. The cost of the aids and devices is over Rs.19 Crore. The objective is to provide assistance through these aids and devices to the daily living and socio-economic development of the Divyangjan (physically challenged) and Senior Citizens.
ADIP Scheme:
- This is the Assistance to Disabled persons for purchasing/fitting of aids/appliances (ADIP) scheme, under the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment, GOI.
- The main objective of the scheme is to assist the needy disabled persons in procuring durable, sophisticated and scientifically manufactured, modern, standard aids and appliances that can promote their physical, social and psychological rehabilitation, by reducing the effects of disabilities and enhance their economic potential.
- The scheme is implemented through implementing agencies such as NGOs, National Institutes under the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment and ALIMCO (a PSU that manufactures artificial limbs).
- Assistive devices are given to PwDs with an aim to improve their independent functioning, and to arrest the extent of disability and occurrence of secondary disability.
- The aids and appliances that are given under the ADIP scheme will be BIS certified to the extent possible.
- Eligibility: A person satisfying all the following conditions are Eligible:
- Indian citizen of any age
- Has 40% disability or more (must have the requisite certificate)
- Monthly income, not more than Rs.20000.
- In the case of dependents, income of parents/guardians should not exceed Rs.20000.
- Must not have received assistance during the last 3 years for the same purpose from any source. However, for children below 12years of age, this limit would be one year.
4. AI – MODULE
Why in News?
- Recently, NITI Aayog, Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) in collaboration with the National Association of Software and Services Companies (NASSCOM) has launched an Artificial Intelligence (AI) based Module.
About:
- It has been introduced with an objective for students to leverage the full potential of AIM’s Atal Tinkering Lab (ATL) and further empowers them to innovate and create valuable solutions benefiting societies at large.
- It contains activities, videos and experiments that enable students to work through and learn the various concepts of AI.
- AIM at NITI Aayog is the Government of India’s flagship initiative to promote a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship.
- It is establishing Atal Tinkering Lab (ATLs) in all districts across India, at the school level.
5. Mini-Moon
Why in News?
- Recently, the NASA’s Catalina Sky Survey (CSS)have observed a small object orbiting Earth.
About 20202 CD3:
- It is named 2020 CD3. It is also called “mini-moon” or “second moon”. It is orbiting at a distance farther from Earth.
- Sometimes, when an asteroid’s orbit crosses Earth’s orbit, it can be captured into the latter orbit. Such an asteroid is called a Temporarily Captured Object(TCO). The orbit of such objects is unstable.
- It was captured into Earth’s orbit over three years ago.
About Catalina Sky Survey:
- It is a project to discover and track near-Earth objects (NEOs). It is based in Arizona in the United States of America.
- It previously discovered 2006 RH120, which orbited Earth for some time in 2006 and escaped its orbit in 2007.
- The near-Earth objects (NEOs) are asteroids or comets with sizes ranging from metres to tens of kilometres that orbit the Sun and whose orbits come close to that of Earth’s.
6. Red Snow
Why in News?
- Recently, the phenomenon of “red snow” or “watermelon” has been observed over the last few weeks around Ukraine’s Vernadsky Research Base, off the coast of Antarctica’s northernmost peninsula.
Key Points:
- It is a phenomenon that has been known since ancient times but now it raises concerns about climate change.
- It is an algae species, Chlamydomonas Chlamydomonas nivalis which exists in the snow in the polar and glacial regions and carries a red pigment to keep itself warm.
- It contains chlorophyll (green pigment) as well as a red carotene layer in their cells which mixes with the green colour to cause snow to look like “raspberry jam”.
- It is also said to protect the algae from ultraviolet radiation. They change the snow’s albedo- the amount of light or radiation the snow surface is able to reflect back.
- The redness increases with the dense presence of the algae. The darker tinge leads to more absorption of heat by the snow. Subsequently, the ice melts faster.
- The melting is good for the microbes that need the liquid water to survive and thrive but it is bad for already melting glaciers.
7. Renewable Energy Management Centers (REMCs)
Why in News?
- The Northern Region Renewable Energy Management Centre (NR-REMC) was recently inaugurated in New Delhi.
About Renewable Energy Management Centers (REMCs):
- It is equipped with Artificial Intelligence based RE forecasting and scheduling tools.
- It provides greater visualization and enhanced situational awareness to the grid operators.
- Currently, 55 GW of Renewable energy is being monitored through the eleven REMCs, located in Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh etc.
- The Government of India had approved the implementation of the REMCs as a Central Scheme and had mandated POWERGRID, a Maharatna CPSE under Ministry of Power as an Implementing Agency.






