STEM CELLS A NEW RAY OF HOPE IN BATTLE AGAINST COVID-19
23, Apr 2020
Prelims level : Science & Technology
Mains level : GS-II Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector or Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Why in News?
- Researchers are now looking at Stem Cells as a cure for Covid-19 Patients.
Highlights:
- Key scientific groups worldwide, including those in China and the US, have been working to test the treatment.
- An Israeli pharmaceutical company, Pluristem Therapeutics, has tested it in seven critical hospitalized patients and found positive results. The company is now seeking approval to begin clinical trials.
- The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has already approved clinical trials to study covid-19 patients who have been administered MSC (mesenchymal stem-cells) derived from the placenta to prevent inflammation of lungs.
Efficacy of Approach against Covid 19:
- The Therapeutic approach involves intravenous injection of mesenchymal stem-cells (MSC) from a human placenta into a covid-19 patient to boost the body’s immune response against the Infection.
- Further Stem-cells have been successful in treating degenerative diseases, especially Alzheimer’s, as well as Type-1 diabetes.
- The advantage that stem-cells have is that they have strong anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, which can help strengthen our immune system.
- This is important in case of covid-19, where they could reduce inflammation of the lungs, which are the most affected.
- It could help build up regenerative cells in the lungs, which could protect the epithelial cells of the lungs, prevent lung damage and help patients recover.
Stem Cells:
- They are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and divide indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell.
- Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells. These daughter cells either become new stem cells (self-renewal) or become specialized cells (differentiation) with a more specific function, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells or bone cells.
- No other cell in the body has the natural ability to Generate New Cell Types.
Classification:
- Based on formation at Different times of Human Life:
- Embryonic stem cells:
- These stem cells come from embryos that are three to five days old. At this stage, an embryo is called a blastocyst and has about 150 cells.
- These are pluripotent stem cells, meaning they can divide into more stem cells or can become any type of cell in the body.
- This versatility allows embryonic stem cells to be used to regenerate or repair diseased tissue and organs
- Adult Stem Cells:
- These stem cells are found in small numbers in most adult tissues, such as bone marrow or fat.
- Compared with embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells have a more limited ability to give rise to various cells of the body.
- However, emerging evidence suggests that adult stem cells may be able to create various types of cells.
- For instance, bone marrow stem cells may be able to create bone or heart muscle cells.
- Induced pluripotent Stem Cells or (iPSC’s):
- These cells are not found in the body but made in the laboratory from cells of the body.
- The iPSC cells have properties similar to those of embryonic stem cells.
- Human iPSCs were generated in 2007.
- Perinatal Stem Cells:
- Researchers have discovered stem cells in amniotic fluid as well as umbilical cord blood.
- These stem cells also have the ability to change into specialized cells.
- Amniotic fluid fills the sac that surrounds and protects a developing fetus in the uterus.
- Based on Potency:
- Totipotent (also known as omnipotent) stem cells can differentiate into embryonic and extraembryonic cell types.
- Such cells can construct a complete, viable organism.
- These cells are produced from the fusion of an egg and sperm cell.
- Cells produced by the first few divisions of the fertilized egg are also totipotent.
- Pluripotent Stem Cells are the descendants of totipotent cells and can differentiate into nearly all cells, i.e. cells derived from any of the three germ layers.
- Multipotent Stem Cells can differentiate into a number of cell types, but only those of a closely related family of cells.
- Oligopotent Stem Cells can differentiate into only a few cell types, such as lymphoid or myeloid stem cells.
- Unipotent Cells can produce only one cell type, their own, but have the property of self renewal, which distinguishes them from non-stem cells
Significance:
- Increase understanding of how diseases occur.
- By watching stem cells mature into cells in bones, heart muscle, nerves, and other organs and tissue, researchers and doctors may better understand how diseases and conditions develop.
- Test new drugs for safety and effectiveness.
- Before using investigational drugs in people, researchers can use some types of stem cells to test the drugs for safety and quality.
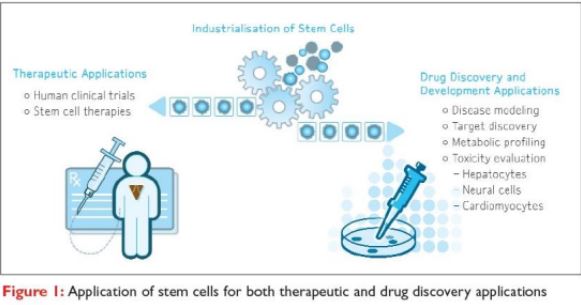
- Generate healthy cells to replace diseased cells (Regenerative Medicine).
- Stem cells can be guided into becoming specific cells that can be used to regenerate and repair diseased or damaged tissues in people.