UTTAR PRADESH TOPS LIST IN CRIMES AGAINST WOMEN, SAYS NCRB
10, Jan 2020

Prelims level : Constitutional Bodies, Regulatory Bodies
Mains level : GS-II Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein
Why in News?
- Recently, the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) published the annual Crime in India Report 2018.
About NCRB:
- NCRB, headquartered in New Delhi, was set-up in 1986 under the Ministry of Home Affairs to function as a repository of information on crime and criminals so as to assist the investigators in linking crime to the perpetrators.
- It was set up based on the recommendations of the National Police Commission (1977-1981) and the MHA’s Task Force (1985).
- NCRB brings out the annual comprehensive statistics of crime across the country (‘Crime in India’ report).Being published since 1953, the report serves as a crucial tool in understanding the law and order situation across the country.
Suicides in India:
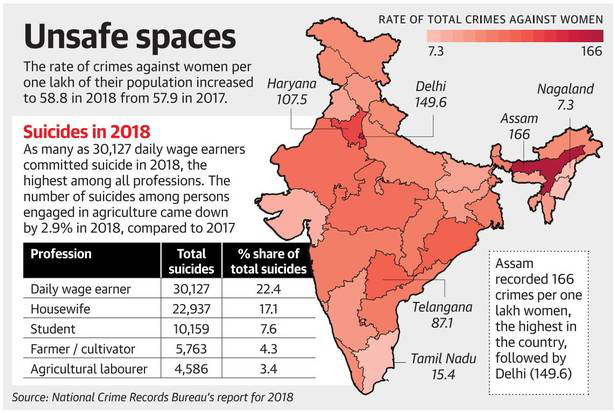
- The NCRB released the Accidental Death and Suicides in India 2018 report, which said that 10,349 people working in the farm sector ended their lives in 2018, accounting for 7 % of the total number of suicides in the country.
- There were 5,763 farmers/cultivators and 4,586 agricultural labourers among those who ended their lives.
- The total number of people who committed suicide in 2018 was 1, 34,516, an increase of 3.6%from 2017 when 1, 29,887 cases were reported.
- The highest number of suicide victims were daily wagers— 26,589, comprising 22.4% of such deaths.
- The majority of the suicideswere reported in Maharashtra (17,972) followed by Tamil Nadu (13,896), West Bengal (13,255), Madhya Pradesh (11,775) and Karnataka (11,561).
- Many States and Union Territories have also reported nil data on suicides by farmers, cultivators and farm labourers.
- “West Bengal, Bihar, Odisha, Uttarakhand, Meghalaya, Goa, Chandigarh, Daman & Diu, Delhi, Lakshadweep and Puducherry reported zero suicidesby farmers/cultivators as well as agricultural labourers,”
Murder Cases:
- The incidents registered under the Scheduled Caste andScheduled Tribes related Acts saw a decline from 6729 incidents reported in 2017 to 4816 in 2018.
- A total of 29,017 cases of murder were registered in 2018, showing an increase of 1.3% over 2017 (28,653 cases).
- A total of 76,851 cases of offences against public tranquillity were registered in 2018, out of which rioting, 57,828 cases, accounted for 75.2% of total such cases, the report said.
- As many as 27,248 cases of cyber-crimes were registered in 2018, up from 21796 cases in 2017.
Crime against Women:
- According to the report, 3, 78,277 cases of crime against women were reported in the country, upward trend from 3, 59,849 in 2017.
- Uttar Pradeshtopped the list with 59,445 cases, followed by Maharashtra (35,497) and West Bengal (30,394).
- The conviction rate in rape-related cases stood at 27.2% even though the rate of filing charge sheets was 85.3% in such cases.
- Cruelty by husband or his relatives (31.9%) followed by assault on women with intent to outrage her modesty (27.6%) constituted the major share of crimes against women.
- A total of 50, 74,634 cognizable crimes — 31, 32,954 Indian Penal Code (IPC) crimes and 19, 41,680 Special & Local Laws (SLL) crimes — were registered in 2018, showing an increase of 1.3% in registration of cases compared to 2017(50, 07,044 cases).
- The crime rate per lakh population, however, came down from 388.6 in 2017 to 383.5 in 2018.
What would be the causes for crimes against Women?
- Gender Disparity is one of the deep rooted causes of violence against women that put women at risk of several forms of violence.
- Discriminatory gender norms and gender stereotypes results into structural inequality.
- Psychiatric Morbidity generally refers to the incidence of both physical and psychological deterioration as a result of a mental or psychological condition, generally caused due to the consumption of alcohol.
- Regular consumption of alcoholby the husband has been strongly associated with poor mental health of women.
- Alcohol operates as a situational factor, increasing the likelihood of violence by the husbands against their wives.
- Socio demographic factors like Patriarchy have been cited as the main cause of violence against women. Where women have a higher economic status than their husbands and are seen as having sufficient power to change traditional gender roles, risk for violence is high.
- Family factors such as exposure to harsh physical discipline during childhood and witnessing the father beating the mother during childhood is a predictor of victimization and perpetration of violence against wife in adulthood.
Few Traditional and cultural practices against Women:
- Female genital mutilation:Can lead to death, infertility, and long-term psychological trauma combined with increased physical suffering.
- Acid attacks:Acid attacks have emerged as a cheap and readily accessible weapon to disfigure and sometimes kill women and girls for reasons as varied as family feuds, inability to meet dowry demands, and rejection of marriage proposals.
- Killing in the name of family honour:In several countries of the world including Bangladesh, Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Pakistan, Turkey, and India, women are killed to uphold the honour of the family due to varied reasons such as-alleged adultery, premarital relationship (with or without sexual relations), rape, falling in love with a person the family disapproves, which justify a male member of the family to kill the woman concerned.
- Early marriages:Early marriage with or without the consent of the girl, constitutes a form of violence as it undermines the health and autonomy of millions of girls.
- Judiciary and law enforcement machinery:An insensitive, inefficient, corrupt and unaccountable judicial system and law enforcement machinery fails to deter against various forms of crimes.
- Socio cultural factors disfavouring women: Stereotypes of gender roles have continued over the ages.
- The primary roles for women have been marriage and motherhood.
- Women must marry because an unmarried, separated or divorced status is a stigma.
- The custom of dowry is still prevalent in Indian marriages.
Need for an hour:
- Gender based legislation:It is important to enact and enforce legislation and develop and implement policies that promote gender equality by ending discrimination against women in marriage, divorce and custody laws, inheritance laws and ownership of assets.
- Financial Independence:Improving women’s access to paid employment.
- Developing and resourcing national plans and policies to address violence against women.
- Improve system of collecting crime surveillance data on violence against women.
- Capacity building and training to service providers and law enforcement officers to handle cases of violence against women.
- Male Mediated Initiatives:Ensure male involvement in devising program for abusers.
- Prevent recurrence of Violence:Through early identification of women and children who are experiencing violence and providing appropriate referral and support
- Promote egalitarian gender norms as part of life skills and comprehensive sexuality education curricula taught to young people.
- Gender Based Surveys:Generate evidence on what works and on the magnitude of the problem by carrying out population-based surveys, or including violence against women in population-based demographic and health surveys, as well as in surveillance and health information systems.