DISEASES OF ANIMAL AND FOREST ORIGIN
04, Apr 2020

Prelims level : Disaster Management
Mains level : GS-III Disaster Management
Why in News?
- The recent rapid spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus across the world has focused attention on the invisible processes that help pathogens originally found in wild animals, infect the humans.
Factors for the origin:
- The destruction of forests and trapping or farming of wild species has brought these animals closer to humans.
- The viruses they harbour find ready hosts in domestic animals, moving to humans.
- Rising Activity: such as road building and mining cutting through forests bring more people in close contact with animals.
- Global trade in wild species: for instance, in Wuhan the trade ranges from wolf pups to rats, civets and foxes, etc. and their sale in markets along with domestic animals.
Consequences:
- Unlike previous epidemics, COVID-19 has extracted a staggering toll, killing people, forcing a lockdown.
- Economic devastation and recession.
- Short-term high growth trajectories can come to an abrupt halt with a pandemic.
- Diseases of animal origin: Examples are Ebola, HIV, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome, bird flu and swine flu.
What does these Pandemics Signify?
- Maintain viable ecosystems: For instance, Nipah and Hendra viruses, involving transfer from bats to pigs in the former, and bats to horses, highlights the need of maintaining an ecosystem.
- Eliminate the need for wild animals like bats to colonise human surroundings.
- Conserve the biodiversity: Biodiversity in forests harmlessly retains dangerous virusesand other pathogens away from people.
- Stop viewing undisturbed landscapes as an impediment to economic growth.
- Warning to hasty development process: hasty permissions granted for new roads, dams, mines and power projects in already enfeebled forests can unleash more scourges.
- Forest should be left undisturbed. Pristine forests with diverse species keep viruses virtually bottled up, out of man’s way.
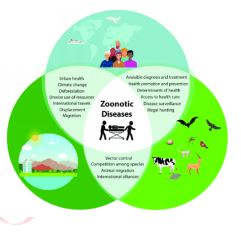
Zoonotic Diseases:
- Zoonotic diseases are an infectious disease caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites that spread from non-human animals (usually vertebrates) to Humans.
Modes of Transmission:
- Direct Zoonosis: the disease is directly transmitted from other animals to humans through media such as air (influenza) or through bites and saliva (rabies).
- Indirect Zoonosis: transmission can also occur via an intermediate species (referred to as a vector), which carry the disease pathogen without getting infected.