LARGEST HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER IS NOW CLOSED
28, Apr 2020
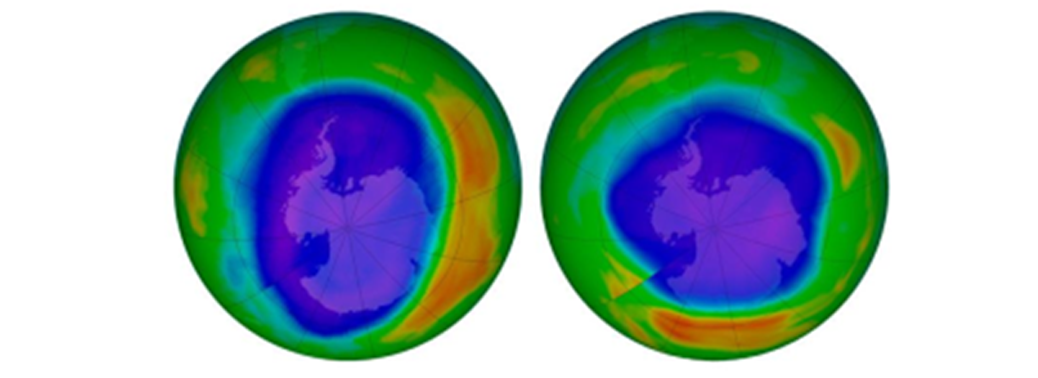
Prelims level : Environment
Mains level : GS-III Important Geophysical Phenomena such as Earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic Activity, Cyclone etc., Geographical Features and Their Location - Changes in Critical geographical features (including waterbodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
Why in News?
- Recently the EU’s Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) announced that a hole in the Arctic ozone layer, believed to be the biggest reported, has closed.
Healed Ozone Hole:
- The ozone hole’s closing was because of a phenomenon called the polar vortex, and not because of reduced pollution levels due to Covid-19 lockdowns around the world.
- The hole in the North Pole’s ozone layer, which was first detected in February, had since reached a maximum extension of around 1 million sq km.
Ozone Hole:
- The ‘ozone hole’ is not really a hole — it refers to a region in the stratosphere where the concentration of ozone becomes extremely low in certain months.
- Ozone, made up of three oxygen atoms, occurs naturally in small amounts.
- Roughly 10 km to 40 km up in the atmosphere (the layer called the stratosphere), the ozone layer is sunscreen, shielding Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
- Manufactured chemicals deplete the ozone layer. Each spring over Antarctica (it now springs there), atmospheric ozone is destroyed by chemical processes.
- This creates the ozone hole, which occurs because of special meteorological and chemical conditions that exist in that region.
The Importance of the Ozone layer:
- Ozone (chemically O3, a molecule of three oxygen atoms) is found mainly in the upper atmosphere, an area called the stratosphere, between 10 and 50 km from the earth’s surface.
- Though it is talked of as a layer, ozone is present in the atmosphere in rather low concentrations.
- Even at places where this layer is thickest, there are not more than a few molecules of ozone for every million air molecules.
- They perform a very important function. By absorbing the harmful ultraviolet radiations from the sun, the ozone molecules eliminate a big threat to life forms on earth.
- UV rays can cause skin cancer and other diseases and deformities in Plants and Animals.
Massive Hole:
- This year, the ozone depletion over the Arctic was much larger.
- Scientists believe that unusual atmospheric conditions, including freezing temperatures in the stratosphere, were responsible.
- Cold temperatures (below -80°C), sunlight, wind fields and substances such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) were responsible for the degradation of the Arctic ozone layer.
- Although Arctic temperatures do not usually fall as low as in Antarctica, this year, powerful winds flowing around the North Pole trapped cold air within what is known asthe polar vortex.
- By the end of the polar winter, the first sunlight over the North Pole initiated this unusually strong ozone depletion—causing the hole to form.
How long it will Take for Complete Recovery?
- As per the Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion data of 2018, the ozone layer in parts of the stratosphere has recovered at a rate of 1-3 per cent per decade since 2000.
- At these projected rates, the Northern Hemisphere and mid-latitude ozone is predicted to recover by around 2030, followed by the Southern Hemisphere around 2050, and polar regions by 2060.







