MEDICAL DEVICES NOTIFIED AS DRUGS FROM 1ST APRIL
02, Apr 2020

Prelims level : Governance
Mains level : Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector or Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Why in News?
- The government’s regulation to classify all Medical Devices as Drugs for the prime purpose of quality control and price monitoring.
Highlights:
- The government is regulating 24 class of medical devices which have been notified as drugs under Drugs & Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Drugs & Cosmetics Rules, 1945.
- Of the above, 4 medical devices viz. (i) Cardiac Stents (ii) Drug Eluting Stents (iii)
- Condoms and (iv) Intra Uterine Device (Cu-T) are scheduled medical devices for which ceiling prices have been fixed.
- The remaining non-scheduled medical devices which are notified as drugs, NPPA is currently monitoring Maximum Retail Prices.
- Thus, with effect from 1st April, 2020, all Medical Devices shall be regulated by the Government as Drugs for quality control and price monitoring.
- Therefore, the Maximum Retail Prices of all the Medical Devices would be monitored by the Government to ensure that no manufacturer/importer increases the MRP of a drug more than ten percent of MRP during preceding twelve months.
- Further, with the Essential Commodities Act, 1955, the manufacturer/importer will also be liable to deposit the overcharged amount along with interest thereon from the date of increase in price in addition to penalty.
Background:
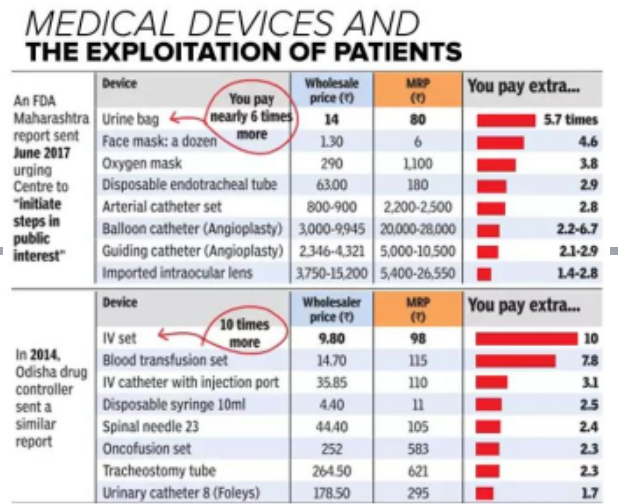
- Need for the Changes in Rules:
- The need for change in rules came in following media reports which brought to the fore the faulty hip implants marketed by pharma major Johnson & Johnson.
- Present State of Regulation:
- Drugs fall under Concurrent List, in this regard, GOI enacted Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940
- Further, some of the Medical devices were classified as drugs in 1982.
- Presently, only 23 categories of medical devices have been classified as drugs under Medical Devices Rules, 2017.
- Of these, only a few including cardiac stents, drug eluting cardiac stents, condoms, intrauterine devices, have been brought under price control.
- Existing Penal Provisions:
- There are various penal provisions under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 for various kinds of offences.
- For manufacturing or sale of substandard items: punishable with imprisonment of at least 10 years, which may extend to imprisonment for life.
Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB):
- It is the highest statutory decision-making body on technical matters related to drugs in the country.
- It is constituted as per the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- It is part of the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) in the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
CDSCO:
- The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) under Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India is the National Regulatory Authority (NRA) of India.
- Under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, CDSCO is responsible for
- Approval of New Drugs
- Conduct of Clinical Trials
- Laying down the standards for Drugs
- Control over the quality of imported Drugs in the country and
- Coordination of the activities of State Drug Control Organizations by providing expert advice with a view to bring about the uniformity in the enforcement of theDrugs and Cosmetics Act.
- CDSCO along with state regulators, is jointly responsible for grant of licenses of certain specialized categories of critical Drugs such as blood and blood products, Vaccine and Sera.
Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Rules 1945:
- It regulates the import, manufacture and distribution of medicines in the country.
- It Also ensures that drugs and cosmetics sold in India are safe, effective and conform to state quality standards.
- Entrusts various responsibilities to central & state regulators for regulation of drugs & Cosmetics.
- The related Rules,1945 contains provisions for classification of drugs under different schedules and prescribes guidelines for the storage, sale, display and prescription of each schedule.








