Priority Sector Lending
Introduction
Priority sector was first properly defined in 1972, after the National Credit Council emphasized that there should be a larger involvement of the commercial banks in the priority sector.
The sector was then defined by Dr. K S Krishnaswamy Committee.
Objective of Priority Sector Lending
To ensure that adequate institutional credit flows into some of the vulnerable sectors of the economy, which may not be attractive for the banks from the point of view of profitability.
Priority Sector Targets
- 1. In 1974, the banks were given a target of 33.33 % as share of the priority sector in the total bank credit.
- 2. On the basis of Dr. K S Krishnaswamy committee, the target was raised to 40%. The current Priority sector targets are as follows:
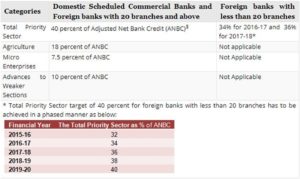
Current Priority Sector Categories
As per the RBI circular dates July 7, 2016, there are eight broad categories of the Priority Sector Lending viz.
- Agriculture
- Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- Export Credit
- Education
- Housing
- Social Infrastructure
- Renewable Energy
- Others
1.Agriculture
The agriculture category includes three sub-categories viz. farm credit, agriculture infrastructure and ancillary activities.
1.1 Farm Credit
- Loans to individual farmers, Self Help Groups and Joint Liability Groups for agriculture and allied activities viz. dairy, fishery, animal husbandry, poultry, bee-keeping and sericulture. This includes loans for crops, purchase of farm inputs, loan for pre and post harvest activities, loan up to Rs. 50 Lakh against pledge of farm produce; Loans under Kisan Credit Card Scheme; Loan for purchase of farm land.
- Loan to corporate farmers, farmers producer organizations and companies, Farm cooperatives up to Rs. 2 Crore.
1.2 Agriculture Infrastructure
- Construction of storage facilities such as warehouses, market yards, godowns, silos, cold storage units and chains for farm produce.
- Soil conservation and watershed development projects.
- Plant tissue culture and agri-biotechnology, seed production, production of bio-pesticides, bio-fertilizer, and vermi composting.
1.3 Ancillary Activities
- Loans up to ₹5 crore to co-operative societies of farmers for disposing of the produce of members.
- Loans for setting up of Agriclinics and Agribusiness Centres.
- Loans for Food and Agro-processing up to an aggregate sanctioned limit of 100 crore per borrower from the banking system.
- Loans to Custom Service Units managed by individuals, institutions or organizations who maintain a fleet of tractors, bulldozers, well-boring equipment, threshers, combines, etc., and undertake farm work for farmers on contract basis.
- Bank loans to Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), Farmers’ Service Societies (FSS) and Large-sized Adivasi Multi-Purpose Societies (LAMPS) for on-lending to agriculture.
- Loans sanctioned by banks to MFIs for on-lending to agriculture sector as per the conditions specified in paragraph 19 of these Master Directions.
- Outstanding deposits under RIDF and other eligible funds with NABARD on account of priority sector shortfall.
2. MSME
Any loan to MSME industries for their business purposes comes under priority sector. MSMEs have been defined by Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises in 2006 as per investment limit in plant & machinery as follows:

For service sector the Bank loans up to Rs. 5 crore per unit to Micro and Small Enterprises and Rs. 10 crore to Medium Enterprises engaged in providing or rendering of services are eligible. This includes all types of services including restaurants, hotels, travel agents, software companies etc.
Further, the following loans are also counted as priority sector loans under MSME:
- Loans to Khadi and Village Industries Sector (KVI)
- Loans to entities which provide inputs to artisans / village / cottage industries and their cooperatives
- Loans to Micro-finance Institutions, which in turn use this loan to disburse to MSME
- Loans under various schemes related to MSME scheme
- Overdraft under Pradhan Mantri Jan-dhan Yojana up to Rs. 5000.
- Outstanding deposits with SIDBI and MUDRA Ltd. on account of priority sector shortfall.
3. Export Credit
Export credit is a part of priority sector loan subject to 2% cap for domestic banks and foreign banks with >20 branches. However, for foreign banks with <20 branches, the export credit limit is up to 32% of the ANBC.
4. Education
This includes loans to individuals for educational purposes including vocational courses up to Rs. 10 lakh irrespective of the sanctioned amount will be considered as eligible for priority sector.
5. Housing
- For housing loans to individuals, limit to be counted as priority sector loans is Rs. 28 Lakh in Metros and Rs. 20 Lakh in other cities, towns and villages.
- For repairing of house, limit is Rs. 5 Lakh in metros and Rs. 2 lakh in others.
- Loans to any government agency for construction of houses subject to ceiling of Rs. 10 Lakh per house / dwelling unit for weaker sections or slum clearing.
- Outstanding deposits with NHB on account of priority sector shortfall.
6. Social Infrastructure
- This includes loans up to 5 crore per borrower for building social infrastructure for activities viz. schools, health care facilities, drinking water facilities and sanitation facilities including construction/ refurbishment of household toilets and household level water improvements in Tier II to Tier VI centres.
- It also includes loan to Micro-finance Institutions (MFIs) for on-lending to SHGs and JLGs for water and sanitation facilities.
7. Renewable Energy
- This includes loan up to Rs. 15 crore to borrowers for purposes like solar based power generators, biomass based power generators, wind mills, micro-hydel plants and for non-conventional energy based public utilities Viz. Street lighting systems, and remote village electrification.
- For individual households, the loan limit will be 10 lakh per borrower.
8. Others
- Personal loans to weaker sections up to Rs. 50,000 per borrower.
- Loans to distressed persons with a limit to Rs. 1,00,000/- per borrower to prepay their debt to non-institutional lenders
- Loans to State Sponsored Organisations for Scheduled Castes/ Scheduled Tribes for the specific purpose of purchase and supply of inputs and/or the marketing of the outputs of the beneficiaries of these organisations.
Small / marginal farmer
For computation of targets, RBI defines marginal farmer as one with less than 1 hectare of land {1 hectare=11959 Yards}, and small farmers as one with 1-2 hectare of land.
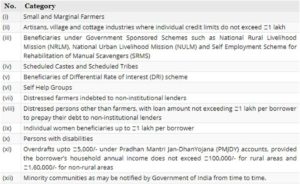
Weaker sections
Priority sector loans to the following borrowers will be considered under Weaker Sections category:
How Priority Sector Lending is linked to so called Double Financial Repression?
- Priority Sector lending in India has been made a salient feature of the banking in India mainly due to the social and economic objectives that underlie PSL.
- However, banks are also required to keep certain amount to maintain Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) and from the remaining disposable amount, 40 per cent is dedicated for the priority sector.
- Thus, large fraction of banks’ resources cause the so called “Double Repression” on the banking system.
- The economic survey has brought this issue to the forefront and has recommended the government to re-structure SLR and Priority Sector Lending.






