AUTO INDUSTRY SLOWDOWN
09, Aug 2019

Prelims level : Economics- Industries
Mains level : GS-III- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment. GS-III- Effects of liberalization on the economy, changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth.
Context:
- Federation of Automobile Dealers Associations has stated that nearly 2 lakh jobs have been cut in the last three months due to the slowdown. The slowdown continued in July, which reflected in the decline in domestic sales of up to 50 per cent announced by leading automobile manufacturers.
- Players from the auto sector petitioned the government for assistance, including a reduction of GST from 28 per cent to 18 per cent on vehicles.
- And called for a temporary relief on GST by way of modification in slabs or removal of cess to put the industry back on track.
Background:
- The Indian auto industry became the 4th largest in the world with sales increasing 9.5 per cent year-on-year to 4.02 million units (excluding two wheelers) in 2017. It was the 7th largest manufacturer of commercial vehicles in 2018.
- The Two Wheelers segment dominates the market in terms of volume owing to a growing middle class and a young population. Moreover, the growing interest of the companies in exploring the rural markets further aided the growth of the sector.
Recent Issue:
Slowdown in Sale of Automobile:
- As per SIAM figures, vehicle sales across all categories declined by 12.35 per cent to 60,85,406 units between April and June 2019 against 69,42,742 units in same period of last year.
- FADA has stated that nearly 2 lakh jobs have been cut in the last three months due to the slowdown.
- The slowdown continued in July, which reflected in the decline in domestic sales of up to 50 per cent announced by leading automobile manufacturers.
Loss of jobs in the sector:
- As a result of the cuts in production, companies have now resorted to reducing headcounts, industry insiders say.
- The job losses have begun across the value chain, including in showrooms, suppliers, and other stakeholders, and companies are now considering reducing their headcount — starting with contractual employees.
Demand for quick resolution:
- Making a case for quick resolution and a cut in GST rates.
- Auto industry contributes revenues of over of Rs 1,80,000 crore to government treasuries, and the current slowdown in the auto industry poses a major threat to the financial arithmetic of the government.
- According to SIAM estimates, the slowdown has resulted in an 8% loss in GST collection in the first six months of 2019.
- Hinting that decline in the auto sector may hurt the economy,
- Automobile sector has a huge multiplier effect.
- Auto Sector constitutes 7.1 per cent of the GDP, and 49% of the manufacturing GDP in the country, and it supports almost 37 million jobs (inclusive of its value chain).
- Alongside a cut in GST rates, the industry has also been demanding that banks and other lenders pass the cut in rates by the Reserve Bank of India to the consumers so that demand is revived.
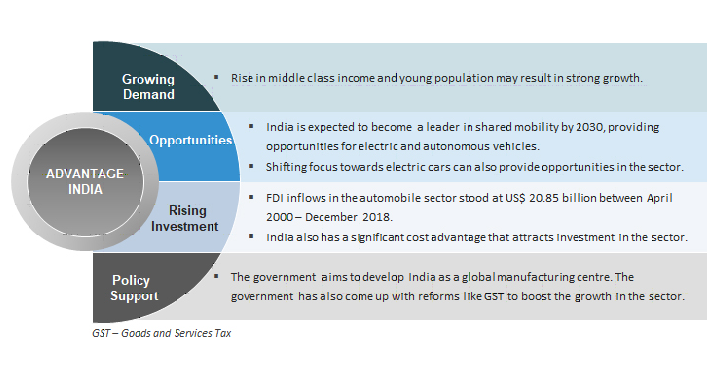
Previous Initiatives of Government in Automobile sector:
- The Government of India encourages foreign investment in the automobile sector and allows 100 per cent FDI under the automatic route.
- Some of the recent initiatives taken by the Government of India:
- The government aims to develop India as a global manufacturing centre and an R&D hub.
- Under National Automotive Testing And R&D Infrastructure Project (NATRIP), the Government of India is planning to set up R&D centres at a total cost of US$ 388.5 million to enable the industry to be on par with global standards
- The Ministry of Heavy Industries, Government of India has shortlisted 11 cities in the country for introduction of electric vehicles (EVs) in their public transport systems under the FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid) and Electric Vehicles in India) scheme. The government will also set up incubation centre for start-ups working in electric vehicles space.
- In February 2019, the Government of India approved the FAME-II scheme with a fund requirement of Rs 10,000 crore (US$ 1.39 billion) for FY20-22.








