Category: Robotics & Artificial Intelligence
FACIAL RECOGNITION
09, Mar 2020

Context:
- In recent years, facial recognition has become a cause for concern in western democracies. The European Commission is considering imposing a five-year moratorium on the use of facial recognition technologies in the European Union (EU). Whereas, the United States (US), municipalities have are considering passing prohibitions, India, however, is rushing to adopt public facial recognition.
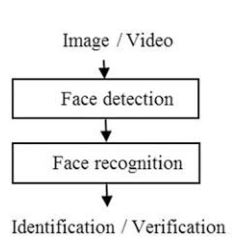
What is Facial Recognition, and how does it work?
- Facial recognition is a technology, based on artificial intelligence (AI), that leverages biometric data to identify a person based on their facial patterns.
- It can be used for the purposes of ‘verification’ and ‘identification’ of individuals.
- Facial recognition has evolved in many ways, from the first cameras that could recognise faces in the mid-1960s up to now.
- It has evolved from looking at 3D contours of a face to recognising even the skin patterns.
- Facial recognition systems analyze the visual data and millions of images and videos created by high-quality Closed-Circuit Television (CCTV) cameras installed in our cities for security, smartphones, social media, and other online activity.
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence capabilities in the software map the distinctive facial features mathematically, look for patterns in the visual data, and compare new images and videos to other data stored in facial recognition databases to determine identity.
- Market research experts believe that the facial recognition market will grow to $9.6 billion by 2022.
What are the uses of Facial Recognition Technology?
- Today, it’s used in a variety of ways from allowing you to unlock your phone, go through security at the airport, purchase products at stores etc,.
- One of the major advantages of facial recognition technology is safety and security.
- Law enforcement agencies use the technology to uncover criminals or to find missing children or seniors.
- In the financial sector, the demand for remote identification services is growing faster than ever, so identity verification technology based on live video is increasingly used such as the Fully-Verified system.
- Airports are increasingly adding facial recognition technology to security checkpoints.
- It can play a critical role in finding missing children, preventing human trafficking, and curbing crime. Experts believe that when people know they are being watched, they are less likely to commit crimes so the possibility of facial recognition technology being used could deter crime.
Where do we find Such Technology in India?
- Facial recognition systems have been active at several major Indian airports, including the Delhi airport. These systems at airports have been installed under the DigiYatra initiative.
- Telangana’s election commission piloted a facial recognition app in its local elections, and claimed that it could address the issue of voter impersonation.
- In the long-term, India plans to build a nation-wide Automated Facial Recognition System (AFRS) under the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), to modernize the process for criminal identification and verification by various police organizations across the country.
What are the Issues Associated with the Technology?
- The accuracy of the facial recognition software is questionable.
- For instance, the Delhi Police applied the facial recognition technology to find missing children, the success rate was less than 1 percent.
- In some cases, the technology could not even differentiate between genders.
- The technology suffers from ethnic and racial biases globally.
- The technology propagates, open collection of private data without putting in place adequate safeguards for individual privacy.
- As a consequence, it infringes upon an individual’s Fundamental Rights.
- There is a possibility that the technology could be used for mass surveillance.
- There’s no sufficient information regarding the type of security that would be employed to ensure the integrity of the repository of the database such that it is not privatized or monetized.
- The level of reliability or admissibility standards that would apply to such data being presented as evidence during legal proceedings cannot be determined.
Finding the Balance:
- The current application of facial recognition for public services does raise reasonable questions and concerns about privacy and rights.
- However, given this technology’s potential to solve problems, if applied properly in specific cases and contexts and with proper regulatory mechanisms, it could be leveraged in a beneficial manner.
NATIONAL MISSION ON QUANTUM TECHNOLOGIES & APPLICATIONS
03, Feb 2020

Why in News?
- The Finance Minister in budget 2020 has announced a National Mission on Quantum Technologies & Applications (NM-QTA).
Quantum Technology:
- Quantum Technology is based on the principles of quantum theory, which explains the nature of energy and matter on the atomic and subatomic level.
- It concerns the control and manipulation of quantum systems, with the goal of achieving information processing beyond the limits of the classical world.
- Its principles will be used for engineering solutions to extremely complex problems in computing, communications, sensing, chemistry, cryptography, imaging and mechanics.
- This key ability makes quantum computers extremely powerful compared to conventional computers when solving certain kinds of problems like finding prime factors of large numbers and searching large databases.
Quantum Mechanics:
- It is a fundamental theory in physics which describes nature at the smallest – including atomic and subatomic – scales.
- At the scale of atoms and electrons, many of the equations of classical mechanics, which describe how things move at everyday sizes and speeds, cease to be useful.
- In classical mechanics, objects exist in a specific place at a specific time.
- However, in quantum mechanics, objects instead exist in a haze of probability; they have a certain chance of being at point A, another chance of being at point B and so on.
NM-QTA:
- The mission will function under the Department of Science & Technology (DST).
- It will be able address the ever increasing technological requirements of the society, and take into account the International Technology Trends.
- The mission will help prepare next generation skilled manpower, boost translational research and also encourage entrepreneurship and start-up ecosystem development.
Significance:
- Quantum technologies are rapidly developing globally with a huge disruptive potential.
- The range of quantum technologies is expected to be one of the major technology disruptions that will change entire paradigm of computation, communication and encryption.
- It is perceived that the countries who achieve an edge in this emerging field will have a greater advantage in Garnering Multifold Economic Growth and Dominant Leadership Role.
- It has become imperative both for government and industries to be prepared to develop these emerging and disruptive changes.
- It will establish standards to be applied to all research and help stimulate a pipeline to support research and applications well into the future.
Cell Sized Robots
13, Oct 2018
- MIT scientists have developed a method to mass produce robots no bigger than a cell that could be used to monitor conditions inside an oil or gas pipeline, or to search out disease while floating through the bloodstream by using Auto perforation technique.
About:
- Tiny robots no bigger than a cell could be mass-produced using a new method developed by researchers at MIT called autoperforation.
- The microscopic devices, called “syncells” (short for synthetic cells), might eventually be used to monitor conditions inside an oil or gas pipeline, or to search out disease while floating through the bloodstream.
- The system uses a two-dimensional form of carbon called graphene, which forms the outer structure of the tiny syncells. One layer of the material is laid down on a surface, then tiny dots of a polymer material, containing the electronics for the devices, are deposited by a sophisticated laboratory version of an inkjet printer. Then, a second layer of graphene is laid on top.
- • Embedded inside these pockets are electronic circuits and materials that can collect, record, and output data.
- • These tiny objects “behave like a living biological cell” which can be used in variety of applications.
MASCOT – New Robot on Asteroid
02, Oct 2018
- A Japanese probe launched a new observation robot towards an asteroid, as it pursues a mission to shed light on the origins of the solar system.
About:
- The French-German Mobile Asteroid Surface Scout, or MASCOT, launched from the Hayabusa2 probe, landed safely on Ryugu asteroid’s surface.
- MASCOT’s launch comes 10 days after the Hayabusa2 dropped a pair of MINERVA-II micro-rovers on the Ryugu asteroid.
- The 10-kilogram box-shaped MASCOT is loaded with sensors. It was the first time that moving, robotic observation devices have been successfully landed on an asteroid.
- MASCOT is expected to collect a wide range of data on the asteroid which is some 300 million kilometres from Earth.
- It can take images at multiple wavelengths, investigate minerals with a microscope, gauge surface temperatures and measure magnetic fields.
- The rover will take advantage of Ryugu’s low gravity to jump around on the surface – travelling as far as 15 metres (49 feet) and staying above the surface for as long as 15 minutes.
- It will do this to better survey the asteroid’s physical features with cameras and sensors. The rovers will spend several months on the asteroid, the MASCOT has a maximum battery life of just 16 hours, and will transmit the data it collects to the Hayabusa2 before running out of juice.
Significance:
- Jaxa’s Hayabusa Two probe is on a mission to study the ancient asteroid Ryugu in a bid to help scientists better understand the origins of the universe.
- Hayabusa -Two is studying soil and rock samples using several pieces of equipment. The probe will then hover over the artificial crater and collect samples using an extended arm.
- The probe is loaded with four surface landers, an array of cameras and even an explosive device that will dig out subsurface rock samples.
- Ryugu, a Type C asteroid, contains traces of water and organic material and it is hoped that analysing this material will reveal what the early conditions were like at the time the solar system formed around 4,6 billion years ago.
- Hayabusa Two is expected to return to Earth in late 2020 carrying samples for further analysis.
RYUGU Asteroid:
- Ryugu was discovered on 10 May 1999 by astronomers with the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the Lincoln Lab’s ETS near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States. The asteroid was officially named “Ryugu”. The name refers to Ryūgū (Dragon Palace), a magical underwater palace in a Japanese folktale.
AI Can Adjust Dosage For Cancer Patients
22, Aug 2018

- MIT researchers are using an artificial intelligence (AI) model that would help determine the correct drug dosage and, in turn, reduce debilitating side effects for brain cancer patients.
About:
- Powered by a “self-learning” machine-learning technique i.e ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENT, the model looks at treatment regimens currently in use, and iteratively adjusts the doses.
- Eventually, it finds an optimal treatment plan, with the lowest possible potency and frequency of doses that should still reduce tumour sizes to a degree comparable to that of traditional regimens.
- Glioblastoma is a type of cancer – malignant tumour that appears in the brain or spinal cord, and prognosis for adults is no more than five years. There is no cure for it.
- Generally, administer maximum safe drug doses to shrink the tumour as much as possible. However, these strong pharmaceuticals still cause debilitating side effects in patients.
- Patients must endure a combination of radiation therapy and multiple drugs taken every month.
- This system provides alternate for it. Can help reduce toxic chemotherapy dosing for the most aggressive form of brain cancer, potentially improving the quality of life for patients.
Task Force on Artificial Intelligence
16, Jul 2018

A Multi stakeholder task force chaired by N. Chandrasekaran appointed in February to with mandate to
- Studied the level of AI development in India in general and specific in the context of defence needs.
- Made recommendations of making India a significant power of AI in defence specifically in the area of aviation, naval, land systems, cyber, nuclear, and biological warfare;
- Made recommendations for policy and institutional interventions that are required to regulate and encourage a robust AI based technologies for defence sector in the country.
- Considering that most AI work is happening in private sector, made recommendations to work with start-ups/commercial industry in the field of use of AI for defence purposes.
- Artificial Intelligence: Artificial intelligence (AI) is an area of computer science that emphasizes the creation of intelligent machines that work and react like humans.
Some of the activities computers with artificial intelligence are designed for include:
- Speech recognition
- Learning
- Planning
- Problem solving






