Category: Indian Society
India’s population to edge ahead of China’s by mid-2023, says UN
21, Apr 2023

Why in News?
- The State of World Population Report 2023 has confirmed that India is expected to edge past China to become the world’s most populous country by mid-2023.
State of World Population Report:
- The State of World Population Report is published by the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA).
- Since 1978, the State of World Population Report has been published every year.
- The State of World Population Report is produced by a group of external advisers, researchers and writers, working alongside UNFPA technical staff.
- The report analyses the trends in world population and demographics. It also throws light on specific regions, countries and population groups and the unique challenges they face.
- The report aims to broaden the understanding of the population and how it can lead to new solutions that build demographic resilience.
India is set to become the most populous country:
- According to the latest report, India’s population is estimated to be 1,428 million by mid-2023 which is marginally ahead of China’s 1,425 million.
- The U.S. is placed third on the list of most populous countries with an estimated population of 34 crores.
- The 2022 edition of the State of World Population Report had estimated China’s population to be 1,448 million by mid-2022 which was more than that of India’s 1,406 million population.
- Experts believe that the emergence of India as the world’s most populous country in 2023 is mainly attributed to a sharp decline in China’s population.
- China witnessed a reduction of 23 million (i.e. 2.3 crores) in just one year.
- Although the numbers released by the reports are only estimates, the UNFPA reports are considered reliable indicators of global population trends.
- The Decennial Census numbers are considered to be the most reliable in India and the 2021 Census exercise was postponed due to the COVID pandemic.
- However, the Census office released population projections for the years 2012 to 2036, according to which, India’s population in 2023 was estimated to be only 1,388 million which is significantly less than the numbers projected by the State of World Population report.
- According to the latest State of World Population report, if India’s population continues to increase at the current pace which is close to 1% every year, then the population would double from the present value in the next 75 years.
Other key findings of the report:
- The report notes that the global population has reached the 800-crore mark by November 2022.
- The report also highlights the fact that population trends across the world indicate slower growth and ageing societies contrary to the concerns about exploding numbers.
- Further, it reveals that only eight countries namely the Democratic Republic of Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines and the United Republic of Tanzania would account for half the projected growth in global population by 2050.
- As per the report, the countries with the highest fertility rates were: Niger (6.7), Chad (6.1), the Democratic Republic of Congo (6.1), Somalia (6.1), Mali (5.8) and the Central African Republic (5.8).
- And, the territories with the lowest birth rates were Hong Kong (0.8), South Korea (0.9), Singapore (1.0), Macau and San Marino (1.1) and China (1.2).
- The report also suggests that two-thirds of the population live in a country where lifetime fertility corresponds with zero growth and this is considered a milestone and indicates advances in medicine, science, health, agriculture and education.
Way forward for India:
- The report has called for a radical rethink of the policies adopted by the countries to address changing demographics and cautioned against the use of family planning as a tool for achieving fertility targets.
- At a time when various states such as Assam are looking at imposing two-child norms, the report says that such type of family planning targets could result in gender-based discrimination and increased instances of prenatal sex determination leading to sex-selective abortion.
- Furthermore, the imposition of such targets could cause an imbalance in sex ratios, denial of the paternity of girl children, violence against women for giving birth to girl children, etc.
- India has a time-bound opportunity to reap benefits from its demographic dividend as about 50% of its population is below the age of 25.
- India must look to maximise he opportunities and convert them into economic benefits by investing in improving the healthcare and education facilities along with creating employment opportunities for young people and also undertaking targeted investments for women and girls.
- Additionally, efforts must be underway to initiate the Census 2021 exercise which has been postponed multiple times in the last two years.
- The delay in completing the 2021 Census could have adverse impacts on various sectors and also the overall growth prospects.
INDIA URBAN OBSERVATORY & VIDEO WALL
11, Mar 2019
GS 1: Social Issues | Urbanization – problems and remedies
Why in News?
Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs has launched the state-of-the-art India Urban Observatory and Video Wall.
Urban Observatory:
- It is a platform that uses data from different sources to enable analysis and visualization over a geospatial platform can make this possible.
- The concept of Urban Observatories was formally initiated at the UN Habitat-II Conference in 1997 in Istanbul. Some examples of well-established Urban Observatories are the Global Urban Observatory network, the Dublin Dashboard and the City Dashboard of London.
- Such platforms churn out interesting analyses and visualizations by collating massive datasets.
India Urban Observatory:
- It is an important component of the recently launched DataSmart Cities strategy that envisions creating a ‘Culture of Data’ in cities, for intelligent use of data in addressing complex urban challenges. Making cities ‘DataSmart’ is key to realizing the full potential of technology interventions and innovation ecosystems in cities.
- The Data Smart Cities Policy allows cities to open their data to public view, such as number of hospitals, gardens, people, public toilets and other city management, the official added. It will be a separate portal for Smart Cities under the data.gov website.
PROMOTION AND PROTECTION OF MAITHILI LANGUAGE AND ITS SCRIPTS
23, Feb 2019
GS 1: Art and Culture
Why in News?
The Ministry of Human Resource Development constituted a Committee in the year 2018 for making a report for the Promotion and Protection of Maithili Language and its scripts.
The Committee has submitted its report to MHRD in which it has made several recommendations for promotion and protection of Maithili language.
Maithili language:
- Maithili is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Indian subcontinent, mainly spoken in India and Nepal. In India, it is spoken in the states of Bihar and Jharkhand and is one of the 22 recognised Indian languages.
- Mithilakshar or Tirhuta is the script of broader cultural Mithila.
- The scripts of Mithilaksar, Bangla, Assamese, Nebari, Odia and Tibetan are part of the family. It is an extremely ancient script and is one of the script and is one of the scripts of the broader North Eastern India.
- Mithilakshar had come to its current shape by 10th Century AD. The oldest form of Mithilakshar is found in the Sahodara stone inscriptions of 950 AD. Afterwards, the scripts have been used throughout Mithila from Champaran to Deoghar.
- Use of this script has been on decline since last 100 years and therefore our culture is getting decimated. Because its own script is not being used, the Maithili language is getting developed in a composite manner despite having been accorded a constitutional status in the constitution.
WORKSHOP FOR VICTIMS OF COMMUNAL VIOLENCE
22, Feb 2019
GS 1: Indian Society
Why in News?
- The National Foundation for Communal Harmony (NFCH) is organizing a special workshop for 42 Youth in the age group of 15 to 22 years, who have been victims of communal violence in the past, under the Know My India Programme beginning in Bengaluru.
- The Youth come from 6 states including Jammu & Kashmir, Manipur, Assam, Chhattisgarh, Bihar and Gujarat along with 10 official mentors.
Highlights:
Its objectives is to help the children deal with the post-traumatic stress, provide them life tools to manage their emotions and eliminate disturbing impressions of the past events, to have them experience deep relaxation and peace, give them a broader and more inclusive view of the world and how each individual is connected with the others beyond social identities, the participants, through fun interactive processes, will be taught various body- breath mechanisms, and practical tools of wisdom. The cornerstone is the powerful rhythmic breathing practice called Sudarshan Kriya, whose regular practice is known to significantly reduce stress hormones, improve clarity of mind and increase one’s happiness quotient.
Know My India programme:
- It is a unique programme initiated by the NFCH to bring together financially assisted children of the Foundation from different States/Regions of the country to promote oneness, fraternity and national integration.
- The programme is all about familiarization with the environment, family life, social customs, etc. of the people living in different parts of the country; developing understanding of the common historical and cultural heritage of the country.
NFCH:
- The NFCH is an autonomous organization under the administrative control of the Ministry of Home Affairs. The main objective of the Foundation is to provide assistance to the children/youth rendered orphan/destitute in communal, caste, ethnic or terrorist violence for their rehabilitation besides promoting communal harmony and national integration through various activities.
- The NFCH sponsors/conducts different activities for the promotion of communal harmony and strengthening of national integration.
TAGORE AWARD FOR CULTURAL HARMONY
20, Feb 2019
GS 1: Art and Culture
Why in News?
The President of India will present the Tagore Award for Cultural Harmony to Shri Rajkumar Singhajit Singh; Chhayanaut (a cultural organization of Bangladesh); and Shri Ram Sutar Vanji for the years 2014, 2015 & 2016.
Tagore Award for Cultural Harmony:
- Tagore Award for Cultural Harmony was instituted by the Government of India from 2012 recognizing the contributions made by Gurudev Rabindranath Tagore to humanity at large with his works and ideas, as part of the Commemoration of his 150thBirth Anniversary in 2012, for promoting values of Cultural Harmony.
- This annual award is given to individuals, associations, institutions or organizations for their outstanding contribution towards promoting values of Cultural Harmony.
- The Award is open to all persons regardless of nationality, race, language, caste, creed or gender.
- Normally, contributions made during ten years immediately preceding the nomination are considered. Older contributions may also be considered if their significance has become apparent only recently.
- A written work, in order to be eligible for consideration, should have been published during the last ten years. Work by a person since deceased cannot be the subject of an Award.
Works of the awardees:
- SHRI RAJKUMAR SINGHAJIT SINGH: Born at Imphal, Manipur on 3 November 1932, Shri Rajkumar Singhajit Singh is a highly accomplished and senior most guru, exponent, choreographer, prolific writer and scholar of Manipuri dance.
- CHHAYANAUT: Chhayanaut (a cultural organisation) was established in 1961 by leading organizers of Tagore centenary celebration. This organization was part of the movement for an independent Bangladesh that provided a platform for cultural expression and assertion of the Bengali identity at a time when such activities were considered anti-state and acts of sedition. During the liberation war, Chhayanaut singers organized performances to inspire freedom fighters and refugees. After independence, Chhayanaut has been involved in seeking creative ways to broaden and intensify the practice and celebration of mainstream music and culture.
- SHRI RAM VANJI SUTAR: Born in Dhule District of Maharashtra on 19 February 1925, Shri Ram Vanji Sutar is a renowned sculptor and scholar. A gold medallist from Sir J. J. School of Art, Bombay in sculpture, Shri Sutar started his career in 1954 as a modeller in the Department of Archaeology, South Western Circle, Aurangabad. From 1959 onwards, he has been working as freelance sculptor making monumental statues.
20th Bharat Rang Mahotsav
20, Feb 2019
GS 1: Art and Culture
Why in news?
The Minister of State for Culture (I/C), Govt. of India, inaugurated the 21-day-long nationwide theatre spectacle at Kamani Auditorium in a program presided over by Dr. Arjun Deo Charan, Acting Chairman, NSD Society and other senior officers of Culture Ministry, in New Delhi.
BHARAT RANG MAHOTSAV:
- The 20th edition of Bharat Rang Mahotsav (BRM), the international theatre festival of India, is organized by National School of Drama (NSD), one of the prominent training institutions in the world.
- The 20th BRM comes with 111 national and international acts in its basket that includes folk and other traditional theatre forms, invitee plays, and productions by the students of the National School of Drama.
NATIONAL SCHOOL OF DRAMA:
- The National School of Drama is one of the foremost theatre training institutions in the world and the only one of its kind in India.
- It was set up by the Sangeet Natak Akademi as one of its constituent units in 1959. In 1975, it became an independent entity and was registered as an autonomous organization under the Societies Registration Act XXI of 1860, fully financed by the Ministry of Culture, Government of India.
- Training in the School is highly intensive and is based on a thorough, comprehensive, carefully planned syllabus which covers every aspect of theatre and in which theory is related to practice. As a part of their training, students are required to produce plays which are then performed before the public.
National Health Profile-2018
15, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- The Central Bureau of Health Intelligence (CBHI), under the aegis of the Directorate General of Health Services released an Analytical Report of the National Health Profile2018.
The Report:
- The National Health Profile covers demographic, socio-economic, health status and health finance indicators, along with comprehensive information on health infrastructure and human resources in health. The National Health Resource Repository (NHRR) – country’s first ever national healthcare facility registry of authentic, standardized and updated geospatial data of all public & private healthcare establishments.
The NHRR project:
- The NHRR project involves conducting a national census for all public and private healthcare facilities including hospitals, doctors, clinics, blood banks, pharmacies, diagnostic labs etc.
- The aim of the project is to develop a comprehensive platform for over 25 lakh healthcare establishments. The platform will be very useful for all key stakeholders – government, private health establishments and the public. Establish a National Health Resource Repository for evidence-based decision making – aligned with Digital India mission.
- The vision of the NHRR project is to strengthen evidence-based decision making and develop a platform for citizen and provider-centric services by creating a robust, standardized and secured IT-enabled repository of India’s healthcare resources. NHRR will be the ultimate platform for comprehensive information of both, Private and Public healthcare establishments including Railways, ESIC, Defense and Petroleum healthcare establishments. NHRR will cohesively work with Ayushman Bharat – National Health Protection Mission (AB-NHPM) and Central TB Division (CTD) on an integrated plan for the larger benefit of ensuing Hospital empanelment and private sector engagement.
Key benefits:
- To create a reliable, unified registry of country’s healthcare resources. It shall generate real-world intelligence to identify gaps in health and service ratios
- Ensure judicious health resource allocation and management.It shall identify key areas of improvement by upgrading existing health facilities or establishing new health facilities keeping in view the population density, geographic nature, health condition, distance, etc.
- To ensure superior health access, service delivery and improve transparency & accountability for effective centre-to-state funding.Improve the visibility of Private providers to enable Public-Private Partnerships.
- Provide access to information on health service providers to the citizen of India.
75th Year of Establishment of Azad Hind Government
12, Oct 2018
Why in News?
- Hon’ble PM will unveil the plaque to celebrate the 75th anniversary of the formation of Azad Hind Government, at the Red Fort, Delhi.
Azad Hind Government:
- The Provisional Government of Free India, or, more simply, Free India (Azad Hind), was an Indian provisional government established in occupied Singapore in 1943.
- C. Bose was the leader of Azad Hind Government (AHG) and also the Head of State of this Provisional Indian Government-in-exile.
- It was established by Indian nationalists-in-exile during the latter part of the Second World War in Singapore with monetary, military and political assistance from Imperial Japan.
- It was a part of the freedom movement, originating in 1940s outside India with a purpose of allying with Axis powers to free India from British rule.
- Pertinently, the role of Azad Hind Fauj or the Indian National Army (INA) had been crucial in bequeathing a much-needed impetus to India’s struggle for Independence.
Administration of the AHG:
- Azad Hind was recognised as a legitimate state by only a small number of countries limited solely to Axis powers and their allies. Azad Hind had diplomatic relations with nine countries: Nazi Germany, the Empire of Japan, Italian Social Republic, Independent State of Croatia and Wang Jingwei Government, Thailand, the State of Burma, Manchukuo and the Second Philippine Republic.
Territories under AHG:
- AHG had been given a limited form of governmental jurisdiction over the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, which had been captured by the Imperial Japanese Navy early on in the war.
- Once under the jurisdiction of Azad Hind, the islands formed the government’s first claims to territory.
- The islands themselves were renamed “Shaheed” and “Swaraj respectively.
Collapse of AHG:
- INA under the leadership of Bose got defeated severely at Rangoon due to lack of support of Japanese. Bose was suggested to leave Burma to continue his struggle for Indian independence and returned to Singapore before the fall of Rangoon.
- The AHG govt in the islands collapsed when the island garrisons of Japanese and Indian troops were defeated by British troops and the islands themselves retaken.
- The Provisional Government of Free India ceased to exist with the deaths of the Axis, the INA, and Bose in 1945.
- It was followed by the Famous Trials at Red Fort. Importance of INA and AHG:
- The true extent to which the AHG and INA activities weakened the very foundation of the British Empire in India was the sparking of mutiny among Indian Soldiers.
- The Royal Indian Navy Mutiny made the British realize that the support of the Indian armed forces could no longer be relied upon.
Global Hunger Index 2018
11, Oct 2018
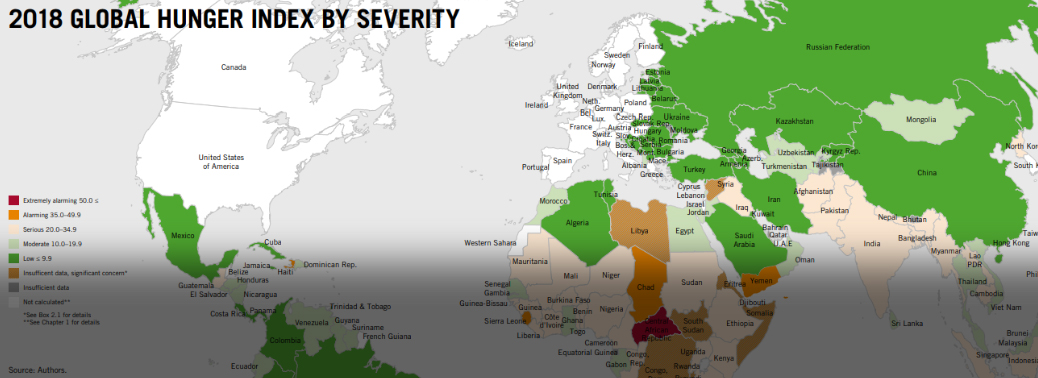
Why in News?
- The Global Hunger Index report 2018 released annually by Welthungerhilfe and Concern Worldwide.
Component indicators of GHI:
- Undernourishment: the share of the population which is undernourished and reflects insufficient caloric intake.
- Child wasting: The share of children under the age of five who are wasted (low weightfor-height), reflecting acute undernutrition.
- Child Stunting: the share of children under the age of five who are stunted (low heightfor-age), reflecting chronic undernutrition.
- Child mortality: the mortality rate of children under the age of five.
Dimensions of hunger:
- The GHI scores are based on a formula that captures three dimensions of hunger-
- Insufficient caloric intake
- Child under nutrition
- Child mortality
Performance of India:
- India has been ranked at 103 out of 119 countries in the Global Hunger Index 2018, with hunger levels in the country categorized as “serious”.
- At least one in five Indian children under the age of five is wasted.
- India’s ranking has dropped three places from last year
- The percentage of undernourished people in the population has dropped from 18.2% in 2000 to 14.8% in 2018. The child mortality rate has halved from 9.2% to 4.3%.
- The child stunting has dropped from 54.2% to 38.4% over the same period
- The only country with a higher prevalence of child wasting is the war-torn nation of South Sudan.
Concerns:
- Hunger and forced migration world wide
- The Index projects that at the current rate of progress, 50 countries will fail to reach the “low” hunger category by 2030.
Sir Chhotu Ram – Agricultural Reforms
10, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- PM unveiled a statue of Deenbandhu Sir Chhotu Ram in Rohtak, Haryana.
Sir Chhotu Ram (1881-1945):
- Sir Chhotu Ram was a prominent politician in British India’s Punjab Province, an ideologue of the peasants of pre-Independent India.He championed the interest of oppressed peasants of the Indian Sub-continent and tried to create a non-sectarian peasant group consciousness.
- He formed the Unionist Party (Zamindara League) in 1923, which was a cross-communal alliance of Hindu Jats and Muslim agriculturists.
- He was awarded the title of ‘Rao Bahadur’ and was accorded knighthood in 1937.He popularly came to be known as Deen Bandhu.
Political activities:
- The Congress boycotted the 1920 elections, while Chhotu Ram got elected on a Zamindara Party ticket.
- His coalition party won the general elections of 1936 and formed a coalition government with himself becoming Revenue Minister.
- Chhotu Ram helped in the British Army recruitment effort for the First World War, and was instrumental in the recruitment of 22,144 from Rohtak area.
- He again backed a massive recruitment drive of the British during the Second World War.
Notable Agricultural Reforms:
- As a member of the pre-Partition Punjab Legislative Council, his first major achievement was the passage of the Punjab Land Revenue (Amendment) Act, 1929, which remains a landmark social legislation till date.
- The exploitation of the peasantry by moneylenders was brought to an end with a series of measures, starting with the Punjab Regulation of Accounts Act, 1930.
- It was followed by the Punjab Debtors Protection Act of 1936 and the Punjab Relief of Indebtedness Act, 1943.
- It became mandatory for moneylenders to register themselves, without which they could not advance loans or prosecute farmers.
- All land attached and sold after June 8, 1901, and mortgaged for 37 years, was restored to its owners. Farmers were required only to give an application on plain paper to the district collector.
- If any moneylender had recovered twice the loan amount, the farmer was given his land back. Reconciliation boards were set up; confiscation of milch cattle, oxen, camels and carts or means of earning was barred. The Punjab Agricultural Produce Markets Act was passed in 1939, popularly called the Mandi Act which provided for the constitution of market committees in notified areas, and helped free the farmer from exploitation.
- A consolidation of land holdings was undertaken after passing the Consolidations Holding Act, 1936, amended in 1945.
- Not only were all these laws passed; Chhotu Ram also ensured their implementation.
First Regional Conference on Women in Detention and Access to Justice
07, Oct 2018

Why in News?
- The Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPR&D), Ministry of Home Affairs is organising the First ever Regional Conference at Shimla on ‘Women in Detention and Access to Justice’ in collaboration with the Prison Department, Himachal Pradesh.
Women in Detention and Access to Justice:
- This conference is organised with a view to provide a platform for the prison personnel of all ranks at the national level to share their candid views on various operational as well as administrative issues not only with their counterparts, but also with other experts of national repute in this field.
- The conference also seeks to identify best practices and standards in the working of Correctional Administration to meet new challenges in the present day’s context to bring out prison reforms in objective terms.
- The Parliamentary Committee on Empowerment of Women on this subject has made several recommendations.
- There is a need to deliberate upon some of the recommendations to devise strategies and programs for bettering conditions of Women Prisoners and upholding their FRs.
- The following themes have been identified for discussions and deliberations:
- Reproductive Health Rights of Women Prisoners: National and International Legal Norms
- Health Needs of Women Prisoners
- Health, Skill, Rehabilitation and Reintegration of Women Inmates and Their Children
- Prison Reforms, Structural Managerial and Legal Issues with Focus on Women Inmates & Comparison to Global Norms
- Neuro-Criminology Program for the Offender
- Transforming Prisons
Why we need reforms:
- Women also tend to lose ties with their children over the years, due to inadequate child custody procedures. Also, a robust grievance redressal mechanism was required to tackle cases of sexual harassment, violence and abuse against women in jails.
- Women in prisons face greater hardships than their male counterparts due to many factors such as social stigma, financial dependence on their families or husbands etc. These difficulties are further exacerbated when the woman has children. Women have to face numerous problems in prisons owing to inadequacy of female staff which often translates to the reality that male staff becomes responsible for female inmates, which is undesirable.
- Women are not provided with meals that are nutritious and according to their bodily requirements.Women are at a most disadvantageous position when it comes to their reintegration in society after release. Many are abandoned or harassed post-release, mainly due to the stigma attached with incarceration, which is even more pronounced in cases of women.
Mobilise your city (MYC) programme
23, Sep 2018
Why in News?
- India and France have signed an implementation agreement on “MOBILISE YOUR CITY” (MYC) programme.
- Based on a proposal made by AFD in 2015, the European Union has agreed to provide funds of Euro 3.5 million through the AFD to contribute to specific investments and technical assistance components within the Mobilise Your City (MYC) programme in India.
Mobilise Your City (MYC):
- MobiliseYourCity (MYC) is a global climate initiative for integrated urban mobility planning, and one of 15 international transport initiatives of the UN Global Climate Action Agenda (GCAA).
- Mobilise Your City (MYC) is part of an international initiative which is supported by the French and the German Governments and was launched at 21st Conference of Parties (COP21) meeting in December, 2015.
- The MYC is an initiative combining urban mobility objectives and climate considerations.
- It aims at providing solutions in a fully integrated manner, analysing different modes of transportation within the urban fabric, with the objective of providing people long-term, sustainable, adequate, reliable and cost-efficient transportation opportunities.
- The project seeks to back 100 cities worldwide in three years, which are engaged in sustainable urban mobility planning to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- In India, the MYC aims at supporting three pilot cities viz. Nagpur, Kochi and Ahmedabad in their efforts to reduce their Green House Gas (GHG) emissions related to urban transport by implementing urban mobility plans at local level and to help India at national level to improve their sustainable transport policy.
- The three pilot cities selected under the programme as well as MoHUA will benefit from the Technical Assistance activities.
- The main components of the proposed assistance are:
- To support planning and implementation of sustainable urban transport projects
- Support to strengthening institutional capacity for regulating, steering and planning urban mobility.
- Learning and exchange formats with other cities across India for exchanges on best practices.
RASHTRIYA POSHAN MAAH CELEBRATIONS
21, Sep 2018
Why in News?
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development, has urged the Ministers of partner Ministries and all the Members of Parliament to extend full support to the ongoing RashtriyaPoshanMaah with outreach activities. The Government is celebrating the month of September, 2018 as the National Nutrition Month under the PoshanAbhiyan.
PoshanMaah:
- The Government is celebrating the month of September, 2018 as the National Nutrition Month under the PoshanAbhiyan.
- The key feature of this programme is mobilization of communities across the country and gets their participation in addressing various aspects of the nutritional challenges.
- National Nutrition Month has eight key themes-
- Antenatal Care
- Optimal Breastfeeding
- Complementary Feeding
- Anaemia
- Growth Monitoring
- Education
- Diet and right age of marriage for girls
- Hygiene and Sanitation and Food fortification
Jan Andolan under the Project:
- POSHAN Abhiyaan seeks to synergise efforts of key stakeholders by leveraging technology and intends to take Nutrition Awareness to the level of Jan Andolan or People’s Movement.
- This People’s Movement intends to reach 11 crore beneficiaries during the RashtriyaPoshanMaah itself.
- Since the launch, Government has organised many Awareness Workshops with an aim to reduce stunting, under-nutrition, anemia and low birth weight.
- Stakeholders across India will be encouraged to undertake activities ranging from State Level Workshops to Nomination of Brand Ambassadors to Multi-Media Campaigns.
Krishna Kutir
21, Sep 2018
Why in News?
- The Minister for Women & Child Development, along with CM of Uttar Pradesh, inaugurated the widows’ home ‘Krishna Kutir’ at a function at Vrindavan, Mathura, Uttar Pradesh.
Krishna Kutir:
- Krishna Kutir is a special home for 1000 widows set up by the Ministry of WCD under SwadharGreh scheme of the Ministry and is the largest ever facility of its kind created by a government organization.
- The Ministry took cognizance of this shocking condition of widows living in Vrindavan who refused to go back to their native place or their home
- In order to provide dignified and humane living conditions to them, the Ministry, as a special case, constructed this Krishna Kutir at the temple town of Vrindavan with all the required facilities
- Widows will be a part of various committees which will be formed to manage the widows’ home.
Particulars of the Krishna Kutir:
- Krishna Kutir has been constructed on 1.4 hectare of land through National Building Construction Corporation (NBCC) with a capacity of 1000 inmates.
- It has beautifully made 100 rooms/dormitories.
- The design of the Home has been prepared in consultation with Helpage India and is old age friendly.
- The facility is also equipped with a large modern kitchen and a skill cum training centre.
Why shelter for Widows?
- The widows’ home has been constructed by the WCD Ministry to mitigate the plight of widows living in pathetic condition in Vrindavan.
Other Initiatives:
- UP Government has become the first State to link the women’s helpline 181 to the One Stop Centres.
- UP has also provided rescue vans for women in distress in every district.






