Category: E-Governance
GUIDE TO DETECT FAKE NEWS
13, May 2020

Why in News?
- The Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD), a think-tank under the Union Home Ministry has published guidelines to aid law enforcement agencies to identify fake News and Videos.
About BPRD:
- The Government of India established the Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPR&D), under the Ministry of Home Affairs in 1970s.
- It replaced Police Research and Advisory Council (1966), with the primary objective of modernization of police force.
- In 1995 Government of India decided to entrust issues relating to Correctional Administration Work to the BPR&D.
- Thereby BPR&D has to ensure the implementation of prison reforms as well.
- The Government of India further decided to create National Police Mission under the administrative control of BPR&D to transform the police forces in the country.
- The primary objective of modernization of police force are:
- To take direct and active interest in the issues
- To promote a speedy and systematic study of the police problems,
- To apply science and technology in the methods and techniques used by police.
Why these Guidelines were Necessary?
- Digital news has led to Increased incidence of Fake News or Yellow Journalism.
- Fake news is published with the intent to damage an agency, entity or a Person and gain financially or politically and it often uses Sensationalist, Dishonest or Outright Fabricated headlines to increase readership.
- In the wake of the pandemic, fake news and videos have spread panic, increased hatred and communal violence. Miscreants have used fake URLs to mislead people who wanted to donate to PM-CARES Fund.
What are the Guidelines Given?
Spotting Fake News:
- The guideline mentions several indicative signs that officials must look for to identify possible fake news.
- The officers should read beyond “outrageous” headlines designed to attract clicks and read the whole article.
- A possible case of fake news could be when headlines, visuals or captions do not support the content or when genuine contents or sources are impersonated with false or made-up sources.
- A search on the author of the article would also enable insights into the veracity of the news.
- The investigating officer must stay alert to clues such as language since such websites and links usually have Spelling Mistakes.
Cross-Checking:
- The officials should refer to trusted news sources to verify whether the story is being reported elsewhere.
- When a story is reported in multiple places, it is more likely to be true.
- The manual also gives an indicative list of websites that could be accessed for fact-checking.
- The guidelines ask police and other investigating agencies to use open domain tools for collecting more information on fake videos.
- BPRD has cautioned that the Investigating officer may consider the case sensitivity before resorting to these tools since there is the risk of data leakage that may influence or mislead an Investigation.
ROBUST DIGITAL INFRASTRUCTURE ENABLING PROMPT TRANSFER OF CASH PAYMENT
16, Apr 2020

Why in News?
- A digital pipeline has been laid to provide the necessary backbone for DBT flows, adoption of social security/pension schemes, etc. under the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package.
Highlights:
- A digital pipeline has been established through linking of Jan-Dhan accounts as well as other accounts with the account holders’ mobile numbers and Aadhaar[Jan DhanAadhaar-Mobile (JAM)]. Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) was launched in August, 2014 with an aim to provide bank accounts to unbanked persons.
- Out of around 126 crore operative current accounts saving accounts (CASA), more than 38 crores have been opened under PMJDY.
Purpose of Creating Digital Infrastructure:
- Enablement of interoperable, speedy and Accurate Transactions:
- The bank accounts are enabled to carry out both cash and digital transactions at bank branches, Business Correspondent (BC) points, merchant locations and on the internet.
- Using biometric ID, highly cost-effective payments solutions like AePS/ Bhim Aadhaar Pay have been created both for banking services and for retail payments.
The Digital Payment Ecosystem includes the Following Modes:
- Aadhar enabled Payment System (AePS): helps in cash withdrawal by using Aadhaar authentication at branch/BC locations.
- Bhim Aadhaar Pay:enables payment to merchants using Aadhaar authentication
- RuPay debit cards:As on 31st March 2020, a total of 60.4crore RuPay cards have been issued including 29 crore issued in PMJDY accounts. These cards could be used at ATMs for cash withdrawal and at Points of Sale (PoS) & e-commerce for digital payments.
- Unified Payment Interface (UPI):Immediate real time payment system which helps in both person to person (P2P) and Person to Merchant (P2M) transactions.
- Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS):helps in payment of utility bills through internet & BC locations both by using cash & digital modes.
- According to the Union Finance Ministry, using the digital payment infrastructure mentioned above, more than 30 crore poor people have received financial assistance of Rs. 28,256 crore under the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package, in order to protect them from the impact of the lockdown due to COVID 19.
TELANGANA: DRONE DELIVERY OF MEDICAL SUPPLIES
06, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- The Telangana government has adopted a framework to use drones for last-mile delivery of essential medical supplies such as blood and medical samples in an effort to increase the access to healthcare to communities across the state.
Details:
- The framework has been co-designed by the World Economic Forum (WEF) and Apollo Hospitals Group Healthnet Global Limited.
- In July, Telangana submitted a proposal for its drone policy to the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA).
- The state hopes to become ‘beyond visual line of sight’ (BVLOS) compliant, making commercial use of drones possible.
- The project is a part of the WEF’s “Medicine from the Sky” initiative that aims to develop source materials for policymakers and health systems to analyse the challenges that come with drone delivery, and to compare this model with other competing delivery models.
What is a Drone?
- A drone is an aircraft that operates without a pilot on board and is referred to as an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV).
- It has three subsets: Remotely Piloted Aircraft (RPA), Autonomous Aircraft, and Model Aircraft.
- An RPA can be further classified into five types on the basis of weight: nano, micro, small, medium and large.
- RPAs are aircraft that are piloted from remote pilot stations.
Why Drones?
- The core advantage of using drones: reduction of the time taken to transport material, and improving supply chain efficiency.
- Example of Rwanda: drone-related pilot projects have been implemented on a national scale to deliver medical supplies without delay and at scheduled intervals.
- Adopting this framework brings Telangana one step closer to rolling out a system that could save lives.
- It outlines what challenges drones can solve, how to oversee operations and how to implement them.
Drone Regulations in India:
- In India, the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) under the Ministry of Civil Aviation acts as the regulatory body in the field of civil aviation, responsible for regulating air transport and ensuring compliance to civil aviation requirements, air safety, and airworthiness standards.
- The DGCA’s drone policy requires all owners of RPAs, except drones in the smallest ‘nano’ category, to seek permission for flights, and comply with regulations including registration, and operating hours (only during the day) and areas (not above designated high security zones).
- There is no blanket permission for flying BVLOS; the visual line of sight being 450 m with a minimum ground visibility of 5 km.
- The food delivery platform Zomato has tried out a drone to deliver a payload of up to 5 kg to a distance of 5 km, flying at a maximum speed of 80 km/h; however, regulations do not yet allow the delivery of food by drones.
- A change of regulations will be required before large-scale use of drones can be made possible for medical or other purposes.
PRAKASH PORTAL
04, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- Ministry of Power launched PRAKASH (Power Rail Koyla Availability through Supply Harmony)
About PRAKASH (Power Rail Koyla Availability through Supply Harmony) Portal:
- The Portal aims at bringing better coordination for coal supplies among all stakeholders viz – Ministry of Power, Ministry of Coal, Coal India, Railways and power utilities.
- The Portal is designed to help in mapping and monitoring entire coal supply chain for power plants, viz:
- Coal Stock at supply end (mines),
- coal quantities/ rakes planned,
- coal quantity in transit and
- coal availability at power generating station.
Benefits of Portal to the Stakeholders:
- The portal makes available following information on a single platform:
- Coal company will be able to track stocks and the coal requirement at power stations for effective production planning.
- Indian Railways will plan to place the rakes as per actual coal available at siding and stock available at power stations.
- Power stations can plan future schedule by knowing rakes in pipe line and expected time to Reach.
- Stock at power generating station
- Ministry of Power /Ministry of Coal/ Central Electricity Authority/ Power System Operation Corporation (POSOCO) can review overall availability of coal at thermal power plants in different regions.
- PRAKASH Portal is developed by NTPC and sources data from different stakeholders such as Central Electricity Authority (CEA), Centre for Railway Information System (CRIS) and coal companies. All reports are available in PDF/Excel format. However, to present information in a user friendly method, the Portal gives graphical representation of reports with details shown on the map of India.
- Currently, the Portal will make available four reports as detailed below:
- Daily Power Plant Status: This report gives Station data related to power generation, coal receipt, consumption and stock. Report can be generated utility wise, state wise and sector wise (default utility-wise).
- Periodic Power Plant Status: Report gives Station data related to power generation, coal receipt, consumption and stock for selected period. Coal materialisation based on dispatch by coal company is available.
- Plant Exception Report: This report gives materialisation and rakes in pipeline through Rail.
- Coal Dispatch Report: Report gives coal subsidiary wise dispatch for particular period. It also gives source wise details of coal dispatch. Dispatch trend is also shown. Plant wise and siding wise details are available.
Present Mechanism:
- Present mechanism to review coal supply situation consists of an inter-ministerial group which has officials from Ministries of Power, Coal, Railways, CEA, power utilities and coal companies.
- This group holds weekly meetings to review coal supply situation as well as railway logistics.
- It was observed that this mechanism faced several issues such as scattered information, correctness of data from different organizations, timely availability of data etc. This often led to difficulties in decision making
- To address such situations, Ministry of Power asked CEA for establishment of a transparent mechanism to monitor the coal availability at loading site (CIL,SCCL), placement of rakes by Railways (CRIS) and availability of coal at power stations (NTPC / DVC /State utilities) and also directed NTPC to facilitate CEA for portal development.
CONSUMER APP
02, Oct 2019

Why in News?
- In order to fast-track consumer grievance redressal process and provide an effective forum for consumers to give their valuable suggestions Union Minister of Consumer Affairs launched the ‘Consumer App’.
Consumer App:
- The app aims to provide a one stop solution for consumer grievance redressal at the palm of every consumer across the nation via mobile phones.
- The complaint status will be monitored on a daily basis by the ministry and on a weekly basis by the minister personally.
- The registered consumer will be informed about their complaint via SMS/E-mail with a unique number which can be tracked by the consumer.
- The knowledgebase available in the app is very useful feature that will help consumers get information pertaining to 42 Sectors including Consumer Durables, Electronic Products, e-commerce, Banking, Insurance, etc.
Grievance Redressal:
- There will be time bound resolution of all grievances and those that are simple in nature will be resolved within 20 days.Those that elicit a feedback from companies or further enquiries will be resolved within 2 months/60 days.If after 60 days the grievance is not resolved, the consumer will be advised to proceed to consumer fora.
- Also, now the consumer will be informed before closure of a complaint and if the consumer is not satisfied then the complaint will be referred further to the concerned department.
DIAL 112: INDIA’S NEW ALL-PURPOSE EMERGENCY NUMBER
30, Sep 2019

Why in News?
- Delhi became the fifth UT after Puducherry, Daman and Diu, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands to implement the Emergency Response Support System (ERSS) since its inaugurat
- In November 2018, Himachal Pradesh became the first state to roll out the ERSS, under which there is a single emergency response number across the country — 112.
Emergency Response Support System (ERSS):
- In India, the decision to launch the ERSS system was taken in the wake of the 2012 Delhi bus gangrape case.The MHA accepted the recommendations of the Justice Verma Committee in the backdrop of unfortunate incident of Nirbhaya in December 2012 and has approved a national project by name of ERSS.
- ERSS was earlier referred as Nationwide Emergency Response System with a view to introduce a Pan-India Single Emergency Response Number ‘112’ to address all kinds of distress calls such as police, fire and ambulance, etc.
Why ‘112’?
- A single emergency number under the ERSS makes it easier for people travelling across states/UTs, since they don’t have to remember the local emergency numbers of every place.The emergency number 112 is easy to remember and moreover it is the only emergency you need to remember in India.
- This is important because people confronted with an emergency can be stressed or even in panic.Existing emergency numbers such as 100 for police, 101 for fire, 108 for health services, the women’s helplines 1091 and 181, the child helpline 1098, etc., will be gradually integrated under 112.A “112 India” app has been launched as well, through which users, after registering, can reach out to police, health, fire, and other services.
- 112 is the common emergency number in several other countries as well, including most countries in Europe.
PORTAL FOR AFFORDABLE CREDIT AND INTEREST SUBVENTION ACCESS (PAISA)
31, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- Deendayan Antyodaya Yojana-National Urban Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NULM), a flagship mission under the MoHUA has been conferred the prestigious SKOCH Governance Gold Award for its PAiSA portal.
PAiSA Portal:
- PAiSA stands for Portal for Affordable Credit and Interest Subvention Access.
- Launched in November 2018, PAiSA is a centralized IT platform which simplifies and streamlines release of interest subvention under the DAY-NULM.
- It has been designed and developed through the Allahabad Bank.
What it offers?
- It offers end to end online solution for processing, payment, monitoring and tracking of interest subvention claims from banks on a monthly basis.
- Claims for subvention are uploaded by banks through their CBS (Core Banking Solution) in respect of the beneficiaries of the Self Employment Programme, which are verified and approved by the ULB and State concerned.
- The approved claim amount gets credited directly to the beneficiary’s loan account through DBT mode.
- SMS is also sent to the beneficiary’s mobile number intimating the credit of subvention amount.
SKOCH Award:
- SKOCH Award, instituted in 2003, is the highest civilian honour in the country conferred by an independent organisation.
- It recognizes people, projects and institutions that go the extra mile to make India a better nation.
- SKOCH Award covers the best of efforts in the area of digital, financial and social inclusion.
BIOMETRIC SEAFARER IDENTITY DOCUMENT (BSID)
30, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- India has become the first country in the world to issue Biometric Seafarer Identity Document (BSID), capturing the facial bio-metric data of seafarers.
BSID:
- In India the BSID project has been taken up in collaboration with Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (CDAC), Mumbai.
- The Government notified the Merchant Shipping (Seafarers Bio-metric Identification Document) Rules in 2016.
- Every Indian seafarer who possesses a valid Continuous Discharge Certificate issued by the Govt. of India will be eligible for issue of a BSID.
- Nine data collection centers have been setup at Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, Noida, Goa, New Mangalore, Kochi, Vizag & Kandla for issue of BSID.
Working of BSID:
- It introduces modern security features. It will have a biometric chip embedded in it.
- The security of the BSID card is ensured at various levels and through different methods.
- At the time of data capturing the live face is cross matched through passport photo using a face matching software.
- The card has two optical security features- Micro prints/micro texts and Unique Guilloche pattern.
- A software has been developed for capturing the facial biometrics and its authentication through the public key infrastructure.
- A record of each SID issued will be maintained in a national database and its related information will be internationally accessible.
Significance:
- The BSID is a marked improvement over the two finger or iris based bio-metric data, with modern security features.
- It will make the identification of the SID holder more reliable and efficient, while protecting their dignity and privacy.
- It will give a fool proof identification to our seafarers which will facilitate their movement, provide ease of getting jobs and help in identifying them from any location in the world.
- The new card is in confirmation of the Convention No. 185 of the International Labour Organisation on BSID. (India ratified the Convention in October 2015.
SHAGUN-INTEGRATED ONLINE JUNCTION FOR SCHOOL EDUCATION
30, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- The Human Resource Development Ministry launched one of the world’s largest Integrated Online Junction for – School Education ‘Shagun’.
Shagun:
- School Education Shagun (URL: htpp://shagun.govt.in/) is an over-arching initiative to improve school education system by creating a junction for all online portals and websites relating to various activities of the Department of School Education and Literacy in the Government of India and all States and Union Territories.
- The word Shagun is coined from two different words- ‘Shala’ meaning Schools and ‘Gunvatta’ meaning Quality and this online junction of different websites and portals into a single platform will enhance the accessibility of information relating to schools and will ensure a holistic approach to transform the education sector.
- The portal seeks to provide a very robust feedback mechanism which will increase public participation and will ensure accountability and transparency.
- The portal seeks to connect approximately 92 lakh teachers and 26 crore students.
Integrated National School Education Treasury:
- Union Human Resource Development Minister has also announced the setting up of the Integrated National School Education Treasury (INSET).
- It will envisage a fully integrated, accessible and seamless information network for all parameters relating to the students, teachers, and schools in the country.
- The main focus will be on the following areas:
- Reinforcing and cleaning the data of the Integrated Online Junction through feedback from Stakeholders
- Ensuring full inter-operability among the websites, portals and applications which are already hosted in the junction
- Creating high quality e-contents, including quizzes and puzzles to enhance learning and also for teachers in aiding classroom transactions
- Using artificial intelligence and deep machine learning in a variety of ways to enhance the quality of school education including for designing evidence based inventions.
NOC ONLINE APPLICATION PROCESSING SYSTEM (NOAPS)
29, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- The Ministry of Culture & Tourism has launched an integrated No Objection Certificate (NOC) online Application Processing System (NOPAS) for National Monuments Authority (NMA) for 517 local bodies of six states.
Highlights:
- The online system automates the process of granting No-Objection Certificate (NOC) for construction-related work in the prohibited and regulated areas of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) protected monuments.
- NMA considers grant of permissions to applicants for construction-related activity in the prohibited and regulated area.
- National Monuments Authority (NMA) under the Ministry of Culture, has been set up as per provisions of the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains AMASR (Amendment and Validation) Act, 2010.
- The applicant needs to fill up a single form which is being sent to the concerned agencies by the Urban Local Body, from whom No Objection Certificate (NOC) is required.
- The Portal has integration with the Smart ‘Smarac’ Mobile App of Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), through which the applicant traverses his plot and the geo-coordinates of his plot along with the images get uploaded into the NIC portal along with the proximity and the approval status.
- NOAPS was launched by the NMA in September 2015 but was limited to only five urban local bodies in Delhi and one civic body in Mumbai. Now, the facility has been expanded to six more states: Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Punjab, Jharkhand and Telangana.
MOBILE APPLICATION- “JANAUSHADHI SUGAM” LAUNCHED
28, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- Union Minister for Chemicals and Fertilizers launched a mobile application “Janaushadhi Sugam”.
Highlights:
- The minister announced that “Jan Aushadhi Suvidha Oxo-Biodegradable Sanitary Napkin” will now be available at only One Rupee per pad.
- Janaushadhi Sugam app will enable people to search for Janaushadhi generic medicines and the stores at the tip of their fingers.
- About 28 million girls are reported to be leaving education because of lack of availability of good quality Sanitary Napkin” pads at a reasonable cost.
- The Government of India launched “Jan Aushadhi Suvidha Oxo-Biodegradable Sanitary Napkin” at Rs 2.50 per pad on the eve of the World Environment Day
- Jan Aushadhi Suvidha comes with a special additive, which makes it biodegradable when it comes in contact with oxygen after being discarded.
- This is an important step in ensuring the health security for the section of Indian women who still use unhygienic aids during menstrual period due to non-affordability of sanitary pads available in the market.
- This will ensure ‘Swachhta, Swasthya and Suvidha’ for the underprivileged women of the country. This step was taken by the Department of Pharmaceuticals.
- “Janaushadhi Sugam” app would have user-friendly options like- to locate nearby stores, direction guidance for the location through Google Map.
- The app will also enable to search Janaushadhi generic medicines, analyse product comparison of Generic vs Branded medicine in form of MRP & overall Savings, etc.
E-COURT
19, Aug 2019

Why in news?
- The High Court of Punjab and Haryana to launch its first virtual court (e-Court) at Faridabad.
Highlights:
- The e-Court would deal with traffic challan cases from across the State.
- The project will be launched under the guidance of e-Committee of the Supreme Court of India.
- Virtual courts will remove the need for the litigant to be present in the court and facilitate adjudication of the case online through the use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT).
E-committee:
- E-committee is a body constituted by the Government of India in pursuance of a proposal received from the supreme court of India for assistance in formulating a National policy on computerization of Indian Judiciary and advise on technological communication and management related changes.
- The E-Committee was set up in 2004 to provide a guide map for the use of I-T and administrative reforms in the judiciary.
e-Courts Project:
- The e-Courts project was conceptualized on the basis of the “National Policy and Action Plan for Implementation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the Indian Judiciary – 2005”submitted by e-Committee, Supreme Court of India with a vision to transform the Indian Judiciary by ICT enablement of Courts.
- The e-Courts Mission Mode Project, is a Pan-India Project, monitored and funded by the Department of Justice,Ministry of Law and Justice, Government of India for the District Courts across the country.
- The following are the functions of e-Courts Project:
- To provide efficient & time-bound citizen-centric services delivery as detailed in e-Court Project Litigant’s Charter.
- To develop, install & implement decision support systems in courts.
- To automate the processes to provide transparency in the accessibility of information to its stakeholders.
- To enhance judicial productivity, both qualitatively & quantitatively, to make the justice delivery system affordable, accessible, cost-effective, predictable, reliable and transparent.
HIRING APP FOR FARMERS
13, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- The agricultural Ministry app will create an invaluable database for policy-makers, who can track the use and cost of equipment.
Highlights:
- The custom hiring centres (CHC) app is already open for registrations by the farmers, societies and entrepreneurs who run these centres. So far, almost 26,800 CHCs have registered to offer more than one lakh pieces of equipment for hire.
- Once the app is officially launched, farmers who wish to hire equipment can register using their names, addresses and mobile numbers, and then punch in their requirements.
- The system would also help to track the usage of new technology that the government wants to promote, such as the Happy Seeder that aims to prevent stubble burning that causes air pollution, or solar dryers that can help farmers process and preserve their produce.
- Farmers save precious groundwater and increase productivity by 10 to 15%.
Customer Hiring Centres:
- Customer Hiring Centres (CHCs) are basically a unit comprising a set of farm machinery, implements and equipment meant for hiring by farmers.
- Marginal farmers (Farmers whose land holdings are less than two hectares of land), by virtue of their economic condition are unable to own farm machinery on their own or through institutional credit.
- Ideally, the CHCs should be located within a radius of 5 to 7 kms of land holdings. This will reduce the transport cost and time of transport of agricultural machinery.
BIOMETRIC TOKEN SYSTEM
07, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- The Western and Central Railways have introduced a new Biometric Token System (BTS) that seeks to streamline the process of boarding unreserved coaches.
Biometric Token System (BTS):
- The Western and Central Railways have introduced a new system by which passengers travelling in the general coach, where seats are not reserved, are given a token roughly three hours before the train’s departure.
- These tokens are given on a first-come, first-served basis, and carry a serial number on them, which governs the order in which passengers will board the train.
- Passengers with valid tickets are required to place their fingers on a scanner, and are issued a token with a serial number against their biometric data.
- Passengers must queue up and enter the compartment in the order of their serial numbers.
- The tokens are issued three hours before a train’s departure. The use of biometrics cuts out the touts, and helps genuine passengers.
Why such move?
- Boarding ‘general’ compartments — in which seating is not reserved — especially in long-distance trains leaving major cities, has always been an ordeal for passengers.
- The massive mismatch between the numbers of travellers and the available seats drives people to queue up on platforms up to 10 hours in advance.
- Chaos at the time of boarding has led to stampedes and even deaths in the past.
- Gangs of touts ‘reserve’ seats for a price, and those who can’t pay suffer.
Significance:
- The use of biometrics (fingerprint) rules out touts and ensures only bonafide travellers receive a token.
- The data (captured in the machines) will be used to analyse the pattern of crowds and the patronage of trains.
- In case of a mishap, officials will have details of the passengers, and with the help of this (biometric information) they can prevent black marketing of unreserved tickets.
ICELAND CANYON WANTS NO MORE VISITORS, THANKS TO JUSTIN BIEBER
20, May 2019

Why in News:
-
After bieber’s I’ll Show You was shot at the spot, the footfall of tourists in the region rose,
leaving deep scars on its vegetation.
Details:
- A large sign warns motorists that Iceland’s Fjadrárgljúfur canyon is closed to visitors but drivers keep on coming down the narrow gravel road.
- A ranger at a roadblock has to explain why no one can pass: the vulnerable landscape cannot sustain more visitors. Bieber’s magical music video I’ll Show You was filmed at the
canyon and seen by millions, creating overwhelming demand for the once-pristine spot - Last year, 2.3 million tourists visited Iceland, compared with just 6,00,000 eight years ago. The 20% annual uptick in visitors has been out of proportion with infrastructure that is needed to protect Iceland’s volcanic landscape, where soil forms slowly and erodes quickly.
- The nearby Skūgar waterfall and the Svţnafells glacier are also backdrops in the fictional Thrones world of warriors and dragons.
Arctic Council
India and Arctic Region
-
Indian researchers have been studying whether there is a co-relation between Indian monsoon and the Arctic region.
-
National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research, an Indian institute under Ministry of Earth Sciences, has set up research station, ‘Himadri’, in Svalbard (Norway). It studies and works on mass balance of glaciers, effect of climate warming on marine system, clouds formation and precipitation and also effect on biodiversity.
- Indian researchers have been studying whether there is a co-relation between Indian monsoon and the Arctic region.
- National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research, an Indian institute under Ministry of Earth Sciences, has set up research station, ‘Himadri’, in Svalbard (Norway). It studies and works on mass balance of glaciers, effect of climate warming on marine system, clouds formation and precipitation and also effect on biodiversity.
ODISHA SET TO INTROSPECT POST-DISASTER COMMUNICATION
13, May 2019
Why in News:
- The State control room was not able to establish regular communication (telephone, FAX, HAM radio and VHF) with the district headquarters, resulting in utter confusion in relief and rescue operations after cyclone Fani.
Background: / Cyclone Fani:
What is the Issue?
- A powerful cyclonic storm named Fani is headed towards the Odisha coast.
- As a cyclone in Bay of Bengal in April-May season, of this nature, is unusual, it is essential to understand the causes.
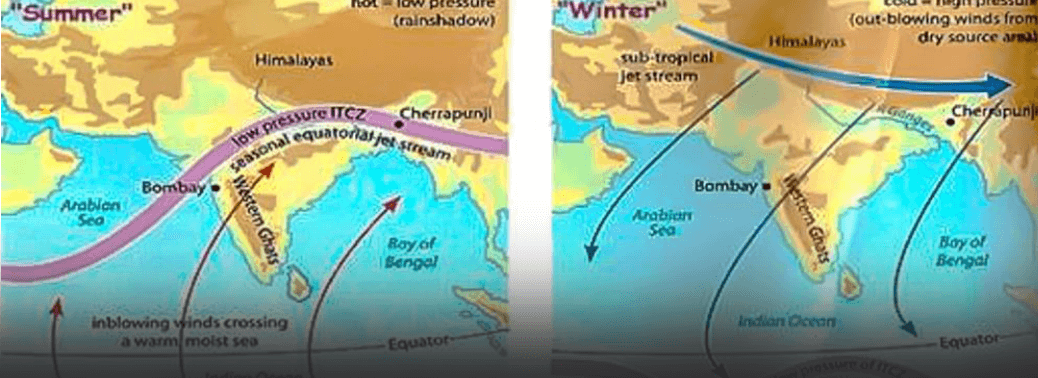
How do tropical cyclones form?
- Cyclones are formed over slightly warm ocean waters. It depends on the temperature of the top layer of the sea, up to a depth of about 60 metres. This has to be at least 28°C to support the formation of a cyclone. This explains why the April-May and October- December periods are conducive for cyclones. Secondly, the low level of air above the waters needs to have an ‘anticlockwise’ rotation in the northern hemisphere and vice versa. During these periods, there lies the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) (a low pressure zone) in the Bay of Bengal region, which shifts with seasons. The southern boundary of the zone experiences winds from west to east and the northern boundary from east to west. The ITCZ and the resultant wind pattern induce the anticlockwise rotation of air. Once formed, cyclones in this area usually move northwest.
- As it travels over the sea, the cyclone gathers more moist air from the warm sea, and adds to its strength.
How and Why is Fani different?
- Tropical cyclones in the Bay of Bengal are graded according to maximum wind speeds at their centre as follows:
- Depressions – 30 to 60 km per hour (kph)
- Cyclonic storms – 61 to 88 kph
- Severe cyclonic storms – 89 to 117 kph
- Very severe cyclonic storms – 118 to 166 kph
- Extremely severe cyclonic storms – 167 to 221 kph
- Super cyclones – 222 kph or higher
- Fani is now categorised as an “extremely severe cyclone”.
- It is expected to generate storms with wind speeds as high as 200 km per hour.
- It has the potential to cause widespread damage in Odisha and neighbouring states.
- Given the above discussed reasons, a cyclone of this nature is unusual for April-May cyclones in India. Fani is different mainly on account of its place of origin, and the route it has taken. Origin – The in situ cyclonic systems in the Bay of Bengal usually originate around latitude 10° N (in line with Chennai).
- But Fani originated quite close to the Equator, around latitude 2° N, well below the Sri Lankan landmass. The forecast landfall on the Odisha coast is at a latitude of almost 20°N. As it has originated very close to the Equator, it has taken a long route to reach the landmass. Resultantly, it has traversed a long way on the sea, and thus gained more strength. Route – Fani was initially headed north-westwards, towards the Tamil Nadu coast. But it changed its course midway and moved northeast away from the coastline to reach Odisha.
- The recurve it has taken gave it more time over the sea and has ensured that it has gathered unusual strength.
B2B TECH START-UPS TREBLE IN 5 YEARS: STUDY
08, May 2019

Why in News:
- Business-to-business (B2B) technology start-ups have more than trebled in the last five years driven by the spurt in the need for digital transformation of enterprises, financial institutions, hospitals, government and small and medium enterprises (SMEs), among others.
Details:
- While the number of such ventures has increased from 900 to over 3,200, the investment in such start-ups touched $3.7 billion in 2018, a rise of 364% from $797 million in 2014, as per a study
- According to the study, 70% of the B2B start-ups are in the area of enterprise technology, financial technology and health technology.
Growth of B2C
- However, the growth in the number of B2C technology start-ups has been comparatively slower since there were 2,200 such B2C ventures in 2014.
- Within the B2B technology segment, ‘advanced tech start-ups’ have grown at a higher pace when compared to the entire technology start-up segment.
- Advanced B2B tech start-ups typically deal in 3D printing, blockchain and robotic process automation.
Bengaluru leads
- Bengaluru is the top city for B2B technology start-ups followed by Delhi NCR and Mumbai, with the three cities accounting for about 60% of all B2B technology start-ups.
- Further, Hyderabad, Pune and Chennai are poised to be the growing start-up hubs on account of flexible economic policies, State government support and access to various industries.
- There are over 50 corporate accelerators and incubators in the country, focussing on technologies such as AI/ML, Big Data, Cloud, Blockchain, Cybersecurity, among others,”
Different types of e-commerce
- Business-to-business (B2B)
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- Business-to-government (B2G)
- Consumer-to-consumer (C2C)
- Government to consumer (G2C)
- Government-to-business (G2B)
BEYOND THE FREE TRADE IDEALISM
25, Apr 2019

Why in News?
- An ambitious ‘Employment and Incomes Policy’ must be the top priority for the next government
Details:
- The U.S. has begun trade skirmishes with India.
- It objects to India increasing import duties on electronic goods and wants India to reduce duties on U.S.-made motorcycles. Meanwhile the World Trade Organisation seems to be in the intensive care unit. It is time to apply fundamental principles to reshape a trade regime that is fair to all.
On free trade
- Dani Rodrik has estimated that for every unit of overall increase in global income, six or seven units of incomes will have to be shuffled around within.
- Moreover, according to this theory, people should not start producing what others are already producing, because they will produce less efficiently until they learn to do it well. According to this theory of free trade, Indians should not have bothered to learn how to produce trucks, buses and two-wheelers when the country became independent. They should have continued to import them from American, European and Japanese companies.
- Free trade purists say that easy import of products from other countries increases consumer welfare. Consumers everywhere welcome a lowering of import barriers because it brings products into their shops they could only dream of before
- Therefore, resistance to free trade does not come from consumers.
- It generally comes from companies which cannot compete: companies in less developed countries which are not able to compete until their country’s infrastructure is improved and they have acquired sufficient capabilities, or even from companies in developed countries when producers in developing countries overtake them.
Job growth:
- However, to benefit from easy imports, citizens need incomes to buy the products and services available. Therefore, they need jobs that will provide them adequate incomes.
- Any government responsible for the welfare of its citizens has to be concerned about the growth of jobs in the country. Domestic producers can provide jobs.
- Therefore, a developing country needs a good ‘industrial policy’ to
- accelerate the growth of domestic production, by building on its
- competitive advantages; and by developing those capabilities, it can compete with producers in countries that ‘developed’ earlier.
- India liberalised imports in the 1990s and Indian consumers have benefited greatly since then from the variety of products available to them from around the world.
- The manufacturing sector in India and China had comparable capabilities in 1990.
- By 2009, China’s was 10 times larger than India’s, and its capital goods production sector was 50 times larger. Not only was the Indian market being flooded with Chinese hand- tools and toys, China was also selling high-tech electrical and telecommunication equipment to India (and around the world too).
- Some people in government recommended the need for an ‘industrial policy’ to stimulate
- the growth of domestic production
- However, many Indian economists, along with others from the World Bank and the U.S., pushed back
- If Indian industry was not growing, it was because India had not ‘reformed’ enough: India should reduce trade barriers further and government should get further out of the way of industry,
The Next step
- By 2019, it has become clear that India’s policy-makers must find a way for economic growth to produce more income-generating opportunities for Indian citizens.
- Employment and incomes are the most pressing issues for Indian citizens according to all pre-election surveys of what citizens expect from the next government
- Therefore, an ambitious ‘Employment and Incomes Policy’ must be the highest priority for the next government.
- The scope of ‘industry’ must be broadened to include all sectors that can build on India’s competitive advantages.
- For example, the tourism and hospitality industry, taking advantage of India’s remarkable diversity of cultures and natural beauty, has the potential to support millions of small enterprises in all parts of the country
- There are lessons India can learn from its own history. With the government’s insistence in the pre-liberalisation era , India’s automobile sector was able to provide Indian consumers with good products. Indian auto-component producers and commercial vehicle producers export to the world’s most competitive markets.
- The WTO’s governance needs to be overhauled to promote the welfare of citizens in all countries, especially poorer ones, rather than lowering barriers to exports of companies in rich countries in the guise of free trade idealism
- A robust ‘Incomes and Employment Policy’, supported by an imaginative Industrial Policy, must guide India’s trade policy.
India’s First Drone Policy
16, Aug 2018

- Government of India’s Ministry of Civil Aviation announced guidelines on Monday for remotely piloted aircraft — or drones as they are more commonly known — which will come into effect from 1 December, aiming to open up an array of opportunities in the Indian civil aviation sector.
- The guidelines would help foster technology and innovation in the development of drones ,devices which have an extensive range of applications ranging from disaster relief to agriculture.
Need of Regulation:
- Drone technologies have been evolving very rapidly.
- Many countries are still experimenting with their drone regulations and no ICAO (International Civil Aviation Organisation) stands have been developed.
- India’s security environment necessitates extra precautions.
- Drone Regulations 1.0 have been formulated as an “all digital process” that will become effective from 1 December, which is when the “Digital Sky” platform will become operative.
- The new Digital Sky platform will be the first-of-its-kind national unmanned traffic management (UTM) platform that implements a ‘no permission, no take-off’ system for remotely piloted aircraft.
- Users will be required to make one-time registration of their drones, pilots and owners on the platform, which will also allow for online filing of a drone’s specific flight path and use.
- Every flight users will be required to ask for permission to fly on a mobile app and an automated process permits or denies the request instantly.
- To prevent unauthorised flights and to ensure public safety, any drone without a digital permit to fly will simply not be able to take-off.
- The UTM platform operates as a traffic regulator in the drone airspace and coordinates closely with the defence and civilian air traffic controllers (ATCs) to ensure that drones remain on approved flight paths.
Types:
- The new regulations have categorised drones into five separate types, on the basis of their weight.
- The rules that apply for the drones will depend on the weight class that they fall into, which begin from under 250 grams and extend to over 150 kilograms.
- The five types are Nano, micro, small, medium and large.
- Other than Nano, all other categories of drones need to be registered with the government and issued with a Unique Identification Number (UIN).
Airspace, too, has been divided by the government into different zones. Here’s what they indicate:
- Red Zone: Flying not permitted
- Yellow Zone: Controlled airspace -permission required before flying
- Green Zone: Uncontrolled airspace – automatic permission
- Beyond these, there are also specific regions around the country that have been marked as ‘No Drone Zones’. Some of these No Drone Zones that have been defined are areas around airports, those near the international border called “strategic locations/vital and military installations”.
Significance:
- The use of remotely piloted aircraft, a kind of drone, is allowed for taking photographs, conducting surveys such as for laying of pipelines and agricultural purposes and surveillance.
- They can be deployed for spraying of pesticides and delivery of relief material during a natural disaster only on a case-by-case basis.
- Operations are allowed in daylight and within the visual range or a range of 450 m. Wedding photographers are allowed to use micro drones during night, if they are taking pictures in an enclosed premise which is also well-lit.
Non-Compliance:
- In addition to the multiple checks and balances put in place for drone operators, the government will also enforce punitive action against those who do not comply with these new regulations after 1 December.
- The following enforcement actions have been stated by the civil aviation ministry
- Suspension or cancellation of UIN/ UAOP in case of violation of regulatory provisions
- Actions as per relevant Sections of the Aircraft Act 1934, or Aircraft Rules, or any statutory provisions
- Penalties as per applicable sections in the Indian Penal Code (such as 287, 336, 337, 338, or other relevant sections in the IPC)
- It will encourage a vast Make in India drone industry. These regulations will place the country among the global leaders in drone technology.
- Our policy roadmap will certainly provide a strong impetus to all players in the drone ecosystem. We hope that these initiatives will enable unto create a vibrant new industry which India’s expertise in technology is characterised by its capacity to devise low-cost solutions.
UPI 2.0
11, Aug 2018

- NPCI launches UPI 2.0 with overdraft facility. National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has upgraded unified payments interface (UPI) with enhanced security features and overdraft facilities.
- With the launch of UPI 2.0 we hope to touch new milestones by expanding UPI’s presence especially in person-to-merchant payment space.
About:
- The UPI 2.0 has enhanced features such as Invoice in the Inbox, Signed Intent/QR, UPI Mandate with Blocking of Funds and UPI for Overdraft Account, all operating in a safe and secure manner.
-
- Overdraft facility in addition to current and savings accounts, customers can link their overdraft account to UPI. Thus UPI 2.0 will serve as an additional digital channel to access OD account.
- One Time Mandate UPI mandate could be used in a scenario where money is to be transferred later by providing commitment at present. UPI 2.0 mandates are created with one-time block functionality for transactions. Customers can pre-authorise a transaction and pay at a later date.
- Invoice in the inbox This feature is designed for customers to check the invoice sent by merchant prior to making payment. It will help customers to view and verify the credentials and check whether it has come from the right merchant or not.
- Signed intent & QR This feature is designed for customers to check the authenticity of merchants while scanning QR code.
- It is a bid to integrate its retail payments infrastructure with businesses, whereby a trader, restaurateur, shopkeeper or SME entrepreneur can send a Goods and Services Tax (GST) invoice or a bill to his customer as an attachment for verification and payment digitally.
- UPI 2.0-member banks as on date are: State Bank of India, HDFC Bank, Axis Bank, ICICI Bank, IDBI Bank, RBL Bank, YES Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank, IndusInd Bank, Federal Bank and HSBC.
- To incorporate signed intent for QR (quick response) code-based payments to provide an additional layer of security.
- The launch has been the result of the calibrated approach adopted by the Reserve Bank – in the initial years as a developer and in later years as a catalyst and facilitator.
- As UPI has grown considerably post demonetisation and has been the catalyst for retail payment systems with many banks building products around the UPI with the fintech industry and other IT players positioned at the edge, providing innovative solutions for end-user delight.
- But UPI 2.0 is a big change and all the apps will need to be changed.
Unified Payments Interface:
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI) is an instant real-time payment system developed by National Payments Corporation of India facilitating inter-bank transactions. The interface is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India and works by instantly transferring funds between two bank accounts on a mobile platform
- It is a system that powers multiple bank accounts into a single mobile application (of any participating bank), merging several banking features, seamless fund routing & merchant payments into one hood.
- It also caters to the “Peer to Peer” collect request which can be scheduled and paid as per requirement and convenience. Each Bank provides its own UPI App for Android, Windows and iOS mobile platforms.
NPCI:
- National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), which is the umbrella body for retail payments in the country which was set up in 2009 as the central infrastructure for various retail payment systems in India and was envisaged by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as the payment utility in the country.
- NPCI is a not-for-profit organisation registered under section 8 of the Companies Act 2013.
The organisation is owned by a consortium of major banks and has been promoted by the country’s central bank, the Reserve Bank of India
Services:
- It looks range of services like switching of interbank ATM transactions through National Financial Service, Cheque Truncation System, National Automated Clearing House (NACH), Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS), USSD based *99#, RuPay card, Immediate Payment Service (IMPS), Unified Payments Interface (UPI), Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM), BHIM Aadhaar, National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) and Bharat Bill Pay.
Innovation Cell and Atal Ranking Of Institutions On Innovation Achievements (Ariia)
11, Aug 2018

Why in news?
- The Centre announced another annual ranking of higher educational institutions, based on how they fare in terms of innovation.
MHRD Innovation Cell (MIC)
- Innovation cell is MHRD’s initiative established at AICTE with a purpose to systematically foster the culture of Innovation in all Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) across the country.
- The primary mandate of Innovation Cell is to encourage, inspire and nurture young students by exposing them to new ideas and processes resulting in innovative activities in their formative years fostered through Network of Innovation clubs in Higher Educational Institutions.
Atal Ranking of Institutions on Innovation Achievements (ARIIA)
- For India to emerge as a global innovation hub, the youth of our country, especially in higher education institutions (HEIs) need to play a crucial role to create a sustainable innovation ecosystem.
- Hence, ideally all HEIs should have a comprehensive and functional mechanism to convert research into innovations.
- This ecosystem will encourage, inspire and nurture young students by exposing them to new ideas and processes resulting in innovative activities in their formative years.
- To ensure that Innovation is primary fulcrum of all HEIs, Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD), Govt. of India is introducing ‘Atal Ranking of Institutions on Innovation Achievements (ARIIA)’ to systematically rank education institutions and universities primarily on innovation related indicators.
- ARIIA considers all major indicators which are commonly used globally to rank most innovative education institutions/ universities in the world.
- ARIIA ranking will certainly inspire Indian institutions to reorient their mind-set and build ecosystems to encourage high quality research, innovation and entrepreneurship.
- More than quantity, ARIIA will focus on quality of innovations and will try to measure the real impact created by these innovations nationally and internationally.
- Moreover, ARIIA will set tone and direction for institutions for future development for making them globally competitive and in forefront of innovation
Parinam Manjusha
10, Aug 2018

Why in news?
- The CBSE has decided to allow students in Kerala who have lost their marksheet, migration certificate and pass certificate in the floods, to retrieve them from its digital academic repository ‘Parinam Manjusha’.
About Parinam Manjusha:
- The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) ‘s digital academic repository called ‘Parinam Manjusha’, will allow students to find their mark sheets, pass and migration certificates online. It has been developed by the board in collaboration with NEGD (DigiLocker)
- According to an HT report, employers and educational institutions can use it to verify academic records and students can have the access to their certificates.
- The users are required to get themselves registered on the website and after paying the verification fee online, they will then be able to check the certificates.
- The documents will be sent to the employer through mail and the applicant will be notified, thus preventing students from submitting fake documents.
- The documents will contain a QR code, which can be checked through a mobile-based scanning app that can be downloaded from the website.
- CBSE and its regional offices can store, access and update academic records of students in a central repository.
UIDAI To Roll Out Face Recognition Feature
04, Aug 2018
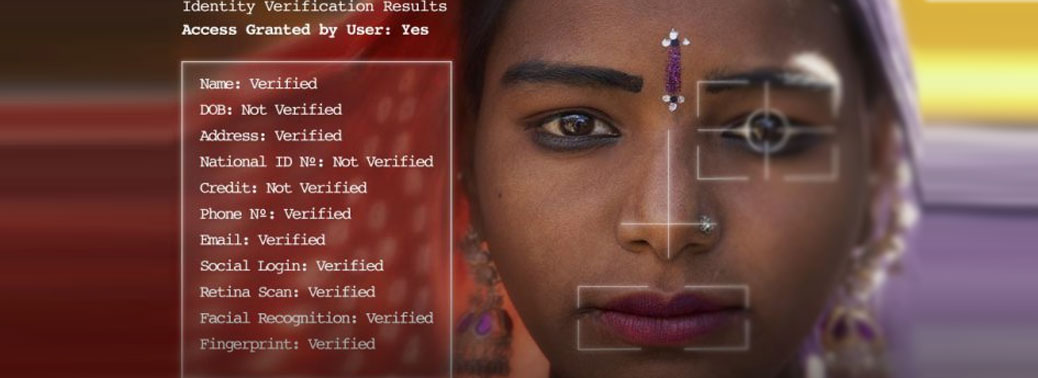
The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) has announced a phased roll out of face recognition feature as an additional mode of authentication
Face Recognition:
- The UIDAI said that ‘live face photo’ capture and its verification with the photo obtained in eKYC will be essential in those cases where Aadhaar is used for issuing mobile SIMs.
- The move aims at curbing the possibility of fingerprint spoofing or cloning, and seeks to tighten the audit process and security around issuance and activation of mobile SIMs.
- The Authority announced to roll out face recognition feature as an additional mode of authentication, starting with telecom service providers, from September 15.
- It has also proposed a monetary disincentive for telcos found slipping on the prescribed targets.
- For authentication agencies other than telecom service providers, the UIDAI said specific instructions will be issued on implementation of face authentication feature, but did not give a new deadline.
- The UIDAI has proposed a two-factor authentication for use of face recognition by telcos. Where an individual provides the Aadhaar number, the authentication will be done using fingerprint or iris and face.
- For individuals providing Virtual ID, the authentication can be on the basis of fingerprint or iris.
Need for face recognition:
- Combination of live face with fingerprint in authentication will also enhance Aadhaar security as it will effectively curb fingerprint spoofing.
- This will ensure that telcos provide face capture facilities to customers who encounter difficulty in authentication due to worn out finger prints.
UIDAI:
- The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI)is a statutory authority established under the provisions of the Aadhaar (Targeted Delivery of Financial and Other Subsidies, Benefits and Services) Act, 2016 (“Aadhaar Act 2016”) under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- UIDAI was created with the objective to issue Unique Identification numbers (UID), named as “Aadhaar”, to all residents of India that is
- Robust enough to eliminate duplicate and fake identities
- Can be verified and authenticated in an easy, cost-effective way
CMSMS and ‘KHAN PRAHARI’ App
29, Jul 2018

- Union Ministry of Coal launched the Coal Mine Surveillance & Management System (CMSMS) and Mobile Application ‘Khan Prahari’.
- Developed by CMPDI, Ranchi a Subsidiary of CIL and Bhaskarcharya Institute of Space Application and Geo-informatics (BISAG).
- CMSMS-The objective of CMSMS is reporting, monitoring and taking suitable action on unauthorised coal mining activities.
- It is a Web-based GIS application through which location of sites for unauthorised mining can be detected.
- The basic platform used in the system is of Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology’s (MeiTY) map which provides village level information. The leasehold boundary of all the coal mines are displayed on this map by which any change in allotted lease area due to unauthorised mining activity can be detected.
- CMSMS also provide other important information like reclamation work being done by Coal India Limited which is being monitored every year by CMPDI using satellite data
The ‘Khan Prahari’ App is for reporting any activity taking place related to illegal coal mining like rat hole mining, pilferage etc. One can upload geo-tagged photographs of the incident along with textual information directly to the system.
The system uses both satellite data and public input to capture information on unauthorised coal mining activities and also take appropriate action on them with due transparency.Central Mine Planning & Design Institute Limited (CMPDI) is a Government of India enterprise having its corporate headquarters at Ranchi in India.
It is a fully owned subsidiary of Coal India Limited India’s largest consultancy organisation and the market leader in an expanding earth resource sector. CMPDI also handles specialised assignments of Ministry of Coal and CIL. Offering services in the sphere of resource exploration & development in Exploration, Mining ,Coal Preparation, Coal Utilisation and Management, Coal Technology, Coal / Material Handling Arrangement, Engineering,and Environmental Management
Digi Yatra
10, Jul 2018

- Under Ministry of Civil Aviation, an Industry – led initiative co-ordinated by the Ministry
- Brings Together entire industry to develop a digital ecosystem that will deliver Indian Customer’s fully digital at every touch point of their Journey
- By this initiative we can optimally link Aadhar to airlines and other ecosystem players at the time of booking for faster airport entry and automated check-ins without requiring any paper -based interventions.
C vigil
05, Jul 2018

- Election commission of India launched a mobile app called cVIGIL.
- A user-friendly and easy to operate Android application, requires an Android smartphone equipped with a camera, good internet connection and GPS access
- Citizens can immediately report on incidents of misconduct within minutes of having witnessed them and upload it on this app, without having to rush to the office of the returning officer to lodge a complaint.
- The automated location mapping will be done using Geographic Information System.
- After its successful submission through the app, the vigilant citizen gets a Unique ID to track and receive the follow up updates on her or his mobile and will get a unique id for each report for follow up updates.
- The identity of the complainant will be kept confidential.
- The app has inbuilt features to prevent its misuse. It will receive complaints only about Model Code of Conduct violations. The user will get 5 minutes to report an incident after having clicked a picture or a video.
- To prevent any misuse, the app will not allow uploading of the pre-recorded or old images and videos. The app will not facilitate saving of the photos or videos recorded using the ‘cVIGIL’ app into the phone gallery either.
- Further, the application will be active only in States where elections have been announced. The moment a citizen exits an election-bound State, the app will become inactive
It will be operational only where elections are announced. cVIGIL will allow anyone in the election-bound state to report violations of Model Code of Conduct.
Drawback in current practice:
- The complaints about violations of Model Code of Conduct often could not be followed instantly, leading to the violators escaping detection from the action squads.
- The lack of any documented evidence in the form of pictures or videos was seen as a hurdle in verifying a complaint.
- The absence of a robust response system to quickly and accurately identify the scene of occurrence of violations with the help of geographical location details hampered election officers’ ability to apprehend the violators
- The new app is expected to fill in all these gaps and create a fast-track complaint reception and redressal system. A significant step towards empowering of vigilant citizens and to hold political parties and politicians accountable.
National Health Stack (NHS)
01, Jul 2018
NITI AAYOG unveiled the blue print of National Health Stack, a shared digital healthcare infrastructure. It is in accordance with National Health Policy 2017 had also envisaged creation of a digital health technology ecosystem aimed at developing an integrated health information system that serves the needs of all stakeholders
- It is in line with the implementation of the Centre’s flagship scheme Ayushman Bharat and other public healthcare programmes in the country.
- It envisages a centralized health record for all citizens of the country in order to streamline the health information and facilitate effective management of the same.
- The components include national health electronic registries, a coverage and claims platform, a federated personal health records framework, a national health analytics platform among others.
The proposed NHS is an approach to address the challenge and seeks to employ latest technology including Big Data Analytics and Machine Learning Artificial Intelligence, a state of the art Policy Mark-up Language and create a unified health identity of citizens – as they navigate across services across levels of care, i.e. Primary, Secondary and Tertiary and also across Public and Private. - This will allow policy makers to further build their projections around upcoming outcomes, experiment with new services as well as fill the existing gaps in the Indian healthcare industry among others.
- Allow states to incorporate horizontal and vertical expansion of scheme
- Avoid duplication of efforts.
- Enable ease of adoption for those without systems or with dysfunctional systems in place.
- The registrant may create a virtual health ID to preserve their privacy when interacting with other users or stakeholders in the system.
- Once implemented, it is expected that National Health Stack will significantly “bring down the costs of health protection, converge disparate systems to ensure a cashless and seamlessly integrated experience for the poorest beneficiaries, and promote wellness across the population
NHS will not only allow policy makers to experiment with policies, detect fraud in health insurance, measure outcomes and move towards smart policy making, but also engage market players (NGOs, researchers, watchdog organisations) to innovate and build relevant services and fill the gaps.






