Category: Defence
BrahMos Deal and India’s Defence Exports
10, Feb 2022

Why in News?
- Germany has become a weaker link in the Western coalition against Moscow and Beijing.
- The US-Russia-China power dynamics:
- There is a convergence between China and Russia on a range of issues from NATO expansion to the AUKUS alliance.
- Despite their problems with the US, both Moscow and Beijing want a productive partnership with Washington.
- Both Russia and China want to leverage the united front to negotiate better terms from America.
- Exploiting the contradiction between Russia and China: Washington, in turn, wants to explore the cleavages between Moscow and Beijing.
- Focus on challenges from China: Biden’s outreach to Putin last year was based on the premise that the US could better focus on the challenges from China in the Indo-Pacific if there was a reasonable relationship with Russia in Europe.
- Putin is trying to take advantage of that proposition by raising the stakes in Europe.
- Exploiting economic means: If Putin is focused on military means to rewrite the European security order with the US, Xi is focused on the economic means to alter the US ties.
- Xi is making a big play for the Wall Street bankers who see merits in engagement with Beijing and lobby Washington to scale down the confrontation with China.
The US Resilience:
- The chaos of American domestic politics and the continuing arguments between the US and its European partners tend to amplify the disagreements within the West.
- It would be a mistake for Putin and Xi to mistake Western disagreements for strategic divergence.
- Consensus on challenging China: The last few years have seen the quick emergence of a new US consensus on challenging China despite the polarisation of the American political class.
- The idea that the US can’t risk a two-front challenge with Russia and China is popular but mistaken.
- Power of the US and its allies: Despite the dramatic rise of China and its new partnership with Russia, the united front can’t really match the comprehensive national power of the US and its allies.
- India is now a strategic partner of the US and faces growing challenges from China.
- In Asia, Biden has revived the Anglosphere (the AUKUS alliance with the UK and Australia), elevated the Quad to the summit level, and reached out to the ASEAN.
- In Europe, the US is getting NATO in order.
- Britain has taken the lead in the diplomatic confrontation with Russia.
- French President Emmanuel Macron is coordinating with the US in dealing with the Ukraine crisis.
- Beyond the rebuilding of US alliances, Washington has an important lever which is the exploitation of the domestic political vulnerabilities of “Czar Putin” and “Emperor Xi”.
- Challenge for India:
- New dynamics between two coalitions: India’s approach will depend upon the new dynamic between the two coalitions as well as its own relations with China, Russia, and the US.
- As both sides consolidate their global coalitions, it will get harder to be in the middle.
- India would like to see Russia find accommodation with the West in Europe; but if Russia’s relations with the West deteriorate further in Europe, Delhi is unlikely to let Moscow undermine its growing partnership with the US and its allies.
Conclusion:
- With the return of great Power Rivalry coinciding with India’s deteriorating ties with China, Delhi now stands closer than ever before to the West.
INDIA FRANCE
24, Mar 2020

Why in News?
- Recently, India and France conducted joint patrolling for the first time from the Reunion Island. The patrolling was conducted in the month of February by a P-8I aircraft.
Highlights
- It is conducted under the ‘Neighbourhood First’ policy and broader maritime cooperation, the Indian Navy undertakes joint Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) surveillance with Maldives, Seychelles and Mauritius and Coordinated Patrols (CORPATs) with Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand and Indonesia.
- The objectives of the CORPATs are to ensure effective implementation of United Nations Conventions on Laws of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- The joint patrolling with France shows India’s intent to expanding its footprint in the Indian Ocean, focusing on the stretch between the East African coastline and the Malacca straits.
- India has carried out CORPATs only with maritime neighbours and had rejected a similar offer by the US in 2016. India has recently become an observer to the Indian Ocean Commission. It consists of Reunion as one of its members.
About Defence Relations between India- France
- The Indian navy is currently inducting French Scorpene conventional submarines, being built in India under technology transfer.
- The Indian Air Force will soon get the first batch of its 36 Rafale fighter jets from France.
- India is working with France to develop strategic and economic partnership involving Madagascar, Reunion Islands-Comoros so as to balance the growing influence of China in that part of the Indian Ocean Region.
- Some of their defence exercises are
- Gagan Shakti is conducted by the Indian Air Force to showcase its air dominance over the entire extended area of the Indian Ocean Region.
- Garuda Shakti is the joint military exercise between India and Indonesia.
- Mitra Shakti is the joint military exercise between India and Sri Lanka.
About P-8I Aircraft:
- The Boeing’s P-8A Poseidon is designed for long-range Anti-Submarine warfare (ASW), Anti-Surface Warfare (ASuW), and intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) missions.
- Its Indian variant is referred to as P-8I. Of a total of 12 ordered aircrafts, India has received eight, making the Indian Navy’s P-8 fleet the second largest in the world. Another four aircrafts are on-schedule to be delivered in 2020.
- It is not just responsible for coastal patrolling but is also used for other critical missions like search-and-rescue, anti-piracy, and supporting operations of other arms of the military.
- Reunion Island is a French overseas department and overseas region in the western Indian Ocean. It is located about 420 miles (680 km) east of Madagascar and 110 miles (180 km) southwest of Mauritius.
About United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS):
- It is an international treaty which was adopted and signed in 1982. It replaced the four Geneva Conventions of April, 1958, which respectively concerned the territorial sea and the contiguous zone, the continental shelf, the high seas, fishing and conservation of living resources on the High Seas.
PRECISION APPROACH RADARS (PARS)
29, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- A contract for installation and commissioning of nine Precision Approach Radars (PARs) was concluded today between Ministry of Defence and M/s Data Pattern (India) Pvt Ltd at a cost of Rs 380 crores under ‘Buy Indian’ category.
- The state-of-the-art radars incorporating latest Phased Array technology will be installed at Indian Naval Air Stations and Indian Air Force Stations.
Precision Approach Radars:
- Precision Approach Radar (PAR) is a primary radar used at aerodromes for approach operations based on specific procedures for the pilot and the controller; however, the use of PARs for civil applications is rapidly decreasing. Precision Approach Radar offers the possibility of a safe landing even in poor visibility conditions.
- The radar is placed near the mid-point of the runway (at a distance up to 6.000 ft) and works remotely. The radar is particularly important in situations when the pilot has limited sight (because of fog, rain, etc.).
- In this situation, the radar has to provide the approach controller with maximum quality radar display complemented by computer evaluation of speed, deviations from glide path (or glide slope) and course line, the distance from the previously approaching aircraft, etc.
- Traffic controller provides highly accurate navigational guidance in azimuth and elevation to a pilot so that he can keep his aircraft aligned with the extended centreline of the runway.
- The accuracy of the radar permits lower minimum descent than a non-precision approach. Thus, the pilot has a better chance of seeing the ship or airfield in bad weather conditions.
DIRECTED ENERGY WEAPONS (DEWs)
12, Aug 2019

- Context- Directed energy weapons or DEWs are among the next bunch of military technologies that the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is working on.
What is Directed Energy Weapons?
- A directed-energy weapon (DEW) is a ranged weapon that damages its target with highly focused energy, including laser, microwaves and particle beams.
- Potential applications of this technology include weapons that target personnel, missiles, vehicles, and optical devices
DRDOs take on Directed Energy Weapons:
- DEWs would play a major role in future warfare.
- DEWs are extremely important today. The world is moving towards them.
- In the country too, DRDO is doing a lot of experiments.
- DRDO have been working in this area for the past three to four years to develop 10kW and 20kW [weapons].
Directed energy weapons could have several Main Advantages over conventional weaponry:
- Direct energy weapons can be used discreetly; radiation above and below the visible spectrum is invisible and does not generate sound.
- Light is only very slightly altered by gravity, giving it an almost perfectly flat trajectory.
- It is also practically immune to both windage and Coriolis force. This makes aim much more precise and extends the range to line-of-sight, limited only by beam diffraction and spread, and absorption or scattering by intervening atmospheric contents.
- Lasers travel at light-speed and have near infinite range and therefore, are suitable for use in space warfare.
- Laser weapons potentially eliminate many logistical problems in terms of ammunition supply, as long as there is enough energy to power it the laser ammunition supply is assured.
- Depending on several operational factors, Directed Energy Weapons may be cheaper to operate than conventional weapons in certain contexts.
Significance of Laser based or Microwave Based high-power DEWs
- Laser based or microwave based high-power DEWs can quietly disable enemy drones or missiles temporarily or permanently without leaving physical debris.
- In contrast, the ASAT or anti-satellite missile that the DRDO tested on March 27, killed an orbiting Indian target satellite and left hundreds of small pieces as debris for a few months.
Problems with laser weapons:
Blooming:
- Laser beams begin to cause plasma breakdown in the atmosphere at energy densities of around one megajoule per cubic centimetre.
- This effect, called “blooming,” causes the laser to defocus and disperse energy into the surrounding air.
- Blooming can be more severe if there is fog, smoke, or dust in the air.
DRDO SUCCESSFULLY FLIGHT-TESTS QRSAM
04, Aug 2019

Why in News?
- Defence Research Development Organisation (DRDO) today successfully flight-tested its state-of-the-art Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missiles (QRSAM) against live aerial targets from Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur.
QRSAM:
- Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile (QRSAM), with a strike range of 25 km, is being developed by the DRDO for the Indian Army.
- The all-terrain and all-weather missile with electronic counter-measures against jamming by enemy aircraft can be mounted on a truck and stored in a canister.
- Before this test, on February 26, two rounds of tests were successfully carried out.
- This missile can be rotated 360 degree while on the way to its target.
- QRSAM is also able to use as an anti-sea skimmer from a ship against low flying attacking missiles. QRSAM employs dual thrust propulsion stage using high-energy solid propellant.
QRSAM Test:
- DRDO conducted two different tests for different altitude and conditions. DRDO closely observed both tests and found that flights successfully demonstrated the Aerodynamics, high manoeuvring capabilities, Robust Control, Structural performance and Propulsion thus proving the design configuration.
- Electro-Optical Systems, Radars, Telemetry and other equipment have monitored and tracked the missiles through the entire flights. DRDO announced that all the mission objectives have been met.
INTEGRATED BATTLE GROUPS (IBG)
29, Jul 2019

- Context– The new concept of Integrated Battle Groups (IBGs) which the Army plans to create as part of overall force transformation is close to implementation,
About IBG:
Significance:
- IBGs are expected to be game changers that will alter the way the Indian Army strategises for wars.
- These specialised groups to ensure better integration and self-sufficiency as compared to the existing formations.
- During hostilities, the current system requires a brigade to wait to be augmented by various types of units, such as artillery and logistics, which raises its time to mobilise.
- This won’t be the case with IBGs, which will be self-sufficient and inbuilt with all such units, and hence, easier to mobilise.
DORNIER SQUADRON INAS 313 AT CHENNAI
24, Jul 2019

Why in News?
- The fifth Dornier squadron Indian Naval Air Squadron (INAS) 313, was commissioned into the Indian Navy by Admiral Karambir Singh.
Dornier Squadron INAS 313:
- It will enhance maritime security and safeguard our nation’s maritime interests
- The strategic position of the squadron will give India, dominance over the North-Eastern part of the Indian Ocean that also consists of trade routes.
- The Squadron will be operating from Chennai International Airport
- With the commissioning of INAS 313, Tamil Nadu will have 3 naval air bases, which is the highest among the Coastal States
- Other two air bases in Tamil Nadu are INS Rajali at Arakkonam and INS Parundu at Ramnad.
- INAS 313 is named ‘Sea Eagle’ from the bird of prey family Accipitridae
- Dornier aircraft is a multi-role Short Range Maritime Reconnaissance (SRMR) aircraft manufactured by HAL (Hindustan Aeronautics Limited).
- The aircraft performs maritime surveillance, Search and Rescue Operations, and targeting data to weapon platforms.
- Dornier aircraft from HAL will Contribute towards indigenous development and self-reliance through “Make in India”.
REGIONAL COOPERATION AGREEMENT ON COMBATING PIRACY AND ARMED ROBBERY AGAINST SHIPS IN ASIA (ReCAAP)
21, Jun 2019

Why in News?
- The Indian Coast Guard (ICG) will be co-hosting an international workshop that aims to deepen knowledge on issues related with piracy and armed robbery, the maritime agency said.
- The two-day workshop has been organised in cooperation with the Regional Cooperation Agreement on Combating Piracy and Armed Robbery against Ships in Asia (ReCAAP) Information Sharing Centre (ISC).
ReCAAP:
- The ReCAAP stands for Regional Cooperation Agreement on Combating Piracy and Armed Robbery against Ships in Asia.
- It is the first regional Government-to-Government agreement to deal with piracy and armed robbery at sea in Asia.
- The ReCAAP Information Sharing Centre (ReCAAP ISC) was established under the Agreement and was officially launched on 29 November 2006 in Singapore.
- Presently, 20 countries are members of the ReCAAP including Australia, US, Japan, China and Bangladesh (Pakistan is not a member).
- India had played an active role in setting up and functioning of the ReCAAP ISC along with Japan and Singapore.
- The Centre has designated the ICG as the focal point within India for the ReCAAP.
PROJECT 75
21, Jun 2019

- Under this project, the Indian Navy intends to acquire Six Diesel-Electric Submarines, which will also feature Advanced Air-Independent Propulsion systems to enable them to stay submerged for longer duration and substantially increase their operational range.
- Project 75 Mazgaon dock ship buliders limited (MDL) will maufacture six Scorpene sub marine for Indian Navy.
- Technology Transfer from Naval Group of France.
Background:
- India’s current arsenal consists of 14 conventional submarines and two nuclear- powered submarines.
- The P75I project is part of a 30-year submarine building plan that ends in 2030.
- As part of this plan, India was to build 24 submarines — 18 conventional submarines and six nuclear-powered submarines (SSNs) — as an effective deterrent against China and Pakistan.
- The first Scorpene submarine INS Kalvari under P75 was launched in October 2015.
- The third in Scorpene series INS Karanj was launched in January 2019. The fifth Scorpene-class submarine INS Vagir and sixth Scorpene-class submarine INS Vagsheer.
INDIA TEST FIRES BRAHMOS SUPERSONIC CRUISE MISSILE FROM CHANDIPUR IN ODISHA
07, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Supersonic cruise missile BrahMos was test fired from the Integrated Test Range (ITR) at Chandipur in Odisha.
- Anti-ship version of the missile launched by complex-3 of the ITR, Defence Research and Development (DRDO) sources.
- World’s fastest supersonic cruise missile with high rate of accuracy
Missile is fired from land, sea and air. - The missile with a strike range of around 290 km is a strategic asset for India which act as a deterrence against any possible threats from China and Pakistan.
- BrahMos is a joint venture between the DRDO and the NPOM (a Russian military technology firm) of Russia.
- BrahMos operationalised in the Indian Army, Indian Navy and Indian Air Force.
- Senior defence officials and scientists from DRDO and BrahMos witnessed the trial.
Background:
- Origin and history of Brahmos
- It brings a supersonic speed when it is separated. At the second stage then takes the missile closer to 3 Mach speed in cruise phase.
- Stealth technology and guidance system with advanced embedded software provides the missile an extraordinary performance
- Type: Cruise missile; Air-launched cruise missile. Variants: Ship-launched; Surface-launched.
- Manufacturer: BrahMos Aerospace Limited
- Place of origin: India / Russia
- About Brahmos
- Speed: Mach 2.8–Mach 3
- Unit cost: US$2.73 million
- Place of origin: India / Russia
- Manufacturer: BrahMos Aerospace Limited
AN-32 WITH 13 ONBOARD MISSING OVER ARUNACHAL PRADESH
04, Jun 2019

Why in News:
- Indian Air Force’s AN-32 transport aircraft goes missing after taking off from Jorhat in Assam. The airborne aircraft had total 13 people on board in Assam. The airborne aircraft had total 13 people on board including eight aircrew and five passengers.
Details:
- AN-32 aircraft got airborne on 3 June from Jorhat at 12:27 p.m. for Mechuka Advanced Landing
Ground (only 29 kms from the China border), in Mechuka Valley in West Siang District of Arunachal Pradesh. It last contacted ground agencies at around 1:00 p.m. after that there has been was no contact with the aircraft. Since the aircraft lost the contact and did not reach the destination also Indian Air Force initiated overdue actions.
Search Operation:
- C 130J Super Hercules aircraft, AN-32 military transport aircraft, two Mi-17 (medium twin-turbine transport helicopter) of Indian Aiir Force (IAF) and ALH (Advanced Light Helicopters) helicopter of Indian Army were launched to locate the missing aircraft.
- Helicopters were routed to the location after some ground reports were received about possible location of a crash site however no wreckage has been sighted so far.
- IAF is in continuous coordination with Indian Army and with various government and civil agencies to locate the missing aircraft. The Search operation to locate the missing IAF AN- 32 aircraft is underway with operation from air by IAF and by ground parties of Indian Army and the Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP).
AN-32:
- It is a tactical transport aircraft and is an extensive used by Indian Air Force (IAF).
- It has been in service since 1984 and has been a trustworthy workhorse for the IAF for many years.
Specification:
- As the service ceiling of Antonov An-32 turboprop aircraft is 31,000ft so it flies lower and slower with a cruising speed of 470 kmph than most commercial jetliners which have a service ceiling of 40,000ft, thus this gives lesser room for the An-32 to outrun bad weather or climb over it.
POST BALAKOT, INDIAN AIR FORCE ZEROES IN ON KEY VULNERABILITY
29, May 2019

Why in News:
- After Balakot air strike, the Indian Air Force (IAF) has identified a shortage of Airborne Warning and Control System (AWACS) aircraft to provide round-the-clock surveillance as a major deficiency
Background:
Airborne Warning and Control System (AWACS):
- This system has the ability to detect incoming cruise missiles, fighter jets or even drones from both Pakistan and China.
- China has over 20 AWACS while Pakistan has 8 AWACS.
- The indigenous AeW&CS has completed all tests and certification.
- Pegged as a “force multiplier”, the system is equipped with a 240-degree coverage radars in contrast to the existing Phalcons, which provide a 360-degree coverage over a 400-km range.
- The AEW&C system will detect, identify and classify threats present in the surveillance area and act as a Command and Control Center to support Air Defence operations.
- Besides, the system will support IAF in offensive strike missions and assist forces in the tactical battle area.
- The Electronic and Communication Support Measures of the system can also intercept and gather electronic and communication intelligence from radar transmissions and communication signals.
IAF RECEIVES FIRST AH-64E APACHE ATTACK HELICOPTER
12, May 2019

Why in News:
- The first AH-64E Apache attack helicopter built for India was formally handed over to the Indian Air Force (IAF) at the Boeing production facility in Mesa, Arizona in the U.S.
Details:
- The helicopter has been customised to suit IAF’s future requirements and would have significant capability in mountainous terrain. The helicopter has the capability to carry out precision attacks at standoff ranges and operate in hostile airspace with threats from ground. The ability of the helicopters, to transmit and receive the battlefield picture, to and from the weapon systems makes it a lethal acquisition.
AH-64E / Features:
- AH-64E Apache is one of the leading multi-role attack helicopters globally and is flown by the US Army.
- The Apaches are armed with stinger air-to-air missiles, Hellfire Longbow air-to-ground missiles, guns and rockets. Its features include joint digital operability, improved survivability and cognitive decision-aiding.
Significance:
-
The addition of AH-64 E (I) helicopter is a significant step towards modernisation of Indian
Air Force’s helicopter fleet. - The helicopter has been customised to suit the IAF’s future requirements and would have
significant capability in mountainous terrain. - It has the capability to carry out precision attacks at standoff ranges and operate in hostile airspace with threats from ground.
- Its ability to transmit and receive the battlefield picture, to and from the weapon systems through data networking makes it a lethal acquisition.
GADCHIROLI NAXAL ATTACK: TROOP PULLOUT MAY HAVE LEFT A HOLE IN RED ZONE SECURITY GRID
05, May 2019
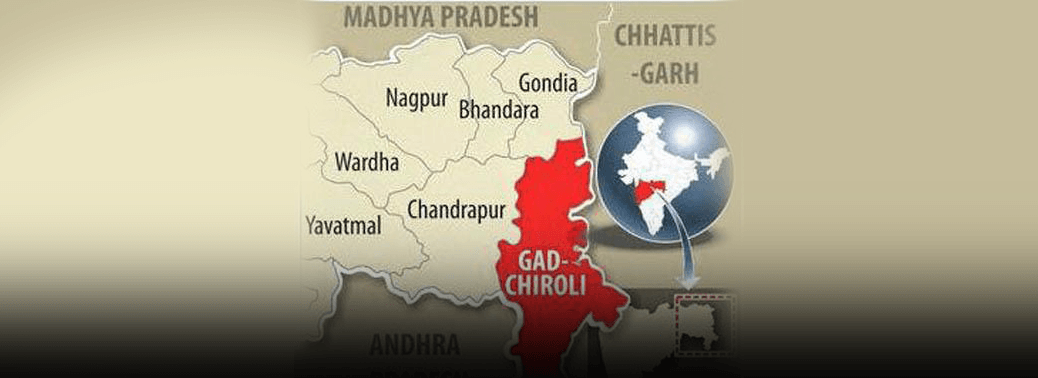
Why in News:
- The unceasing requisitioning of paramilitary forces for the elections in West Bengal may have weakened the security grid around Maharashtra’s Maoist heartland, where an IED blast killed 15 jawans
Details:
- Maoists torched 25 vehicles at a road
- construction site in Kurkheda of Gadchiroli early in the morning.
- A team of the Quick Response Team of the Gadchiroli police was on way to inspect this.
- While on road in a private vehicle, these fifteen policemen and their driver were killed by a powerful explosion set off by Maoists.
- An improvised explosive device (IED) blast was set off. The slain fighters were members of the elite C-60 wing.
- This is the fourth Maoist attack, since the national election began in April, 2019, in Gadchiroli which borders Chattisgarh.
Maoists:
- Maoists in India are anti-state rebellion groups spread in mainland country covering tribal areas of seven states. The insurgency began in 1967 in remote forests of West Bengal’s village ‘Naxalbari’. While Naxalism originated in India, Maoism in China. The common thread between the two is “armed resistance” and “violence”.
- The Maoists consider Parliamentary democracy to be tools of exploiting their rivers and natural resources by capitalists and politicians. They want to establish a ‘communist society’ through armed revolution against the government.
Measures taken to deal with Left Wing Extremism:
- In 2017, a security operations doctrine called ‘SAMADHAN’ was launched.
- The acronym SAMADHAN stands for Smart leadership, Aggressive strategy, Motivation and training, Actionable intelligence, Dashboard Based KPIs (key performance indicators) and KRAs (key result areas), Harnessing technology, Action plan for each theater, and No access to financing. The MHA suggested the use of trackers for weapons, and bio-metrics in smart guns. Unique Identification number (UID) for Gelatin sticks and explosives.
- At least one UAV or Mini UAV for each of the Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) battalions deployed in the Maoist hotbed. Joint Task Forces for operations along inter-State boundaries to be set up. Better inter-state coordination and intelligence sharing.
- 400 fortified police stations to be set up in Naxal belt.
- Resumption of Left-Wing Extremism (LWE) – specific schemes such as SRE, SIS, IAP/ACA, CIAT schools. Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) to be reviewed to ensure effective choking of fund flow to LWE groups. Fast tracking building infrastructure, with a focus on solar lights, mobile towers with 3G connectivity, and road-rail connectivity.
- Indian Army or specialized forces – such as Greyhounds – to train forces to take on naxals.
C-60 wing:
- The C-60 was created as a batch of 60 commandos to counter Maoist violence in Gadchiroli.
- As Naxal activities heightened in the coming years, a second branch was also created in 1994. They are similar to the Greyhound forces in Telangana and the SOG (Special Operation Group) units in Andhra Pradesh.
- The contribution of C-60 has been a notable one, and they have been alternatively referred to as ‘crack commandos’. The commandos were recruited from the same regions where the Naxals enlisted their own fighters.
- Having the same roots, the C-60 had operational advantages compared to other units of the state police. These include faster maneuvering, and the greater ability to converse with the local population. The C-60 is qualified for combat in difficult battlegrounds, such as dense forests and over hilly terrain. Apart from actual combat, the C-60’s task also includes facilitating Maoists to surrender and join the mainstream.
- For this, members of the unit meet the families of Maoists to apprise them of government schemes made for ex-Maoists.
Way Forward:
- The forces should be more proactive and aggressive in owning operations, rather than being reactive. To overcome the Maoist Challenge, there needs to be a comprehensive policy and not just a military or security centric approach.
ARMY TO BUILD TUNNELS TO STORE AMMUNITION
25, Apr 2019

Why in News:
- Indian Army is planning to construct underground tunnels for storage of ammunition along the border with China and Pakistan
Details:
- The Army has also involved the National Hydroelectric Power Corporation Ltd (NHPC), a public sector undertaking, to construct the caves or tunnels and a memorandum of understanding (MoU) will soon be signed with the NHPC.
- The Army is also increasing its ammunition stockpile. Last year, it had finalised a Rs15,000 crore long-term plan to get domestic private sector players to manufacture seven different types. Army needs specialised areas to store them. The tunnels and caves would be constructed and NHPC was chosen for the task because of its best technical expertise, capability and capacity to construct them without any glitches. Major armies, including China and the U.S., already use underground ammunition storage.
- The tunnels will be built-in high-altitude areas in the Northern and Eastern borders. Number of caverns with storage capacity of 200 metric tonnes will be built in mountain folds in identified areas.
- Four pilot projects would be taken up at four different locations along the Northern border and in Jammu and Kashmir at a cost of 15 crore and are expected to be completed within two years. A range of ammunition used by the Army, ranging from bullets, rockets to anti- tank and surface to air missiles, can be stored in the caverns.
Advantages:
- It is cost-effective and each such cave or tunnel would have a capacity between 150 to 250 metric tonnes. Underground tunnel storage offers improved safety, easier camouflage from enemy observation and satellite imagery and protection from enemy strikes like Balakot air strike when Pakistan Air Force jets targeted Indian army installations along the Line of Control (LoC).
Way Forward:
- Even it had many advantages, it ensures better safety of sensitive ammunition minimising accidental explosions.
RAFALE: GOVT GAVE UNPRECEDENTED WAIVERS IN OFFSET AGREEMENTS
09, Apr 2019

Why in News?
The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) gave exceptional and unprecedented waivers to
- The twin-engine Rafale combat jet is designed from the beginning as a multi-role fighter for air-to-air and air-to-ground attack is nuclear-capable and its on-board Electronic Warfare (EW) systems can also perform reconnaissance and radar jamming roles.
- Officials say that due to national security reasons, there is a confidentiality clause in the Rafale deal which bars the buyer and seller from talking about the pricing, making it impossible for any government to reveal any detail about the defence deals.
What are offset agreements?
- Offsets are kind of a quid pro quo between countries and defence companies. Basically, since a government spends a large part of its budget buying equipment from these companies, it asks these companies to invest a portion of the deal amount in their countries. The clause allows for economic growth of the country in the process of completing the deal. While some offset clauses may ask for investments, others may impose terms like onboarding of local suppliers in the process.
Two key issues of offset waivers
- The waivers concerned two key issues — the provisions to be made in the offset contracts for arbitration (Article 9) and access to books of accounts of the industrial suppliers (Article 12).
0% offsets in first three years
- According to the offset schedule, the two private French companies will discharge 0% of the value of the total offsets for ‘Make in India’ in the first three years and 4% in the fourth year. No less than 57% of the value of total offset obligations will be discharged in the seventh year.
French reluctance to mention ‘offsets
- The INT report reveals that the French negotiators were initially “not ready to mention the word ‘offsets’ in the IGA” but upon insistence by the Indian side, they “relented and added ‘Make in India’ initiative through Offsets at Article 12 of the IGA”. It was only after extended discussions that the two industrial suppliers agreed to provide their offset offer “as per the format specified in DPP-2013”.
Subject to France’s blocking statute
- There is France’s controversial blocking statute which criminalises the communication of economic, commercial, industrial, financial, or technical documents or information to foreign individuals or foreign legal entities. The blocking statute remains in place and can be invoked if needed.
Offsets are made for controversy
- Although the practice is often criticised for being trade-distorting, non-transparent, and riddled with corruption and has been generally prohibited by the World Trade Organisation (with an exception made for protection of the essential interests of a country’s national security), offsets are increasingly in vogue in the defence sector.
F 16 Aircraft
02, Mar 2019

In News
- A day after India raked up contract details between the United States and Pakistan on the AMRAAM missile fired from an F-16 aircraft and shared the information with American interlocutors to bolster its case about the misuse of the fighter aircraft against India, the US sought more information on the matter.
About:
- US State Department was seeking more information on the potential misuse of American-made F-16 fighter jets by Pakistan against India in violation of the end-user agreement.
- Due to non-disclosure agreements in Foreign Military Sales contracts, it cannot discuss the specifics of end user-agreements contained within.
- There is enough evidence to show that F-16s were used in this mission and Pakistan is trying to hide this fact.
- Also, parts of AMRAAM air-to-air missile, which is carried only on the F-16s in PAF, were recovered east of Rajouri within Indian territory.
- Tthe contract details and the part of the missile show the use of F-16s in the air strike since the US, which sold the fighter jets to Pakistan, does not allow these platforms to be used in an offensive role.
- Previously Pakistan said that no F-16 fighter jets were used and denied that one of its planes had been downed by the Indian Air Force. It claimed that no F-16 was part of the operation any such admission would violate US sale conditions of not letting Pakistan use F-16s in an offensive role.
Background:
- The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is a single-engine supersonic multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force (USAF).
- Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it evolved into a successful all-weather aircraft.
- The F-16 is a single-engine, highly manoeuvrable, supersonic, multi-role tactical fighter aircraft with a maximum speed of over Mach 2.
- In 2016, India had strongly opposed the US decision to sell eight F-16s to Pakistan, which also could not pass the muster in US Congress for Foreign Military Funding. This meant that the order was never placed.
- The United States, which is the largest seller of high-tech defence equipment globally, and has a strong end-user monitoring agreement, as a matter of practice takes all allegations of misuse of defence articles very seriously.
- But before making any judgement or arriving at any conclusion, it needs to establish some facts on the ground, if there has been any violation by Pakistan to the F-16 end-user agreement it signed by the United States.
- F-16 jets were meant to be used to “enhance Pakistan’s ability to conduct counter-insurgency and counterterrorism operations. Publicly available documents reveal that the US has imposed nearly a dozen restriction on Pakistan related to its use of F-16.
- AMRAAM missiles allow a fighter pilot to target an enemy aircraft that is beyond visual range, in day or night, and in all-weather conditions. The AMRAAM has an autonomous guidance capability, which allows the pilot to manoeuvre immediately after the missile’s launch.
Qrsam Missile
27, Feb 2019

- India on Tuesday successfully test fired the short-range Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missile (QRSAM) from a test range along the coast of Odisha.
About:
- Developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), the QRSAM missile has a strike range of 25 km to 30 km and has a capability of engaging multiple targets. The sleek and highly mobile air defence system has been developed for the Indian Army.
- The indigenously developed QRSAM will replace the ‘Akash’ missile defence system which is on its way out due to technological obsolescence.
- A QRSAM is different from normal air defence system, as this is an all-weather, all-terrain missile with electronic counter measures against jamming by aircraft radars.
- The QRSAM, which has already been tested in the past, was test fired from a rotatable truck-based launch unit at Chandipur in Odisha’s Balasore district. According to sources, two missiles were tested from Integrated Test Range (ITR) at Chandipur.
Background:
- The missile was first tested on June 4, 2017 and this was followed by the second successful test on July 3.
- The test firing comes on a day when a dozen of Indian Air Force fighter jets blew up terror camps across the Line of Control in Pakistan. India launched an airstrike inside Pakistan territory early today in response to the Pulwama attack of February 14 that claimed the lives of 40 CRPF jawans.
- The jets dropped 1,000 kg laser-guided bombs on terrorist camps in Balakot in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, Muzaffarabad, and Chakothi. India’
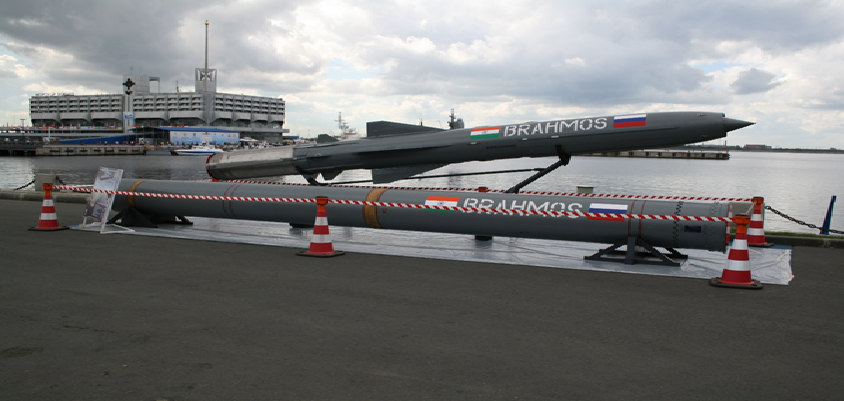
BRAHMOS
22, Feb 2019

- A sleeker, more lethal version of the supersonic cruise missile BrahMos is under development and the prototype should be ready for testing in about three years.
About:
- The idea is to have a smaller missile with the same capabilities. So the missile will fly at 3.5 times the speed of sound instead of 2.8 Mach. The range will remain at 300 km.
- For this several mechanical components in the missile are being replaced with electrical components which will also reduce the size. A structural study has been carried out and several sub-systems have already been developed.
- BrahMos is a joint venture between India and Russia and named after Brahmaputra and Moscowa rivers. It is capable of being launched from land, sea, sub-sea and air against surface and sea-based targets. The development trials of an anti-shipping variant began in 2003 and combat trials began in 2005.
- The reduced weight enables the NG variant to be carried by the indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA). An LCA can carry two missiles while a Su-30MKI can carry five of them.
Tejas – FOC
21, Feb 2019

- More than three-and-half decades after the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) or Tejas was conceived, the programme got a shot in the arm as it was accorded the Final Operational Clearance (FOC) by aviation certifying authorities, raising the hope of the Indian Air Force (IAF) that has been grappling to cope with its ageing fleet.
About:
- The release to service document, known as FOC, was handed over at the ongoing Aero India in Bengaluru. The LCA, that began as an ambitious programme in 1983, had proved that it could not just sustain a very high sortie rate but also carry out accurate weapon delivery of both air-to-air and air-to-ground targets.
- The FOC coming at a time when several defence procurements of successive governments have been held to public scrutiny over alleged scams and kickbacks, especially in the run up to the parliamentary elections, scheduled to be held later this year.
- Procedural delays among other hurdles has had a crippling effect on the Indian armed forces who are forced to continue using outdated technology, weapons and systems despite the consistently swelling defence budget.
- The IAF’s interests in acquiring more Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) developed products raising the hope for the cash strapped public sector unit, whose fortunes and order books have slimmed down in recent years.
AERO India – 2019
21, Feb 2019

Asia’s biggest air show Aero India-2019 will open Yelahanka air force station in Bengaluru, showcasing aerospace majors and their technologies and products, which include helicopters, fighter jets and transport aircraft.
About:
- The 12th edition of Asia’s premier show will be a five-day-long biennial event, exhibiting India’s defence prowess will also have aerobatic teams like India’s Sarang (ALH-Dhruv) and UK-based Yakovlevs will engross the audience present at the show.
- The will also be a platform for aviation companies to forge new alliances and contracts.
- Aero India 2019 endeavours to put India as the global runway of a billion opportunities as invitees includes Ministers, heads of global defence aerospace companies, corporate and government policymakers, military brass, entrepreneurs, delegates and exhibitors from across the world were at the event. After many years, the edition brings civil aviation back to a largely military show. The Ministry said it was the biggest so far, with 403 exhibitors and 61 aircraft in static or flying displays. 61 metal birds, including HAL’s indigenous products Light Combat Aircraft Tejas will soar high in the city’s skies. On static display will be HAL’s Light Utility Helicopter (PT-1), Light Combat Helicopter (TD-2), Advanced Light Helicopter (Rudra) and ALH MICU (Medical Intensive Care Unit).
- However, the event will be shrouded by the tragic death of an Indian Air Force (IAF) pilot from its aerobatic team Surya Kiran during the rehearsal earlier. Two British-origin Hawk advanced jet trainers collided and crashed mid-air during a rehearsal session.
- Another controversy surrounding this edition of the event were reports that it has been shifted to Uttar Pradesh, leading the state government to lash out at the central government for the alleged move.
- According to the Aero India official website, a total of 61 aircraft will be put on display and 403 exhibitors will be a part of the 5-day event.
The Last of the Elusive Pangolins
19, Feb 2019

- Obsession for its supposedly medicinal scales in China is believed to have made the ant-eating Chinese Pangolin, one of two species found in South Asia, extinct in India.
- The pangolin is the most trafficked mammal in the world.
- Though hunted for its meat across the north-eastern States and in central India
- The Demand for its scales in China has made it the most critically endangered animal in less than a decade.
- On World Pangolin Day, wildlife experts mourned the “possible extinction” of the Chinese Pangolin in the northeast and the likelihood of the Indian Pangolin found elsewhere in India of being wiped out in a decade or so. The third Saturday of February is observed as the day of the scaly nocturnal ant-eater, which activists say is an animal very few even forest officials know about.
- The Chinese Pangolin was officially categorised as critically endangered in 2014, but it is extinct today. The Indian Pangolin, marked endangered that year, is now critically endangered and disappearing fast,”
- The STF had busted one of the biggest international gangs of wildlife body parts smugglers. It arrested 159 people across 14 States and registered 12 cases, mostly for pangolin scale smuggling.
Northeastern gateway:
- Investigations by wildlife crime sleuths have revealed that almost 90% of smuggling of pangolin and pangolin scales is through the northeast.
- From elsewhere in India, the scales are smuggled out to China via Myanmar at Moreh in Manipur and Champhai in Mizoram. But there are numerous gateways along the border with Myanmar. This is why checking the smuggling network in the northeast is crucial for the survival of the last of the pangolins.
- Smaller animals like pangolins get indirect benefit of the focus on larger ones such as rhino, tiger, and elephant.
Killed Cruelly:
- Sadly, there is no survey of pangolin, which get smoked out of their burrows and killed cruelly by being thrown into boiling water. The animal used to be killed for meat until people learnt there was illegal money in its scales.
- The Chinese Pangolin has not gone the way of the dodo. Conservation policies have to look beyond major species, but the world needs to tell China that pangolin scales – like rhino horns – are made of keratin that produces human hair and nails and has no medicinal value.
DRDO Looking for Partnership
19, Feb 2019

- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is looking for potential partners to co-develop an engine for its planned Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) and five other future technologies.
About:
- It is on the lookout for collaborators to realise the other military technologies that it hopes to have in around five years Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicles (UCAVs) and UAVs, materials, sensors, avionics, and artificial intelligence, he said at the inauguration of a two-day international seminar connected with Aero India 2019.
- In all six areas, DRDO looking for partners with the capability and experience, within the country or outside. An aeroengine of the 110-kilo Newton type that we want for the AMCA is not available. Materials development is another very important area for making aircraft or missiles light and stealthy [or undetected]..
- Industry would be enlisted at the beginning of a project so that it can begin production as a natural partner. At present, the focus is on consolidating ongoing R&D activities and ensuring they reach the logical end.
- Indigenous technologies were being given a push. Minor innovators and startups are also being tapped for new concepts that the DRDO can try out. The new time-bound ‘Dare to Dream’ challenge has received 1,000 responses from individuals and startups.
Navy to set up New Air base in Port Blair
08, Jan 2019

Context:
- The Navy to commission a new airbase 100 miles north of Port Blair in the strategically located Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Details:
- Upon commission, this will be India’s fourth air base and the third naval air facility in the archipelago, which are closer to Southeast Asia than to the Indian mainland, overlooking key sea lanes of communication and strategic choke points. According to the officials, the base will initially operate choppers and Dornier short-range surveillance aircraft and will have a runway of about 3,000 m which will in phases be extended to 9000 m to support all kinds of aircraft including fighter jets.
- As part of the upgrade, the base will feature staging facilities, a fuel dump and maintenance and repair facilities.
Chinese Lunar Rover Named as ‘YUTU 2’
05, Jan 2019

Context:
- China has named the lunar rover, successfully deployed to carry out a string of experiments on the unexplored far side of the moon, as ‘Yutu 2’.
Details:
- It is said that China’s lunar probe is part of its ‘Made in China-2025’ project, which focuses on advanced technology, including space applications.
- The lunar rover follows the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System — China’s homegrown Global Positioning System that started worldwide service last month. Next year China plans to launch its Mars explorer mission. In 2022, it hopes to complete its own earth-orbiting space station. The rover has been programmed to launch ground penetration radar that would help map the moon’s inner structures. It would also analyse soil and rock samples for minerals, apart from activating a radio telescope to search for possible signals from deep space.
About Lunar Rover:
- The lunar rover has been launched to experiment the far side of the moon.
- The robotic spacecraft is carrying instruments to analyse the unexplored region’s geology and will conduct biological experiments.
- This is the pioneering achievement as earlier moon missions that have landed only on the Earth-facing side, this is the first time any craft has landed on the unexplored and rugged far side of the moon.The scientific tasks of the mission include low-frequency radio astronomical observation, surveying the terrain and landforms, detecting the mineral composition and shallow lunar surface structure, and measuring the neutron radiation and neutral atoms to study the environment on the far side of the moon.
Improved Light combat Aircraft gets green Light for Production
04, Jan 2019

Context:
- Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas progressed towards manufacture in an enhanced, battle standard format.
Details:
- The LCA is being designed and developed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) in Bengaluru.
- A new limited clearance from military airworthiness certifier CEMILAC for the Indian fighter green-lights its production in a superior lethal version.
- HAL aims to get the first aircraft out in late 2019.
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) has asked Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) to make 40 LCA aircraft.
- Of this, 20 will be in the advanced Final Operational Clearance (FOC) format. Another 20 are in the earlier Initial Operational Clearance (IOC) version.
- The IAF has modified and upgraded its trainer requirement in its old package order of 40 LCA aircraft.
Light Combat Aircraft:
- A Light combat aircraft is a light multirole military aircraft most coming from advanced trainers that have been modified or designed for engaging in light combat missions, either in light strike or attack missions, reconnaissance or interdiction roles while some keeping its trainer role.
- They are also slower than their bigger counterparts capable only of subsonic speed though some are capable of reaching mach 1+.
- Although equipped with either guns or short range air-to-air missiles it is usually for self-defense purpose or anti-hostile aircraft/helicopter missions not for air defense as lightweight fighters do, though some are capable of air combat or point air defense missions due to integrated or have variants capable of carrying powerful multi-mode radar systems, most LCAs don’t have such due to their small limited design or are less powerful.
- However, they can still be used to patrol the skies and implement border patrol or air policing.
NSG Must Have its own AIR WING
13, Dec 2018

Context:
- A Parliamentary panel has recommended that the Centre urgently take steps to ensure that the National Security Guard (NSG) — the country’s premier counter-terrorist and contingency force — is equipped with its own dedicated air wing.
Reason for this measure:
- Non-availability of dedicated aircraft has at times hampered NSG’s rapid reaction capabilities. For example, the NSG’s delay in reaching Mumbai during the November 2008 terrorist attacks on the city had come under severe criticism
- The 215th Parliamentary Standing Committee Report on Home Affairs tabled in the Rajya Sabha on Wednesday recommended that the “Ministry of Home Affairs should make urgent and sincere efforts to commission a dedicated Air Wing of NSG and provide requisite types and number of air assets to strengthen the aviation capability of the force.”
About National Security Guard:
- The National Security Guard (NSG) is an Indian special forces unit under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- It was raised in 1984, following Operation Blue Star and the assassination of Indira Gandhi, “for combating terrorist activities with a view to protect states against internal disturbances”.
- NSG is under the authority of Ministry of Home Affairs. However, it is not categorized under the uniform nomenclature of Central Armed Police Forces.
- It has a special forces mandate, and its core operational capability is provided by the Special Action Group (SAG) which is drawn from the Indian Army.
- The Special Rangers Group (SRG), the police component of NSG, which also handles VIP security, is composed of personnel on deputation from other Central Armed Police Forces and State Police Forces
- The NSG personnel are often referred to in the media as Black Cats because of the black outfit and black cat insignia worn on their uniform.
India Successfully Test-Fires Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile Agni-5
11, Dec 2018

In News:
- The indigenously built Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile Agni-V has been test-fired successfully from Abdul Kalam island under Chandipur Interim Test Range.
- This is the fourth successful test of this missile. Previously the test of Agni 4 was unsuccessful. It can carry both nuclear and traditional weapons.
Agni V Missile – Important Facts:
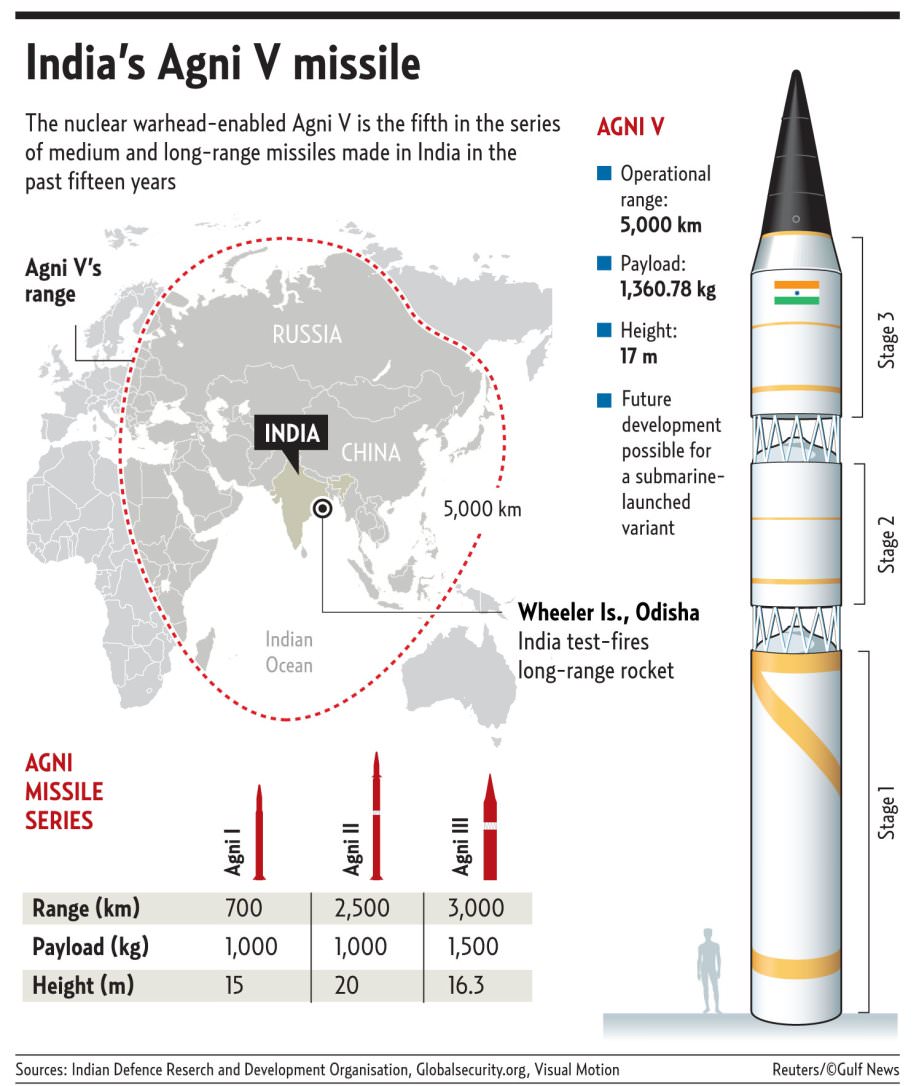
- Agni V ballistic missile is the brainchild of Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). It is the most advanced in the series.
- Agni-V is a nuclear capable long-range missile with new technologies in terms of navigation and guidance, warhead and engine.
- The three stage, 17- meter tall, two-meter wide Agni-V missile has a range of 5000 km.
- It can carry a nuclear warhead weighing up to 1.5 tonnes.
- Agni-V uses Ring Laser Gyro based Inertial Navigation System RINS. It is the most modern and gives very high accuracy.
- The Micro Navigation System or MINS helped the missile reach its target with precision.
- Other features of Agni- V missile include a high speed on- board computer, fault tolerant software and a robust reliable bus.
- The advanced computer and the inertial navigation system are the highlights of the missile as they aid in precision of the path.
- The missile is highly reliable, has longer shelf life and enhanced mobility compared to the other versions.
Nuclear-Capable Agni-V Successfully Test-Fired Off Odisha
11, Dec 2018

Context:
- India successfully test-fired nuclear-capable long-range ballistic missile Agni-V. The missile was launched from a canister on a road mobile-launcher from Dr. Abdul Kalam Island off Odisha.
Details:
- This is the third successful launch of Agni-V this year and the fifth launch of the missile in a canisterised form
- The mission critical avionics were indigenously designed and developed by Research Centre Imarat (RCI), Hyderabad
- All the mission objectives were successfully achieved. This launch comes after a series of successful launches of the missile. It further strengthens the country’s deterrence capability, which has been developed indigenously by assiduous efforts of scientists
About Agni V:
- Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) with a strike range of over 5,000 km and can reach most parts of China.
- It is three-stage solid propellant nuclear-capable missile
- It is a surface-to-surface missile. Capable of carrying nuclear warheads of over one tonne
- It carries Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicles (MIRV) payloads. A single MIRV equipped missile that can deliver multiple warheads at different targets.
- It is also a fire and forget missile, which once fired cannot be stopped, except by interceptor missile which only US, Russia and Israel have.
- The missile has been designed to hit the designated target point accurately, guided by the on-board computer with the support of a Ring Laser Gyro-based Inertial Navigation System, the Micro Inertial Navigation System, fully-digital control system and advanced compact avionics.
EX AVIAINDRA 2018
11, Dec 2018

Why in News?
- The second edition of the service-specific exercise AVIAINDRA between Indian Air Force (IAF) and Russian Federation Aerospace Force (RFAF), has been commenced at Air Force Station Jodhpur in Rajasthan on December 10, 2018. This bi-annual air-service exercise will conclude on December 22, 2017.
Highlights:
- The primary objective of this bi-annual air service exercise is to strengthen both of the air forces for anti-terrorist operations.
- Besides strengthening air forces, it also seeks to increase cooperation and build understanding between IAF and RFAS. This air service exercise takes place in two phases.
- This exercise allows foreign partners to participate without their assets. Indian Air Force pilots and Russian Federation Aerospace Force pilots flew aircraft when this air exercise was held at Lipetsk, Russia in September 2018.
- Similarly, RFSAF and IAF pilots will fly aircraft during in this 12-day long service specific exercise.
- Russia has been a major partner of India in the defence sector and the cooperation has been steadily growing further.
- In October 2017, India and Russia held a 10-day mega war game involving their armies, navies and air forces for the first time ramp up military ties.
- The exercise Indra, which took place in Russia, primarily focused on achieving coordination between forces of the two countries in tri-services integrated theatre command scenario.
- It was the first time, India participated in tri-services exercise with a foreign country with large scale participation by the Navy, the Army and the Air Force.
Mehar Baba Prize
05, Oct 2018
- The Indian Air Force has announced India’s first competition in the defence sector, the Mehar Baba Prize. The competition, in line with Make in India, is spread over three phases, from ideation to production.
About:
- In the wake of floods, cyclones and other natural disasters across the country, the IAF is holding a competition for participants to build a swarm of 50 drones to lead Humanitarian Aid and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
- The IAF will pick up to three winners, each of whom will get Rs 10 lakh in prize money and an opportunity to co-produce a Rs 100 crore order for induction of the drones to the Force.
- The competition is divided into three phases.
New Akash Missiles Get Green Light
16, Sep 2018

Why in news?
- The Army, which is inducting the indigenously developed Akash short-range surface-toair missile (SRSAM) system, will get an upgraded variant. The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) gave its procedural approval to the variant.
About the missile:
- Akash missiles are designed to be launched from static or mobile platforms such as battle tanks and wheeled trucks, providing flexible deployment.
- It can handle multiple targets and destroy manoeuvring targets, including unmanned aerial vehicles, fighter aircraft, cruise missiles and missiles launched from helicopters. Deployment of Aakash significantly improves defence capabilities from incoming air attacks.
- Akash missile system is an indigenously developed supersonic short-range surface-to-air missile system with the capability to engage a wide variety of aerial threats like aircraft, helicopters and unmanned aerial vehicles up to a maximum range of 25 km and up to an altitude of 20 km.
- This approval is for the procurement of an upgraded version of Aakash missiles which are much sleeker and more accurate compared to previous versions already in operation.
- Each Akash battery includes four 3D passive electronically scanned array (PESA) radars and four self-propelled launchers with three missiles each, all of which are interconnected. It also has battery level radar known as Rajendra, as well as a battery control centre. It can track and attack multiple targets concurrently.
- The Akash SAM system was produced by Bharat Electronics (BEL). Bharat Dynamics (BDL) serves as nodal agency for Akash SAM production for the army.
- The missile is guided by a phased array fire control radar called ‘Rajendra’ which is termed as Battery Level Radar (BLR) with a tracking range of about 60 km.
- The tracking and missile guidance radar configuration consists of a slew able phased array antenna of more than 4000 elements, spectrally pure TWT transmitter, two stage super heterodyne correlation receiver for three channels, high speed digital signal processor, real time management computer and a powerful radar data processor.
- The Akash is powered by Ramjet-rocket propulsion system which renders thrust for the missile to intercept the target at supersonic speed without any retardation.
- The engine is ‘on’ throughout the flight. The thrust is on till the missile intercepts the target. Most other surface-to-air missiles, including the U.S. Patriot and the Russian S-300 series, use solid-fuel rocket propulsion.
Surgical Strike Day- Parakram Parv
14, Sep 2018

Why in news?
- Union Minister of Human Resource Development Prakash Javadekar said that the celebration of September 29 as Surgical Strike Day in universities was not compulsory but claimed that it was decided on the advice of many students.
Surgical strike:
- On 29 September 2016, border skirmishes between India and Pakistan began following reported “surgical strikes” by India against militant launch pads across the Line of Control in Pakistani-administered Azad Kashmir.
- The operations began at 12.30 am when the commandos of Indian Army were dropped at Line of Control (LoC) in the region of Pakistan controlled and administered Kashmir. The surgical operations were conducted in Bhimber, Holspring, Kel and Lipa sectors across the LoC in Pakistan. As claimed by India, during the surgical strike, 7 military launch pads were destroyed and 38 terrorists and 2 Pakistani soldiers were killed. Before the attack, the army forces walked for 1-3 km destroying terrorist bases. All the Indian soldiers returned safely, except one who accidently stepped on a land mile.
- Pakistan rejected India’s reports of any other casualties. Pakistani sources reported that at least 8 Indian soldiers were killed in the exchange, and one was captured. India confirmed that one of its soldiers was in Pakistani custody.
- The Indian operation was said to be in retaliation for a militant attack on the Indian army at Uri on 18 September in the Indian-administered state of Jammu and Kashmir that left 19 soldiers dead.
- In the succeeding days and months, India and Pakistan continued to exchange fire along the border in Kashmir, resulting in dozens of military and civilian casualties on both sides.
After Effect of Surgical Strike:
- Pakistan claimed that there had been no surgical strike conducted at LoC by India. It also increased the terrorist activities in India and strained the relations shared by both the countries.
- It also had a negative impact on the film industry, encountering a significant uprising amongst the citizens on the issue of casting Pakistani actors despite the tension across the border.
- It also saw the formation of allied groups as Pakistan feared of another attack on a larger scale. The Modi government began gathering support from the neighbouring countries like Japan and Germany whereas Pakistan tried to improve their relationship with China.
- In today’s political scenario, every country is trying to strengthen their powers hoping against the odds.
India’s DRDO test fires
13, Sep 2018

Why in news?
- India’s Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) has conducted the first successful test firing of a new indigenously designed and developed man portable antitank guided missile (MPATGM) at the Ahmednagar test range in the western Indian state of Maharashtra.
MPATGM:
- The MPATGM is a third-generation anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), which has been under development by DRDO in partnership with Indian defence contractor VEM Technologies Ltd. since 2015.
- Fitted with a high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead, the MPATGM reportedly boasts a top attack capability and has a maximum engagement range of about 2.5 kilometres.
- The man-portable missile is said to be a derivative of the NAG weapon system, and will be the third iteration of the missile following the baseline vehicle-launched version and air-launched version HELINA.
- The Indian Army finally opened its doors to the baseline NAG missile earlier this year after the MoD cleared an inaugural $70 million deal for 300 NAG missiles across 25 tracked launcher vehicles.
- The MPATGM program was sanctioned in January 2015, envisaging modifications to the NAG missile along with a launch tube and launcher system. Design configurations were frozen by the end of 2015.
- In 2016, the DRDO conducted eight static tests of the rocket motor to monitor ballistic performance for shoulder launch.
- India has a large requirement of anti-tank guided missiles running into more than 40,000 missiles for its hundreds of infantry and mechanised Army units.
- It has in the past turned down offers of the U.S.-built Javelin system and has oscillated over the Israeli SPIKE system.
- The indigenous MPATGM is finally off the ground, but has a journey ahead, including an unforgiving user trial phase (that endlessly bedevilled the original NAG system) following the current phase of development launch tests.
- The DRDO has been involved in researching man-portable anti-tank infantry weapons for years now. In 2009, it unveiled a separate light-weight 84mm anti-tank system
India’s First Missile tracking ship is readying for sea trials
12, Sep 2018
Why in news?
- Hindustan Shipyard Limited (HSL) is gearing up to undertake sea trials of India’s first missile tracking ship by the first week of October.
Background:
- Once ready, it will be India’s first, a force multiplier and cruise the country into a global elite club. The keel of the ship, is being built for the National Technical Research Organisation, the technical intelligence agency working directly under the supervision of the Prime Minister’s Office and the National Security Adviser.
- This will be the first of its kind ocean surveillance ship being built as part of the efforts under the NDA government to strengthen the country’s strategic weapons programme.
- Considered a “topmost secret project”, a lot of confidentiality is being maintained in executing the project costing about ₹750 crore.
- It will be named after its induction into the Indian Navy. For now, it is simply referred as VC 11184.
- It has the capacity to carry 300-strong crew with hi-tech gadgets and communication equipment, powered by two 9000 KW diesel engines, and a large deck capable of helicopter landing.
- 14 MW power is needed to activate the tracking radars.
- The ship can be move at an average speed of 21 knots.
Hindustan Shipyard Limited:
- HSL, set up in 1941, it is poised to get orders for construction of five fleet support ships costing ₹9,000 crore and finalise request for proposal for design collaborator for construction of two Special Operation Vessels called mini submarines.
- It is also banking on the order for medium refit of Russia-made third Sindhughosh class submarine INS Sindhuratna for which it has submitted technical bids.
Ship Building Centre:
- Visakhapatnam is considered a strategic location on the East Coast for the Indian defence forces as it is home for Ship Building Centre to build nuclear powered submarine INS Arihant class.
- Naval Alternate Operational Base at Rambilli, the second naval base after Eastern Naval Command headquarters, training centre for Marine Commandos and headquarters of the submarine arm.
Logistic deal with Russia
11, Sep 2018

- India and Russia are in the process of concluding a logistics agreement, with both sides targeting to conclude consultations before the annual summit.
Logistics agreement with other countries:
- India signed the Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Understanding (LEMOA), with the U.S. in August 2016 after a decade of negotiations.
- Since then it has concluded several such agreements with France, Oman, Philippines, Singapore and for access to the Sabang port in Indonesia.
Importance with Russia:
- India has longstanding and wide-ranging cooperation with Russia in the field of defence. India-Russia military technical cooperation has evolved from a simple buyer-seller framework to one involving joint research, development and production of advanced defence technologies and systems.
- It increases operational flexibility
- Logistics agreements are administrative arrangements facilitating access to military facilities for exchange of fuel and provisions on mutual agreement simplifying logistical support and increasing operational turnaround of the military when operating away from India.
S-300 Missile
10, Sep 2018

- Russia will transfer two to four S-300 air defence missile systems to Syria. It is a long-range, multi-channel anti-ballistic missile defence system which provides war fighters with enhanced combat capabilities.
- Venezuela received two S-300VM air defence systems in April 2013. Russia has also offered the missile system to Turkey and Saudi Arabia.
ISRO incubation centre
10, Sep 2018

- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) launched a space technology incubation centre in Tripura capital Agartala. The incubation centre will be located in the National Institute of Technology, Agartala.
About:
- The Centre was launched at the first edition of ‘Spacetronics’ organised by the India Electronics and Semiconductor Association (IESA). ISRO’s first Space Technology Incubation Centre
- It is the first of six such centres planned nationally to build capacity in new locations. More such space research activities will be splashed in a big way across small cities to tap their talent and include them in the space footprint
- The space agency’s new Capacity Building Programme directorate will invest ₹2 crore. Within the next six months, ISRO plans to set up five more space technology incubation centres at Jalandhar in Punjab, Bhubaneswar in Odisha, Nagpur in Maharashtra, Indore in Madhya Pradesh and Tiruchirapalli in Tamil Nadu.
- The centres will bring out prototypes and innovations for ISRO in electronics, propulsion and others. ISRO will buy the innovations back if we can use them in our programmes.
- It is to incubate start-ups which would build applications, offer services and products which can be used internally and exploit opportunities globally given enough help to scale up. It is put in place policies and framework to ensure that the ecosystem is favourable to more partnerships, access to funds, ease of business, networking in the domestic and international market and more importantly, inculcating this new initiative – ISRO Space Technology Incubation Centre of the NIT, Agartala.
- This facility, with active support from the state government of Tripura and IESA, the Ecosystem Partner, will be a big boost for the process in every sense.
- The state is working to emerge as a prominent place in Indian technology map by nurturing innovation, entrepreneurship and invention.
- This is a kind of process to develop start-ups by ISRO and the government initiative of Transforming India.
Significance:
- ISRO will also provide the necessary mentorship and guidance to individuals and businesses at the incubation centres.
- Those locations to set up incubation centres where there is no space activity happening, but there is a presence of strong academic institutions and industry, so as to spur research and innovations in the country.
- If the prototypes developed by the start-ups along with the industry meet the standards required, ISRO will acquire the technologies and components for use in its future space missions.
- The incubation centre will provide Tripura with an opportunity to steer ahead in the Information Technology (IT) and manufacturing sectors.
- The space agency aims to make use of the brightest minds across the length and breadth of the country.
- With India forced to import over 75 % of its electronics needs, there is a huge opportunity for Indian industry to expand their businesses
SMART Fencing of India Borders
09, Sep 2018

- Union Home Minister Rajnath Singh on Monday inaugurated the first phase of hi-tech ‘smart fencing’ of a 11 km stretch on the International Border (IB) in Jammu as the system would prevent the infiltration of terrorists and will reduce the casualties of security forces at the border.
- He also mentioned a future plan of covering more than 2000 km of ‘vulnerable’ and unfenced areas through CIBMS.
About:
- The launch of two pilot projects of ‘smart fencing’ along India’s International Border with Pakistan, is being implemented at a 60 km patch. A part of the project is functional.
- The smart fencing project will initially be implemented to cover gaps in the physical fencing. Eventually, this technology will be implemented across the entire border, which is planned to be launched by December.
- The BSF had taken up the initiative as part of the comprehensive integrated border management system. Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS) would provide for round-the-clock laser-guided surveillance of the borders.
- The CIBMS- a concept and nomenclature written by Commandant Jagdish Maithaniintegrates different sensors to maintain surveillance over an area. The data collected is sent to a command and control centre, from where operations can be directed.
- It consists of five types of sensors- radar, electro optics, unattended ground sensors, OFC based sensors and mini aerostat.
In Assam:
- A similar setup that was planned border along the Brahmaputra river in Dhubri later this month has hit rough weather.
- Due to its geographical features, no outpost could be erected in the area which often led to incidents like illegal migrations going unchecked. The smart fencing can be a solution for this problem.
- The Border Security Force (BSF), which is implementing this project in Assam, says that it is facing a few challenges such as setting up technological equipment on the riverbed with the river changing course regularly, finding sensors that can work in water and shortage of power and data connectivity.
- The Dhubri project was supposed to have technical issues, if someone is infiltrating through the riverine stretch, the problem is that there is so much ambient noise that it requires a software of the capability of a sonar to bring out the characteristic signature. For example, cattle could be crossing or a boat is passing by, the software should be able to differentiate each one of them.
- The river changes course and a whole installation can get washed away. It is important to make a project which is dynamic, so that even if the river changes course it should still work.
- Only a few sensors can work in rivers such as sonars and getting them is another challenge. There is also no power and data connectivity in these areas, so have to setup these things ourselves.
Border Fencing:
- India’s geostrategic location, its relatively sound economic position vis-à-vis its neighbours and its liberal democratic credentials have induced the government to undertake proper management of Indian borders, which is vital to national security.
- India shares 15,106.7 km of its boundary with seven nations Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, Bangladesh and Afghanistan. These land borders run through different terrains, managing a diverse land border is a complex task but very significant for security point of view.
- What further increase the complexity and criticality are the varied climatic conditions and relationship with some of the neighbouring countries.
- The traditional approach to border management, i.e. focussing only on border security, has become inadequate. India needs to not only ensure seamlessness in the legitimate movement of people and goods across its borders but also undertake reforms to curb illegal flow
- With the adoption of new technologies for border control and surveillance and the development of integrated systems for entering, exchange and storage of data, will facilitate the movement of people and products without endangering security.
- Smart border management is an attempt to identify and implement controls which aim to improve border security by
- Enabling effective communication and coordination among all security agencies
to arrive at a common entity picture. - Neutralising threats linked to terrorism and organised crime.
- Checking illegal migration.
- Enabling effective communication and coordination among all security agencies
Current system:
- A variety of measures are taken to safeguard land borders. These measures are grouped
into three categories people, process and technology.- Comprises the various types of forces and manpower deployed for safeguarding
our borders. - Outlines a few initiatives taken by the Government of India to streamline the
process of border control. - Lists the technological controls into which the Government of India continues to
invest in order to strengthen border management.
- Comprises the various types of forces and manpower deployed for safeguarding
Indo-Pak Border Challenges:
- Critical issues like the Pakistan occupied Kashmir, Sir Creek dispute, cross-border terrorism and ceasefire violation are key challenges plaguing this part of the Indian border and our armed forces.
- The harsh and varied climatic conditions along this 3,323-km of border compound the challenges faced by our armed forces in securing these areas.
- An increase in ceasefire violation and infiltration amount have been observed during the pre-winter season, when vigilance becomes extremely tough due to snowfall along the mountainous terrain.
- Other factors like the political instability and crisis in Pakistan also lead to an upsurge in cross-border tension along the border areas.
Russia, China Set To Launch Joint Military Exercises
19, Aug 2018

Why in news?
- China will join Russia in a giant military exercise, sending a message of deterrence to the U.S. which has designated Beijing and Moscow as “revisionist powers”.
5-day Exercise Vostok 2018:
- The five-day Vostok 2018 exercises, to be held from September 11, will be bigger than Zapad 81 — the mammoth manoeuvres carried out in Eastern Europe by the former Soviet Union in 1981.
- Mongolia will be the third country participating in the drills.
- The Vostok-2018 will involve 300,000 troops. They will engage in tri-service mock-operations, involving 1,000 military aircraft, two of Russia’s naval fleets and all its airborne units.
- Nearly 36,000 military vehicles will participate in the drills that will take place at Russia’s Tsugol training range in the trans-Baikal region.
- China will dispatch about 3,200 troops, along with more than 900 pieces of weaponry, as well as 30 fixed-wing aircraft and helicopters state-run Xinhua.
- These exercises are taking place amid Washington’s growing friction with Russia and China, which include mounting sanctions and a trade war.
- The Pentagon’s national defence strategy unveiled in January focused on Russia and China as principle strategic challenges to the U.S. In presenting the new strategy, U.S. Defence Secretary called China and Russia “revisionist powers” that “seek to create a world consistent with their authoritarian models”.
- China quoted that exercise as a response to the intentions of “hegemonic powers”. Some hegemonic powers target China and Russia as their biggest threats, giving heavy blows to the two countries in political, economic and military areas.
- Such actions have severely threatened regional and even global peace and stability. Therefore, the China-Russia alliance is a reasonable stance against the hegemonic impulse and for safeguarding peace and stability of the region and the world.
- Since last year, China and Russia have begun joint missile defence exercises — a signal that Beijing and Moscow “foresee that any strategic nuclear conflict that embroils one would, naturally, involve both”.
Anti-Runway and Anti-Tank Missiles Tested Successfully
18, Aug 2018

- The defence ministry announced the success of two major new indigenous weapon systems developed by the Defence R&D Organisation (DRDO).
Missiles that are tested:
- Smart anti-airfield weapon (SAAW)
- Helina (Helicopter launched Nag missile)
SAAW:
- The SAAW is an accurate bomb and is termed a long-range precision-guided munition (PGM).
- After its release from an aircraft, a sophisticated “inertial navigation system” on the bomb guides it precisely to its target — typically an enemy airfield up to 100 km away.
Advantages of SAAW:
- Striking the airfield’s runway precisely with one bomb is more economical than using traditional free-fall bombs, which are less accurate and must therefore be released in large numbers to be assured of incapacitating the target airfield.
- Another advantage of SAAW is that, after releasing it at a distance from the enemy airbase, the aircraft can return without exposing itself to anti-aircraft defences surrounding most air bases.
- It is capable of destroying runways, bunkers, aircraft hangers and other reinforced structures.
- The bomb, which is said to have higher precision and much cheaper compared with missiles, can be carried on IAF’s various aircraft like Jaguar and MiG
Helina:
- Indigenous Dhruv helicopter launched a HELINA anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) at a tank target seven kilometres away, successfully striking and destroying it.
- The missile is one of the most advanced anti-tank weapons in the world.
- It is a heavier and longer-range version of the vehicle mounted Nag missile with a 4-km range.
- The Missile is guided by an Infrared Imaging Seeker (IIR) operating in the Lock on Before Launch mode.
Exercise Peace Mission 2018
08, Aug 2018

- Exercise Peace Mission 2018, the joint military exercise of Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), ended in Russia
- The eight-member states undertaking joint training on combating terrorism.
Significance:
- It will play a positive role in enhancing the ability of all member states to work together to cope with new threats and challenges, promoting the SCO’s defence and security cooperation to go further both in substance and depth, and safeguarding regional peace and stability.
- The joint exercise will strengthen mutual confidence, interoperability and enable sharing of best practices among armed forces of the SCO nations.
- The scope of the exercise includes professional interaction, mutual understanding of drills & procedures, establishment of joint command and control structures and elimination of terrorist threat in urban counter terrorist scenario.
- This is the first time India and Pakistan participated in the exercise which brings stability between the two countries which was significant to the peace and development of the region and the whole world.
SCO:
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a permanent intergovernmental international organisation
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation Charter was signed during the St. Petersburg SCO Heads of State meeting in June 2002, and entered into force on September 2003
- The status of a full member of the Organization was granted to the Republic of India and the Islamic Republic of Pakistan during the Astana summit
- The SCO’s main goals are as follows: strengthening mutual trust and neighbourliness among the member states; promoting their effective cooperation in politics, trade, the economy, research, technology and culture, as well as in education, energy, transport, tourism, environmental protection, and other areas; making joint efforts to maintain and ensure peace, security and stability in the region; and moving towards the establishment of a democratic, fair and rational new international political and economic order.
Member States:
- The Republic of India
- The Republic of Kazakhstan
- The People’s Republic of China
- The Kyrgyz Republic
- The Islamic Republic of Pakistan
- The Russian Federation
- The Republic of Tajikistan and
- The Republic of Uzbekistan
Brahmos Missile
28, Jul 2018

Why in News?
India achieved another milestone in its defence preparedness by successfully test firing BrahMos supersonic cruise missile amidst extreme weather conditions at sea state 7 (waves as high as 9 meter with strong wind) at Balasore, odisha.
The missile was tested as part of the service life extension program for the Indian Army as it is the first missile whose life has been extended from 10 years to 15 years.
About the Missile:
Brahmos is a supersonic (app. thrice the sound of the speed) cruise missile.
It is a joint venture of DRDO of India and NPOM of Russia which has been named after two rivers Brahmaputra and Moskva (river in western Russia).
Technical specification:
- It is two stage missile where first stage is being a solid and second stage is ramjet liquid propellent.
- It is self-propelled guided missile which operates on “fire and forget principle”.
- It has low radar signature along with pin point accuracy.
- It is capable of being launched from land, sea, sub-sea and air against sea and land targets. • It carry both conventional and nuclear warhead weighing Upto 300 kg.
- It has unique feature of quicker engagement time and non-interception by any known weapon system in the world. • Its Airforce version is under developmental tests, the missile has already been inducted in the Army and the Navy. • Initially, developed for 299 km, the strike range of the weapon system has been increased to 450 km after India’s full membership to the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), which removed caps on range of cruise missiles.
Border Connectivity
28, Jul 2018

Why in News?
- Connectivity issues are troubling people living in areas bordering china in the Ladakh region, which was discussed during the BADP meeting chaired by Union Home Minister.
- The Ladakh region, which has high significance from strategic considerations, remains cut-off for almost half of the year throughout the winter season from the rest of India.
Geographical features of Ladakh:
- Ladakh is the highest plateau of the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir with much of it being over 3,000m.
- Ladakh (“land of high passes”) is a region that currently extends from the Kunlun mountain range to the main Great Himalayas to the south, inhabited by people of Indo Aryan and Tibetan descent.
Border Area Development Program:
- Connectivity is one of the major hinderance which limits the development prospectus in border areas.
- In order to improve infrastructure, Border area development program along with India-Pakistan border was initiated in 1987 during the seventh five year plan period.
- It is implemented by the department of border management, Ministry of Home affairs through state government.
Objective:
- The objective was to meet the special development in socio-economic conditions of the people living in inaccessible and remote areas near the international border.
- The funds under BADP are provided to the States as a 100% non-lapsable Special Central Assistance.
Areas covered under BADP:
The programme has been expanded since to cover the border blocks of the 17 States (including 8 North Eastern States), which have international land borders with Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar and Bangladesh.
BADP Guidelines:
- Coverage of BADP has been extended to cover all the villages which are located within the 0-10 Km of the International Border
- The list of schemes permissible under BADP has been expanded to include schemes/ activities relating to Swatchhta Aabhiyan , Skill Development programmes, Promotion of sports activities in border areas , Promotion of Rural Tourism/ Border Tourism, Protection of heritage sites.
- Construction of helipads in remote and inaccessible hilly areas, which do not have road connectivity, Construction of toilets in schools, public places particularly for women; Skill development training to farmers for the use of modern/ scientific technique in farming, Organic farming, etc.
- Provision for Third Party Inspection and Quality Control Mechanism under MHA for random inspections of the BADP schemes.
- Warehouses for food grains and fodder in hilly areas particularly in snow bound areas of Jammu & Kashmir Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh and, E-chaupals, Agri shops, mobile media vans etc. have been made.
- Special/Specific area schemes such as composite development of at least one village of sizeable population surrounded by five-six or more villages close to the border as Model Village.
Reason for the hinderance of the program:
- Difficult terrain
- Political interference
- Corruption
- Faulty implementation
- Poor planning and lack of coordination
- Fund diversion.
LEG up for the Private sector Participation
27, Jul 2018

- Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) has approved the Implementation of strategic partnership guidelines.
- Objective: To Enhance defence industries (Domestic) and progressively build indigenous capability in private sector and to develop complex weapon systems for the army.
- It has four components
SUBMARINES SINGLE ENGINE FIGHTER AIRCRAFT HELICOPTERS ARMOURED CARRIES - Under this policy one Indian Private Company would be selected in each segment mentioned above and will tie-up with their foreign counterpart and work with technology transferred by them.
- DAC also approved acquisition of Eight Fast Patrol Vessels which will be indigenously designed and manufactured.
What is strategic model and why do we need private sector participation?
- Strategic model in defense simply means a struct set of regulations to enhance procurement process.
- In a time when PSU’s are stressed and fiscal deficit has widened, we need more investment from private sector, so we to build ‘Make in India’ Initiative
- Broad based eligibility criteria for selection of private partner’s
1. Financial capability – Profitability net worth
2. Financial Prudence – Credit Ratings
3. Technical Capability – Domain of specialisation
4. Research and Development Capability – Track Record
5. Capacitive infrastructure – Global Benchmarks
6. Executive track record – Timely deliveries
7. Ownership structure – Private, Public or Promoter
Pitch Black
27, Jul 2018

For the first time, the Indian Air Force will be participating in Exercise Pitch Black 2018 (PB-18), a three-week multinational drill scheduled from 24 July in Australia.
- The Exercise Pitch Black which was first started in the year 1981 for different RAAF units, takes place every two years in the Australian continent.
- The last exercise in 2016, was attended by France, Indonesia, New Zealand, Thailand, Canada, Germany, Netherlands, Singapore, and the United States.
- Singapore was the first nation to be included in the exercise in the year 1990 following with the Australian administration opened the exercise to other countries too Background:
- Through the exercise the countries aim to practice OCA and DCA, more commonly known as the offensive and defensive counter air combat.
- The exercise takes place in New South Wales’ Glenbrook region, at the Australian Air Force base in a simulated environment.
- The other joint exercise between India and Australia which includes the AUSINDEX from 2015.
BIMSTEC Military Exercise
05, May 2018

India will host the first military exercise of the BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) group focussing on counter terrorism.
About:
- In a first such initiative, militaries of BIMSTEC member nations barring Nepal today began a week-long anti-terror exercise at Aundh near Pune to enhance cooperation in dealing with the challenge of terrorism in the region.
- The exercise is focused on boosting inter-operability among the forces and exchanging best practices to contain terror related activities, training in search-and-cordon operations and handling and neutralisation of improvised explosive devices (IEDs) among other things.
- The exercise is taking place nearly two weeks after leaders of the BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) countries, in their summit talks in Kathmandu, resolved to join hands to combat the scourge of terrorism effectively.
- India had organised the BIMSTEC Leaders’ Retreat in Goa in October 2016 during which the grouping had endorsed New Delhi’s effort to corner Pakistan on terror.
- special “tactical level” anti-terror operations will be practiced in semi urban setting.
- India has been pushing for making the BIMSTEC a vibrant form for regional collaboration as cooperation under the SAARC (South Asian Association of Regional Cooperation) framework was not moving forward visit topjuegos.net/. As BIMSTEC excludes Pakistan.
BIMSTEC:
- The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is an international organisation of seven nations of South Asia and South East Asia, The BIMSTEC member states are Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Bhutan, and Nepal are among the countries dependent on the Bay of Bengal.
- Leadership is rotated in alphabetical order of country names. Sri Lanka is the current chair. The permanent secretariat is in Dhaka.
- The main objective of BIMSTEC is technological and economic cooperation among south Asian and southeast Asian countries along the coast of the Bay of Bengal. Commerce, Investment, Technology, Tourism, Human Resource Development, Agriculture, Fisheries, Transport and Communication, Textiles, Leather etc. have been included in it.
- BIMSTEC Free Trade Area Framework Agreement (BFTAFA) has been signed by all member nations to stimulate trade and investment in the parties, and attract outsiders to trade with and invest in BIMSTEC at a higher level.






